New Functional Motifs for the Targeted Localization of Proteins to the Nucleolus in Drosophila and Human Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
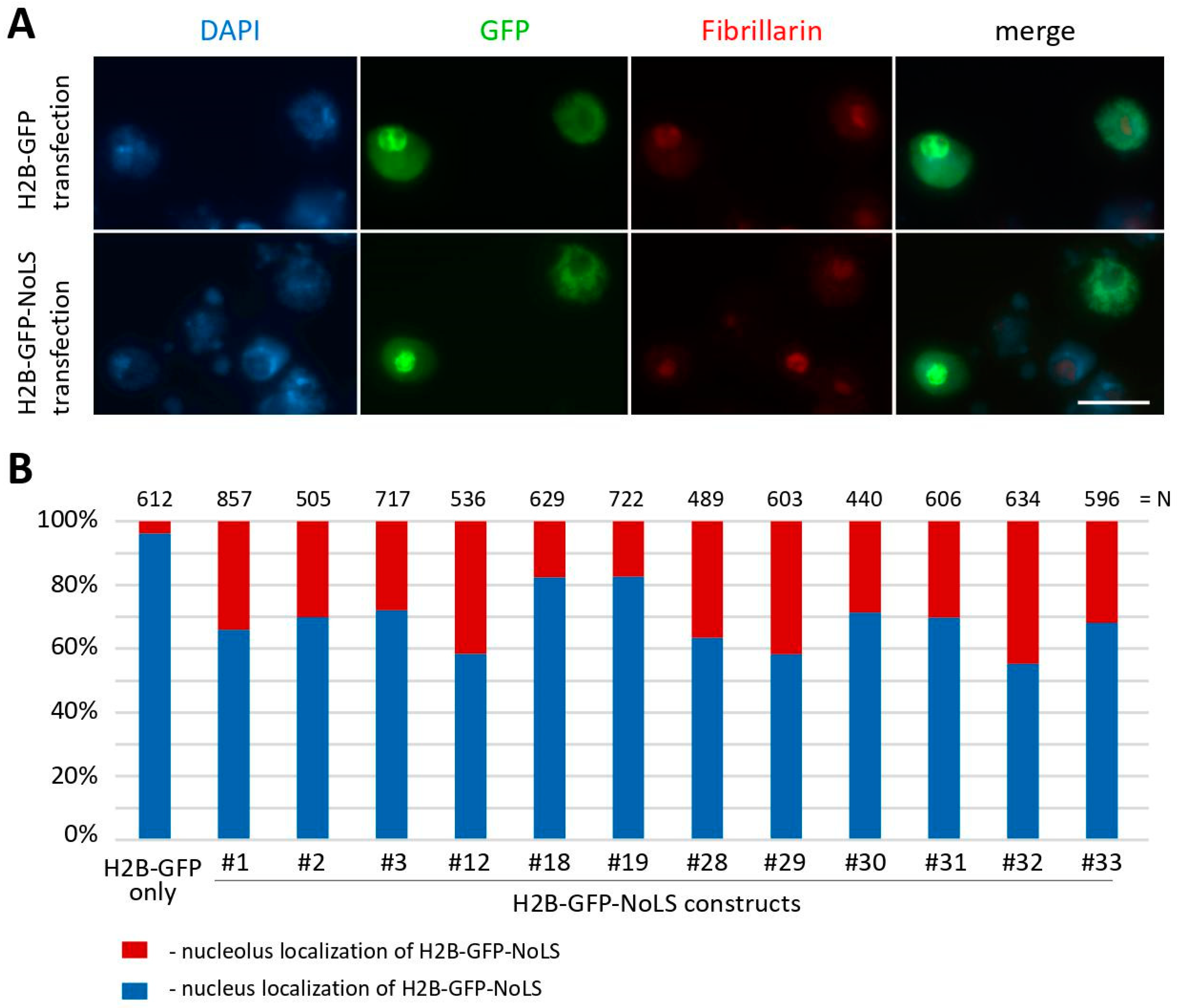
2.1. Testing of Previously Characterized NoLS Motifs in Drosophila Cell Cultures
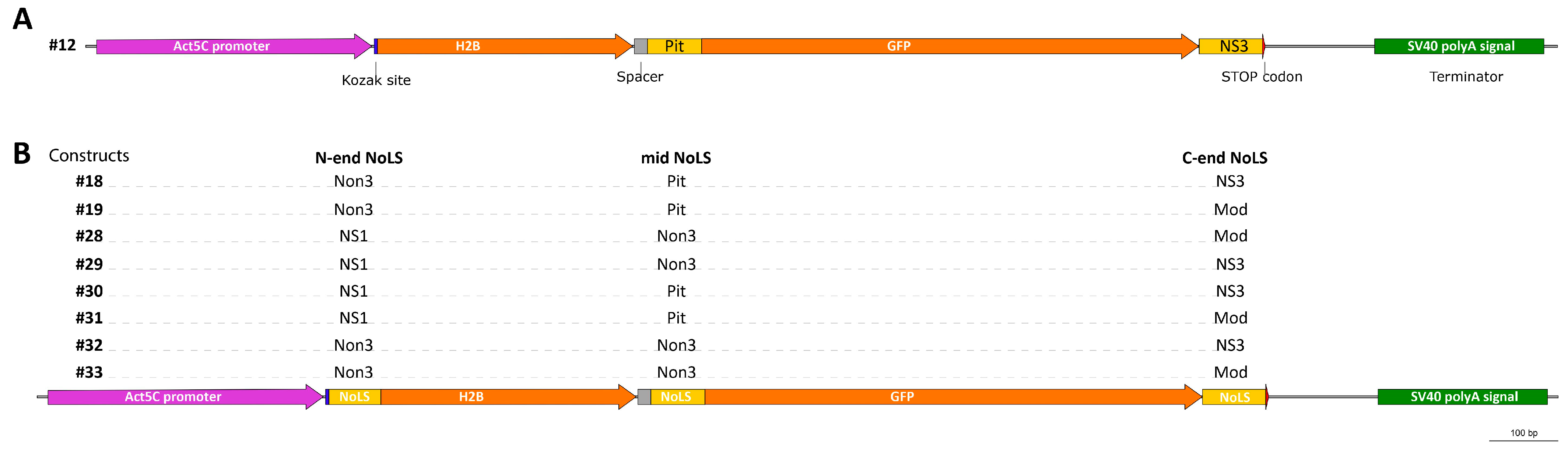
2.2. NoLS Motifs from Drosophila Nucleolus Proteins
2.3. NoLS Motifs from Drosophila Nucleolus Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of total RNA, Reverse Transcription
4.2. Isolation of Genomic DNA
4.3. Generation of the p-p.Actin5C-H2B-GFP Constructs Encoding Proteins with the RKKRKKK, RRRRRRRRR and WRRQARFK NoLS Motifs
4.4. Generation of the p-p.Actin5C-H2B-GFP Constructs Encoding Proteins with Different Predicted Drosophila NoLS Motifs
4.5. Transfection of Kc167, S2 and HEK293T Cells
4.6. Immunofluorescence Staining and Microscope Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lafontaine, D.L.J.; Riback, J.A.; Bascetin, R.; Brangwynne, C.P. The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, T. The nucleolus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a000638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersaglieri, C.; Santoro, R. Genome organization in and around the nucleolus. Cells 2019, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Santoro, R. Regulation and roles of the nucleolus in embryonic stem cells: From ribosome biogenesis to genome organization. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noller, H.F. RNA structure: Reading the ribosome. Science 2005, 309, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Koningsbruggen, S.; Gierliński, M.; Schofield, P.; Martin, D.; Barton, G.J.; Ariyurek, Y.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Lamond, A.I. High-resolution whole-genome sequencing reveals that specific chromatin domains from most human chromosomes associate with nucleoli. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 3735–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillinger, S.; Straub, T.; Németh, A. Nucleolus association of chromosomal domains is largely maintained in cellular senescence despite massive nuclear reorganisation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg Olausson, K.; Nistér, M.; Lindström, M.S. Loss of nucleolar histone chaperone NPM1 triggers rearrangement of heterochromatin and synergizes with a deficiency in DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A to drive ribosomal DNA transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34601–34619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoni, N.; Langer, S.; Fauth, C.; Bernardi, G.; Cremer, T.; Turner, B.M.; Zink, D. Nuclear organization of mammalian genomes: Polar chromosome territories build up functionally distinct higher order compartments. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Paolella, G.; Ramos, C.; Lamond, A.I. Spatial organization of large-scale chromatin domains in the nucleus: A magnified view of single chromosome territories. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoriw, A.M.; Starmer, J.; Yee, D.; Magnuson, T. Nucleolar association and transcriptional inhibition through 5S rDNA in mammals. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakočiūnas, T.; Domange Jordö, M.; Aït Mebarek, M.; Bünner, C.M.; Verhein-Hansen, J.; Oddershede, L.B.; Thon, G. Subnuclear relocalization and silencing of a chromosomal region by an ectopic ribosomal DNA repeat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4465–E4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizhanova, A.; Yan, A.; Yu, J.; Zhu, L.J.; Kaufman, P.D. Distinct features of nucleolus-associated domains in mouse embryonic stem cells. Chromosoma 2020, 129, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Verdun, D.; Roussel, P.; Thiry, M.; Sirri, V.; Lafontaine, D.L.J. The nucleolus: Structure/function relationship in RNA metabolism. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2010, 1, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizhanova, A.; Kaufman, P.D. Close to the edge: Heterochromatin at the nucleolar and nuclear peripheries. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2021, 1864, 194666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenström, L.; Mahdessian, D.; Gnann, C.; Cesnik, A.J.; Ouyang, W.; Leonetti, M.D.; Uhlén, M.; Cuylen-Haering, S.; Thul, P.J.; Lundberg, E. Mapping the nucleolar proteome reveals a spatiotemporal organization related to intrinsic protein disorder. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, A.V.; Lemos, B. Ribosomal DNA and the nucleolus as keystones of nuclear architecture, organization, and function. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.; MacQuarrie, K.L.; Freeman, E.; Lin, A.; Willis, A.B.; Xu, Z.; Alvarez, A.A.; Ma, Y.; White, B.E.P.; Foltz, D.R.; et al. Nucleoli and the nucleoli-centromere association are dynamic during normal development and in cancer. Mol. Biol. Cell 2023, 34, br5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padeken, J.; Mendiburo, M.J.; Chlamydas, S.; Schwarz, H.-J.; Kremmer, E.; Heun, P. The nucleoplasmin homolog NLP mediates centromere clustering and anchoring to the nucleolus. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarovaia, O.V.; Minina, E.P.; Sheval, E.V.; Onichtchouk, D.; Dokudovskaya, S.; Razin, S.V.; Vassetzky, Y.S. Nucleolus: A central hub for nuclear functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersaglieri, C.; Kresoja-Rakic, J.; Gupta, S.; Bär, D.; Kuzyakiv, R.; Panatta, M.; Santoro, R. Genome-wide maps of nucleolus interactions reveal distinct layers of repressive chromatin domains. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertii, A.; Ou, J.; Yu, J.; Yan, A.; Pagès, H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.J.; Kaufman, P.D. Two contrasting classes of nucleolus-associated domains in mouse fibroblast heterochromatin. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragoczy, T.; Telling, A.; Scalzo, D.; Kooperberg, C.; Groudine, M. Functional redundancy in the nuclear compartmentalization of the late-replicating genome. Nucleus 2014, 5, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, A.; Längst, G. Genome organization in and around the nucleolus. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickersgill, H.; Kalverda, B.; de Wit, E.; Talhout, W.; Fornerod, M.; van Steensel, B. Characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster genome at the nuclear lamina. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guelen, L.; Pagie, L.; Brasset, E.; Meuleman, W.; Faza, M.B.; Talhout, W.; Eussen, B.H.; de Klein, A.; Wessels, L.; de Laat, W.; et al. Domain organization of human chromosomes revealed by mapping of nuclear lamina interactions. Nature 2008, 453, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peric-Hupkes, D.; Meuleman, W.; Pagie, L.; Bruggeman, S.W.M.; Solovei, I.; Brugman, W.; Gräf, S.; Flicek, P.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; van Lohuizen, M.; et al. Molecular maps of the reorganization of genome-nuclear lamina interactions during differentiation. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bemmel, J.G.; Pagie, L.; Braunschweig, U.; Brugman, W.; Meuleman, W.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; van Steensel, B. The insulator protein SU(HW) fine-tunes nuclear lamina interactions of the Drosophila genome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, K.; Egelhofer, T.A.; Strome, S.; Lieb, J.D. Caenorhabditis elegans chromosome arms are anchored to the nuclear membrane via discontinuous association with LEM-2. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindyurin, A.V.; Ilyin, A.A.; Ivankin, A.V.; Tselebrovsky, M.V.; Nenasheva, V.V.; Mikhaleva, E.A.; Pagie, L.; van Steensel, B.; Shevelyov, Y.Y. The large fraction of heterochromatin in Drosophila neurons is bound by both B-type lamin and HP1a. Epigenet. Chromatin 2018, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, S.G.; Dauban, L.; van Steensel, B. Lamina-associated domains: Tethers and looseners. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2022, 74, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feric, M.; Vaidya, N.; Harmon, T.S.; Mitrea, D.M.; Zhu, L.; Richardson, T.M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Pappu, R.V.; Brangwynne, C.P. Coexisting liquid phases underlie nucleolar subcompartments. Cell 2016, 165, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersaglieri, C.; Santoro, R. Methods for mapping 3D-chromosome architecture around nucleoli. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2023, 81, 102171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, M.; Smetana, K.; Busch, H. Quantitative aspects of isolation of nucleoli of the Walker carcinosarcoma and liver of the rat. Cancer Res. 1963, 23, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, G.J.; Bridger, J.M.; Cuthbert, A.P.; Newbold, R.F.; Bickmore, W.A.; McStay, B. Human acrocentric chromosomes with transcriptionally silent nucleolar organizer regions associate with nucleoli. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2867–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontvianne, F.; Carpentier, M.-C.; Durut, N.; Pavlištová, V.; Jaške, K.; Schořová, Š.; Parrinello, H.; Rohmer, M.; Pikaard, C.S.; Fojtová, M.; et al. Identification of nucleolus-associated chromatin domains reveals a role for the nucleolus in 3D organization of the A. thaliana genome. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinodoz, S.A.; Ollikainen, N.; Tabak, B.; Palla, A.; Schmidt, J.M.; Detmar, E.; Lai, M.M.; Shishkin, A.A.; Bhat, P.; Takei, Y.; et al. Higher-order inter-chromosomal hubs shape 3D genome organization in the nucleus. Cell 2018, 174, 744–757.e724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Lemos, B. The long-range interaction map of ribosomal DNA arrays. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Yun, J.; Zheng, S.; Ollikainen, N.; Pierson, N.; White, J.; Shah, S.; Thomassie, J.; Suo, S.; Eng, C.-H.L.; et al. Integrated spatial genomics reveals global architecture of single nuclei. Nature 2021, 590, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, F.M.; Han, S.; Parker, K.R.; Kaewsapsak, P.; Xu, J.; Boettiger, A.N.; Chang, H.Y.; Ting, A.Y. Atlas of subcellular RNA localization revealed by APEX-Seq. Cell 2019, 178, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Steensel, B.; Delrow, J.; Henikoff, S. Chromatin profiling using targeted DNA adenine methyltransferase. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmott, E.; Hiscox, J.A. Nucleolar targeting: The hub of the matter. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbach, A.; Bailey, S.T.; Ghosh, S.; Schmid, J.A. Cytosolic, nuclear and nucleolar localization signals determine subcellular distribution and activity of the NF-κB inducing kinase NIK. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, M.L.; Dove, B.K.; Jackson, R.M.; Collins, R.; Brooks, G.; Hiscox, J.A. Delineation and modelling of a nucleolar retention signal in the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. Traffic 2006, 7, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musinova, Y.R.; Lisitsyna, O.M.; Golyshev, S.A.; Tuzhikov, A.I.; Polyakov, V.Y.; Sheval, E.V. Nucleolar localization/retention signal is responsible for transient accumulation of histone H2B in the nucleolus through electrostatic interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.S.; Boisvert, F.-M.; McDowall, M.D.; Lamond, A.I.; Barton, G.J. Characterization and prediction of protein nucleolar localization sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7388–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.S.; Troshin, P.V.; Barton, G.J. NoD: A nucleolar localization sequence detector for eukaryotic and viral proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, G.J.; van Bemmel, J.G.; Braunschweig, U.; Talhout, W.; Kind, J.; Ward, L.D.; Brugman, W.; de Castro, I.J.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Bussemaker, H.J.; et al. Systematic protein location mapping reveals five principal chromatin types in Drosophila cells. Cell 2010, 143, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bemmel, J.G.; Filion, G.J.; Rosado, A.; Talhout, W.; de Haas, M.; van Welsem, T.; van Leeuwen, F.; van Steensel, B. A network model of the molecular organization of chromatin in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.D.; Kuo, M.-L.; Bothner, B.; DiGiammarino, E.L.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J. Cooperative signals governing ARF-Mdm2 interaction and nucleolar localization of the complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horke, S.; Reumann, K.; Schweizer, M.; Will, H.; Heise, T. Nuclear trafficking of La protein depends on a newly identified nucleolar localization signal and the ability to bind RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26563–26570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viiri, K.M.; Korkeamäki, H.; Kukkonen, M.K.; Nieminen, L.K.; Lindfors, K.; Peterson, P.; Mäki, M.; Kainulainen, H.; Lohi, O. SAP30L interacts with members of the Sin3A corepressor complex and targets Sin3A to the nucleolus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3288–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMario, P.; James, A.; Raje, H. rDNA and Nucleologenesis in Drosophila. In Proteins of the Nucleolus; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 39–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawardena, S.R.; Ruis, B.L.; Meyer, J.A.; Kapoor, M.; Conklin, K.F. NOM1 targets protein phosphatase I to the nucleolus. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Zheng, X.; McNutt, M.A.; Guang, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Gong, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhang, B. NAT10, a nucleolar protein, localizes to the midbody and regulates cytokinesis and acetylation of microtubules. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Goda, N.; Iwaya, N.; Tenno, T.; Shirakawa, M.; Hiroaki, H. Structure and function of the N-terminal nucleolin binding domain of nuclear valosin-containing protein-like 2 (NVL2) harboring a nucleolar localization signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21732–21741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, J.A. RNA viruses: Hijacking the dynamic nucleolus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępiński, D. Functional ultrastructure of the plant nucleolus. Protoplasma 2014, 251, 1285–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindyurin, A.V. Genome-wide cell type-specific mapping of in vivo chromatin protein binding using an FLP-inducible DamID system in Drosophila. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1654, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renda, F.; Pellacani, C.; Strunov, A.; Bucciarelli, E.; Naim, V.; Bosso, G.; Kiseleva, E.; Bonaccorsi, S.; Sharp, D.J.; Khodjakov, A.; et al. The Drosophila orthologue of the INT6 onco-protein regulates mitotic microtubule growth and kinetochore structure. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


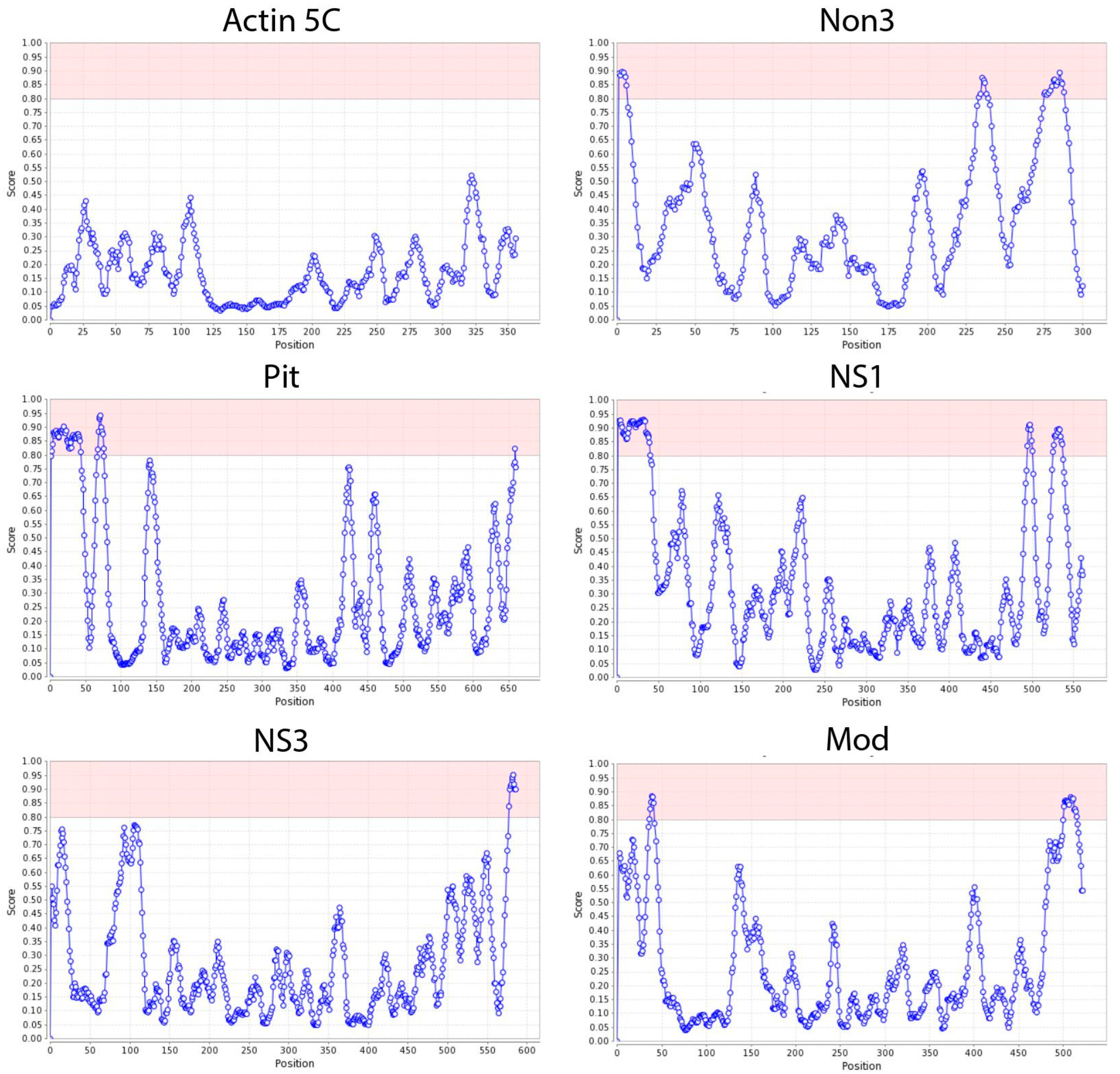

| Protein | N-End NoLS | Middle NoLS | C-End NoLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novel nucleolar protein 3 (Non3) | MSLLRIRKPKTRKGKKVLLAREPQL (positions 1–25) | EDLYKQARKQPKQLKVGKKKNISTDA (positions 233–258) | SIQTRRVKALRKTPEEKKENRQRKKVALKAAAA (positions 275–307) |
| Pitchoune (Pit) | SIREKLLMKKIVKREKMKKELSQKKGNKNAQKQEPPKQNGNKPSKKPEKLSKKHVAKDEDD (positions 2–62) | DFQEAPLPKKKQQKQPPKKQQIQVANSD (positions 67–94) | GSASKQRHFKQVNRDQAKKF (positions 659–678) |
| Nucleostemin 1 (NS1) | MALKRLKTKKSKRLTGRLKHKIEKKVRDHNKKERRAAKKNPKKGSKKQKLIQIPNICPF (positions 1–59) | VIDEKEKPAKGRKRKLDEEKEKVDPS (positions 494–519) | NQSLNKGIKQMQKLKKKQNVRNEKKISKITD (positions 525–555) |
| Nucleostemin 3 (NS3) | - | - | GNDPAAKPWRHVKKERREKLRKKFSHLDEH (positions 577–606) |
| Modulo (Mod) | ETVVPQSPSKKSRKQPVKEVPQFSE (positions 36–60) | - | IGQTRAPRKFQKDTKPNFGKKPFNKRPAQENGGK (positions 501–534) |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′- > 3′) |
|---|---|
| EGFP-EcoRI-fwd | ggcatcatgaattcgtttgtgaacgacattttcgagc |
| EGFP-RKKRKKK-NoLS-XbaI-rev | ttaatctagattacttcttttttcgcttctttctcttgtacagctcgtccatgccgagagtg |
| EGFP-R9-NoLS-XbaI-rev | ttaatctagattatctccttctccttctccttctccttctcttgtacagctcgtccatgccgagagtg |
| EGFP-WRRQARFK-NoLS-XbaI-rev | ttaatctagattacttaaacctggcttggcgtctccacttgtacagctcgtccatgccgagagtg |
| Fr1_for_Kozak_H2B | gagaccccggatcggggtacccaccatgcctccgaaaactag |
| Fr1_rev_pitch | cctggaaatcggtggcgaccggtgg |
| Fr2_for_pitch | ggtcgccaccgatttccaggaggcgccg |
| Fr2_rev_pitch | tgctcaccatatccgagttggccacctg |
| Fr3_for_pitch_EGFP | caactcggatatggtgagcaagggcgag |
| Fr2_rev_EGFP_NS3 | gatcattgcccttgtacagctcgtccatgc |
| Fr3_for_NS3 | gctgtacaagggcaatgatccggcgg |
| Fr3_rev_NS3 | gcttaccttcgaagggccctctagattagtgctcgtccaggtgc |
| Fr1_for_Non3 | gagaccccggatcggggtacccaccatgtcgcttttacgcatcag |
| Fr1_rev_Non3_H2B | tcggaggcatgagttgcggctccctgg |
| Fr2_for_Non3_H2B | gccgcaactcatgcctccgaaaactagtggaaag |
| Fr1_for_NS1 | gagaccccggatcggggtacccaccatggctttaaaaaggttgaagacc |
| Fr1_rev_NS1 | tcggaggcatgaagggacagatgtttgggatctg |
| Fr2_for_NS1_H2B | ctgtcccttcatgcctccgaaaactagtggaaag |
| Fr1_rev_Non3 | tacagatcctcggtggcgaccggtgg |
| Fr2_for_Non3 | ggtcgccaccgaggatctgtacaaacaggcacg |
| Fr2_rev_Non3 | tgctcaccatggcgtctgtgctaatgttcttct |
| Fr3_for_Non3_EGFP | cacagacgccatggtgagcaagggcgag |
| Fr2_rev_EGFP_mod | tctgaccaatcttgtacagctcgtccatgc |
| Fr3_for_mod | gctgtacaagattggtcagacccgcg |
| Fr3_rev_mod | gcttaccttcgaagggccctctagattatttaccaccattctcttgtgcc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogienko, A.A.; Korepina, M.O.; Pindyurin, A.V.; Omelina, E.S. New Functional Motifs for the Targeted Localization of Proteins to the Nucleolus in Drosophila and Human Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021230
Ogienko AA, Korepina MO, Pindyurin AV, Omelina ES. New Functional Motifs for the Targeted Localization of Proteins to the Nucleolus in Drosophila and Human Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021230
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgienko, Anna A., Mariya O. Korepina, Alexey V. Pindyurin, and Evgeniya S. Omelina. 2024. "New Functional Motifs for the Targeted Localization of Proteins to the Nucleolus in Drosophila and Human Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021230
APA StyleOgienko, A. A., Korepina, M. O., Pindyurin, A. V., & Omelina, E. S. (2024). New Functional Motifs for the Targeted Localization of Proteins to the Nucleolus in Drosophila and Human Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021230







