Visual Detection of Dopamine with CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots Bearing by ZIF-8 and Nanofiber Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
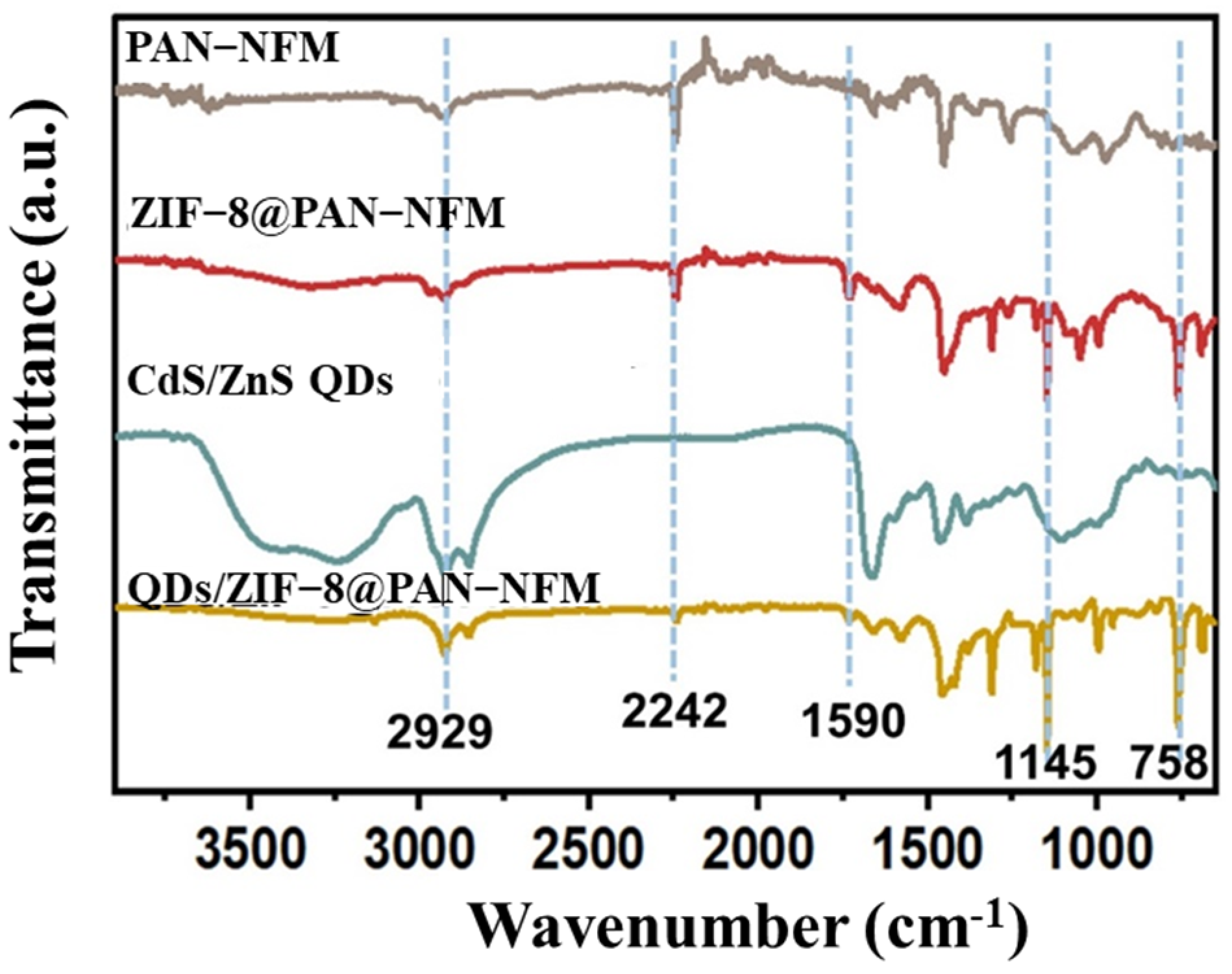
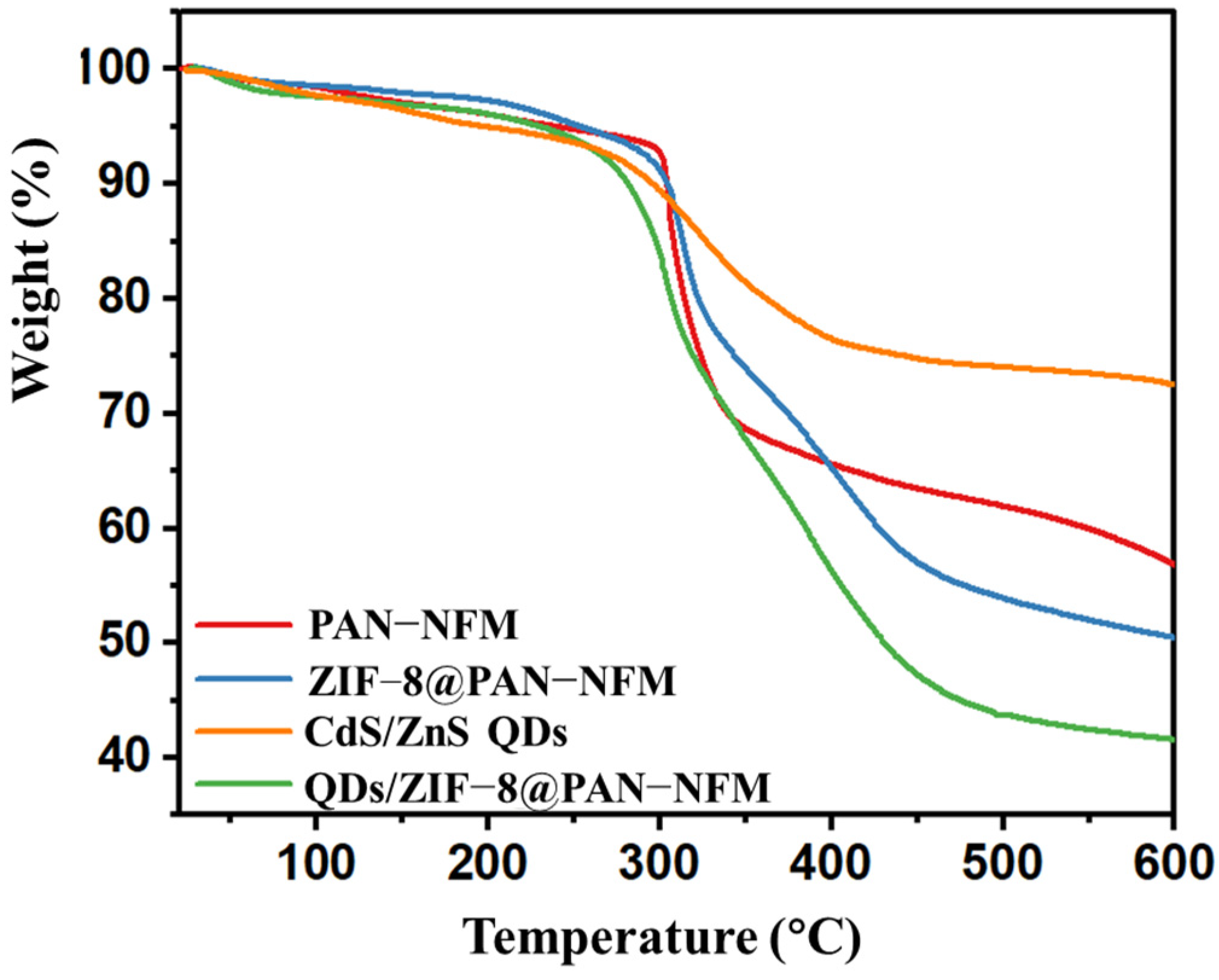
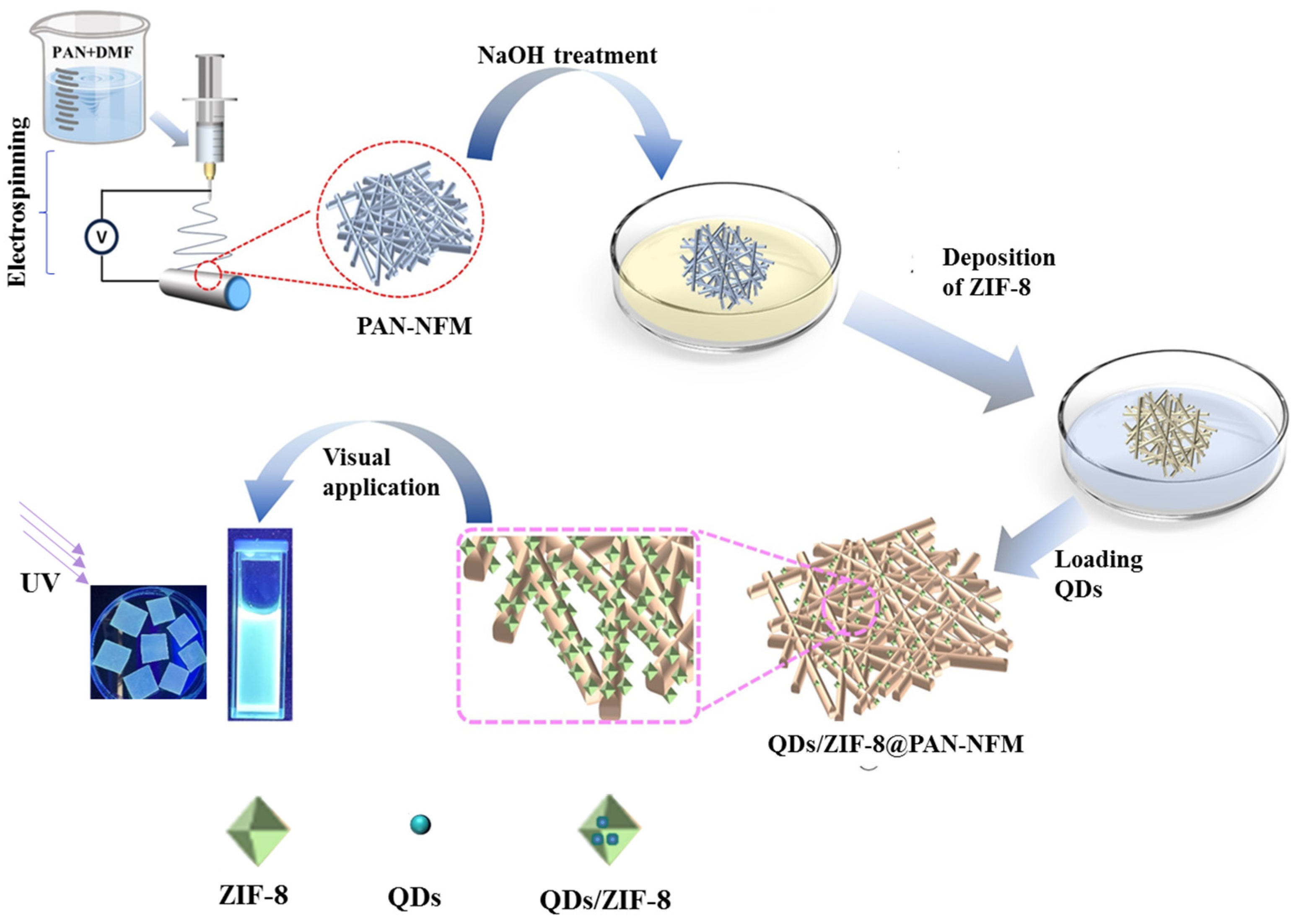
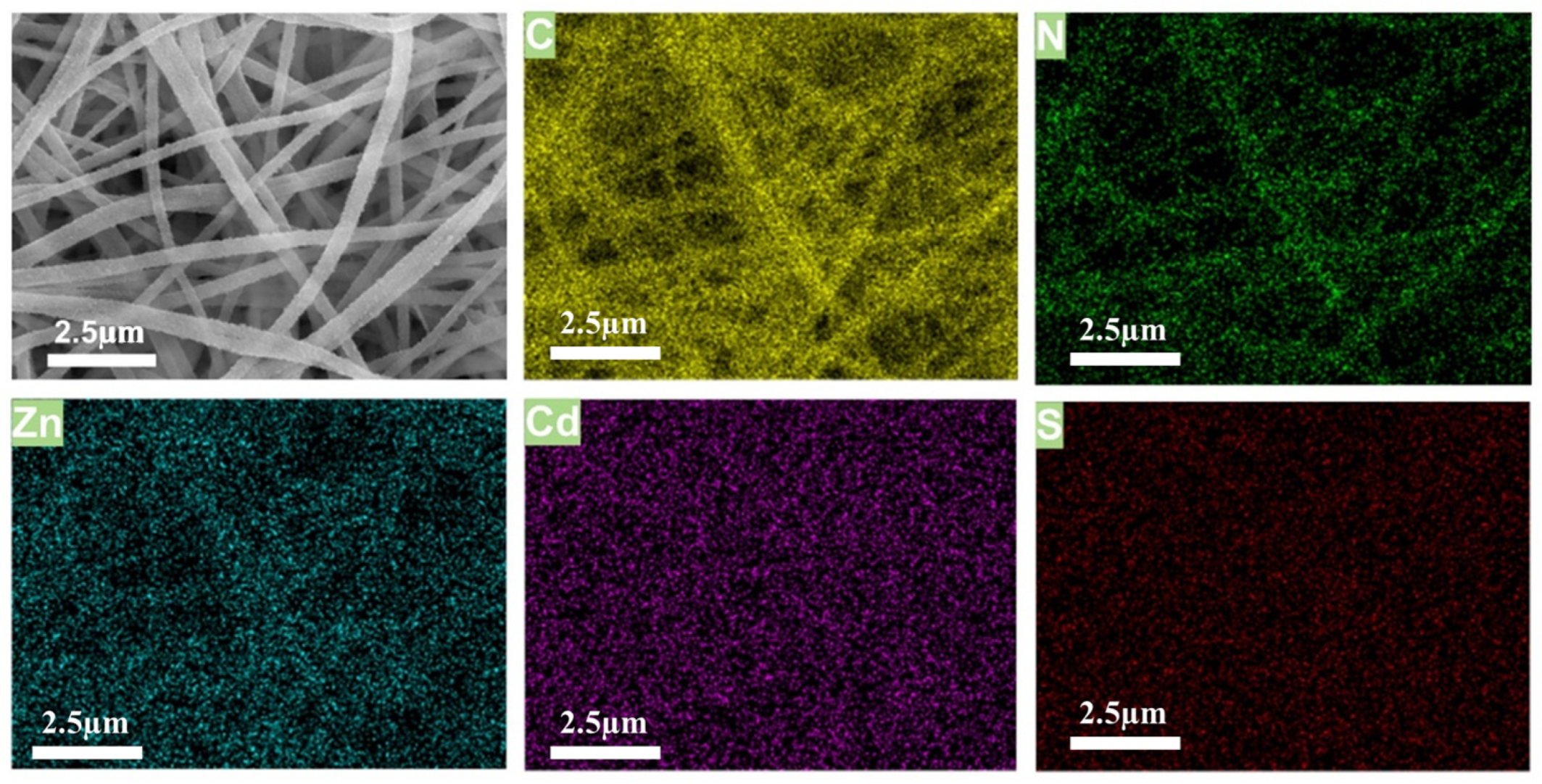
2.1. Morphology and Structures of the Composite PAN-NFM
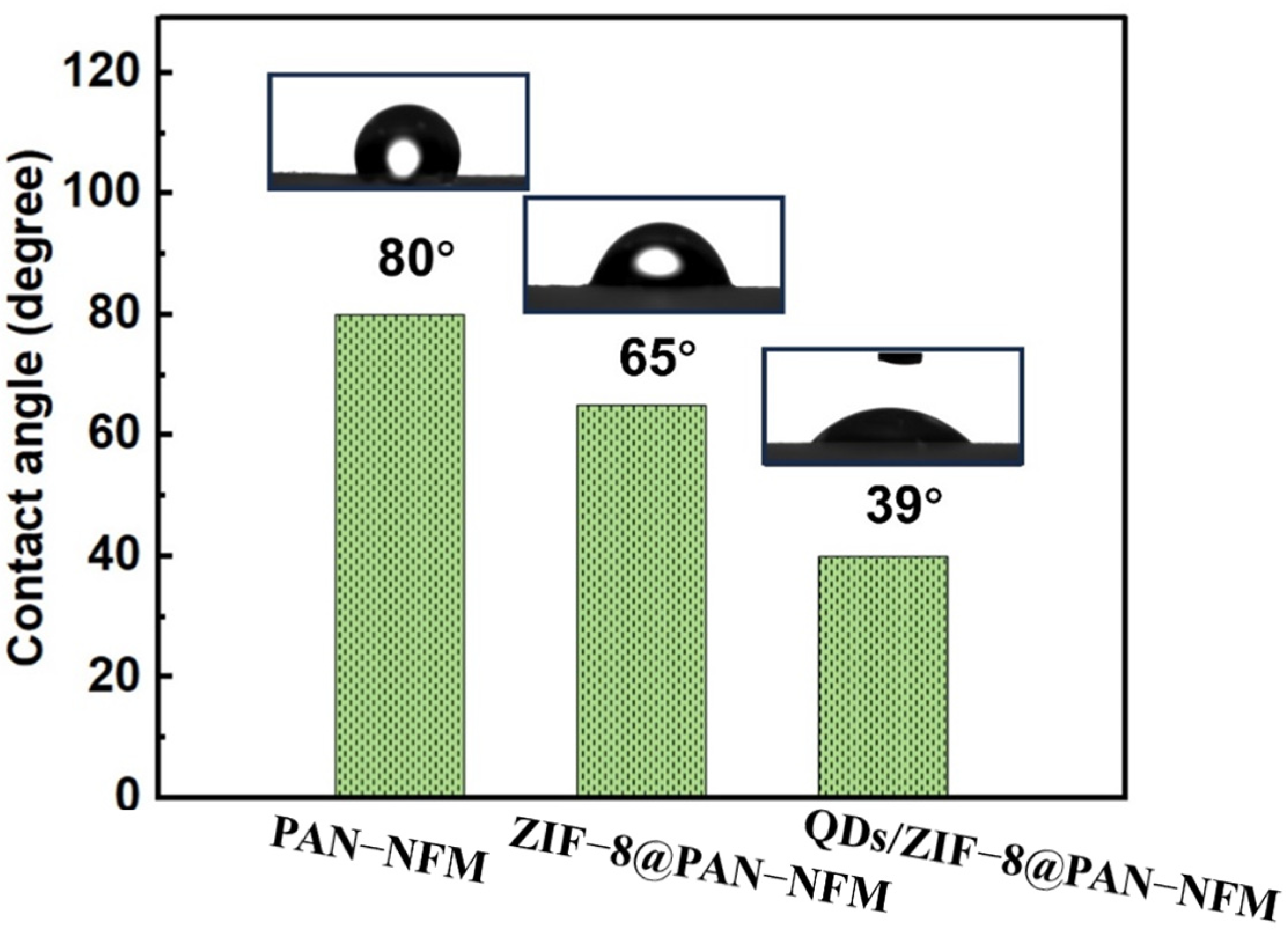
2.2. Wettability
2.3. Pore Size Distribution
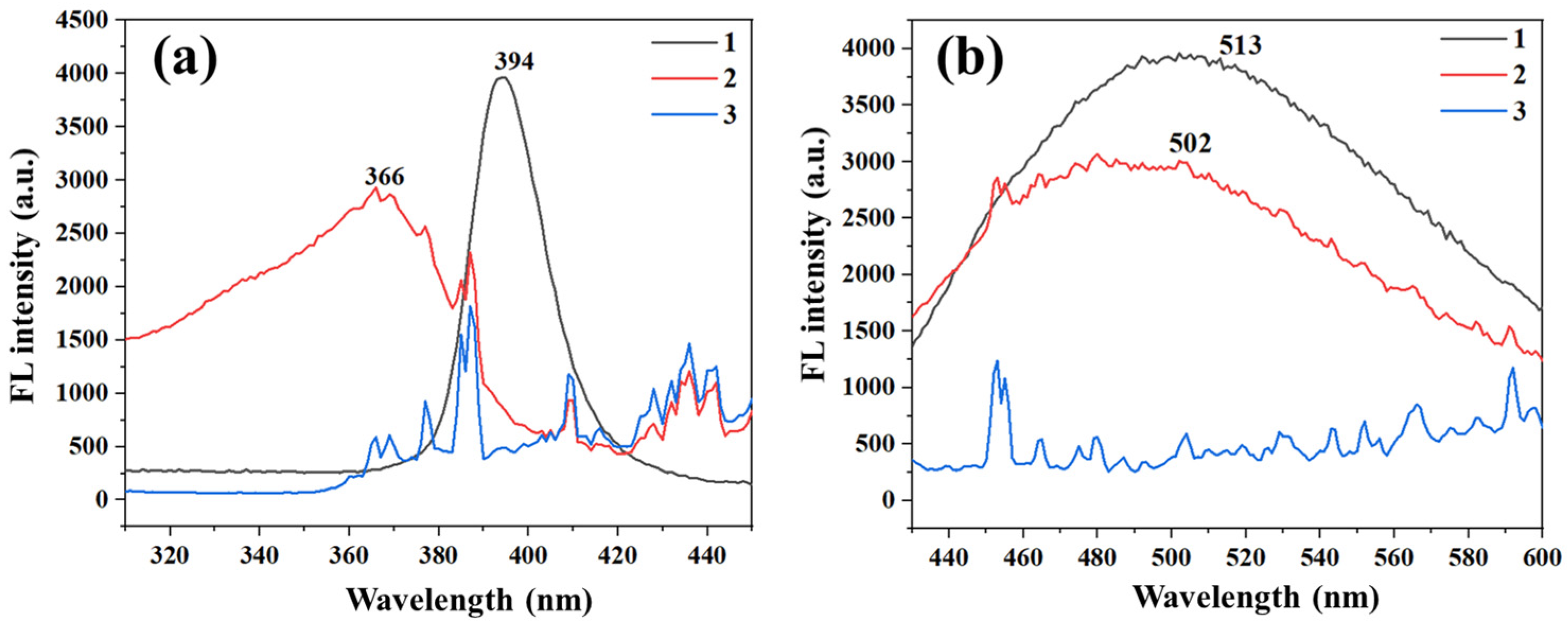
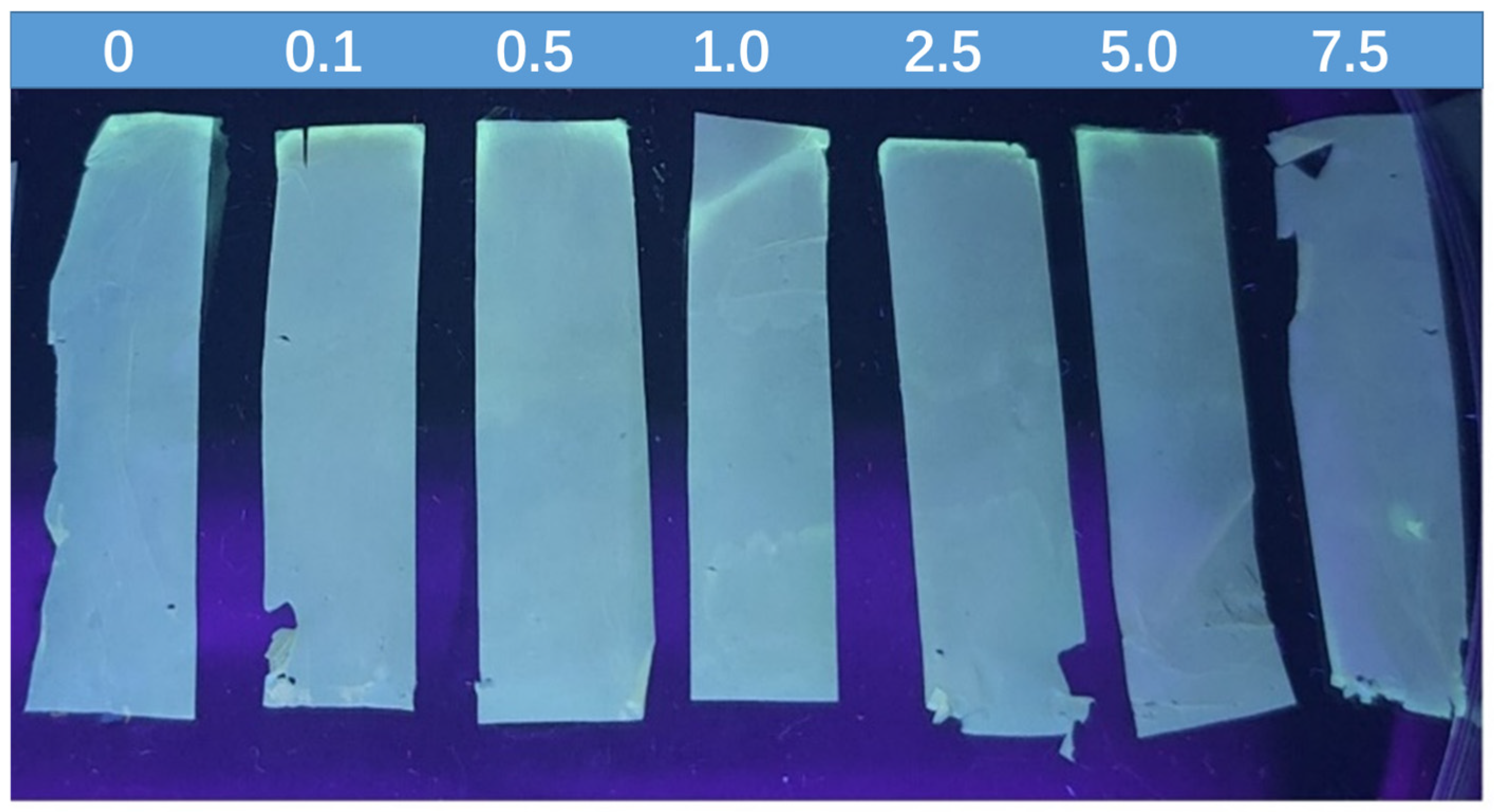
2.4. Fluorescence of the QDs/ZIF-8@PAN-NFM
2.5. Application of the QDs/ZIF-8@PAN-NFM for Visual Test of DA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Section
4.2.1. Preparation of the PAN-NFM
4.2.2. In Situ Growth of ZIF-8 on the PAN-NFM Surface
4.2.3. The Adsorption of CdS/ZnS QDs onto the ZIF-8@PAN-NFM for Visually Testing DA
4.3. Characterization
The Morphology and Properties of the ZIF-8@PAN-NFM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pifl, C.; Giros, B.; Caron, M.G. Dopamine transporter expression confers cytotoxicity to low doses of the parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 4246–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usiello, A.; Baik, J.H.; Rougé-Pont, F.; Picetti, R.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Piazza, P.V.; Borrelli, E. Distinct functions of the two isoforms of dopamined receptors. Nature 2000, 408, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, R.M.; May, L.J.; Michael, A.C. Detection of dopamine dynamics in the brain. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 769–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masato, A.; Plotegher, N.; Boassa, D.; Bubacco, L. Impaired dopamine metabolism in parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaus, S.; Antke, C.; Müller, H.W. In vivo imaging of synaptic function in the central nervous system: II. Mental and affective disorders. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 204, 32–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F.T.; Girgis, R.R.; Gray, D.I.; Mailman, R.B. Novel dopamine therapeutics for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 81, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.L.; Hermans, A.; Seipel, A.T.; Wightman, R.M. Monitoring rapid chemical communication in the brain. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2554–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, O.; Moal, M.L.; Koob, G.F. Allostasis and addiction: Role of the dopamine and corticotropin-releasing factor systems. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, R.A.; Robble, M.A. Dopamine and Addiction. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.X.; Liu, J.W. Biosensors and sensors for dopamine detection. VIEW 2020, 2, 20200102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikraman, A.E.; Jose, A.R.; Jacob, M.; Kumar, K.G. Thioglycolic acid capped CdS quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for the nanomolar determination of dopamine. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Li, X.; Guo, X.H.; Zhang, B.; Jia, X.; Dai, B. A simple, fast and low-cost turn-on fluorescence method for dopamine detection using in situ reaction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 944, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulghobra, A.; Bonose, M.; Billault, I.; Pallandre, A. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of dopamine and serotonin metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid based on UHPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1200, 123264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, R.; Ogra, Y. Determination of intracellular dopamine by liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection with post-column derivatization using the König reaction. J. Chromatogr. B 2024, 1232, 123956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashkhourian, J.; Dehbozorgi, A. Determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic and uric acids by fluorometric method using graphene quantum dots. Spectrosc. Lett. 2016, 49, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, Y.; Shi, F.P.; Wang, G.N.; Mazhar, S.S.; Su, X.G. Determination of catecholamine in human serum by a fluorescent quenching method based on a water-soluble fluorescent conjugated polymerenzyme hybrid system. Analyst 2012, 137, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Jiang, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, H. High-sensitive detection of dopamine using graphitic carbon nitride by electrochemical method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 74, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Nelson, G.W.; Abda, J.; Foord, J.S. Novel Modifications to Carbon-Based Electrodes to Improve the Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 28338–28348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Yoon, J.; Shin, M.; Choi, J.W. Electrochemical Dopamine Biosensor Composed of Silver Encapsulated MoS Hybrid Nanoparticle. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2019, 24, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.B.; Zhou, X.L. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-modified carbon paste electrodes for selective determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid. Bioelectrochemistry 2007, 70, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.M.; Xie, K.; Ye, L.Q.; Li, G.Q.; Lu, Z.W.; He, J.B. Gold-nanoparticle-based colorimetric array for detection of dopamine in urine and serum. Talanta 2015, 139, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, S.J.; Liu, L.L.; Deng, D.H.; Xia, N. Simple, sensitive and selective detection of dopamine using dithiobis(succinimidylpropionate)-modified gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Analyst 2012, 137, 3794–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syslová, K.; Rambousek, L.; Kuzma, M.; Věra, N.; Věra, B.V.; Šlamberová, R.; Kačer, P. Monitoring of dopamine and its metabolites in brain microdialysates: Method combining freeze-drying with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3382–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorn, F.A.; Boomsma, F.; Veld, A.J. Improved measurement of urinary catecholamines by liquid-liquid extraction, derivatization and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J. Chromatogr. 1991, 563, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biju, V.; Itoh, T.; Ishikawa, M. Delivering quantum dots to cells: Bioconjugated quantum dots for targeted and nonspecific extracellular and intracellular imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3031–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Chen, X.K.; Kai, S.Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Wu, F.G.; Chen, Z. Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of dopamine Using One-Pot Synthesized Highly Photoluminescent Silicon Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3360–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasheena, M.; Ratnamala, A.; Noorjahan, M.; Reddy, G.D.; Shiprath, K.; Manjunatha, H.; Naidu, K.; Chandra, B. Graphene Oxide Decorated Tin Sulphide Quantum Dots for Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Tyrosine. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 4160–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, A.; Rahmani, S. The Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots through One-step Hydrothermal Approach by Orange Juice for Rapid, and Accurate Detection of Dopamine. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.S.; Deng, M.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.L.; Li, W.H.; Huang, X.H. Alginate capped and manganese doped ZnS quantum dots as a phosphorescent probe for time-resolved detection of copper(II). Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 186, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.E.; Nie, S.M. Alloyed semiconductor quantum dots: Tuning the optical properties without changing the particle size. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7100–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Yang, H.; Holloway, P.H.; Stanley, J.T.; Mericle, R.A. Synthesis of water-dispersible fluorescent, radio-opaque, and paramagnetic CdS:Mn/ZnS quantum dots: A multifunctional probe for bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1656–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Zhou, Y.M.; Liang, X.Z.; Zhou, Z.P.; Luo, J.Q.; Liu, S.J.; Ma, J.G. Permselectivity of Electrodeposited Polydopamine/Graphene Composite for Voltammetric Determination of Dopamine. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barglik-Chory, C.; Remenyi, C.; Dem, C.; Schmitt, M.; Gerd, M. Synthesis and characterization of manganese-doped CdS nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, M.H.; Fow, K.L.; Chen, G.Z. Synthesis and applications of MOF-derived porous nanostructures. Green. Energy Environ. 2017, 2, 218–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.B.; Song, Y.F.; Pei, H.B.; Mo, Z.L. Synthesis strategies and applications of metal-organic framework-quantum dot (MOF@QD) functional composites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 128, 17–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chiang, W.H.; Kurniawan, D.; Yeh, P.C.; Otake, K.I. Impregnation of Graphene Quantum Dots into a Metal-Organic Framework to Render Increased Electrical Conductivity and Activity for Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 35319–35326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Cui, X.C.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.Y.; Deng, Y.K.; Cheng, W.X.; Xiong, R.H.; Huang, C.B. Xylan derived carbon dots composite ZIF-8 and its immobilized carbon fibers membrane for fluorescence selective detection Cu in real samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Tiwari, A.P.; Ko, T.H.; Kim, H.Y. Metal-organic frameworks of rare earth metals embedded side-by-side nanofiber as a switchable luminescent sensor for Fe3+ and Cu2+ in aqueous media. J. Lumin. 2022, 249, 119029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Zhang, S.B.; Du, G.C.; Li, R.G.; He, H.W.; Guo, Q.Q. CdS/ZnS quantum dots based on an amphipathic polymer platform for fluorescent probe of dopamine with high sensitivity and selectivity. Mater. Lett. 2024, 367, 136603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Bo, D.; Fang, S. Audoped polyacrylonitrile-polyaniline core-shell electrospun nanofibers having high field-effect mobilities. Small 2015, 7, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Cao, Z.J.; Grande, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Dou, Y.B.; Li, X.S.; Kaiser, A. A phase conversion method to anchor ZIF-8 onto a PAN nanofiber surface for CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2021, 12, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyagari, S.; Al-Haik, M.; Ren, Y.; Abbott, A.; Koerner, H. Metal organic frameworks modification of carbon fiber composite interface. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2021, 224, 109197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Du, G.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Zhou, R.; He, H. Visual Detection of Dopamine with CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots Bearing by ZIF-8 and Nanofiber Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910346
Hu J, Li J, Guo Q, Du G, Li C, Li R, Zhou R, He H. Visual Detection of Dopamine with CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots Bearing by ZIF-8 and Nanofiber Membranes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910346
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jiadong, Jiaxin Li, Qunqun Guo, Guicai Du, Changming Li, Ronggui Li, Rong Zhou, and Hongwei He. 2024. "Visual Detection of Dopamine with CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots Bearing by ZIF-8 and Nanofiber Membranes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910346
APA StyleHu, J., Li, J., Guo, Q., Du, G., Li, C., Li, R., Zhou, R., & He, H. (2024). Visual Detection of Dopamine with CdS/ZnS Quantum Dots Bearing by ZIF-8 and Nanofiber Membranes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910346




