Administration of Spermidine and Eugenol Demonstrates Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy on Metastatic SW620 and Primary Caco-2 Colorectal Cancer Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
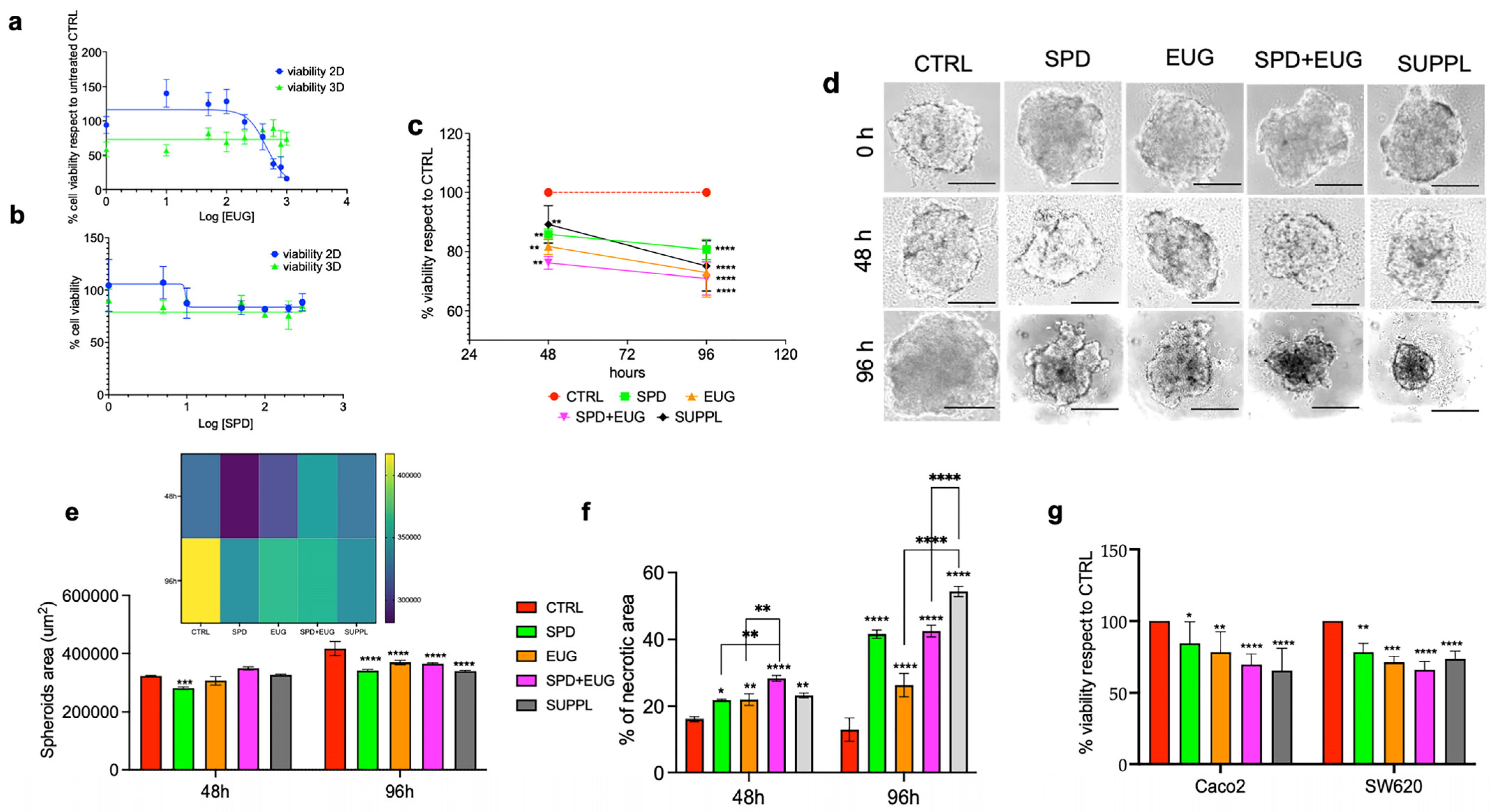
2.1. Effects of SPD and EUG Alone and in Combination on the Proliferation, Structure, and Viability of Metastatic SW620 Spheroids Compared to Untreated Controls
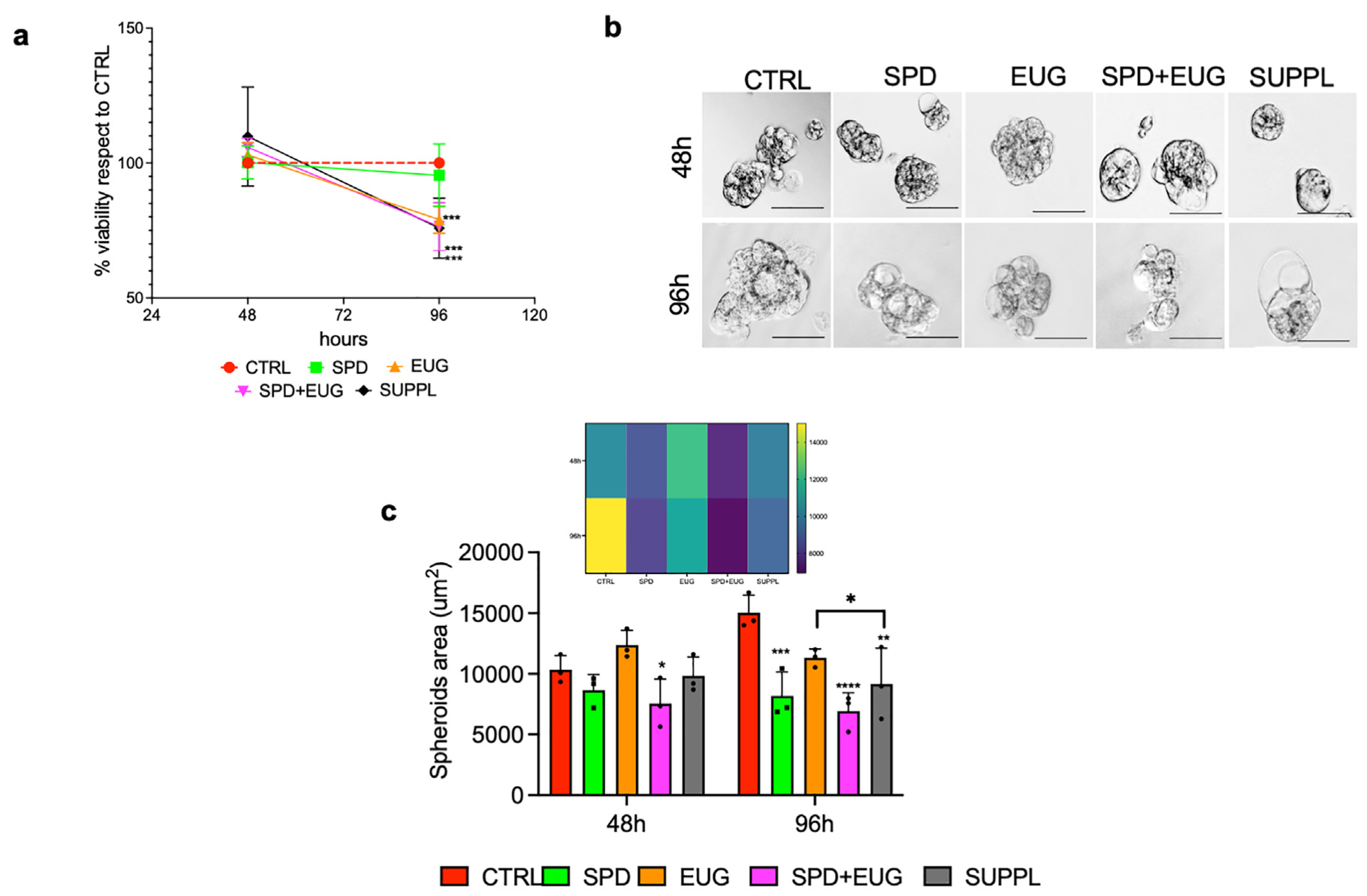
2.2. Effects of SPD and EUG Alone and in Combination on the Proliferation and Structure of Primary Caco-2 Spheroids Compared to the Untreated CTRLs
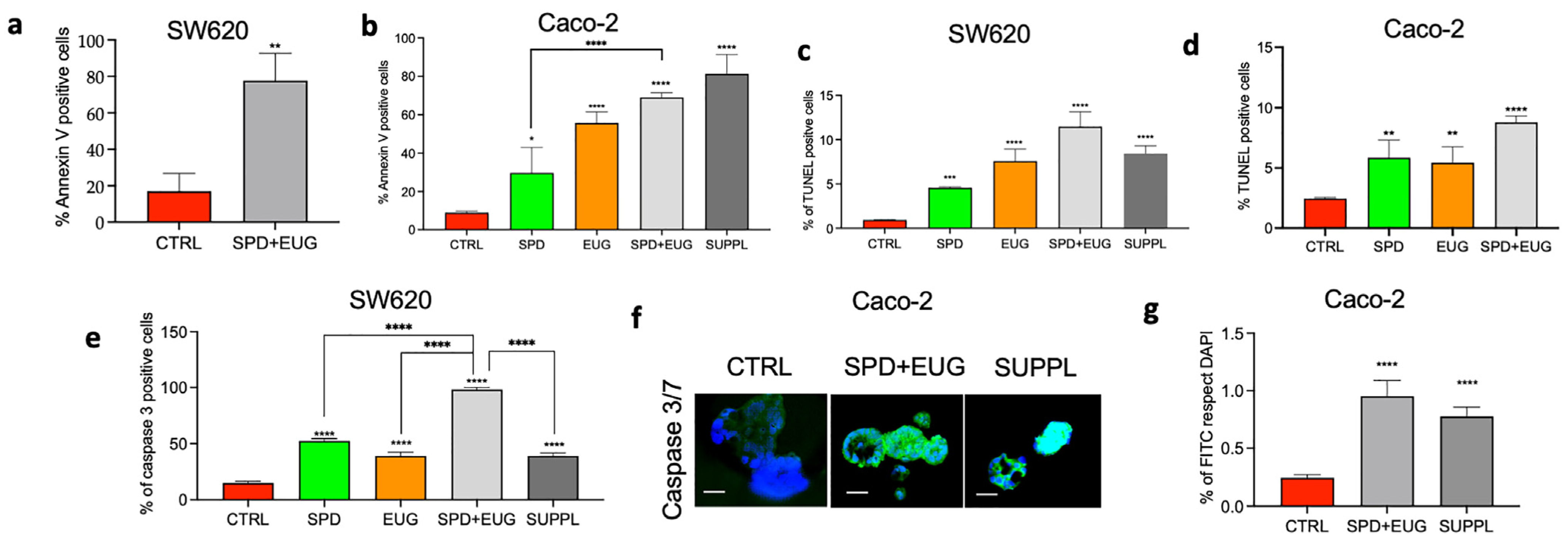
2.3. Effects of SPD and EUG Alone and in Combination on Apoptosis in Homotypic SW620 and Caco-2 Spheroids Compared to Untreated CTRLs
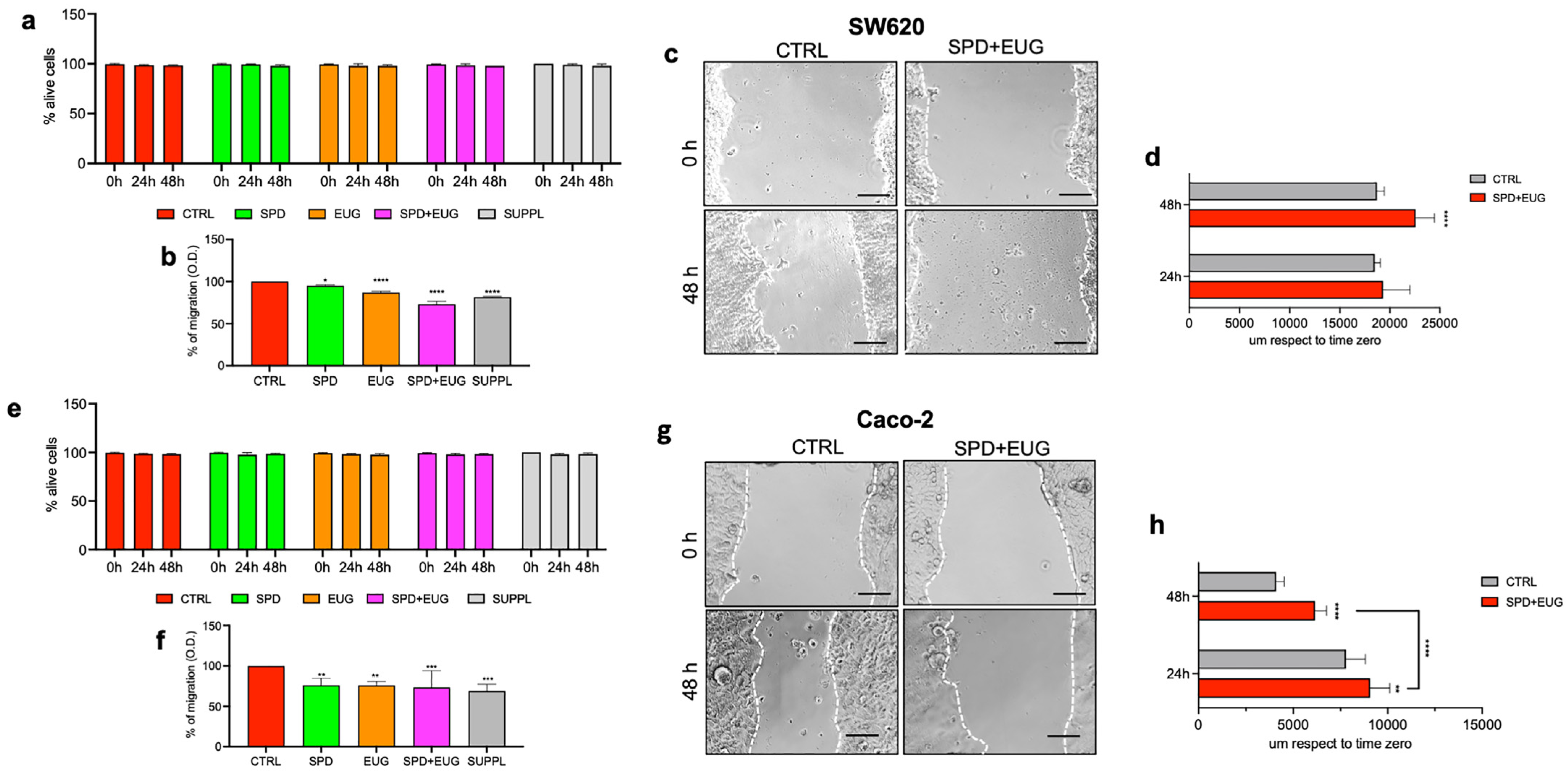
2.4. Effects of SPD and EUG Alone and in Combination on the Migration of SW620 and Caco-2 Cells in 2D Compared to the Untreated CTRLs
2.5. Analysis of the Contribution Plus Interaction of SPD and EUG
2.6. Discrimination Analysis of Cellular Response to SPD, EUG, SPD+EUG, and the SUPPL
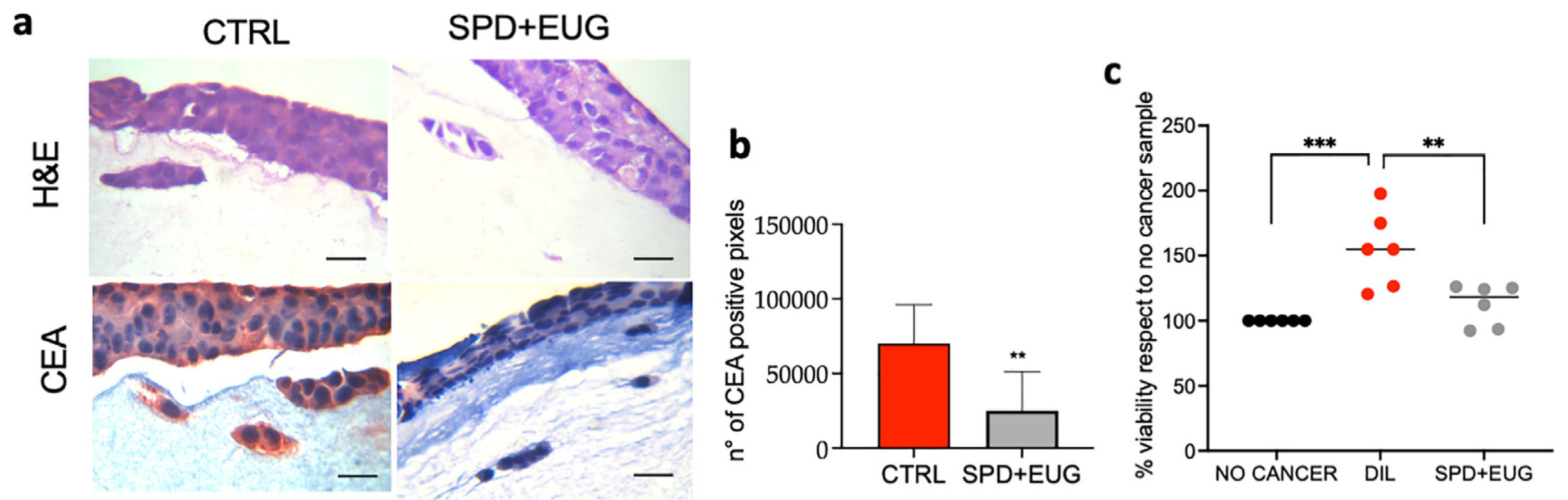
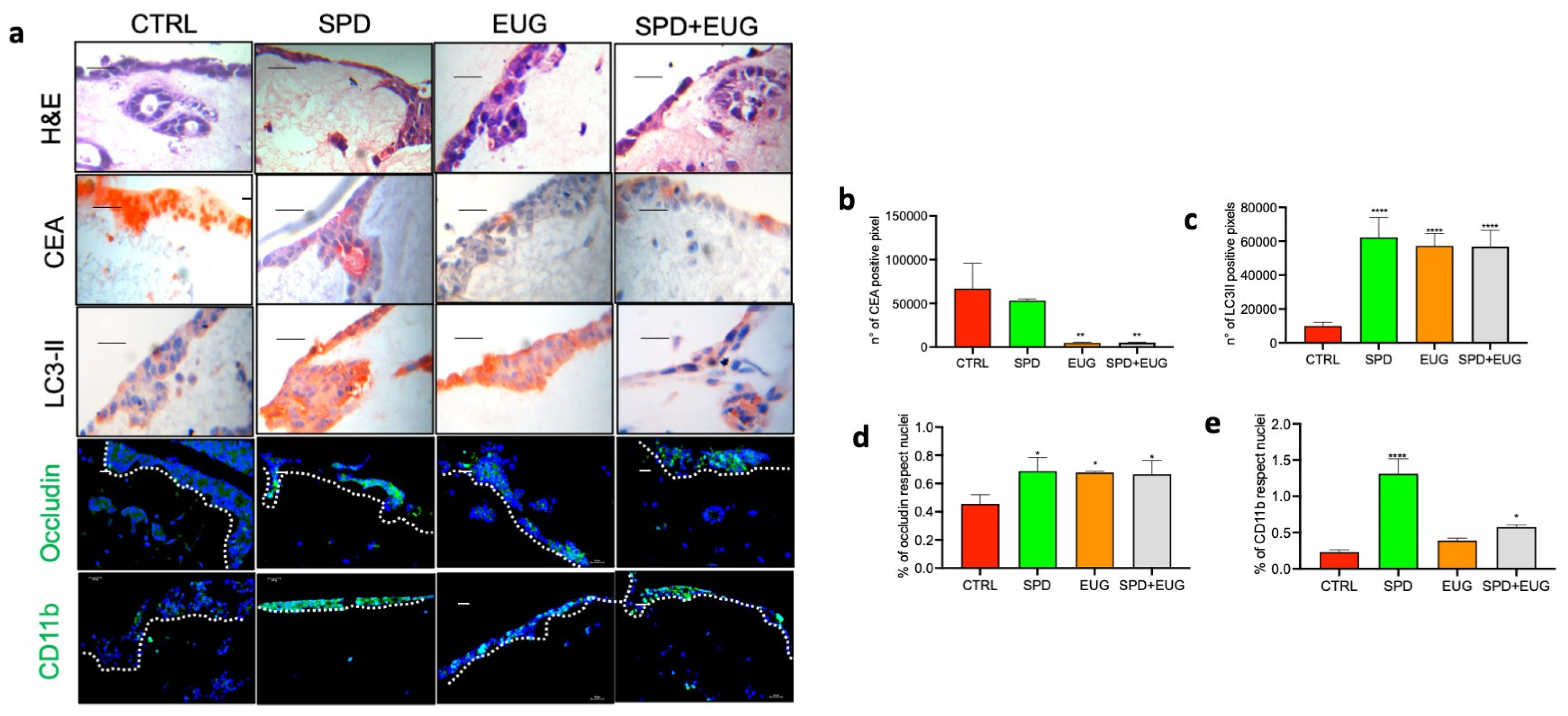
2.7. Effects of SPD and EUG Alone and in Combination on 3D Co-Culture of Intestinal Mucosa Containing SW620/Caco-2 Spheroids Embedded in the Extracellular Matrix
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. SPD and EUG Sources
4.3. Generation of Homotypic 3D Spheroids Using SW620 and Caco-2 Cell Lines and Treatment with SPD and EUG Alone and in Combination
4.4. Construction of 3D Co-Culture Intestinal Mucosa Models (Containing Embedded SW620 and Caco-2 Spheroids) and SPD and EUG Treatments
4.5. Viability (MTT) and Vitality (Trypan Blue) Measurements
4.6. Determination of Spheroid Area and Necrotic Zone Areas
4.7. Immunofluorescence Detection of Apoptosis Markers in Homotypic Spheroids
4.8. Cell Morphology and Immunofluorescence/Immunocytochemistry Staining of Markers in 3D Co-Culture Intestinal Mucosa Equivalents
4.9. Quantification of Markers of Interest in the 3D Homotypic Spheroid and 3D Co-Culture Intestinal Mucosa Equivalents
4.10. Migration of SW620 and Caco-2 Cells in Monolayer
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GLOBOCAN 2020: New Global Cancer Data. 2020. Available online: https://www.uicc.org/news/globocan-2020-new-global-cancer-data (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, P.; Xu, X. Risk factors for early-onset colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, S.M.; Al Doghaither, H.A.; Al-Ghafari, A.B. General insight into cancer: An overview of colorectal cancer (Review). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Shi, J.; Zhu, J. Cellular and molecular events in colorectal cancer: Biological mechanisms, cell death pathways, drug resistance and signalling network interactions. Discov. Onc. 2024, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, P.; Toska, E.; Engelman, J.A.; Scaltriti, M. The present and future of PI3K inhibitors for cancer therapy. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliceti, C.; Punzo, A.; Silla, A.; Simoni, P.; Roda, G.; Hrelia, S. New Insights into Bile Acids Related Signaling Pathways in the Onset of Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, D.J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal cancer: A review of carcinogenesis, global epidemiology, current challenges, risk factors, preventive and treatment strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Chen, S.; Tai, J. Mechanisms on chemotherapy resistance of colorectal cancer stem cells and research progress of reverse transformation: A mini-review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 995882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, S.; Ali, T.A.; Akhtar, S.; Nisar, S.; Sageena, G.; Ali, S.; Al-Mannai, S.; Therachiyil, L.; Mir, R.; Elfaki, I.; et al. Targeting cancer signaling pathways by natural products: Exploring promising anti-cancer agents. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilas, L.G.; Cruceriu, D.; Mocan, A.; Loghin, F.; Miere, D.; Balacescu, O. Plant-derived bioactive compounds in colorectal cancer: Insights from combined regimens with conventional chemotherapy to overcome drug-resistance. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Akash, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Nowrin, F.T.; Akter, T.; Shohag, S.; Rauf, A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Simal-Gandara, J. Colon cancer and colorectal cancer: Prevention and treatment by potential natural products. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Yan, C.; Yin, Y.; He, S.; Qiu, L.; Li, G. Natural polyphenols for treatment of colorectal cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qu, L.; Du, X.; Song, P.; Ng, J.P.L.; Wong, V.K.W.; Law, B.Y.K.; Fu, X. Natural products and derivatives targeting metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review. Metabolites 2024, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetemelk, M.; Rausch, M.; Colin, D.J.; Dormond, O.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P. Short-term 3D culture systems of various complexity for treatment optimization of colorectal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, A.M.; Meléndez, C.M.; Uribe, D.; Pedroza-Díaz, J. Synergistic effects of natural compounds and conventional chemotherapeutic agents: Recent insights for the development of cancer treatment strategies. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Ji, S.Y.; Bang, E.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Cheong, J. Auranofin accelerates spermidine-induced apoptosis via reactive oxygen species generation and suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 26, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoto, K.; Zhang, B.; Tajima, M.; Honjo, T.; Fagarasan, S. Spermidine—An old molecule with a new age-defying immune function. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, F.; Whittaker, A.; D’Amen, E.; Valerii, M.C.; Abduazizova, V.; Spisni, E.; Dinelli, G. Spermidine-eugenol supplement preserved inflammation-challenged intestinal cells by stimulating autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocelli, G.; Farabegoli, F.; Valerii, M.C.; Giovannini, C.; Sardo, A.; Spisni, E. Molecules present in plant essential oils for prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Molecules 2021, 26, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.N.; Ray, A.S.; Rahaman, C.H. A comprehensive and systematic review on potential anticancer activities of eugenol: From pre-clinical evidence to molecular mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhy, I.; Paul, P.; Sharma, T.; Banerjee, S.; Mondal, A. Molecular mechanisms of action of eugenol in cancer: Recent trends and advancement. Life 2022, 12, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwan, S.; Hatem, T.; Abid, H. Molecular mechanisms of eugenol as an antitumour bioactive compound: A comprehensive review. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 125, 03007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, S.K.; Mazumdar, A.D.; Mondhe, A.; Mandal, M. Apoptotic effect of eugenol in human colon cancer cell lines. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, H.; Antoniou, J.; Fang, Z. Apoptotic effects of eugenol-loaded nanoemulsions in human colon and liver cancer cell lines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 9159–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, D.; An, W.; Lai, H.; Li, X.; Cao, S.; Lin, X. Active fraction of clove induces apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated autophagy in human colorectal cancer HCT-116 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola, F.; Castoldi, F.; Kepp, O.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Spermidine reduces cancer-related mortality in humans. Autophagy 2019, 15, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.P.; Latour, Y.L.; Asim, M.; Barry, D.P.; Allaman, M.M.; Finley, J.L.; Smith, T.M.; McNamara, K.M.; Singh, K.; Sierra, J.C.; et al. Protective role of spermidine in colitis and colon carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 813–827.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M.; Singh, S.; Gulati, M.; Chellappan, D.K.; Rajput, R.; Gupta, G.; Ydyrys, A.; Kulbayeva, M.; Abdull, A.F.A.; et al. Spermidine as a promising anticancer agent: Recent advances and newer insights on its molecular mechanisms. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1164477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Hofer, S.J.; Madeo, F. Molecular targets of spermidine: Implications for cancer suppression. Cell Stress. 2023, 7, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, A.L.; Chiang, G.G.; Lang, E.S.; Ho, C.B.; Powis, G.; Vuori, K.; Abraham, R.T. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, PX-866, is a potent inhibitor of cancer cell motility and growth in three-dimensional cultures. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2505–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinci, M.; Gowan, S.; Boxall, F.; Patterson, L.; Zimmermann, M.; Court, W.; Lomas, C.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; Eccles, S.A. Advances in establishment and analysis of three-dimensional tumor spheroid-based functional assays for target validation and drug evaluation. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasova, V.S.; Riedl, A.; Strobl, M.; Flandorfer, J.; Unterleuthner, D.; Weindorfer, C.; Neuhold, P.; Stang, S.; Hengstschläger, M.; Bergmann, M.; et al. Selective eradication of colon cancer cells Harboring PI3K and/or MAPK pathway mutations in 3D Culture by Combined PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and MEK Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, D.; Patni, P.; Bishayee, A.; Sah, A.N.; Bishayee, A. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijewantha, N.; Sane, S.; Eikanger, M.; Antony, R.M.; Potts, R.A.; Lang, L.; Rezvani, K.; Sereda, G. Enhancing anti-tumorigenic efficacy of eugenol in human colon cancer cells using enzyme-responsive nanoparticles. Cancers 2023, 15, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X. Spermidine-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis via autophagic activation in cervical cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.; Liang, J.; Bian, Y.; Shan, G.; Huang, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhang, H.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, M.; et al. Polyamine-mediated ferroptosis amplification acts as a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, I.; Horky, P.; Abbas, S.Q.; Majid, M.; Bilal, A.H.M.; Ali, F.; Behl, T.; Hassan, S.S.U.; Bungau, S. Ferroptosis: A new road towards cancer management. Molecules 2022, 27, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siminzar, P.; Tohidkia, M.R.; Eppard, E.; Vahidfar, N.; Tarighatnia, A.; Aghanejad, A. Recent trends in diagnostic biomarkers of tumor microenvironment. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2023, 25, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.N.N.; Adriani, G. Three-dimensional heterotypic colorectal cancer spheroid models for evaluation of drug response. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1148930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnique, A.d.M.B.; Parducci, N.S.; de Miranda, L.B.L.; de Almeida, B.O.; Sanches, L.; Machado-Neto, J.A. Two-dimensional and spheroid-based three-dimensional cell culture systems: Implications for Drug Discovery in Cancer. Drugs Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.B.; Reis, R.L.; Pirraco, R.P. Modelling the complex nature of the tumor microenvironment: 3D tumor spheroids as an evolving tool. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, J.; Yuhas, J.M. Liquid-overlay culture of cellular spheroids. In Spheroids in Cancer Research; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 95, 23p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, F.; Dilloo, S.; Chang, X.; Whittaker, A.; D’Amen, E.; Dinelli, G. Basic three-dimensional (3D) intestinal model system with an immune component. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 199, e65484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNI EN ISO 10993-5:2009; Annex C. MTT Cytotoxicity Test. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Truzzi, F.; Whittaker, A.; D’Amen, E.; Tibaldi, C.; Abate, A.; Valerii, M.C.; Spisni, E.; Dinelli, G. Wheat germ spermidine and clove eugenol in combination stimulate autophagy in vitro showing potential in supporting the immune system against viral infections. Molecules 2022, 27, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltari, A.; Truzzi, F.; Quadri, M.; Lotti, R.; Palazzo, E.; Grisendi, G.; Tiso, N.; Marconi, A.; Pincelli, C. CD271 Down-regulation promotes melanoma progression and invasion in three-dimensional models and in zebrafish. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandárová, H.; Hayden, P.; Klausner, M.; Kubilus, J.; Sheasgreen, J. An in vitro skin irritation test (SIT) using the EpiDerm reconstructed human epidermal (RHE) model. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; Wu, X.; Guan, J.L. Wound-healing assay. In Cell Migration; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 294, pp. 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
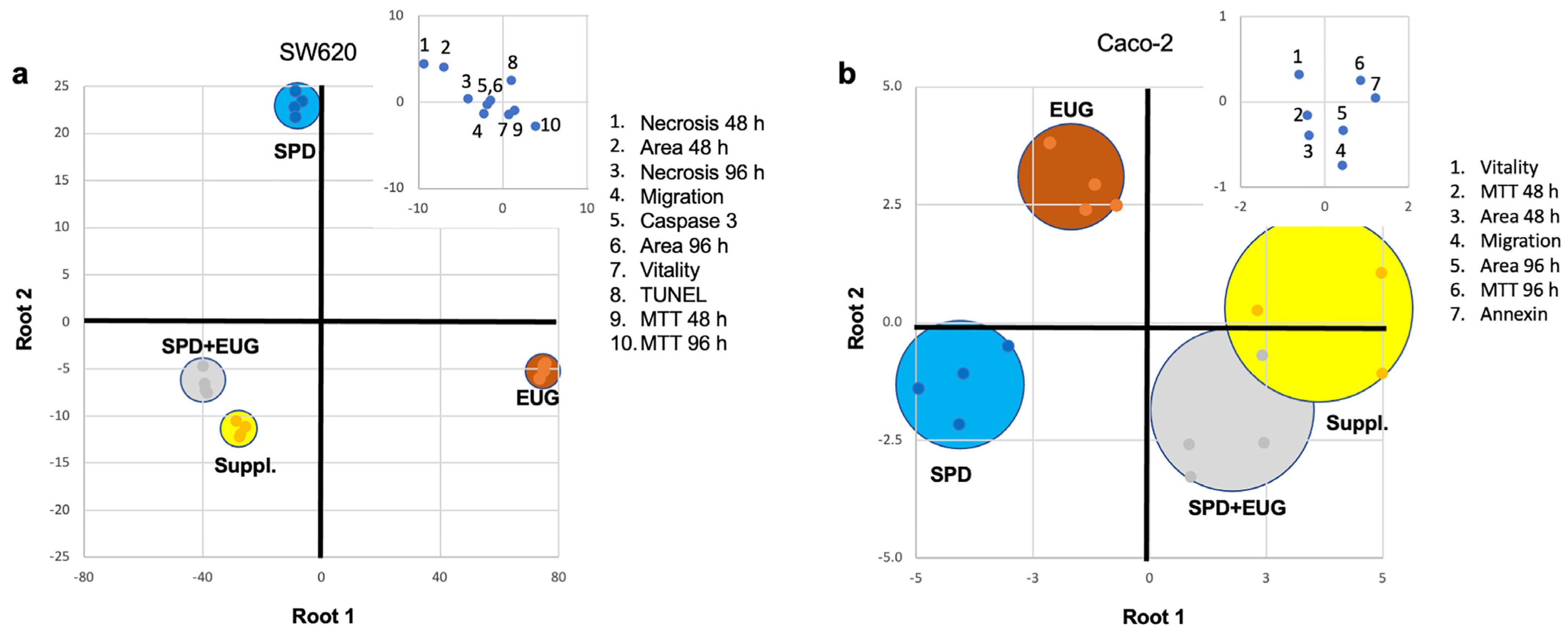
| Variables Analyzed | SPD, EUG and SPD+EUG, p < 0.05 | SPD+EUG ↑ Than Both SPD and EUG, p < 0.05 | Interaction Type p < 0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SW620 | |||
| MTT 48 h | SPDc, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Antagonistic *** |
| MTT 96 h | SPDb, EUGa, SPD+EUGa | Antagonistic * | |
| Area 48 h | SPDa, EUGb, SPD+EUGc | Antagonistic *** | |
| Area 96 h | SPDa, EUGb, SPD+EUGb | Antagonistic *** | |
| Necrosis 48 h | SPDb, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Antagonistic *** |
| Necrosis 96 h | SPDa, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Antagonistic *** | |
| Vitality | NS | Antagonistic ** | |
| TUNEL | SPDc, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Indifferent NS |
| Caspase-3 | SPDb, EUGc, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Synergistic ** |
| Migration % | SPDc, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Synergistic *** |
| Caco-2 | |||
| MTT 96 h | SPDb, EUGa, SPD+EUGa | Antagonistic * | |
| Area 48 h | SPDa, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Synergistic * | |
| Area 96 h | SPDa, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Antagonistic * | |
| Vitality | NS | Indifferent NS | |
| Annexin-V | SPDc, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Antagonistic * |
| TUNEL | SPDb, EUGb, SPD+EUGa | Significant | Indifferent NS |
| Migration % | NS | Indifferent NS | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dilloo, S.; Whittaker, A.; Chang, X.; D’Amen, E.; Spisni, E.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C.; Malaguti, M.; Dinelli, G.; Truzzi, F. Administration of Spermidine and Eugenol Demonstrates Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy on Metastatic SW620 and Primary Caco-2 Colorectal Cancer Spheroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413362
Dilloo S, Whittaker A, Chang X, D’Amen E, Spisni E, Hrelia S, Angeloni C, Malaguti M, Dinelli G, Truzzi F. Administration of Spermidine and Eugenol Demonstrates Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy on Metastatic SW620 and Primary Caco-2 Colorectal Cancer Spheroids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413362
Chicago/Turabian StyleDilloo, Silvia, Anne Whittaker, Xinyue Chang, Eros D’Amen, Enzo Spisni, Silvana Hrelia, Cristina Angeloni, Marco Malaguti, Giovanni Dinelli, and Francesca Truzzi. 2024. "Administration of Spermidine and Eugenol Demonstrates Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy on Metastatic SW620 and Primary Caco-2 Colorectal Cancer Spheroids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413362
APA StyleDilloo, S., Whittaker, A., Chang, X., D’Amen, E., Spisni, E., Hrelia, S., Angeloni, C., Malaguti, M., Dinelli, G., & Truzzi, F. (2024). Administration of Spermidine and Eugenol Demonstrates Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy on Metastatic SW620 and Primary Caco-2 Colorectal Cancer Spheroids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413362











