Evolution of ZW Sex Chromosomes in Ptyas Snakes (Reptilia, Colubridae): New Insights from a Molecular Cytogenetic Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Karyotypes and C-Positive Heterochromatin
2.2. Satellite DNA Content of Ptyas korros and Their Chromosomal Location
2.3. Amplification of PkoSatDNAs in Other Species
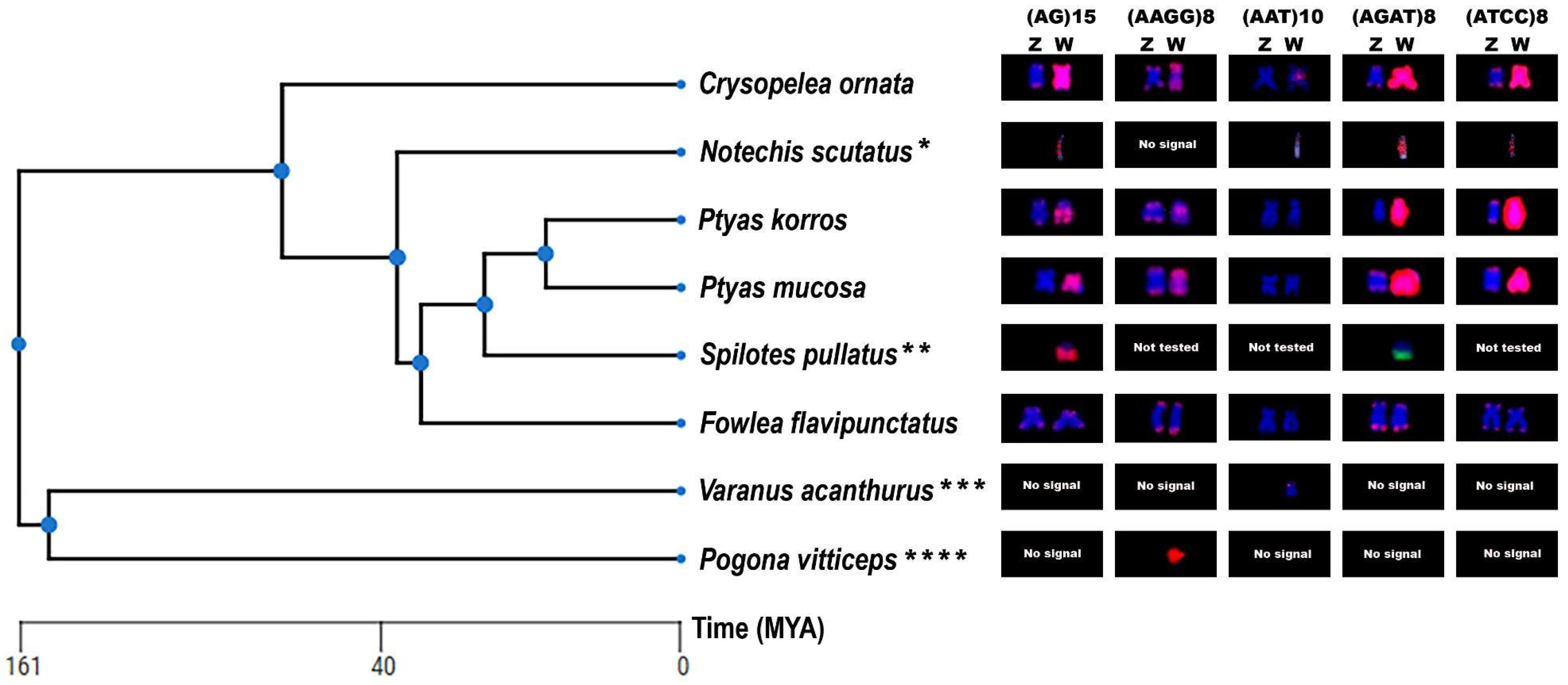
2.4. Chromosomal Mapping of (TTAGGG)n and Microsatellite Motifs
2.5. Comparative Genomic Hybridizations
2.6. Sex Chromosome Homology Between Snakes and Lizards
3. Discussion
3.1. General Karyotypic Organization of Colubridae
3.2. Genomic Composition and Organization of Satellite DNA in Ptyas korros and Its Shared Characteristics with Snakes and Lizards
3.3. The Impact of Repeated Sequences on the Evolution of the W Chromosome in Caenophidian Snakes: Heterochromatinization Versus Heteromorphism
3.4. Genetic Content of Sex Chromosomes in Lizards and Their Relationship to the Genus Ptyas
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling, Mitotic Chromosomal Preparations, and C-Banding
4.2. DNA Extraction and Genome Sequencing
4.3. Bioinformatic Analyses: The Characterization of Ptyas korros Satellitome
4.4. Estimating the Abundance and Diversity of satDNAs
4.5. Primer Design, DNA Amplification, and Preparation of satDNA Probes
4.6. Microsatellite and Telomeric (TTAGGG)n Probes
4.7. Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH): Experimental Design and Probe Preparation
4.8. Investigation of Sex Chromosome Homology Between Snakes and Lizards
4.9. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
4.10. Microscopic Analyses and Image Processing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| satDNA | Satellite DNA |
| BAC | Bacterial artificial chromosome |
| rDNA | Ribosomal DNA |
| ITS | Interstitial sequences |
| PKO | Ptyas korros |
| PMU | Ptyas mucosa |
| COR | Crysopelea ornata |
| FFL | Fowlea flavipunctatus |
| RUL | Repeat unit length |
| PKOsatDNA | Satellite DNA from Ptyas korros |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| FISH | Fluorescent in situ hybridization |
| gDNA | whole genomic DNA |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| CGH | Comparative genomic hybridization |
References
- Uetz, P. The Reptile Database 2025. Available online: https://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Vidal, N.; Delmas, A.-S.; David, P.; Cruaud, C.; Couloux, A.; Hedges, S.B. The phylogeny and classification of caenophidian snakes inferred from seven nuclear protein-coding genes. C. R. Biol. 2006, 330, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaher, H.; Grazziotin, F.G.; Cadle, J.E.; Murphy, R.W.; de Moura-Leite, J.C.; Bonatto, S.L. Molecular phylogeny of advanced snakes (Serpentes, Caenophidia) with an emphasis on South American Xenodontines: A revised classification and descriptions of new taxa. Pap. Avulsos Zool. 2009, 49, 115–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, J.W.; Wiens, J.J. Phylogenomic analyses reveal novel relationships among snake families. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 100, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyron, R.; Burbrink, F.T.; Wiens, J.J. A phylogeny and revised classification of Squamata, including 4161 species of lizards and snakes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovatsos, M.; Vukić, J.; Lymberakis, P.; Kratochvíl, L. Evolutionary stability of sex chromosomes in snakes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.Y.; Hugall, A.F.; Lawson, R.; Scanlon, J.D. Phylogeny of snakes (Serpentes): Combining morphological and molecular data in likelihood, Bayesian and parsimony analyses. Syst. Biodivers. 2007, 5, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyron, R.A.; Reynolds, R.G.; Burbrink, F.T. A Taxonomic Revision of Boas (Serpentes: Boidae). Zootaxa 2014, 3846, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyron, R.A.; Hendry, C.R.; Chou, V.M.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Burbrink, F.T. Effectiveness of phylogenomic data and coalescent species-tree methods for resolving difficult nodes in the phylogeny of advanced snakes (Serpentes: Caenophidia). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 81, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguiura, N.; Ferrarezzi, H.; Batistic, R.F. Cytogenetics and Molecular Data in Snakes: A Phylogenetic Approach. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 127, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.J.; Mengden, G.A.; Bull, J.J. Karyotypic Studies of Thirty-Eight Species of North American Snakes. Copeia 1972, 1972, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Solorzano, A.; Cerdas, L.; Vannini, J.P. Karyotypes of Five Species of Coral Snakes (Micrurus). J. Herpetol. 1988, 22, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, G.C. The Chromosomes of Laticauda and a Review of Karyotypic Evolution in the Elapidae. J. Herpetol. 1981, 15, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, P.F.; Ezaz, T.; Cioffi, M.D.B.; Liehr, T.; Al-Rikabi, A.; Tavares-Pinheiro, R.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Feldberg, E. Revisiting the Karyotype Evolution of Neotropical Boid Snakes: A Puzzle Mediated by Chromosomal Fissions. Cells 2020, 9, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beçak, W.; Beçak, M.L.; Nazareth, H.R.S. Karyotypic Studies of two Species of South American Snakes (Boa constrictor amarali and Bothrops jararaca). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 1962, 1, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Sharma, T.; Ray-Chaudhuri, S.P. W chromosome in the Indian water snake (checkered keel back) Natrix piscator (Colubridae). Experientia 1968, 24, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beçak, W.; Beçak, M.L. Cytotaxonomy and chromosomal evolution in Serpentes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 1969, 8, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengden, G.A.; Stock, A.D. Chromosomal evolution in serpentes; a comparison of G and C chromosome banding patterns of some colubrid and boid genera. Chromosoma 1980, 79, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pšenička, T.; Augstenová, B.; Frynta, D.; Kornilios, P.; Kratochvíl, L.; Rovatsos, M. Sex Chromosome Turnovers and Stability in Snakes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2025, 42, msae255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beçak, W.; Beçak, M.L.; Nazareth, H.R.S.; Ohno, S. Close karyological kinship between the reptilian suborder serpentes and the class aves. Chromosoma 1964, 15, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augstenová, B.; Johnson Pokorná, M.; Altmanová, M.; Frynta, D.; Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L. ZW, XY, and yet ZW: Sex chromosome evolution in snakes even more complicated: Brief Communication. Evolution 2018, 72, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Tarui, H.; Toriba, M.; Yamada, K.; Nishida-Umehara, C.; Agata, K.; Matsuda, Y. Evidence for different origin of sex chromosomes in snakes, birds, and mammals and step-wise differentiation of snake sex chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18190–18195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.; Campos, P.; Ching, A.; Mackessy, S. Colubrid Venom Composition: An -Omics Perspective. Toxins 2016, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Franceschi, J.; Hyslop, S. South American Colubrid Envenomations. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2002, 21, 117–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Eatwell, K. Nonvenomous Colubrid Snakes (Colubridae). In Companion Animal Care and Welfare; Yeates, J., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 412–424. ISBN 978-1-118-68879-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ching, A.T.C.; Rocha, M.M.T.; Paes Leme, A.F.; Pimenta, D.C.; De Fátima, D.; Furtado, M.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Ho, P.L.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M. Some aspects of the venom proteome of the Colubridae snake Philodryas olfersii revealed from a Duvernoy’s (venom) gland transcriptome. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4417–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.E.; Mackessy, S.P. Characterization of venom (Duvernoy’s secretion) from twelve species of colubrid snakes and partial sequence of four venom proteins. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1663–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackessy, S.P. Biochemistry and pharmacology of colubrid snake venoms. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2002, 21, 43–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyborne, W.H.; Mackessy, S.P. Identification and characterization of a taxon-specific three-finger toxin from the venom of the Green Vinesnake (Oxybelis fulgidus; family Colubridae). Biochimie 2013, 95, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, G.; Tu, A.T. Toxicology and Biochemistry of Colubridae Venom. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1993, 12, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L. Evolution of karyotypes in snakes. Chromosoma 1972, 38, 185–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Purdom, I.F.; Jones, K.W. Satellite DNA and evolution of sex chromosomes. Chromosoma 1976, 59, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, P.F.; Ezaz, T.; De Bello Cioffi, M.; Almeida, B.J.; Feldberg, E. Evolutionary Insights of the ZW Sex Chromosomes in Snakes: A New Chapter Added by the Amazonian Puffing Snakes of the Genus Spilotes. Genes 2019, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; McKelvy, A.D.; Grismer, L.L.; Bell, C.D.; Lailvaux, S.P. A Species-Level Phylogeny of Extant Snakes with Description of a New Colubrid Subfamily and Genus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Marshall Graves, J.A.; Ezaz, T. Highly Differentiated ZW Sex Microchromosomes in the Australian Varanus Species Evolved through Rapid Amplification of Repetitive Sequences. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; O’Meally, D.; Azad, B.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.D.; Graves, J.A.M.; Matsuda, Y.; Ezaz, T. Amplification of microsatellite repeat motifs is associated with the evolutionary differentiation and heterochromatinization of sex chromosomes in Sauropsida. Chromosoma 2016, 125, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezaz, T.; Azad, B.; O’Meally, D.; Young, M.J.; Matsubara, K.; Edwards, M.J.; Zhang, X.; Holleley, C.E.; Deakin, J.E.; Marshall Graves, J.A.; et al. Sequence and gene content of a large fragment of a lizard sex chromosome and evaluation of candidate sex differentiating gene R-spondin 1. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobry, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wapstra, E.; Deakin, J.E.; Ezaz, T. The role of unbalanced segmental duplication in sex chromosome evolution in Australian ridge-tailed goannas. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzasalma, M.; Macirella, R.; Odierna, G.; Brunelli, E. Karyotype Diversification and Chromosome Rearrangements in Squamate Reptiles. Genes 2024, 15, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L. Chromosomes of Six Species of Indian Snakes; Herpetologists’ League: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Donbundit, N.; Bausriyod, P.; Tanomtong, A.; Srisamoot, N.; Sumontha, M.; Thongnetr, W.; Patawang, I.; Supiwong, W.; Ditcharoen, S.; Muanglen, N.; et al. Karyomorphological delineation, and the NOR loci on the sex chromosome in three species of Chrysopeleinid (Chrysopeleinae: Colubridae) from Thailand. Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2022, 23, 3813–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donbundit, D.; Thongnetr, W.; Patawang, I.; Tanomtong, A. First Study on Chromosomal Feature and NORs Localization of the Yellow-spotted Keelback Snake, Fowlea flavipunctatus (Squamata, Natricinae) in Thailand. Sci. Technol. Eng. J. STEJ 2020, 6, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Singchat, W.; Panthum, T.; Srikulnath, K. Impact of Repetitive DNA Elements on Snake Genome Biology and Evolution. Cells 2021, 10, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yamada, K.; Nishida-Umehara, C.; Matsuda, Y. Characterization and chromosomal distribution of novel satellite DNA sequences of the lesser rhea (Pterocnemia pennata) and the greater rhea (Rhea americana). Chromosome Res. 2002, 10, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Nishida-Umehara, C.; Matsuda, Y. A new family of satellite DNA sequences as a major component of centromeric heterochromatin in owls (Strigiformes). Chromosoma 2004, 112, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, Y.; Nishida-Umehara, C.; Ishijima, J.; Yamada, K.; Matsuda, Y. Comparison of the Z and W sex chromosomal architectures in elegant crested tinamou (Eudromia elegans) and ostrich (Struthio camelus) and the process of sex chromosome differentiation in palaeognathous birds. Chromosoma 2007, 116, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifitdinova, A.F.; Derjusheva, S.E.; Malykh, A.G.; Zhurov, V.G.; Andreeva, T.F.; Gaginskaya, E.R. Centromeric tandem repeat from the chaffinch genome: Isolation and molecular characterization. Genome 2001, 44, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangouzov, I.A.; Derjusheva, S.E.; Saifitdinova, A.F.; Malykh, A.G.; Gaginskaya, E.R. Monomers of a satellite DNA sequence of chaffinch (Fringilla coelebs L., Aves: Passeriformes) contain short clusters of the TTAGGG repeat. Russ. J. Genet. 2002, 38, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryusheva, S.; Krasikova, A.; Kulikova, T.; Gaginskaya, E. Tandem 41-bp repeats in chicken and Japanese quail genomes: FISH mapping and transcription analysis on lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 2007, 116, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciò, S.; Perani, P.; Saccone, S.; Kadi, F.; Bernardi, G. Single-copy sequence homology among the GC-richest isochores of the genomes from warm-blooded vertebrates. J. Mol. Evol. 1994, 39, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Jones, K.W. Localisation of satellite DNA in the microchromosomes of the Japanese quail by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 1972, 38, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamovits, C.H.; Cook, J.A.; Lessa, E.P.; Rossi, M.S. Recurrent Amplifications and Deletions of Satellite DNA Accompanied Chromosomal Diversification in South American Tuco-tucos (Genus Ctenomys, Rodentia: Octodontidae): A Phylogenetic Approach. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazrimas, J.A.; Hatch, F.T. Similarity of satellite DNA properties in the order Rodentia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977, 4, 3215–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adega, F.; Guedes-Pinto, H.; Chaves, R. Satellite DNA in the Karyotype Evolution of Domestic Animals—Clinical Considerations. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 126, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaya, G.; Cortadas, J.; Bernardi, G. An Analysis of the Bovine Genome by Density-Gradient Centrifugation: Preparation of the dG+dC-Rich DNA Components. Eur. J. Biochem. 1978, 84, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudeiro, A.; Adega, F.; Robinson, T.J.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S.; Chaves, R. Conservation, Divergence, and Functions of Centromeric Satellite DNA Families in the Bovidae. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourc’h, C.; Biamonti, G. Transcription of Satellite DNAs in Mammals. In Long Non-Coding RNAs; Ugarkovic, D., Ed.; Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 51, pp. 95–118. ISBN 978-3-642-16501-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenko, A.; Pšenička, T.; Mora, P.; Ortega, J.A.M.; Baca, A.S.; Rovatsos, M. Cytogenetic Analysis of Satellitome of Madagascar Leaf-Tailed Geckos. Genes 2024, 15, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagoshi, T.; Nishida, C.; Ota, H.; Kumazawa, Y.; Endo, H.; Matsuda, Y. Molecular structures of centromeric heterochromatin and karyotypic evolution in the Siamese crocodile (Crocodylus siamensis) (Crocodylidae, Crocodylia). Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, S.A.; Prokopov, D.Y.; Proskuryakova, A.A.; Davletshina, G.I.; Tupikin, A.E.; Kasai, F.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Trifonov, V.A. The Cytogenetic Map of the Nile Crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus, Crocodylidae, Reptilia) with Fluorescence In Situ Localization of Major Repetitive DNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomia, R.; Silva, D.M.Z.D.A.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Goes, C.A.G.; Melo, S.; Ramos, L.P.; Oliveira, C.; Porto-Foresti, F.; Foresti, F.; Hashimoto, D.T. Satellitome landscape analysis of Megaleporinus macrocephalus (Teleostei, Anostomidae) reveals intense accumulation of satellite sequences on the heteromorphic sex chromosome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, C.; Parise-Maltempi, P.P. Heteromorphic Sex Chromosomes and Their DNA Content in Fish: An Insight through Satellite DNA Accumulation in Megaleporinus elongatus. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2020, 160, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, C.A.G.; Dos Santos, R.Z.; Aguiar, W.R.C.; Alves, D.C.V.; Silva, D.M.Z.D.A.; Foresti, F.; Oliveira, C.; Utsunomia, R.; Porto-Foresti, F. Revealing the Satellite DNA History in Psalidodon and Astyanax Characid Fish by Comparative Satellitomics. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 884072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.P.B.; Kretschmer, R.; Deon, G.A.; Toma, G.A.; Ezaz, T.; Goes, C.A.G.; Porto-Foresti, F.; Liehr, T.; Utsunomia, R.; Cioffi, M.D.B. Following the Pathway of W Chromosome Differentiation in Triportheus (Teleostei: Characiformes). Biology 2023, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deon, G.A.; Glugoski, L.; Vicari, M.R.; Nogaroto, V.; Sassi, F.D.M.C.; Cioffi, M.D.B.; Liehr, T.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Moreira-Filho, O. Highly Rearranged Karyotypes and Multiple Sex Chromosome Systems in Armored Catfishes from the Genus Harttia (Teleostei, Siluriformes). Genes 2020, 11, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongchum, R.; Singchat, W.; Laopichienpong, N.; Tawichasri, P.; Kraichak, E.; Prakhongcheep, O.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Muangmai, N.; Baicharoen, S.; Suntrarachun, S.; et al. Diversity of PBI-DdeI satellite DNA in snakes correlates with rapid independent evolution and different functional roles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Purdom, I.F.; Jones, K.W. Behaviour of sex chromosome associated satellite DNAs in somatic and germ cells in snakes. Chromosoma 1979, 71, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Purdom, I.F.; Jones, K.W. Sex chromosome associated satellite DNA: Evolution and conservation. Chromosoma 1980, 79, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, S.G.; Singh, L. Banded krait minor satellite (Bkm) contains sex and species-specific repetitive DNA. Chromosoma 1994, 103, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Uno, Y.; Srikulnath, K.; Seki, R.; Nishida, C.; Matsuda, Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of satellite DNA sequences from constitutive heterochromatin of the habu snake (Protobothrops flavoviridis, Viperidae) and the Burmese python (Python bivittatus, Pythonidae). Chromosoma 2015, 124, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquesi, G.I.M.; Adams, R.H.; Card, D.C.; Schield, D.R.; Corbin, A.B.; Perry, B.W.; Reyes-Velasco, J.; Ruggiero, R.P.; Vandewege, M.W.; Shortt, J.A.; et al. Squamate reptiles challenge paradigms of genomic repeat element evolution set by birds and mammals. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Singchat, W.; Jehangir, M.; Panthum, T.; Srikulnath, K. Consequence of Paradigm Shift with Repeat Landscapes in Reptiles: Powerful Facilitators of Chromosomal Rearrangements for Diversity and Evolution. Genes 2020, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, T.R. Animal Genome Size Database 2025. Available online: https://www.genomesize.com/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Lisachov, A.; Rumyantsev, A.; Prokopov, D.; Ferguson-Smith, M.; Trifonov, V. Conservation of Major Satellite DNAs in Snake Heterochromatin. Animals 2023, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, P.G.; Deon, G.A.; Dos Santos, R.Z.; Goes, C.A.G.; Garnero, A.D.V.; Gunski, R.J.; De Oliveira, E.H.C.; Porto-Foresti, F.; De Freitas, T.R.O.; Silva, F.A.O.; et al. Evolution of bird sex chromosomes: A cytogenomic approach in Palaeognathae species. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2024, 24, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestrovic, N.; Plohl, M.; Mravinac, B.; Ugarkovic, D. Evolution of satellite DNAs from the genus Palorus—experimental evidence for the “library” hypothesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mravinac, B.; Plohl, M.; Mestrović, N.; Ugarković, Đ. Sequence of PRAT Satellite DNA “Frozen” in Some Coleopteran Species. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navajas-Pérez, R.; Del Bosque, M.E.Q.; Garrido-Ramos, M.A. Effect of location, organization, and repeat-copy number in satellite-DNA evolution. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2009, 282, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Chaudhuri, S.P.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, T. Karyotypes of Five Indian Species of Microchiroptera. Caryologia 1971, 24, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Augstenová, B.; Mazzoleni, S.; Kratochvíl, L.; Rovatsos, M. Evolutionary Dynamics of the W Chromosome in Caenophidian Snakes. Genes 2017, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovatsos, M.; Altmanová, M.; Pokorná, M.J.; Augstenová, B.; Kratochvíl, L. Cytogenetics of the Javan file snake (Acrochordus javanicus) and the evolution of snake sex chromosomes. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2018, 56, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Meally, D.; Patel, H.R.; Stiglec, R.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Marshall Graves, J.A.; Ezaz, T. Non-homologous sex chromosomes of birds and snakes share repetitive sequences. Chromosome Res. 2010, 18, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorná, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Kejnovský, E. Microsatellite distribution on sex chromosomes at different stages of heteromorphism and heterochromatinization in two lizard species (Squamata: Eublepharidae: Coleonyx elegans and Lacertidae: Eremias velox). BMC Genet. 2011, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.A.; Ezaz, T.; Valenzuela, N.; Georges, A.; Marshall Graves, J.A. An XX/XY heteromorphic sex chromosome system in the Australian chelid turtle Emydura macquarii: A new piece in the puzzle of sex chromosome evolution in turtles. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorná, M.; Rábová, M.; Ráb, P.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Rens, W.; Kratochvíl, L. Differentiation of sex chromosomes and karyotypic evolution in the eye-lid geckos (Squamata: Gekkota: Eublepharidae), a group with different modes of sex determination. Chromosome Res. 2010, 18, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.M.I.; Sarre, S.D.; Gleeson, D.; Georges, A.; Ezaz, T. Did Lizards Follow Unique Pathways in Sex Chromosome Evolution? Genes 2018, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezaz, T.; Moritz, B.; Waters, P.; Marshall Graves, J.A.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.D. The ZW sex microchromosomes of an Australian dragon lizard share no homology with those of other reptiles or birds. Chromosome Res. 2009, 17, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, L.; Gamble, T.; Rovatsos, M. Sex chromosome evolution among amniotes: Is the origin of sex chromosomes non-random? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorná, M.J.; Altmanová, M.; Rovatsos, M.; Velenský, P.; Vodička, R.; Rehák, I.; Kratochvíl, L. First Description of the Karyotype and Sex Chromosomes in the Komodo Dragon (Varanus komodoensis). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 148, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, A.T. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaz, T.; Quinn, A.E.; Miura, I.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Marshall Graves, J.A. The dragon lizard Pogona vitticeps has ZZ/ZW micro-sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobry, J.; Wapstra, E.; Stringer, E.J.; Gruber, B.; Deakin, J.E.; Ezaz, T. Widespread chromosomal rearrangements preceded genetic divergence in a monitor lizard, Varanus acanthurus (Varanidae). Chromosome Res. 2023, 31, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harb: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Fast Identification and Removal of Sequence Contamination from Genomic and Metagenomic Datasets. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker Open, version 4.0; Institute for Systems Biology location: Seattle, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; López-León, M.D.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P.M. High-throughput analysis of the satellitome illuminates satellite DNA evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Knopp, T.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Ezaz, T. Karyotypic analysis and FISH mapping of microsatellite motifs reveal highly differentiated XX/XY sex chromosomes in the pink-tailed worm-lizard (Aprasia parapulchella, Pygopodidae, Squamata). Mol. Cytogenet. 2013, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannucci, A.; Altmanová, M.; Ciofi, C.; Ferguson-Smith, M.; Pereira, J.C.; Rehák, I.; Stanyon, R.; Velenský, P.; Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; et al. Isolating Chromosomes of the Komodo Dragon: New Tools for Comparative Mapping and Sequence Assembly. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2019, 157, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkel, D.; Straume, T.; Gray, J.W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2934–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonová, R.; Sember, A.; Majtánová, Z.; Ráb, P. Characterization of fish genomes by GISH and CGH. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques: Ray-Fin Fishes and Chondrichthyans; Ozouf-Costaz, C., Pisano, E., Foresti, F., Eds.; Toledo LFA: Toledo, Spain, 2015; pp. 118–131. [Google Scholar]





| Species (Abbreviation, When Used) | Origin of Samples | N |
|---|---|---|
| Ptyas korros (PKO) | Khon Kaen, Thailand | 02♀; 01♂ |
| Ptyas mucosa (PMU) | Khon Kaen, Thailand | 02♀; 02♂ |
| Chrysopelea ornata (COR) | Khon Kaen, Thailand | 01♀; 01♂ |
| Fowlea flavipunctatus (FFL) | Khon Kaen, Thailand | 01♀; 01♂ |
| Notechis scutatus (NSC) | Canberra, Australia | 01♀ |
| Pogona vitticeps (PVI) | Canberra, Australia | 01♀ |
| Varanus acanthurus (VAC) | Canberra, Australia | 02♀ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Setti, P.G.; Ezaz, T.; Deon, G.A.; Utsunomia, R.; Tanomtong, A.; Ditcharoen, S.; Donbundit, N.; Sumontha, M.; Seetapan, K.; Buasriyot, P.; et al. Evolution of ZW Sex Chromosomes in Ptyas Snakes (Reptilia, Colubridae): New Insights from a Molecular Cytogenetic Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104540
Setti PG, Ezaz T, Deon GA, Utsunomia R, Tanomtong A, Ditcharoen S, Donbundit N, Sumontha M, Seetapan K, Buasriyot P, et al. Evolution of ZW Sex Chromosomes in Ptyas Snakes (Reptilia, Colubridae): New Insights from a Molecular Cytogenetic Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104540
Chicago/Turabian StyleSetti, Príncia Grejo, Tariq Ezaz, Geize Aparecida Deon, Ricardo Utsunomia, Alongklod Tanomtong, Sukhonthip Ditcharoen, Nattasuda Donbundit, Montri Sumontha, Kriengkrai Seetapan, Phichaya Buasriyot, and et al. 2025. "Evolution of ZW Sex Chromosomes in Ptyas Snakes (Reptilia, Colubridae): New Insights from a Molecular Cytogenetic Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104540
APA StyleSetti, P. G., Ezaz, T., Deon, G. A., Utsunomia, R., Tanomtong, A., Ditcharoen, S., Donbundit, N., Sumontha, M., Seetapan, K., Buasriyot, P., Pinthong, K., Thongnetr, W., dos Santos, N., Porto-Foresti, F., Liehr, T., & Cioffi, M. d. B. (2025). Evolution of ZW Sex Chromosomes in Ptyas Snakes (Reptilia, Colubridae): New Insights from a Molecular Cytogenetic Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104540









