Novel KCNQ2 Variants Related to a Variable Phenotypic Spectrum Ranging from Epilepsy with Auditory Features to Severe Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
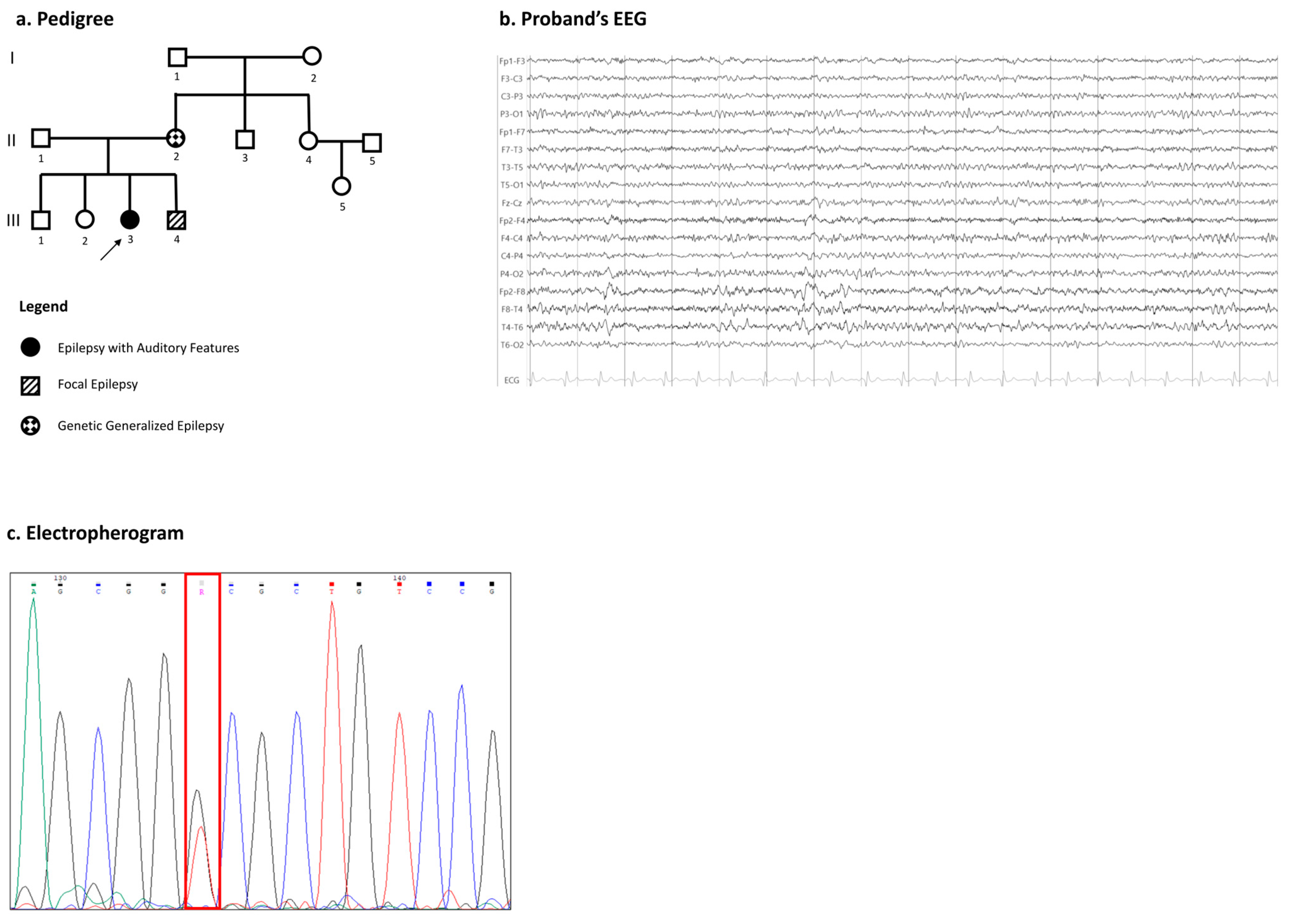
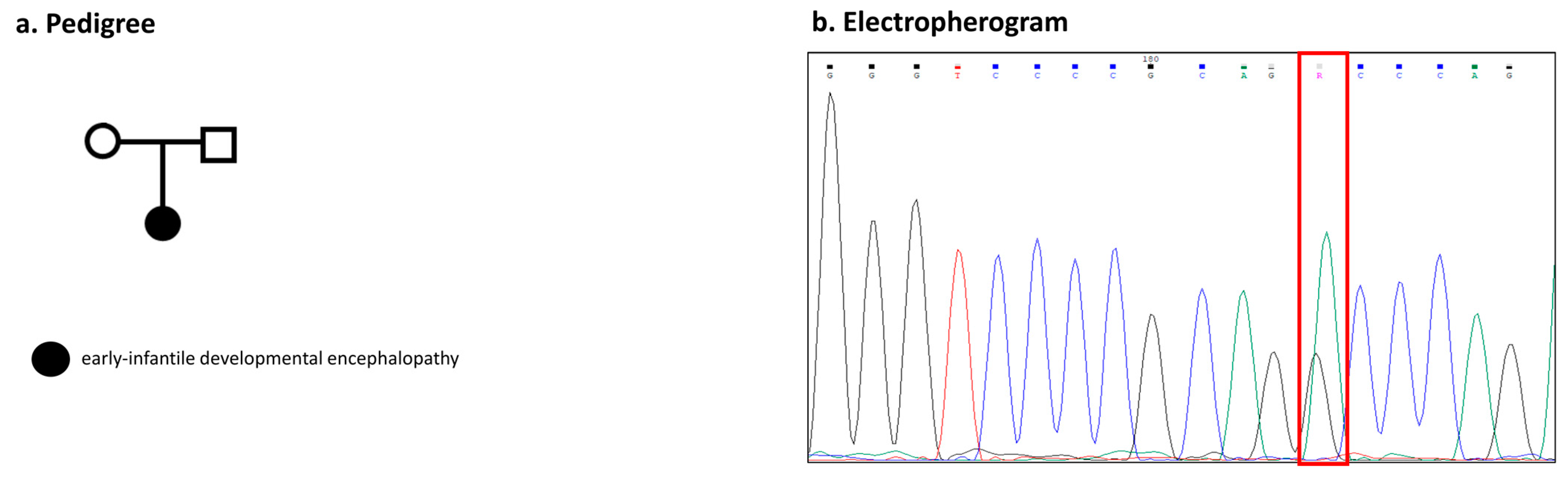
2.1. Clinical Features
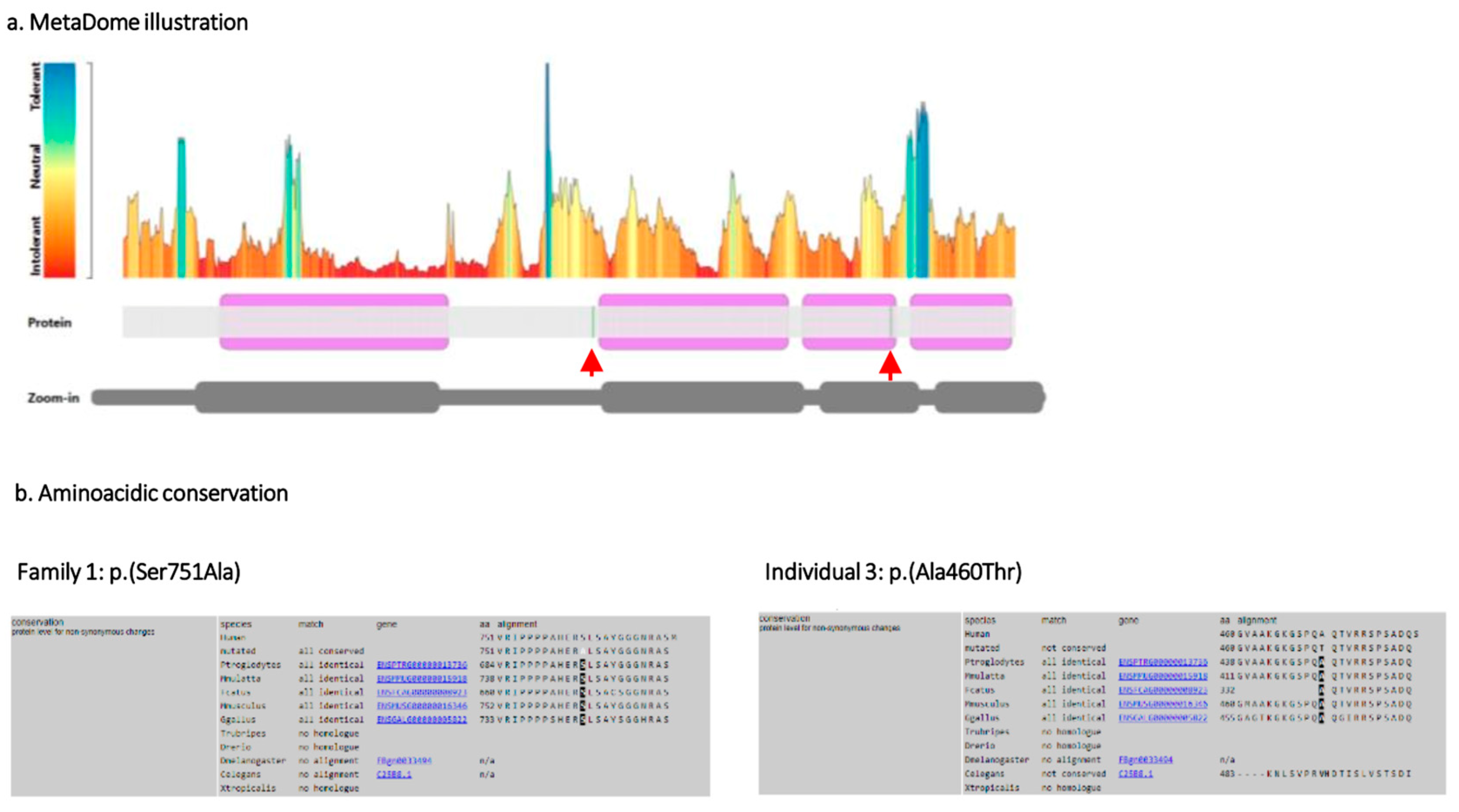
2.2. Molecular Genetic Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Genetic Findings
3.2. Phenotypic Variability in Family 1
3.3. Phenotypic Variability in Family 2 and Individual 3
3.4. Contribution of This Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4. Sanger Sequencing
4.5. Predictive Tools
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Z.; Kao, T.; Horvath, Z.; Lemos, J.; Sul, J.Y.; Cranstoun, S.D.; Bennett, V.; Scherer, S.S.; Cooper, E.C. A Common Ankyrin-G-Based Mechanism Retains KCNQ and NaV Channels at Electrically Active Domains of the Axon. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2599–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, A.; Ishii, A.; Shibata, M.; Ihara, Y.; Cooper, E.C.; Hirose, S. Characteristics of KCNQ2 variants causing either benign neonatal epilepsy or developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specchio, N.; Curatolo, P. Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies: What we do and do not know. Brain 2021, 144, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuberi, S.M.; Wirrell, E.; Yozawitz, E.; Wilmshurst, J.M.; Specchio, N.; Riney, K.; Pressler, R.; Auvin, S.; Samia, P.; Hirsch, E.; et al. ILAE classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in neonates and infants: Position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1349–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, D.; Balestrini, S.; Parrini, E.; Gambardella, A.; Annesi, G.; De Giorgis, V.; Gana, S.; Bassi, M.T.; Zucca, C.; Elia, M.; et al. National survey on the prevalence of single-gene aetiologies for genetic developmental and epileptic encephalopathies in Italy. J. Med. Genet. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Yang, D.; Kim, S.H.; Won, D.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.R.; Lee, S.-T.; Kang, H.-C. Clinical characteristics of KCNQ2 encephalopathy. Brain Dev. 2021, 43, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, F.; Millevert, C.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Mosca, I.; Ambrosino, P.; Carotenuto, L.; Schrader, D.; Lee, H.K.; Riviello, J.; Hong, W.; et al. KCNQ2 R144 variants cause neurodevelopmental disability with language impairment and autistic features without neonatal seizures through a gain-of-function mechanism. EBioMedicine 2022, 81, 104130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mulkey, S.B.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Nicolai, J.; Carroll, J.L.; Grønborg, S.; Jiang, Y.; Joshi, N.; Kelly, M.; Koolen, D.A.; Mikati, M.A.; et al. Neonatal nonepileptic myoclonus is a prominent clinical feature of KCNQ2 gain-of-function variants R201C and R201H. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Millichap, J.J.; Miceli, F.; De Maria, M.; Keator, C.; Joshi, N.; Tran, B.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Ambrosino, P.; Shashi, V.; Mikati, M.A.; et al. Infantile spasms and encephalopathy without preceding neonatal seizures caused by KCNQ2 R198Q, a gain-of-function variant. Epilepsia 2017, 58, e10–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Devaux, J.; Abidi, A.; Roubertie, A.; Molinari, F.; Becq, H.; Lacoste, C.; Villard, L.; Milh, M.; Aniksztejn, L. A Kv7.2 mutation associated with early onset epileptic encephalopathy with suppression-burst enhances Kv7/M channel activity. Epilepsia 2016, 57, e87–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Deng, X.; He, F.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. A novel KCNQ2 missense variant in non-syndromic intellectual disability causes mild gain-of-function of Kv7.2 channel. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 530, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, B.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Zhuang, D.; et al. Clinical Study of 30 Novel KCNQ2 Variants/Deletions in KCNQ2-Related Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 809810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nappi, M.; Alberini, G.; Berselli, A.; Roscioni, A.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Servettini, I.; Barrese, V.; Weckhuysen, S.; Chiu, T.-G.A.; Scheffer, I.E.; et al. Constitutive opening of the Kv7.2 pore activation gate causes KCNQ2-developmental encephalopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2412388121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Furia, A.; Licchetta, L.; Muccioli, L.; Ferri, L.; Mostacci, B.; Mazzoni, S.; Menghi, V.; Minardi, R.; Tinuper, P.; Bisulli, F. Epilepsy With Auditory Features: From Etiology to Treatment. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 807939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grinton, B.E.; Heron, S.E.; Pelekanos, J.T.; Zuberi, S.M.; Kivity, S.; Afawi, Z.; Williams, T.C.; Casalaz, D.M.; Yendle, S.; Linder, I.; et al. Familial neonatal seizures in 36 families: Clinical and genetic features correlate with outcome. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.A.; Charlier, C.; Stauffer, D.; DuPont, B.R.; Leach, R.J.; Melis, R.; Ronen, G.M.; Bjerre, I.; Quattlebaum, T.; Murphy, J.V.; et al. A novel potassium channel gene, KCNQ2, is mutated in an inherited epilepsy of newborns. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riney, K.; Bogacz, A.; Somerville, E.; Hirsch, E.; Nabbout, R.; Scheffer, I.E.; Zuberi, S.M.; Alsaadi, T.; Jain, S.; French, J.; et al. International League Against Epilepsy classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset at a variable age: Position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1443–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisulli, F.; Rinaldi, C.; Pippucci, T.; Minardi, R.; Baldassari, S.; Zenesini, C.; Mostacci, B.; Fanella, M.; Avoni, P.; Menghi, V.; et al. Epilepsy with auditory features: Contribution of known genes in 112 patients. Seizure 2021, 85, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International League Against Epilepsy Consortium on Complex Epilepsies. GWAS meta-analysis of over 29,000 people with epilepsy identifies 26 risk loci and subtype-specific genetic architecture. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- FalsFalsaperla, R.; Criscione, R.; Cimino, C.; Pisani, F.; Ruggieri, M. KCNQ2-Related Epilepsy: Genotype-Phenotype Relationship with Tailored Antiseizure Medication (ASM)-A Systematic Review. Neuropediatrics 2023, 54, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, F.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Weckhuysen, S.; Cooper, E.; Taglialatela, M. KCNQ2-Related Disorders; updated 2022 May 19; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talarico, M.; Fortunato, F.; Labalme, A.; Januel, L.; Chatron, N.; Sanlaville, D.; Sammarra, I.; Gagliardi, M.; Procopio, R.; Valentino, P.; et al. Idiopathic generalized epilepsy in a family with SCN4A-related myotonia. Epilepsia Open 2024, 9, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wiel, L.; Baakman, C.; Gilissen, D.; Veltman, J.A.; Vriend, G.; Gilissen, C. MetaDome: Pathogenicity analysis of genetic variants through aggregation of homologous human protein domains. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dawes, R.; Bournazos, A.M.; Bryen, S.J.; Bommireddipalli, S.; Marchant, R.G.; Joshi, H.; Cooper, S.T. SpliceVault predicts the precise nature of variant-associated mis-splicing. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nykamp, K.; Anderson, M.; Powers, M.; Garcia, J.; Herrera, B.; Ho, Y.-Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Patil, N.; Thusberg, J.; Westbrook, M.; et al. Sherloc: A comprehensive refinement of the ACMG-AMP variant classification criteria. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Pt n. | Age at Genetic Testing | Variant Type | cDNA Coordinates (NM_172107.3) | Protein Consequences | db SNP | Inheritance | GnomAD v4.1.0 | MutationTaster | Polyphen2 | Revel | CADD-Phred | MetaDome | ACMG class | ACMG Criteria | Clinical Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 y | Missense | c.2251T>G | p.(Ser751Ala) | - | Mat. | 0.000003654 | Disease-causing | Benign | 0.502 | 21.70 | 0.44 | LP | PM2+PM5+PP1+PP2 | Epilepsy with auditory features. No neonatal seizures. |
| 2 | 20 y | Splice site | c.1631+1G>A | p.(?) | rs1057516121 | Pat. | 0 | - | - | - | 34.00 | - | P | PVS1+PM2+PP1+PP3+PP5 | Focal epilepsy. Neonatal seizures. |
| 3 | NA | Missense | c.1378G>A | p.(Ala460Thr) | rs1284566908 | de novo | 0.00000412 | Disease-causing | Probably damaging | 0.550 | 21.00 | 0.55 | LP | PS2+PM2+PP2 | DEE. Neonatal seizures. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talarico, M.; Procopio, R.; Gagliardi, M.; Sarubbi, M.C.; Fortunato, F.; Sammarra, I.; Lesca, G.; Malanga, D.; Annesi, G.; Gambardella, A. Novel KCNQ2 Variants Related to a Variable Phenotypic Spectrum Ranging from Epilepsy with Auditory Features to Severe Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010295
Talarico M, Procopio R, Gagliardi M, Sarubbi MC, Fortunato F, Sammarra I, Lesca G, Malanga D, Annesi G, Gambardella A. Novel KCNQ2 Variants Related to a Variable Phenotypic Spectrum Ranging from Epilepsy with Auditory Features to Severe Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010295
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalarico, Mariagrazia, Radha Procopio, Monica Gagliardi, Maria Chiara Sarubbi, Francesco Fortunato, Ilaria Sammarra, Gaetan Lesca, Donatella Malanga, Grazia Annesi, and Antonio Gambardella. 2025. "Novel KCNQ2 Variants Related to a Variable Phenotypic Spectrum Ranging from Epilepsy with Auditory Features to Severe Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010295
APA StyleTalarico, M., Procopio, R., Gagliardi, M., Sarubbi, M. C., Fortunato, F., Sammarra, I., Lesca, G., Malanga, D., Annesi, G., & Gambardella, A. (2025). Novel KCNQ2 Variants Related to a Variable Phenotypic Spectrum Ranging from Epilepsy with Auditory Features to Severe Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010295







