BMP Stimulation Differentially Affects Phosphorylation and Protein Stability of β-Catenin in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
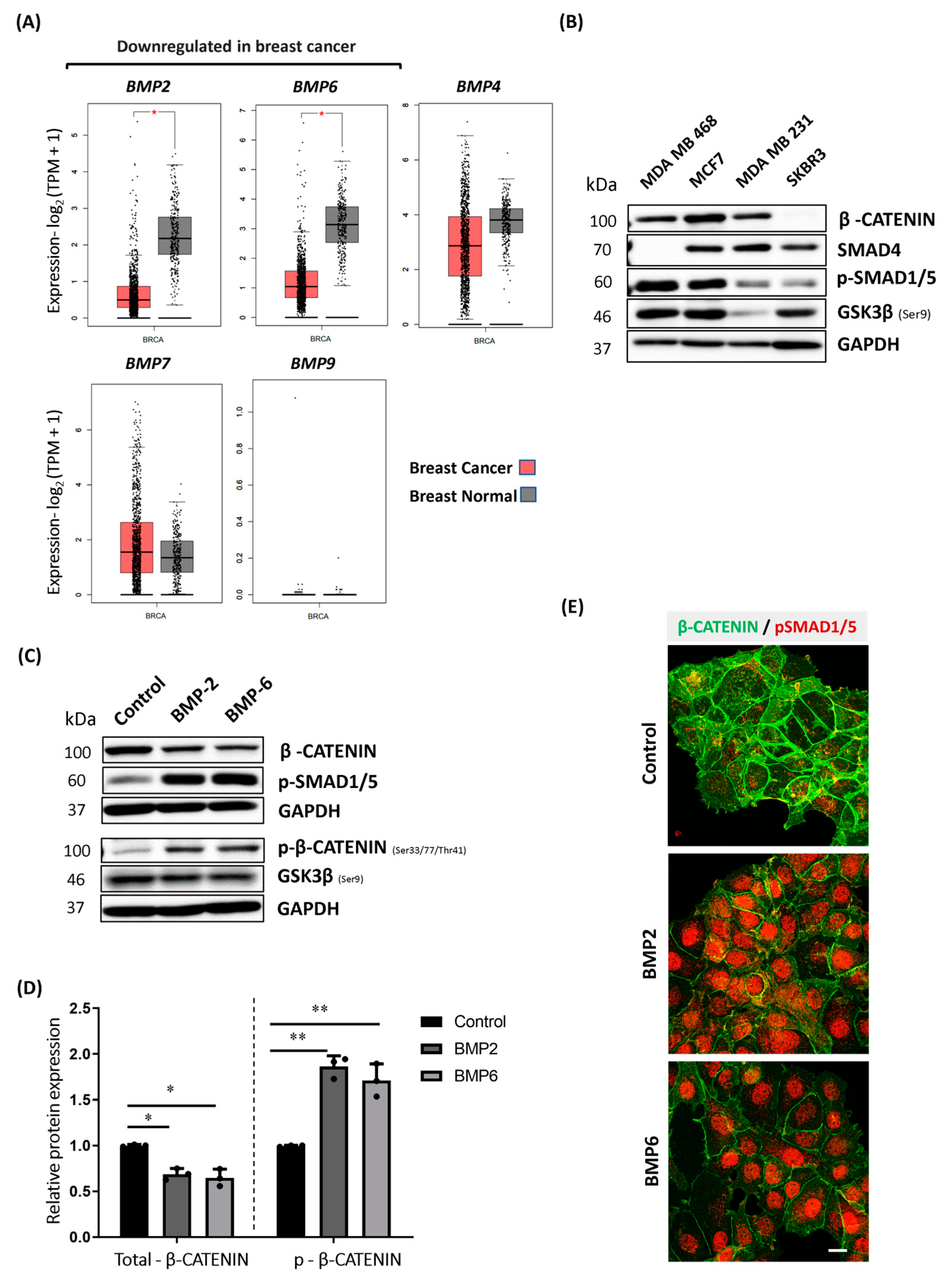
2.1. BMP Stimulation Triggers Phosphorylation and Proteasomal Degradation of β-CATENIN in MCF7 Cells
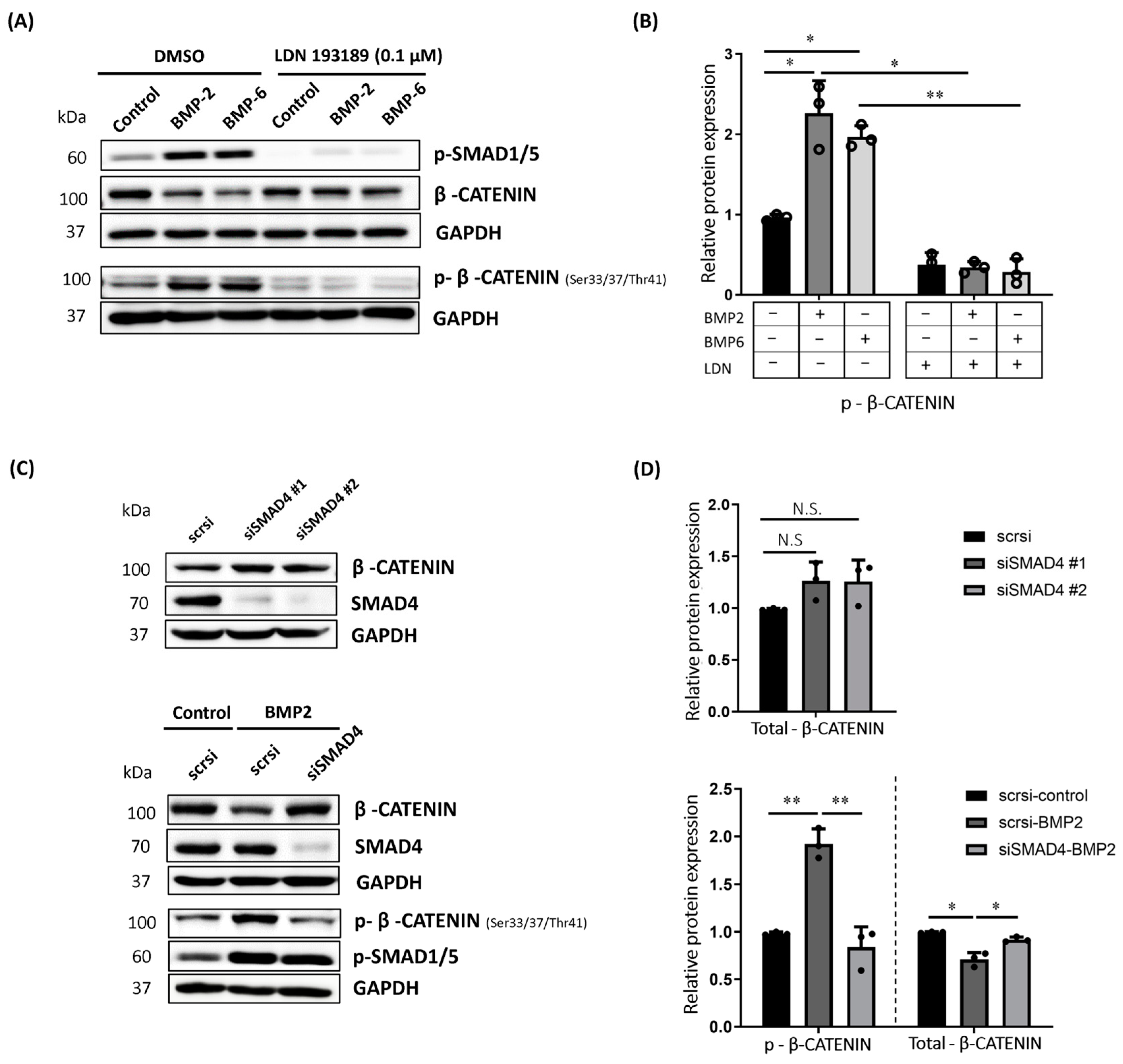
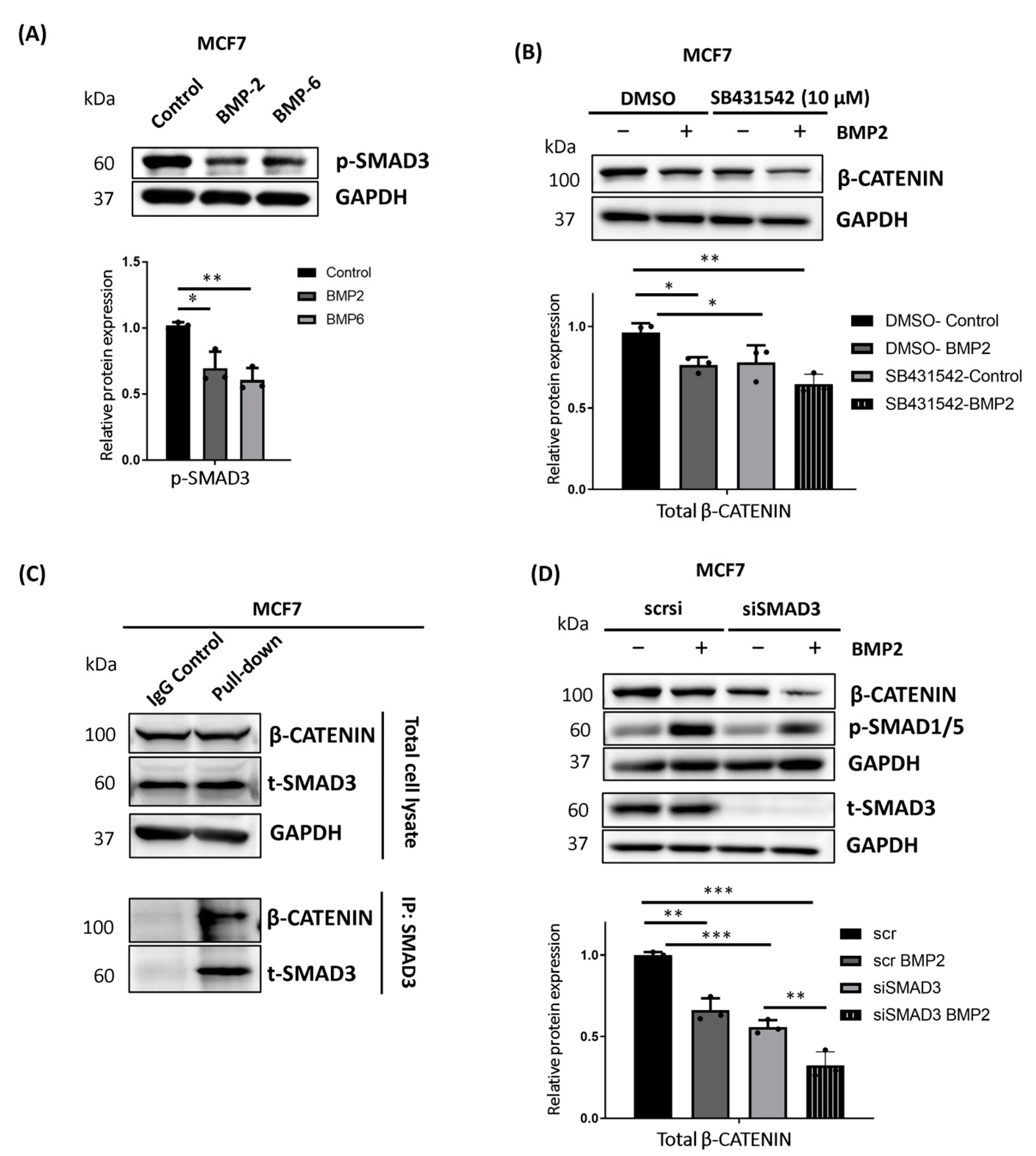
2.2. BMP-Induced Phosphorylation of β-CATENIN Requires BMP Type I Receptor Kinase Activity and SMAD4 in MCF7 Cells
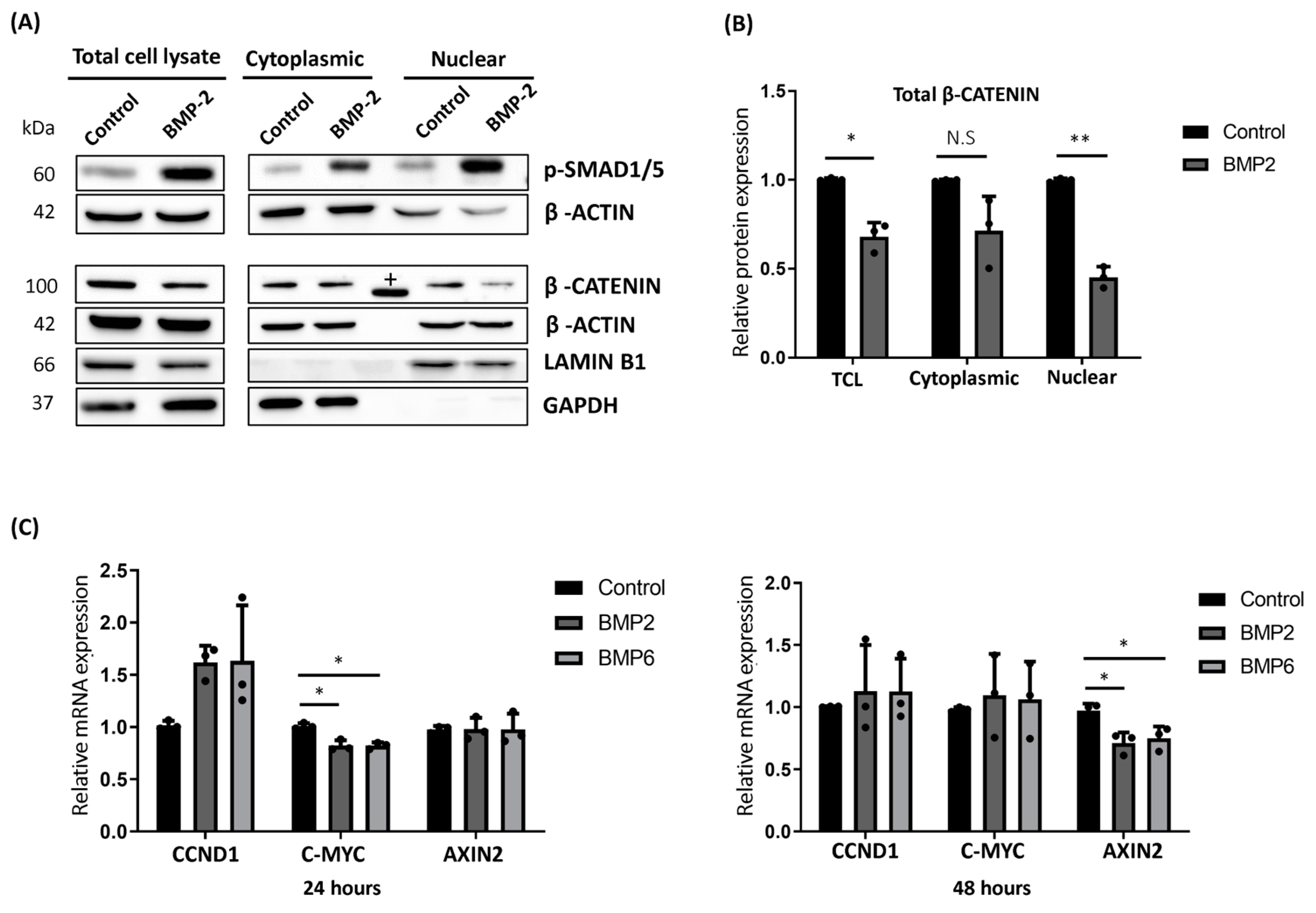
2.3. BMP Stimulation Reduced the Cytoplasmic Accumulation and Nuclear Translocation of β-CATENIN in MCF7 Cells
2.4. BMP-Induced Degradation of β-CATENIN Alters E-CADHERIN Localization in MCF7 Cells

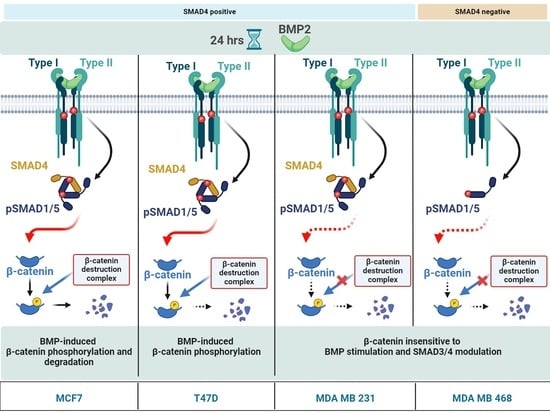
2.5. BMP Stimulation Differentially Affects β-CATENIN Protein Level in MDA MB 468, T47D and MDA MB 231 Cells
2.6. TGF-β Pathway Suppression Contributes to the Regulation of β-CATENIN Protein Stability in MCF7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. Cell Stimulation and Chemical Inhibition
4.3. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
4.4. Transient Transfections
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Cellular Fractionation Assay
4.7. Immunostaining and Confocal Microscopy
4.8. Wound Healing Migration Assay
4.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obradovic Wagner, D.; Sieber, C.; Bhushan, R.; Borgermann, J.H.; Graf, D.; Knaus, P. BMPs: From Bone to Body Morphogenetic Proteins. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, mr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt Signaling in Cancer. Oncogene 2016, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohe, A. Signal Transduction of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptors. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazono, K.; Kamiya, Y.; Morikawa, M. Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptors and Signal Transduction. J. Biochem. 2009, 147, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-Dependent and Smad-Independent Pathways in TGF-β Family Signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, R.; Manzoor, M.; Hussain, A. Wnt Signaling Pathway: A Comprehensive Review. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Semenov, M.; Han, C.; Baeg, G.-H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, X. Control of β-Catenin Phosphorylation/Degradation by a Dual-Kinase Mechanism. Cell 2002, 108, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, S. Axin-Mediated CKI Phosphorylation of Beta -Catenin at Ser 45: A Molecular Switch for the Wnt Pathway. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.C.; Sparks, A.B.; Rago, C.; Hermeking, H.; Zawel, L.; da Costa, L.T.; Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Identification of C-MYC as a Target of the APC Pathway. Science 1998, 281, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, E.; Zhang, T.; Domon, C.; Joo, C.-K.; Freund, J.-N.; Costantini, F. Wnt/β-Catenin/Tcf Signaling Induces the Transcription of Axin2, a Negative Regulator of the Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, G.; Müller, T.; Wang, X.; Papkoff, J. Activated Beta-Catenin Induces Osteoblast Differentiation of C3H10T1/2 Cells and Participates in BMP2 Mediated Signal Transduction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmen, S.L.; Zylstra, C.R.; Mukherjee, A.; Sigler, R.E.; Faugere, M.-C.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Deng, L.; Clemens, T.L.; Williams, B.O. Essential Role of β-Catenin in Postnatal Bone Acquisition. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21162–21168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Whetstone, H.; Youn, A.; Nadesan, P.; Chow, E.; Lin, A.; Alman, B.A. β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Is Crucial for Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 to Induce New Bone Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvério, K.G.; Davidson, K.C.; James, R.G.; Adams, A.M.; Foster, B.L.; Nociti, F.H.; Somerman, M.J.; Moon, R.T. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Regulates Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP2)-Mediated Differentiation of Dental Follicle Cells. J. Periodontal Res. 2011, 47, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yan, Y.; Lim, Y.B.; Tang, D.; Xie, R.; Chen, A.; Tai, P.; Harris, S.E.; Xing, L.; Qin, Y.X.; et al. BMP-2 Modulates β-Catenin Signaling through Stimulation of Lrp5 Expression and Inhibition of β-TrCP Expression in Osteoblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Oyajobi, B.O.; Harris, S.E.; Chen, D.; Tsao, C.; Deng, H.-W.; Zhao, M. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Activates Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 Expression in Osteoblasts. Bone 2013, 52, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.C.; Zhang, J.; Tong, W.-G.; Tawfik, O.; Ross, J.; Scoville, D.H.; Tian, Q.; Zeng, X.; He, X.; Wiedemann, L.M.; et al. BMP Signaling Inhibits Intestinal Stem Cell Self-Renewal through Suppression of Wnt–β-Catenin Signaling. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroyer, N.F.; Wong, M.H. BMP Signaling in the Intestine: Cross-Talk Is Key. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramis, A.P.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; van Es, J.; Jonkheer, S.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Clevers, H. De Novo Crypt Formation and Juvenile Polyposis on BMP Inhibition in Mouse Intestine. Science 2004, 303, 1684–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ille, F.; Atanasoski, S.; Falk, S.; Ittner, L.M.; Märki, D.; Büchmann-Møller, S.; Wurdak, H.; Suter, U.; Taketo, M.M.; Sommer, L. Wnt/BMP Signal Integration Regulates the Balance between Proliferation and Differentiation of Neuroepithelial Cells in the Dorsal Spinal Cord. Dev. Biol. 2007, 304, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotewold, L.; Rüther, U. The Wnt Antagonist Dickkopf-1 Is Regulated by Bmp Signaling and C-Jun and Modulates Programmed Cell Death. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.C.; Beddington, R.S.P.; Harland, R.M. Wnt Signaling in Xenopus Embryos Inhibits Bmp4 Expression and Activates Neural Development. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 3149–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.-E.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Yang, G.; Li, X. BAMBI Promotes C2C12 Myogenic Differentiation by Enhancing Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17734–17745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Dong, P.; Chu, G.; Yang, G.; Sun, S. BMP and Activin Membrane-Bound Inhibitor (BAMBI) Inhibits the Adipogenesis of Porcine Preadipocytes through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; He, L.; Lee, H.; Glinka, A.; Andresen, C.; Hübschmann, D.; Jeremias, I.; Müller-Decker, K.; Pabst, C.; Niehrs, C. RSPO2 Inhibits BMP Signaling to Promote Self-Renewal in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrall, A.L.; Riemer, P.; Leushacke, M.; Sreekumar, A.; Grimm, C.; Herrmann, B.G.; Morkel, M. Wnt and BMP Signals Control Intestinal Adenoma Cell Fates. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, D.; Li, A.; Song, H.; Zhang, W.; Davis, D.L.; Gilbert, M.R.; Liu, F.; et al. Autocrine BMP4 Signaling Enhances Tumor Aggressiveness via Promoting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in IDH1-Mutant Gliomas. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Hall, C.L.; Escara-Wilke, J.; Mizokami, A.; Keller, J.M.; Keller, E.T. Prostate Cancer Induces Bone Metastasis through Wnt-Induced Bone Morphogenetic Protein-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5785–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.T.; Kang, D.I.; Ha, Y.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Chung, J.; Min, K.; Kim, T.H.; Moon, K.H.; Chung, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Prostate Cancer Bone Metastases Acquire Resistance to Androgen Deprivation via WNT5A-Mediated BMP-6 Induction. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA—Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.L.V.; Trewin, C.B.; Fredriksson, I.; Reinertsen, K.V.; Russnes, H.; Ursin, G. In Modern Times, How Important Are Breast Cancer Stage, Grade and Receptor Subtype for Survival: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, K.L.; Sosa, M.S.; Entenberg, D.; Hosseini, H.; Cheung, J.F.; Nobre, R.; Avivar-Valderas, A.; Nagi, C.; Girnius, N.; Davis, R.J.; et al. Mechanism of Early Dissemination and Metastasis in Her2+ Mammary Cancer. Nature 2016, 540, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellenstein, M.D.; Coffelt, S.B.; Duits, D.E.M.; van Miltenburg, M.H.; Slagter, M.; de Rink, I.; Henneman, L.; Kas, S.M.; Prekovic, S.; Hau, C.-S.; et al. Loss of P53 Triggers Wnt-Dependent Systemic Inflammation to Drive Breast Cancer Metastasis. Nature 2019, 572, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Prosperi, J.R.; Choudhury, N.; Olopade, O.I.; Goss, K.H. β-Catenin Is Required for the Tumorigenic Behavior of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Knowles, E.; Zardawi, S.J.; McNeil, C.M.; Millar, E.K.A.; Crea, P.; Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L.; O’Toole, S.A. Cytoplasmic Localization of β-Catenin Is a Marker of Poor Outcome in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Meng, S.; Wu, Y.; Shuai, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, G. Recent Advances of β-Catenin Small Molecule Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: Current Development and Future Perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schie, E.H.; van Amerongen, R. Aberrant WNT/CTNNB1 Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in Human Breast Cancer: Weighing the Evidence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, C. Wnt Signaling in Human and Mouse Breast Cancer: Focusing on Wnt Ligands, Receptors and Antagonists. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3368–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarmann, G.J.; Decker, A.; Farrar, W.L. Epigenetic Gene Silencing in the Wnt Pathway in Breast Cancer. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Yue, S.; Alfayez, M.; Kassem, M.; Liu, F.-F.; Aldahmash, A.; Alajez, N.M. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP2) Induces Growth Suppression and Enhances Chemosensitivity of Human Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabkiewicz, C.; Resaul, J.; Hargest, R.; Jiang, W.G.; Ye, L. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins, Breast Cancer, and Bone Metastases: Striking the Right Balance. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, R349–R366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An Enhanced Web Server for Large-Scale Expression Profiling and Interactive Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sui, L.; Fang, Z.; Wen Guo, J.; Ye, L. Aberrant Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in the Disease Progression and Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1166955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.B.; Deng, D.Y.; Lai, C.S.; Hong, C.C.; Cuny, G.D.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Hong, D.W.; McManus, P.M.; Katagiri, T.; Sachidanandan, C.; et al. BMP Type I Receptor Inhibition Reduces Heterotopic Ossification. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboni, A.; Hutchinson, J.A.; DeCastro, A.; Cherukuri, P.; Liby, K.T.; Sporn, M.B.; Schwartz, G.N.; Wells, W.A.; Sempere, L.F.; Yu, P.B.; et al. ΔNp63α-Mediated Activation of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Governs Stem Cell Activity and Plasticity in Normal and Malignant Mammary Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boergermann, J.H.; Kopf, J.; Yu, P.B.; Knaus, P. Dorsomorphin and LDN-193189 Inhibit BMP-Mediated Smad, P38 and Akt Signalling in C2C12 Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Fukuda, R.; Tanabe, R.; Koinuma, D.; Koyama, H.; Hashizume, Y.; Moustakas, A.; Miyazono, K.; Heldin, C.-H. BMP Signaling Is a Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, C.; Xu, M.; Yu, J.; Li, G. Expression and Significance of Wnt Signaling Components and Their Target Genes in Breast Carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 9, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.D.; Chien, A.J.; Dawson, D.W. Dysregulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.-B.; Kim, J.-Y.; Cho, S.-D.; Park, K.-S.; Jung, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Hong, I.-S.; Nam, J.-S. Blockade of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting CSC-like Phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khramtsov, A.I.; Khramtsova, G.F.; Tretiakova, M.; Huo, D.; Olopade, O.I.; Goss, K.H. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation Is Enriched in Basal-like Breast Cancers and Predicts Poor Outcome. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2911–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buijs, J.T.; van der Horst, G.; van den Hoogen, C.; Cheung, H.; de Rooij, B.; Kroon, J.; Petersen, M.; van Overveld, P.G.M.; Pelger, R.C.M.; van der Pluijm, G. The BMP2/7 Heterodimer Inhibits the Human Breast Cancer Stem Cell Subpopulation and Bone Metastases Formation. Oncogene 2011, 31, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Chen, A.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; He, S.; Xiao, G.; et al. BMP-2 Induces EMT and Breast Cancer Stemness through Rb and CD44. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemler, R. From Cadherins to Catenins: Cytoplasmic Protein Interactions and Regulation of Cell Adhesion. Trends Genet. 1993, 9, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.H.; Weis, W.I. The Structure of the β-Catenin/E-Cadherin Complex and the Molecular Basis of Diverse Ligand Recognition by β-Catenin. Cell 2001, 105, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Pi, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, F.; Shao, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J. BMP2 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells via Cytoskeletal Reorganization and Adhesion Decrease: An AFM Investigation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezovjakova, H.; Tomlinson, C.; Mohd Naim, N.; Swiatlowska, P.; Erasmus, J.C.; Huveneers, S.; Gorelik, J.; Bruche, S.; Braga, V.M. Junction Mapper Is a Novel Computer Vision Tool to Decipher Cell–Cell Contact Phenotypes. eLife 2019, 8, e45413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Hedrick, L.; Cho, K.R.; Nadasdy, G.M.; Weinstein, C.L.; Bova, S.G.; Isaacs, W.B.; Cairns, P.; Nawroz, H.; et al. DPC4 Gene in Various Tumor Types. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2527–2530. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Tan, X.; Li, T.-F.; Zhang, Y.E.; Chen, D. Smad3 Prevents β-Catenin Degradation and Facilitates β-Catenin Nuclear Translocation in Chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8703–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Shen, X.; Liu, I.; Semenov, M.; He, X.; Wang, X.F. Smad3-Dependent Nuclear Translocation of Beta-Catenin Is Required for TGF-Beta1-Induced Proliferation of Bone Marrow-Derived Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, G.J.; Nicolás, F.J.; Callahan, J.F.; Harling, J.D.; Gaster, L.M.; Reith, A.D.; Laping, N.J.; Hill, C.S. SB-431542 Is a Potent and Specific Inhibitor of Transforming Growth Factor-β Superfamily Type I Activin Receptor-like Kinase (ALK) Receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Toyota, M.; Caraway, H.; Gabrielson, E.; Ohmura, T.; Fujikane, T.; Nishikawa, N.; Sogabe, Y.; Nojima, M.; Sonoda, T.; et al. Frequent Epigenetic Inactivation of Wnt Antagonist Genes in Breast Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhaj, K.; Akcali, K.; Ozturk, M. Redundant Expression of Canonical Wnt Ligands in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, T.; Watabe, T. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinecke, K.; Seher, A.; Schmitz, W.; Mueller, T.D.; Sebald, W.; Nickel, J. Receptor Oligomerization and Beyond: A Case Study in Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, R.M.; Guo, J.; Wood, J.H.; Tong, Z.; Beech, J.S.; Lawera, A.; Yu, M.; Grainger, D.J.; Reckless, J.; Morrell, N.W.; et al. Molecular Basis of ALK1-Mediated Signalling by BMP9/BMP10 and Their Prodomain-Bound Forms. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L. Attacking C-Myc: Targeted and Combined Therapies for Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 6543–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K. Signaling Cross Talk between TGF-β/Smad and Other Signaling Pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 9, a022137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Mote, R.D.; Freimer, J.W.; Tiwari, M.; Bansi Singh, S.; Arumugam, S.; Narayana, Y.V.; Rajan, R.; Subramanyam, D. Cell–Cell Adhesions in Embryonic Stem Cells Regulate the Stability and Transcriptional Activity of β-Catenin. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 1647–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguti, M.; Nistor, P.A.; Blin, G.; Pegg, A.; Zhou, X.; Lowell, S. Bone Morphogenic Protein Signalling Suppresses Differentiation of Pluripotent Cells by Maintaining Expression of E-Cadherin. eLife 2013, 2, e01197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Du, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, W.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Yin, J.; Sun, B.; et al. BMP-6 Promotes E-Cadherin Expression through Repressing ΔEF1 in Breast Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosshauer, P.W.; Brown, S.A.; Eisinger, K.; Yan, Q.; Guglielminetti, E.R.; Parsons, R.; Ellenson, L.H.; Kitajewski, J. APC truncation and increased beta-catenin levels in a human breast cancer cell line. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, S.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Lo, K.M.; Nigjeh, S.E.; Keong, Y.S.; Dehghan, F.; Soori, R.; Abdulla, M.A.; Chow, K.M.; Ali, H.M.; et al. Anticancer Activity of a Monobenzyltin Complex C1 against MDA-MB-231 Cells through Induction of Apoptosis and Inhibition of Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Yazdanparast, A.; Li, M.; Pawar, A.V.; Liu, Y.; Inavolu, S.M.; Cheng, L. Comprehensive Comparison of Molecular Portraits between Cell Lines and Tumors in Breast Cancer. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, E.; Oren, M.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Downregulation of β-Catenin by P53 Involves Changes in the Rate of β-Catenin Phosphorylation and Axin Dynamics. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4444–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordenonsi, M.; Dupont, S.; Maretto, S.; Insinga, A.; Imbriano, C.; Piccolo, S. Links between Tumor Suppressors. Cell 2003, 113, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorneveld, P.W.; Kodach, L.L.; Jacobs, R.J.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Korkmaz, K.S.; Molendijk, I.; Dekker, E.; Morreau, H.; van Pelt, G.W.; et al. The BMP Pathway Either Enhances or Inhibits the Wnt Pathway Depending on the SMAD4 and P53 Status in CRC. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 112, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagatay, T.; Ozturk, M. P53 Mutation as a Source of Aberrant β-Catenin Accumulation in Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7971–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasielewski, M.; Elstrodt, F.; Klijn, J.G.M.; Berns, E.M.J.J.; Schutte, M. Thirteen New P53 Gene Mutants Identified among 41 Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 99, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, B.; Girard, L.; Hollestelle, A.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Soussi, T. Analysis of TP53 Mutation Status in Human Cancer Cell Lines: A Reassessment. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; Synnott, N.C.; Crown, J. Mutant P53 in Breast Cancer: Potential as a Therapeutic Target and Biomarker. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olafson, L.R.; Gunawardena, M.; Nixdorf, S.; McDonald, K.L.; Rapkins, R.W. The Role of TP53 Gain-of-Function Mutation in Multifocal Glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 147, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Yin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, R.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z. Mutant P53 Activates HnRNPA2B1-AGAP1-Mediated Exosome Formation to Promote Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. Cancer Lett. 2023, 562, 216154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junk, D.J.; Vrba, L.; Watts, G.S.; Oshiro, M.M.; Martinez, J.D.; Futscher, B.W. Different Mutant/Wild-Type P53 Combinations Cause a Spectrum of Increased Invasive Potential in Nonmalignant Immortalized Human Mammary Epithelial Cells. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yallowitz, A.; Ozog, L.; Marchenko, N. A Gain-of-Function Mutant P53–HSF1 Feed Forward Circuit Governs Adaptation of Cancer Cells to Proteotoxic Stress. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Marchenko, N.; Erster, S.; Nemajerova, A.; Dehner, A.; Klein, C.; Pan, H.; Kessler, H.; Pancoska, P.; Moll, U.M. WT P53, but Not Tumor-Derived Mutants, Bind to Bcl2 via the DNA Binding Domain and Induce Mitochondrial Permeabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8600–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the Right Cell Line for Breast Cancer Research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzmenko, A.; Takeyama, K.; Ito, S.; Furutani, T.; Sawatsubashi, S.; Maki, A.; Suzuki, E.; Kawasaki, Y.; Akiyama, T.; Tabata, T.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin and Estrogen Signaling Converge in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40255–40258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Schmitt, F.; Grebhardt, S.; Mayer, D. β-Catenin Is a Positive Regulator of Estrogen Receptor-α Function in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2011, 3, 2990–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aka, J.A.; Lin, S.-X. Comparison of Functional Proteomic Analyses of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines T47D and MCF7. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstrasser, M. Origin and Function of Ubiquitin-like Proteins. Nature 2009, 458, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.A.; Jeon, Y.J. How Is the Fidelity of Proteins Ensured in Terms of Both Quality and Quantity at the Endoplasmic Reticulum? Mechanistic Insights into E3 Ubiquitin Ligases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.; Wang, B.; Armstrong, S.R.; Abuetabh, Y.; Leng, S.; Roa, W.H.Y.; Atfi, A.; Marchese, A.; Wilson, B.; Sergi, C.; et al. Hsp70 Acts as a Fine-Switch That Controls E3 Ligase CHIP-Mediated TAp63 and ΔNp63 Ubiquitination and Degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 2740–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Messer, J.S.; Goss, K.H.; Hart, J.; Bissonnette, M.; Chang, E.B. Hsp70 Exerts Oncogenic Activity in the Apc Mutant Min Mouse Model. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioda, T.; Lechleider, R.J.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; Li, H.; Yahata, T.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Fenner, M.H.; Roberts, A.B.; Isselbacher, K.J. Transcriptional Activating Activity of Smad4: Roles of SMAD Hetero-Oligomerization and Enhancement by an Associating Transactivator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9785–9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilhan, M.; Hastar, N.; Kampfrath, B.; Spierling, D.N.; Jatzlau, J.; Knaus, P. BMP Stimulation Differentially Affects Phosphorylation and Protein Stability of β-Catenin in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094593
Ilhan M, Hastar N, Kampfrath B, Spierling DN, Jatzlau J, Knaus P. BMP Stimulation Differentially Affects Phosphorylation and Protein Stability of β-Catenin in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):4593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094593
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlhan, Mustafa, Nurcan Hastar, Branka Kampfrath, Deniz Neslihan Spierling, Jerome Jatzlau, and Petra Knaus. 2024. "BMP Stimulation Differentially Affects Phosphorylation and Protein Stability of β-Catenin in Breast Cancer Cell Lines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 4593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094593
APA StyleIlhan, M., Hastar, N., Kampfrath, B., Spierling, D. N., Jatzlau, J., & Knaus, P. (2024). BMP Stimulation Differentially Affects Phosphorylation and Protein Stability of β-Catenin in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 4593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094593