NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Etiology of HCC
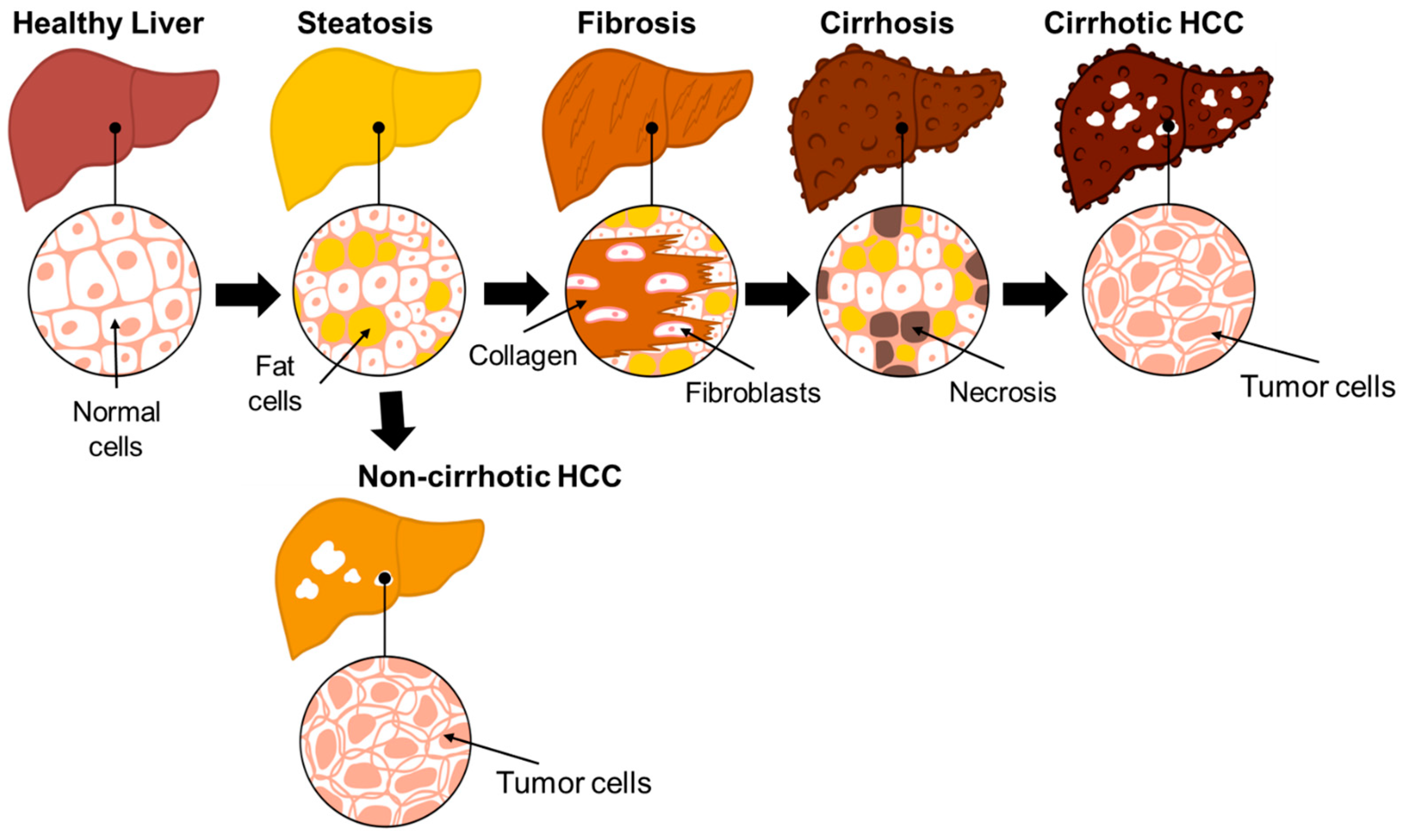
3. Progression of NAFLD to HCC
4. Limitations of HCC Diagnosis and Treatment
5. Clinical Trials
5.1. Changes in Lifestyle (Diet, Exercise, and Naturopathy)
5.2. Diagnostic Screening and Surveillance
5.3. Surgical Procedures
5.4. Drug Intervention
5.5. Combination Drug Therapy
6. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karlsen, T.H.; Sheron, N.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Carrieri, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Bugianesi, E.; Pryke, R.; Hutchinson, S.J.; Sangro, B.; Martin, N.K.; et al. The EASL-Lancet Liver Commission: Protecting the next generation of Europeans against liver disease complications and premature mortality. Lancet 2022, 399, 61–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; International Consensus, P. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y. Statin can reduce the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 35, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty, S.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, etiology and molecular classification. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, A.M.; Singal, A.G.; Tapper, E.B. Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2650–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangpunsakul, S.; Haber, P.; McCaughan, G.W. Alcoholic Liver Disease in Asia, Europe, and North America. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffy, G.; Brunt, E.M.; Caldwell, S.H. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging menace. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancatelli, G.; Federle, M.P.; Grazioli, L.; Carr, B.I. Hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver: CT, clinical, and pathologic findings in 39 U.S. residents. Radiology 2002, 222, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzeako, U.C.; Goodman, Z.D.; Ishak, K.G. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic livers. A clinico-histopathologic study of 804 North American patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 105, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, F.; Gairing, S.J.; Muller, L.; Galle, P.R. NAFLD-driven HCC: Safety and efficacy of current and emerging treatment options. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; El-Serag, H.B. Rational HCC screening approaches for patients with NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Villanueva, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Schwartz, M.; Meyer, T.; Galle, P.R.; Lencioni, R.; Greten, T.F.; Kudo, M.; Mandrekar, S.J.; et al. Trial Design and Endpoints in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: AASLD Consensus Conference. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. 1), 158–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.H.; Yang, B.H.; Tang, Z.Y. Randomized controlled trial of screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 130, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.G.; Liu, S.Y.; Lu, W.F.; Liang, L.; Ye, B. Survival Benefits From Adjuvant Lenvatinib for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Microvascular Invasion After Curative Hepatectomy. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2023, 17, 11795549231180351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puoti, C. New insights on hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and clinical aspects. Hepatoma Res. 2018, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: Where are we? Where do we go? Hepatology 2014, 60, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.C.S.; Huang, J.L.W.; George, J.; Huang, J.; Leung, C.; Eslam, M.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Ng, S.C. The changing epidemiology of liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal Chaudhary, S.; Reyes, S.; Chase, M.L.; Govindan, A.; Zhao, L.; Luther, J.; Bhan, I.; Bethea, E.; Franses, J.W.; Paige Walsh, E.; et al. Resection of NAFLD/NASH-related Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Clinical Features and Outcomes Compared with HCC Due to Other Etiologies. Oncologist 2023, 28, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makri, E.; Goulas, A.; Polyzos, S.A. Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Emerging Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolman, K.G.; Fonseca, V.; Dalpiaz, A.; Tan, M.H. Spectrum of liver disease in type 2 diabetes and management of patients with diabetes and liver disease. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Xin, X.; Ma, J.; Tan, C.; Osna, N.; Mahato, R.I. Therapeutic targets, novel drugs, and delivery systems for diabetes associated NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.T.; Kuo, P.L.; Su, S.B.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yeh, M.L.; Huang, C.I.; Yang, J.F.; Lin, C.I.; Hsieh, M.H.; Hsieh, M.Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease severity is associated with the ratios of total cholesterol and triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 420–425.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.; Finck, B.N. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geh, D.; Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L. NAFLD-Associated HCC: Progress and Opportunities. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, T.; Khare, S.; Angdisen, J.J.; Zhang, Q.; Stuckel, A.; Mooney, B.P.; Ridenhour, S.E.; Gitan, R.S.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Defects in long-chain 3-hydroxy acyl-CoA dehydrogenase lead to hepatocellular carcinoma: A novel etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassir, F. NAFLD: Mechanisms, Treatments, and Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kubota, N.; Crouchet, E.; Koneru, B.; Marquez, C.A.; Jajoriya, A.K.; Panda, G.; Qian, T.; Zhu, S.; Goossens, N.; et al. Molecular signatures of long-term hepatocellular carcinoma risk in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Lim, J.K.; Patton, H.; El-Serag, H.B. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Screening and Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmera, V.; Loomba, R. Imaging biomarkers of NAFLD, NASH, and fibrosis. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Raciti, M.V.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Nichetti, M.; De Cata, P.; Rondanelli, M.; Chiovato, L.; Calliada, F.; et al. Detection of Liver Steatosis with a Novel Ultrasound-Based Technique: A Pilot Study Using MRI-Derived Proton Density Fat Fraction as the Gold Standard. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoien, R.; Richardson, M.M.; Jonsson, J.R.; Powell, E.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bhathal, P.S.; Dixon, J.B.; O’Brien, P.E.; Tilg, H.; et al. Heterogeneity of fibrosis patterns in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease supports the presence of multiple fibrogenic pathways. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallsworth, K.; Adams, L.A. Lifestyle modification in NAFLD/NASH: Facts and figures. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5; quiz e314–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Rajak, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Tewari, A.; Anthony Sinha, R. Current treatment paradigms and emerging therapies for NAFLD/NASH. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2021, 26, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Yoneda, M.; Fujita, K.; Inamori, M.; Tamano, M.; Hiriishi, H.; Nakajima, A. Transient elastography in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Gut 2007, 56, 1330–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallio, M.; Masarone, M.; Romeo, M.; Tuccillo, C.; Morisco, F.; Persico, M.; Loguercio, C.; Federico, A. PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and MBOAT7 Influence on Nutraceutical Therapy Response for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 734847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Urrutia, A.; Lopez-Uribe, A.R.; El Hafidi, M.; Gonzalez-Salazar, M.D.C.; Posadas-Sanchez, R.; Jorge-Galarza, E.; Del Valle-Mondragon, L.; Juarez-Rojas, J.G. Chia (Salvia hispanica)-supplemented diet ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its metabolic abnormalities in humans. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Takai, K.; Hanai, T.; Suetsugu, A.; Shiraki, M.; Shimizu, M. Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance for Predicting the Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Kawada, N.; Japan Study Group of Nafld (JSG-NAFLD). The Role of Insulin Resistance and Diabetes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Que, S.; Xu, J.; Peng, T. Alanine aminotransferase-old biomarker and new concept: A review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, S.; Goyal, N.; Gupta, S. Preoperative CT evaluation of potential donors in living donor liver transplantation. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2014, 24, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, I.; Li, D.; Nasir, K.; Katz, R.; Larijani, V.N.; Budoff, M.J. Computed tomography scans in the evaluation of fatty liver disease in a population based study: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Acad. Radiol. 2012, 19, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldelli, A. Insulin resistance and reduced metabolic flexibility: Cause or consequence of NAFLD? Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2701–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsani, Z.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S.; Kia, V.; Karimkhanloo, H.; Zarghami, N.; Paryan, M. WNT1 Gene from WNT Signaling Pathway Is a Direct Target of miR-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzanegi, P.; Dana, A.; Ebrahimpoor, Z.; Asadi, M.; Azarbayjani, M.A. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Morris, R.T.; Laye, M.J.; Borengasser, S.J.; Booth, F.W.; Ibdah, J.A. Daily exercise increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation and prevents steatosis in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G619–G626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Sohn, J.H. Pharmacological advances in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases: Focused on global results of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S268–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.J.; VanWormer, J.J.; Crain, A.L.; Boucher, J.L.; Histon, T.; Caplan, W.; Bowman, J.D.; Pronk, N.P. Weight-loss outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of weight-loss clinical trials with a minimum 1-year follow-up. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif El Dahan, K.; Daher, D.; Singal, A.G. Hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S207–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B.; Sada, Y.H.; Kanwal, F.; Duan, Z.; Temple, S.; May, S.B.; Kramer, J.R.; Richardson, P.A.; Davila, J.A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Absence of Cirrhosis in United States Veterans is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 124–131.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Seko, Y.; Ishiba, H.; Hara, T.; Toyoda, H.; Yasuda, S.; Kumada, T.; Hayashi, H.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Surveillance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farci, P.; Roskams, T.; Chessa, L.; Peddis, G.; Mazzoleni, A.P.; Scioscia, R.; Serra, G.; Lai, M.E.; Loy, M.; Caruso, L.; et al. Long-term benefit of interferon alpha therapy of chronic hepatitis D: Regression of advanced hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowell, A.J.; Iredale, J.P. Emerging therapies for liver fibrosis. Dig. Dis. 2006, 24, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannah, W.N., Jr.; Harrison, S.A. Noninvasive imaging methods to determine severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Chang, Z.; Harrison, S.; Lomonaco, R.; Bril, F.; Orsak, B.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Hecht, J.; Feldstein, A.E.; Webb, A.; et al. Limited value of plasma cytokeratin-18 as a biomarker for NASH and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, R.; Tse, Y.K.; Wong, G.L.; Ha, Y.; Lee, A.U.; Ngu, M.C.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—The role of transient elastography and plasma cytokeratin-18 fragments. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J.; Bechmann, L.P.; Sowa, J.P.; Sydor, S.; Dechene, A.; Pflanz, K.; Bedreli, S.; Schotten, C.; Geier, A.; Berg, T.; et al. GALAD Score Detects Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma in an International Cohort of Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 728–735.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panera, N.; Gnani, D.; Crudele, A.; Ceccarelli, S.; Nobili, V.; Alisi, A. MicroRNAs as controlled systems and controllers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15079–15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuta, N.; Kawamura, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; Fujiyama, S.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Analysis of association between circulating miR-122 and histopathological features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients free of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braza-Boils, A.; Mari-Alexandre, J.; Molina, P.; Arnau, M.A.; Barcelo-Molina, M.; Domingo, D.; Girbes, J.; Giner, J.; Martinez-Dolz, L.; Zorio, E. Deregulated hepatic microRNAs underlie the association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary artery disease. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.J.; Fernandez Gianotti, T.; Castano, G.O.; Mallardi, P.; San Martino, J.; Mora Gonzalez Lopez Ledesma, M.; Flichman, D.; Mirshahi, F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sookoian, S. Circulating microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From serum non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut 2015, 64, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.H.; Wei, W.; Krawczyk, M.; Wang, W.; Luo, H.; Flagg, K.; Yi, S.; Shi, W.; Quan, Q.; Li, K.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA methylation markers for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, J.W.; Rosenberg, W.M. The enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) test in diagnosis and management of liver fibrosis. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 79, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; McCullough, A.J. Noninvasive Diagnosis of NASH and Liver Fibrosis Within the Spectrum of NAFLD. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 8, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhry, T.K.; Mhaskar, R.; Schwitalla, T.; Muradova, E.; Gonzalvo, J.P.; Murr, M.M. Bariatric surgery improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, G.; Panunzi, S.; Castagneto-Gissey, L.; Pellicano, F.; De Gaetano, A.; Pompili, M.; Riccardi, L.; Garcovich, M.; Raffaelli, M.; Ciccoritti, L.; et al. Accurate liquid biopsy for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Gut 2023, 72, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Damas, J.K.; Konopski, Z.; Loberg, E.M.; Haaland, T.; Goverud, I.; Torjesen, P.A.; Birkeland, K.; Bjoro, K.; Aukrust, P. Systemic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by elevated levels of CCL2. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Song, W.; Yuan, F. Diagnostic Value of CK-18, FGF-21, and Related Biomarker Panel in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9729107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Chalasani, N. Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Clinical prediction rules and blood-based biomarkers. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, P.S.; Kim, W.R.; Advanced Liver Disease Study, G. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology 2007, 45, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, F.; Valla, D. Assessment of the prognosis of cirrhosis: Child-Pugh versus MELD. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42 (Suppl S1), S100–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsakos, T.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Bakasis, A.D.; Kyrou, I.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Randeva, H.S.; Kassi, E. SGLT-2 Inhibitors in NAFLD: Expanding Their Role beyond Diabetes and Cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, B.G.; Park, W.Y.; Park, E.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Cha, S.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, Y.D.; et al. A prospective comparative assessment of the accuracy of the FibroScan in evaluating liver steatosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathani, R.R.; Bansal, M.B. Update on Clinical Trials for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 19, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, D.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Farnesoid X receptor (FXR): Structures and ligands. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stofan, M.; Guo, G.L. Bile Acids and FXR: Novel Targets for Liver Diseases. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Ratziu, V.; Loomba, R.; Anstee, Q.M.; Kowdley, K.V.; Rinella, M.E.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Trotter, J.F.; Knapple, W.; Lawitz, E.J.; et al. Results from a new efficacy and safety analysis of the REGENERATE trial of obeticholic acid for treatment of pre-cirrhotic fibrosis due to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juluri, R.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Olson, J.; Unalp, A.; Van Natta, M.L.; Cummings, O.W.; Tonascia, J.; Chalasani, N. Generalizability of the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network histologic scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Orsak, B.; Bril, F.; Lomonaco, R.; Hecht, J.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Tio, F.; Hardies, J.; Darland, C.; Musi, N.; et al. Long-Term Pioglitazone Treatment for Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.; Holm Nielsen, S.; Eslam, M.; Genovese, F.; Nielsen, M.J.; Vongsuvanh, R.; Uchila, R.; van der Poorten, D.; George, J.; Karsdal, M.A.; et al. Cross-Linked Multimeric Pro-Peptides of Type III Collagen (PC3X) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Biomarker That Provides Additional Prognostic Value in AFP Positive Patients. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2020, 7, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, A.; Guddati, A.K. Clinical endpoints in oncology—A primer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.A.; Bruinstroop, E.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypercholesterolemia: Roles of Thyroid Hormones, Metabolites, and Agonists. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, R.; Chiang, E.; Chabot-Blanchet, M.; Kelly, M.J.; Reeves, R.A.; Guertin, M.C.; Tardif, J.C. Lipid lowering in healthy volunteers treated with multiple doses of MGL-3196, a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Noureddin, M.; Kowdley, K.V.; Kohli, A.; Sheikh, A.; Neff, G.; Bhandari, B.R.; Gunn, N.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.; et al. Combination Therapies Including Cilofexor and Firsocostat for Bridging Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Attributable to NASH. Hepatology 2021, 73, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, M.; Seyedkazemi, S.; Francque, S.; Sanyal, A.; Rinella, M.; Charlton, M.; Loomba, R.; Ratziu, V.; Kochuparampil, J.; Fischer, L.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, phase 2b study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a combination of tropifexor and cenicriviroc in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis: Study design of the TANDEM trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2020, 88, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.J.; Bhandari, B.R.; Ruane, P.J.; Kohli, A.; Harting, E.; Ding, D.; Chuang, J.C.; Huss, R.S.; Chung, C.; Myers, R.P.; et al. Fenofibrate Mitigates Hypertriglyceridemia in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Patients Treated with Cilofexor/Firsocostat. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 143–152.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, D.C.; Rucker, P.V.; Chianelli, D.; Williams, J.; Vidal, A.; Alper, P.B.; Mutnick, D.; Bursulaya, B.; Schmeits, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Discovery of Tropifexor (LJN452), a Highly Potent Non-bile Acid FXR Agonist for the Treatment of Cholestatic Liver Diseases and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9960–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Zollner, G.; Trauner, M. Nuclear bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor meets nuclear factor-kappaB: New insights into hepatic inflammation. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Antonelli, E.; Rizzo, G.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Riccardi, L.; Orlandi, S.; Pellicciari, R.; Morelli, A. The nuclear receptor SHP mediates inhibition of hepatic stellate cells by FXR and protects against liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.; Sanyal, A.; Goodman, Z.; Lefebvre, E.; Gottwald, M.; Fischer, L.; Ratziu, V. Efficacy and safety study of cenicriviroc for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adult subjects with liver fibrosis: CENTAUR Phase 2b study design. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2016, 47, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Trial # | # of Participants | Eligible Age/Sex | Intervention | Target | Conditions | Phase or Study Type/Status | Start and End Date | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04861571 | 20 | 18–70 years old/all | Very low-calorie diet | Steatosis/transient elastography | NAFLD | Phase 1/ recruiting | Oct. 2023 to Dec. 2025 | Trial contd. |
| NCT04640324 | 92 | 18–80 years old/all | Nutraceutical therapy | HOMA-IR over 6 months/ALT | NAFLD and insulin resistance | Not applicable (NA)/completed | Jan. 2017 to Apr. 2018 | [46] |
| NCT06031532 | 110 | 20–80 years old/all | Vitamin A and Calcium | Serum vitamin A and calcium level, FibroScan, and ultrasound | NAFLD | Observational/completed | May. 2023 to Aug. 2023 | No results posted |
| NCT03354247 | 100 | 18–75 years old/all | Lifestyle | Changes in food intake and Mediterranean diet adherence score, physical activity level, BMI, abdominal girth, and liver steatosis score | NAFLD | NA/unknown | Jul. 2017 to Dec. 2020 | No results posted |
| NCT03467282 | 46 | 18–80 years old/all | Probiotic | Hepatic fibrosis and cardiovascular risk | NAFLD | NA/unknown | Nov. 2017 to Dec. 2021 | No results posted |
| NCT03942822 | 25 | 30–70 years old/all | Milled chia seeds | Liver/spleen attenuation index | NAFLD | NA/completed | Sep. 2016 to Sep. 2017 | [47] |
| NCT04835831 | 105 | 18–90 years old/all | Adapted physical activity and dietetic advice | Continuous CAP decreased by 10% | NAFLD | NA/recruiting | Sep. 2021 to Apr. 2026 | Trial contd. |
| Clinical Trial # | # of Participants | Eligible Age/Sex | Intervention | Target | Conditions | Phase or Study Type/Status | Start and End Date | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04834063 | 80 | 20–80 years/all | Serum zinc and selenium level and FibroScan measurement | Serum zinc and selenium levels and their association with hepatic fibrosis | NAFLD | Observational/completed | Mar. 2021 to Sep. 2021 | No results posted |
| NCT05870969 | 20000 | 18–75 years/all | Behavioral/liver cancer surveillance | Three-month, six-month, and yearly surveillance of liver cancer | Hep B, Hep C, HCC/Cirrhosis, and NAFLD | Observational/recruiting | Mar. 2023 to Mar. 2028 | Trial contd. |
| NCT05802199 | 300 | 18 years and older/all | Hepatic fat and hepatic fibrosis | The efficiency of UDFF (in %) for hepatic steatosis in comparison with MRI-PDFF (in %). | NAFLD | NA/recruiting | Jan. 2023 to Dec. 2023 | No results posted |
| NCT05754385 | 260 | 18–65 years/all | Ambulatory monitoring of liver fat and standard of care | Percentage of subjects with significant change in hepatic fat | NAFLD | NA/recruiting | May. 2023 to Oct. 2025 | Trial contd. |
| NCT06101758 | 125 | 18–69 years/all | Handgrip strength test, total body dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, and muscle ultrasound | Prevalence of sarcopenia in patients | NAFLD, liver cirrhosis, and HCC | NA/recruiting | Oct. 2023 to Jul. 2027 | Trial contd. |
| NCT03811236 | 26 | 18–50 years/all | Cold exposure | Hepatic lipid content (%) over six weeks by magnetic resonance imaging-proton density and brown adipose tissue volume over six weeks by 18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging | NAFLD | NA/recruiting | Jan. 2019 to Dec. 2026 | Trial contd. |
| NCT04820036 | 20 | 18–65 years/all | Insulin resistance, quality-of-life assessment, liver function test, radiologic and serologic features of NASH, endoscopic ultrasound, and endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty | EUS-guided liver biopsy with portal pressure gradient measurement from 0–12 months | NASH, NAFLD, Fibrosis, and Obesity | NA/active, not recruiting | May 2021 to Dec. 2024 | Trial contd. |
| NCT05486429 | 100 | 18–65 years/all | Abdominal ultrasound and lipid profile in different grades of NAFLD | Serum total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, LDL, and VLDL in 6 months | NAFLD | Observational/unknown | Jul. 2022 to Jan. 2023 | Results submitted |
| NCT03307408 | 180 | 18 years and older/all | Blood collection | Assessment of liver stages by biochemical, genetic, and immunocytochemistry methods | HCC | Observational/unknown | Feb. 2017 to Feb. 2020 | No results posted |
| NCT04264754 | 120 | 22 years and older/all | Blood collection | Methylation patterns-based blood test | HCC/cirrhosis | Observational/terminated | Feb. 2018 to Feb. 2021 | Trial terminated |
| NCT05370053 | 450 | 18 years and older/all | ELF test | F3-F4 fibrosis over 2 years | NAFLD and fatty liver | NA/Unknown | Sep. 2020 to Dec. 2022 | No results posted |
| NCT04785937 | 50 | 18 years and older/all | Ultrasound and magnetic resonance | False positives and negatives, sensitivity, and specificity | NAFLD, NASH, and liver fibrosis | NA/unknown | Jan. 2019 to Jun. 2022 | No results posted |
| NCT05165446 | 35 | 18–99 years/all | Image-based surveillance | Tissue viscoelasticity assessment by novel MRE | NASH | Observational/active, not recruiting | Jan. 2022 to Mar. 2024 | No results posted |
| NCT06328283 | 90 | All/all | Glutamine synthetase and BCLAF1 | Glutamine synthetase and BCLAF1 measurement | HCC | Observational/not yet recruiting | Apr. 2024 to Mar. 2026 | Trial contd. |
| Clinical Trial # | # of Participants | Eligible Age/Sex | Intervention | Target | Conditions | Phase or Study Type/Status | Start and End Date | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03536650 | 14 | 28–75 years/All | Duodenal mucosal resurfacing | Adverse device effects over one year | NASH | NA/completed | Nov. 2017 to Dec. 2020 | No results posted |
| NCT03524365 | 288 | 25–70 years/All | RYGB vs. SG with intensive lifestyle modifications | Histological resolution of NASH without worsening of fibrosis at 1 year after the interventions | NASH | NA/completed | Dec. 2018 to July 2022 | [76] |
| NCT04677101 | 150 | All/All | Liver biopsy | Validate blood biomarker sensitivity and accuracy in predicting NASH and fibrosis stage | NASH and Liver fibrosis | Observational/completed | Dec. 2020 to Apr. 2021 | [76] |
| NCT05623150 | 710 | 18 years and older/All | Liver biopsy | Variations in metabolic gene markers | NAFLD, AFLD, NASH, and HCC/cirrhosis | Observational/not yet recruiting | Dec. 2022 to Mar. 2032 | Trial contd. |
| NCT04281303 | 10 | 18–65 years/All | Endoscopic vertical gastroplasty | Adverse events, MELD, and Child–Pugh score | NASH/cirrhosis and obesity | Observational /unknown | Apr. 2020 to Apr. 2022 | No results posted |
| NCT04653311 | 100 | 18–70 years old/All | Endoscopic sutured gastroplasty and endomina device | Rate of disappearance of NASH without worsening of fibrosis grade | NASH | NA/unknown | Jun. 2023 to Dec. 2023 | No results posted |
| Clinical Trial # | # of Participants | Eligible Age/Sex | Intervention | Targets | Conditions | Phase or Study Type/Status | Start and End Date | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05694923 | 55 | 18–70 years/all | Empagliflozin or diet control | Assessment of steatosis and fibrosis by FibroScan as a CAP score over 3 months | Non-diabetic NAFLD | NA/completed | Apr. 2023 to Apr. 2024 | No results posted |
| NCT06256926 | 30 | 18–70 years old/all | Curcuvail or placebo | Change in NAFLD grading based on liver ultrasound from baseline to day 60 | NAFLD | Phase 2/completed | Jan. 2021 to Nov. 2021 | No results posted |
| NCT03439254 | 919 | 18 years and older/all | Obeticholic acid or placebo | Participants showing improvement in fibrosis by at least one stage without worsening of NASH | Compensated cirrhosis and NASH | Phase 3/completed | Aug. 2017 to Sep. 2022 | Results posted |
| NCT05254626 | 100 | 18–65 years/all | Dapagliflozin and Pioglitazone | NAS score | NASH/diabetic/non-diabetic | Phase 2/completed | Aug. 2022 to Sep. 2024 | No results posted |
| NCT04501406 | 166 | 21–75 years/all | Pioglitazone or placebo | Achieve an improvement of ≥2 points in NAS score without an increase in fibrosis stage. | NASH and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Phase 2/recruiting | Dec. 2020 to Aug. 2027 | Trial contd. |
| NCT04550481 | 45 | 18 years and older/all | Lisinopril MRI MRE LUE PDFF | PRO-C3, PC3X, steatosis, NFS, and inflammatory markers | HCC and NASH | Phase 2/ recruiting | May 2021 to Sep. 2025 | Trial contd. |
| NCT05622071 | 50 | 18 years and older/all | Tislelizumab | ORR, limiting toxicity, OS, and PFS | HCC by BCLC stage | Phase 2/recruiting | Oct. 2023 to Apr. 2028 | Trial contd. |
| NCT05391867 | 70 | 18–65 years/all | Lenvatinib vs. sorafenib | Overall Survival | HCC | NA/unknown | Jan. 2022 to Jun. 2023 | No results posted |
| NCT05733897 | 150 | All/all | Hydroxychloroquine | ALT levels over 1 year | NASH | Observational/recruiting | Jun. 2022 to Jul. 2025 | Trial contd. |
| NCT06400771 | 12 | 19–55 years/male | DNP007 | Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of DNP007 | NASH and Liver Transplant Rejection/Complications | Phase 1/recruiting | May 2024 to Dec. 2024 | Trial contd. |
| NCT03479125 | 40 | 18 years and older/all | Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scan in HCC patients previously treated with Emricasan or placebo | Adjusted event rate for HCC in patients previously treated with Emricasan or placebo | Liver diseases | Observational/terminated because the production of Emricasan by the sponsor was discontinued | Feb. 2018 to Sep. 2019 | Trial terminated |
| NCT03900429 | 1759 | 18 years or older/all | MGL-3196 (resmetirom) or placebo and liver biopsy | Two-point reduction in NAS score without worsening of fibrosis stage over 52 weeks | NASH | Phase 3/active, not recruiting | Mar. 2019 to Jan. 2028 | [91] |
| NCT05500222 | 700 | 18 years or older/all | MGL-3196 (resmetirom) or placebo | Liver related outcomes with confirmed increase in MELD score <12 to ≥ 15 | NASH/Cirrhosis | Phase3/recruiting | Aug. 2022 to Jan. 2027 | Trial contd. |
| Clinical Trial # | # of Participants | Eligible Age/Sex | Intervention | Targets | Conditions | Phase/Status | Start and End Date | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03449446 | 395 | 18 years to 80 years/all | Selonsertib, firsocostat, and cilofexor | Safety and tolerability (alone or in combination), change in liver fibrosis without worsening of NASH | Bridging fibrosis (F3) or compensated cirrhosis (F4) | Phase 2/completed | Mar. 2018 to Nov. 2019 | [97] |
| NCT03517540 | 193 | 18 years or older/all | Tropifexor and cenicriviroc | Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of combination therapy, adverse and serious adverse event | NASH with fibrosis stage F2/F3 | Phase2/completed | Sep. 2018 to Oct. 2020 | [98] |
| NCT04065841 | 234 | 18 years or older/All | Tropifexor, licogliflozin, or placebo | At least 1-stage reduction in fibrosis without worsening of NASH | NASH with fibrosis | Phase2/terminated | Dec. 2019 to Oct. 2022 | Terminated |
| NCT03987074 | 109 | 18 years to 75 years/All | Semaglutide, firsocostat, and cilofexor | Safety, tolerability of monotherapy and combination therapy | NASH with stage 2–3 fibrosis | Phase2/completed | July 2019 to July 2020 | Completed |
| NCT05415722 | 162 | 18 years to 75 years/All | TERN-501 and TERN-101 or Placebo | Safety, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of mono or combination therapy | NASH/non-cirrhotic | Phase2/completed | July 2022 to July 2023 | Completed |
| NCT02781584 | 220 | Selonsertib, firsocostat, cilofexor, fenofibrate, and/or Vascepa | Safety and tolerability of drugs in patients with NASH/NAFLD | NASH/NAFLD | Phase2/completed | June 2016 to Dec. 2020 | [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khare, T.; Liu, K.; Chilambe, L.O.; Khare, S. NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010306
Khare T, Liu K, Chilambe LO, Khare S. NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010306
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhare, Tripti, Karina Liu, Lindiwe Oslee Chilambe, and Sharad Khare. 2025. "NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010306
APA StyleKhare, T., Liu, K., Chilambe, L. O., & Khare, S. (2025). NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010306






