Clinical Validation of Plasma Metabolite Markers for Early Lung Cancer Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Cohorts
2.2. Univariate and Multivariate Statistical Analysis
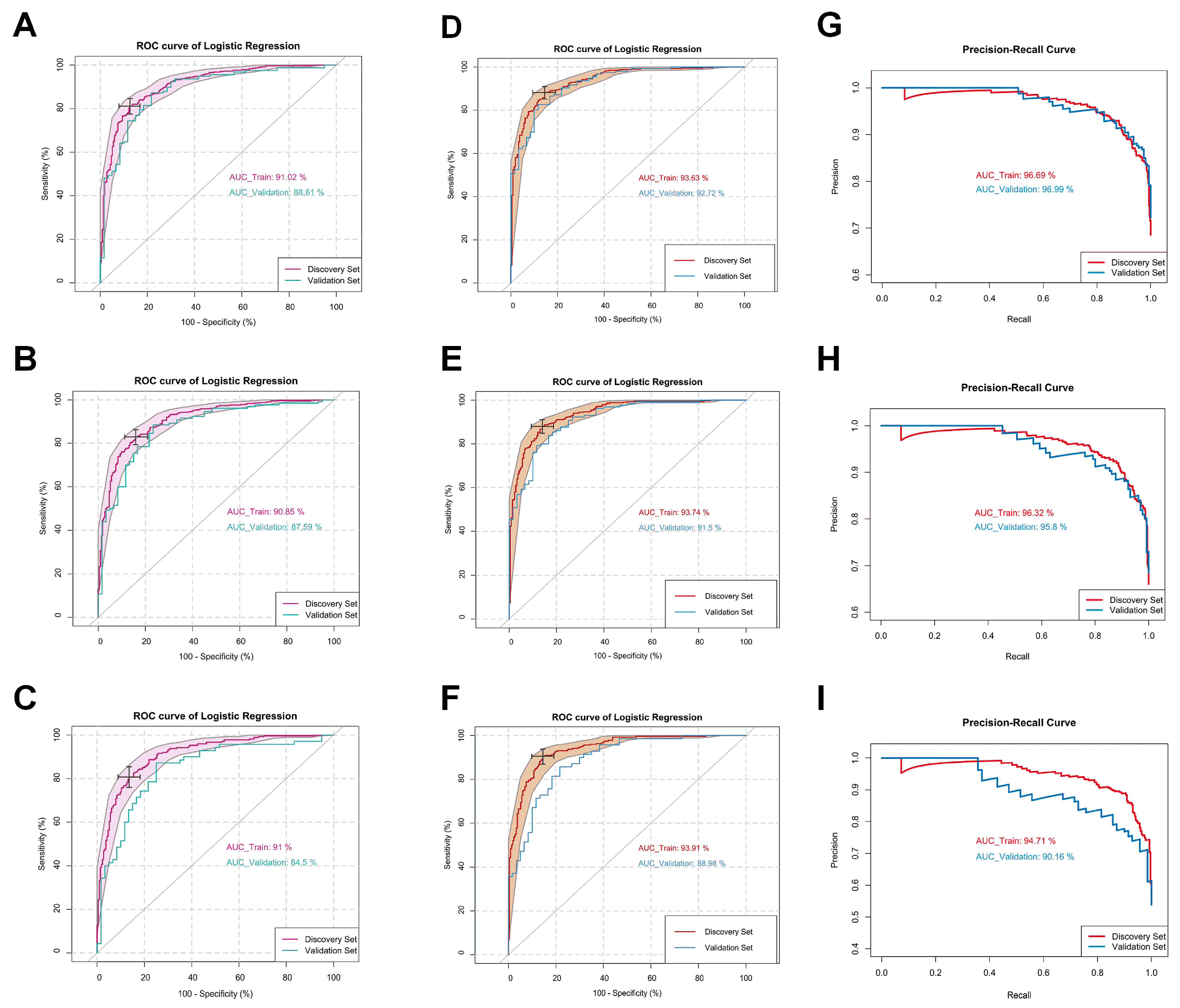
2.3. Logistic Regression Modeling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Regulatory and Institutional Review Board Approvals
4.2. Study Population and Sample Collection
4.3. Chemicals, Reagents, and Materials Used for the Quantitative Metabolomic Assays
4.4. Stock Solutions, Internal Standard (ISTD) Mixture, and Calibration Curve Standards for Metabolomic Assays
4.5. Sample Preparation and Liquid Chromatography/Direct Injection Mass Spectrometry for Metabolomic Assays
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Release Notice Canadian Cancer Statistics: A 2020 Special Report on Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/reports-publications/health-promotion-chronic-disease-prevention-canada-research-policy-practice/vol-40-no-10-2020/canadian-cancer-statistics-lung-cancer.html (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (Eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarenheimo, J.; Eigeliene, N.; Andersen, H.; Tiirola, M.; Jekunen, A. The value of liquid biopsies for guiding therapy decisions in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; Sicks, J.D. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.A.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, K.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. High-resolution metabolomic biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derveaux, E.; Louis, E.; Vanhove, K.; Bervoets, L.; Mesotten, L.; Thomeer, M.; Adriaensens, P. Diagnosis of lung cancer: What metabolomics can contribute. In Lung Cancer—Strategies for Diagnosis and Treatment; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X. Next-generation metabolomics in lung cancer diagnosis, treatment and precision medicine: Mini review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115774–115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lazar, L.; Fang, Z.; Tang, C.; Zhao, J. Metabolomics workflow for lung cancer: Discovery of biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madama, D.; Martins, R.; Pires, A.S.; Botelho, M.F.; Alves, M.G.; Abrantes, A.M.; Cordeiro, C.R. Metabolomic profiling in lung cancer: A systematic review. Metabolites 2021, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Ahmed, R.; Huang, G.; Reid, J.; Mandal, R.; Maksymuik, A.; Sitar, D.S.; Tappia, P.S.; Ramjiawan, B.; et al. A high-performing plasma metabolite panel for early-stage lung cancer detection. Cancers 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, J.; Li, L.; Min, L.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Dai, L. Simultaneous quantification of serum monounsaturated and polyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines as potential biomarkers for diagnosing non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Song, Y.; Cao, J.; Bi, N.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Bai, J.; Dong, L.; et al. Global and targeted metabolomics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma discovers potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmanová, J.; Slavík, J.; Ciganek, M.; Ovesná, P.; Tylichová, Z.; Karasová, M.; Zapletal, O.; Straková, N.; Procházková, J.; Bouchal, J.; et al. Complex alterations of fatty acid metabolism and phospholipidome uncovered in isolated colon cancer epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.C.; Fanidi, A.; Ueland, P.M.; Relton, C.; Midttun, O.; Vollset, S.E.; Gunter, M.J.; Seckl, M.J.; Travis, R.C.; Wareham, N.; et al. Circulating biomarkers of tryptophan and the kynurenine pathway and lung cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deja, S.; Porebska, I.; Kowal, A.; Zabek, A.; Barg, W.; Pawelczyk, K.; Stanimirova, I.; Daszykowski, M.; Korzeniewska, A.; Jankowska, R.; et al. Metabolomics provide new insights on lung cancer staging and discrimination from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Barupal, D.K.; Taguchi, A.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Wikoff, W.R.; Yoneda, K.Y.; Gandara, D.R.; Hanash, S.M.; Kim, K.; et al. Systemic metabolomic changes in blood samples of lung cancer patients identified by gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolites 2015, 5, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.P.; Tang, A.G.; Zhou, Q.X.; Xiang, Z.Y. Clinical significance of simultaneous determination of serum tryptophan and tyrosine in patients with lung cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2011, 25, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupczynska, A.; Dereziński, P.; Garrett, T.J.; Rubio, V.Y.; Dyszkiewicz, W.; Kasprzyk, M.; Kokot, Z.J. Study of early stage non-small-cell lung cancer using Orbitrap-based global serum metabolomics. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Jerónimo, C.; Henrique, R.; Belo, L.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; de Pinho, P.G.; Carvalho, M. Biomarkers in bladder cancer: A metabolomic approach using in vitro and ex vivo model systems. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, H.; Paik, M.J.; Xuan, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Ham, I.H.; Yun, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, G.; Han, S.U. Quantitative measurement of organic acids in tissues from gastric cancer patients indicates increased glucose metabolism in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.W.; Lane, A.N.; Higashi, R.M.; Farag, M.A.; Gao, H.; Bousamra, M.; Miller, D.M. Altered regulation of metabolic pathways in human lung cancer discerned by (13)C stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM). Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiburcio, P.D.; Choi, H.; Huang, L.E. Complex role of HIF in cancer: The known, the unknown, and the unexpected. Hypoxia 2014, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bamji-Stocke, S.; van Berkel, V.; Miller, D.M.; Frieboes, H.B. A review of metabolism-associated biomarkers in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshet, R.; Szlosarek, P.; Carracedo, A.; Erez, A. Rewiring urea cycle metabolism in cancer to support anabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, F.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lange, T.; Ma, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Associations of genetic risk, BMI trajectories, and the risk of non-small cell lung cancer: A population-based cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Hu, C.; Quan, C.; Yi, X.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, M.; Yu, T.; Kourouma, A.; Yang, K. Body mass index and risk of lung cancer: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Cancer Society. Risk Factors for Lung Cancer [Internet]. Available online: https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/lung/risks (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Takiguchi, Y.; Sekine, I.; Iwasawa, S. Overdiagnosis in lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, e101–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, D.E.; Reuland, D.S.; Reddy, S.M.; Nagle, M.; Clark, S.D.; Weber, R.P.; Enyioha, C.; Malo, T.L.; Brenner, A.T.; Armstrong, C.; et al. Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography: Updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2021, 325, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid biopsies come of age: Towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouliere, F.; Chandrananda, D.; Piskorz, A.M.; Moore, E.K.; Morris, J.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Mair, R.; Goranova, T.; Marass, F.; Heider, K.; et al. Enhanced detection of circulating tumor DNA by fragment size analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.; Chandrananda, D.; Moore, E.; Mouliere, F.; Morris, J.; Brenton, J.D.; Smith, C.G.; Rosenfeld, N. Refined characterization of circulating tumor DNA through biological feature integration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaniani, Y.; Lipfert, M.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Perez Pineiro, R.; Zheng, J.; Wishart, D.S. A simple and convenient synthesis of unlabeled and 13C-labeled 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid and its quantification in human urine samples. Metabolites 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Johnson, M.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S. Comprehensive targeted metabolomic assay for urine analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10627–10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S. Chapter 14 Computational Approaches to Metabolomics. In Bioinformatics Methods in Clinical Research; Methods in Molecular Biology 593; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Discovery Set | |||||||||||||
| Class | Group | Number of Samples | Age | Histology | Gender | Smoking Status | |||||||
| Range | Mean | Median | Adenocarcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Male | Female | Never | Former | Current | Median Pack * × Years (Former + Current) | |||
| Lung Cancer | Stage I NSCLC | 275 | 31–81 | 64.8 | 66 | 200 | 75 | 137 | 138 | 15 | 187 | 73 | 39 |
| Stage II NSCLC | 141 | 38–82 | 65.9 | 66 | 98 | 43 | 68 | 73 | 3 | 110 | 28 | 40 | |
| Stage III + IV NSCLC | 50 | 49–78 | 64.8 | 63 | 32 | 18 | 28 | 22 | 7 | 41 | 2 | 35.3 | |
| Control | 214 | 28–90 | 60.7 | 61 | / | / | 116 | 98 | 98 | 88 | 28 | 0.9 | |
| Total | 680 | 28–90 | 63.5 | 64 | / | / | 349 | 331 | 123 | 426 | 131 | 34 | |
| Validation Set | |||||||||||||
| Class | Group | Number of Samples | Age | Histology | Gender | Smoking Status | |||||||
| Range | Mean | Median | Adenocarcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Male | Female | Never | Former | Current | Median Pack * × Years (Former + Current) | |||
| Lung Cancer | Stage I NSCLC | 70 | 49–79 | 66.1 | 67 | 50 | 20 | 26 | 44 | 14 | 40 | 16 | 30 |
| Stage II NSCLC | 60 | 59–79 | 63 | 63 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 5 | 50 | 5 | 30 | |
| Stage III + IV NSCLC | 26 | 42–79 | 61.7 | 63 | 20 | 6 | 14 | 12 | 0 | 18 | 8 | 40 | |
| Control | 60 | 49–77 | 62.6 | 63 | / | / | 26 | 34 | 38 | 22 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 216 | 42–79 | 64 | 65 | 110 | 46 | 86 | 130 | 57 | 130 | 29 | 33 | |
| Name of Metabolites | p-Value | Odds | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary of Each Feature | Citric acid | 7.30 × 10−7 | 0.47 |
| Tryptophan | 1.56 × 10−4 | 0.53 | |
| LysoPC a C18:2 | 1.44 × 10−9 | 0.31 | |
| Glutamine | 1.01 × 10−5 | 2.09 | |
| Succinic acid | 1.61 × 10−2 | 0.68 | |
| Citrulline | 1.22 × 10−7 | 2.11 | |
| PC aa C38:0 | 4.79 × 10−7 | 4.48 | |
| PC ae C40:6 | 4.26 × 10−6 | 0.23 | |
| LysoPC a C20:3 | 4.79 × 10−2 | 1.40 | |
| Carnitine | 9.29 × 10−2 | 1.29 | |
| Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year) | 1.56 × 10−14 | 3.55 | |
| Model Performance | AUC (95% CI) | 93.63% (91.76–95.50%) | |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | 88.20% (85.19–91.20%) | ||
| Specificity (95% CI) | 85.51% (80.84–90.19%) | ||
| Note: the numeric value of each named metabolite was scaled as follows: | |||
| Citric acid = (log10([Citric acid]/102.00) − 1.73)/0.16 | |||
| Tryptophan = (log10([Tryptophan]/43.10) − 1.34)/0.14 | |||
| LysoPC a C18:2 = (log10([LysoPC a C18:2]/18.62) − 1.00)/0.19 | |||
| Glutamine = (log10([Glutamine]/479.00) − 2.40)/0.11 | |||
| Succinic acid = (log10([Succinic acid]/2.21) + 0.09)/0.07 | |||
| Citrulline = (log10([Citrulline]/31.30) − 1.22)/0.15 | |||
| PC aa C38:0 = (log10([PC aa C38:0]/3.63) − 0.29)/0.14 | |||
| PC ae C40:6 = (log10([PC ae C40:6]/4.38) − 0.37)/0.13 | |||
| LysoPC a C20:3 = (log10([LysoPC a C20:3]/2.98) − 0.18)/0.15 | |||
| Carnitine = (log10([Carnitine]/34.64) − 1.26)/0.13 | |||
| Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year) = (log10([Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year)]/35.00) − 0.92)/0.83 | |||
| Name of Metabolites | p-Value | Odds | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary of Each Feature | Citric acid | 1.80 × 10−5 | 0.50 |
| Tryptophan | 6.80 × 10−4 | 0.56 | |
| LysoPC a C18:2 | 6.19 × 10−10 | 0.29 | |
| Glutamine | 1.42 × 10−5 | 2.09 | |
| Succinic acid | 6.22 × 10−3 | 0.63 | |
| Citrulline | 2.03 × 10−7 | 2.12 | |
| PC aa C38:0 | 7.99 × 10−8 | 5.45 | |
| PC ae C40:6 | 1.32 × 10−6 | 0.20 | |
| LysoPC a C20:3 | 3.01 × 10−2 | 1.45 | |
| Carnitine | 9.10 × 10−2 | 1.30 | |
| Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year) | 1.13 × 10−14 | 4.01 | |
| Model Performance | AUC (95% CI) | 93.74% (91.84–95.64%) | |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | 87.98% (84.62–90.86%) | ||
| Specificity (95% CI) | 85.98% (81.31–91.20%) | ||
| Note: the numeric value of each named metabolite was scaled as follows: | |||
| Citric acid = (log10([Citric acid]/105.00) − 1.90)/0.53 | |||
| Tryptophan = (log10([Tryptophan]/42.6) − 1.39)/0.15 | |||
| LysoPC a C18:2 = (log10([LysoPC a C18:2]/18.43) − 1.04)/0.20 | |||
| Glutamine = (log10([Glutamine]/472.00) − 2.45)/0.11 | |||
| Succinic acid = (log10([Succinic acid]/2.23) + 0.08)/0.07 | |||
| Citrulline = (log10([Citrulline]/30.7) − 1.24)/0.16 | |||
| PC aa C38:0 = (log10([PC aa C38:0]/3.54) − 0.33)/0.14 | |||
| PC ae C40:6 = (log10([PC ae C40:6]/4.32) − 0.42)/0.13 | |||
| LysoPC a C20:3 = (log10([LysoPC a C20:3]/2.94) − 0.23)/0.16 | |||
| Carnitine = (log10([Carnitine]/34.44) − 1.24)/0.16 | |||
| Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year) = (log10([Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year)]/33.00) − 0.88)/0.89 | |||
| Name of Metabolites | p-Value | Odds | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary of Each Feature | Citric acid | 1.54 × 10−4 | 0.49 |
| Tryptophan | 2.70 × 10−4 | 0.49 | |
| LysoPC a C18:2 | 4.21 × 10−9 | 0.27 | |
| Glutamine | 7.54 × 10−5 | 2.06 | |
| Succinic acid | 2.51 × 10−2 | 0.66 | |
| Citrulline | 2.85 × 10−8 | 2.58 | |
| PC aa C38:0 | 1.19 × 10−6 | 6.30 | |
| PC ae C40:6 | 7.59 × 10−6 | 0.17 | |
| LysoPC a C20:3 | 2.42 × 10−2 | 1.52 | |
| Carnitine | 4.44 × 10−2 | 1.42 | |
| Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year) | 2.67 × 10−12 | 4.43 | |
| Model Performance | AUC (95% CI) | 93.91% (91.86–95.95%) | |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | 90.54% (86.91–93.82%) | ||
| Specificity (95% CI) | 85.51% (80.37–90.19%) | ||
| Note: the numeric value of each named metabolite was scaled as follows: | |||
| Citric acid = (log10([Citric acid]/112.00) − 1.95)/0.58 | |||
| Tryptophan = (log10([Tryptophan]/43.1) − 1.40)/0.15 | |||
| LysoPC a C18:2 = (log10([LysoPC a C18:2]/19.05) − 1.06)/0.20 | |||
| Glutamine = (log10([Glutamine]/470.00) − 2.44)/0.11 | |||
| Succinic acid = (log10([Succinic acid]/2.28) + 0.08)/0.07 | |||
| Citrulline = (log10([Citrulline]/30.6) − 1.24)/0.16 | |||
| PC aa C38:0 = (log10([PC aa C38:0]/3.53) − 0.33)/0.15 | |||
| PC ae C40:6 = (log10([PC ae C40:6]/4.34) − 0.42)/0.14 | |||
| LysoPC a C20:3 = (log10([LysoPC a C20:3]/2.99) − 0.23)/0.16 | |||
| Carnitine = (log10([Carnitine]/34.74) − 1.32)/0.14 | |||
| Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year) = (log10([Amount of Smoking (Pack × Year)]/30.00) − 0.76)/0.95 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Bux, R.A.; Haince, J.-F.; Torres-Calzada, C.; Mandal, R.; Maksymiuk, A.; Huang, G.; Tappia, P.S.; Joubert, P.; et al. Clinical Validation of Plasma Metabolite Markers for Early Lung Cancer Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104519
Zhang L, Zheng J, Bux RA, Haince J-F, Torres-Calzada C, Mandal R, Maksymiuk A, Huang G, Tappia PS, Joubert P, et al. Clinical Validation of Plasma Metabolite Markers for Early Lung Cancer Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104519
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lun, Jiamin Zheng, Rashid A. Bux, Jean-François Haince, Claudia Torres-Calzada, Rupasri Mandal, Andrew Maksymiuk, Guoyu Huang, Paramjit S. Tappia, Philippe Joubert, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Validation of Plasma Metabolite Markers for Early Lung Cancer Detection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104519
APA StyleZhang, L., Zheng, J., Bux, R. A., Haince, J.-F., Torres-Calzada, C., Mandal, R., Maksymiuk, A., Huang, G., Tappia, P. S., Joubert, P., Rolfo, C. D., & Wishart, D. S. (2025). Clinical Validation of Plasma Metabolite Markers for Early Lung Cancer Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104519







