Association of DPP-4 Concentrations with the Occurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Use of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Postpartum Women
1.2. Phenomenon of Maternal Programming
2. Results
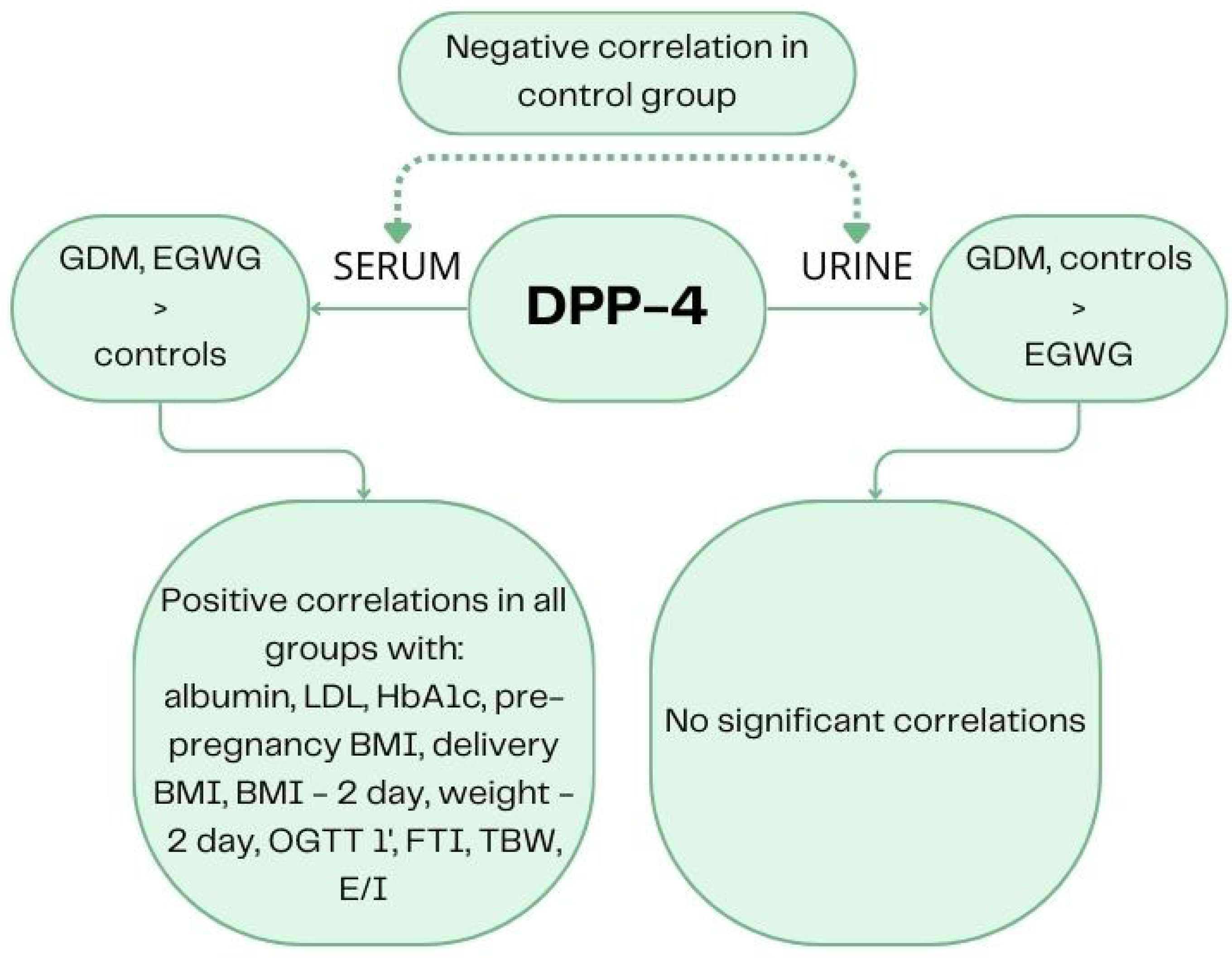
2.1. Comparison of DPP-4 Concentration in GDM Patients, EGWG Patients, and Healthy Controls
2.2. Correlations of DPP-4 Determinations in Serum and Urine in Delivery Day
2.2.1. All Groups
2.2.2. GDM Group
2.2.3. EGWG Group
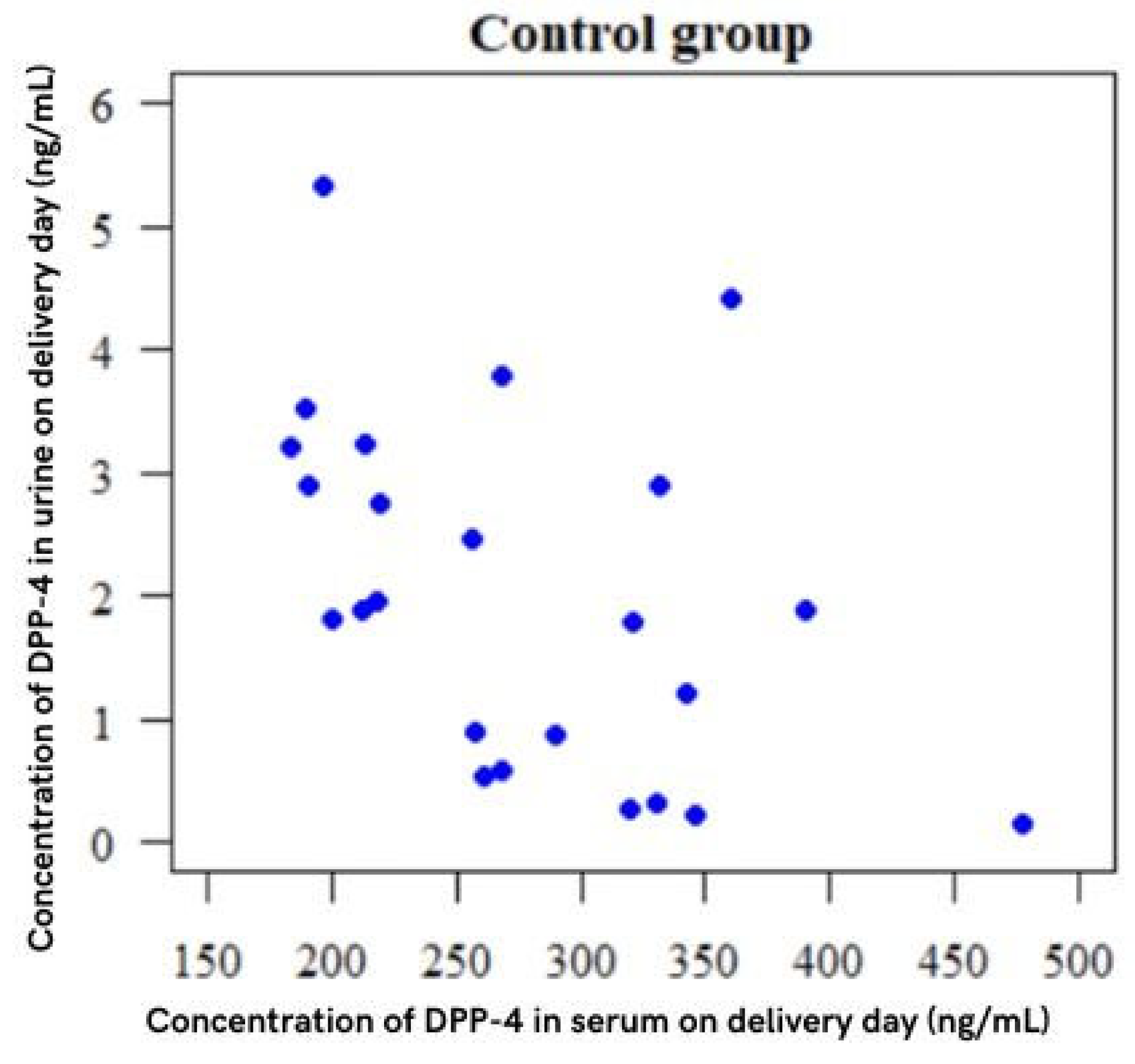
2.2.4. Control Group
2.3. Correlations with DPP-4 Concentrations in All Groups
3. Discussion
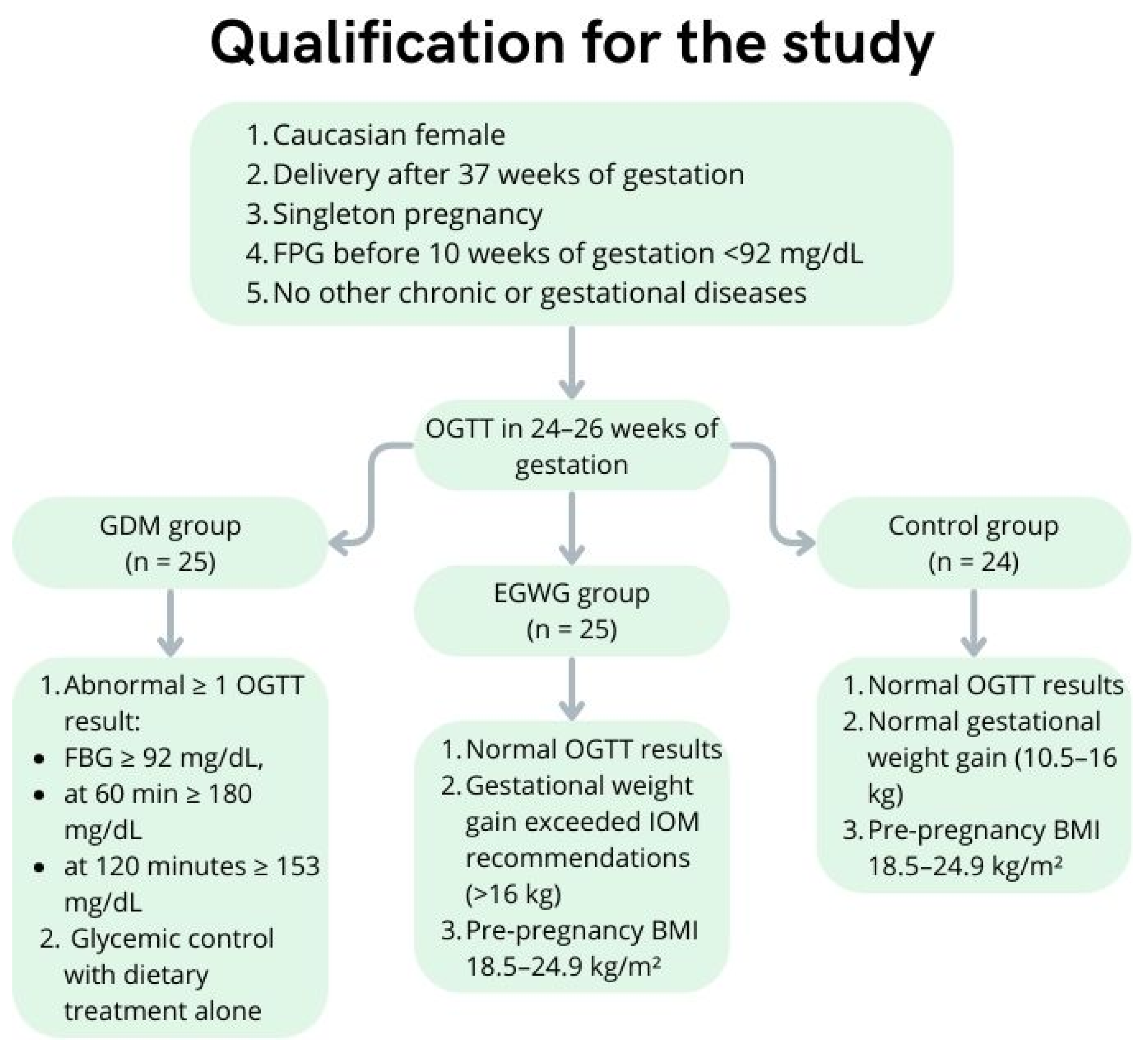
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, T.R.; Diabetes Mellitus and Pregnancy. MedScape. 2022. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/127547-overview?form=fpf&scode=msp&st=fpf&socialSite=apple&icd=login_success_ap_match_fpf#a7 (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Dong, G.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, Z. The effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The pathophysiology of gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, A.H.Y.; Godfrey, K.M. Gestational diabetes mellitus and developmental programming. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76 (Suppl. S3), 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozińska, E.; Zamora, J.; Marlin, N.; Betrán, A.P.; Astrup, A.; Bogaerts, A.; Cecatti, J.G.; Dodd, J.M.; Facchinetti, F.; Geiker, N.R.W.; et al. Gestational weight gain outside the Institute of Medicine recommendations and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Analysis using individual participant data from randomised trials. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.B.; Lobo, C.V.; Miranda, A.E.D.S.; Carvalho, B.D.C.; Santos, L.C.D. Dietary Patterns during Pregnancy and Gestational Weight Gain: A Systematic Review. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2022, 44, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.M.; Yaktine, A.L. (Eds.) Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Goławski, K.; Giermaziak, W.; Ciebiera, M.; Wojtyła, C. Excessive Gestational Weight Gain and Pregnancy Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominiarek, M.A.; Peaceman, A.M. Gestational weight gain. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Jin, J.; Hu, K.L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Gestational Weight Gain Restriction in Overweight/Obese Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Peng, X.; Yi, H.; Tang, S.; You, H. Determinants of excessive gestational weight gain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Public. Health 2022, 80, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Biochemical properties of recombinant prolyl dipeptidases DPP-IV and DPP8. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 575, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular mechanisms by which GLP-1 RA and DPP-4i induce insulin sensitivity. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaniel, K.R.C.; Bucher, M.; Phillips, E.A.; Li, C.; Sullivan, E.L.; Kievit, P.; Rugonyi, S.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Maloyan, A. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition delays developmental programming of obesity and metabolic disease in male offspring of obese mothers. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2022, 13, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H.; Sun, H.; Ji, X. Sitagliptin down-regulates retinol-binding protein 4 and reduces insulin resistance in gestational diabetes mellitus: A randomized and double-blind trial. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilszyk, A.; Niebrzydowska, M.; Pilszyk, Z.; Wierzchowska-Opoka, M.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż. Incretins as a potential treatment option for gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, A.; Atkinson, S.A.; Bertram, V.; Vanniyasingam, T.; Thabane, L.; Mottola, M.F.; Phillips, S.M.; BHIP Study Team. Exploring comparative assessment of adiposity measures during pregnancy and postpartum. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makama, M.; Skouteris, H.; Moran, L.J.; Lim, S. Reducing postpartum weight retention: A review of the implementation challenges of postpartum lifestyle interventions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowska, A.; Standyło, A.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. The possibility of using bioelectrical impedance analysis in pregnant and postpartum women. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Sung, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Roh, C.R. Obstetric and neonatal outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus in twin pregnancies according to changes in its diagnostic criteria from National Diabetes Data Group criteria to Carpenter and Coustan criteria: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantham, P.; Aye, I.L.; Powell, T.L. Inflammation in maternal obesity and gestational diabetes mellitus. Placenta 2015, 36, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, P.; Houshmand-Oeregaard, A.; Kelstrup, L.; Lauenborg, J.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Clausen, T.D. Gestational diabetes mellitus and long-term consequences for mother and offspring: A view from Denmark. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1396–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Page, K.A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Risks and management during and after pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Deng, S.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Geng, H.; Wang, Z. Association between maternal and umbilical cord serum dipeptidyl peptidase IV in pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2016, 42, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain with Maternal and Infant Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.A.; Deshmukh, H.; Atkin, S.; Sathyapalan, T. The potential role of incretin-based therapies for polycystic ovary syndrome: A narrative review of the current evidence. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 27, 2042018821989238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subrahmanyan, N.A.; Koshy, R.M.; Jacob, K.; Pappachan, J.M. Efficacy and Cardiovascular Safety of DPP-4 Inhibitors. Curr. Drug Saf. 2021, 16, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandzija, N.; Zhang, W.; Motta-Mejia, C.; Mhlomi, V.; McGowan-Downey, J.; James, T.; Cerdeira, A.S.; Tannetta, D.; Sargent, I.; Redman, C.W.; et al. Placental extracellular vesicles express active dipeptidyl peptidase IV; levels are increased in gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2019, 8, 1617000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, S.; Beyerlein, A.; Pfirrmann, M.; Hofelich, A.; Much, D.; Hivner, S.; Bunk, M.; Herbst, M.; Peplow, C.; Walter, M.; et al. Efficacy of vildagliptin for prevention of postpartum diabetes in women with a recent history of insulin-requiring gestational diabetes: A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mol. Metab. 2018, 9, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkind-Hirsch, K.E.; Paterson, M.S.; Shaler, D.; Gutowski, H.C. Short-Term Sitagliptin-Metformin Therapy Is More Effective Than Metformin or Placebo in Prior Gestational Diabetic Women with Impaired Glucose Regulation. Endocr. Pract. 2018, 24, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrettini, S.; Caroli, A.; Torlone, E. Nutrition and Metabolic Adaptations in Physiological and Complicated Pregnancy: Focus on Obesity and Gestational Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 30, 611929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Yadav, D.; Sharma, N.; Jin, J.O. Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP)-IV Inhibitors with Antioxidant Potential Isolated from Natural Sources: A Novel Approach for the Management of Diabetes. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K.; Sharma, S.; Khan, Y. DPP-4 inhibitors for treating T2DM—Hype or hope? An analysis based on the current literature. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 23, 1130625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrborn, D.; Wronkowitz, N.; Eckel, J. DPP4 in Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2015, 27, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.L.; Deng, J.T.; Guan, G.J.; Chen, S.H.; Liu, Y.T.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.W.; Zhuang, X.H.; Sun, F.D.; Deng, H.P. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV is a potential molecular biomarker in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2012, 9, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Tammen, H.; Mark, M.; Benetti, E.; Delić, D.; Schepers, C.; von Eynatten, M. Urinary dipeptidyl peptidase-4 protein is increased by linagliptin and is a potential predictive marker of urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1968–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitic, B.; Lazarevic, G.; Vlahovic, P.; Rajic, M.; Stefanovic, V. Diagnostic Value of the Aminopeptidase N, N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase and Dipeptidylpeptidase IV in Evaluating Tubular Dysfunction in Patients with Glomerulopathies. Ren. Fail. 2008, 30, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziennik Ustaw Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej. Rozporządzenie Ministra Zdrowia z Dnia 16 Sierpnia 2018 r. w Sprawie Standardu Organizacyjnego Opieki Okołoporodowej. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20180001756/O/D20181756.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Zalecenia Kliniczne Dotyczące Postępowania u Osób z Cukrzycą 2023 Stanowisko Polskiego Towarzystwa Diabetologicznego. Available online: https://ptdiab.pl/zalecenia-ptd/zalecania-aktywni-czlonkowie-2023 (accessed on 8 December 2023).

| Variables | GDM Group n = 25 A | EGWG n = 25 B | Control Group n = 24 C | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin [mg/mL] | Mean (SD) | 3.49 (0.25) | 3.58 (0.25) | 3.73 (0.15) | p = 0.002 * |
| C > B, A | |||||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | Mean (SD) | 222.9 (36.08) | 222.24 (40.19) | 225.62 (35.63) | p = 0.904 |
| Range | 176–312 | 164–313 | 176–287 | ||
| HDL (mg/dL) | Mean (SD) | 64.76 (9.04) | 64.76 (16.13) | 64.76 (11.52) | p = 0.039 * |
| C > A | |||||
| LDL (mg/dL) | Mean (SD) | 115.52 (26.27) | 111.96 (27.35) | 112.08 (27.55) | p = 0.784 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | Mean (SD) | 204.04 (52.8) | 210.2 (55.21) | 160.79 (28.83) | p < 0.001 * |
| A, B > C | |||||
| HgbA1c (IFCC) (mmol/mol) | Mean (SD) | 5.42 (0.35) | 5.34 (0.33) | 5.12 (0.29) | p = 0.011 * |
| A, B > C | |||||
| MCV [fl] | Mean (SD) | 89.90 (3.41) | 87 (2.57) | 87.78 (4.78) | p = 0.009 * |
| A > B, C | |||||
| Pre-pregnancy BMI [kg/m2] | Mean (SD) | 26.46 (3.6) | 22.55 (1.49) | 22.24 (2.15) | p < 0.001 * |
| A > C, B | |||||
| OGTT-0’ [mmol/L] | Mean (SD) | 93.64 (5.11) | 78.62 (4.92) | 79.83 (4.02) | p < 0.001 * |
| A > C, B | |||||
| OGTT-1’ [mmol/L] | Mean (SD) | 175.16 (13.92) | 124.82 (23.32) | 126.5 (20.8) | p = 0.011 * |
| A, B > C | |||||
| OGTT-2’ [mmol/L] | Mean (SD) | 154.64 (26.56) | 104.41(16.62) | 102.96 (20.65) | p < 0.001 * |
| A > B, C | |||||
| Delivery BMI (kg/m2) | Mean (SD) | 30.69 (3.85) | 31.12 (3.66) | 26.52 (3.29) | p < 0.001 * |
| B, A > C | |||||
| BMI—2 day (kg/m2) | Mean (SD) | 28.87 (3.87) | 28.52 (2.52) | 24.19 (2.87) | p < 0.001 * |
| A, B > C | |||||
| Weight—2 day (kg) | Mean (SD) | 79.25 (11.88) | 79.63 (9.92) | 65.97 (6.86) | p < 0.001 * |
| LTI (kg/m2) | Mean (SD) | 12.22 (1.23) | 13.28 (1.43) | 12.23 (1.6) | p < 0.05 |
| B > C, A | |||||
| FTI (kg/m2) | Mean (SD) | 16.11 (3.9) | 14.76 (2.68) | 11.87 (2.07) | p < 0.001 * |
| A, B > C | |||||
| TBW (%) | Mean (SD) | 34.15 (2.74) | 36.81 (3.81) | 31.96 (3.19) | p < 0.001 * |
| B > A, C | |||||
| E/I | Mean (SD) | 0.97 (0.08) | 0.94 (0.08) | 0.90 (0.07) | p = 0.007 * |
| A, B > C | |||||
| BCM (kg) | Mean (SD) | 17.91 (2.46) | 21.13 (3.65) | 19.26 (3.56) | p = 0.005 * |
| B > A |
| Parameter | GDM Group n = 25 A | EGWG n = 25 B | Control Group n = 24 C | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of DPP-4 in serum on delivery day (ng/mL) | Mean (SD) | 344.5 (67.87) | 323.85 (58.34) | 276.96 (75.45) | p = 0.003 |
| A, B > C | |||||
| Concentration of DPP-4 in urine on delivery day (ng/mL) | Mean (SD) | 3.4 (3.96) | 0.94 (0.75) | 2.04 (1.44) | p = 0.007 |
| C, A > B |
| Concentration of DPP-4 in Serum on Delivery Day (ng/mL) | Concentration of DPP-4 in Urine on Delivery Day (ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| Albumin | r = −0.25, p = 0.032 * | r = 0.16, p = 0.174 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | r = 0.211, p = 0.072 | r = −0.015, p = 0.9 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | r = 0.035, p = 0.766 | r = 0.083, p = 0.481 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | r = 0.242, p = 0.038 * | r = −0.109, p = 0.354 |
| TG (mg/dL) | r = 0.072, p = 0.544 | r = −0.067, p = 0.569 |
| HgbA1c (%) | r = 0.238, p = 0.041 * | r = −0.038, p = 0.749 |
| MCV (fl) | r = 0.006, p = 0.956 | r = 0.162, p = 0.167 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | r = 0.347, p = 0.002 * | r = 0.197, p = 0.092 |
| OGTT-0’ | r = 0.061, p = 0.604 | r = 0.157, p = 0.182 |
| OGTT-1’ | r = 0.388, p = 0.001 * | r = 0.182, p = 0.12 |
| OGTT-2’ | r = 0.19, p = 0.105 | r = 0.168, p = 0.152 |
| Delivery BMI (kg/m2) | r = 0.418, p < 0.001 * | r = −0.06, p = 0.61 |
| BMI—2 day (kg/m2) | r = 0.373, p = 0.001 * | r = −0.03, p = 0.798 |
| Weight—2 day (kg) | r = 0.456, p < 0.001 * | r = −0.08, p = 0.498 |
| LTI (kg/m2) | r = −0.022, p = 0.853 | r = −0.193, p = 0.1 |
| FTI (kg/m2) | r = 0.353, p = 0.002 * | r = 0.021, p = 0.862 |
| TBW (%) | r = 0.424, p < 0.001 * | r = −0.132, p = 0.263 |
| E/I | r = 0.446, p < 0.001 * | r = 0.01, p = 0.931 |
| BCM (kg) | r = 0.078, p = 0.506 | r = −0.133, p = 0.258 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niebrzydowska-Tatus, M.; Pełech, A.; Bień, K.; Mekler, J.; Santiago, M.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Trojnar, M. Association of DPP-4 Concentrations with the Occurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031829
Niebrzydowska-Tatus M, Pełech A, Bień K, Mekler J, Santiago M, Kimber-Trojnar Ż, Trojnar M. Association of DPP-4 Concentrations with the Occurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031829
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiebrzydowska-Tatus, Magdalena, Aleksandra Pełech, Katarzyna Bień, Julia Mekler, Miracle Santiago, Żaneta Kimber-Trojnar, and Marcin Trojnar. 2024. "Association of DPP-4 Concentrations with the Occurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031829
APA StyleNiebrzydowska-Tatus, M., Pełech, A., Bień, K., Mekler, J., Santiago, M., Kimber-Trojnar, Ż., & Trojnar, M. (2024). Association of DPP-4 Concentrations with the Occurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031829







