Cross-Reactive Immune Response of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein to SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
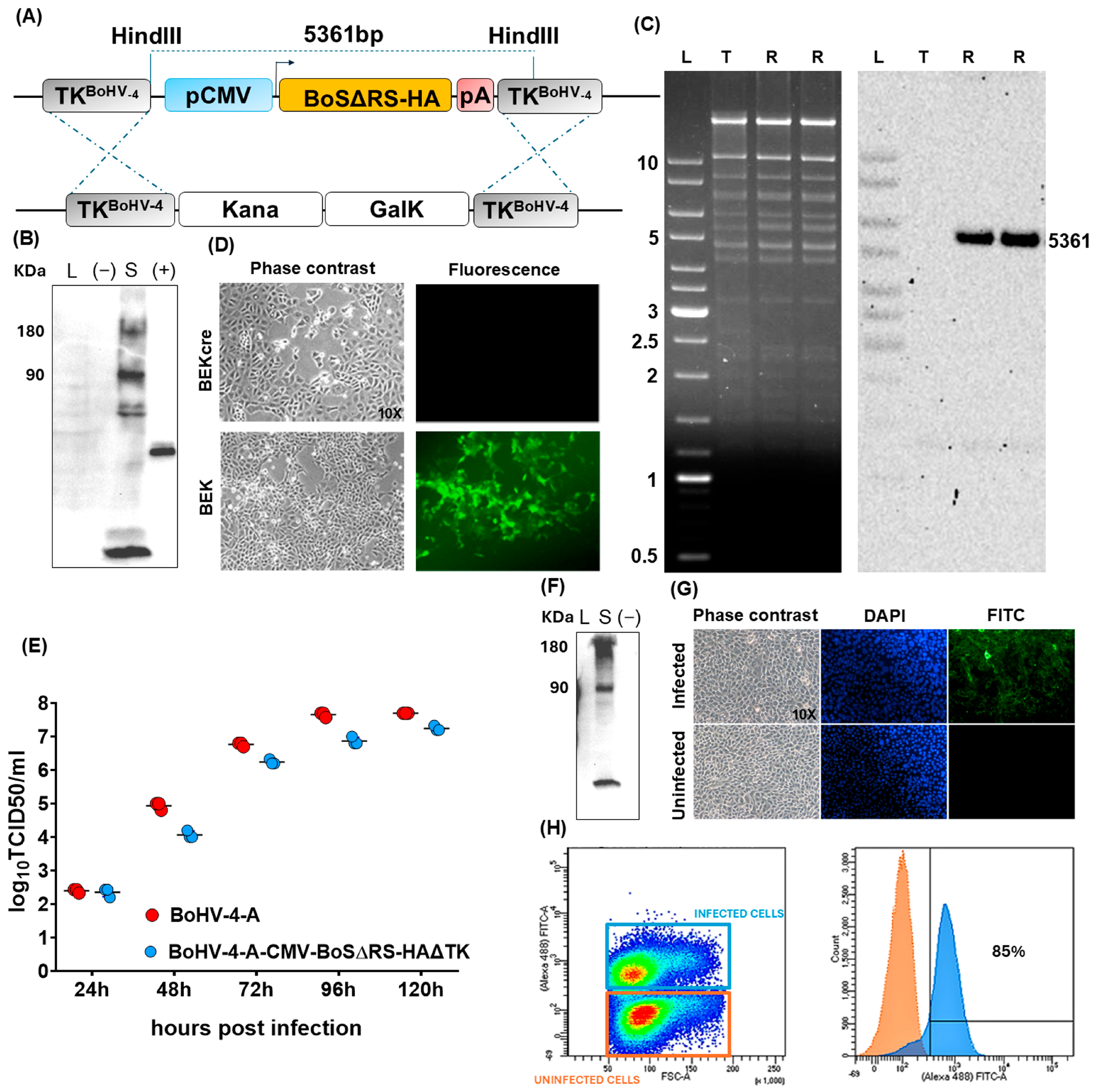
2.1. Generation and Characterization of a Viral Vector Encoding for BoS
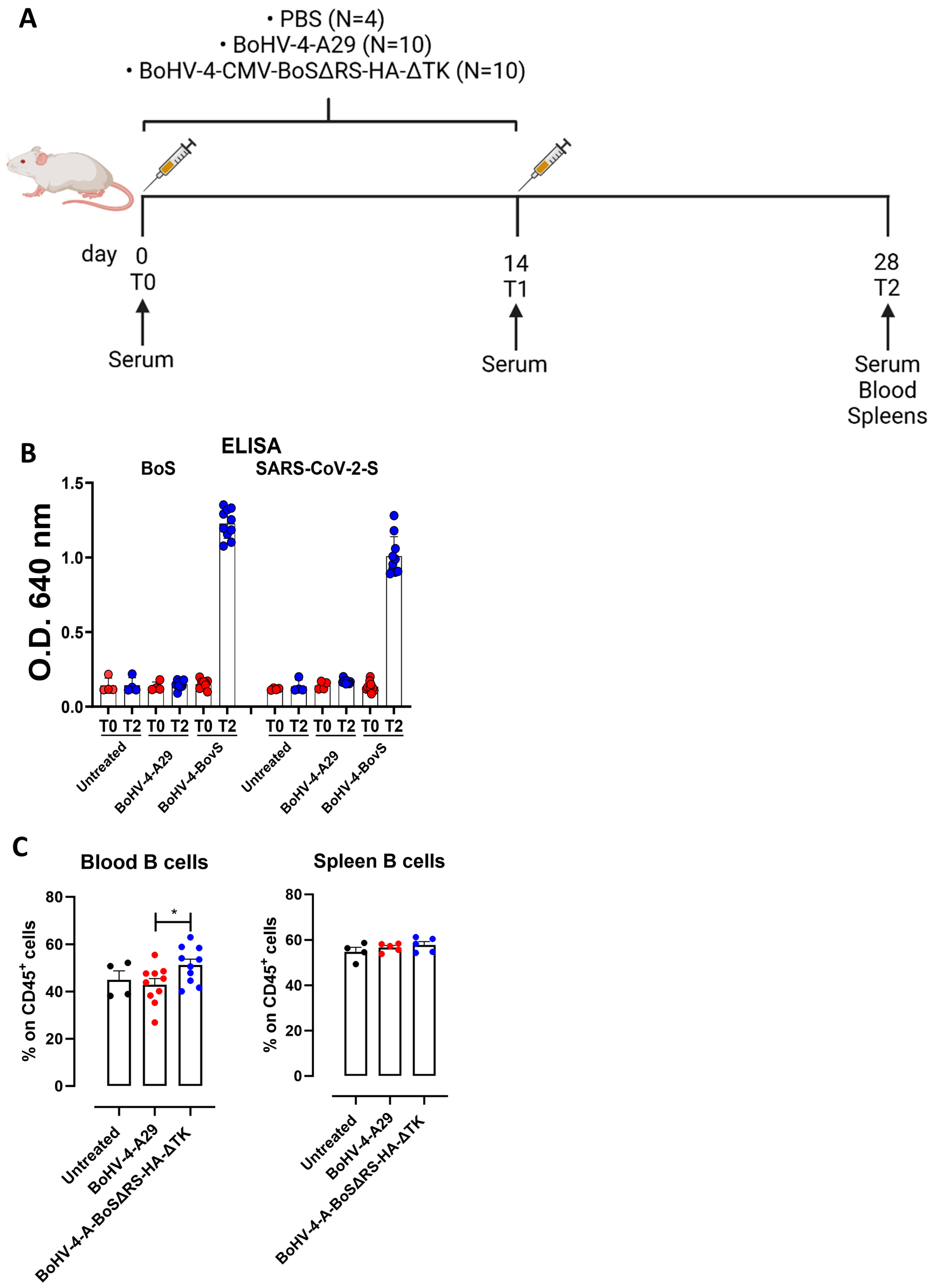
2.2. BoHV-4-CMV-BoSΔRS-HA-ΔTK Induces Antibodies That Cross-React with the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
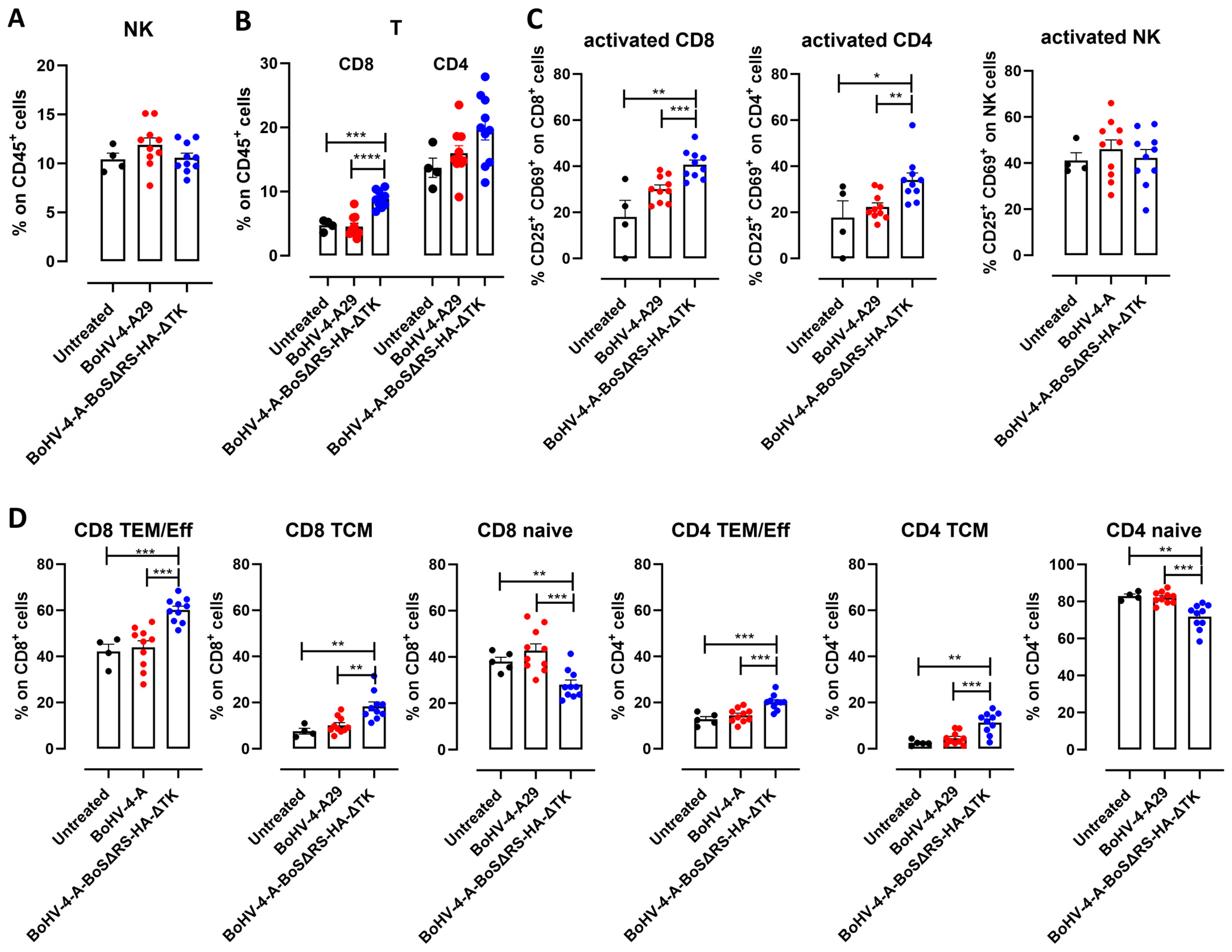
2.3. Immunization with BoHV-4-CMV-BoSΔRS-HA-ΔTK Induces Spike-Specific T Cell Responses
2.4. T Lymphocytes Specific for BoS Cross-React with SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Kill Spike-Expressing Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Plasmids Construction and Transfection in HEK293T Cells
4.3. Immunoblotting
4.4. Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) Recombineering, Selection, and Southern Blotting Analyses
4.5. Cell Electroporation and Reconstitution, Production, and Titration of the Recombinant Virus
4.6. Viral Growth Curves
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining and Cytofluorimetric Analyses of BoHV-4-CMV-BoSΔRS-HA-ΔTK Infected Cells
4.8. Induction of BoV-S-Specific Immune Responses in Mice
4.9. Assessment of Spike Cross-Reactive Antibody Levels After Vaccination in Mice by ELISA
4.10. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.11. FACS Analysis
4.12. ELISpot
4.13. SARS-CoV Neutralization Assay Against the Original Viral Strain and Variants
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, S.M.; Ansari, A.M.; Frater, J.; Klenerman, P.; Dunachie, S.; Barnes, E.; Ogbe, A. The impact of pre-existing cross-reactive immunity on SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, A.; Hiller, K.; Scheer, M.; Munch, R.; Nortemann, B.; Hempel, D.C.; Jahn, D. JCat: A novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, A.A.T.; Fatima, K.; Mohammad, T.; Fatima, U.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A.; Atif, S.M.; Hariprasad, G.; Hasan, G.M.; Hassan, M.I. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.; Loyal, L.; Frentsch, M.; Wendisch, D.; Georg, P.; Kurth, F.; Hippenstiel, S.; Dingeldey, M.; Kruse, B.; Fauchere, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-reactive T cells in healthy donors and patients with COVID-19. Nature 2020, 587, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulien, I.; Kemming, J.; Oberhardt, V.; Wild, K.; Seidel, L.M.; Killmer, S.; Sagar; Daul, F.; Salvat Lago, M.; Decker, A.; et al. Characterization of pre-existing and induced SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8(+) T cells. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaago, M.; Rahni, A.; Pupina, N.; Pihlak, A.; Sadam, H.; Tuvikene, J.; Avarlaid, A.; Planken, A.; Planken, M.; Haring, L.; et al. Differential patterns of cross-reactive antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detected for chronically ill and healthy COVID-19 naive individuals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Bovine Coronavirus and the Associated Diseases. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 643220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, B.; Sun, D. Advances in Bovine Coronavirus Epidemiology. Viruses 2022, 14, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Herbst, W.; Kousoulas, K.G.; Storz, J. Biological and genetic characterization of a hemagglutinating coronavirus isolated from a diarrhoeic child. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 44, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.G.; Cheon, D.S.; Zhang, X.; Saif, L.J. Cross-protection against a human enteric coronavirus and a virulent bovine enteric coronavirus in gnotobiotic calves. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12350–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, H.M. Bovine-like coronaviruses in domestic and wild ruminants. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2018, 19, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Moes, E.; Thoelen, I.; Wollants, E.; Lemey, P.; Vandamme, A.M.; Van Ranst, M. Complete genomic sequence of human coronavirus OC43: Molecular clock analysis suggests a relatively recent zoonotic coronavirus transmission event. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kin, N.; Miszczak, F.; Diancourt, L.; Caro, V.; Moutou, F.; Vabret, A.; Ar Gouilh, M. Comparative molecular epidemiology of two closely related coronaviruses, bovine coronavirus (BCoV) and human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43), reveals a different evolutionary pattern. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 40, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanski, A.; Owczarek, K.; Bzowska, M.; Gula, K.; Drebot, I.; Ochman, M.; Maksym, B.; Rajfur, Z.; Mitchell, J.A.; Pyrc, K. Canine Respiratory Coronavirus, Bovine Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus OC43: Receptors and Attachment Factors. Viruses 2019, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, A.; Borge, C.; Carbonero, A.; Garcia-Bocanegra, I.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Caballero, J.; Arenas-Montes, A. Bovine Coronavirus Immune Milk Against COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilocca, B.; Soggiu, A.; Musella, V.; Britti, D.; Sanguinetti, M.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Molecular basis of COVID-19 relationships in different species: A one health perspective. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Conti, L.; Franceschi, V.; Oh, B.; Yang, M.S.; Ham, G.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Bolli, E.; Cavallo, F.; Kim, B.; et al. Assessment of BoHV-4-based vector vaccine intranasally administered in a hamster challenge model of lung disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1197649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, L.; Bolli, E.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Franceschi, V.; Macchi, F.; Riccardo, F.; Ruiu, R.; Russo, L.; Quaglino, E.; Donofrio, G.; et al. Immunotargeting of the xCT Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter Potentiates the Efficacy of HER2-Targeted Immunotherapies in Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donofrio, G.; Franceschi, V.; Macchi, F.; Russo, L.; Rocci, A.; Marchica, V.; Costa, F.; Giuliani, N.; Ferrari, C.; Missale, G. A Simplified SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Neutralization Assay. Vaccines 2021, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, P.; Rosati, E.; Esser, D.; Martini, G.R.; Saggau, C.; Schiminsky, E.; Dargvainiene, J.; Schroder, I.; Wieters, I.; Khodamoradi, Y.; et al. Low-Avidity CD4(+) T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Unexposed Individuals and Humans with Severe COVID-19. Immunity 2020, 53, 1258–1271.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bert, N.; Tan, A.T.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Hafezi, M.; Chia, A.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Lin, M.; Tan, N.; Linster, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls. Nature 2020, 584, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.I.; Mateus, J.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Rawlings, S.A.; Sutherland, A.; Premkumar, L.; Jadi, R.S.; et al. Targets of T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus in Humans with COVID-19 Disease and Unexposed Individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, S.; Kode, V.; Bhojak, K.; Karunakaran, C.; Lee, K.; Manoharan, M.; Ramesh, A.; Hv, S.; Srivastava, A.; Sathian, R.; et al. Immunodominant T-cell epitopes from the SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen reveal robust pre-existing T-cell immunity in unexposed individuals. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelde, A.; Bilich, T.; Heitmann, J.S.; Maringer, Y.; Salih, H.R.; Roerden, M.; Lubke, M.; Bauer, J.; Rieth, J.; Wacker, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-derived peptides define heterologous and COVID-19-induced T cell recognition. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Cai, L.; Liao, C.; Yi, H.; Li, Q.; Hu, H.; Deng, Q.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Z.; et al. Pre-Existing Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses Do Not Significantly Impact Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Neutralization. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 772511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wolf, J.; Brice, D.C.; Sun, Y.; Locke, M.; Cherry, S.; Castellaw, A.H.; Wehenkel, M.; Crawford, J.C.; Zarnitsyna, V.I.; et al. Pre-existing humoral immunity to human common cold coronaviruses negatively impacts the protective SARS-CoV-2 antibody response. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 83–96.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.M.; Goodwin, E.C.; Verma, A.; Arevalo, C.P.; Bolton, M.J.; Weirick, M.E.; Gouma, S.; McAllister, C.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Weaver, J.; et al. Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell 2021, 184, 1858–1864.E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, A.; Cranage, M.; Zipeto, D. Is Cross-Reactive Immunity Triggering COVID-19 Immunopathogenesis? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 567710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donofrio, G.; Sartori, C.; Franceschi, V.; Capocefalo, A.; Cavirani, S.; Taddei, S.; Flammini, C.F. Double immunization strategy with a BoHV-4-vectorialized secreted chimeric peptide BVDV-E2/BoHV-1-gD. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6031–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratelli, A.; Capozza, P.; Minesso, S.; Lucente, M.S.; Pellegrini, F.; Tempesta, M.; Franceschi, V.; Buonavoglia, C.; Donofrio, G. Humoral Immune Response in Immunized Sheep with Bovine Coronavirus Glycoproteins Delivered via an Adenoviral Vector. Pathogens 2024, 13, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrera, M.; Macchi, F.; McLean, R.K.; Franceschi, V.; Thakur, N.; Russo, L.; Medfai, L.; Todd, S.; Tchilian, E.Z.; Audonnet, J.C.; et al. Bovine Herpesvirus-4-Vectored Delivery of Nipah Virus Glycoproteins Enhances T Cell Immunogenicity in Pigs. Vaccines 2020, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J.; et al. A serological assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cossu, C.; Franceschi, V.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Bolli, E.; Minesso, S.; Cotti, C.; Conti, L.; Donofrio, G. Cross-Reactive Immune Response of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein to SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111509
Cossu C, Franceschi V, Di Lorenzo A, Bolli E, Minesso S, Cotti C, Conti L, Donofrio G. Cross-Reactive Immune Response of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein to SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111509
Chicago/Turabian StyleCossu, Chiara, Valentina Franceschi, Antonino Di Lorenzo, Elisabetta Bolli, Sergio Minesso, Camilla Cotti, Laura Conti, and Gaetano Donofrio. 2024. "Cross-Reactive Immune Response of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein to SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111509
APA StyleCossu, C., Franceschi, V., Di Lorenzo, A., Bolli, E., Minesso, S., Cotti, C., Conti, L., & Donofrio, G. (2024). Cross-Reactive Immune Response of Bovine Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein to SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111509







