Shed Syndecans (1–3), ELA-32, BDNF, NLR, and hs-CRP in Parkinson’s Disease: Appropriate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers When Combined in a Unique Panel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of the Baseline Demographic Characteristics and Laboratory Indices Between the PD Group and the HC Group
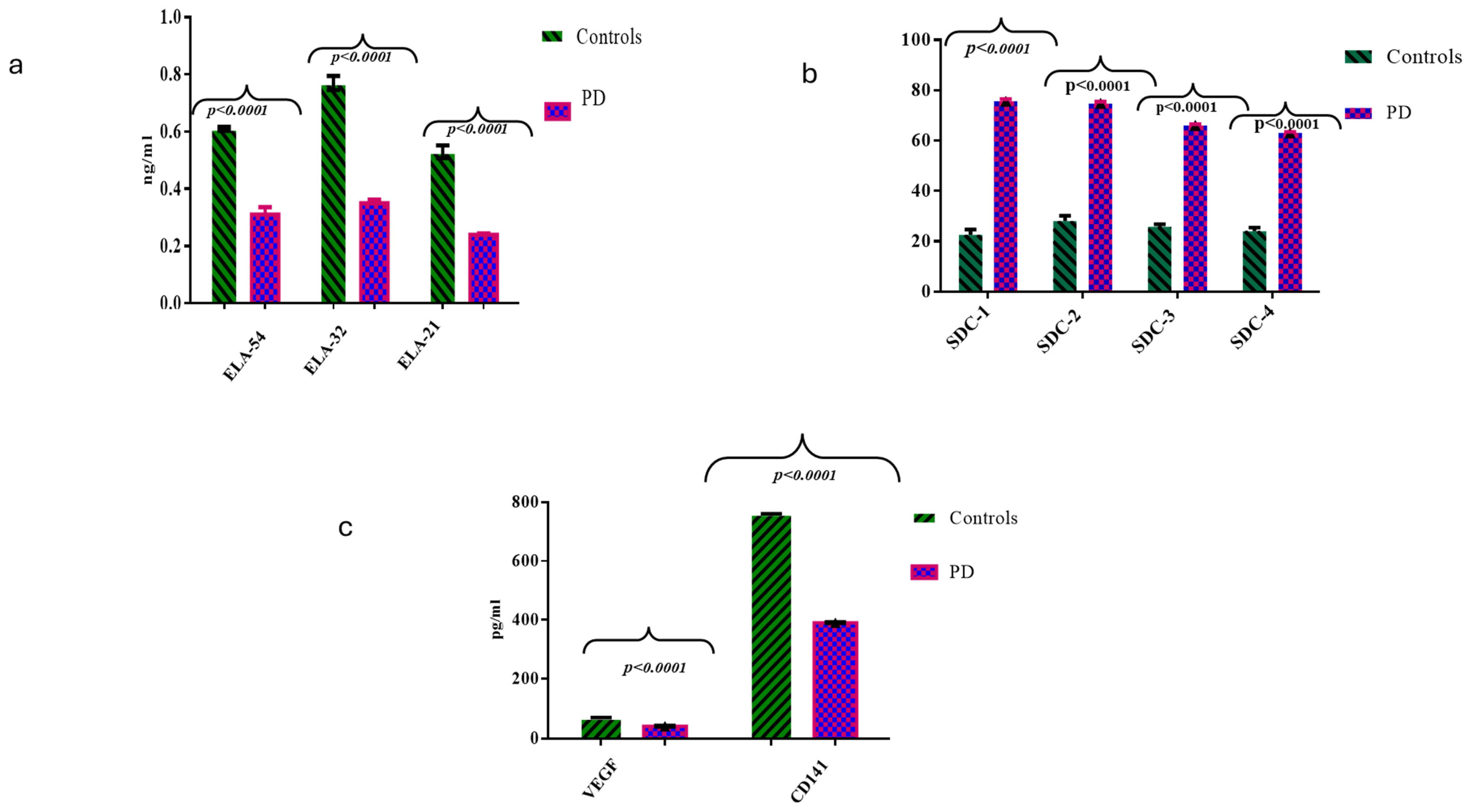
2.2. Comparisons of ELAs, SDCs, CD141, and VEGF Molecules Between the HC and PD Cases
2.3. Univariate and Multivariate Regression Analyses
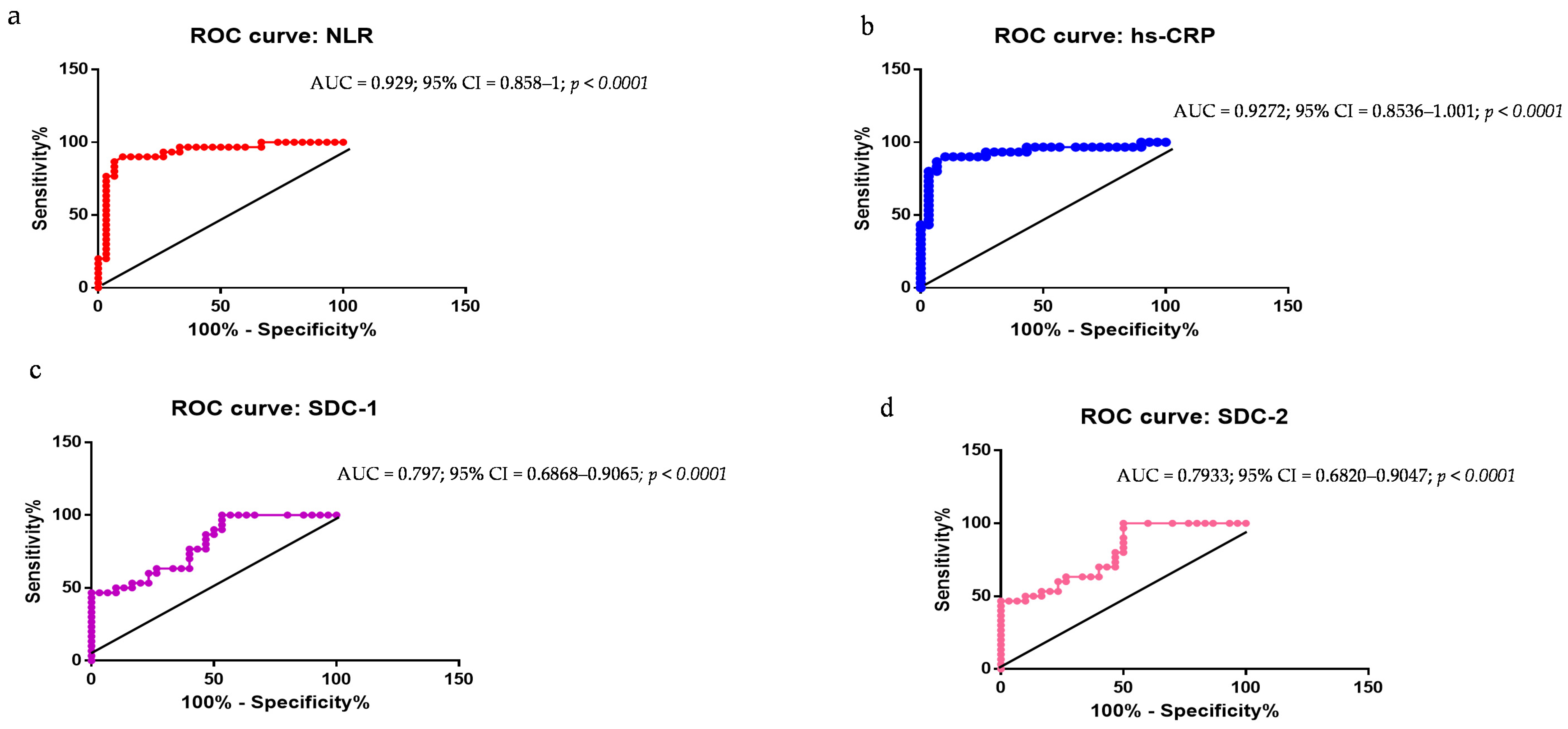
2.4. Evaluation of NLR, hs-CRP, SDC-1, SDC-2, SDC-3, ELA-32, and BDNF as PD Biomarkers: ROC Curve Analyses
3. Discussion, limitations and suggested strategies
3.1. Limitations
3.2. Strategies to Address Limitations
4. Population and Methods
4.1. Population Enrolled
4.2. Clinical Participants’ Information Collection
4.3. Quantification of Plasma Levels of hs-CRP, BDNF, ELAs, SDCs, CD141, and VEGF Molecules
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanner, C.M.; Ostrem, J.L. Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X.; Xue, Y.; Deng, Q. Current trends in blood biomarkers detection and neuroimaging for Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 104, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Fu, Q.; Guo, X.; He, H.; Yang, G. Potential biomarkers and treatment of neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2025, 53, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.L.; Teunissen, C.E.; Fiske, B.K.; Le Ber, I.; Wildsmith, K.R.; Schöll, M.; Dunn, B.; Scheltens, P. Biomarker-guided decision making in clinical drug development for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, G.; D’Antongiovanni, V.; Palermo, G.; Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Ceravolo, R.; Bernardini, N.; Derkinderen, P.; Pellegrini, C. α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: From bench to bedside. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 45, 909–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, C.C.; Maple-Grødem, J.; Lange, J. A systematic review of biofluid phosphorylated α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2024, 132, 107240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.X.; Tan, E.K.; Zhou, Z.D. The α-synuclein seeding amplification assay for Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R. Vascular ageing and the related complications in the brain: New insights on related mechanisms and their translational applications. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 196, 111469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.N.; Stoyanov, D.S.; Pavlov, S.P.; Tonchev, A.B. Distribution, function, and expression of the apelinergic system in the healthy and diseased mammalian brain. Genes 2022, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Libby, J.B.; Dumitrescu, L.; De Jager, P.L.; Menon, V.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Hohman, T.J. Association of ten VEGF family genes with Alzheimer’s disease endophenotypes at single cell resolution. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 21, e14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Monastero, R. Neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases: How much do we still not know? Brain Sci. 2023, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Hu, C.J.; Tu, Y.K. Endothelial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastero, R.; Magro, D.; Venezia, M.; Pisano, C.; Balistreri, C.R. A promising therapeutic peptide and preventive/diagnostic biomarker for age-related diseases: The Elabela/Apela/Toddler peptide. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Hu, B.; Cai, F.; Xu, Q.; Pan, S.; Wu, Y.; Song, W. Distinct effects of SDC3 and FGFRL1 on selective neurodegeneration in AD and PD. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Di Giorgi, L.; Monastero, R. Focus of endothelial glycocalyx dysfunction in ischemic stroke and Alzheimer’s disease: Possible intervention strategies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 99, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Collier, J.M.; Abdul-Rahman, N.H.; Capuk, O.; Zhang, Z.; Begum, G. Dysregulation of ion channels and transporters and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 1748–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Monastero, R. Syndecans in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogenetic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 2594–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Monastero, R. Promising biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: Levels of soluble eGCX products. Neural Regen Res. 2026; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Kisler, K.; Montagne, A.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. The role of brain vasculature in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, N.J.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. α-Synuclein Strains and Their Relevance to Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple System Atrophy, and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 24, 12134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirò, G.; Iacono, S.; Ragonese, P.; Aridon, P.; Salemi, G.; Balistreri, C.R. A brief overview on BDNF-Trk pathway in the nervous system: A potential biomarker or possible target in treatment of multiple sclerosis? Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 917527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriat, F.; Lobsiger, C.S.; Boillée, S. The contribution of the peripheral immune system to neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloske, C.M.; Mahinrad, S.; Barnum, C.J.; Batista, A.F.; Bradshaw, E.M.; Butts, B.; Carrillo, M.C.; Chakrabarty, P.; Chen, X.; Craft, S.; et al. Advancements in immunity and dementia research: Highlights from the 2023 AAIC Advancements: Immunity Conference. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 21, e14291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.L.; Chappard, A.; Singh, B.P.; Maclachlan, C.; Rodrigues, M.; Fedotova, E.I.; Berezhnov, A.V.; De, S.; Peddie, C.J.; Athauda, D.; et al. Pathological structural conversion of α-synuclein at the mitochondria induces neuronal toxicity. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hroudová, J.; Fišar, Z. Alzheimer’s disease approaches—Focusing on pathology, biomarkers and clinical trial candidates. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.J.; Heiman, M. Molecular and cellular characteristics of cerebrovascular cell types and their contribution to neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Neurodegener. 2025, 20, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio: An emerging marker of the relationships between the immune system and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doenyas, C.; Clarke, G.; Cserjési, R. Gut-brain axis and neuropsychiatric health: Recent advances. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Shafiabadi, N.; Khanzadeh, M.; Ghaedi, A.; Ghorbanzadeh, R.; Azarhomayoun, A.; Bazrgar, A.; Pezeshki, J.; Bazrafshan, H.; Khanzadeh, S. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, P.; Sancesario, G.M.; Bovenzi, R.; Zenuni, H.; Bissacco, J.; Mascioli, D.; Simonetta, C.; Forti, P.; Degoli, G.R.; Pieri, M.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte count reflect alterations in central neurodegeneration-associated proteins and clinical severity in Parkinson disease patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 112, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J.; Gan, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. C-reactive protein and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. A systematic review and meta-analysis of serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.X.; Wei, Y.D.; Hu, L. Lipid metabolic dysregulation is involved in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhao, P. Serum lipids and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Guo, W.; Li, S. Lower blood lipid level is associated with the occurrence of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 9773038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Quan, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Plasma lipidome, circulating inflammatory proteins, and Parkinson’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1424056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.H.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; AlAseeri, A.A.; Alruwaili, M.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E. BDNF/TrkB activators in Parkinson’s disease: A new therapeutic strategy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.T.; Schwinghamer, K.M.; Siahaan, T.J. Delivery of neuroregenerative proteins to the brain for treatments of neurodegenerative brain diseases. Life 2024, 14, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, M.; Kim, S.J. Insulin on activation of autophagy with integrins and syndecans against MPP+-induced α-synuclein neurotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 633, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudák, A.; Kusz, E.; Domonkos, I.; Jósvay, K.; Kodamullil, A.T.; Szilák, L.; Hofmann-Apitius, M.; Letoha, T. Contribution of syndecans to cellular uptake and fibrillation of α-synuclein and tau. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudák, A.; Letoha, A.; Vizler, C.; Letoha, T. Syndecan-3 as a novel biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Vincent, J.; Ezeanii, A.; Wakade, S.; Yerigenahally, S.; Mor, D.E. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate prion-like α-synuclein toxicity in Parkinson’s in vivo models. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202201366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, D.; Venezia, M.; Balistreri, C.R. The omics technologies and liquid biopsies: Advantages, limitations, applications. Med. Omics 2024, 11, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nader, M.A.; Deep, G. Emergence of extracellular vesicles as “liquid biopsy” for neurological disorders: Boom or bust. Pharmacol. Rev. 2024, 76, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Vinciguerra, C.; Magro, D.; Di Stefano, V.; Monastero, R. Towards personalized management of myasthenia gravis phenotypes: From the role of multi-omics to the emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, B.A. Uncovering the molecular mechanisms behind Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease through multi-omics: An interview with Bruno A. Benitez. BioTechniques. 2025, 77, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, F.; Ghirimoldi, M.; Fortunato, G.; Palomba, N.P.; Ianiro, L.; De Giorgis, V.; Khoso, S.; Giloni, T.; Pietracupa, S.; Modugno, N.; et al. Multiomics approach identifies dysregulated lipidomic and proteomic networks in Parkinson’s disease patients mutated in TMEM175. NPJ Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Halteren, A.D.; Munneke, M.; Smit, E.; Thomas, S.; Bloem, B.R.; Darweesh, S.K.L. Personalized care management for persons with Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10 (Suppl. S1), S11–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosefsky, K.N.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.N.; Lam, J.S.T.; Cammalleri, A.; Appel-Cresswell, S. The Role of Diet in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2024, 14 (Suppl. S1), S21–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.E.; Goh, L.; Canning, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Clemson, L.; Close, J.C.; Lord, S.R.; Lewis, S.J.G.; Edwards, S.; Harkness, S.; et al. Feasibility of a Multidomain Intervention for Safe Mobility in People with Parkinson’s Disease and Recurrent Falls. J. Mov. Disord. 2025, 18, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppala, S.N.; Tryphena, K.P.; Naren, P.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, S.B.; Khatri, D.K. Involvement of miRNA on epigenetics landscape of Parkinson’s disease: From pathogenesis to therapeutics. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 213, 111826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, W.R.; Lees, A.J. The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographic and Clinical Variables | HCs (N = 30) | PD (N = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 71.8 ± 2.8 | 71.2 ± 4.8 | 0.27 * |
| Gender (N, %) Male Female | 15 (50%) 15 (50%) | 19 (63%) 11 (37%) | 0.29 ** |
| WBC (×109/L) | 5.6 ± 1.4 | 6.7 ± 2.88 | 0.03 * |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 1.8 ± 2.2 | 1.63 ± 2.7 | 0.39 * |
| Neutrophils | 3.3 ± 1.18 | 4.4 ± 1.9 | 0.0052 * |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 55 ± 0.48 | 52 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 * |
| TG TC | 1.6 ± 0.71 4.8 ± 1.0 | 1.11 ± 0.52 4.1 ± 1.02 | 0.0057 * 0.0039 * |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 2.4 ± 2.9 | 8.8 ± 6.9 | <0.0001 * |
| NLR | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 2.7 ± 1.7 | 0.016 * |
| NHR LHR | 54.4 ± 2.9 34.4 ± 1.4 | 59.95 ± 3.1 36.7 ± 2.6 | <0.0001 * <0.0001 * |
| BDNF (pg/mL) | 8.2 ± 1.2 | 4.5 ± 2.2 | <0.0001 * |
| H&Y | N/A | 2.8 ± 1.9 (2–4) | - |
| Variables | OR (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | 5.2 (1.28–10.6) | 0.0051 |
| HDL-C | 4.2 (2.23–7.8) | 0.0001 |
| TG | 3.2 (1.27–8.9) | 0.0003 |
| TC | 3.3 (1.45–6.9) | 0.0048 |
| hs-CRP | 10.3 (0.23–19.8) | <0.0001 |
| NLR | 6.2 (1.28–10.6) | 0.0003 |
| NHR | 9.5 (1.23–16.8) | <0.0001 |
| LHR | 7.9 (1.23–9.6) | 0.0001 |
| BDNF | 7.5 (0.26–10.1) | 0.0001 |
| ELA-32 | 2.5 (1.56–7.2) | 0.003 |
| SDC-1 | 3.1 (3.7–6.9) | 0.0001 |
| SDC-2 | 4.1 (2.3–7.9) | 0.0004 |
| SDC-3 | 5.1 (2.3–7.9) | 0.0001 |
| CD141 | 2.5 (4.3–8.7) | 0.02 |
| VEGF | 3.9 (8.7–11.3) | 0.045 |
| Variables | OR (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| hs-CRP | 9.7 (0.29–15.8) | 0.0001 |
| NLR | 4.1 (1.23–9.1) | 0.003 |
| BDNF | 6.9 (0.25–9.1) | 0.0001 |
| ELA-32 | 2.5 (1.56–7.2) | 0.003 |
| SDC-1 | 5.1 (3.7–6.9) | 0.0001 |
| SDC-2 | 4.1 (2.3–7.9) | 0.0003 |
| SDC-3 | 5.9 (2.6–9.7) | 0.0001 |
| Variables | β | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|
| hs-CRP | 0.16 | 0.0001 |
| Neutrophils | 0.19 | 0.0002 |
| NLR | 0.22 | 0.003 |
| ELA-32 | −0.24 | 0.004 |
| BDNF | −0.17 | 0.0001 |
| H&Y scale | 0.15 | 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balistreri, C.R.; Magro, D.; Scola, L.; Aridon, P.; Ragonese, P.; Dos Santos Mendes, F.A.; Schirò, G.; D’Amelio, M. Shed Syndecans (1–3), ELA-32, BDNF, NLR, and hs-CRP in Parkinson’s Disease: Appropriate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers When Combined in a Unique Panel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104503
Balistreri CR, Magro D, Scola L, Aridon P, Ragonese P, Dos Santos Mendes FA, Schirò G, D’Amelio M. Shed Syndecans (1–3), ELA-32, BDNF, NLR, and hs-CRP in Parkinson’s Disease: Appropriate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers When Combined in a Unique Panel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104503
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalistreri, Carmela Rita, Daniele Magro, Letizia Scola, Paolo Aridon, Paolo Ragonese, Felipe Augusto Dos Santos Mendes, Giuseppe Schirò, and Marco D’Amelio. 2025. "Shed Syndecans (1–3), ELA-32, BDNF, NLR, and hs-CRP in Parkinson’s Disease: Appropriate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers When Combined in a Unique Panel" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104503
APA StyleBalistreri, C. R., Magro, D., Scola, L., Aridon, P., Ragonese, P., Dos Santos Mendes, F. A., Schirò, G., & D’Amelio, M. (2025). Shed Syndecans (1–3), ELA-32, BDNF, NLR, and hs-CRP in Parkinson’s Disease: Appropriate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers When Combined in a Unique Panel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104503







