Could Targeting NPM1c+ Misfolding Be a Promising Strategy for Combating Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
Abstract
1. Introduction
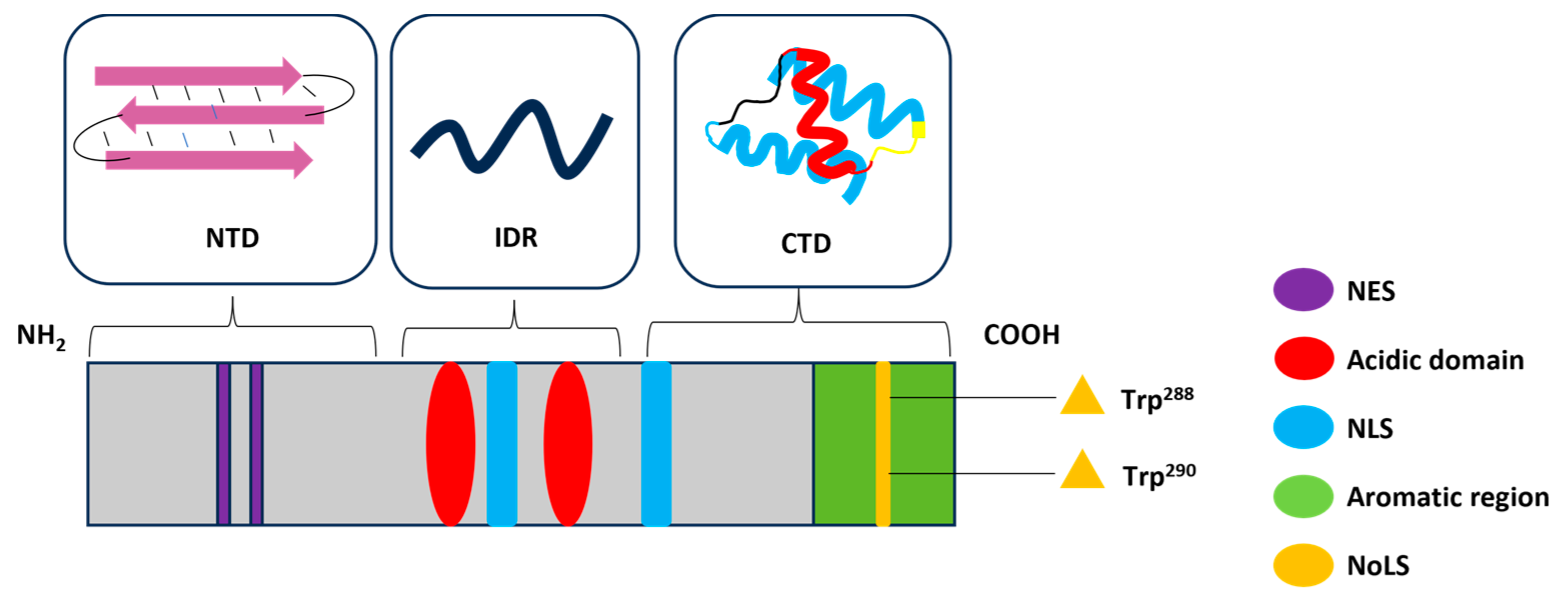
2. Structure and Functions of NPM1
3. NPM1 Is the Most Commonly Mutated Gene in Adult AML
3.1. Common NPM1 Mutations and Structural Consequences
3.2. Rare Mutations of Exon 5 and Fusion Transcripts of NPM1c+
3.3. Consequences of Cytoplasmic Mislocation of NPM1c+
4. NPM1c+ Mutations Govern the Amyloidogenicity of the CTD
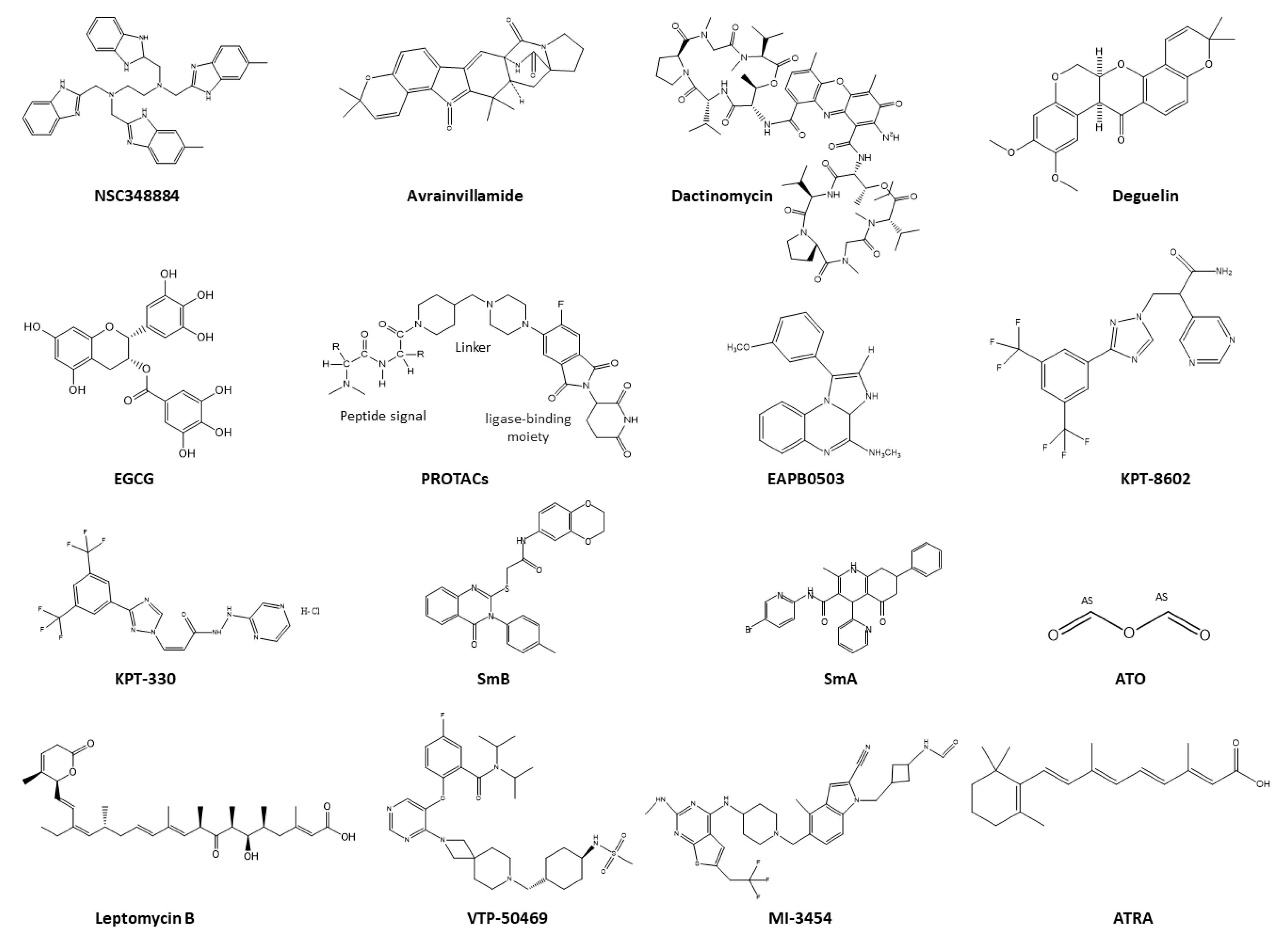
5. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting NPM1c+

5.1. Therapeutics Targeting NPM1 Protein–Protein Interactions
5.2. Therapeutics Targeting the Nucleolus of NPM1c+
5.3. Therapeutics Targeting NPM1c+ Localization
5.4. Therapeutics as Menin Inhibitors
5.5. Therapeutics Targeting Aggregation of NPM1c+
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dohner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, J.; Ling, V.Y.; Hill, G.R.; Lane, S.W. The impact of age, NPM1(mut), and FLT3(ITD) allelic ratio in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2018, 131, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohner, H.; Estey, E.; Grimwade, D.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Buchner, T.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 2017, 129, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Goudswaard, C.S.; Van Putten, W.; Bijl, M.A.; Sanders, M.A.; Hugens, W.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Erpelinck, C.A.; Delwel, R.; Löwenberg, B. Mutations in nucleophosmin (NPM1) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Association with other gene abnormalities and previously established gene expression signatures and their favorable prognostic significance. Blood 2005, 106, 3747–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; International Agency for Research on Cancer Lyon: Lyon, France, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Falini, B.; Gionfriddo, I.; Cecchetti, F.; Ballanti, S.; Pettirossi, V.; Martelli, M.P. Acute myeloid leukemia with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1): Any hope for a targeted therapy? Blood Rev. 2011, 25, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuwaki, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Tsujimoto, M.; Nagata, K. Function of nucleophosmin/B23, a nucleolar acidic protein, as a histone chaperone. FEBS Lett. 2001, 506, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahana, K.; Bhat, K.P.; Jin, A.; Itahana, Y.; Hawke, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Zhang, Y. Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, S.; Bernardi, R.; Rossi, M.; Cheng, K.; Khandker, L.; Manova, K.; Pandolfi, P.P. Role of nucleophosmin in embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Nature 2005, 437, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, A.; Kusler, B.; Pang, W.W.; Weissman, I.L.; Mitchell, B.S.; Park, C.Y. Effect of nucleophosmin1 haploinsufficiency on hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 2012, 26, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Sportoletti, P.; Clohessy, J.G.; Silvia, G.; Pandolfi, P.P. The role of nucleophosmin in hematopoietic stem cells and the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2010, 116, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogev, O.; Saadon, K.; Anzi, S.; Inoue, K.; Shaulian, E. DNA damage–dependent translocation of B23 and p19ARF is regulated by the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, S.K.; Clair, D.K.S. Nucleophosmin blocks mitochondrial localization of p53 and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 16409–16418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.; Alcalay, M.; Pelicci, P. Nucleophosmin and its complex network: A possible therapeutic target in hematological diseases. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2595–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, L.B., Jr.; Kuchenruether, M.; Dadey, D.Y.; Schwope, R.M.; Grisendi, S.; Townsend, R.R.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Weber, J.D. Nucleophosmin serves as a rate-limiting nuclear export chaperone for the Mammalian ribosome. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 7050–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Wang, X.W. Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran–Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, B.I.; Ha, J.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Lim, S.O.; Jung, G.; Suh, S.W. Crystal structure of human nucleophosmin-core reveals plasticity of the pentamer-pentamer interface. Proteins 2007, 69, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, D.; Vascotto, C.; Marasco, D.; D’ambrosio, C.; Romanello, M.; Vitagliano, L.; Pedone, C.; Poletto, M.; Cesaratto, L.; Quadrifoglio, F. Critical lysine residues within the overlooked N-terminal domain of human APE1 regulate its biological functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 8239–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Grace, C.R.; Buljan, M.; Yun, M.-K.; Pytel, N.J.; Satumba, J.; Nourse, A.; Park, C.-G.; Madan Babu, M.; White, S.W. Structural polymorphism in the N-terminal oligomerization domain of NPM1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, 4466–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Cika, J.A.; Guy, C.S.; Ban, D.; Banerjee, P.R.; Stanley, C.B.; Nourse, A.; Deniz, A.A.; Kriwacki, R.W. Nucleophosmin integrates within the nucleolus via multi-modal interactions with proteins displaying R-rich linear motifs and rRNA. eLife 2016, 5, e13571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolli, N.; Nicoletti, I.; De Marco, M.F.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; Mannucci, R.; Martelli, M.P.; Liso, A.; Mecucci, C.; Fabbiano, F. Born to be exported: COOH-terminal nuclear export signals of different strength ensure cytoplasmic accumulation of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6230–6237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hisaoka, M.; Nagata, K.; Okuwaki, M. Intrinsically disordered regions of nucleophosmin/B23 regulate its RNA binding activity through their inter- and intra-molecular association. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gadad, S.S.; Senapati, P.; Syed, S.H.; Rajan, R.E.; Shandilya, J.; Swaminathan, V.; Chatterjee, S.; Colombo, E.; Dimitrov, S.; Pelicci, P.G.; et al. The multifunctional protein nucleophosmin (NPM1) is a human linker histone H1 chaperone. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 2780–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, V.; Kishore, A.H.; Febitha, K.K.; Kundu, T.K. Human histone chaperone nucleophosmin enhances acetylation-dependent chromatin transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7534–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, L.; Falini, B. Nucleophosmin mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: A tale of protein unfolding and mislocalization. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Cika, J.A.; Stanley, C.B.; Nourse, A.; Onuchic, P.L.; Banerjee, P.R.; Phillips, A.H.; Park, C.G.; Deniz, A.A.; Kriwacki, R.W. Self-interaction of NPM1 modulates multiple mechanisms of liquid-liquid phase separation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 842. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Kriwacki, R.W. Phase separation in biology; Functional organization of a higher order. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Kriwacki, R.W. On the relationship status for Arf and NPM1—It’s complicated. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, K.; Szebeni, A.; Olson, M.O. Mapping the functional domains of nucleolar protein B23. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24451–24457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummitt, C.G.; Townsley, F.M.; Johnson, C.M.; Warren, A.J.; Bycroft, M. Structural consequences of nucleophosmin mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23326–23332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Furuichi, Y.; Umekawa, H. Tryptophans 286 and 288 in the C-terminal region of protein B23.1 are important for its nucleolar localization. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burra, S.; Marasco, D.; Malfatti, M.C.; Antoniali, G.; Virgilio, A.; Esposito, V.; Demple, B.; Galeone, A.; Tell, G. Human AP-endonuclease (Ape1) activity on telomeric G4 structures is modulated by acetylatable lysine residues in the N-terminal sequence. DNA Repair 2019, 73, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Tiacci, E.; Martelli, M.P.; Ascani, S.; Pileri, S.A. New classification of acute myeloid leukemia and precursor-related neoplasms: Changes and unsolved issues. Discov. Med. 2010, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Welch, J.S.; Ley, T.J.; Link, D.C.; Miller, C.A.; Larson, D.E.; Koboldt, D.C.; Wartman, L.D.; Lamprecht, T.L.; Liu, F.; Xia, J. The origin and evolution of mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell 2012, 150, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, K.; Schlenk, R.F.; Habdank, M.; Scholl, C.; Rücker, F.G.; Corbacioglu, A.; Bullinger, L.; Fröhling, S.; Döhner, H.; for the AML Study Group (AMLSG). Mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1) predicts favorable prognosis in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: Interaction with other gene mutations. Blood 2005, 106, 3740–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, S.; Schoch, C.; Kern, W.; Mecucci, C.; Tschulik, C.; Martelli, M.F.; Haferlach, T.; Hiddemann, W.; Falini, B. Nucleophosmin gene mutations are predictors of favorable prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. Blood 2005, 106, 3733–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpermann, T.; Schnittger, S.; Eder, C.; Dicker, F.; Meggendorfer, M.; Kern, W.; Schmid, C.; Aul, C.; Staib, P.; Wendtner, C.-M. Molecular subtypes of NPM1 mutations have different clinical profiles, specific patterns of accompanying molecular mutations and varying outcomes in intermediate risk acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpermann, T.; Haferlach, C.; Dicker, F.; Eder, C.; Kohlmann, A.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Schnittger, S. Evaluation of different NPM1 mutations in AML patients according to clinical, cytogenetic and molecular features and impact on outcome. Blood 2013, 122, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Bolli, N.; Shan, J.; Martelli, M.P.; Liso, A.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Mannucci, R.; Rosati, R.; et al. Both carboxy-terminus NES motif and mutated tryptophan(s) are crucial for aberrant nuclear export of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants in NPMc+ AML. Blood 2006, 107, 4514–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M. Nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1819–1820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Sportoletti, P.; Martelli, M.P. NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: From bench to bedside. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2020, 136, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, L.; Gundry, M.C.; Sorcini, D.; Guzman, A.G.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ramabadran, R.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Nabet, B. Mutant NPM1 maintains the leukemic state through HOX expression. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 499–512.e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, M.P.; Rossi, R.; Venanzi, A.; Meggendorfer, M.; Perriello, V.M.; Martino, G.; Spinelli, O.; Ciurnelli, R.; Varasano, E.; Brunetti, L. Novel NPM1 exon 5 mutations and gene fusions leading to aberrant cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in AML. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2021, 138, 2696–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, M.P.; Rossi, R.; Varasano, E.; Specchia, G.; Di Raimondo, F.; Avvisati, G.; Tiacci, E.; Falzetti, F.; Sportoletti, P.; Falini, B. Identification and characterization of novel rare nucleophosmin (NPM1) gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by a combinatorial approach of immunohistochemistry and molecular analyses. Blood 2016, 128, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, C.; Gu, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H. Identification of a novel NPM1 mutation in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, F.L.C.; Mecucci, C.; Falini, B.; Pelicci, P.G.; Meani, N.; Diverio, D.; Bernard, L.; Tizzoni, L.; Volorio, S.; Luzi, L. Acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML) shows a distinct gene expression profile characterized by up-regulation of genes involved in stem-cell maintenance. Blood 2005, 106, 899–902. [Google Scholar]
- Ozyerli-Goknar, E.; Nizamuddin, S.; Timmers, H.M. A box of chemistry to inhibit the MEN1 tumor suppressor gene promoting leukemia. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.H.; Aboukameel, A.; Khan, H.; Bannoura, S.; Deol, A.; Yang, J.; Dyson, G.; Azmi, A.; Polin, L.; Maciejewski, J.P. The Clinical Menin Inhibitor Ziftomenib and the Nuclear Export Inhibitor Selinexor Synergistically Inhibit the Growth of MLL-r AML. Blood 2023, 142, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, B.J.; Heller, M.; Toma, S.; Pavlu, J. The cytological features of NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, O.K.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Baraban, E.; Ok, C.Y.; Geyer, J.T.; Philip, J.K.; Kurzer, J.H.; Rogers, H.J.; Nardi, V.; Stone, R.M. Clinical, immunophenotypic, and genomic findings of acute undifferentiated leukemia and comparison to acute myeloid leukemia with minimal differentiation: A study from the bone marrow pathology group. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, B.J.; Béné, M.C. Morphological and immunophenotypic clues to the WHO categories of acute myeloid leukaemia. Acta Haematol. 2019, 141, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redner, R.L.; Rush, E.A.; Faas, S.; Rudert, W.A.; Corey, S.J. The t(5;17) variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia expresses a nucleophosmin-retinoic acid receptor fusion. Blood 1996, 87, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.; Kirstein, M.; Valentine, M.; Dittmer, K.; Shapiro, D.; Look, A.; Saltman, D. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1995, 267, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Nicoletti, I.; Martelli, M.F.; Mecucci, C. Acute myeloid leukemia carrying cytoplasmic/mutated nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML): Biologic and clinical features. Blood 2007, 109, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motea, E.A.; Berdis, A.J. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase: The story of a misguided DNA polymerase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 1151–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Sportoletti, P.; Ito, K.; Clohessy, J.G.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Kutok, J.L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The cytoplasmic NPM mutant induces myeloproliferation in a transgenic mouse model. Blood 2010, 115, 3341–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarka, J.; Short, N.J.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Issa, G.C. Nucleophosmin 1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes 2020, 11, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, D.H.; Young, M.A.; Lamprecht, T.L.; Helton, N.M.; Fulton, R.; O’Laughlin, M.; Fronick, C.; Magrini, V.; Demeter, R.T.; Miller, C.A. Epigenomic analysis of the HOX gene loci reveals mechanisms that may control canonical expression patterns in AML and normal hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianigiani, G.; Betti, C.; Bigerna, B.; Rossi, R.; Brunetti, L. PU. 1 subcellular localization in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.; Gudgin, E.; Horton, S.; Giotopoulos, G.; Meduri, E.; Robson, S.; Cannizzaro, E.; Osaki, H.; Wiese, M.; Putwain, S. Recurrent mutations, including NPM1c, activate a BRD4-dependent core transcriptional program in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 28, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, D.; Ruggiero, A.; Vascotto, C.; Poletto, M.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Tell, G.; Vitagliano, L. Role of mutual interactions in the chemical and thermal stability of nucleophosmin NPM1 domains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; La Manna, S.; De Benedictis, I.; Brandi, P.; Marasco, D. Perspectives in peptide-based vaccination strategies for syndrome coronavirus 2 pandemic. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 578382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Cascella, R.; Cecchi, C.; Russo, A.; Leone, M.; Penco, A.; Relini, A.; Federici, L.; Di Matteo, A. Nucleophosmin contains amyloidogenic regions that are able to form toxic aggregates under physiological conditions. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3689–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Diaferia, C.; La Manna, S.; Giannini, C.; Sibillano, T.; Accardo, A.; Morelli, G.; Novellino, E.; Marasco, D. Insights into amyloid-like aggregation of H2 region of the C-terminal domain of nucleophosmin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, P.L.; Di Natale, C.; Leone, M.; Cascella, R.; Cecchi, C.; Lirussi, L.; Antoniali, G.; Riccardi, D.; Morelli, G.; Tell, G. Destabilisation, aggregation, toxicity and cytosolic mislocalisation of nucleophosmin regions associated with acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 59129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, P.L.; Di Natale, C.; Leone, M.; Poletto, M.; Vitagliano, L.; Tell, G.; Marasco, D. G-quadruplex DNA recognition by nucleophosmin: New insights from protein dissection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; La Manna, S.; Krauss, I.R.; Malfitano, A.M.; Novellino, E.; Federici, L.; De Cola, A.; Di Matteo, A.; D’Errico, G.; Marasco, D. Nucleophosmin-1 regions associated with acute myeloid leukemia interact differently with lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Florio, D.; Di Somma, S.; Di Matteo, A.; Federici, L.; Netti, P.A.; Morelli, G.; Malfitano, A.M.; Marasco, D. Proteostasis unbalance of nucleophosmin 1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: An aggregomic perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3501–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; La Manna, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Di Somma, S.; Florio, D.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Novellino, E.; Netti, P.A.; Marasco, D. Structural insights into amyloid structures of the C-terminal region of nucleophosmin 1 in type A mutation of acute myeloid leukemia. Biochim. Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 2019, 1867, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florio, D.; Cuomo, M.; Iacobucci, I.; Ferraro, G.; Mansour, A.M.; Monti, M.; Merlino, A.; Marasco, D. Modulation of amyloidogenic peptide aggregation by photoactivatable CO-releasing ruthenium (II) complexes. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manna, S.; Florio, D.; Di Natale, C.; Napolitano, F.; Malfitano, A.M.; Netti, P.A.; De Benedictis, I.; Marasco, D. Conformational consequences of NPM1 rare mutations: An aggregation perspective in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 113, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manna, S.; Florio, D.; Di Natale, C.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Sibillano, T.; Netti, P.A.; Giannini, C.; Marasco, D. Type F mutation of nucleophosmin 1 Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A tale of disorder and aggregation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manna, S.; Roviello, V.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Diaferia, C.; Giannini, C.; Sibillano, T.; Morelli, G.; Novellino, E.; Marasco, D. Amyloid fibers deriving from the aromatic core of C-terminal domain of nucleophosmin 1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Manna, S.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Roviello, V.; Borbone, F.; Florio, D.; Di Natale, C.; Bigi, A.; Cecchi, C.; Cascella, R.; Giannini, C. The acute myeloid leukemia-associated Nucleophosmin 1 gene mutations dictate amyloidogenicity of the C-terminal domain. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2311–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Manna, S.; Florio, D.; Di Natale, C.; Lagreca, E.; Sibillano, T.; Giannini, C.; Marasco, D. Type C mutation of nucleophosmin 1 acute myeloid leukemia: Consequences of intrinsic disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2022, 1866, 130173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, Z.L.; Brito, R.M. Structure and aggregation mechanisms in amyloids. Molecules 2020, 25, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, D.; La Manna, S.; Di Natale, C.; Leone, M.; Mercurio, F.A.; Napolitano, F.; Malfitano, A.M.; Marasco, D. Insights into Network of Hot Spots of Aggregation in Nucleophosmin 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, P.; Chang, L.-L.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Zhu, H.-H. Targeted therapy in NPM1-mutated AML: Knowns and unknowns. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 972606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, R.; Pianigiani, G.; Sciabolacci, S.; Perriello, V.M.; Marra, A.; Cardinali, V.; Pierangeli, S.; Milano, F.; Gionfriddo, I.; Brunetti, L.; et al. Current status and future perspectives in targeted therapy of NPM1-mutated AML. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2351–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Martelli, M.P. Dactinomycin in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1180–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Shakalya, K.; Stejskal, A.; Goldman, A.; Beeck, S.; Cooke, L.; Mahadevan, D. NSC348884, a nucleophosmin inhibitor disrupts oligomer formation and induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4210–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.F.; Han, L.L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, F. The effect of small molecule inhibitor NSC348884 on nucleophosmin 1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 9145–9151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Šašinková, M.; Heřman, P.; Holoubek, A.; Strachotová, D.; Otevřelová, P.; Grebeňová, D.; Kuželová, K.; Brodská, B. NSC348884 cytotoxicity is not mediated by inhibition of nucleophosmin oligomerization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, H.; Chan, K.-P.; Andresen, V.; Hanley, M.L.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Myers, A.G. Interactions of the natural product (+)-avrainvillamide with nucleophosmin and exportin-1 mediate the cellular localization of nucleophosmin and its AML-associated mutants. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, V.; Erikstein, B.S.; Mukherjee, H.; Sulen, A.; Popa, M.; Sørnes, S.; Reikvam, H.; Chan, K.-P.; Hovland, R.; McCormack, E. Anti-proliferative activity of the NPM1 interacting natural product avrainvillamide in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollstein, U. Actinomycin. Chemistry and mechanism of action. Chem. Rev. 1974, 74, 625–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionfriddo, I.; Brunetti, L.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Cardinali, V.; Ranieri, R.; Venanzi, A.; Pierangeli, S.; Vetro, C.; Spinozzi, G. Dactinomycin induces complete remission associated with nucleolar stress response in relapsed/refractory NPM1-mutated AML. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2552–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.P.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Pierangeli, S.; Mulas, F.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; Pettirossi, V.; Rossi, R. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 125, 3455–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Rerolle, D.; Berthier, C.; Hleihel, R.; Sakamoto, T.; Quentin, S.; Benhenda, S.; Morganti, C.; Wu, C.; Conte, L.; et al. Actinomycin D Targets NPM1c-Primed Mitochondria to Restore PML-Driven Senescence in AML Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 3198–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.; Mann, K.K.; Miller, W.H., Jr. Arsenic trioxide: Mechanisms of action. Semin. Hematol. 2002, 39, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddikuzzaman, N.; Guruvayoorappan, C.; Berlin Grace, V.M. All trans retinoic acid and cancer. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2010, 33, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajj, H.; Dassouki, Z.; Berthier, C.; Raffoux, E.; Ades, L.; Legrand, O.; Hleihel, R.; Sahin, U.; Tawil, N.; Salameh, A.; et al. Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide trigger degradation of mutated NPM1, resulting in apoptosis of AML cells. Blood 2015, 125, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y. Molecular mechanisms of deguelin-induced apoptosis in transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagle, D.G.; Ferreira, D.; Zhou, Y.-D. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Chemical and biomedical perspectives. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Wen, L.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, Y. Deguelin, a selective silencer of the NPM1 mutant, potentiates apoptosis and induces differentiation in AML cells carrying the NPM1 mutation. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.T.; Ly, B.T.; Vu, H.A.; Sato, Y.; Dung, P.C.; Xinh, P.T. Down-regulated expression of NPM1 in IMS-M2 cell line by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaille, F.; Solassol, I.; Enjalbal, C.; Bertrand, B.; Doulain, P.-E.; Vappiani, J.; Bonnet, P.-A.; Deleuze-Masquéfa, C.; Bressolle, F.M. Structural characterization of in vitro metabolites of the new anticancer agent EAPB0503 by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 88, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skayneh, H.; Jishi, B.; Hleihel, R.; Hamie, M.; El Hajj, R.; Deleuze-Masquefa, C.; Bonnet, P.-A.; El Sabban, M.; El Hajj, H. EAPB0503, an imidazoquinoxaline derivative modulates SENP3/ARF mediated SUMOylation, and induces NPM1c degradation in NPM1 mutant AML. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabbouh, A.I.; Hleihel, R.S.; Saliba, J.L.; Karam, M.M.; Hamie, M.H.; Wu, H.C.J.; Berthier, C.P.; Tawil, N.M.; Bonnet, P.A.A.; Deleuze-Masquefa, C. Imidazoquinoxaline derivative EAPB0503: A promising drug targeting mutant nucleophosmin 1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2017, 123, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Crews, C.M. PROTACs: Past, present and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5214–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; He, L.; Hu, C.; Yang, S. Proteolysis-targeting chimeras: A promising technique in cancer therapy for gaining insights into tumor development. Cancer Lett. 2022, 539, 215716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Khan, S.; Huo, Z.; Lv, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Hromas, R.; Xu, M.; Zheng, G. Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) are emerging therapeutics for hematologic malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, T.; Pradeep, S.; Wu, S.Y.; Rupaimoole, R.; Zand, B.; Wen, Y.; Gharpure, K.M.; Nagaraja, A.S.; Hu, W.; Cho, M.S. XPO1/CRM1 inhibition causes antitumor effects by mitochondrial accumulation of eIF5A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3286–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, N.; Wolff, B.; Sekimoto, T.; Schreiner, E.P.; Yoneda, Y.; Yanagida, M.; Horinouchi, S.; Yoshida, M. Leptomycin B inhibition of signal-mediated nuclear export by direct binding to CRM1. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 242, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Q.; Burstein, E.; Yang, S.; Jia, D. Inhibiting cancer cell hallmark features through nuclear export inhibition. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 16010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, R.; Savona, M.; Baz, R.; Andreeff, M.; Gabrail, N.; Gutierrez, M.; Savoie, L.; Mau-Sorensen, P.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Yee, K. A phase 1 clinical trial of single-agent selinexor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2017, 129, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchin, J.; Berezovskaya, A.; Conway, A.S.; Galinsky, I.A.; Stone, R.M.; Baloglu, E.; Senapedis, W.; Landesman, Y.; Kauffman, M.; Shacham, S. KPT-8602, a second-generation inhibitor of XPO1-mediated nuclear export, is well tolerated and highly active against AML blasts and leukemia-initiating cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.A.; Friedlander, S.Y.; Arrate, M.P.; Chang, H.; Gorska, A.E.; Fuller, L.D.; Ramsey, H.E.; Kashyap, T.; Argueta, C.; Debler, S. Venetoclax response is enhanced by selective inhibitor of nuclear export compounds in hematologic malignancies. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkar, S.; Thiel, A.; Hua, X. Menin: A scaffold protein that controls gene expression and cell signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiropoulos, B.; Humphries, R. Hox genes in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6766–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klossowski, S.; Miao, H.; Kempinska, K.; Wu, T.; Purohit, T.; Kim, E.; Linhares, B.M.; Chen, D.; Jih, G.; Perkey, E. Menin inhibitor MI-3454 induces remission in MLL1-rearranged and NPM1-mutated models of leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckelmann, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Wong, E.M.; Hatton, C.; Giovinazzo, H.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Rücker, F.G.; Döhner, K.; McGeehan, G.M. Therapeutic targeting of preleukemia cells in a mouse model of NPM1 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Science 2020, 367, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, M.; Bourgeois, W.; Armstrong, S.A.; Wang, E.S. Menin inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia—What does the future hold? Cancer J. 2022, 28, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Evans, K.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Eschle, B.K.; Hatton, C.; Uckelmann, H.J.; Ross, K.N.; Perner, F.; Olsen, S.N.; Pritchard, T. A menin-MLL inhibitor induces specific chromatin changes and eradicates disease in models of MLL-rearranged leukemia. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 660–673.e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.C.; Querolle, O.; Dai, X.; Thuring, J.W.; Verhulst, T.; Marien, A.; Goffin, D.; Cai, W.; Keersmaekers, V.; Eyassu, F. Pharmacological characterization of JNJ-75276617, a menin-KMT2A inhibitor, as targeted treatment for KMT2A-altered and NPM1-mutant acute leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 5928–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somanath, P.; Lu, D.; Law, B.; Archer, T.C.; Cacovean, A.; Palmer, J.T.; Kinoshita, T.; Butler, T. Novel Irreversible Menin Inhibitor, BMF-219, Shows Potent Single Agent Activity in Clinically Relevant DLBCL Cells. Blood 2021, 138, 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Kishtagari, A.; Carraway, H.; Schiller, G.; Curran, E.; Yadav, B.; Cacovean, A.; Morris, S.; Butler, T.; Lancet, J. P587: COVALENT-101: A phase 1 study of BMF-219, a novel oral irreversible menin inhibitor, in patients with relapsed/refractory acute leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 486–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Shimizu, T.; Kato, D.; Furuta, Y.; Kamioka, S.; Ban, H.; Ymamoto, S.; Yokoyama, A.; Kitabayashi, I. Preclinical Evaluation of a Novel Orally Bioavailable Menin-MLL Interaction Inhibitor, DSP-5336, for the Treatment of Acute Leukemia Patients with MLL-Rearrangement or NPM1 Mutation. Blood 2021, 138, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, M.R. Protein Misfolding and Aggregation in Proteinopathies: Causes, Mechanism and Cellular Response. Diseases 2023, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, D.; Roviello, V.; La Manna, S.; Napolitano, F.; Maria Malfitano, A.; Marasco, D. Small molecules enhancers of amyloid aggregation of C-terminal domain of Nucleophosmin 1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 127, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Martelli, M.P.; Brunetti, L.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Andresen, V. The NPM1 mutant defines AML irrespective of blast count. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, E187–E189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Martelli, M.P. How I diagnose and treat NPM1-mutated AML. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2021, 137, 589–599. [Google Scholar]


| Nucleotide Sequence | Protein | |
|---|---|---|
| wt NPM1 | GATCTCTG…GCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQWRKSL294 |
| Common mutations | GATCTCTGTCTGGCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCLAVEEVSLRK298 |
| GATCTCTGCATGGCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCMAVEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTGCGTGGCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCVAVEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTGCCTGGCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCLAVEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTG…GCAGTCTCTTGCCCAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQSLAQVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTG…GCAGTCCCTGGAGAAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQSLEKVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTG…GCAGTCTCTTTCTAAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQSLSKVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTCCCGGGCAGT…AAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLSRAVEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTG…GCAGTCCCTTTCCAAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQSLSKVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTGTAGCGCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCTAVEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTGCCACGCAGT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCHAVEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTGGCAGCGTTTCCAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQRFQEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTGTACCTTCCT…GGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLCTFLEEVSLRK298 | |
| GATCTCTG…GCAGAGGATGGAGGAAGTCTCTTTAAGAAAATAG | 286DLWQRMEEVSLRK298 | |
| Nucleotide Change | ||
| Rare mutations | c.864_876delinsTCGGAGTCTCGGCGGAC | 286DLCRSLGGLSLRKA299 |
| c.864_873delinsTCAAGACTTTCTTA | 286DLCQDFLKVSLRKA299 | |
| c.867_875delinsAGATTTCTTAAATC | 286DLWQDFLNRLFKRIVA301 | |
| c.868_876delinsGGGATAGCGATGC | 286DLWQGIAMLSLRKA299 | |
| c.868_876delinsGGGGTGGGGAATC | 286DLWQGVGNLSLRKA299 | |
| c.863_871delinsCGACCCTCCTGGG | 286DLSTLLGEVSLRKA299 |
| In-Frame Insertion/Duplications | Protein | |
|---|---|---|
| Exon 5 Mutations | c408–409 (F,5′-GCGGAGGATGTGAAACTCTTA) | DVKLL136AEDVKLL…286DLWQWRKSL294 |
| c409–410 (F,5′-AATGATCTGTCACTTCTG) | DVKLL137K | |
| c424–425 (F,5′-TTTCTGCCTTAAGTATATCTGGAAAGC) | ISGK141LSALSISGK…286DLWQWRKSL294 | |
| c399–400 (F,5′-CAACTCTTA) and c400–401 (F,5′-GTGGGCTGC) | EEDV134QLLSGLQ…286DLWQWRKSL294 | |
| c406–423 (F,5′-GCCCTGGAACTGGGGAAC) | DVKL135ALELGNLSI…286DLWQWRKSL294 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florio, D.; Marasco, D. Could Targeting NPM1c+ Misfolding Be a Promising Strategy for Combating Acute Myeloid Leukemia? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020811
Florio D, Marasco D. Could Targeting NPM1c+ Misfolding Be a Promising Strategy for Combating Acute Myeloid Leukemia? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020811
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorio, Daniele, and Daniela Marasco. 2024. "Could Targeting NPM1c+ Misfolding Be a Promising Strategy for Combating Acute Myeloid Leukemia?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020811
APA StyleFlorio, D., & Marasco, D. (2024). Could Targeting NPM1c+ Misfolding Be a Promising Strategy for Combating Acute Myeloid Leukemia? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020811








