Functional Characterization of Plant Peptide-Containing Sulfated Tyrosine (PSY) Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the TaPSY Gene Family
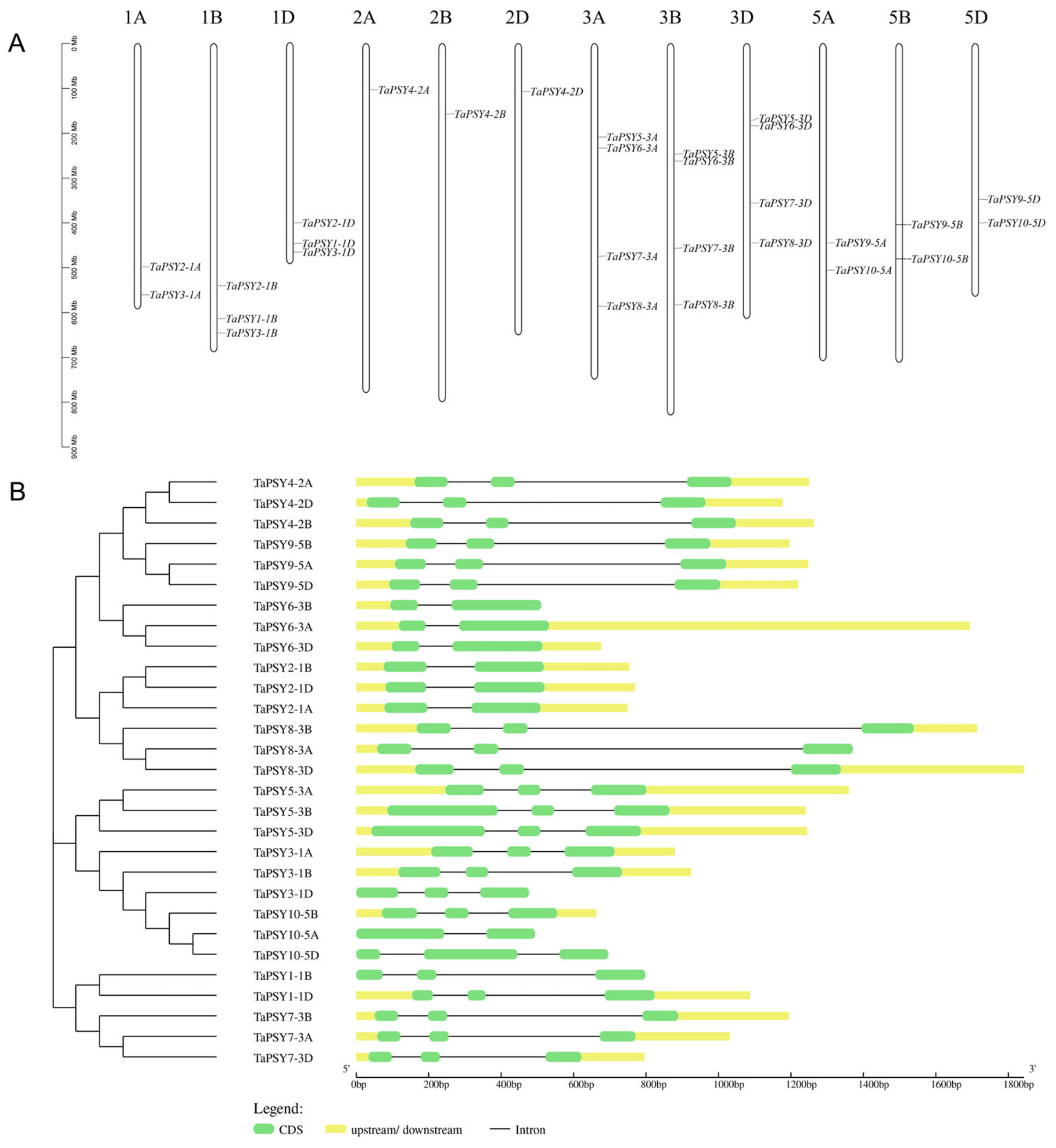
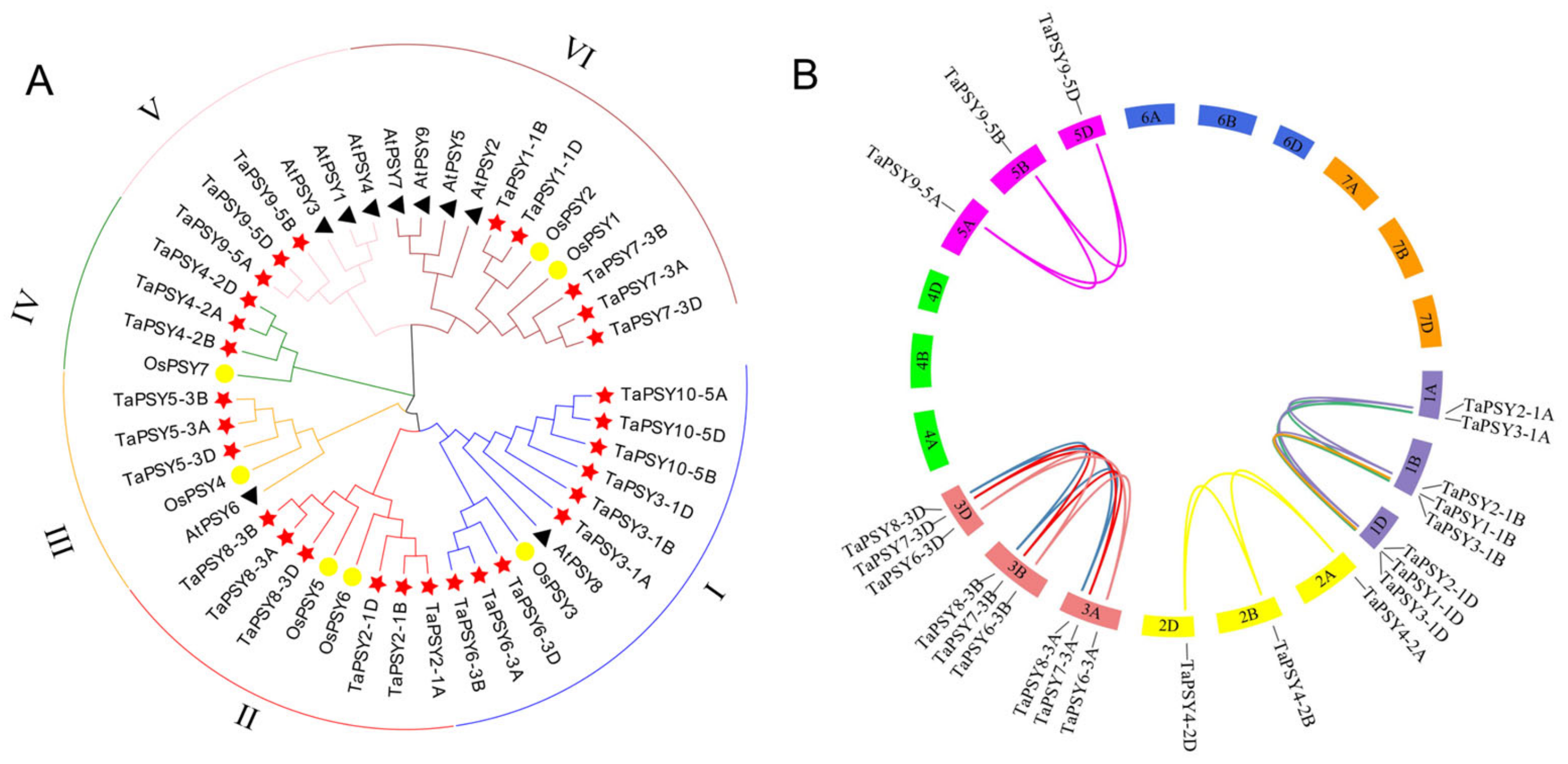
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Duplication of TaPSYs
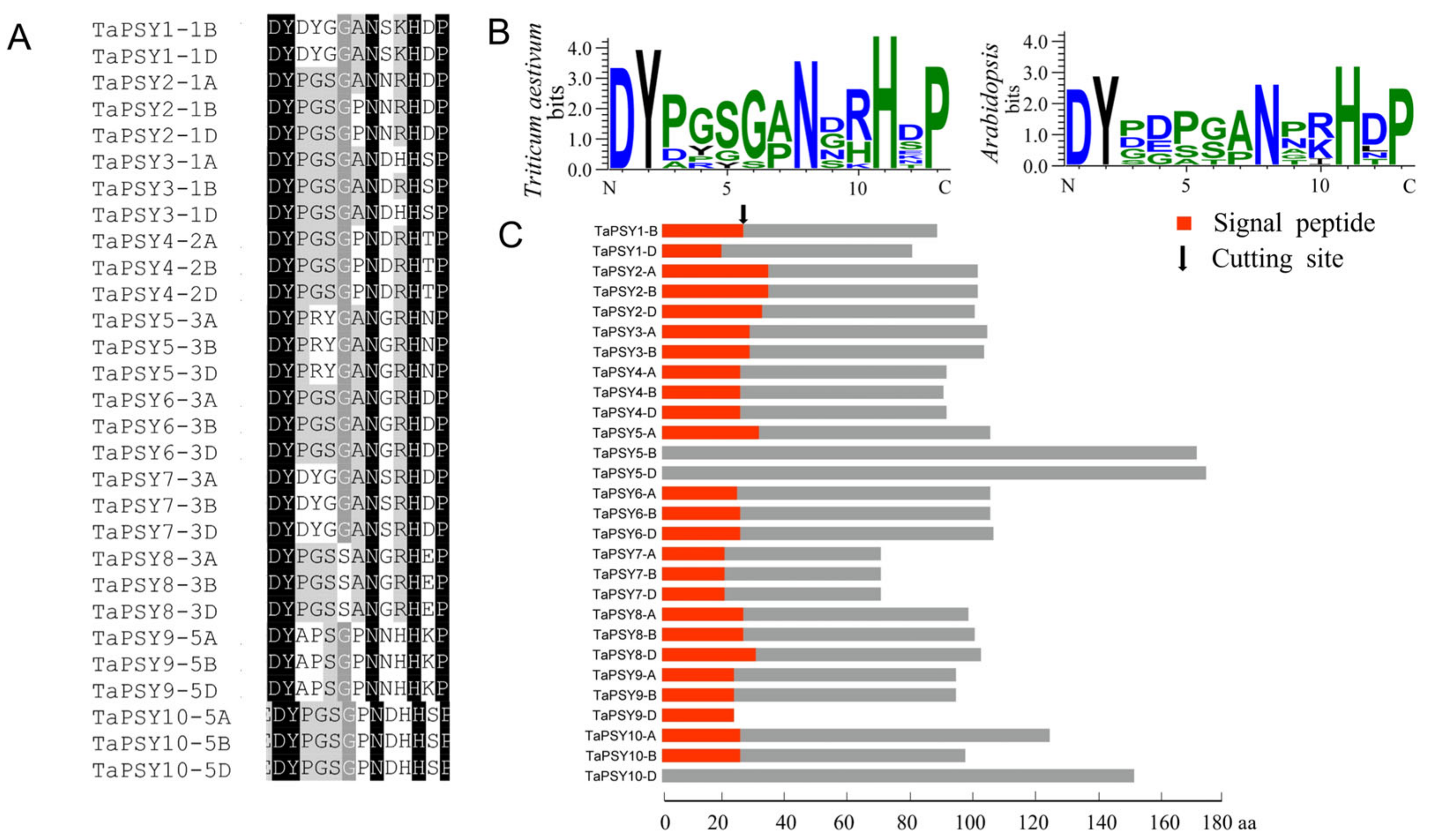
2.3. Multiple Alignment and Conserved Domain Analysis of TaPSYs
2.4. Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements in TaPSY Promoters
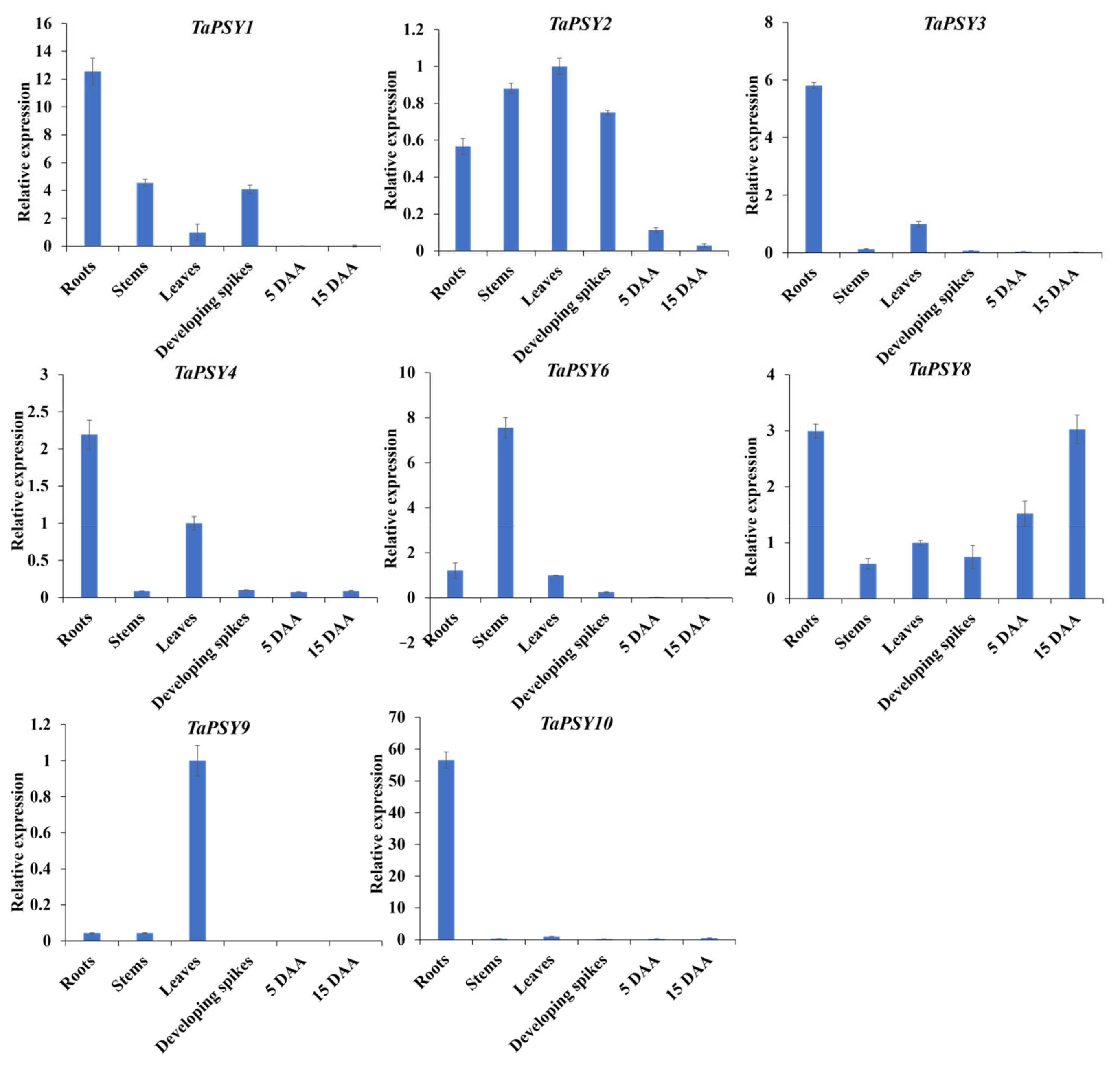
2.5. Expression Patterns of TaPSY Genes in Different Tissues
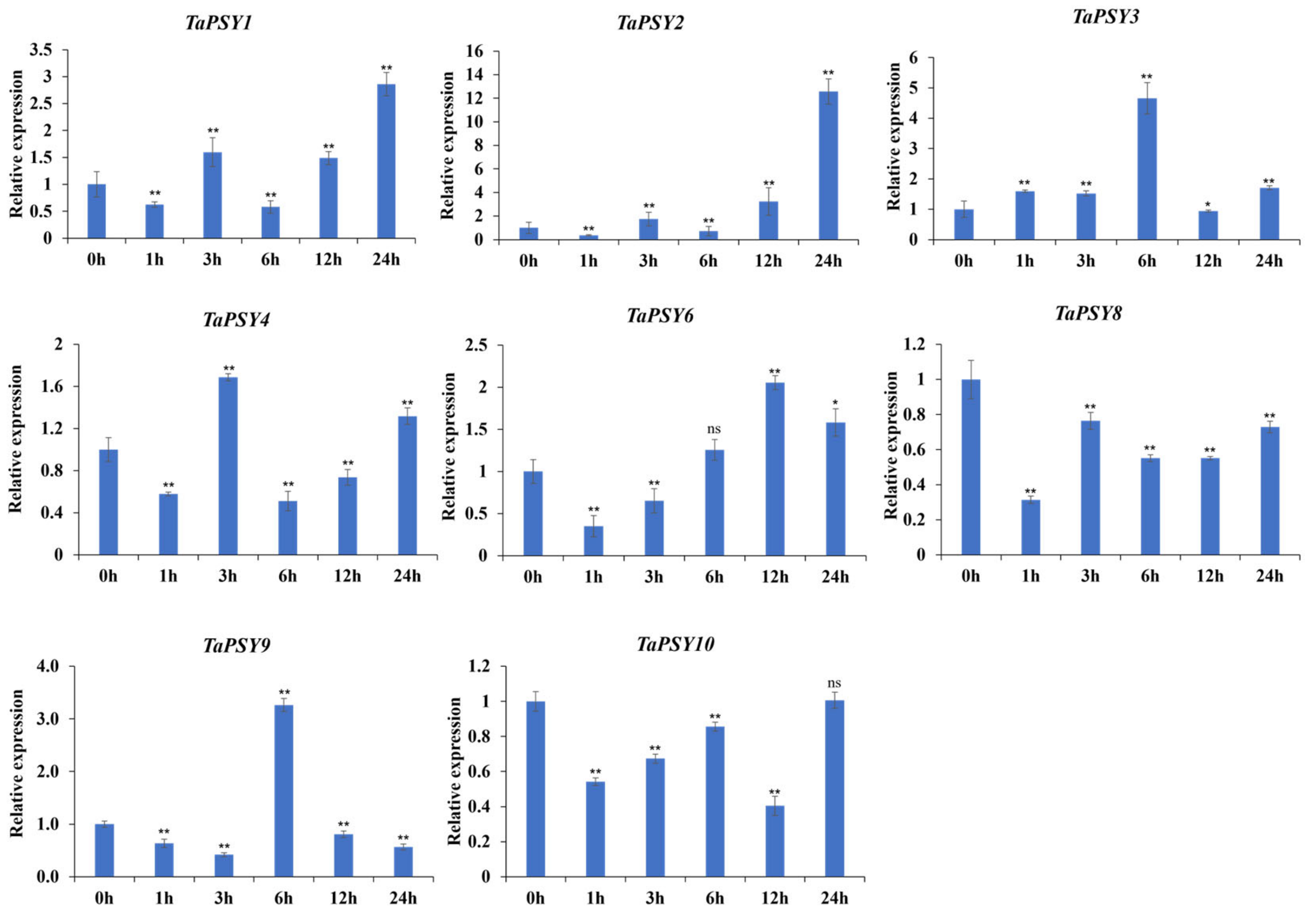
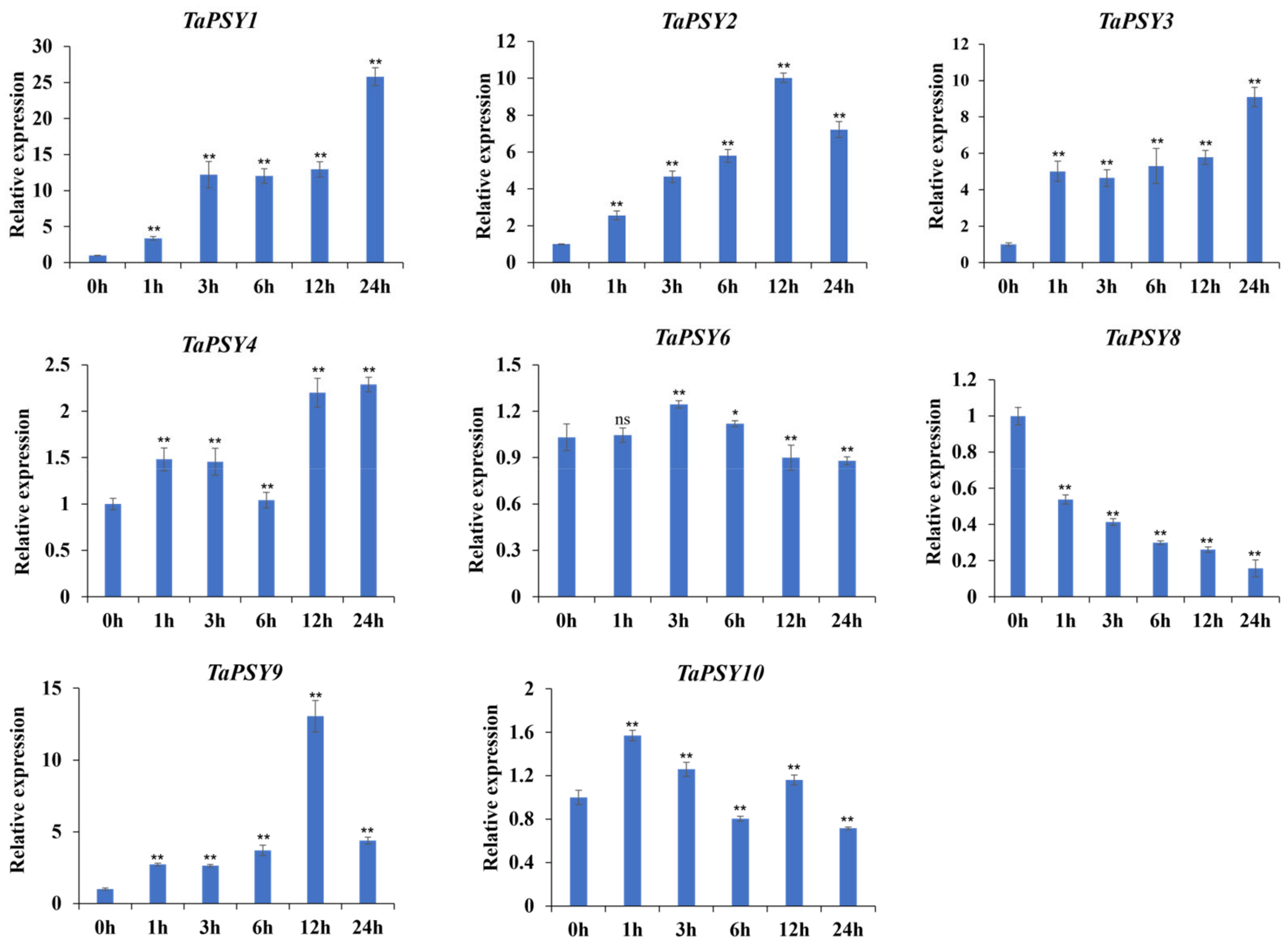
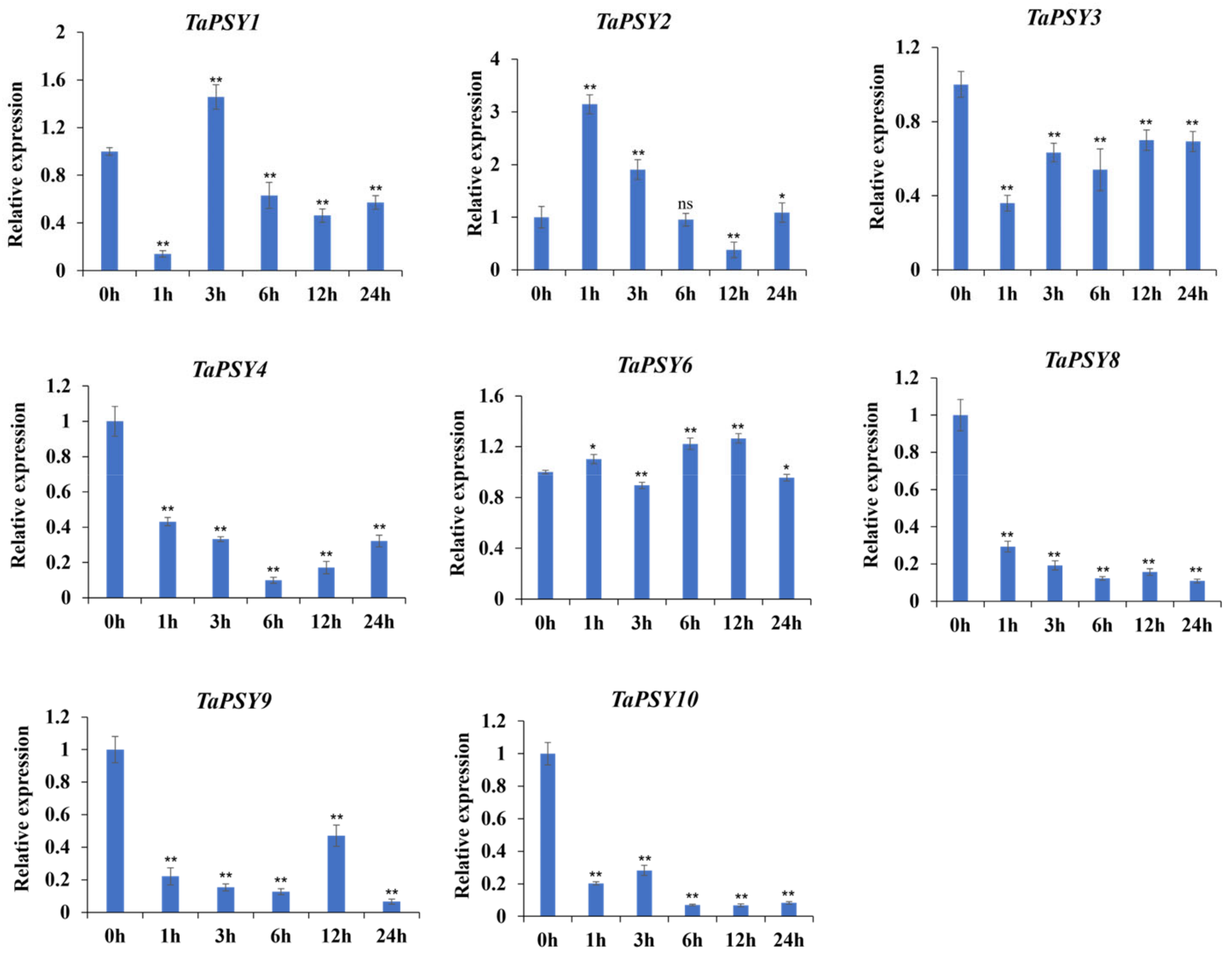
2.6. TaPSYs Respond to Various Environmental and Hormonal Stimuli
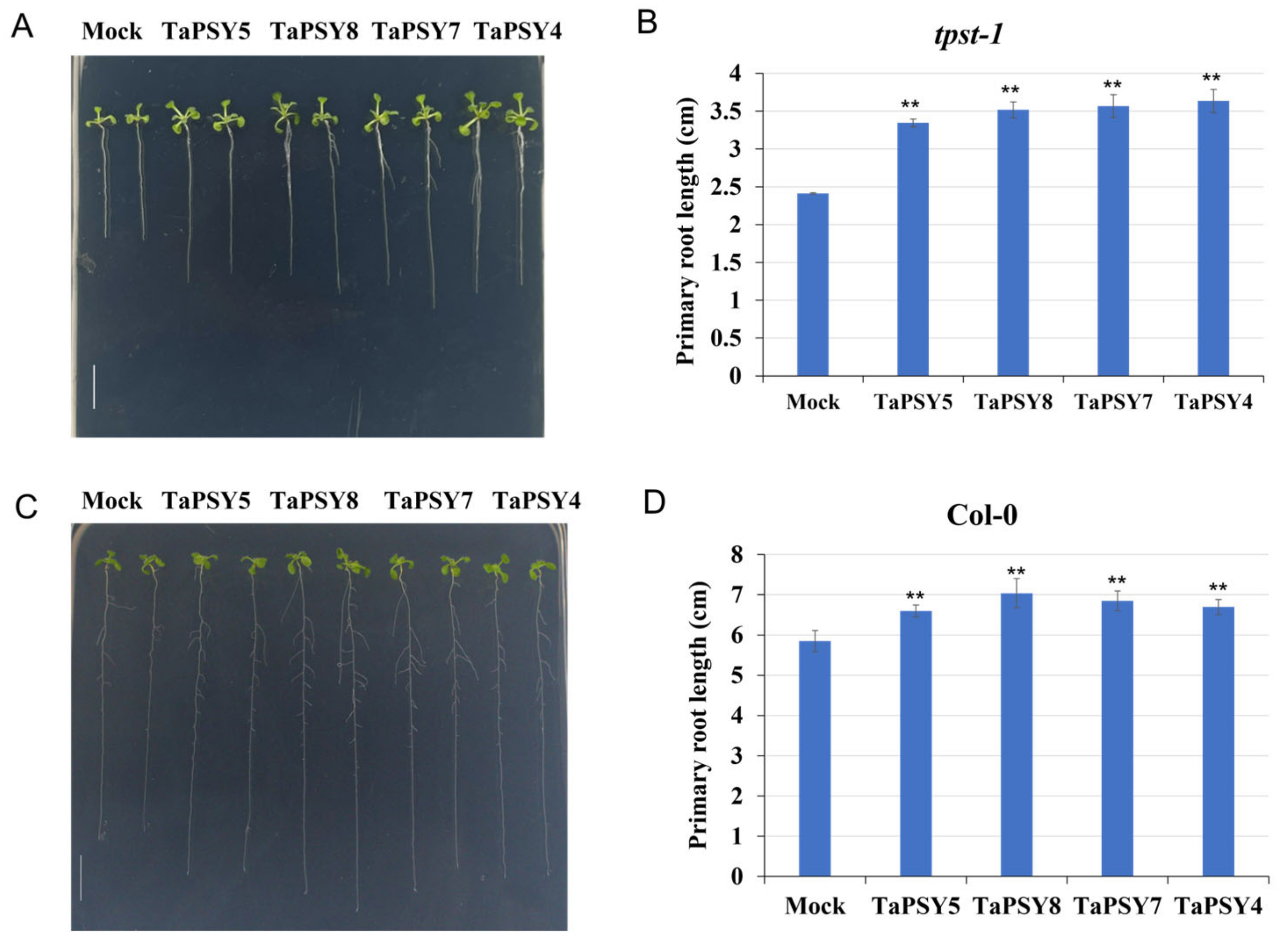
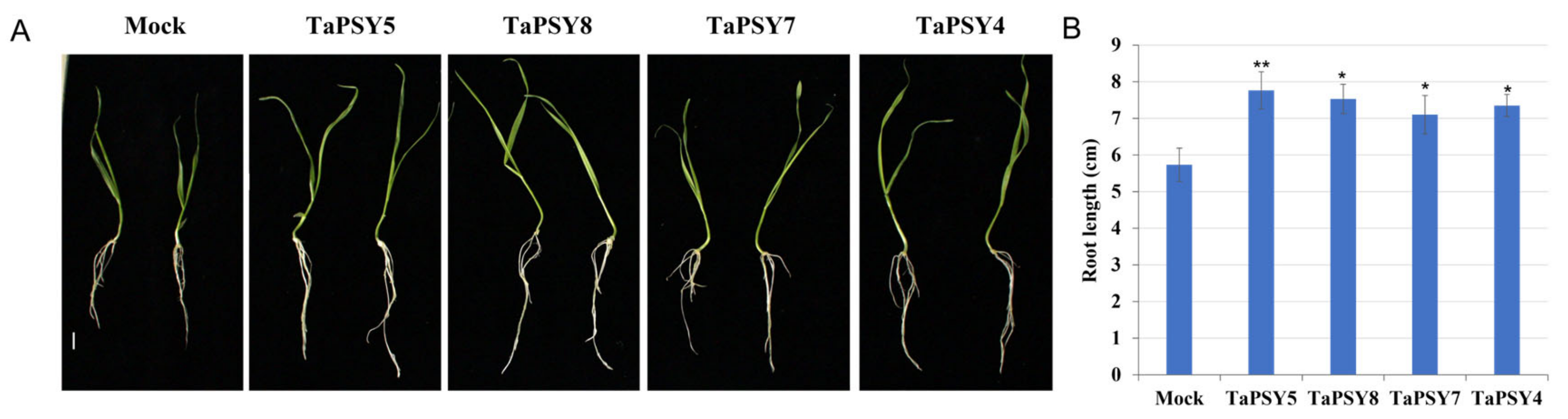
2.7. TaPSY Peptides Promote Primary Root Growth in Wheat and Arabidopsis
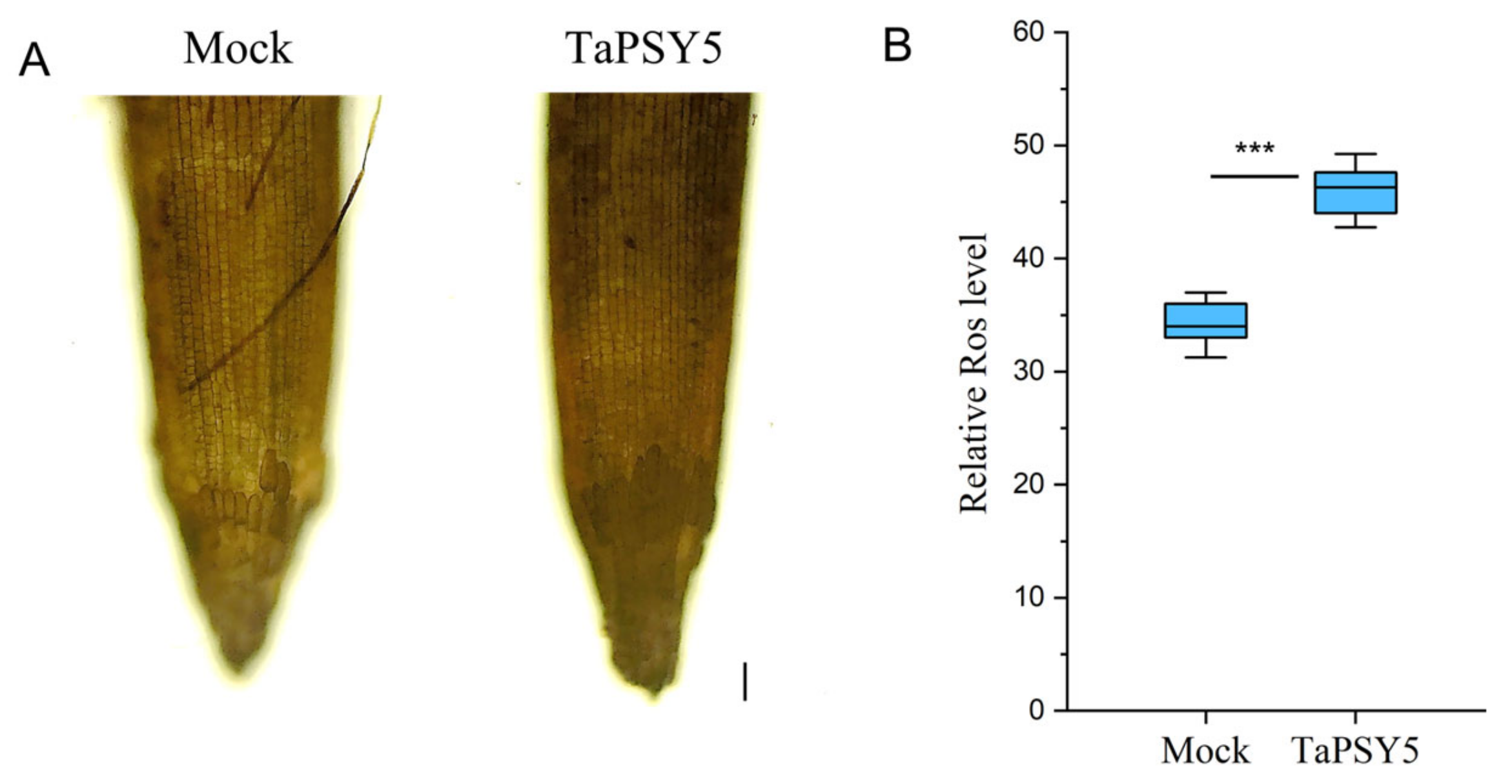
2.8. TaPSY5-Meditated Root Growth in Wheat Is Associated with Hydrogen Peroxide Accumulation
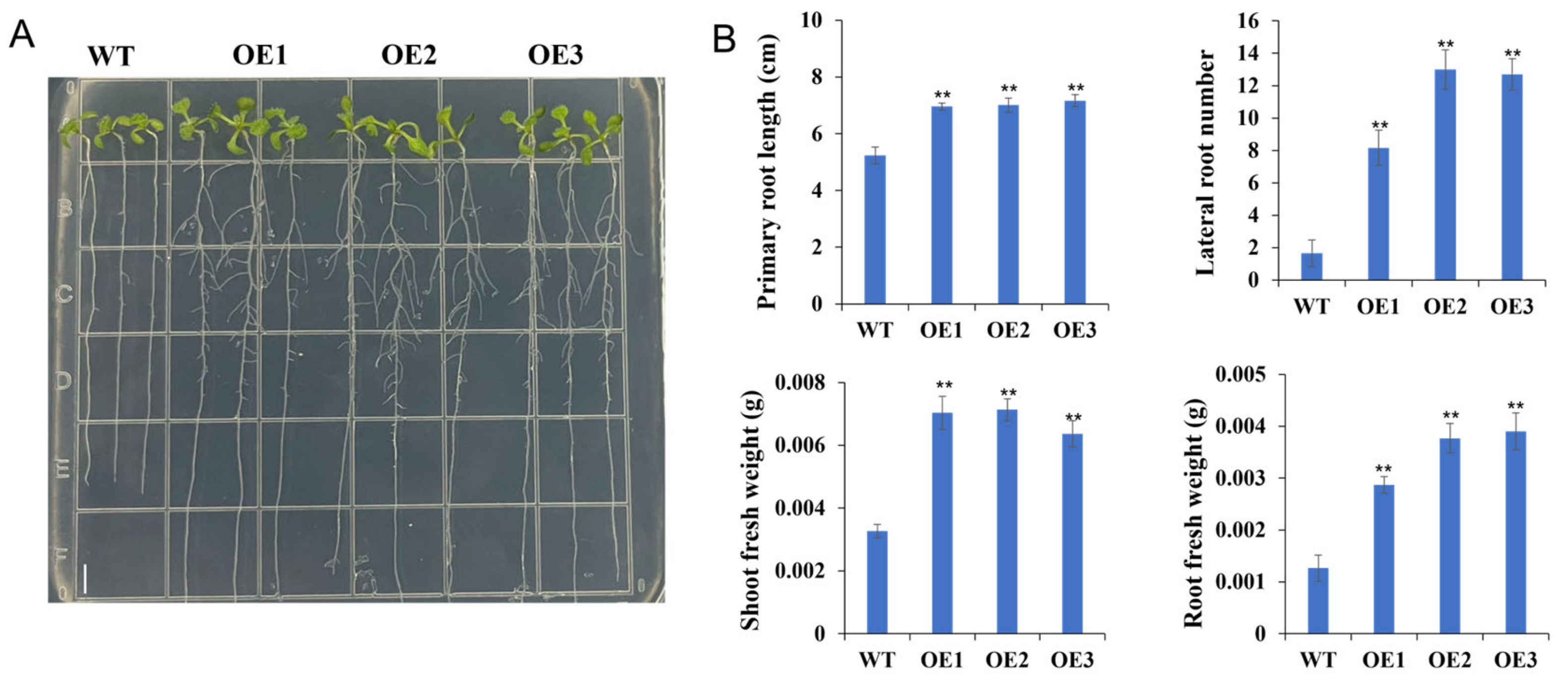
2.9. Overexpression of TaPSY10 Promotes Root Growth in Arabidopsis Thaliana
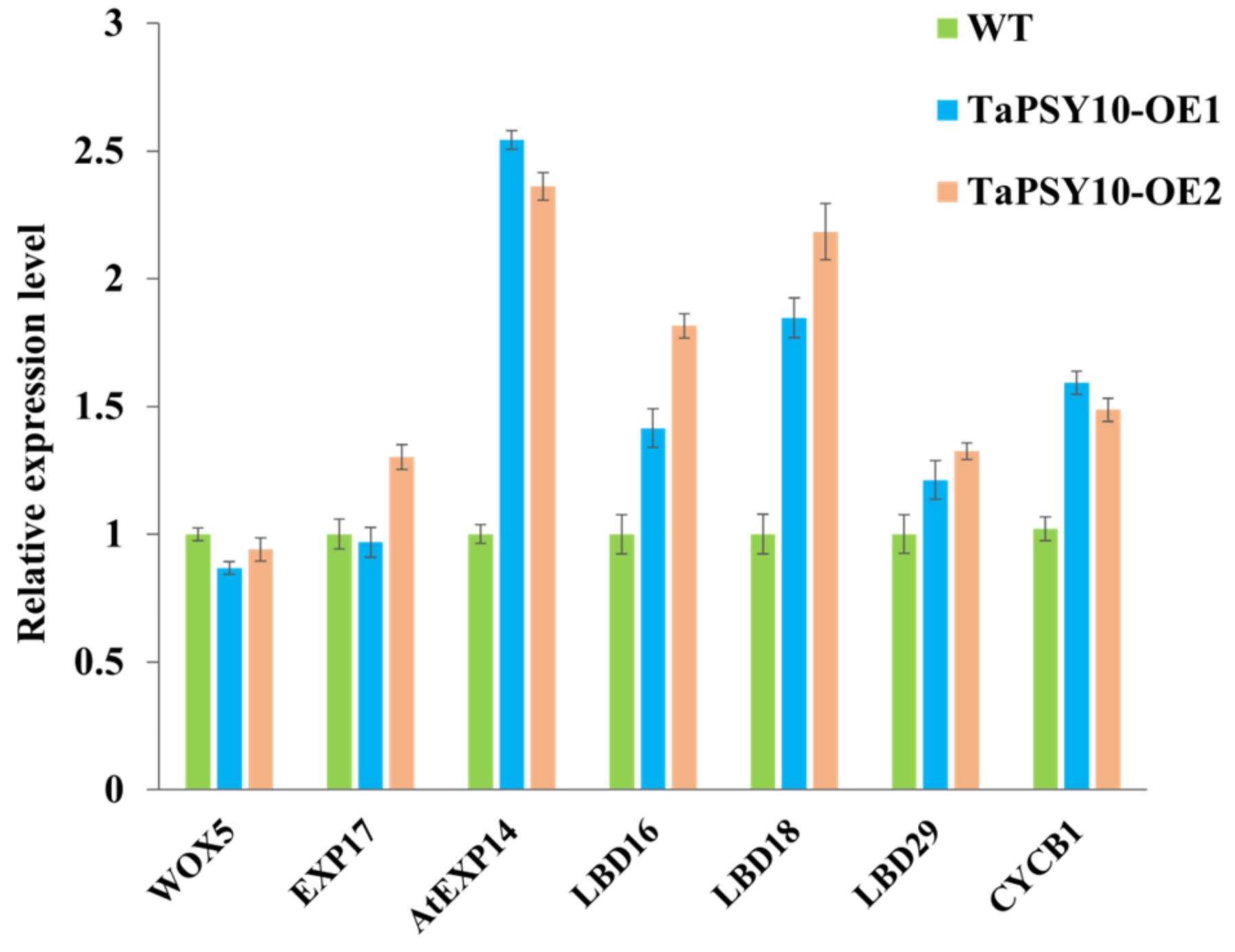
2.10. Overexpression of TaPSY10 Positively Regulates Genes Related to Root Morphogenesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of the TaPSY Gene Family
4.2. Chromosome Location, Sequence Alignment, and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Gene Structure and Cis-Element Analysis
4.4. Analysis of Wheat PSY Gene Replication
4.5. Expression Analysis of TaPSY Genes Using RNA-Seq Datasets
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis of TaPSY Genes
4.7. Synthesis of the TaPSY Peptides
4.8. Plant Material, Growth Conditions, and Root Length Quantification
4.9. H2O2 Detection
4.10. Phonotypic Analysis of TaPSY10 Overexpression Lines in Arabidopsis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSY | Plant peptide containing sulfated tyrosine |
| PSY1R | PSY RECEPTOR1 |
| PSK | Phytosulfokine |
| TPST | Tyrosine protein sulfotransferase |
| RGF1 | Root growth meristem factors |
| PTMs | Post-translational modifications |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| EXP | EXPANSIN |
| CYCB1 | Cell cycle |
| LBD | Lateral organ boundaries domain |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Xoo | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
References
- Olsson, V.; Joos, L.; Zhu, S.; Gevaert, K.; Butenko, M.A.; De Smet, I. Look closely, the beautiful may be small: Precursor-derived peptides in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 153–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubayashi, Y. Posttranslationally modified small-peptide signals in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 385–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Lei, C.; Zheng, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, S.; Li, X.; Xia, X.; Cai, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. A plant phytosulfokine peptide initiates auxin-dependent immunity through cytosolic Ca2+ signaling in tomato. Plant Cell. 2018, 30, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, H.; Mori, A.; Yasue, N.; Sumida, K.; Matsubayashi, Y. Identification of three LRR-RKs involved in perception of root meristem growth factor in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3897–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Liu, J.-X.; Guo, H.; Yin, Y.; Howell, S.H. Regulation and processing of a plant peptide hormone, AtRALF23, in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 59, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, C.; Sauter, M. Sulfated plant peptide hormones. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4267–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Han, X.W.; Benfey, P.N. RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signalling. Nature 2020, 577, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavormina, P.; De Coninck, B.; Nikonorova, N.; De Smet, I.; Cammue, B.P. The plant peptidome: An expanding repertoire of structural features and biological functions. Plant Cell. 2015, 27, 2095–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubayashi, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Kihara, H.; Niwa, M.; Sakagami, Y. Disruption and overexpression of Arabidopsis phytosulfokine receptor gene affects cellular longevity and potential for growth. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhrwohldt, N.; Dahlke, R.I.; Kutschmar, A.; Peng, X.; Sun, M.X.; Sauter, M. Phytosulfokine peptide signaling controls pollen tube growth and funicular pollen tube guidance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Lv, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Foyer, C.H.; Shi, K. Phytosulfokine peptide optimizes plant growth and defense via glutamine synthetase GS2 phosphorylation in tomato. EMBO J. 2022, 42, e111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; Luo, L. Phytosulfokine-α promotes root growth by repressing expression of Pectin Methylesterase Inhibitor (PMEI) genes in Medicago truncatula. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 89, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, Y.; Tsubouchi, T.; Shinohara, H.; Ogawa, M.; Matsubayashi, Y. Tyrosine-sulfated glycopeptide involved in cellular proliferation and expansion in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18333–18338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, R.; Amano, Y.; Ogawa-Ohnishi, M.; Matsubayashi, Y. Identification of tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15067–15072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tost, A.S.; Kristensen, A.; Olsen, L.I.; Axelsen, K.B.; Fuglsang, A.T. The PSY peptide family-expression, modification and physiological implications. Genes 2021, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, A.T.; Kristensen, A.; Cuin, T.A.; Schulze, W.X.; Persson, J.; Thuesen, K.H.; Ytting, C.K.; Oehlenschlaeger, C.B.; Mahmood, K.; Sondergaard, T.E.; et al. Receptor kinase-mediated control of primary active proton pumping at the plasma membrane. Plant J. 2014, 80, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Joe, A.; Zhang, W.; Feng, W.; Stewart, V.; Schwessinger, B.; Dinneny, J.R.; Ronald, P.C. A microbially derived tyrosine-sulfated peptide mimics a plant peptide hormone. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Schwessinger, B.; Joe, A.; Thomas, N.; Liu, F.; Albert, M.; Robinson, M.R.; Chan, L.J.G.; Luu, D.D.; Chen, H.; et al. The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgi, J.; Fuchs, C.; Iwasaki, M.; Kim, W.; Piskurewicz, U.; Gully, K.; Utz-Pugin, A.; Mene-Saffrane, L.; Waridel, P.; Nawrath, C.; et al. The Arabidopsis mature endosperm promotes seedling cuticle formation via release of sulfated peptides. Dev. Cell. 2021, 56, 3066–3081.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa-Ohnishi, M.; Yamashita, T.; Kakita, M.; Nakayama, T.; Ohkubo, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Nomura, T.; Noda, S.; Shinohara, H.; et al. Peptide ligand-mediated trade-off between plant growth and stress response. Science 2022, 378, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liang, S.; Song, W.; Lin, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Han, Z.; Chai, J. Functional and structural characterization of a receptor-like kinase involved in germination and cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, B.W.; Kim, M.J.; Pandey, S.K.; Oh, E.; Seo, P.J.; Kim, J. Recent advances in peptide signaling during Arabidopsis root development. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Kui, H.; Li, J. Receptor-like kinases in root development: Current progress and future directions. Mol. Plant. 2021, 14, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.Y.; Benfey, P.N. Small but mighty: Functional peptides encoded by small ORFs in plants. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1700038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Li, Q.; Yin, H.; Qi, K.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Paterson, A.H. Gene duplication and evolution in recurring polyploidization-diploidization cycles in plants. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.C.; Purugganan, M.D. The evolutionary dynamics of plant duplicate genes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, H.; Ogawa, M.; Sakagami, Y.; Matsubayashi, Y. Identification of ligand binding site of phytosulfokine by on-column photoaffinity labeling. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 282, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, S.; Seybold, H.; Rodriguez, P.; Stahl, M.; Davies, K.A.; Dayaratne, S.; Morillo, S.A.; Wierzba, M.; Favery, B.; Keller, H.; et al. The tyrosine-sulfated peptide receptors PSKR1 and PSY1R modify the immunity of Arabidopsis to biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens in an antagonistic manner. Plant J. 2013, 73, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, M. Phytosulfokine peptide signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5161–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubayashi, Y.; Sakagami, Y. Phytosulfokine, sulfated peptides that induce the proliferation of single mesophyll cells of Asparagus officinalis L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 7623–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.T.C.; Kim, J. PSY-PSYR peptide-receptor pairs control the trade-off between plant growth and stress response. Plant Signal. Behav. 2023, 18, 2260638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yimer, H.Z.; Luu, D.D.; Coomer Blundell, A.; Ercoli, M.F.; Vieira, P.; Williamson, V.M.; Ronald, P.C.; Siddique, S. Root-knot nematodes produce functional mimics of tyrosine-sulfated plant peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2304612120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Yan, K.; Yang, G.; Wu, C.; Zheng, C.; Huang, J. Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase suppresses ABA signaling via sulfation of SnRK2.2/2.3/2.6. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2023, 65, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Lamattina, L.; Spoel, S.H.; Loake, G.J. Nitric oxide function in plant biology: A redox cue in deconvolution. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, N.; Ji, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Lyu, M.; You, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A GmSIN1/GmNCED3s/GmRbohBs feed-forward loop acts as a signal amplifier that regulates root growth in soybean exposed to salt stress. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2107–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Qin, G.; Liu, Y.; Kou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhu, J.-K.; et al. SYNTAXIN OF PLANTS81 regulates root meristem activity and stem cell niche maintenance via ROS signaling. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 1365–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.; Moriconi, J.I.; Zhao, X.; Hegarty, J.; Fahima, T.; Santa-Maria, G.E.; Dubcovsky, J. A wheat/rye polymorphism affects seminal root length and yield across different irrigation regimes. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4027–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Zuo, T.T.; Qiu, Z.W.; Zhuang, K.Q.; Hu, S.P.; Han, H.B. Genome-wide identification reveals the function of CEP peptide in cucumber root development. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 169, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tao, W.; Sun, R.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Kong, X.; Tian, H.; Ding, Z. PRH1 mediates ARF7-LBD dependent auxin signaling to regulate lateral root development in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berckmans, B.; Vassileva, V.; Schmid, S.P.C.; Maes, S.; Parizot, B.; Naramoto, S.; Magyar, Z.; Kamei, C.L.A.; Koncz, C.; Boegre, L.; et al. Auxin-dependent cell cycle reactivation through transcriptional regulation of Arabidopsis E2Fa by lateral organ boundary proteins. Plant Cell. 2011, 23, 3671–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.P.; Li, J.P.; Paterson, A.H. MCScanX-transposed: Detecting transposed gene duplications based on multiple colinearity scans. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.L.; Feng, J.T.; Chen, H.; He, Y.H.; et al. TBtools-II: A "one for all, all for one"bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant. 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.P.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Yu, J. Nonsynonymous substitution rate (Ka) is a relatively consistent parameter for defining fast-evolving and slow-evolving protein-coding genes. Biol. Direct. 2011, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xin, M.; Qin, J.; Peng, H.; Ni, Z.; Yao, Y.; Sun, Q. Temporal transcriptome profiling reveals expression partitioning of homeologous genes contributing to heat and drought acclimation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshitha, R.; Arunraj, D.R. Real-time quantitative PCR: A tool for absolute and relative quantification. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2021, 49, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, C.; Stuhrwohldt, N.; Sauter, M. Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-dependent and -independent regulation of root development and signaling by PSK LRR receptor kinases in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5508–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Gao, W.; Guo, L.; Chen, M.; Ma, J.; Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. Functional Characterization of Plant Peptide-Containing Sulfated Tyrosine (PSY) Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312663
Zhang P, Gao W, Guo L, Chen M, Ma J, Tian T, Wang Y, Zhang X, Wei Y, Chen T, et al. Functional Characterization of Plant Peptide-Containing Sulfated Tyrosine (PSY) Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312663
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peipei, Weidong Gao, Lijian Guo, Ming Chen, Jingfu Ma, Tian Tian, Yanjie Wang, Xiwei Zhang, Yongtong Wei, Tao Chen, and et al. 2024. "Functional Characterization of Plant Peptide-Containing Sulfated Tyrosine (PSY) Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312663
APA StyleZhang, P., Gao, W., Guo, L., Chen, M., Ma, J., Tian, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Wei, Y., Chen, T., & Yang, D. (2024). Functional Characterization of Plant Peptide-Containing Sulfated Tyrosine (PSY) Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312663



