P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation
Abstract
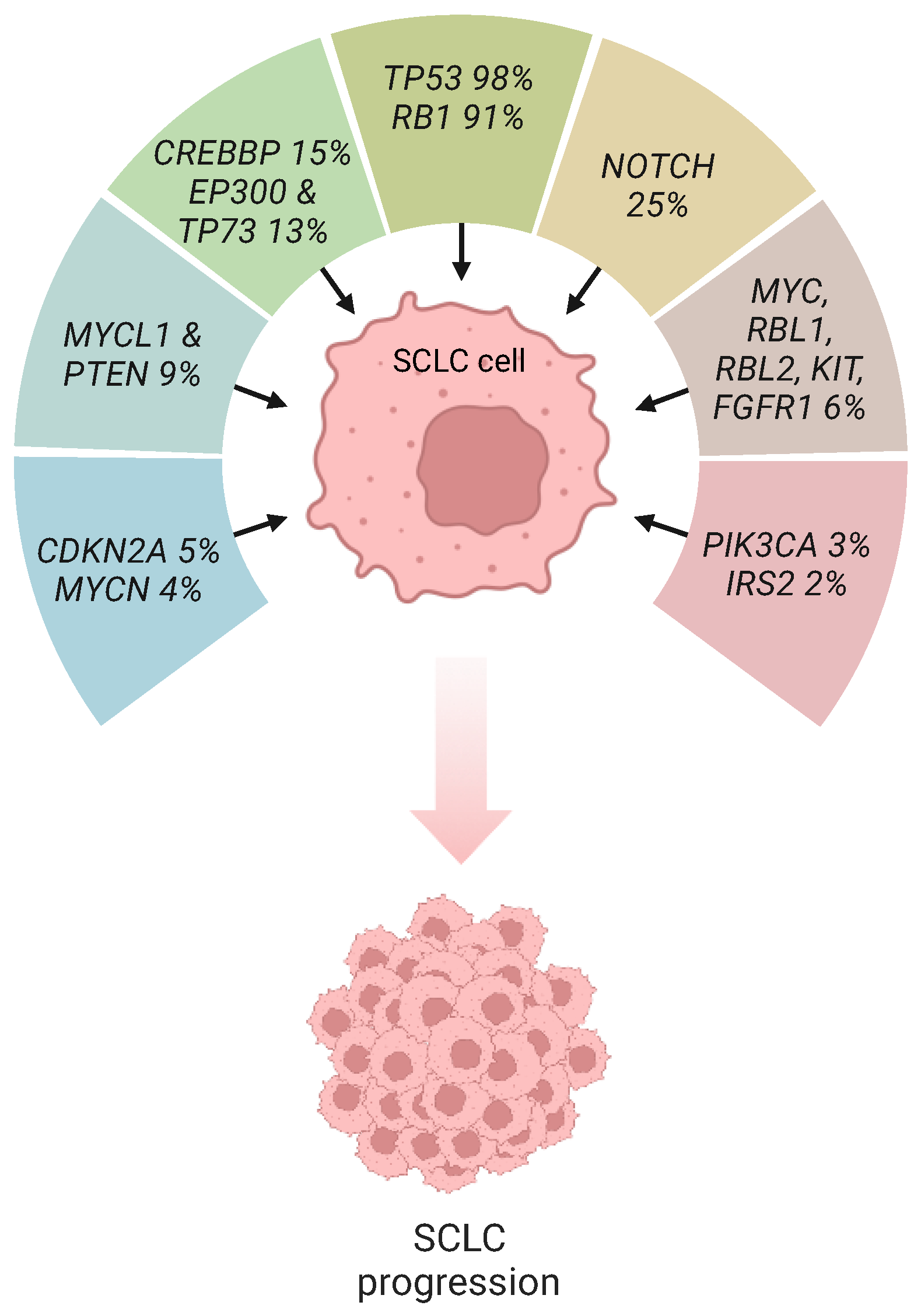
1. Introduction
2. P53 and Rb Inactivation in SCLC
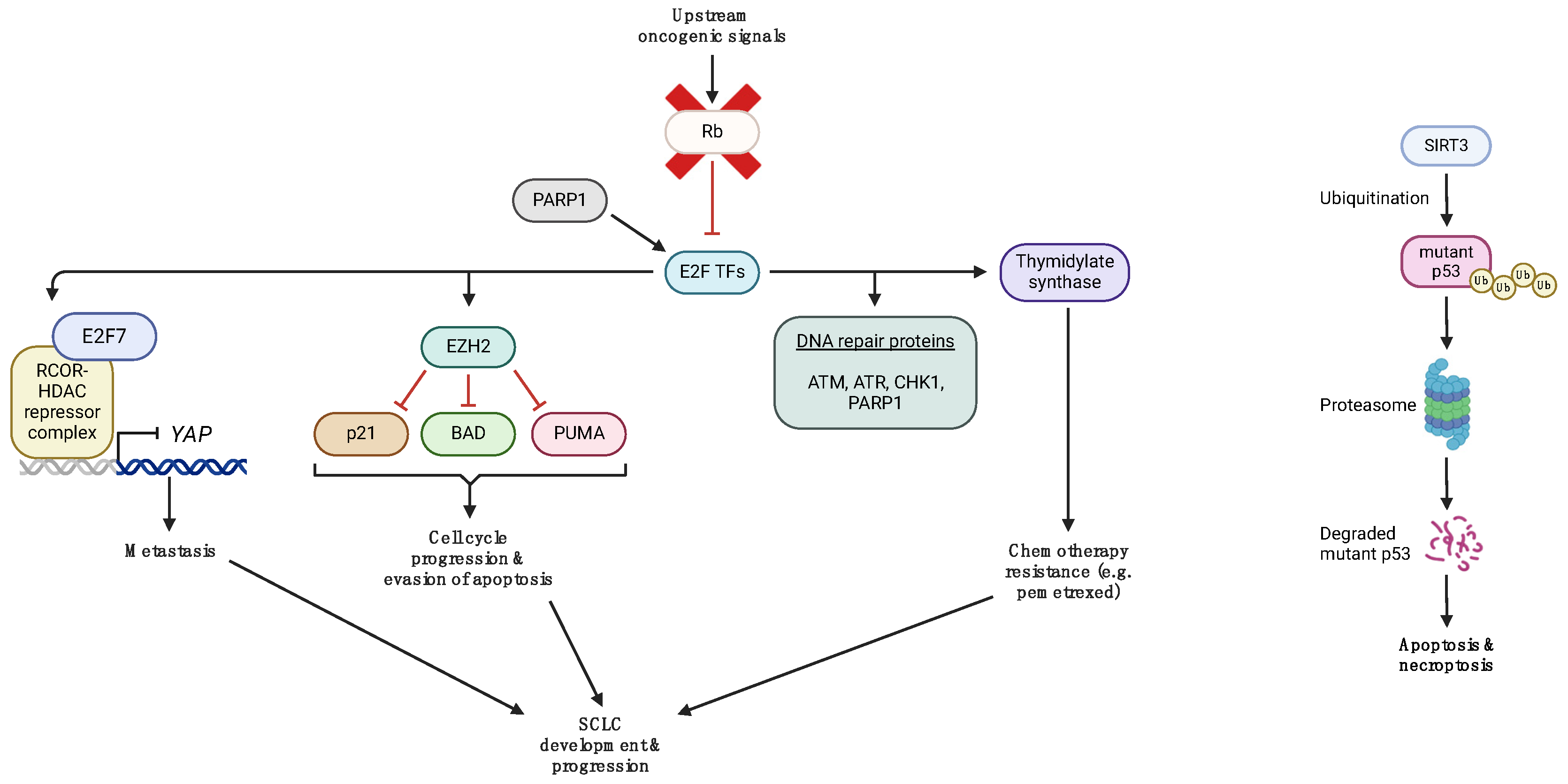
3. Aberrant p53 and Rb Signaling in SCLC
4. Targeted Therapies in p53 and RB Deficient SCLC Cells
4.1. AURK A/B Inhibitors
4.2. CDK7 Inhibitors
4.3. DDR Inhibitors
4.3.1. CHK1 Inhibitors
4.3.2. PARP Inhibitors
4.3.3. ATM/ATR Inhibitors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, A.; Khan, N.A.; Uddin, S.; Khan, A.Q.; Steinhoff, M. Deregulated transcription factors in the emerging cancer hallmarks. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 18, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, K.B.; Dunn, C.T.; Park, K.S. Transcriptional deregulation underlying the pathogenesis of small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drapkin, B.J.; Rudin, C.M. Advances in Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Translational Research. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Borrero, L.J.; El-Deiry, W.S. Tumor suppressor p53: Biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, R.; D’Anneo, A.; Tesoriere, G.; Vento, R. RB1 in cancer: Different mechanisms of RB1 inactivation and alterations of pRb pathway in tumorigenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2013, 228, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Knudsen, K.E. Tailoring to RB: Tumour suppressor status and therapeutic response. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, Y.; Maya, R.; Kazaz, A.; Oren, M. Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 1997, 387, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Jambhekar, A.; Lahav, G. The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, V.J.N.; Eriksson, S.E.; Bianchi, J.; Wiman, K.G. Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.D.; Galbraith, M.D.; Andrysik, Z.; Espinosa, J.M. Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by p53. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, F.A.; Rubin, S.M. Molecular mechanisms underlying RB protein function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Heuvel, S.; Dyson, N.J. Conserved functions of the pRB and E2F families. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.R.; Deshong, A.J.; Pelton, J.G.; Rubin, S.M. Phosphorylation-induced conformational changes in the Retinoblastoma Protein Inhibit E2F Transactivation Domain Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16286–16293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, S.M.; Sage, J.; Skotheim, J.M. Integrating Old and New Paradigms of G1/S Control. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolupaeva, V.; Janssens, V. PP1 and PP2A phosphatases–cooperating partners in modulating retinoblastoma protein activation. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J.; McCormick, F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, R.; Linn, S.C.; Linnoila, R.I.; Zevenhoven, J.; Mooi, W.J.; Berns, A. Induction of small cell lung cancer by somatic inactivation of both Trp53 and Rb1 in a conditional mouse model. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D.G.; Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Stewart, C.; Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Bhutkar, A.; McKenna, A.; Dooley, A.; Vernon, A.; et al. Genetic and clonal dissection of murine small cell lung carcinoma progression by genome sequencing. Cell 2014, 156, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, B.E.; Park, K.S.; Yiu, G.; Conklin, J.F.; Lin, C.; Burkhart, D.L.; Karnezis, A.N.; Sweet-Cordero, E.A.; Sage, J. Loss of p130 accelerates tumor development in a mouse model for human small-cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Savage, T.K.; Johnson, J.E.; Berns, A.; Sage, J.; Linnoila, R.I.; MacPherson, D.; McFadden, D.G.; Farago, A.; Jacks, T.; et al. The comparative pathology of genetically engineered mouse models for neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.C.; Berns, A. Mouse models for lung cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, S.; Pérez-Crespo, M.; Enguita, A.B.; Hernández, P.; Martínez-Palacio, J.; Oteo, M.; Sage, J.; Paramio, J.M.; Santos, M. Ablating all three retinoblastoma family members in mouse lung leads to neuroendocrine tumor formation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4373–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, E.A.; Kwon, M.C.; Monkhorst, K.; Song, J.Y.; Bhaskaran, R.; Krijgsman, O.; Kuilman, T.; Peters, D.; Buikhuisen, W.A.; Smit, E.F.; et al. Transcription Factor NFIB Is a Driver of Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression in Mice and Marks Metastatic Disease in Patients. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaoglu, G.; Guthrie, M.R.; Böhm, S.; Brägelmann, J.; Can, I.; Ballieu, P.M.; Marx, A.; George, J.; Heinen, C.; Chalishazar, M.D.; et al. MYC Drives Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer to a Variant Neuroendocrine Subtype with Vulnerability to Aurora Kinase Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Augert, A.; Rongione, M.; Conkrite, K.; Parazzoli, S.; Nikitin, A.Y.; Ingolia, N.; MacPherson, D. PTEN is a potent suppressor of small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Wu, N.; Kim, Y.C.; Cheng, P.F.; Basom, R.; Kim, D.; Dunn, C.T.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, C.S.; et al. Genetic requirement for Mycl and efficacy of RNA Pol I inhibition in mouse models of small cell lung cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A. Rb family proteins differentially regulate distinct cell lineages during epithelial development. Development 2004, 131, 4299–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, S.; Moore, J.A.; Montesion, M.; Sharaf, R.; Lin, D.I.; Colón, C.I.; Fleishmann, Z.; Ebot, E.M.; Newberg, J.Y.; Mills, J.M.; et al. Integrative Analysis of a Large Real-World Cohort of Small Cell Lung Cancer Identifies Distinct Genetic Subtypes and Insights into Histologic Transformation. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1572–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.; Wildey, G.; Sakre, N.; Lipka, M.B.; Behtaj, M.; Kresak, A.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Velcheti, V.; Fu, P.; et al. Reciprocal expression of INSM1 and YAP1 defines subgroups in small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73745–73756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, A.; Abbas, A.; Chan, T.; Henick, B.; Wang, X.; Doshi, P.; Fu, P.; Patel, J.; Kuo, F.; Chang, H.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Blockade Outcome in Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Its Relationship with Retinoblastoma Mutation Status and Function. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2200257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubaux, R.; Thu, K.L.; Coe, B.P.; MacAulay, C.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L. EZH2 promotes E2F-driven SCLC tumorigenesis through modulation of apoptosis and cell-cycle regulation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Wang, J.; Nilsson, M.B.; Fujimoto, J.; Saintigny, P.; Yordy, J.; Giri, U.; Peyton, M.; Fan, Y.H.; Diao, L.; et al. Proteomic profiling identifies dysregulated pathways in small cell lung cancer and novel therapeutic targets including PARP1. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Ohta, M.; Hirabayashi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Iuchi, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Maeda, H.; Kido, T.; Miyoshi, S.; Matsuda, H. Thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase mRNA levels in tumor tissues and the efficacy of 5- fluorouracil in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2004, 45, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Liu, D.; Nakano, J.; Yokomise, H.; Ueno, M.; Kadota, K.; Wada, H. E2F1 overexpression correlates with thymidylate synthase and survivin gene expressions and tumor proliferation in non small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socinski, M.A.; Smit, E.F.; Lorigan, P.; Konduri, K.; Reck, M.; Szczesna, A.; Blakely, J.; Serwatowski, P.; Karaseva, N.A.; Ciuleanu, T.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed plus carboplatin compared with etoposide plus carboplatin in chemotherapy-naive patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4787–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Su, J.; Sun, L.; et al. Sirtuin 3 induces apoptosis and necroptosis by regulating mutant p53 expression in small-cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Su, J.; Li, F.L.; Chen, T.; Mayner, J.; Engler, A.; Ma, S.; Li, Q.; Guan, K.L. YAP silencing by RB1 mutation is essential for small-cell lung cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, A.; Piro, G.; Schietroma, F.; Strusi, A.; Vita, E.; Fiorani, S.; Barone, D.; Monaca, F.; Sparagna, I.; Valente, G.; et al. Unweaving the Mitotic Spindle: A Focus on Aurora Kinase Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1026020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraldi, P. Aurora-A Overexpression Reveals Tetraploidization as a Major Route to Centrosome Amplification in P53−/− Cells. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xi, Z.; Zhong, N.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, X. Knocking down the Expression of Aurora-A Gene Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces G2/M Phase Arrest in Human Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liewer, S.; Huddleston, A. Alisertib: A Review of Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy and Toxicity in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies and Solid Tumors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Niu, H.; Nackaerts, K.; Csoszi, T.; Ostoros, G.; Mark, Z.; Baik, C.; Joy, A.A.; Chouaid, C.; Jaime, J.C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Paclitaxel plus Alisertib versus Paclitaxel plus Placebo as Second-Line Therapy for SCLC: Primary and Correlative Biomarker Analyses. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Duplaquet, L.; Hong, D.; Durmaz, Y.T.; Jones, K.L.; Cho, H.; Morrow, M.; Protti, A.; Poitras, M.J.; et al. Aurora A Kinase Inhibition Induces Accumulation of SCLC Tumor Cells in Mitosis with Restored Interferon Signaling to Increase Response to PD-L1. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, M.M.; Fisher, R.P. The CDK-Activating Kinase Cdk7: Taking Yes for an Answer. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3239–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Christensen, C.L.; Dries, R.; Oser, M.G.; Deng, J.; Diskin, B.; Li, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Y.; et al. CDK7 Inhibition Potentiates Genome Instability Triggering Anti-Tumor Immunity in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 37–54.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N. Targeting the DNA Damage Response Machinery for Lung Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Tong, P.; Stewart, C.A.; Cristea, S.; Valliani, A.; Shames, D.S.; Redwood, A.B.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, L.; Glisson, B.S.; et al. CHK1 Inhibition in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Produces Single-Agent Activity in Biomarker-Defined Disease Subsets and Combination Activity with Cisplatin or Olaparib. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3870–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, L.A.; Navarro, A.; Schaefer, E.; Johnson, M.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Han, J.-Y.; Bondarenko, I.; Cicin, I.; Dragnev, K.H.; Abel, A.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Prexasertib (LY2606368) in Patients with Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woll, P.; Gaunt, P.; Danson, S.; Steele, N.; Ahmed, S.; Mulatero, C.; Shah, R.; Bhosle, J.; Hodgkinson, E.; Watkins, B.; et al. Olaparib as Maintenance Treatment in Patients with Chemosensitive Small Cell Lung Cancer (STOMP): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial. Lung Cancer 2022, 171, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sica, G.L.; Wagner, L.I.; Wade, J.L.; Srkalovic, G.; Lash, B.W.; Leach, J.W.; Leal, T.B.; Aggarwal, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Etoposide in Combination with Veliparib or Placebo for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ECOG-ACRIN 2511 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Bentsion, D.; Gans, S.; Penkov, K.; Son, C.; Sibille, A.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Groen, H.J.M.; Gay, C.M.; Fujimoto, J.; et al. Veliparib in Combination with Carboplatin and Etoposide in Patients with Treatment-Naïve Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Study. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3884–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Pan, Y.; Shi, J.; Yang, N.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; He, J.; Li, X.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Niraparib as Maintenance Treatment in Patients with Extensive-Stage SCLC After First-Line Chemotherapy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietanza, M.C.; Waqar, S.N.; Krug, L.M.; Dowlati, A.; Hann, C.L.; Chiappori, A.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Woo, K.M.; Cardnell, R.J.; Fujimoto, J.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Temozolomide in Combination with Either Veliparib or Placebo in Patients with Relapsed-Sensitive or Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farago, A.F.; Yeap, B.Y.; Stanzione, M.; Hung, Y.P.; Heist, R.S.; Marcoux, J.P.; Zhong, J.; Rangachari, D.; Barbie, D.A.; Phat, S.; et al. Combination Olaparib and Temozolomide in Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1372–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouw, K.W.; Goldberg, M.S.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; D’Andrea, A.D. DNA Damage and Repair Biomarkers of Immunotherapy Response. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Chen, L.; Corte, C.M.D.; Morikawa, N.; Fujimoto, J.; Cristea, S.; Nguyen, T.; Diao, L.; Li, L.; et al. Targeting DNA Damage Response Promotes Antitumor Immunity through STING-Mediated T-cell Activation in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitai, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Sueyoshi, T.; Kobiyama, K.; Ishii, K.J.; Zou, J.; Akira, S.; Matsuda, T.; Kawai, T. DNA-Containing Exosomes Derived from Cancer Cells Treated with Topotecan Activate a STING-Dependent Pathway and Reinforce Antitumor Immunity. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, E.E.; Walker, S.M.; Taggart, L.E.; McCabe, N.; Knight, L.A.; Wilkinson, R.; McCloskey, K.D.; Buckley, N.E.; Savage, K.I.; Salto-Tellez, M.; et al. Activation of STING-Dependent Innate Immune Signaling By S-Phase-Specific DNA Damage in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 109, djw199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Niimi, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Permata, T.B.M.; Hagiwara, Y.; Isono, M.; Nuryadi, E.; Sekine, R.; Oike, T.; Kakoti, S.; et al. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Vilimas, R.; Trindade, C.; Erwin-Cohen, R.; Roper, N.; Xi, L.; Krishnasamy, V.; Levy, E.; Mammen, A.; Nichols, S.; et al. Durvalumab in Combination with Olaparib in Patients with Relapsed SCLC: Results from a Phase II Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Delord, J.-P.; Jeffry Evans, T.R.; De Jonge, M.; Kim, S.-W.; Meurer, M.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Angell, H.K.; Rocher-Ros, V.; et al. Olaparib and Durvalumab in Patients with Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer (MEDIOLA): An Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase 1/2, Basket Study. Lung Cancer 2023, 180, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Takahashi, N.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ceribelli, M.; Wilson, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Beck, E.; Sciuto, L.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of ATR Yields Durable Regressions in Small Cell Lung Cancers with High Replication Stress. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 566–579.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.W.; Zhang, Y.; Elmeskini, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Fu, H.; Murai, Y.; Wangsa, D.; Kumar, S.; Takahashi, N.; Atkinson, D.; et al. ATR Inhibition Augments the Efficacy of Lurbinectedin in Small-cell Lung Cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Agent | NCT ID Number | Phase | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| AURK inhibitors | NCT00858377 | I | AMG 900 monotherapy |
| n/a | I | Danusertib monotherapy (24 h infusion) | |
| NCT01045421 | I-II | Alisertib monotherapy | |
| NCT01923337 | I | Alisertib + Irinotecan | |
| NCT01094288 | I | Alisertib + Docetaxel | |
| NCT01677559 | I | Alisertib + Nab-paclitaxel | |
| 2006-003772-35 | II | Danusertib monotherapy | |
| NCT02038647 | II | Alisertib + Paclitaxel vs. Placebo + Paclitaxel | |
| CHK1 inhibitors | NCT02735980 | II | Prexasertib monotherapy |
| PARP inhibitors | NCT01642251 | I/II | cisplatin-etoposide (CE) + Veliparib vs. Placebo + Veliparib |
| NCT02446704 | I/II | Olaparib + TMZ | |
| NCT02734004 | I/II | Olaparib + Durvalumab | |
| ISRCTN 73164486, EudraCT 2010-021165-76 | II | Olaparib monotherapy | |
| NCT02289690 | II | 1:1:1: veliparib + carboplatin + etoposide followed by veliparib maintenance, veliparib + carboplatin + etoposide followed by placebo, placebo+ carboplatin + etoposide followed by placebo | |
| NCT02484404 | II | Olaparib + Durvalumab | |
| NCT03958045 | II | Rucaparib + Nivolumab | |
| NCT01638546 | II | TMZ/veliparib vs. TMZ/placebo | |
| ZL-2306-005 | III | Niraparib monotherapy | |
| ATR inhibitors | NCT02487095 | II | Berzosertib + Topotecan |
| NCT04768296 | II | Berzosertib + Topotecan |
| Agent | NCT ID Number | Phase | Treatment Regimen |
|---|---|---|---|
| AURK inhibitors | NCT05271292 | Ib/II | Chiauranib |
| NCT05505825 | Ib/II | AK104 + Chiauranib | |
| NCT03216343 | I | Chiauranib | |
| NCT04830813 | III | Chiauranib Capsule | |
| NCT06095505 | II | Alisertib | |
| CDK7 inhibitors | NCT04247126 | I | SY 5609 + gemcitabine |
| PARP inhibitors | NCT05002868 | I | RP12146 |
| NCT03227016 | I | Veliparib + Topotecan | |
| NCT03532880 | I | Olaparib + Low-dose radiotherapy | |
| NCT03923270 | I | Radiotherapy + durvalumab vs. durvalumab combinations (tremelimumab or olaparib) | |
| ES-SCLC-2nd-IIT-SHR3162-APA | n/a | Camrelizumab + Fluzoparib | |
| NCT04644068 | I/II | AZD5305 monotherapy or in combination with anti-cancer agents | |
| NCT04826341 | I/II | Sacituzumab Govitecan + Berzosertib | |
| NCT04209595 | I/II | PLX038 (PEGylated SN38) + Rucaparib | |
| NCT04728230 | I/II | Carboplatin + etoposide + durvalumab + olaparib and/or radiation therapy | |
| NCT03830918 | I/II | Niraparib + Temozolomide + Atezolizumab | |
| NCT05975944 | I/II | Olaparib + Selinexor | |
| NCT02769962 | I/II | EP0057 + Olaparib | |
| NCT04434482 | I/II | IMP4297 + Temozolomide | |
| NCT04400188 | I/II | Fluzoparib + Temozolomide ± SHR-1316 | |
| NCT04659785 | I/II | Fluzoparib + Apatinib | |
| NCT04538378 | II | Olaparib + Durvalumab | |
| NCT05411679 | II | EP0057 + Olaparib | |
| NCT05718323 | II | Niraparib + Anti-PD-L1 therapy | |
| NCT04334941 | II | Talazoparib + Atezolizumab | |
| NCT05162196 | II | Radiotherapy + Niraparib + Toripalimab | |
| NCT04701307 | II | Niraparib + Dostarlimab | |
| NCT03672773 | II | Talazoparib + low-dose Temozolomide | |
| NCT02498613 | II | Cediranib + Olaparib | |
| NCT05623319 | II | Olaparib + Pembrolizumab | |
| NCT05245994 | II | Olaparib + Durvalumab | |
| NCT04939662 | II | Olaparib + Bevacizumab | |
| NCT04624204 | III | Pembrolizumab + Chemoradiation followed by pembrolizumab ± Olaparib vs. Pembrolizumab + Chemoradiation | |
| NCT04790955 | Observational | SBRT and low-dose radiotherapy + PARPi + temozolomide + PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors | |
| ATR inhibitors | NCT04491942 | I | Elimusertib + chemotherapy (cisplatin, or cisplatin and gemcitabine) |
| NCT02595931 | I | Berzosertib + Irinotecan hydrochloride | |
| NCT04802174 | I/II | Berzosertib + Lurbinectedin | |
| NCT04826341 | I/II | Berzosertib + Sacituzumab govitecan | |
| NCT02487095 | I/II | Berzosertib + Topotecan | |
| NCT03896503 | II | Berzosertib + Topotecan | |
| ATM inhibitors | NCT04939662 | II | Olaparib + Bevacizumab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papavassiliou, K.A.; Sofianidi, A.A.; Gogou, V.A.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Papavassiliou, A.G. P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052479
Papavassiliou KA, Sofianidi AA, Gogou VA, Anagnostopoulos N, Papavassiliou AG. P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052479
Chicago/Turabian StylePapavassiliou, Kostas A., Amalia A. Sofianidi, Vassiliki A. Gogou, Nektarios Anagnostopoulos, and Athanasios G. Papavassiliou. 2024. "P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052479
APA StylePapavassiliou, K. A., Sofianidi, A. A., Gogou, V. A., Anagnostopoulos, N., & Papavassiliou, A. G. (2024). P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052479









