Study of Insulin Aggregation and Fibril Structure under Different Environmental Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
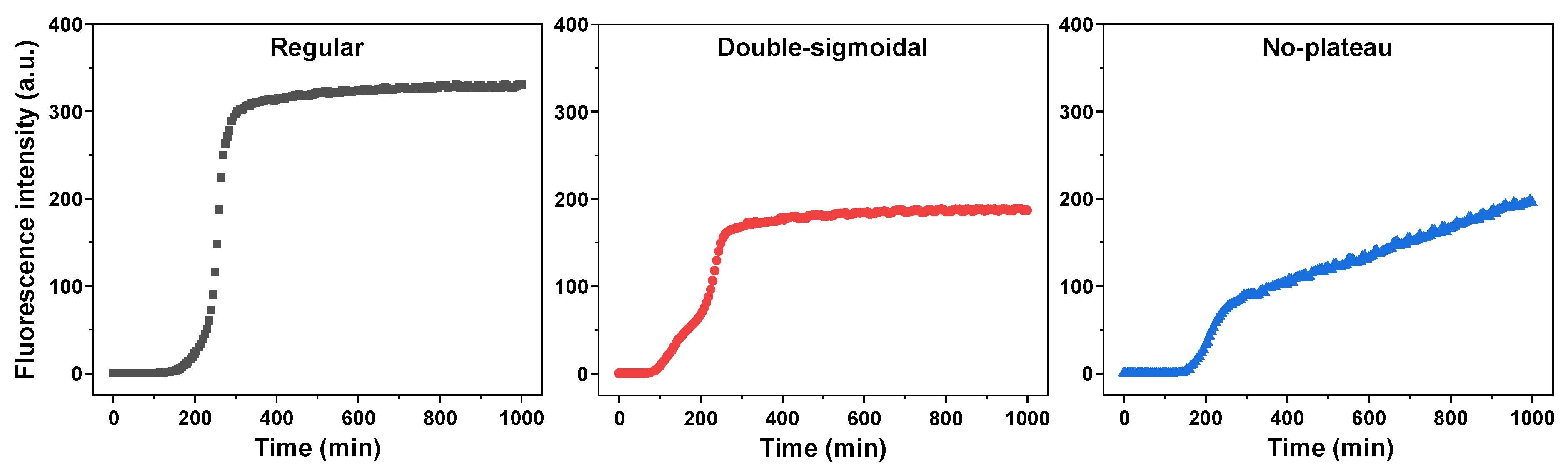
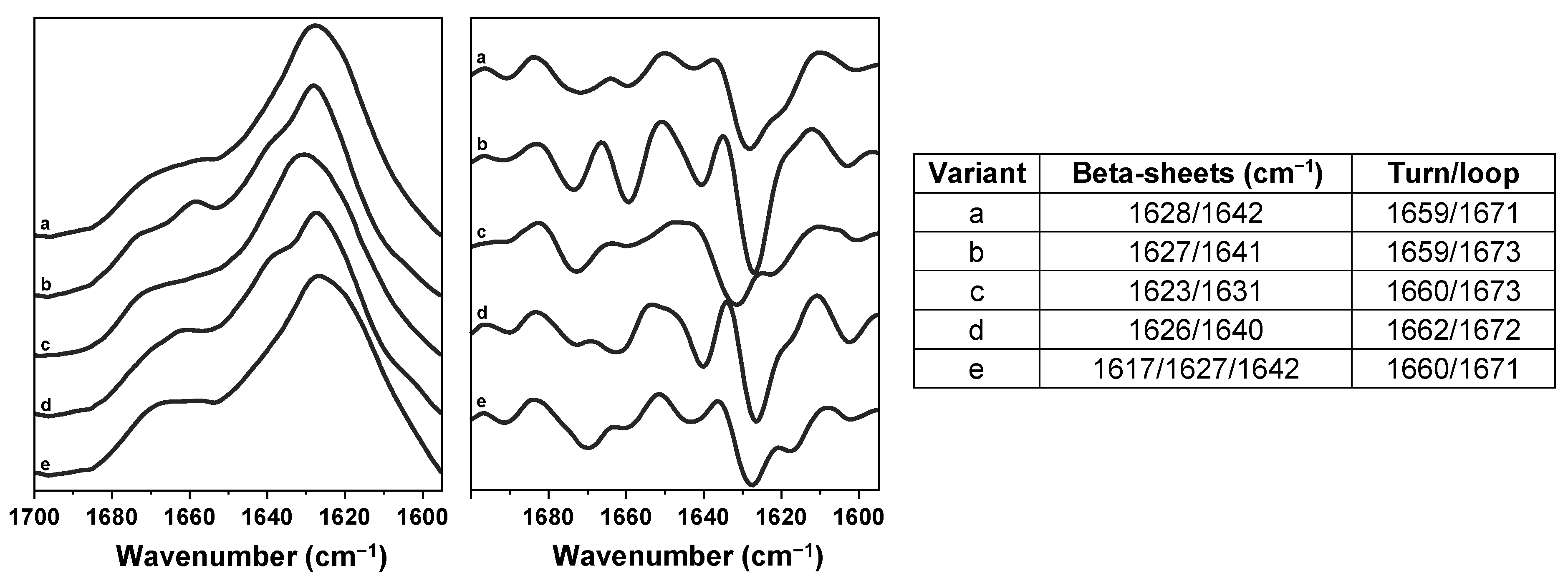
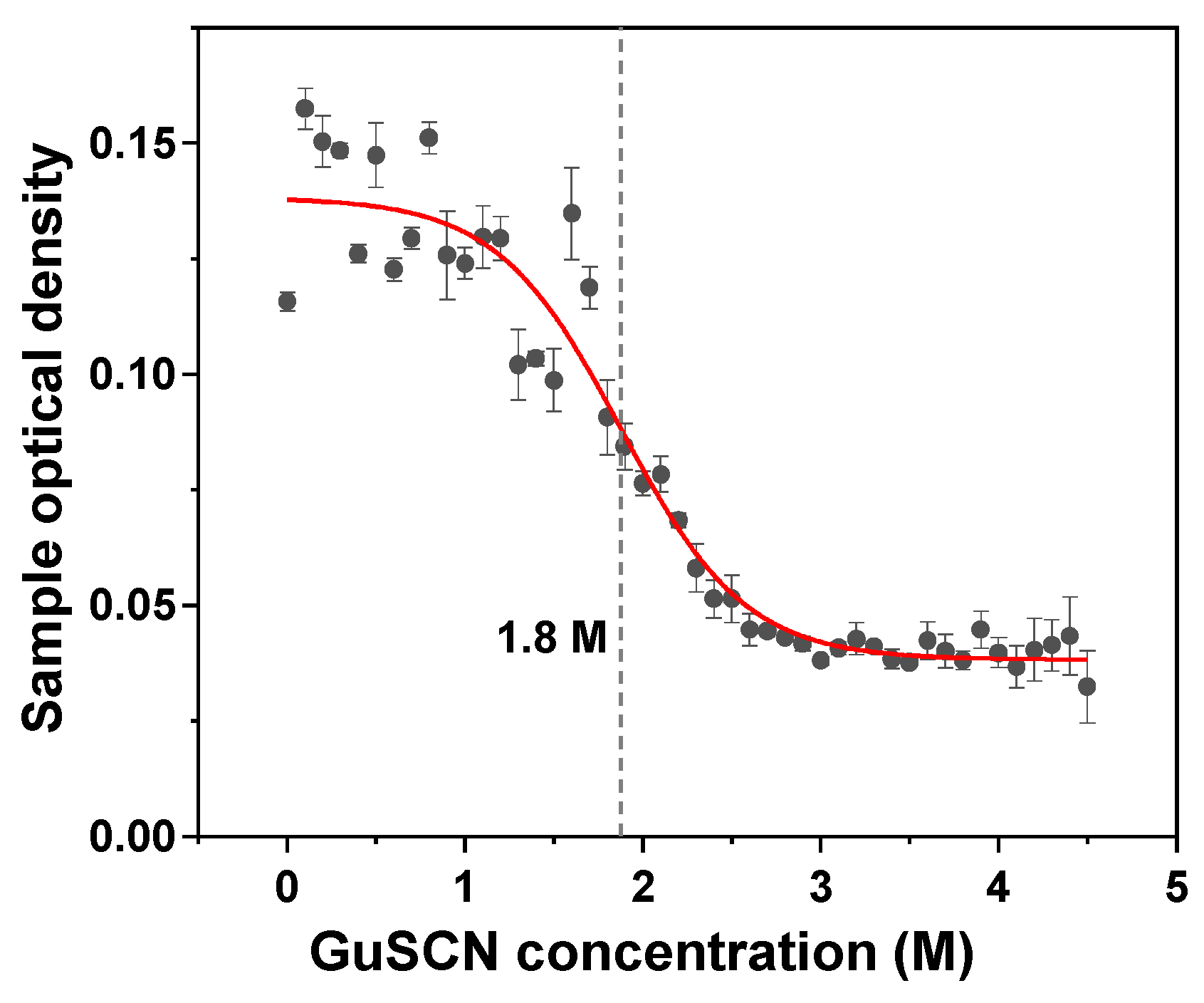
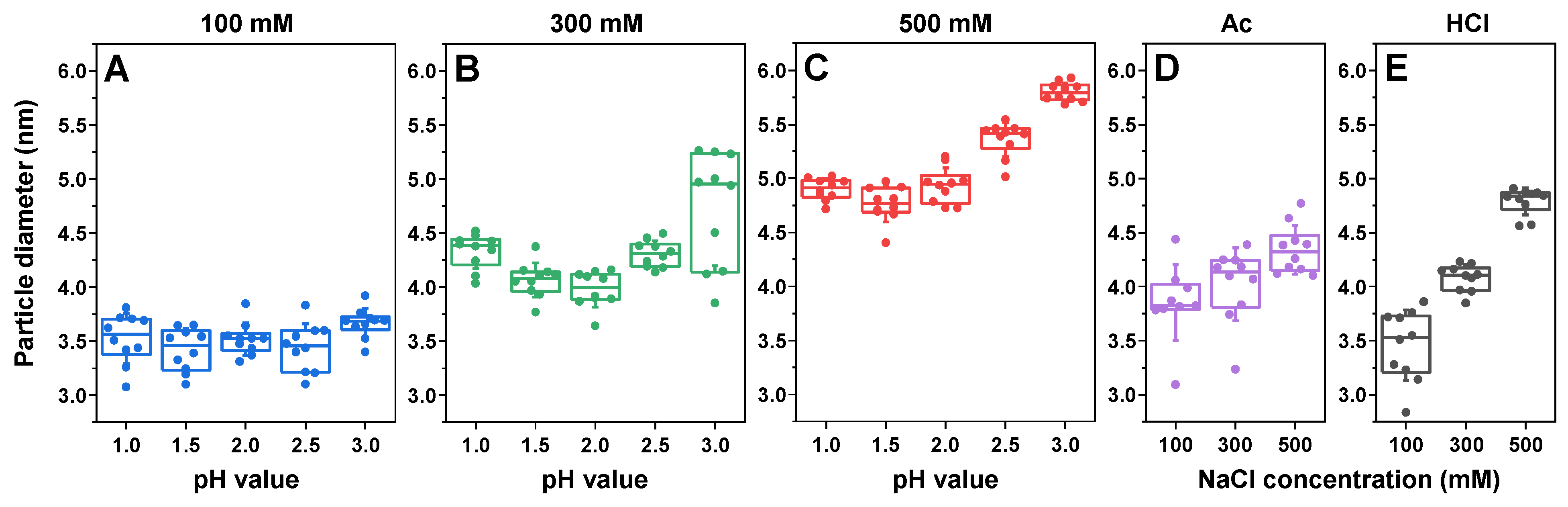
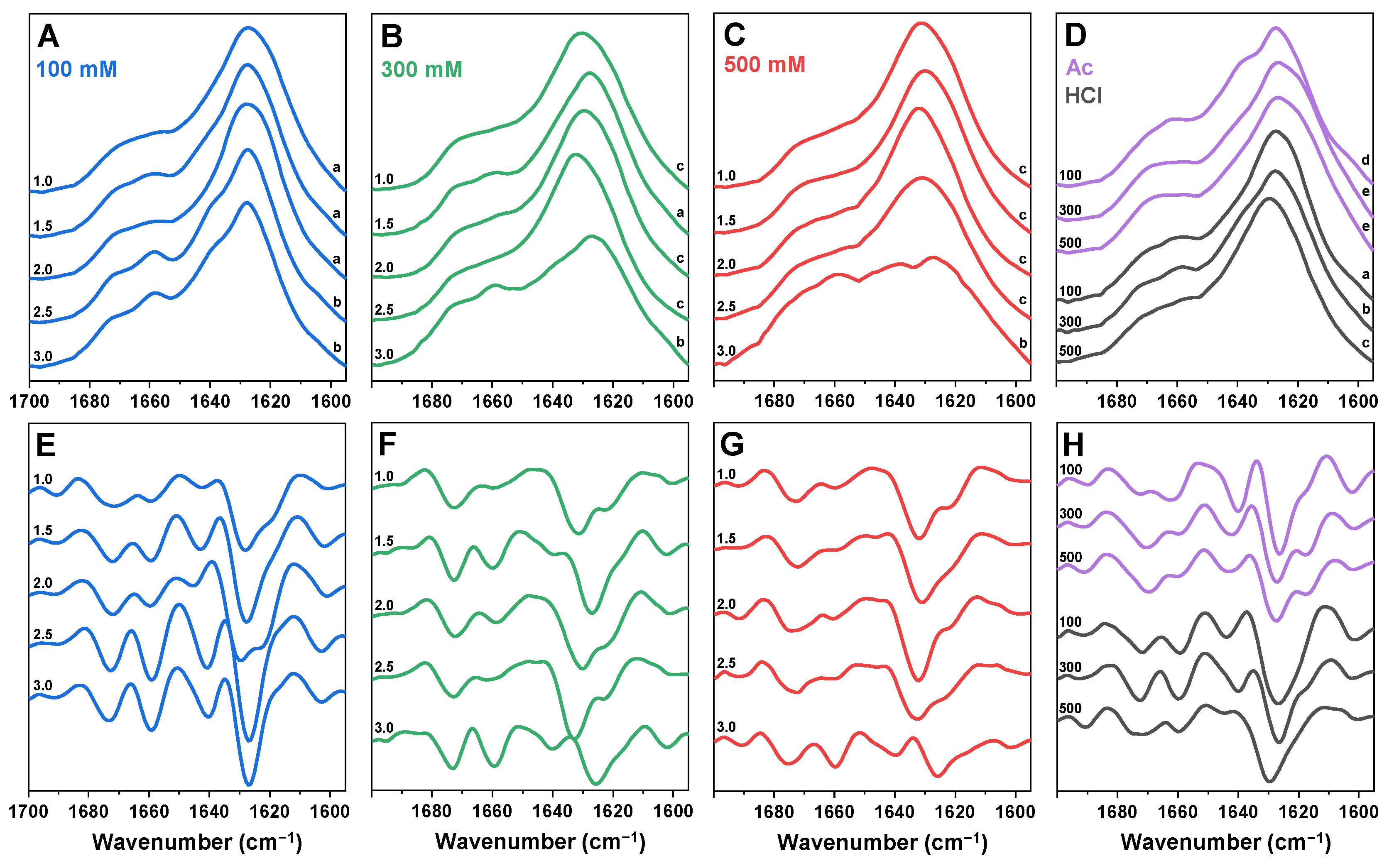
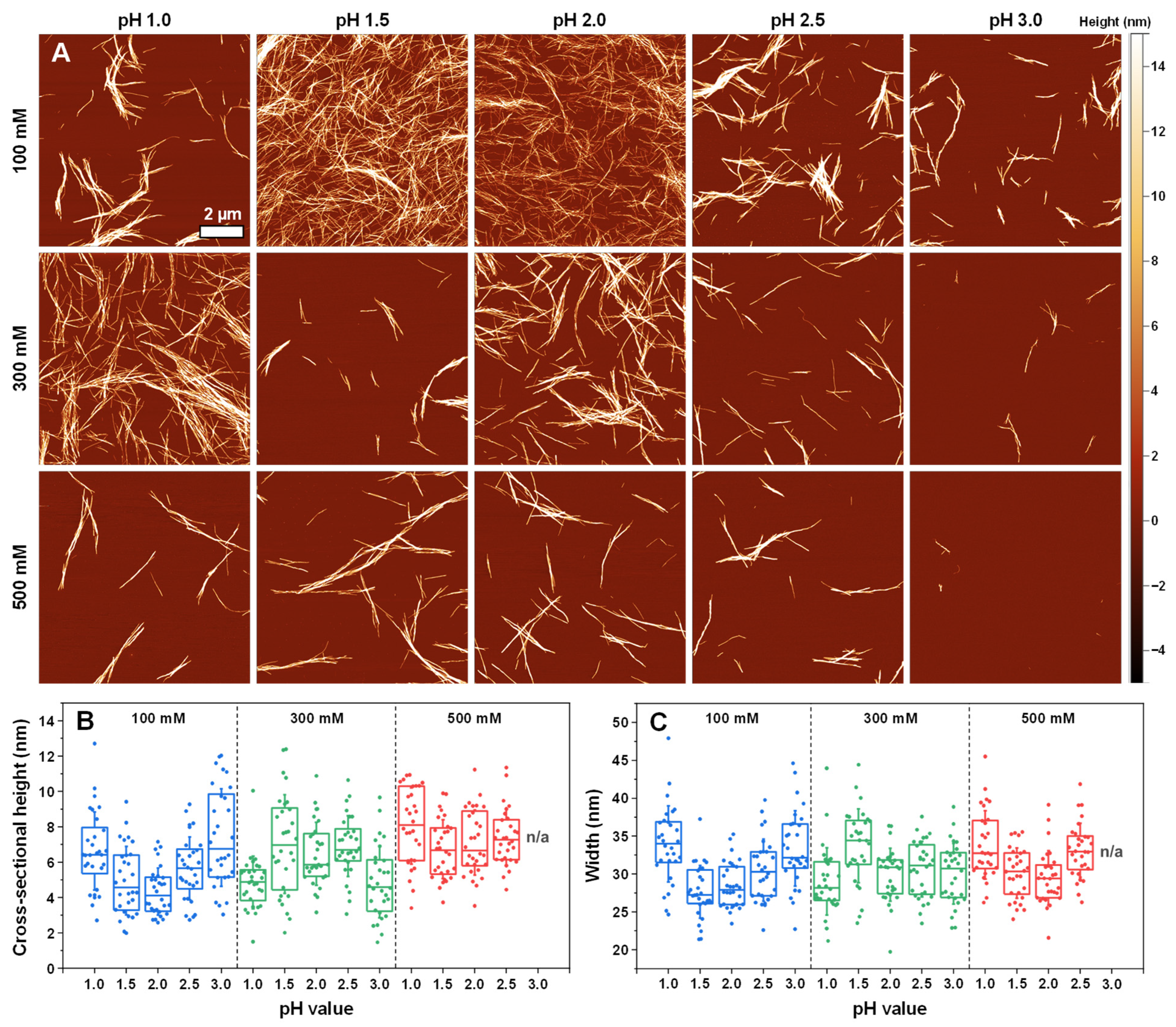
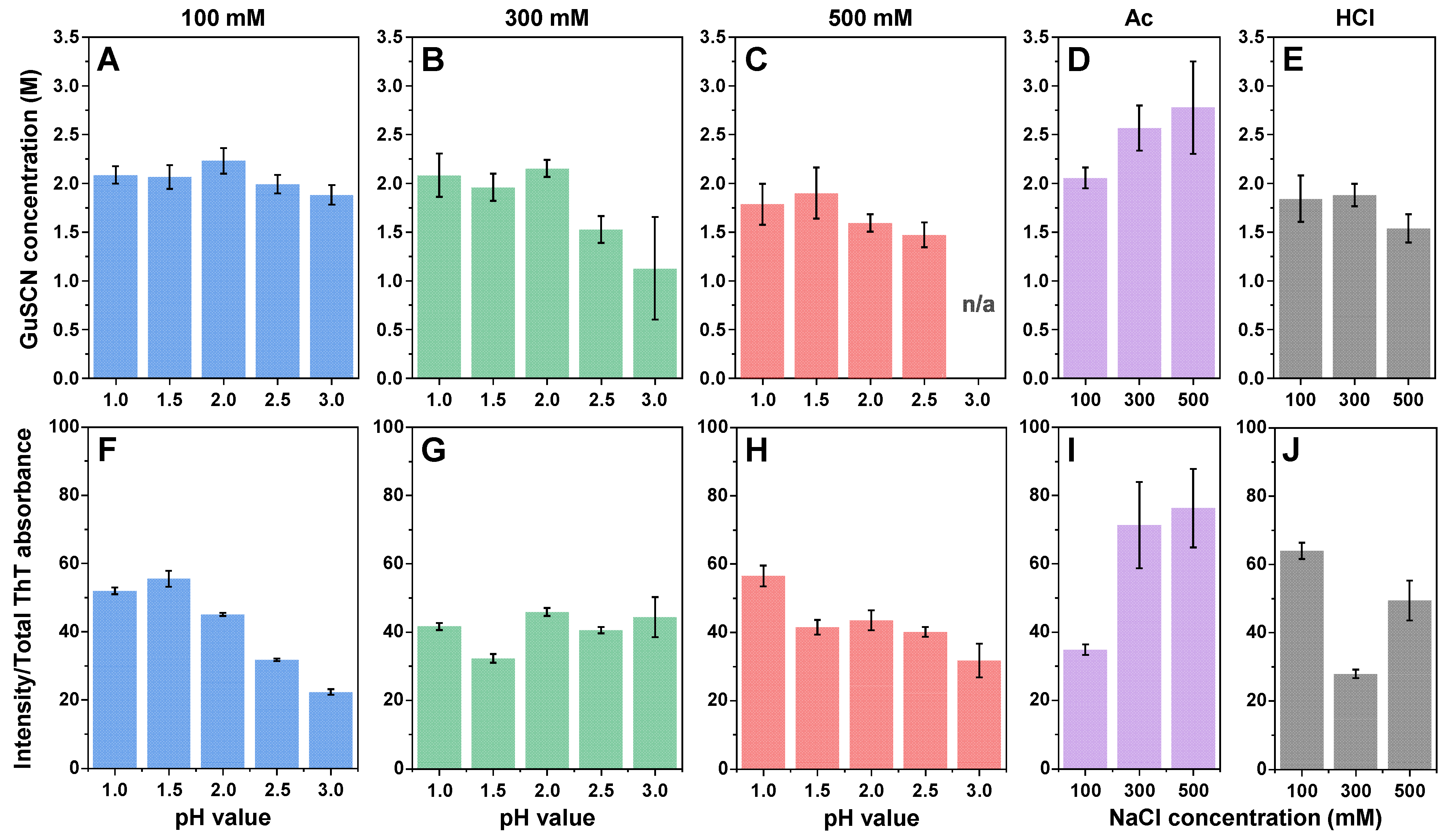
2. Results
3. Discussion
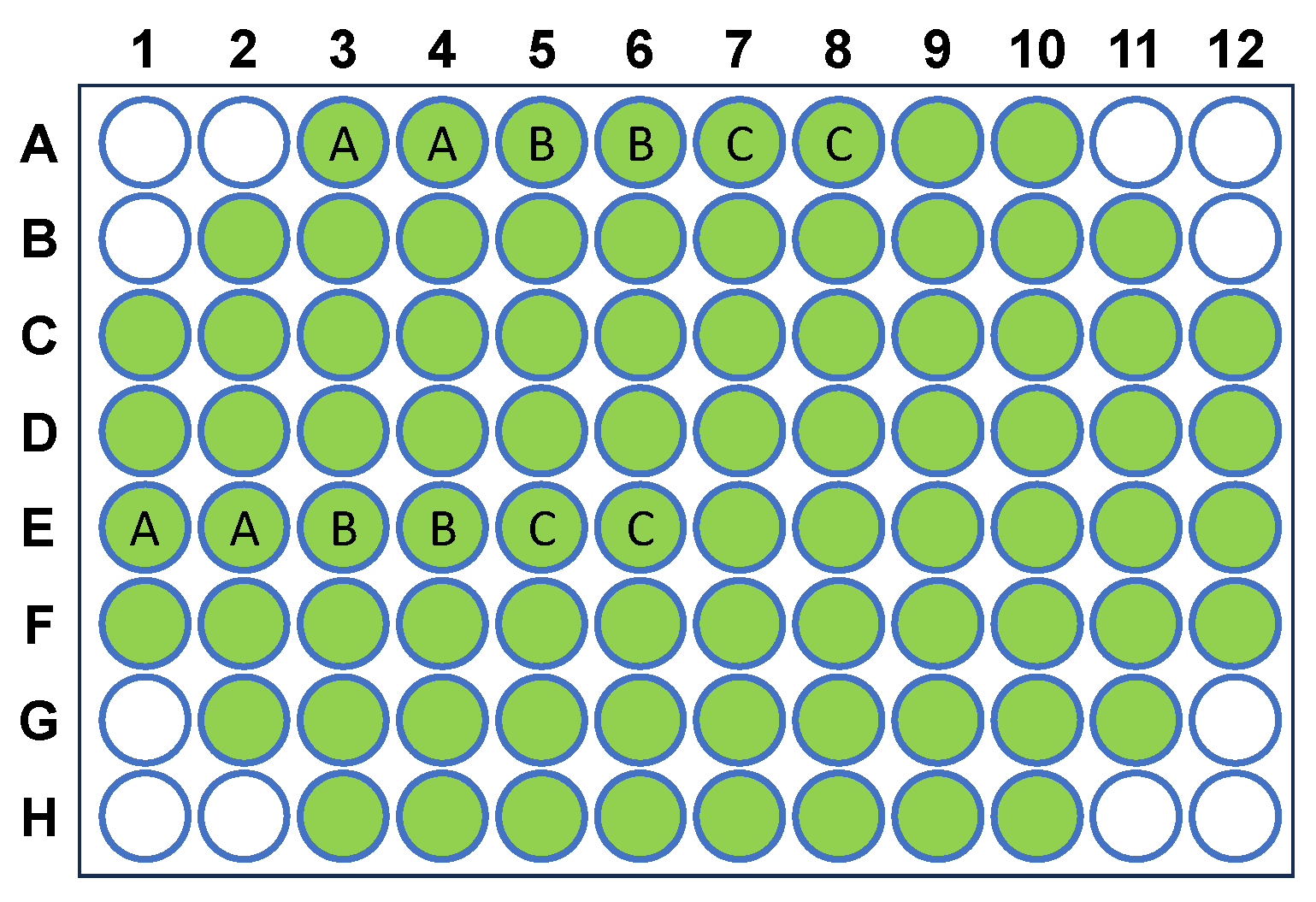
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reaction Solution Preparation
4.2. Insulin Aggregation
4.3. Dynamic Light Scattering
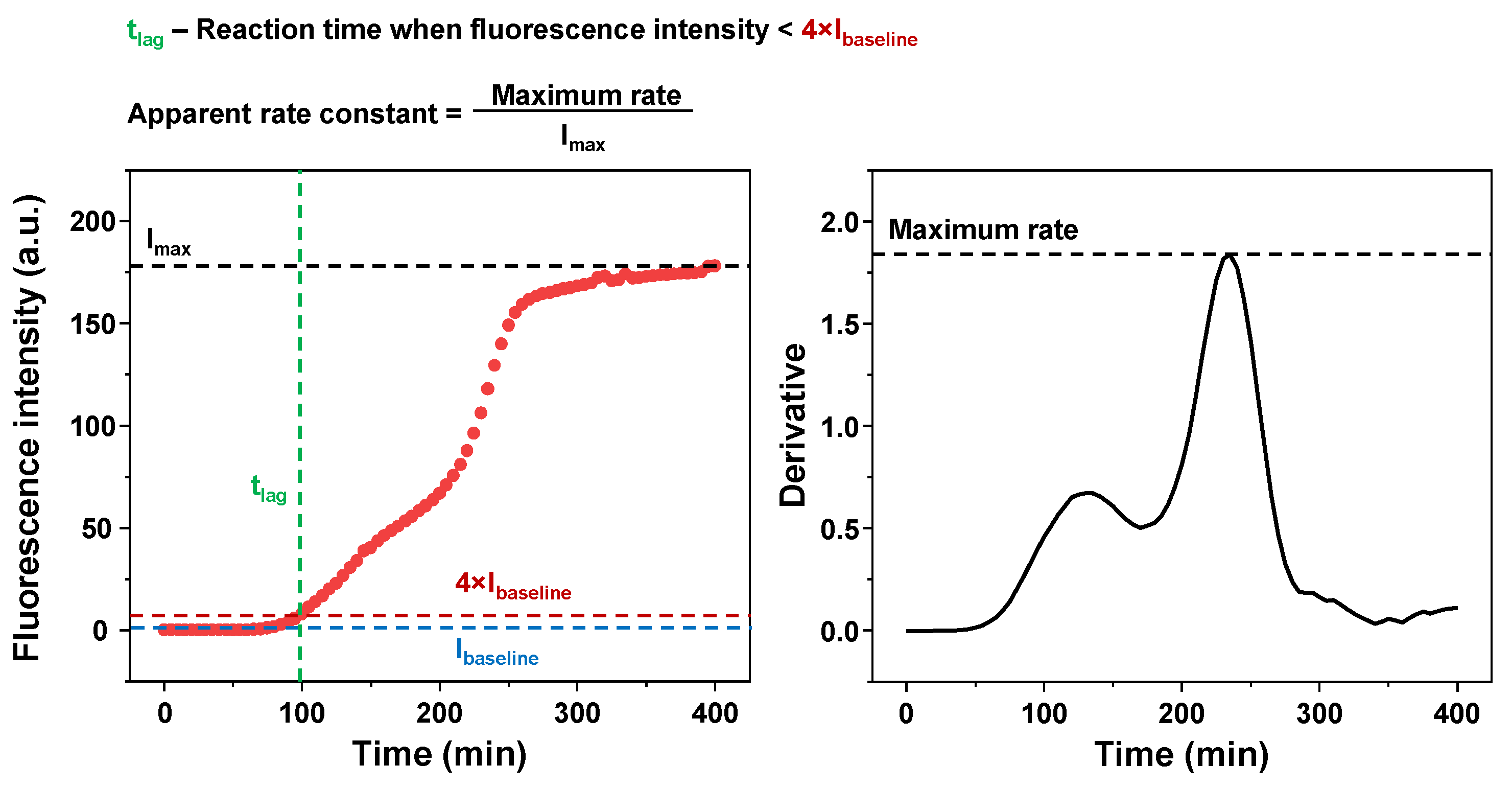
4.4. Kinetic Data Analysis
4.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.6. ThT-Binding Assay
4.7. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4.8. Aggregate Denaturation Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Knowles, T.P.J.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. The amyloid state and its association with protein misfolding diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.; Lee, G.; Nahed, P.; Kambar, M.E.Z.N.; Zhong, K.; Fonseca, J.; Taghva, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2022. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2022, 8, e12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, K.C.; Calvo, A.; Price, T.R.; Geiger, J.T.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. Projected increase in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from 2015 to 2040. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookmeyer, R.; Gray, S.; Kawas, C. Projections of Alzheimer’s disease in the United States and the public health impact of delaying disease onset. Am. J. Public Health 1998, 88, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatani, E.; Yamamoto, N. Recent progress on understanding the mechanisms of amyloid nucleation. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousset, L.; Pieri, L.; Ruiz-Arlandis, G.; Gath, J.; Jensen, P.H.; Habenstein, B.; Madiona, K.; Olieric, V.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Thackray, A.M.; Hopkins, L.; Monie, T.P.; Burke, D.F.; Bujdoso, R. Polymorphisms at amino acid residues 141 and 154 influence conformational variation in ovine PrP. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 372491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fändrich, M.; Meinhardt, J.; Grigorieff, N. Structural polymorphism of Alzheimer Aβ and other amyloid fibrils. Prion 2009, 3, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Falcon, B.; Murzin, A.G.; Fan, J.; Crowther, R.A.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S.H.W. Heparin-induced tau filaments are polymorphic and differ from those in Alzheimer’s and pick’s diseases. eLife 2019, 8, e43584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surewicz, W.K.; Apostol, M.I. Prion Protein and Its Conformational Conversion: A Structural Perspective. In Peptide-Based Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 310, pp. 135–167. ISBN 978-3-540-73346-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, A.; Segers-Nolten, I.; Raussens, V.; Claessens, M.M.A.E.; Subramaniam, V. Distinct Mechanisms Determine α-Synuclein Fibril Morphology during Growth and Maturation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaunys, M.; Sakalauskas, A.; Smirnovas, V. Identifying Insulin Fibril Conformational Differences by Thioflavin-T Binding Characteristics. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocanu, M.-M.; Ganea, C.; Siposova, K.; Filippi, A.; Demjen, E.; Marek, J.; Bednarikova, Z.; Antosova, A.; Baran, I.; Gazova, Z. Polymorphism of hen egg white lysozyme amyloid fibrils influences the cytotoxicity in LLC-PK1 epithelial kidney cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycko, R. Amyloid Polymorphism: Structural Basis and Neurobiological Relevance. Neuron 2015, 86, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternke-Hoffmann, R.; Peduzzo, A.; Bolakhrif, N.; Haas, R.; Buell, A.K. The aggregation conditions define whether EGCG is an inhibitor or enhancer of α-synuclein amyloid fibril formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnige, T. Molecular mechanisms of amyloid formation in living systems. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 7080–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ow, S.-Y.; Dunstan, D.E. The effect of concentration, temperature and stirring on hen egg white lysozyme amyloid formation. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 9692–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawer, J.; Szociński, M.; Olszewski, M.; Piątek, R.; Naczk, M.; Krakowiak, J. Influence of the ionic strength on the amyloid fibrillogenesis of hen egg white lysozyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneideris, T.; Darguzis, D.; Botyriute, A.; Grigaliunas, M.; Winter, R.; Smirnovas, V. pH-Driven Polymorphism of Insulin Amyloid-Like Fibrils. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; Bird, S.; Shaw, M.; Jean, L.; Vaux, D.J. Combined effects of agitation, macromolecular crowding, and interfaces on amyloidogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38006–38019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y. Elevated temperatures accelerate the formation of toxic amyloid fibrils of hen egg-white lysozyme. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Orrú, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Surewicz, K.; Abskharon, R.; Imamura, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Kim, Y.S.; Vander Stel, K.J.; et al. Self-propagating, protease-resistant, recombinant prion protein conformers with or without in vivo pathogenicity. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittingham, J.L.; Scott, D.J.; Chance, K.; Wilson, A.; Finch, J.; Brange, J.; Guy Dodson, G. Insulin at pH 2: Structural analysis of the conditions promoting insulin fibre formation. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 318, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nettleton, E.J.; Tito, P.; Sunde, M.; Bouchard, M.; Dobson, C.M.; Robinson, C.V. Characterization of the Oligomeric States of Insulin in Self-Assembly and Amyloid Fibril Formation by Mass Spectrometry. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, V.L.; MacDonald, P.E.; Klip, A. The cell biology of systemic insulin function. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2273–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Protein Misfolding, Amyloid Formation, and Human Disease: A Summary of Progress over the Last Decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foderà, V.; Librizzi, F.; Groenning, M.; Van De Weert, M.; Leone, M. Secondary nucleation and accessible surface in insulin amyloid fibril formation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 3853–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormägi, A.; Valmsen, K.; Tõugu, V.; Palumaa, P. Insulin Fibrillization at Acidic and Physiological pH Values is Controlled by Different Molecular Mechanisms. Protein J. 2015, 34, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamani, J.; Shanmugam, G. Gallic acid, one of the components in many plant tissues, is a potential inhibitor for insulin amyloid fibril formation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Zhu, W.; Peng, J.; Ge, Z.; Li, C. A-type dimeric epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is a more potent inhibitor against the formation of insulin amyloid fibril than EGCG monomer. Biochimie 2016, 125, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; He, Z.; Peng, A.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, B.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, K. Effects of several quinones on insulin aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert-Gaudig, T.; Deckert, V. High resolution spectroscopy reveals fibrillation inhibition pathways of insulin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katebi, B.; Mahdavimehr, M.; Meratan, A.A.; Ghasemi, A.; Nemat-Gorgani, M. Protective effects of silibinin on insulin amyloid fibrillation, cytotoxicity and mitochondrial membrane damage. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 659, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz-Trillo, F.; Groenning, M.; van Maarschalkerweerd, A.; Tauler, R.; Vestergaard, B.; Bernadó, P. Structural Analysis of Multi-Component Amyloid Systems by Chemometric SAXS Data Decomposition. Structure 2017, 25, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Zhu, W.; Peng, J.; Ge, Z.; Li, C. Comparison of disaggregative effect of A-type EGCG dimer and EGCG monomer on the preformed bovine insulin amyloid fibrils. Biophys. Chem. 2017, 230, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Lazo, N.D. Mechanistic Studies of the Inhibition of Insulin Fibril Formation by Rosmarinic Acid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2323–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusrat, S.; Zaman, M.; Masroor, A.; Siddqi, M.K.; Zaidi, N.; Neelofar, K.; Abdelhameed, A.S.; Khan, R.H. Deciphering the enhanced inhibitory, disaggregating and cytoprotective potential of promethazine towards amyloid fibrillation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Tsuhara, S.; Tamura, A.; Chatani, E. A specific form of prefibrillar aggregates that functions as a precursor of amyloid nucleation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Jing, B.; Sorci, M.; Belfort, G.; Zhu, Y. Accelerated insulin aggregation under alternating current electric fields: Relevance to amyloid kinetics. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 044123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saithong, T.; Thilavech, T.; Adisakwattana, S. Cyanidin-3-rutinoside reduces insulin fibrillation and attenuates insulin fibrils-induced oxidative hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Sárkány, Z.; Fraga, J.S.; Taboada, P.; Macedo-Ribeiro, S.; Martins, P.M. Probing the occurrence of soluble oligomers through amyloid aggregation scaling laws. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, Z.; Grannemann, H.; Baffour, K.; Koti, N.; Taylor, E.; Grier, E.; Sutton, C.; Johnson, D.; Dandawate, P.; Patel, R.; et al. Mechanistic Insights Behind the Self-Assembly of Human Insulin under the Influence of Surface-Engineered Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Zhaliazka, K.; Holman, A.P.; Kurouski, D. Elucidation of the Role of Lipids in Late Endosomes on the Aggregation of Insulin. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3551–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazeri, G.; Povinelli, A.P.R.; Pavan, N.M.; Jones, A.M.; Ximenes, V.F. Solvent-Induced Lag Phase during the Formation of Lysozyme Amyloid Fibrils Triggered by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: Biophysical Experimental and In Silico Study of Solvent Effects. Molecules 2023, 28, 6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.M.; Malik, A.; Alresaini, S.M. Molecular mechanism of insulin aggregation in the presence of a cationic surfactant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Shah, M.; Saraogi, I. Molecular Aspects of Insulin Aggregation and Various Therapeutic Interventions. ACS Bio Med Chem Au 2022, 2, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaunys, M.; Mikalauskaite, K.; Sakalauskas, A.; Smirnovas, V. Interplay between epigallocatechin-3-gallate and ionic strength during amyloid aggregation. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banga, A.K. Therapeutic Peptides and Proteins; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780429099908. [Google Scholar]
- Grudzielanek, S.; Smirnovas, V.; Winter, R. Solvation-assisted Pressure Tuning of Insulin Fibrillation: From Novel Aggregation Pathways to Biotechnological Applications. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 356, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalauskas, A.; Ziaunys, M.; Smirnovas, V. Concentration-dependent polymorphism of insulin amyloid fibrils. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaunys, M.; Sakalauskas, A.; Mikalauskaite, K.; Smirnovas, V. Exploring the occurrence of thioflavin-T-positive insulin amyloid aggregation intermediates. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoury, M.; Hamed, M.; Karmustaji, R.; Al Hannan, F.; Safrany, S.T. The edge effect: A global problem. The trouble with culturing cells in 96-well plates. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 100987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalauskaite, K.; Ziaunys, M.; Sneideris, T.; Smirnovas, V. Effect of Ionic Strength on Thioflavin-T Affinity to Amyloid Fibrils and Its Fluorescence Intensity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikalauskaite, K.; Ziaunys, M.; Smirnovas, V. Lysozyme Amyloid Fibril Structural Variability Dependence on Initial Protein Folding State. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaunys, M.; Smirnovas, V. Additional Thioflavin-T Binding Mode in Insulin Fibril Inner Core Region. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 8727–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziaunys, M.; Mikalauskaite, K.; Sakalauskas, A.; Smirnovas, V. Study of Insulin Aggregation and Fibril Structure under Different Environmental Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9406. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179406
Ziaunys M, Mikalauskaite K, Sakalauskas A, Smirnovas V. Study of Insulin Aggregation and Fibril Structure under Different Environmental Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9406. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179406
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiaunys, Mantas, Kamile Mikalauskaite, Andrius Sakalauskas, and Vytautas Smirnovas. 2024. "Study of Insulin Aggregation and Fibril Structure under Different Environmental Conditions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9406. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179406
APA StyleZiaunys, M., Mikalauskaite, K., Sakalauskas, A., & Smirnovas, V. (2024). Study of Insulin Aggregation and Fibril Structure under Different Environmental Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9406. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179406






