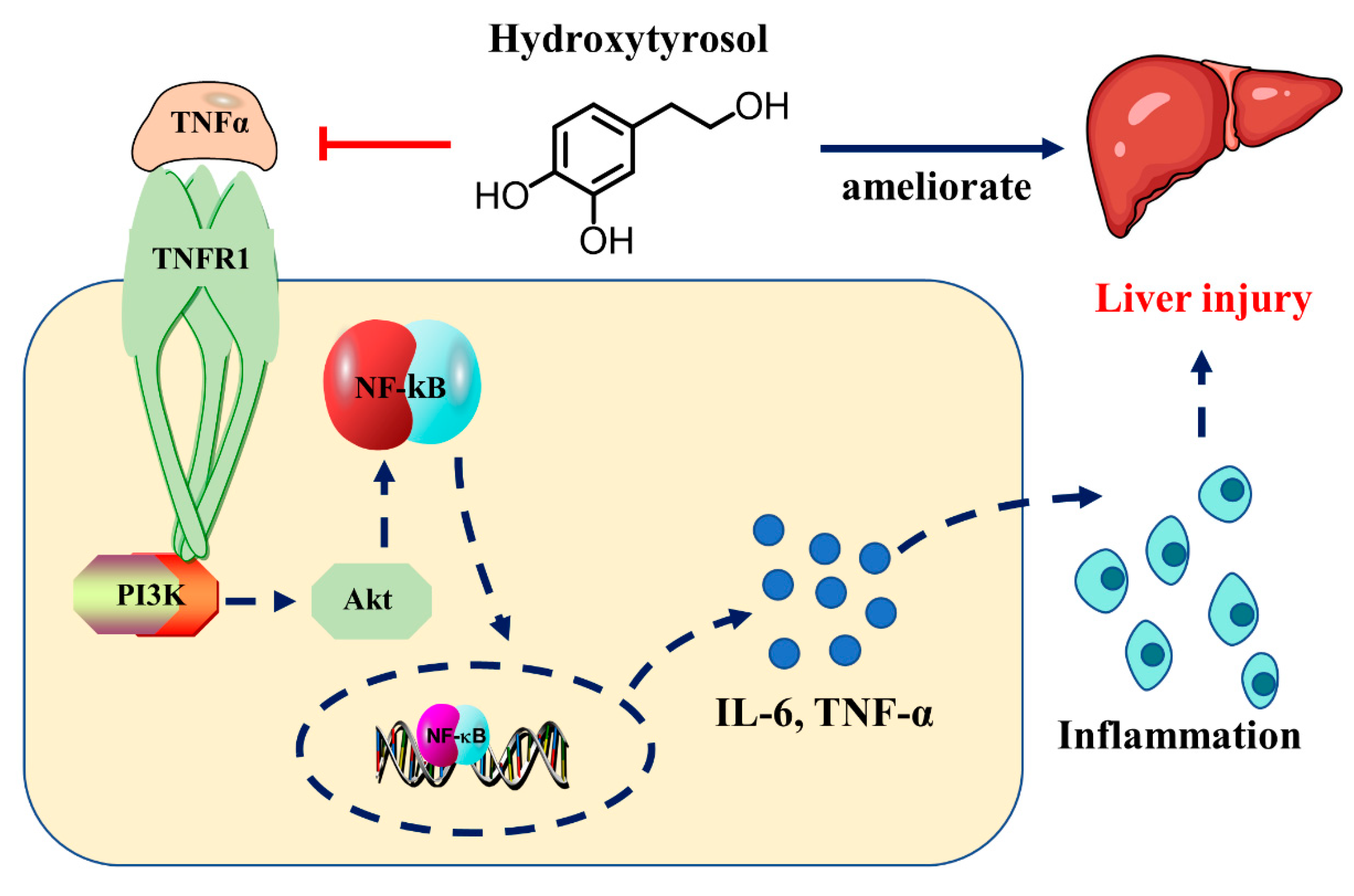
Hydroxytyrosol Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting the TNF-α/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway via Targeting TNF-α Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HT Improved Liver Injury in LPS/D-GalN Induced ALI
2.2. HT Regulates the Expression Level of TNF-α Related Proteins in ALI Mice
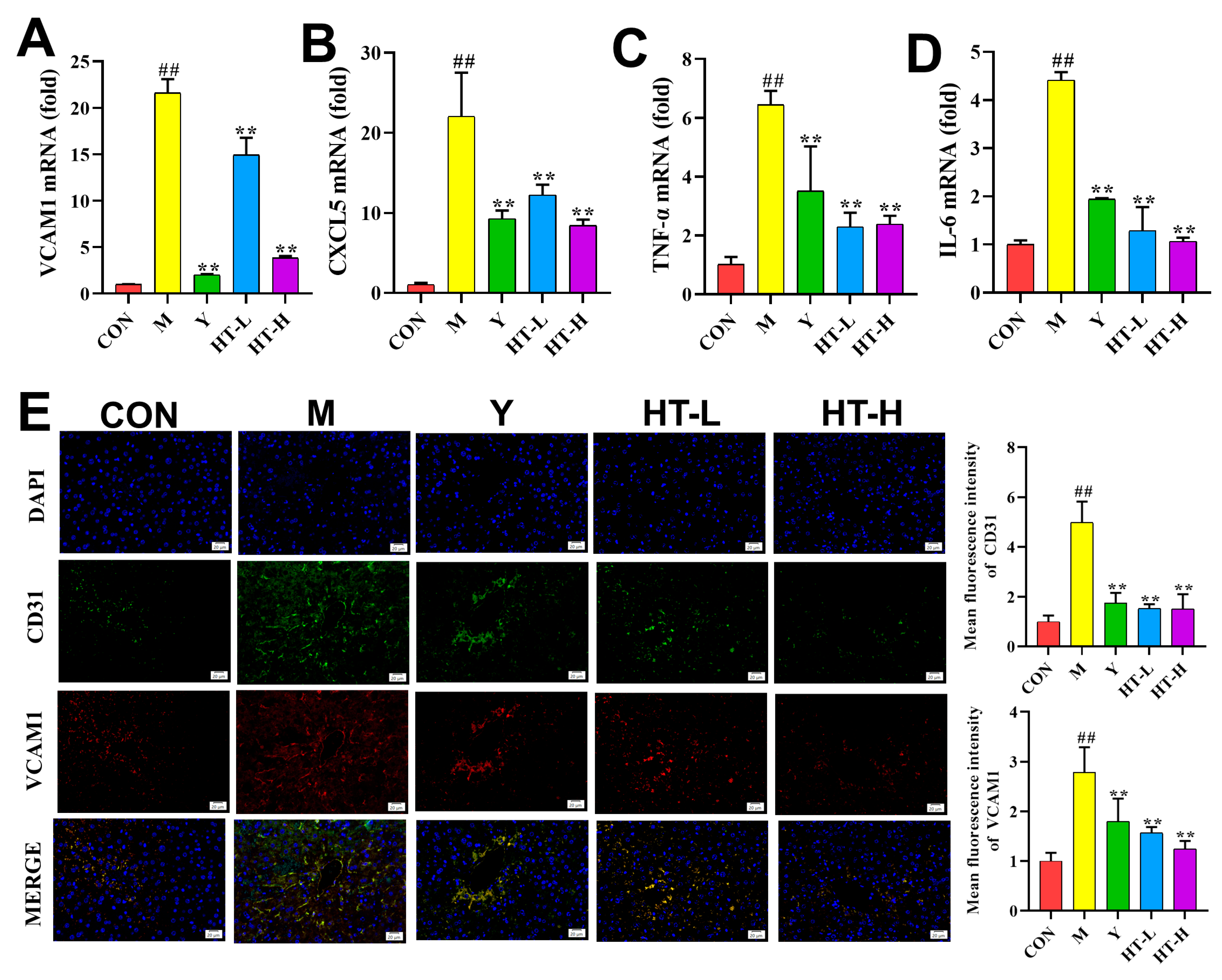
2.3. HT Improves Inflammation-Related Gene Expression Levels
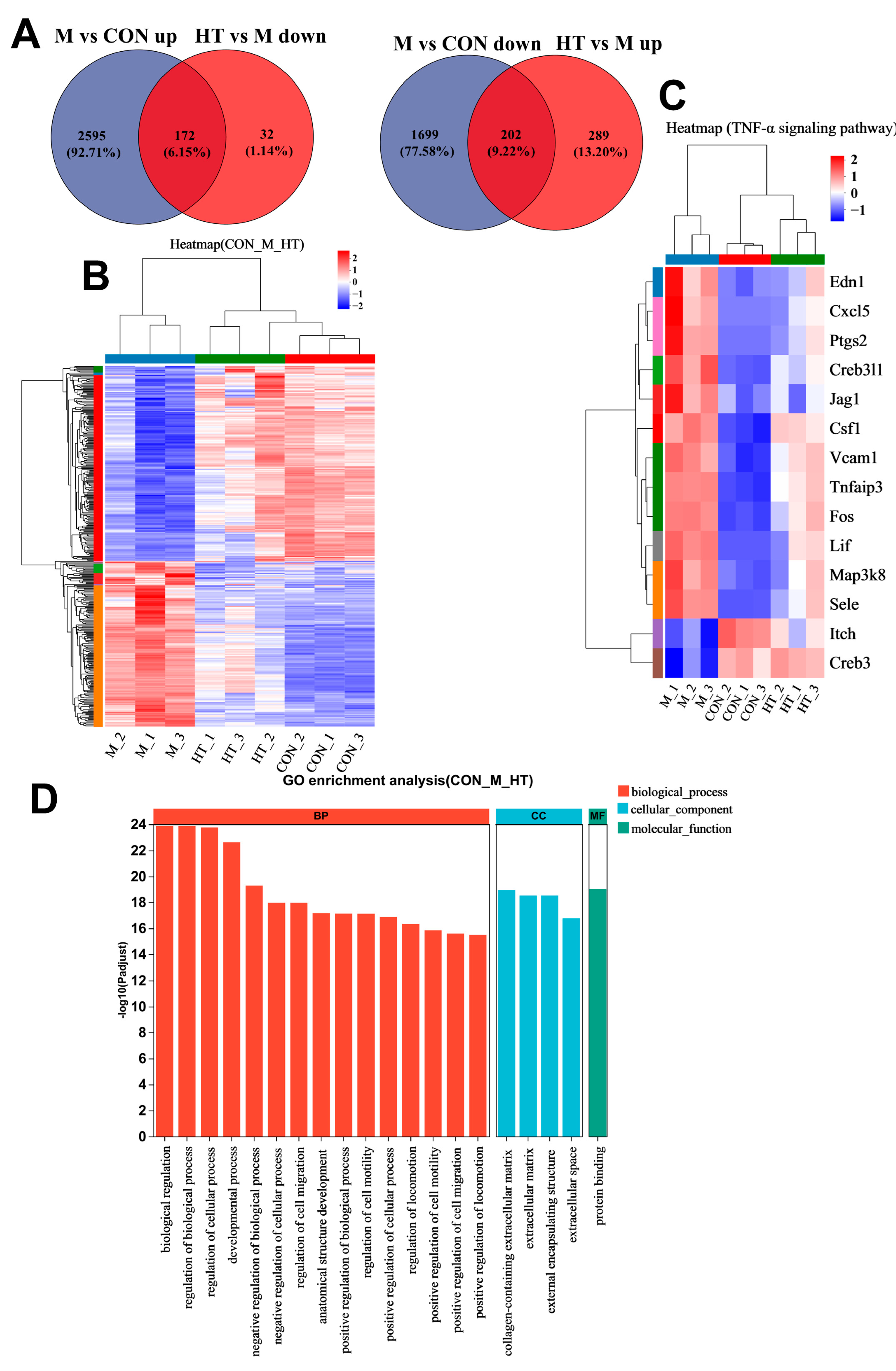
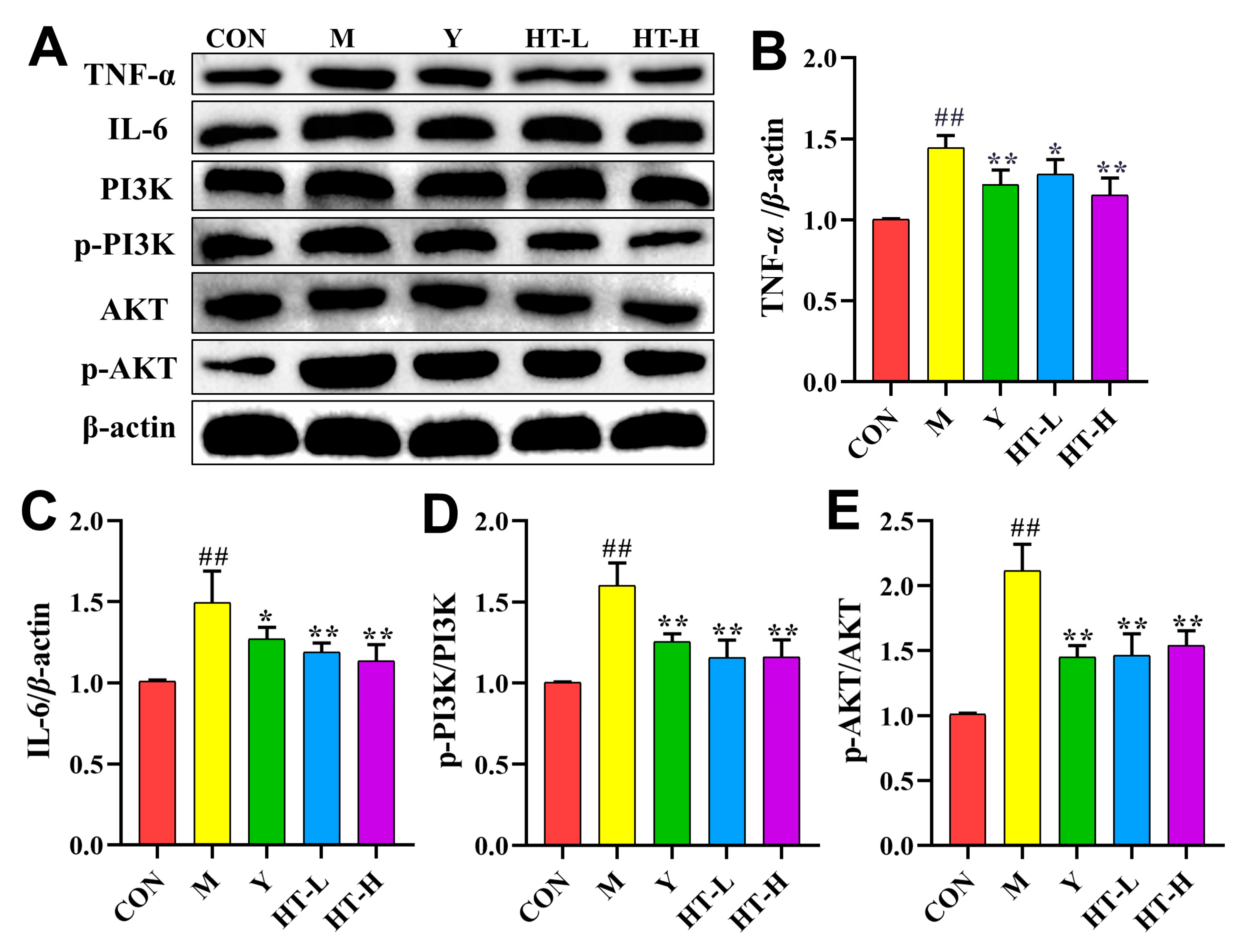
2.4. HT Regulates TNF-α Signaling Pathway in LPS/D-GalN-Induced ALI
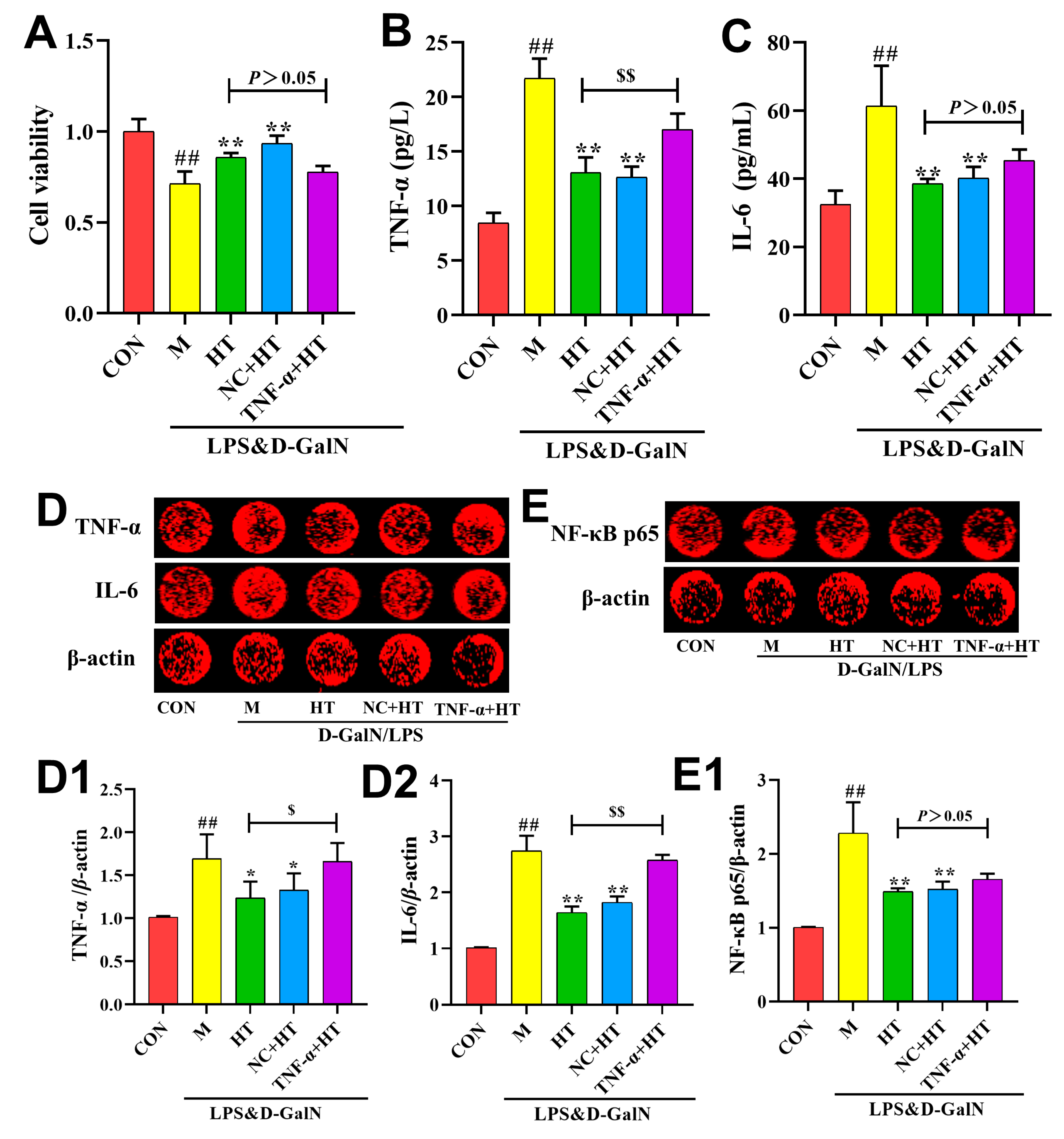
2.5. HT Regulates Inflammatory Responses Through the TNF-α Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Pathology Assay
4.4. Detection of Liver Biochemical Indicators in Serum
4.5. RNA-Seq
4.6. qRT-PCR Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Cell Culture
4.10. In-Cell Western
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Liao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wei, Z.; Dai, Y. Silibinin, a commonly used therapeutic agent for non-alcohol fatty liver disease, functions through upregulating intestinal expression of fibroblast growth factor 15/19. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 3663–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, H.; Ohashi, W.; Tomita, K.; Hattori, K.; Shimada, Y.; Hattori, Y. Prostacyclin mimetics afford protection against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Mao, Z.; Wen, Y.; Liu, S.; Tang, L. Oridonin alleviates d-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Drug Dev. Res. 2020, 82, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Vinken, M.; Jaeschke, H. Experimental models of hepatotoxicity related to acute liver failure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 290, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, B. Substance basis and pharmacological mechanism of heat-clearing herbs in the treatment of ischaemic encephalopathy: A systematic review and network pharmacology. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2308077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azem, N.; Pulido-Moran, M.; Ramirez-Tortosa, C.L.; Quiles, J.L.; Cara, F.E.; Sanchez-Rovira, P.; Granados-Principal, S.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M. Modulation by hydroxytyrosol of oxidative stress and antitumor activities of paclitaxel in breast cancer. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Licata, P.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E. Effects of Hydroxytyrosol against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells: A Natural Therapeutic Tool for Bovine Mastitis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, A.; Nikolaou, P.E.; Symeonidi, L.; Katogiannis, K.; Pechlivani, L.; Nikou, T.; Varela, A.; Chania, C.; Zerikiotis, S.; Efentakis, P.; et al. Cardioprotective potential of oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, oleocanthal and their combination: Unravelling complementary effects on acute myocardial infarction and metabolic syndrome. Redox Biol. 2024, 76, 103311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Ma, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X. Hydroxytyrosol ameliorates stress-induced liver injury through activating autophagy via HDAC1/2 inhibition. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 5103–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ni, T.; Zhang, M.; Fu, S.; Ren, D.; Feng, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Treatment with β-Adrenoceptor Agonist Isoproterenol Reduces Non-parenchymal Cell Responses in LPS/D-GalN-Induced Liver Injury. Inflammation 2024, 47, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Jiang, A.; Du, C.; Xie, G. Pterostilbene Exerts Hepatoprotective Effects through Ameliorating LPS/D-Gal-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Inflammation 2020, 44, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, X.; Duan, Z.; Xu, M.; Kong, M.; Zheng, S.; Bai, L.; Chen, Y. The novel hepatoprotective mechanisms of silibinin-phospholipid complex against d-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 116, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Bo, L.; Wang, C.; Bian, J.; Deng, X. Sophocarpine Attenuates LPS-Induced Liver Injury and Improves Survival of Mice through Suppressing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 5871431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Wen, H.; Zheng, L.; Ni, Y.; Bi, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Z.Z. Discovery of 7-alkoxybenzofurans as PDE4 inhibitors with hepatoprotective activity in D-GalN/LPS-induced hepatic sepsis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 275, 116576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Kuang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, B.; Yin, X.; Gong, X.; Wan, J. Mangiferin Attenuates LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Promoting HO-1 in Kupffer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Márquez, J.M.; Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Varela-López, A.; Puentes, J.G.; Sánchez-González, C.; Sumalla-Cano, S.; Battino, M.; García-Ruiz, R.; Sánchez, S.; et al. Effect of olive leaf phytochemicals on the anti-acetylcholinesterase, anti-cyclooxygenase-2 and ferric reducing antioxidant capacity. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.S.; Fuhro, V.M.; de Souza Nogueira, J.; Romana-Souza, B. Polyphenol hydroxytyrosol present olive oil improves skin wound healing of diabetic mice. Wound Repair Regen. 2024, 32, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Espinosa-Oliva, A.M. Hydroxytyrosol and Parkinson’s disease: Protective actions against alpha-synuclein toxicity. Neural Regener. Res. 2023, 19, 1427–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guan, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, L.; He, Q.; Zhang, T.; et al. Co-catalpol alleviates fluoxetine-induced main toxicity: Involvement of ATF3/FSP1 signaling-mediated inhibition of ferroptosis. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jing, H.; Li, S.; Ren, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, L. Hepatoprotection of enzymatic-extractable mycelia zinc polysaccharides by Pleurotus eryngii var. tuoliensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 157, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Cramb, R.; Davison, S.M.; Dillon, J.F.; Foulerton, M.; Godfrey, E.M.; Hall, R.; Harrower, U.; Hudson, M.; Langford, A.; et al. Guidelines on the management of abnormal liver blood tests. Gut 2017, 67, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrovo, J.P.; Boe, D.M.; Kaahui, S.; Yang, W.L.; Kovacs, E.J. Hepatic inflammation after burn injury is associated with necroptotic cell death signaling. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 89, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myśliwiec, M.; Balcerska, A.; Zorena, K.; Myśliwska, J.; Lipowski, P.; Raczyńska, K. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 79, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Qin, B.; Yu, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Diao, L.; Liu, H. Dingxian pill alleviates hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in epileptic mice through TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling pathway inhibition. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 334, 118579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Lin, K.; Zhang, X.; Yan, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y. PTEN-mediated AKT/β-catenin signaling enhances the proliferation and expansion of Lgr5+ hepatocytes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Han, J.; Lin, K.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Gao, Y. PTEN/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways regulate the proliferation of Lgr5+ cells in liver cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 683, 149117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Tian, R.; Zhang, Y.; Drutskaya, M.S.; Wang, C.; Ge, J.; Fan, Z.; Kong, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Macrophages induce AKT/β-catenin-dependent Lgr5+ stem cell activation and hair follicle regeneration through TNF. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Fan, Z.; Sadia, S.; Zhang, R.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y. AKT and its related molecular feature in aged mice skin. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhari, U.; Ambujakshan, A.; Ahmed, M.; Washimkar, K.; Kachari, J.; Mugale, M.N.; Sahu, B.D. Nuciferine inhibits TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK signaling axis and alleviates adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 982, 176940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.R.; Yin, N.N.; Bu, F.T.; Yu, H.X.; Du, X.S.; Li, J.; Huang, C. PTP1B promotes macrophage activation by regulating the NF-κB pathway in alcoholic liver injury. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 319, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Huang, Y.; Cai, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J. Gut Microbiota Disorders Promote Inflammation and Aggravate Spinal Cord Injury Through the TLR4/MyD88 Signaling Pathway. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yang, F.; Hu, Y.; Fan, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, S. Forsythoside A regulates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and lung fibroblast proliferation via the PTPRB signaling. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 155715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Fan, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Feng, W. Evening primrose and its compounds of 1-Oxohederagenin and remangilone C ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating β-catenin signaling. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| VCAM-1 | GGAAAAGCTCTTGTTTGCCG | ATTGTCACAGCACCACCCTCTT |
| CXCL5 | AGTGCCCTACGGTGGAAGTCATA | AGTGCATTCCGCTTAGCTTTCTT |
| NLRP3 | TAAGAACTGTCATAGGGTCAAAACG | GTCTGGAAGAACAGGCAACATG |
| TNF-α | CCCTCACACTCACAAACCACC | CTTTGAGATCCATGCCGTTG |
| GAPDH | CCTCGTCCCGTAGACAAAATG | TGAGGTCAATGAAGGGGTCGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.; Bu, C.; Chen, S. Hydroxytyrosol Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting the TNF-α/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway via Targeting TNF-α Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312844
Gao Z, Dai H, Zhang Q, Yang F, Bu C, Chen S. Hydroxytyrosol Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting the TNF-α/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway via Targeting TNF-α Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312844
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhining, Haoyang Dai, Qinqin Zhang, Fan Yang, Chenxi Bu, and Suiqing Chen. 2024. "Hydroxytyrosol Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting the TNF-α/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway via Targeting TNF-α Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312844
APA StyleGao, Z., Dai, H., Zhang, Q., Yang, F., Bu, C., & Chen, S. (2024). Hydroxytyrosol Alleviates Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting the TNF-α/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway via Targeting TNF-α Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312844





