The Preventive Effect of Ulinastatin on Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Rats with Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction After General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane
Abstract
1. Introduction
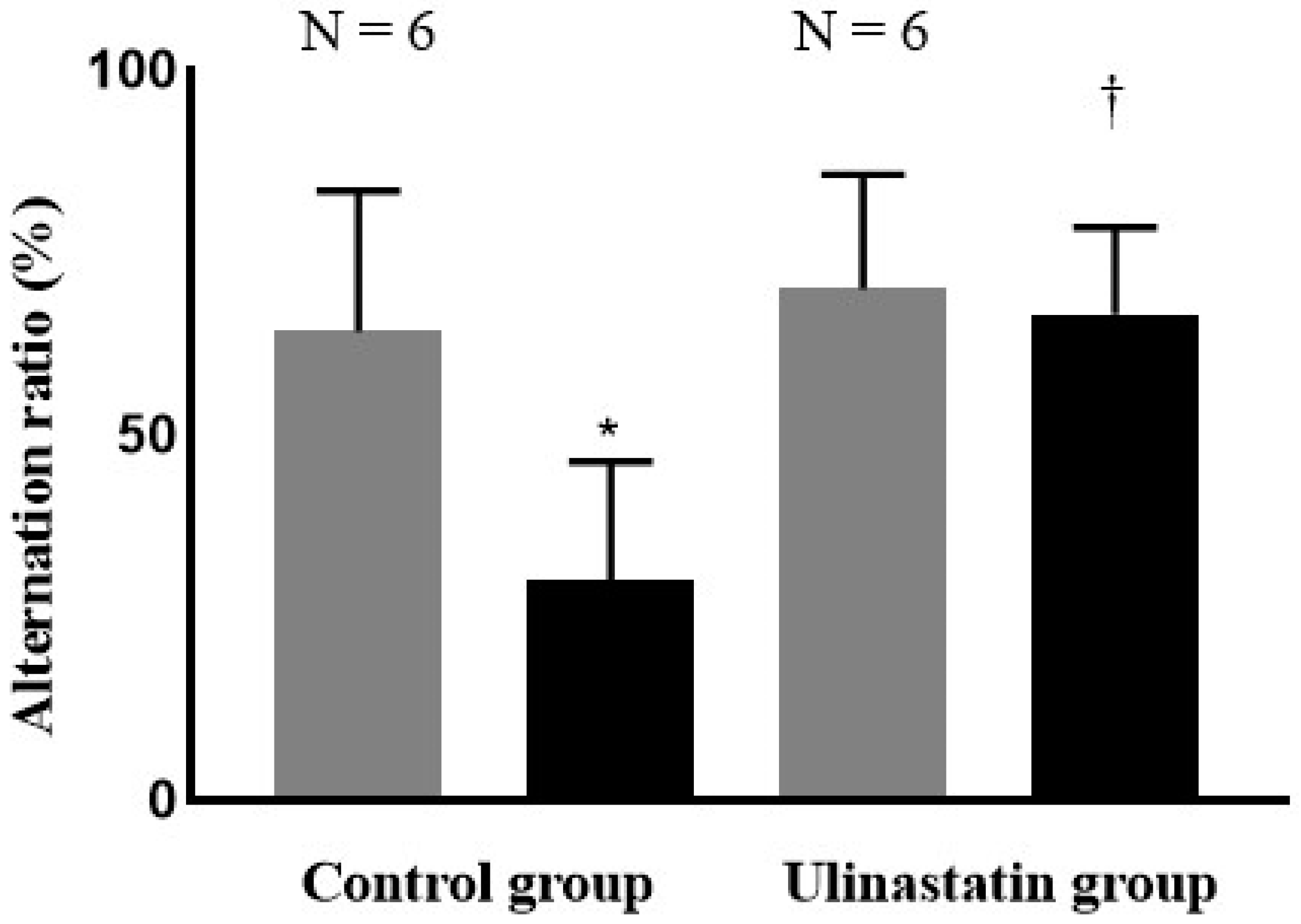
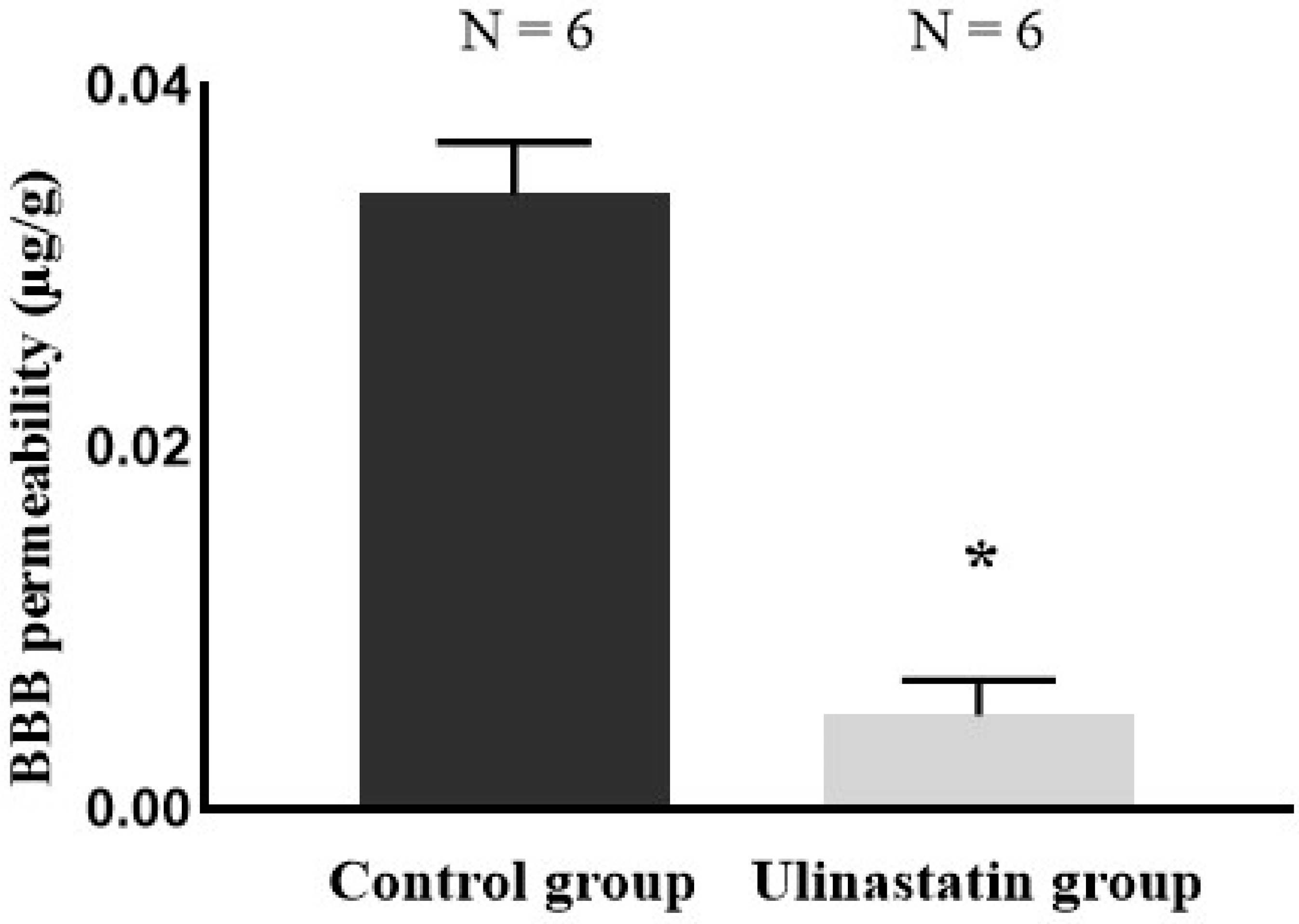
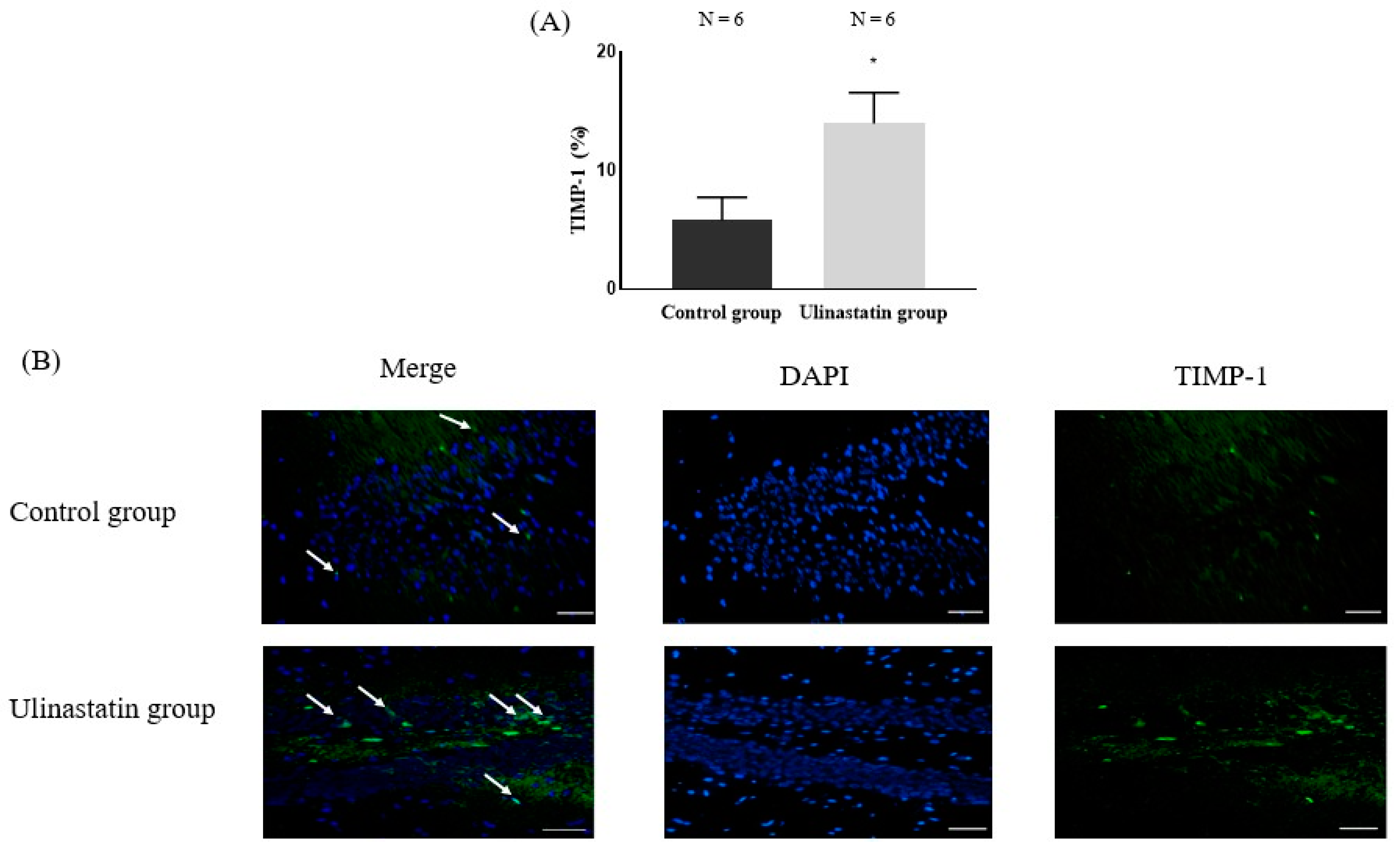
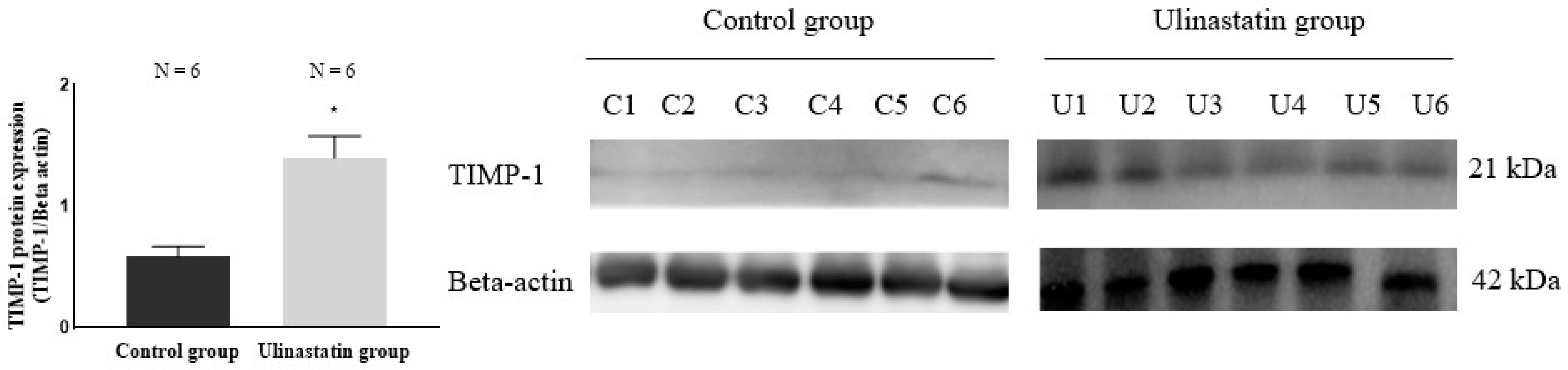
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Preparation
4.2. Behaviour Test
4.3. Grouping and General Anesthesia
4.4. Brain Tissue Preparation After Evans Blue Staining for BBB Permeability
4.5. Quantification of BBB Permeability
4.6. Immunofluorescence Staining for TIMP-1 in the Brain
4.7. Western Blotting for Quantification of TIMP-1 in the Brain
4.8. ELISA for Detection of Cytokines
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, X.; Zha, T.; Abudurousuli, G.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, B. Effects of regional cerebral oxygen saturation monitoring on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H. Identification of individuals at risk for postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2022, 15, 17562864221114356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Hu, B.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Pan, M.; Sun, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, H. The effect of intravenous lidocaine on postoperative cognitive dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhenyu, H.; Qiaoli, Y.; Guangxiang, C.; Maohua, W. The effect of Ulinastatin on postoperative course in cardiopulmonary bypass patients in Asia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ma, W.; Chen, J.; Jiao, W.; Wang, Y. Ulinastatin alleviates early brain injury after traumatic brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Acta Cir. Bras. 2022, 37, e370108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Ma, L.; Cao, A.; Wen, A.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Deng, J. Real-world safety of ulinastatin: A post-marketing surveillance of 11,252 patients in China. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.H.; In, C.B.; Lee, G.W.; Hong, S.W.; Seo, E.H.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, S.H. The Preventive Effect of Urinary Trypsin Inhibitor on Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction, on the Aspect of Behavior, Evaluated by Y-Maze Test, via Modulation of Microglial Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, J.; Zou, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, M. Effect of ulinastatin on the permeability of the blood-brain barrier on rats with global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury as assessed by MRI. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Su, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ban, T.; Xie, K.; Wei, C.; Lin, C. Neuroprotective effects of ulinastatin on Escherichia coli meningitis rats through inhibiting PKCα phosphorylation and reducing zonula occludens-1 degradation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kaushik, P.; Jain, S.; Sharma, B.M.; Awasthi, R.; Kulkarni, G.T.; Sharma, B. Efficacy of ulinastatin and sulforaphane alone or in combination in rat model of streptozotocin diabetes induced vascular dementia. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2021, 19, 470–489. [Google Scholar]
- Abo El gheit, R.E.; Atef, M.M.; Badawi, G.A.; Elwan, W.M.; Alshenawy, H.; Emam, M.N. Role of serine protease inhibitor, ulinastatin, in rat model of hepatic encephalopathy: Aquaporin 4 molecular targeting and therapeutic implication. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 76, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Teng, Z.; Yan, J. The protective roles of urinary trypsin inhibitor in brain injury following fat embolism syndrome in a rat model. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Yang, J.; Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Structure, function, and regulation of the blood-brain barrier tight junction in central nervous system disorders. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segarra, M.; Aburto, M.R.; Acker-Palmer, A. Blood–brain barrier dynamics to maintain brain homeostasis. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 393–405. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, M.A.; Banks, W.A. Age-associated changes in the immune system and blood–brain barrier functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, K.; White, J.A.; McMurran, C.E.; Rivera, F.J.; de la Fuente, A.G. Aging and neurodegenerative disease: Is the adaptive immune system a friend or foe? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 572090. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Driscoll, C.M. The blood-brain barrier in aging and neurodegeneration. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2659–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Qin, S.; Chai, J. Neuroinflammation as the underlying mechanism of postoperative cognitive dysfunction and therapeutic strategies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 843069. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Tian, W.; Chen, X.; Xu, H.; Dai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yu, W.; Tian, J.; Su, D. Peripheral neutrophils-derived matrix metallopeptidase-9 induces postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 683295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Mo, C.; Xu, S.; Chen, L.; Ye, W.; Kang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhu, T. Research progress on perioperative blood-brain barrier damage and its potential mechanism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1174043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Sun, J.; Zheng, J.; Xie, W.; Jiang, C.; Kang, Z.; Huang, Y. Energy intake restriction significantly improves POCD after internal fixation of tibial fractures in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, S.; Hua, D. Cefazolin improves anesthesia and surgery-induced cognitive impairments by modulating blood-brain barrier function, gut bacteria and short chain fatty acids. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 748637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo, B.L.; Jasiulionis, M.G. Characteristics of TIMP1, CD63, and β1-integrin and the functional impact of their interaction in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimic-Janjic, S.; Hoda, M.A.; Milenkovic, B.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Stjepanovic, M.; Gompelmann, D.; Jankovic, J.; Miljkovic, M.; Milin-Lazovic, J.; Djurdjevic, N. The usefulness of MMP-9, TIMP-1 and MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio for diagnosis and assessment of COPD severity. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Kang, Y.; Huang, L.; Wu, L.; Peng, Y. TIMP1 preserves the blood–brain barrier through interacting with CD63/integrin β1 complex and regulating downstream FAK/RhoA signaling. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadighadykolaei, H.; Lambert, J.A.; Raeeszadeh-Sarmazdeh, M. TIMP-1 Protects Tight Junctions of Brain Endothelial Cells From MMP-Mediated Degradation. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, R.; Hamano, S.-i.; Daida, A.; Horiguchi, A.; Nonoyama, H.; Kubota, J.; Ikemoto, S.; Hirata, Y.; Koichihara, R.; Kikuchi, K. Serum matrix metallopeptidase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 levels may predict response to adrenocorticotropic hormone therapy in patients with infantile spasms. Brain Dev. 2022, 44, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.; Monteiro, A.; Silva, R.; Moreira, J.; Lobo, J.S.; Silva, A. Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, J.; He, A.; Zhao, M.; Yang, C.; Yang, W. Evaluation of decompressive craniectomy in mice after severe traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 898813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Gharami, K.; Paidi, R.K.; Srikumar, B.N.; Biswas, S.C. An astrocyte-derived cytokine TIMP-1 restores synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer’s disease model. bioRxiv 2023, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Lavayen, B.P.; Larochelle, J.; Gunraj, R.E.; Butler, A.A.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Therapeutic benefits of adropin in aged mice after transient ischemic stroke via reduction of blood-brain barrier damage. Stroke 2023, 54, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Fu, H.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Wang, T.-L. Ulinastatin may significantly improve postoperative cognitive function of elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery by reducing the translocation of lipopolysaccharide and systemic inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.; Baumgärtner, W.; Gerhauser, I.; Seeliger, F.; Haist, V.; Deschl, U.; Alldinger, S. MMP-12, MMP-3, and TIMP-1 are markedly upregulated in chronic demyelinating theiler murine encephalomyelitis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygårdas, P.; Hinkkanen, A. Up-regulation of MMP-8 and MMP-9 activity in the BALB/c mouse spinal cord correlates with the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 128, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, G.E.; Wolfer, D.P.; Timmesfeld, N.; Kanzler, B.; Schrewe, H.; Pagenstecher, A. Long-term expression of tissue-inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in the murine central nervous system does not alter the morphological and behavioral phenotype but alleviates the course of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, N.R.; Dziegielewska, K.M.; Møllgård, K.; Habgood, M.D. Markers for blood-brain barrier integrity: How appropriate is Evans blue in the twenty-first century and what are the alternatives? Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolden, C.T.; Olson, S.D.; Cox Jr, C.S. A decade of blood-brain barrier permeability assays: Revisiting old traumatic brain injury rat data for new insights and experimental design. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 145, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Roh, D.H.; Choi, J.W.; Ryu, Y.; Lee, J.H. Repetitive Treatment with Diluted Bee Venom Attenuates the Induction of Below-Level Neuropathic Pain Behaviors in a Rat Spinal Cord Injury Model. Toxins 2015, 7, 2571–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, Y.; Qin, L.H.; Nishihara, M.; Sawada, K.; Kato, K.; Inoue, S. Vulnerability of synaptic plasticity in the complexin II knockout mouse to maternal deprivation stress. Brain Res. 2005, 1056, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainmueller, T.; Bartos, M. Dentate gyrus circuits for encoding, retrieval and discrimination of episodic memories. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.A.; Nassar, A.Y.; Meligy, F.Y.; Omar, Y.A.; Nassar, G.A.; Ezzat, G.M. Acetylated oligopeptide and N-acetylcysteine protect against iron overload-induced dentate gyrus hippocampal degeneration through upregulation of Nestin and Nrf2/HO-1 and downregulation of MMP-9/TIMP-1 and GFAP. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control Group | Ulinastatin Group | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pro-inflammatory cytokines | |||
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 23.62 ± 2.55 | 6.88 ± 0.90 | 0.0385 |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 19.76 ± 5.16 | 7.70 ± 1.37 | 0.0002 |
| Anti-inflammatory cytokines | |||
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | 23.46 ± 3.74 | 25.24 ± 3.33 | 0.4035 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 6.66 ± 1.50 | 15.34 ± 0.95 | 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, E.-H.; Seo, E.-H.; Hong, S.-W.; Kim, S.-H. The Preventive Effect of Ulinastatin on Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Rats with Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction After General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312505
Cho E-H, Seo E-H, Hong S-W, Kim S-H. The Preventive Effect of Ulinastatin on Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Rats with Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction After General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312505
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Eun-Hwa, Eun-Hye Seo, Seung-Wan Hong, and Seong-Hyop Kim. 2024. "The Preventive Effect of Ulinastatin on Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Rats with Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction After General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312505
APA StyleCho, E.-H., Seo, E.-H., Hong, S.-W., & Kim, S.-H. (2024). The Preventive Effect of Ulinastatin on Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Rats with Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction After General Anaesthesia with Isoflurane. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312505





