Physiological and Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis Provides New Insights into Tolerance to Waterlogging Stress in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
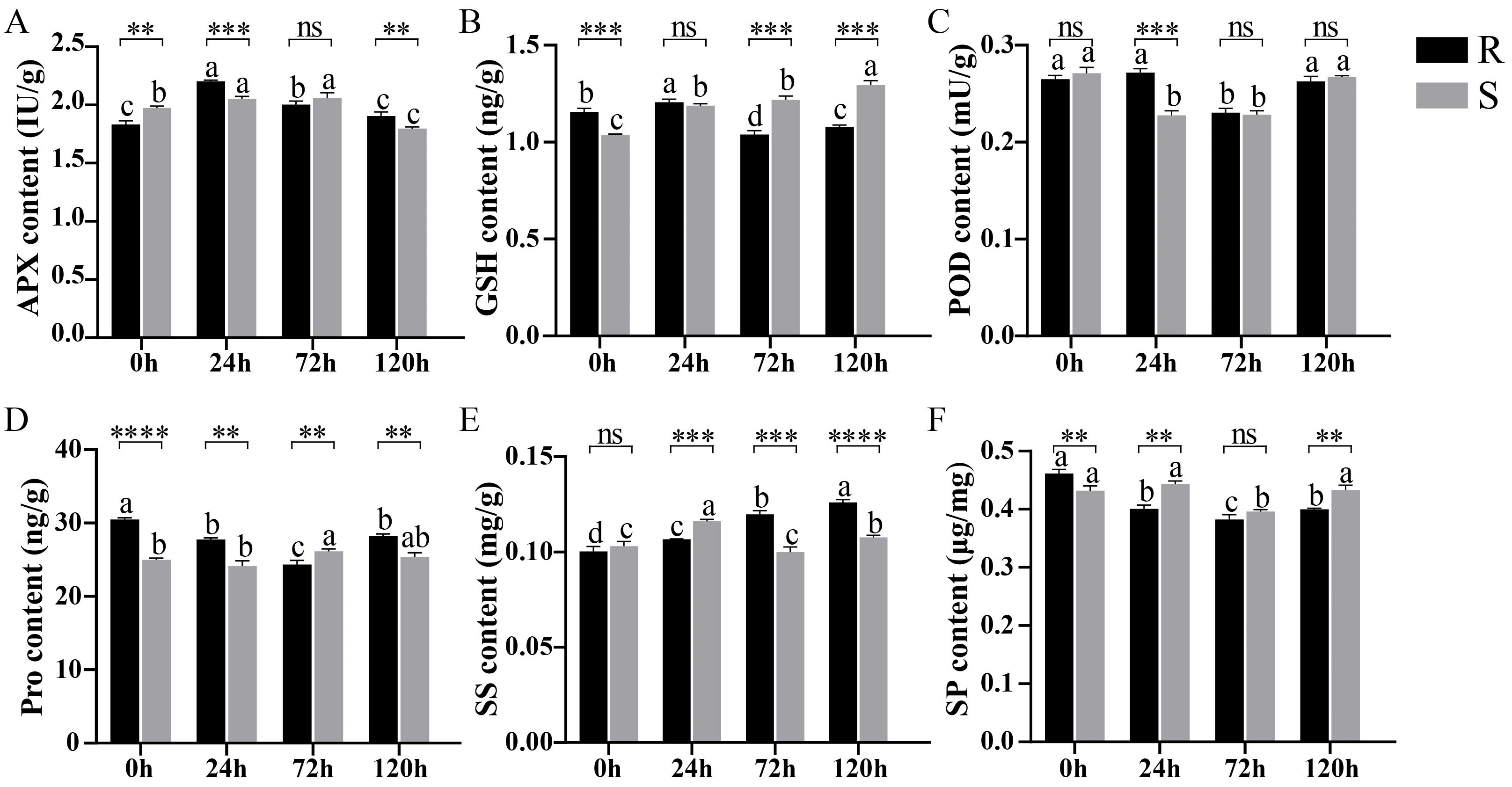
2.1. Analysis of the Physiological Indicators of Sesame Under Waterlogging Stress
2.2. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in Sesame Under Waterlogging Stress
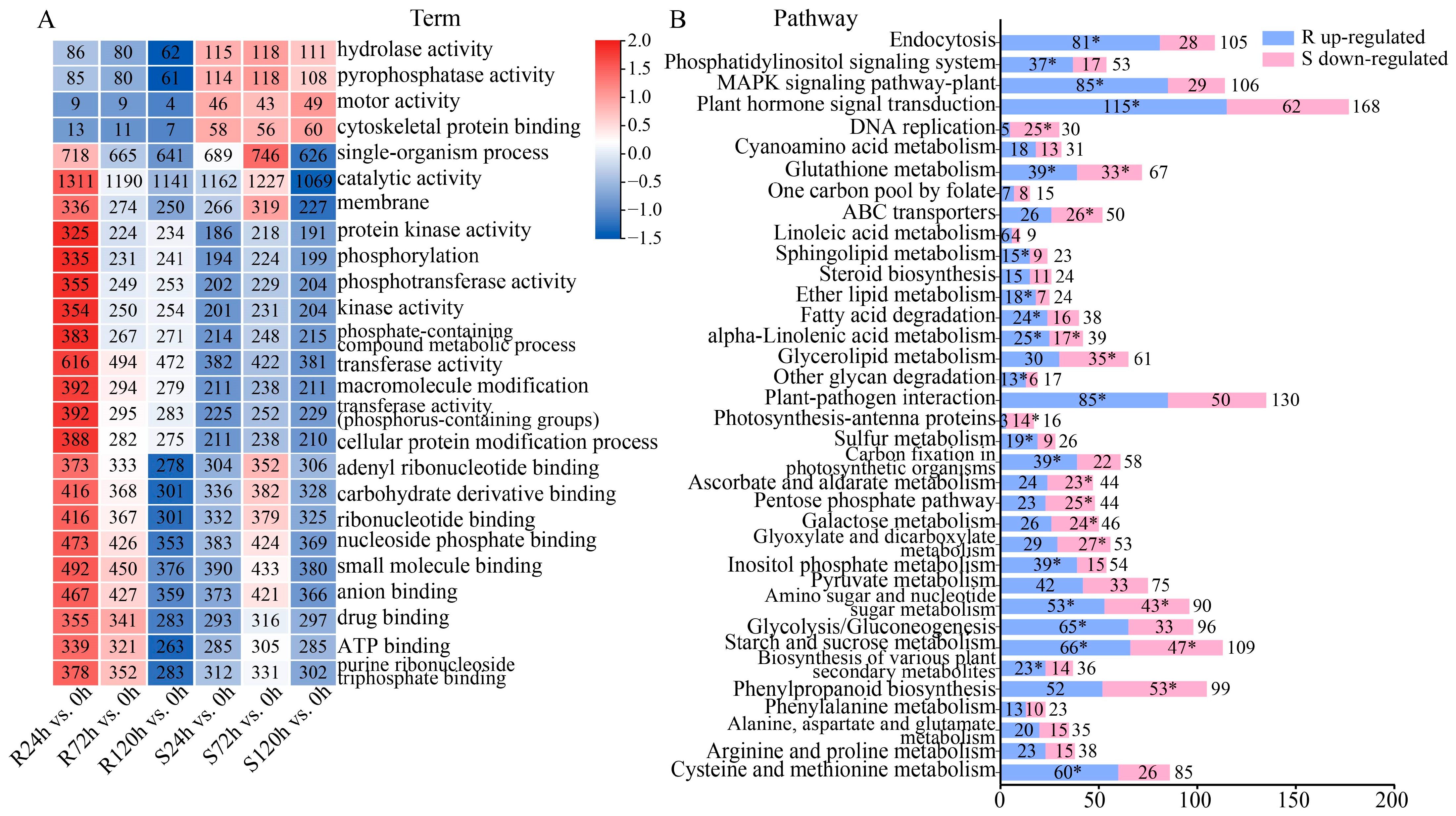
2.3. Analysis of DEGs Function Under Waterlogging Stress
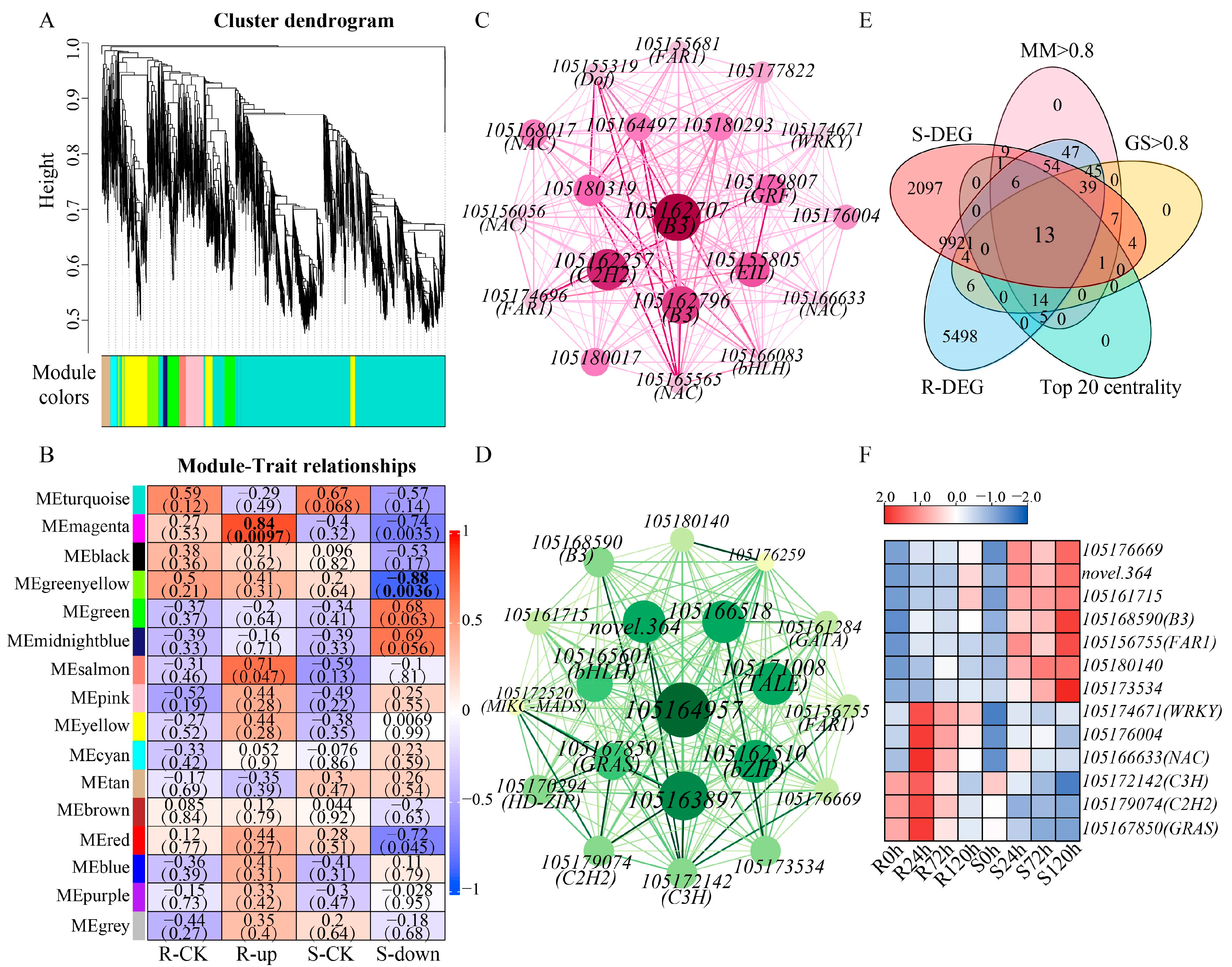
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) of Sesame Under Waterlogging Stress
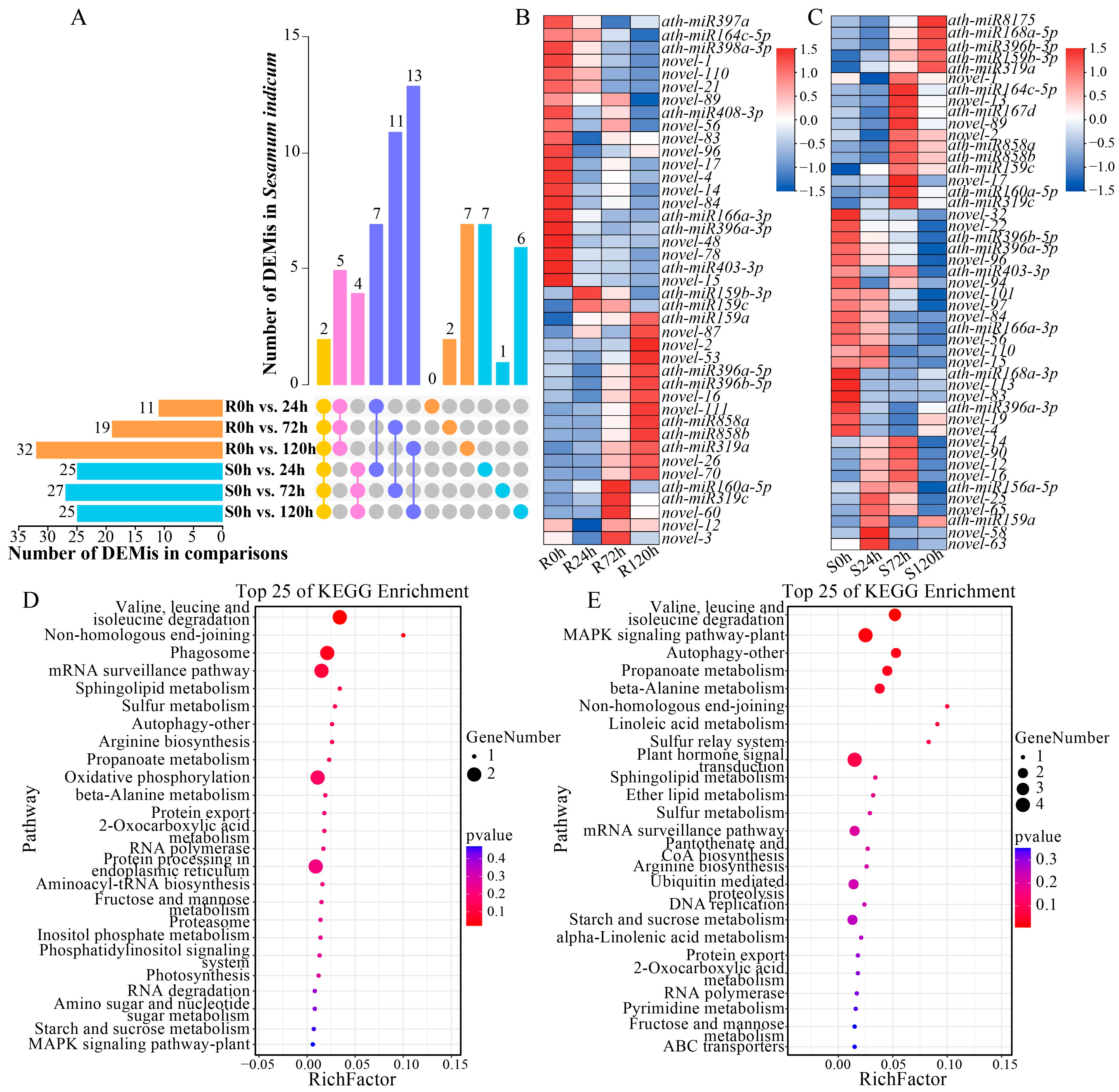
2.5. Differentially Expressed miRNAs (DEMis) Analysis of Sesame Under Waterlogging Stress
2.6. Construction of DEMi and DEG Co-Expression Networks
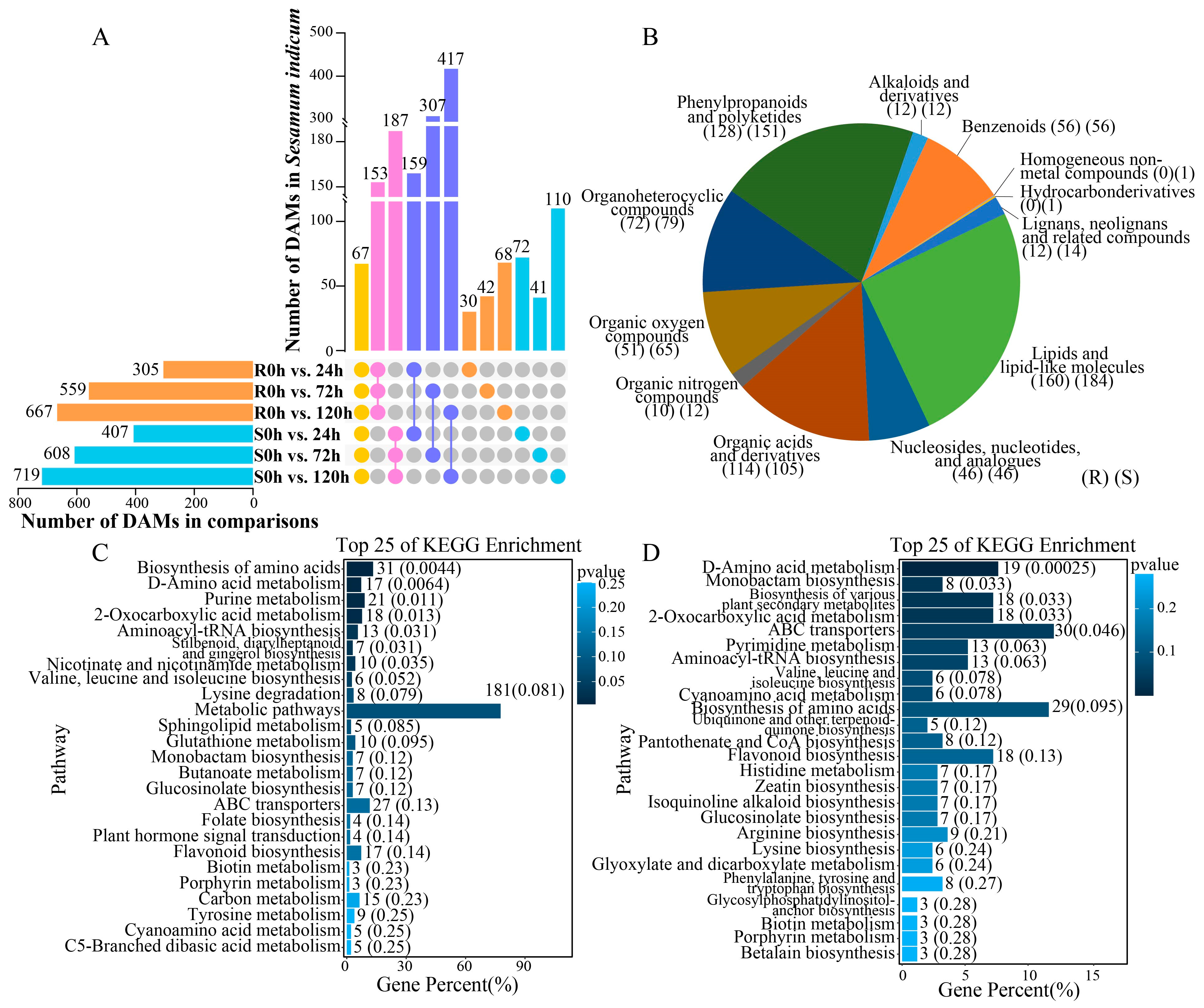
2.7. Analysis of Sesame Metabolites Under Waterlogging Stress
2.8. KEGG Pathway Analysis of the Integrated DEGs and DAMs
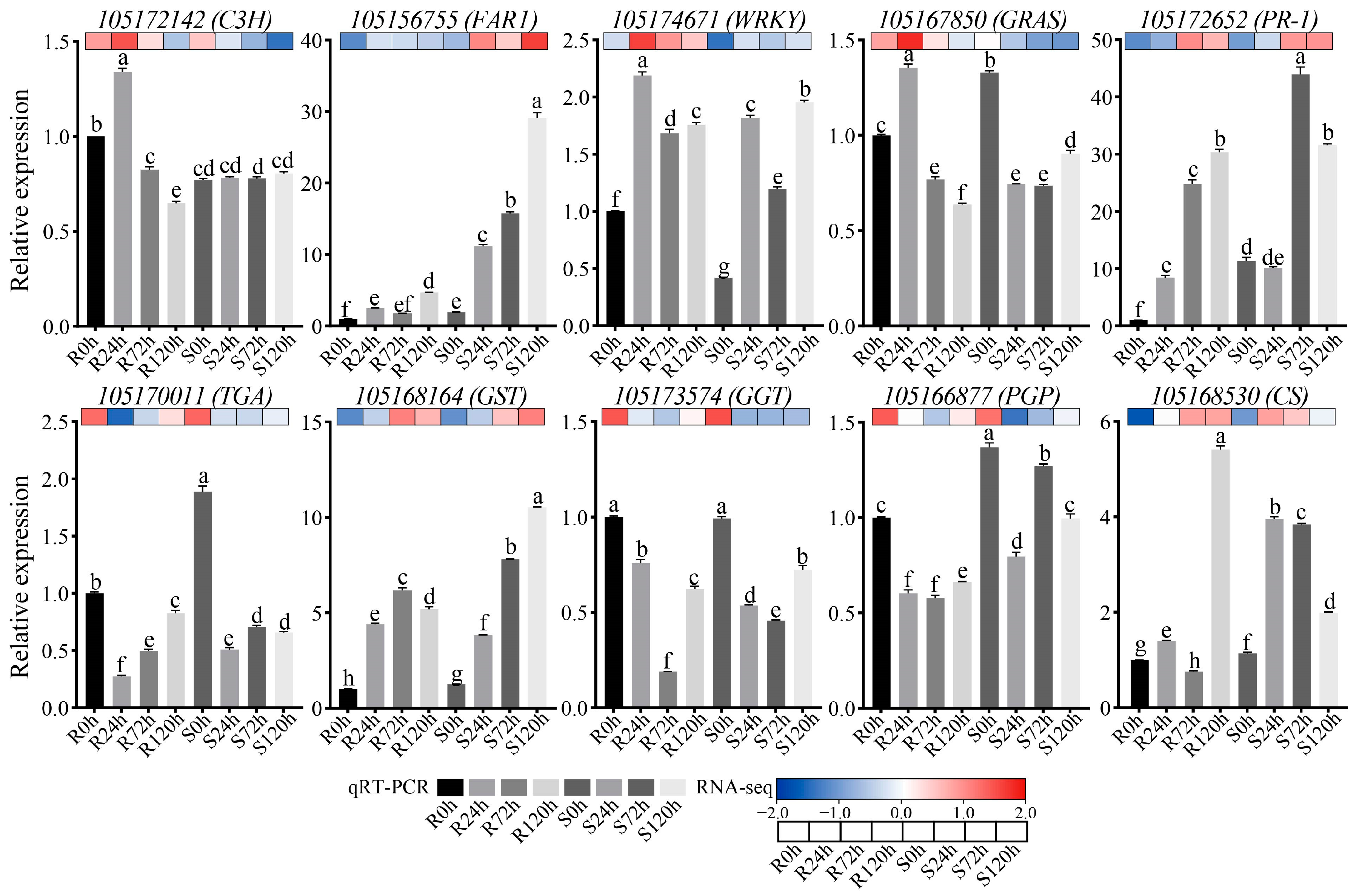
2.9. qRT-PCR Validation
3. Discussion
3.1. Transcriptome Analysis
3.2. Small RNA Sequencing Analysis
3.3. Metabolomics Analysis
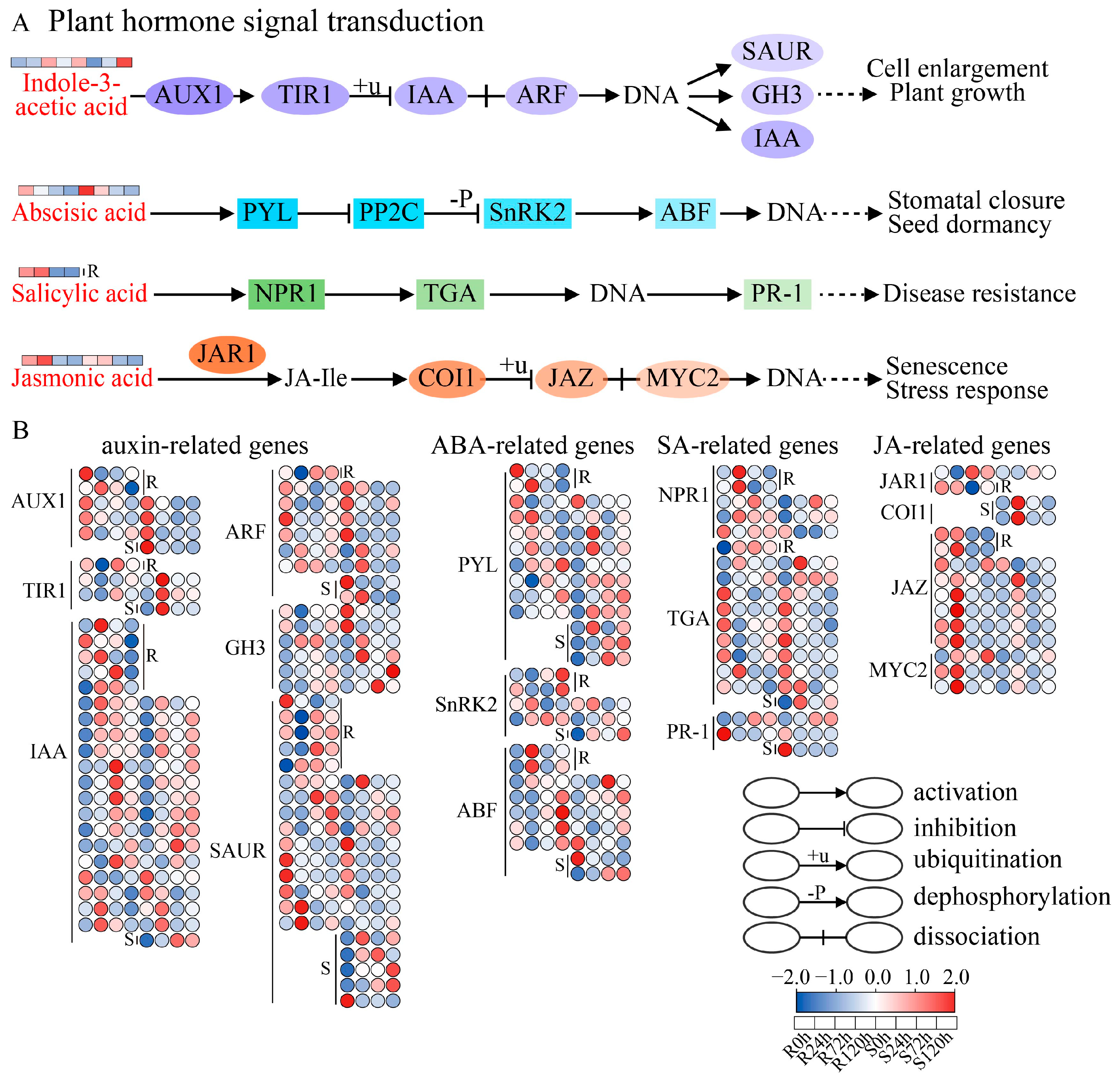
3.4. Plant Hormone Signal Transduction Pathway in Response to Sesame Waterlogging Stress
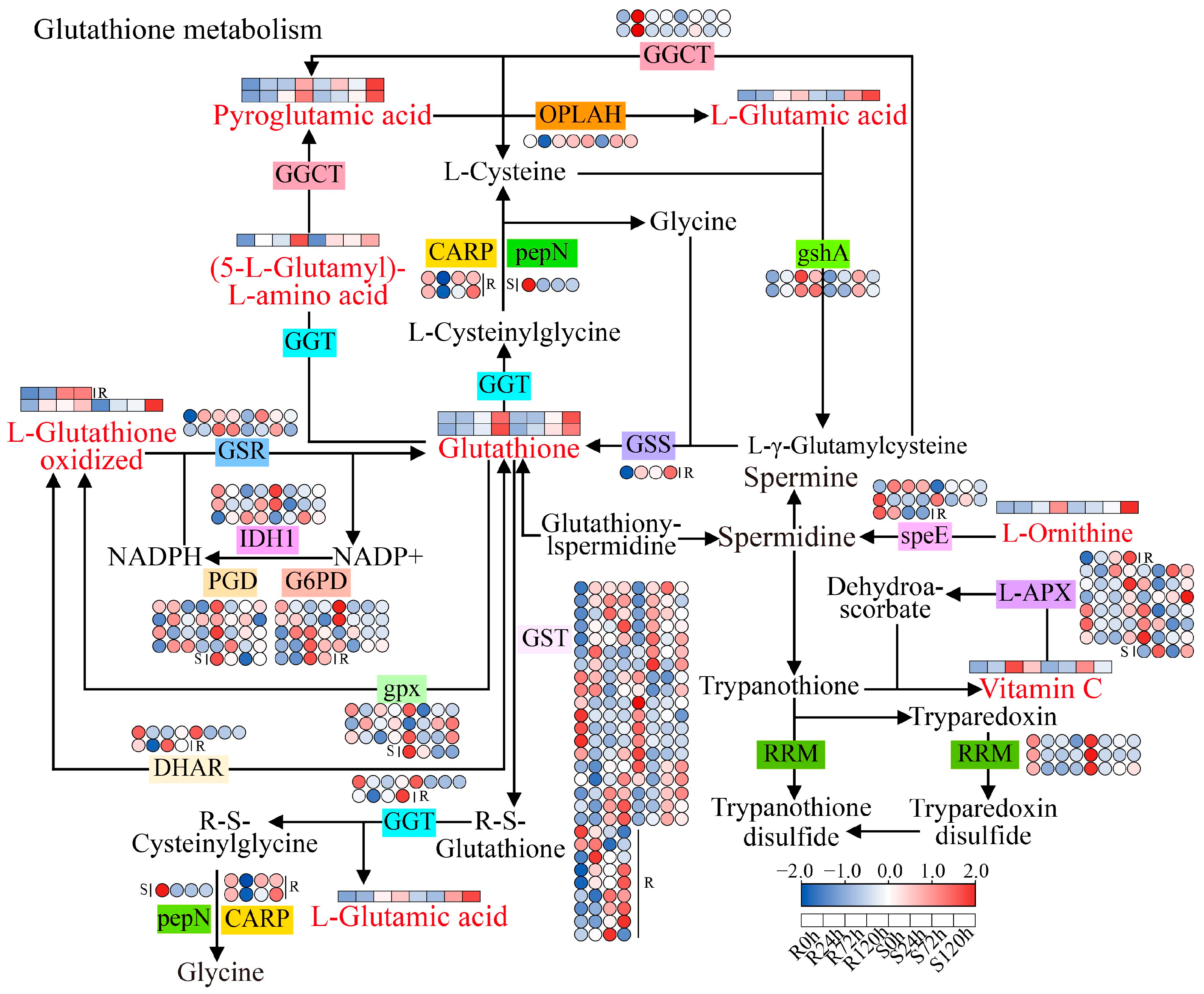
3.5. Glutathione Metabolic Pathway in Response to Sesame Waterlogging Stress
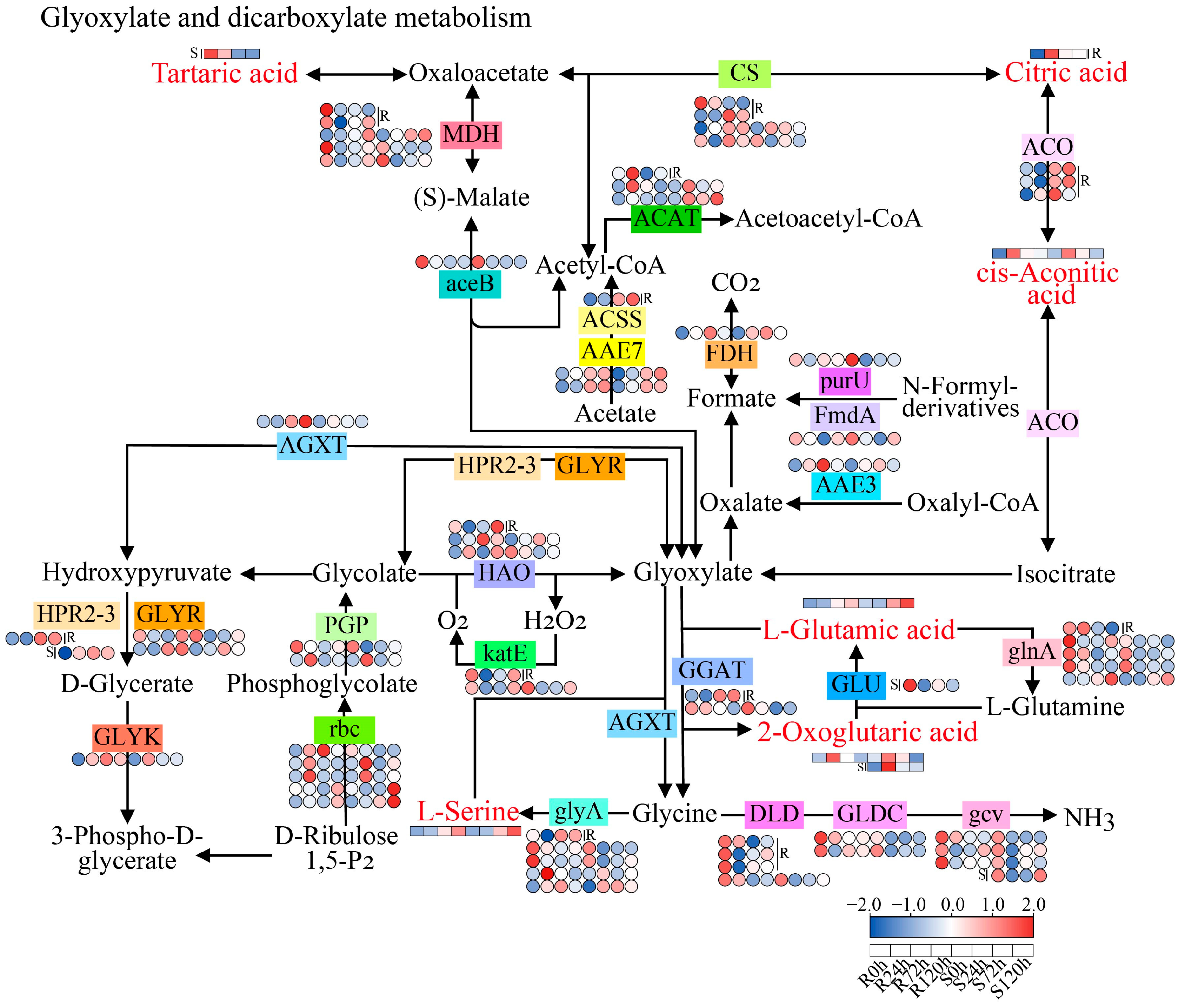
3.6. Glyoxylate and Dicarboxylate Metabolism Pathway in Response to Sesame Waterlogging Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Waterlogging Treatment
4.2. Physiological Phenotype of Sesame Under Waterlogging Treatment
4.3. Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis
4.4. Small RNA (sRNA) Sequencing Analysis
4.5. Metabolomics Sequencing Analysis
4.6. qRT-PCR Verification of Genes
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, J.; Sharif, R.; Xu, X.; Chen, X. Mechanisms of waterlogging tolerance in plants: Research progress and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 627331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, A.; Ullah, S.; Dar, A.A.; Sardar, M.F.; Mehmood, T.; Tufail, M.A.; Shakoor, A.; Haris, M. Nexus on climate change: Agriculture and possible solution to cope future climate change stresses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 14211–14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striker, G.G.; Colmer, T.D. Flooding tolerance of forage legumes. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1851–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domisch, T.; Qian, J.; Sondej, I.; Martz, F.; Lehto, T.; Piirainen, S.; Finér, L.; Silvennoinen, R.; Repo, T. Here comes the flood Stress effects of continuous and interval waterlogging periods during the growing season on Scots pine saplings. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 869–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.F.M.S.; Alam, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Akter, S.; Khan, M.A.H. Selection of waterlogging tolerant sesame genotypes (Sesamum indicum L.) from a dataset using the MGIDI index. Data Brief 2024, 53, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliappa, S.H.; Bomma, N.; Pranati, J.; Soregaon, C.D.; Hingane, A.J.; Basavaraj, P.S.; Satheesh Naik, S.J.; Lohithaswa, H.C.; Muniswamy, S.; Mushoriwa, H.; et al. Breeding for water-logging tolerance in pigeonpea: Current status and future prospects. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2024, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, P.R.; Ambros, S.; Müller, J.T.; Bammer, B.; Álvarez-Cansino, L.; Konnerup, D.; Pedersen, O.; Mustroph, A. Two Brassica napus cultivars differ in gene expression, but not in their response to submergence. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbona, V.; Hossain, Z.; López-Climent, M.F.; Pérez-Clemente, R.M.; Gómez-Cadenas, A. Antioxidant enzymatic activity is linked to waterlogging stress tolerance in citrus. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zheng, L.; Li, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Niu, X.; Geng, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Luo, K.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling suggests candidate molecular responses to waterlogging in cassava. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liang, K.; Fang, T.; Zhao, H.; Han, X.; Cai, M.; Qiu, F. A group VII ethylene response factor gene, ZmEREB180, coordinates waterlogging tolerance in maize seedlings. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 2286–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.H.M.; Komatsu, S. Jasmonic acid induced protein response to biophoton emissions and flooding stress in soybean. J. Proteom. 2016, 133, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreti, E.; Valeri, M.C.; Novi, G.; Perata, P. Gene regulation and survival under hypoxia requires starch availability and metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, L.; Hua, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Pei, X.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Creech, D.L. Identification and functional analysis of ThADH1 and ThADH4 genes involved in tolerance to waterlogging stress in Taxodium hybrid ‘Zhongshanshan 406’. Genes 2021, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, G.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, W.; Liu, F. Application of multi-omics analysis to plant flooding response. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1389379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Xu, Y.; Mattson, N.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, D. Identification of submergence-responsive microRNAs and their targets reveals complex miRNA-mediated regulatory networks in Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, C.; Covarrubias, A.A.; Reyes, J.L. A dicistronic precursor encoding miR398 and the legume-specific miR2119 coregulates CSD1 and ADH1 mRNAs in response to water deficit. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Singh, A.; Gandhi, N.; Sarkar Das, S.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, A.; Sarkar, A.K. A unique miR775-GALT9 module regulates leaf senescence in Arabidopsis during post-submergence recovery by modulating ethylene and the abscisic acid pathway. Development 2022, 149, dev199974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z. Response mechanism of Cynodon dactylon to flooding stress based on integrating metabonomics and transcriptomics analysis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 225, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Guo, B.; Lv, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Xu, R. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal molecular insights into waterlogging tolerance in Barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, P.; Shen, B.; Zeng, B.; Bi, L.; Qu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; et al. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomics analysis of the root responses of orchardgrass to submergence stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Zhang, L. Identification of genes/proteins related to submergence tolerance by transcriptome and proteome analyses in soybean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanni, G.B.T.A.; Ezin, V.; Chabi, I.B.; Missihoun, A.A.; Florent, Q.; Hamissou, Z.; Niang, M.; Ahanchede, A. Production and achievements of Sesamum indicum industry in the world: Past and current state. Oil Crop Sci. 2024, 9, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghery, M.A.; Kazemitabar, S.K.; Dehestani, A.; Mehrabanjoubani, P. Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) response to drought stress: Susceptible and tolerant genotypes exhibit different physiological, biochemical, and molecular response patterns. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2023, 29, 1353–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Gadol, N.; Priya, G.; Mishra, P.; Rao, M.; Singh, N.K.; Kumar, R.; Kalia, S.; Rai, V. Morpho-physiological and metabolites alteration in the susceptible and tolerant genotypes of sesame under waterlogging stress and post-waterlogging recovery. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, D.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. Global gene expression responses to waterlogging in roots of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, V.; Mishra, V.; Sharma, V.; Kumar, M.; Ghorbel, M.; Kumar, H.; Rai, A.; Kumar, R. Deciphering physio-biochemical basis of tolerance mechanism for sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes under waterlogging stress at early vegetative stage. Plants 2024, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimpong, D.; Zhao, L.; Ran, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Fang, Z.; Hu, Z.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the regulatory mechanisms of messenger RNA (mRNA) and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in response to waterlogging stress in rye (Secale cereale L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koramutla, M.K.; Tuan, P.A.; Ayele, B.T. Salicylic acid enhances adventitious root and aerenchyma formation in wheat under waterlogged conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; He, F.; Li, M.; Zi, Y.; Long, R.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, L.; Hong, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Multi-omics integrative analysis provided new insights into alkaline stress in alfalfa. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 215, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Tao, S.; Hu, Z.R.; Yang, J.S.; Cheng, X.; Hu, R.; Zhang, W. Transcriptome-based gene regulatory network analyses of differential cold tolerance of two tobacco cultivars. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Rossi, R.; Paesano, L.; Marmiroli, N.; Marmiroli, M. miRNA regulation and stress adaptation in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 184, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Kumari, S.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ware, D. Characterization of miRNAs in response to short-term waterlogging in three inbred lines of Zea mays. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kell, D.B.; Oliver, S.G. The metabolome 18 years on: A concept comes of age. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X. Morpho-anatomical and physiological responses to waterlogging of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Plant Sci. 2013, 208, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Zhou, B.; Peng, Z.; Yao, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Guan, C.; Guan, M. Tissue-specific transcriptome and metabolome analysis reveals the response mechanism of Brassica napus to waterlogging stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Yoshida, T.; Katagiri, T.; Kidokoro, S.; Kanamori, N.; Umezawa, T.; Fujita, M.; Maruyama, K.; Ishiyama, K.; et al. Three SnRK2 protein kinases are the main positive regulators of abscisic acid signaling in response to water stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.R.; Assmann, S.M. Hormone interactions in stomatal function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, T.; Yang, X.; Visser, E.J.; Te Beek, T.A.; Kensche, P.R.; Cristescu, S.M.; Lee, S.; Floková, K.; Nguyen, D.; Mariani, C.; et al. A co-opted hormonal cascade activates dormant adventitious root primordia upon flooding in Solanum dulcamara. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2351–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, D.; Seo, S.; Yamada, S.; Kano, A.; Miyamoto, A.; Shishido, H.; Miyoshi, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Akimitsu, K.; Gomi, K. Jasmonic acid and salicylic acid activate a common defense system in rice. Plant Signal Behav. 2013, 8, e24260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Zhan, M.; Cao, C.; Han, Y.; Ling, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Ye, M.; Jiang, Y. γ-Aminobutyric acid promotes chloroplast ultrastructure, antioxidant capacity, and growth of waterlogged maize seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateeq, M.; Khan, A.H.; Zhang, D.; Alam, S.M.; Shen, W.; Wei, M.; Meng, J.; Shen, X.; Pan, J.; Zhu, K.; et al. Comprehensive physio-biochemical and transcriptomic characterization to decipher the network of key genes under waterlogging stress and its recuperation in Prunus persica. Tree Physiol. 2023, 43, 1265–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Ahmed, N.; Saha, T.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, K.; Alam, M.M.; Rohman, M.M.; Nahar, K. Exogenous salicylic acid and kinetin modulate reactive oxygen species metabolism and glyoxalase system to confer waterlogging stress tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Stress 2022, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Vikal, Y.; Kaur, L.; Kalia, A.; Mittal, A.; Kaur, D.; Yadav, I. Elucidating the morpho-physiological adaptations and molecular responses under long-term waterlogging stress in maize through gene expression analysis. Plant Sci. 2021, 304, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreadeli, A.; Flemetakis, E.; Axarli, I.; Dimou, M.; Udvardi, M.K.; Katinakis, P.; Labrou, N.E. Cloning and characterization of Lotus japonicus formate dehydrogenase: A possible correlation with hypoxia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anee, T.I.; Nahar, K.; Rahman, A.; Mahmud, J.A.; Bhuiyan, T.F.; Alam, M.U.; Fujita, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Oxidative damage and antioxidant defense in Sesamum indicum after different waterlogging durations. Plants 2019, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, A.; Berardino, R.; de Pinto, M.C.; Sanità di Toppi, L.; Storelli, M.M.; Tommasi, F.; De Gara, L. Increase in ascorbate-glutathione metabolism as local and precocious systemic responses induced by cadmium in durum wheat plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; He, W.; Guo, J.; Chang, X.; Su, P.; Zhang, L. Increased sensitivity to salt stress in an ascorbate-deficient Arabidopsis mutant. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Tong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hua, W.; et al. Genome sequencing of the high oil crop sesame provides insight into oil biosynthesis. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. 2010. edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan microRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.J. PsRobot: A web-based plant small RNA meta-analysis toolbox. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling procedures for urine using UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xie, D.; Lu, M.; Li, P.; Lv, H.; Yang, C.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characterization of white tea metabolome: Comparison against green and black tea by a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haspel, J.A.; Chettimada, S.; Shaik, R.S.; Chu, J.H.; Raby, B.A.; Cernadas, M.; Carey, V.; Process, V.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Ifedigbo, E.; et al. Circadian rhythm reprogramming during lung inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; He, L.; Hu, L.; Tang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Physiological and Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis Provides New Insights into Tolerance to Waterlogging Stress in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010351
Zhang L, Wang S, Yang X, He L, Hu L, Tang R, Li J, Liu Z. Physiological and Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis Provides New Insights into Tolerance to Waterlogging Stress in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010351
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lu, Suhua Wang, Xuele Yang, Luqiu He, Liqin Hu, Rui Tang, Jiguang Li, and Zhongsong Liu. 2025. "Physiological and Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis Provides New Insights into Tolerance to Waterlogging Stress in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010351
APA StyleZhang, L., Wang, S., Yang, X., He, L., Hu, L., Tang, R., Li, J., & Liu, Z. (2025). Physiological and Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis Provides New Insights into Tolerance to Waterlogging Stress in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010351





