Designing Analogs of SAAP-148 with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Anti-LPS Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Designing and Forecasting the Physicochemical Properties of Peptides
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
2.3. Haemolytic Activity of SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
2.4. Cytotoxicity Activity of SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
2.5. The Therapeutic Index (TI) of SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
2.6. Membrane Damage Induced by SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
2.7. Anti-LPS Property of SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Regents
4.2. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectra and Physicochemical Properties Forecasting of the Peptides
4.3. Haemolytic Activity of the Peptides
4.4. Cytotoxicity of the Peptides
4.5. Antimicrobial Activity of the Peptides
4.6. Cell Membrane Damage Induced by the Peptides
4.7. Inhibition of Nitric Oxide (NO) Production of SAAP-148 and Its Analogues
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019; Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/data-research/threats/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/DrugResistance/Biggest-Threats.html (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations/the Review on Antimicrobial Resistance Chaired by Jim O’Neill. Available online: https://wellcomecollection.org/works/rdpck35v (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Li, G.; Lai, Z.; Shan, A. Advances of Antimicrobial Peptide-Based Biomaterials for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzaro, B.P.; Zasloff, M.; Rolff, J. Antimicrobial peptides: Application informed by evolution. Science 2020, 368, eaau5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B.; Bo, L.; Chen, Z.S.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Antimicrobial peptides for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections. Drug Resist. Updates 2023, 68, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: Functions and clinical potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, M.; Pushpanathan, M.; Santos, A.L.; Leanse, L.; Fernandez, M.; Ioannidis, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Apidianakis, Y.; Bradfute, S.; Ferguson, A.L.; et al. The value of antimicrobial peptides in the age of resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e216–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hao, W.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, J.; Deng, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Antimicrobial peptides, conventional antibiotics, and their synergistic utility for the treatment of drug-resistant infections. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1377–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Petrone, A.M.; Salvia, R.; Manniello, M.D.; Franco, A.; Lucchetti, D.; Vassallo, A.; Vogel, H.; Sgambato, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: A New Hope in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Fields. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 668632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, S.; Turton, K.L.; Kainth, T.; Kumar, A.; Wieden, H.J. Strategies for improving antimicrobial peptide production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 59, 107968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulukutla, A.; Shreshtha, R.; Kumar Deb, V.; Chatterjee, P.; Jain, U.; Chauhan, N. Recent advances in antimicrobial peptide-based therapy. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 145, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Hafeez, A.; Jiang, X.; Bergen, P.J.; Zhu, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides: An Update on Classifications and Databases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehbach, J.; Craik, D.J. The Vast Structural Diversity of Antimicrobial Peptides. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.; Rolff, J.; Friedman, J.; Hayouka, Z. Antimicrobial Peptide Combination Can Hinder Resistance Evolution. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0097322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Structure, mechanism, and modification. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 255, 115377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Hall, K.N.; Aguilar, M.I. Antimicrobial Peptide Structure and Mechanism of Action: A Focus on the Role of Membrane Structure. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziato, G.; Costantino, G. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): A patent review (2015–2020). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 931–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.K.; Song, J.W.; Gong, F.; Li, S.B.; Chang, H.Y.; Xie, H.M.; Gao, H.W.; Tan, Y.X.; Ji, S.P. Design of an α-helical antimicrobial peptide with improved cell-selective and potent anti-biofilm activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, U.H.; Sudheendra, U.S.; Ramamoorthy, A. LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1408–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.G.; Davidson, D.J.; Gold, M.R.; Bowdish, D.; Hancock, R.E. The human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 is a multifunctional modulator of innate immune responses. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3883–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Breij, A.; Riool, M.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Malanovic, N.; de Boer, L.; Koning, R.I.; Ravensbergen, E.; Franken, M.; van der Heijde, T.; Boekema, B.K.; et al. The antimicrobial peptide SAAP-148 combats drug-resistant bacteria and biofilms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, M.E.; Klodzinska, S.N.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Nielsen, H.M.; Nibbering, P.H. Encapsulation in oleyl-modified hyaluronic acid nanogels substantially improves the clinical potential of the antimicrobial peptides SAAP-148 and Ab-Cath. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 193, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, R.; Douguet, D.; Antonny, B.; Drin, G. HELIQUEST: A web server to screen sequences with specific alpha-helical properties. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2101–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Determination of stereochemistry stability coefficients of amino acid side-chains in an amphipathic alpha-helix. J. Pept. Res. 2002, 59, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jekhmane, S.; Derks, M.G.N.; Maity, S.; Slingerland, C.J.; Tehrani, K.; Medeiros-Silva, J.; Charitou, V.; Ammerlaan, D.; Fetz, C.; Consoli, N.A.; et al. Host defence peptide plectasin targets bacterial cell wall precursor lipid II by a calcium-sensitive supramolecular mechanism. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1778–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.H.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Santos, N.C.; Zasloff, M.A.; Franco, O.L. Influence of antimicrobial peptides on the bacterial membrane curvature and vice versa. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresti, L.; Cappello, G.; Pini, A. Antimicrobial Peptides towards Clinical Application-A Long History to Be Concluded. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugrue, I.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Bacteriocin diversity, function, discovery and application as antimicrobials. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.A.E.; Hammami, R. Recent insights into structure-function relationships of antimicrobial peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epand, R.M.; Walker, C.; Epand, R.F.; Magarvey, N.A. Molecular mechanisms of membrane targeting antibiotics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juretić, D.; Simunić, J. Design of α-helical antimicrobial peptides with a high selectivity index. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, S.; Ridgway, Z.M.; Picciano, A.L.; Caputo, G.A. Impacts of Hydrophobic Mismatch on Antimicrobial Peptide Efficacy and Bilayer Permeabilization. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.C.; Wu, T.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, J.Y. Distribution of positively charged amino acid residues in antimicrobial peptide epinecidin-1 is crucial for in vitro glioblastoma cytotoxicity and its underlying mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 315, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, J.; Murail, S.; de Vries, S.; Derreumaux, P.; Tuffery, P. PEP-FOLD4: A pH-dependent force field for peptide structure prediction in aqueous solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W432–W437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, M.K.; Rahman, A.; Dey, H.; Anderssen, T.; Zilioli, F.; Haug, T.; Blencke, H.M.; Stensvåg, K.; Strøm, M.B.; Bayer, A. A concise SAR-analysis of antimicrobial cationic amphipathic barbiturates for an improved activity-toxicity profile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhlongo, J.T.; Waddad, A.Y.; Albericio, F.; de la Torre, B.G. Antimicrobial Peptide Synergies for Fighting Infectious Diseases. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.P.; Lin, Q.; Chen, C.; Montelaro, R.C.; Doi, Y.; Deslouches, B. Enhanced therapeutic index of an antimicrobial peptide in mice by increasing safety and activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, A.; Edwards, A.M. Lipopolysaccharide as an antibiotic target. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2023, 1870, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Su, S.; Yan, Y.; Yin, L.; Liu, L. Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa activity of natural antimicrobial peptides when used alone or in combination with antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1239540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, F.; Sauer, J.B.; Qiu, X.; Corey, R.A.; Cassidy, C.K.; Mynors-Wallis, B.; Mehmood, S.; Bolla, J.R.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Robinson, C.V. Dynamics of an LPS translocon induced by substrate and an antimicrobial peptide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qu, W.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Shang, D. The antimicrobial peptide chensinin-1b alleviates the inflammatory response by targeting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and LPS-mediated sepsis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Moussong, É.; Wien, F.; Boros, E.; Vadászi, H.; Murvai, N.; Lee, Y.H.; Molnár, T.; Réfrégiers, M.; Goto, Y.; et al. BeStSel: Webserver for secondary structure and fold prediction for protein CD spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, W90–W98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
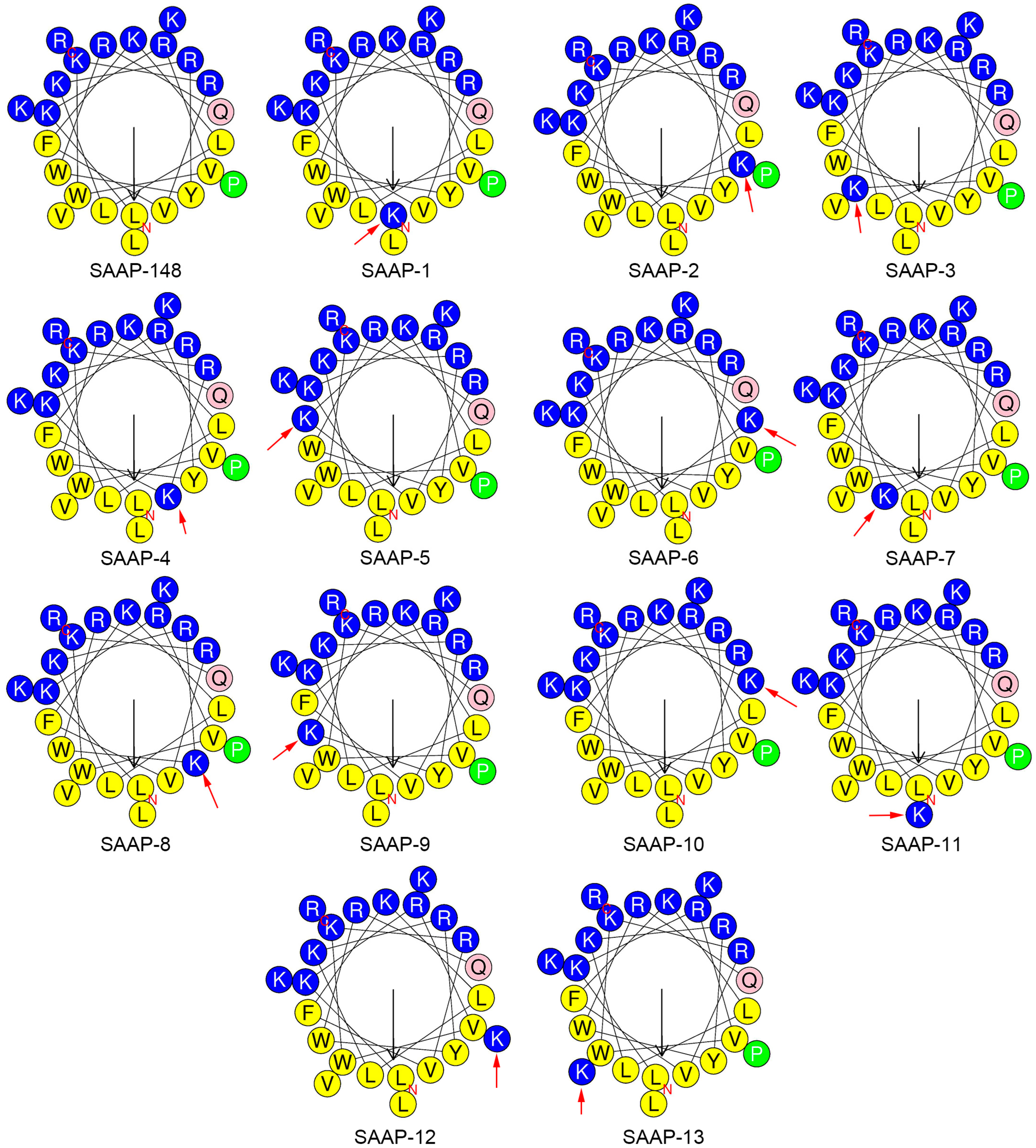
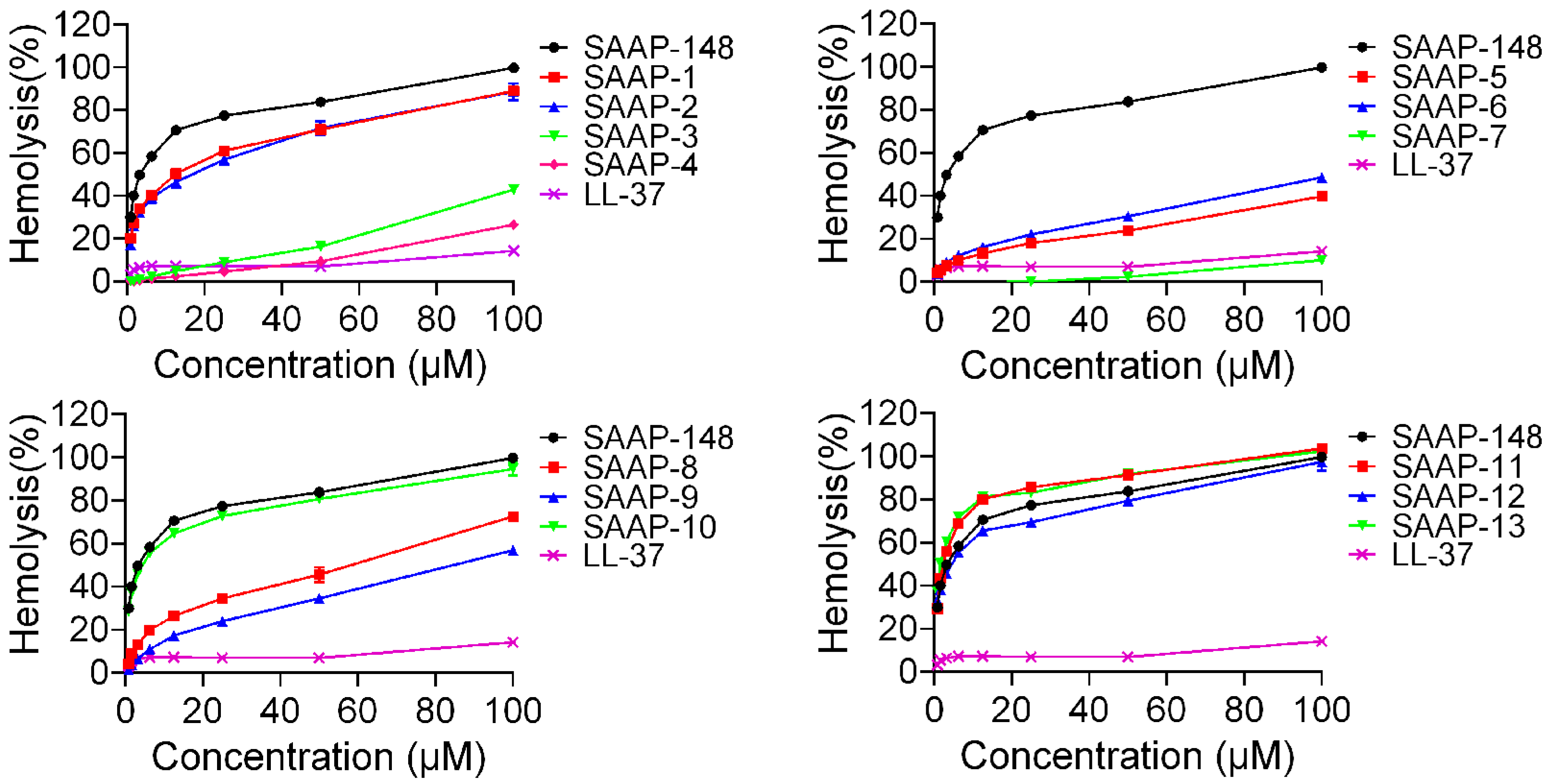
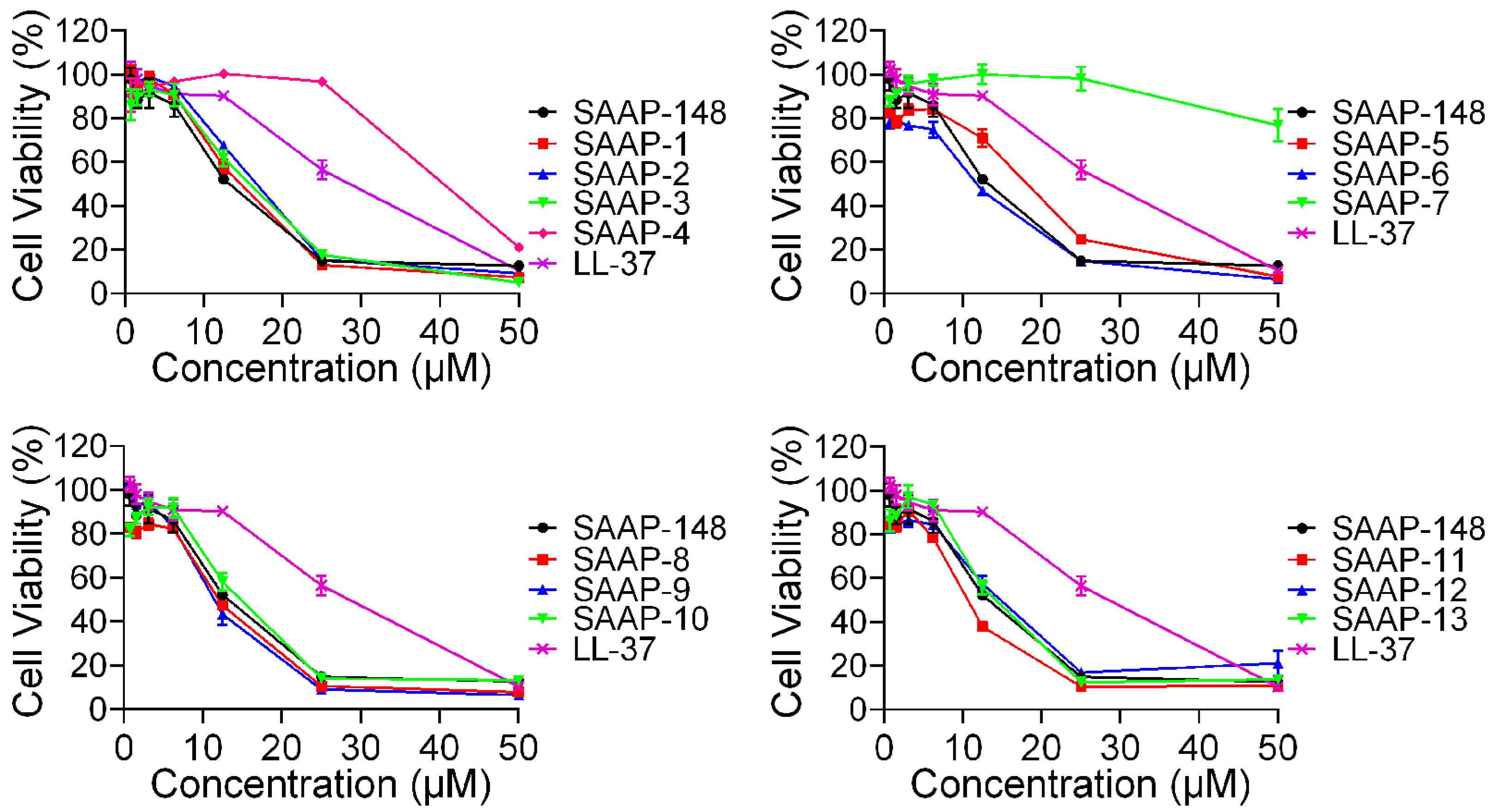
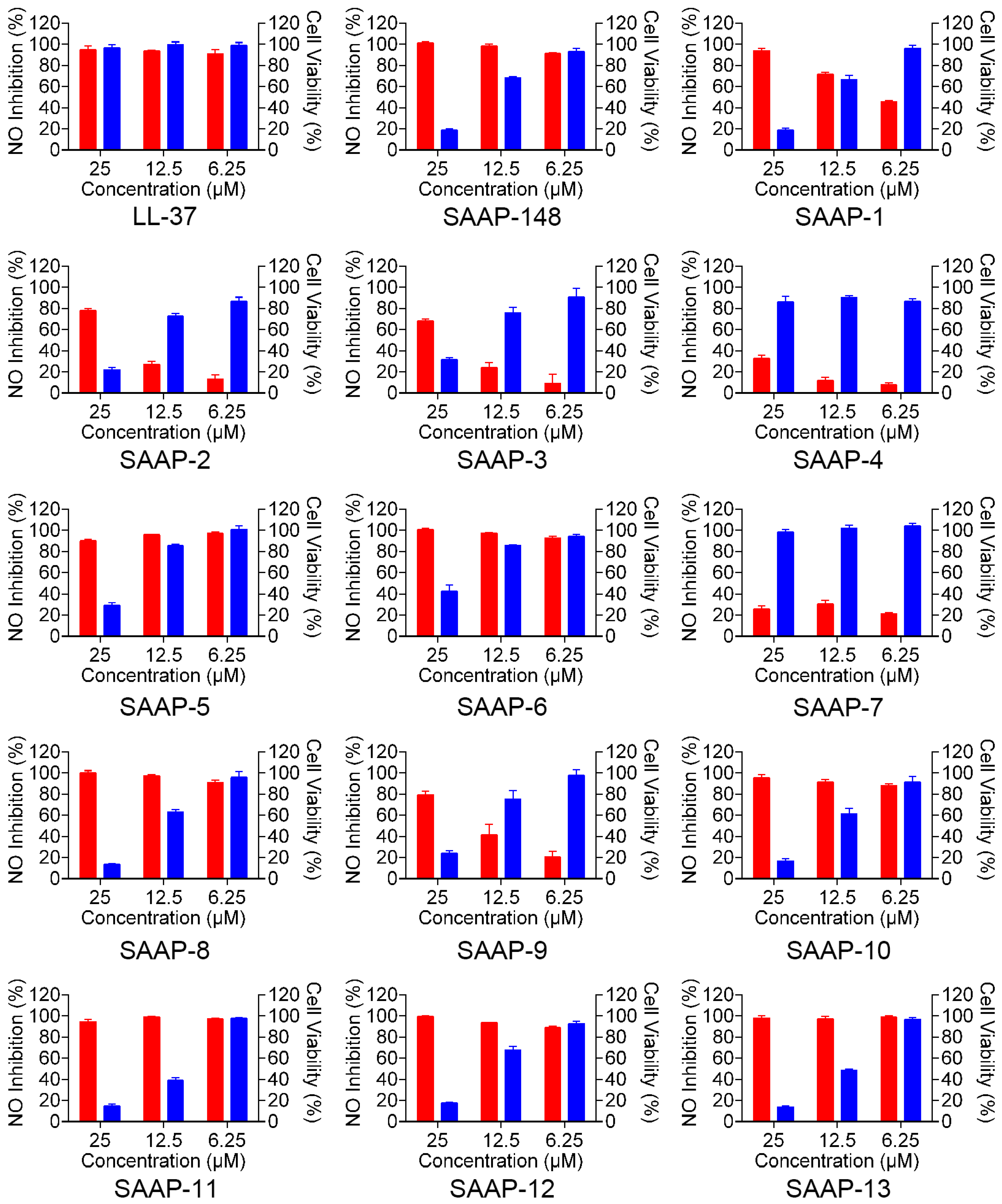
| Peptides | Sequence | MW by MS 1 | Theroretical MW 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LL-37 | LLGDFFRKSKEKIGKEFKRIVQRIKDFLRNLVPRTES.NH2 | 4493.3 | 4493.32 |
| SAAP-148 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3224.7 | 3225.03 |
| SAAP-1 | KKRVWKRVFKLLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3239.4 | 3240.04 |
| SAAP-2 | LKRKWKRVFKLLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3252.9 | 3254.06 |
| SAAP-3 | LKRVKKRVFKLLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3166.8 | 3166.98 |
| SAAP-4 | LKRVWKRKFKLLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3254 | 3254.06 |
| SAAP-5 | LKRVWKRVKKLLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3206 | 3206.2 |
| SAAP-6 | LKRVWKRVFKKLKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3240 | 3240.04 |
| SAAP-7 | LKRVWKRVFKLKKRYWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3240 | 3240.04 |
| SAAP-8 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRKWRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3189.6 | 3190.2 |
| SAAP-9 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRYKRQLKKPVR.NH2 | 3166.4 | 3166.98 |
| SAAP-10 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRYWRKLKKPVR.NH2 | 3223.9 | 3225.07 |
| SAAP-11 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRYWRQKKKPVR.NH2 | 3240 | 3240.4 |
| SAAP-12 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRYWRQLKKKVR.NH2 | 3255.7 | 3256.08 |
| SAAP-13 | LKRVWKRVFKLLKRYWRQLKKPKR.NH2 | 3253.8 | 3254.06 |
| Peptides | Hydrophobicity (H) 1 | Hyd. Moment (μH) 2 | Charge (z) 3 | Rt (min) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL-37 | 0.20081 | 0.52117 | 4 | 11.125 |
| SAAP-148 | 0.30083 | 0.82272 | 11 | 12.416 |
| SAAP-1 | 0.18875 | 0.71063 | 12 | 11.419 |
| SAAP-2 | 0.20875 | 0.78127 | 12 | 12.532 |
| SAAP-3 | 0.16583 | 0.72391 | 12 | 11.208 |
| SAAP-4 | 0.20875 | 0.73708 | 12 | 9.96 |
| SAAP-5 | 0.185 | 0.80996 | 12 | 10.681 |
| SAAP-6 | 0.18875 | 0.81149 | 12 | 9.213 |
| SAAP-7 | 0.18875 | 0.71815 | 12 | 12.897 |
| SAAP-8 | 0.21958 | 0.76261 | 12 | 13.475 |
| SAAP-9 | 0.16583 | 0.76344 | 12 | 11.941 |
| SAAP-10 | 0.26875 | 0.82908 | 12 | 13.69 |
| SAAP-11 | 0.18875 | 0.71063 | 12 | 15.926 |
| SAAP-12 | 0.22958 | 0.7899 | 12 | 16.604 |
| SAAP-13 | 0.20875 | 0.75411 | 12 | 16.867 |
| Peptides | MIC (μM) 1 | GM to G− 2 | MIC (μM) 1 | GM to G+ 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | P. aeruginosa | K. pneumoniae | S. aureus | S. epidermidis | |||
| LL-37 | 1.56 | 12.50 | 100.00 | 12.49 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100 |
| SAAP-148 | 6.25 | 3.13 | 6.25 | 4.96 | 50.00 | 3.13 | 12.51 |
| SAAP-1 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 6.25 | 3.94 | 50.00 | 3.13 | 12.51 |
| SAAP-2 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 12.50 | 4.97 | 50.00 | 3.13 | 12.51 |
| SAAP-3 | 1.56 | 3.13 | 6.25 | 3.12 | 100.00 | 3.13 | 17.69 |
| SAAP-4 | 1.56 | 3.13 | 100.00 | 7.87 | 100.00 | 3.13 | 17.69 |
| SAAP-5 | 1.56 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 3.94 | 25.00 | 3.13 | 8.85 |
| SAAP-6 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 6.25 | 2.48 | 25.00 | 1.56 | 6.24 |
| SAAP-7 | 3.13 | 3.13 | 100.00 | 9.93 | 100.00 | 12.50 | 35.36 |
| SAAP-8 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 25.00 | 3.93 | 25.00 | 1.56 | 6.24 |
| SAAP-9 | 3.13 | 1.56 | 12.50 | 3.94 | 50.00 | 3.13 | 12.51 |
| SAAP-10 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 25.00 | 9.92 | 50.00 | 3.13 | 12.51 |
| SAAP-11 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 100.00 | 15.75 | 50.00 | 3.13 | 12.51 |
| SAAP-12 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 100.00 | 25 | 25.00 | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| SAAP-13 | 6.25 | 12.50 | 25.00 | 12.5 | 50.00 | 6.25 | 17.68 |
| Peptides | MIC (GM) 1 | MHC 2 | TI (MHC/MIC) 3 | Fold 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL-37 | 28.72 | 100.00 | 3.48 | |
| SAAP-148 | 7.18 | 0.78 | 0.11 | |
| SAAP-1 | 6.25 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 1.1 |
| SAAP-2 | 7.18 | 0.78 | 0.11 | 1 |
| SAAP-3 | 6.25 | 50.00 | 8.00 | 72.73 |
| SAAP-4 | 10.88 | 100.00 | 9.19 | 83.55 |
| SAAP-5 | 5.44 | 6.25 | 1.15 | 10.45 |
| SAAP-6 | 3.59 | 6.25 | 1.74 | 15.82 |
| SAAP-7 | 16.49 | 100.00 | 6.06 | 55.09 |
| SAAP-8 | 4.74 | 3.13 | 0.66 | 6 |
| SAAP-9 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 1.00 | 9.09 |
| SAAP-10 | 10.88 | 0.78 | 0.07 | 0.64 |
| SAAP-11 | 14.36 | 0.78 | 0.05 | 0.45 |
| SAAP-12 | 18.95 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 0.36 |
| SAAP-13 | 14.36 | 0.78 | 0.05 | 0.45 |
| Peptides | BEAS-2B | E.coli | S. aureus |
|---|---|---|---|
| LL-37 | 31.2 | 78.9 | 46.9 |
| SAAP-148 | 76.2 | 79.9 | 68 |
| SAAP-1 | 62.1 | 75.8 | 60.5 |
| SAAP-2 | 79.4 | 79.2 | 64.2 |
| SAAP-3 | 36.4 | 54.1 | 48.5 |
| SAAP-4 | 48.6 | 62 | 38 |
| SAAP-5 | 54 | 73.2 | 52.4 |
| SAAP-6 | 58.1 | 72 | 56.2 |
| SAAP-7 | 30.1 | 34.9 | 21.1 |
| SAAP-8 | 55.6 | 57.7 | 51.6 |
| SAAP-9 | 81.7 | 53.4 | 48.8 |
| SAAP-10 | 87.1 | 79.1 | 60.9 |
| SAAP-11 | 53.3 | 69.2 | 65.5 |
| SAAP-12 | 32.8 | 70.3 | 60.5 |
| SAAP-13 | 31.7 | 75.6 | 64.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, L.; Chi, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, S.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, S. Designing Analogs of SAAP-148 with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Anti-LPS Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111776
Gan L, Chi Y, Peng Y, Li S, Gao H, Zhang X, Ji S, Feng Z, Zhang S. Designing Analogs of SAAP-148 with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Anti-LPS Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111776
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Lingmin, Yulang Chi, Yunhui Peng, Subo Li, Hongwei Gao, Xue Zhang, Shouping Ji, Zili Feng, and Shikun Zhang. 2024. "Designing Analogs of SAAP-148 with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Anti-LPS Activities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111776
APA StyleGan, L., Chi, Y., Peng, Y., Li, S., Gao, H., Zhang, X., Ji, S., Feng, Z., & Zhang, S. (2024). Designing Analogs of SAAP-148 with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Anti-LPS Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111776






