Galectin-1 Attenuates PDGF-Mediated AKT Signaling in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
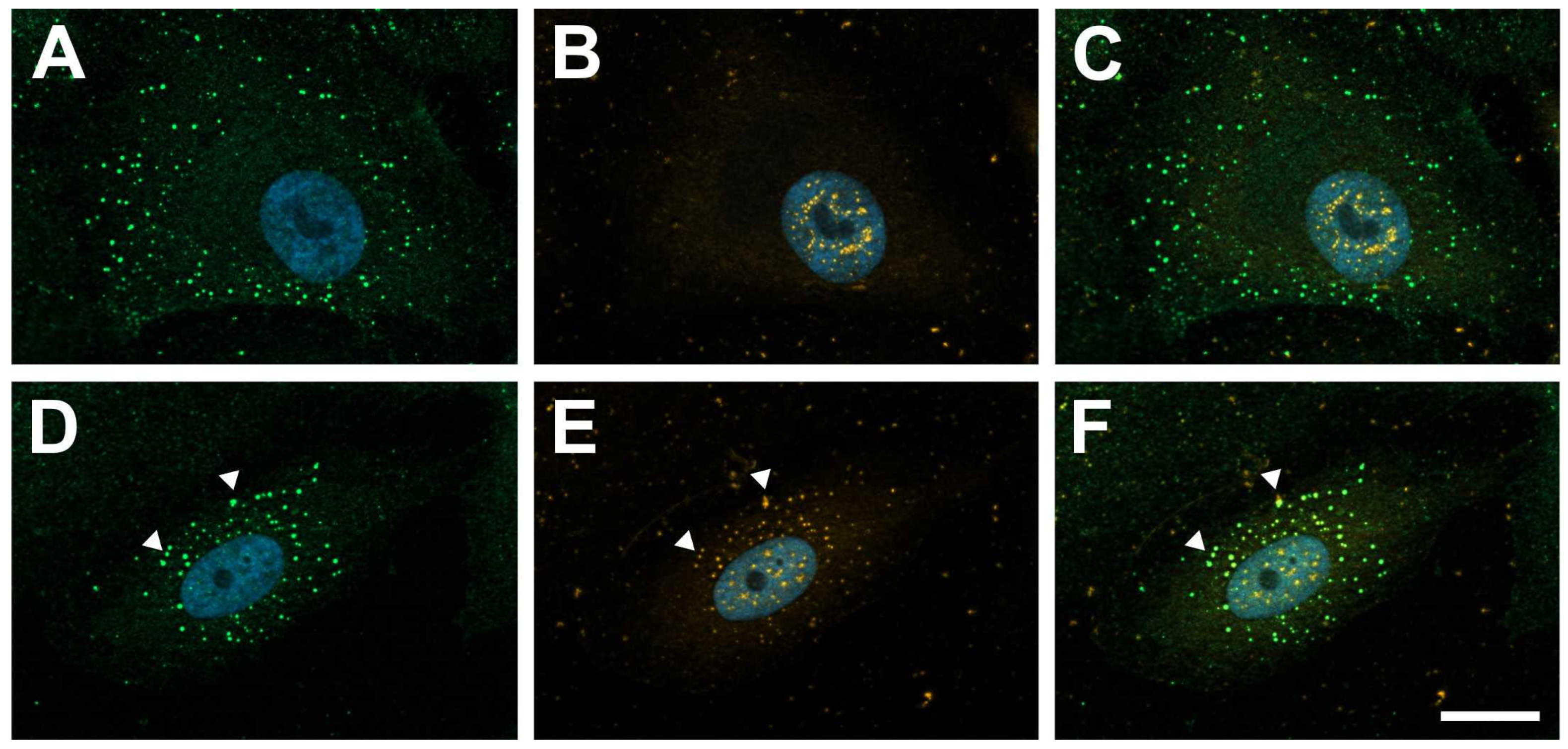
2.1. Galectin-1 Colocalizes with PDGF-BB-Induced Clusters of PDGF-Rβ
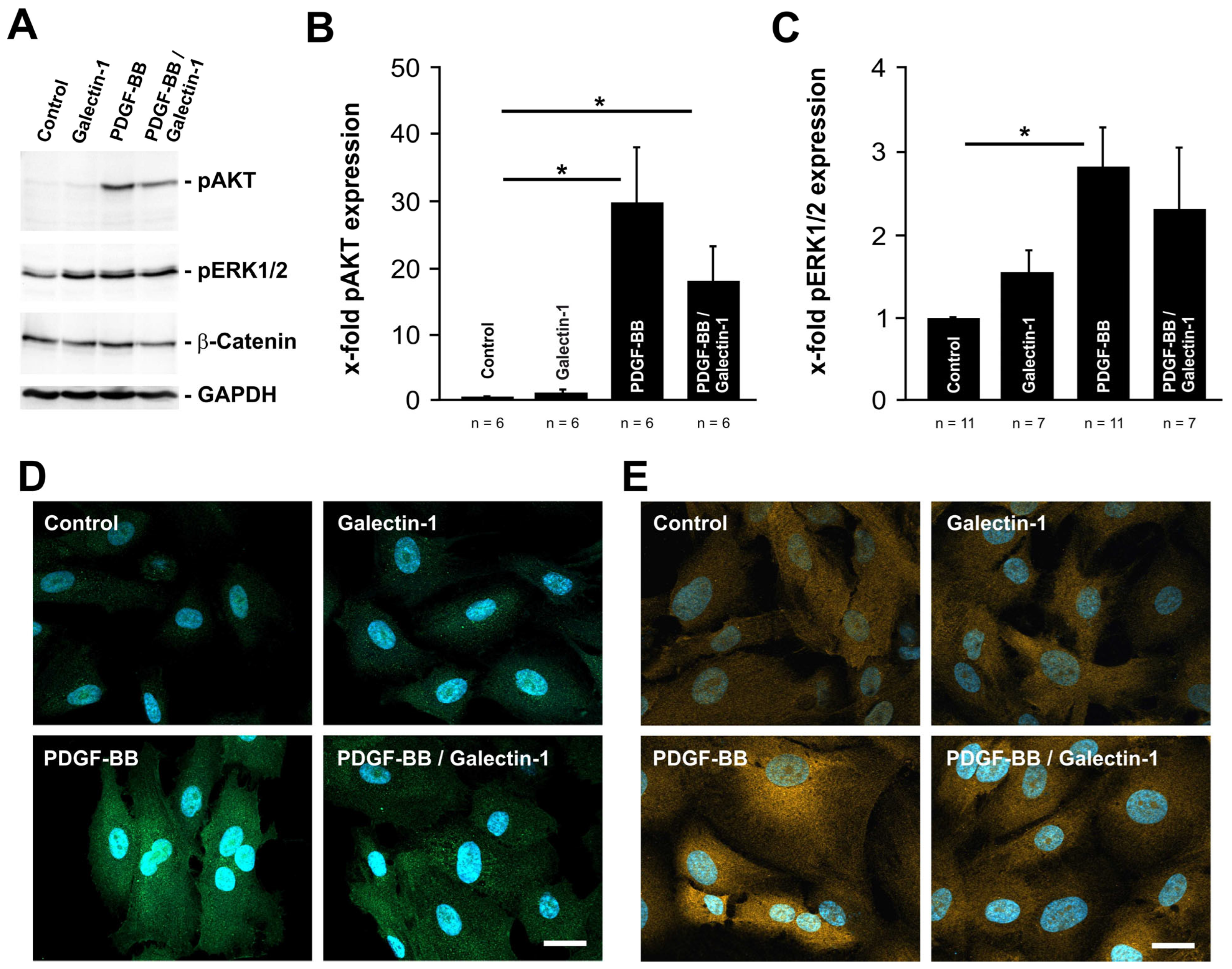
2.2. PDGF-BB-Induced AKT and ERK1/2 Signaling Is Reduced by hr-Galectin-1
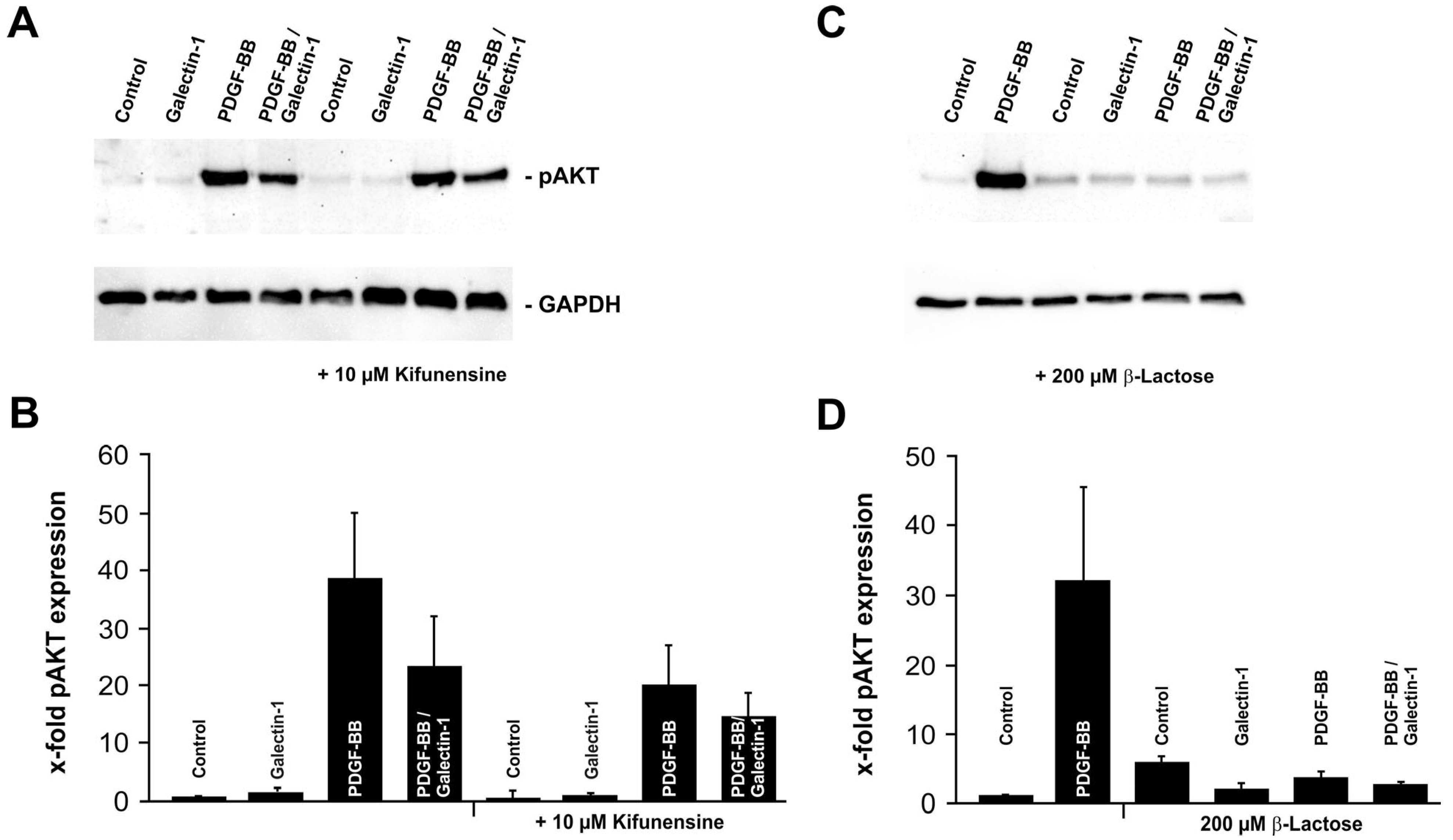
2.3. Galectin-1 Reduces PDGF-BB-Induced AKT Signaling in a Glycosylation-Dependent Manner
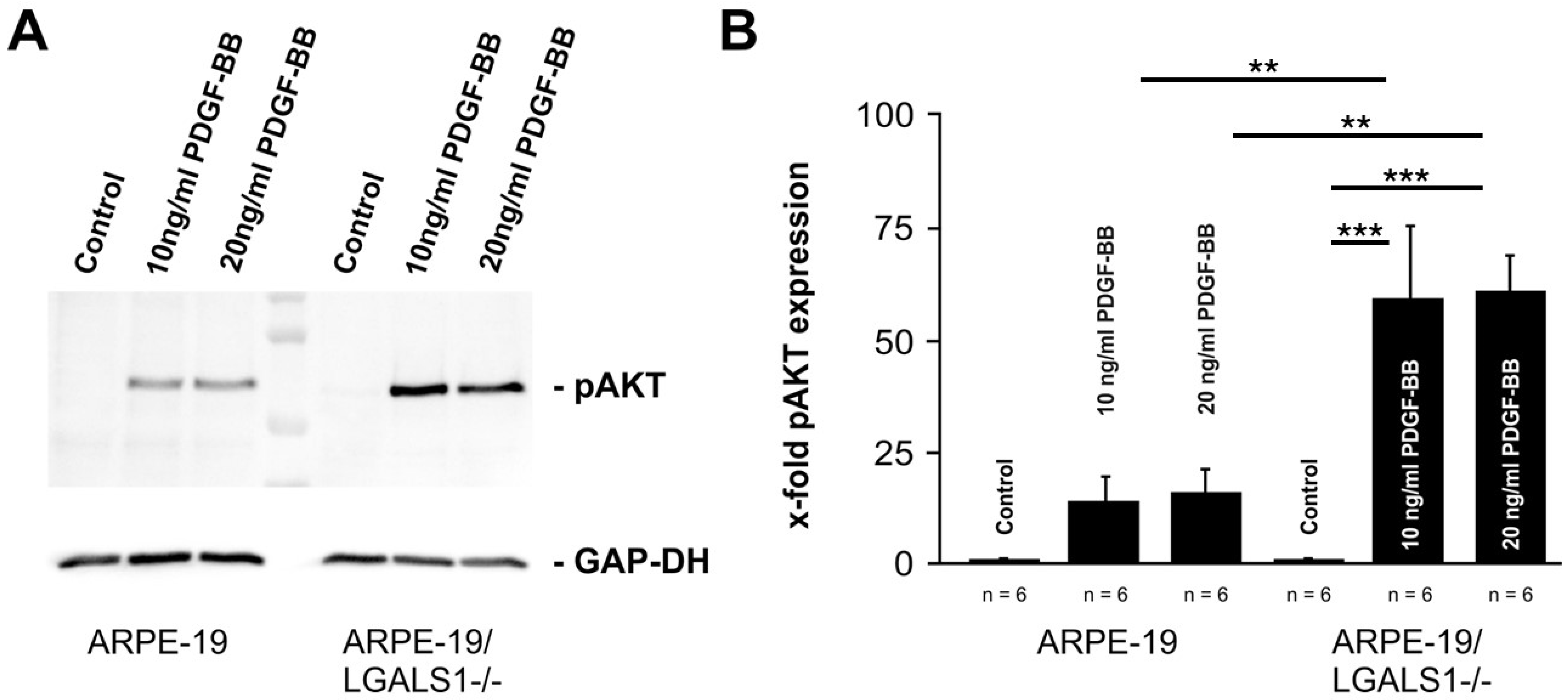
2.4. Lack of Endogenous Galectin-1 Enhances PDGF-BB-Mediated pAKT Signaling
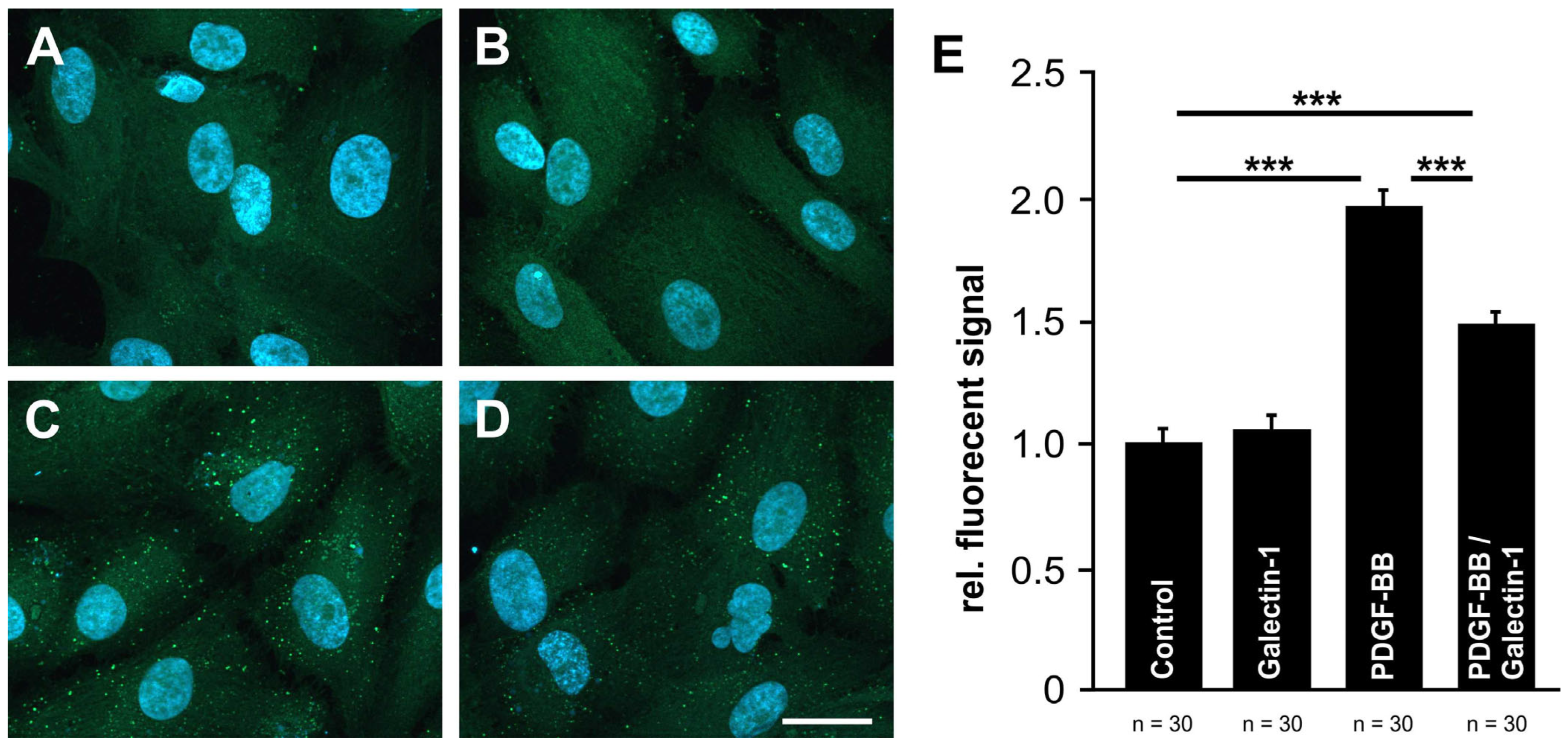
2.5. Galectin-1 Reduces PDGF-BB-Mediated Clustering of PDGF-Rβ
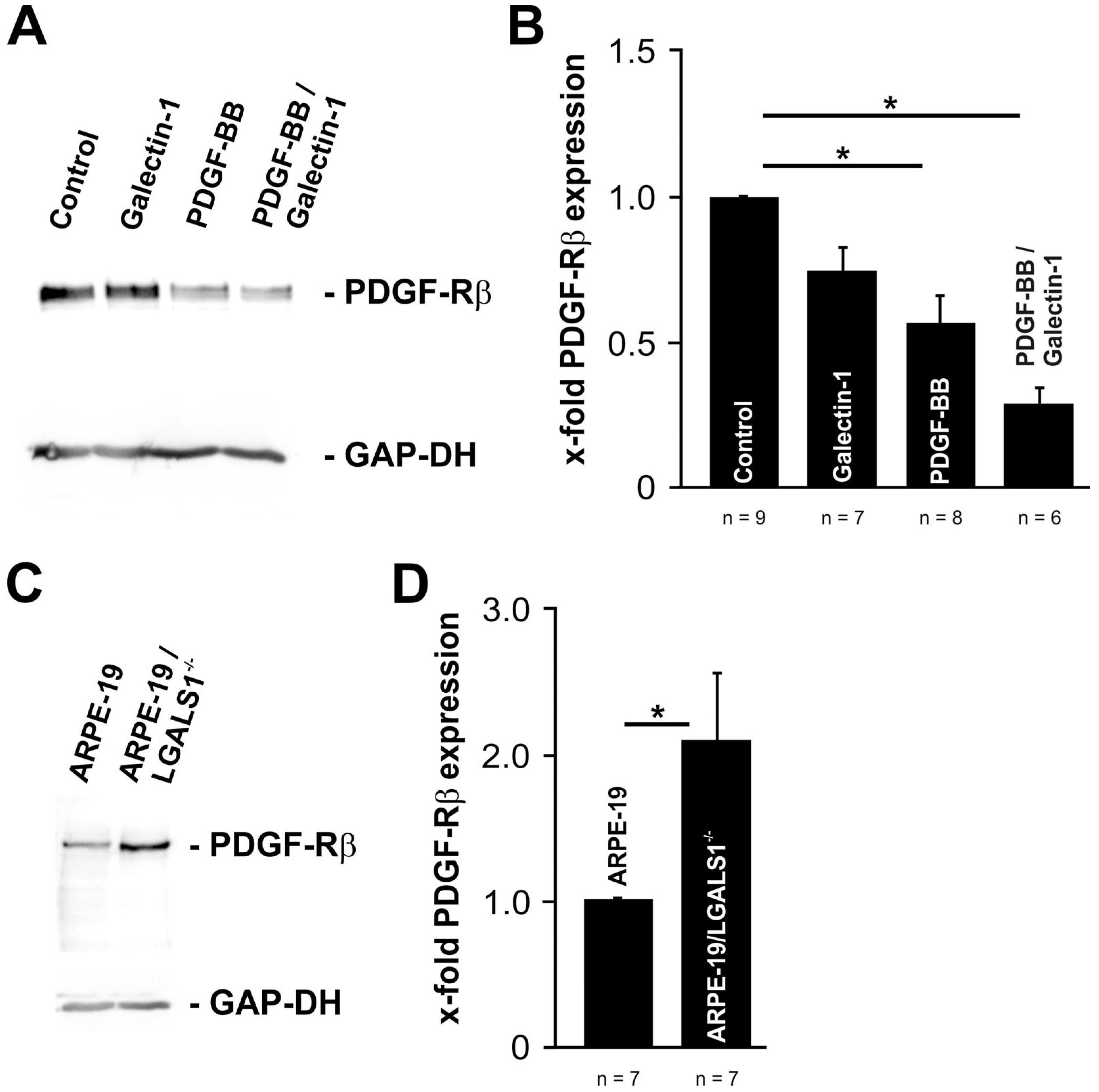
2.6. Exogenous and Endogenous Galectin-1 Mitigates PDGF-BB-Mediated pAKT Signaling by Reducing PDGF-Rβ Expression in RPE Cells
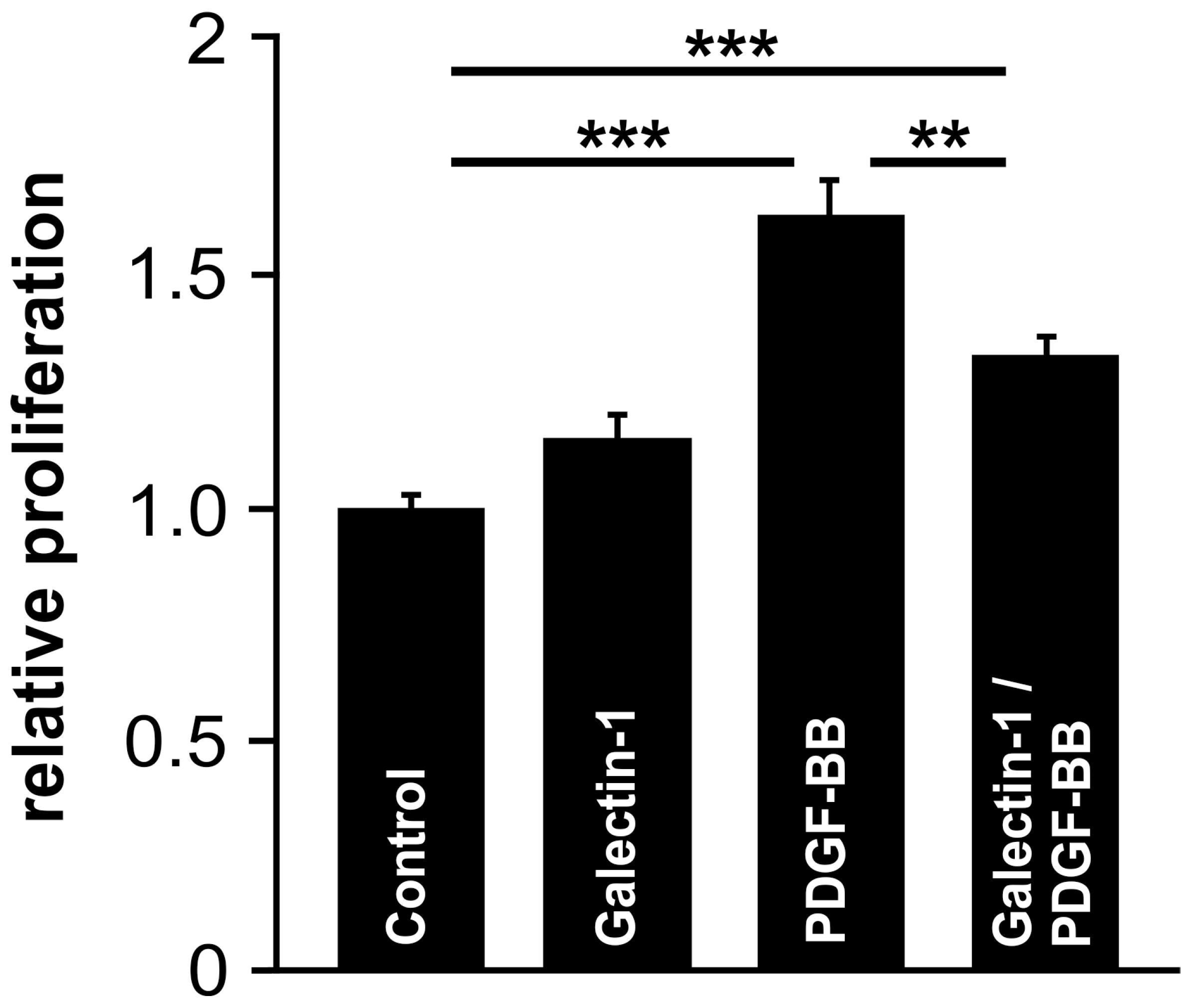
2.7. Galectin-1 Attenuates PDGF-Induced RPE Cell Proliferation
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Isolation of hr-Galectin-1
4.3. Cell Proliferation
4.4. Immunocytochemistry
4.5. Protein Preparation and Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barondes, S.H.; Castronovo, V.; Cooper, D.N.; Cummings, R.D.; Drickamer, K.; Feizi, T.; Gitt, M.A.; Hirabayashi, J.; Hughes, C.; Kasai, K.; et al. Galectins: A family of animal β-galactoside-binding lectins. Cell 1994, 76, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laaf, D.; Bojarova, P.; Elling, L.; Kren, V. Galectin-Carbohydrate Interactions in Biomedicine and Biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.W.; Hong, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, D.H.; Song, H.K. Structural basis for recognition of autophagic receptor NDP52 by the sugar receptor galectin-8. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camby, I.; Le Mercier, M.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R. Galectin-1: A small protein with major functions. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 137R–157R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Jacob, R.; Leffler, H. Galectins at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs208884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, D. Galectin-1 Regulates RNA Expression and Alternative Splicing of Angiogenic Genes in HUVECs. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2023, 28, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, J.A.; Chang, M.H.; Wang, S.; Almazan, T.; Hashimi, S.T.; Eriksson, A.U.; Wen, X.; Pang, M.; Baum, L.G.; Singh, R.R.; et al. Galectin-1 co-clusters CD43/CD45 on dendritic cells and induces cell activation and migration through Syk and protein kinase C signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26860–26870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Hernandez, E.; Sanchez-Maldonado, C.; Mayoral Chavez, M.A.; Hernandez-Zimbron, L.F.; Patricio Martinez, A.; Zenteno, E.; Limon Perez de Leon, I.D. The therapeutic potential of galectin-1 and galectin-3 in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, K.V.; Cagnoni, A.J.; Croci, D.O.; Rabinovich, G.A. Targeting galectin-driven regulatory circuits in cancer and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryk, E.; Silva, V.R.R.; Jansson, P.A. Galectin-1 in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutine, A.M.; Bach, C.A.; Veigas, F.; Merlo, J.P.; Laporte, L.; Manselle Cocco, M.N.; Massaro, M.; Sarbia, N.; Perrotta, R.M.; Mahmoud, Y.D.; et al. Tissue-specific control of galectin-1-driven circuits during inflammatory responses. Glycobiology 2021, 31, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alge, C.S.; Priglinger, S.G.; Kook, D.; Schmid, H.; Haritoglou, C.; Welge-Lussen, U.; Kampik, A. Galectin-1 influences migration of retinal pigment epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.R.; Lagrew, M.K.; Tillit, S.M.; Roohipourmoallai, R.; Korntner, S. The Vitreous Ecosystem in Diabetic Retinopathy: Insight into the Patho-Mechanisms of Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragiotta, S.; Bassis, L.; Abdolrahimzadeh, B.; Marino, A.; Sepe, M.; Abdolrahimzadeh, S. Exploring Current Molecular Targets in the Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration toward the Perspective of Long-Term Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Rheaume, M.A.; Kazlauskas, A. Recent developments in our understanding of how platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and its receptors contribute to proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, L.; Li, H.; Eriksson, U. The PDGF family: Four gene products form five dimeric isoforms. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F.; Upadhyay, T.K.; Seungjoon, M.; Park, M.N.; Kim, B. New insights about the PDGF/PDGFR signaling pathway as a promising target to develop cancer therapeutic strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.; Lennartsson, J. The PDGF/PDGFR pathway as a drug target. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 62, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzebski, K.; Zdzalik-Bielecka, D.; Maminska, A.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Hellberg, C.; Miaczynska, M. Multiple routes of endocytic internalization of PDGFRβ contribute to PDGF-induced STAT3 signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Qiao, J. Galectin-1 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells through the inactivation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, J.; Priglinger, C.S.; Merl-Pham, J.; Geerlof, A.; Priglinger, S.; Gotz, M.; Hauck, S.M. Proteome-wide Identification of Glycosylation-dependent Interactors of Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 on Mesenchymal Retinal Pigment Epithelial (RPE) Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 1528–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesenhoff, C.; Paulus, S.M.; Havertz, C.; Geerlof, A.; Priglinger, S.; Priglinger, C.S.; Ohlmann, A. Endogenous Galectin-1 Modulates Cell Biological Properties of Immortalized Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayakiri, H.; Kasahara, C.; Oku, T.; Hashimoto, M. Synthesis of kifunensine, an immunomodulating substance isolated from microbial source. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbein, A.D. Glycosidase inhibitors: Inhibitors of N-linked oligosaccharide processing. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 3055–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbein, A.D.; Tropea, J.E.; Mitchell, M.; Kaushal, G.P. Kifunensine, a potent inhibitor of the glycoprotein processing mannosidase I. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 15599–15605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesmelova, I.V.; Ermakova, E.; Daragan, V.A.; Pang, M.; Menendez, M.; Lagartera, L.; Solis, D.; Baum, L.G.; Mayo, K.H. Lactose binding to galectin-1 modulates structural dynamics, increases conformational entropy, and occurs with apparent negative cooperativity. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 1209–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.H.; Chen, X.; He, X. Platelet-derived growth factors and their receptors: Structural and functional perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.; Orcholski, M.; Yuan, K.; de Jesus Perez, V. PDGF-dependent β-catenin activation is associated with abnormal pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.H.; Westermark, B. Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1283–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollborn, M.; Bringmann, A.; Faude, F.; Wiedemann, P.; Kohen, L. Signaling pathways involved in PDGF-evoked cellular responses in human RPE cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abroun, S.; Otsuyama, K.; Shamsasenjan, K.; Islam, A.; Amin, J.; Iqbal, M.S.; Gondo, T.; Asaoku, H.; Kawano, M.M. Galectin-1 supports the survival of CD45RA(-) primary myeloma cells in vitro. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Han, H.J. Galectin-1 upregulates glucose transporter-1 expression level via protein kinase C, phosphoinositol-3 kinase, and mammalian target of rapamycin pathways in mouse embryonic stem cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masamune, A.; Satoh, M.; Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K.; Satoh, K.; Shimosegawa, T. Galectin-1 induces chemokine production and proliferation in pancreatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G729–G736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, C.L.; Lu, D.W.; Liang, C.M.; Tai, M.C.; Chen, J.T. Silibinin Inhibits Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-Driven Cell Proliferation via Downregulation of N-Glycosylation in Human Tenon’s Fibroblasts in a Proteasome-Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, L.K.; Sorkin, A. Endocytosis of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a017459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, N.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Bertout, J.; Paz, I.; Freche, B.; Van Nhieu, G.T.; van der Goot, F.G.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Lafont, F. Shigella phagocytic vacuolar membrane remnants participate in the cellular response to pathogen invasion and are regulated by autophagy. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, J.W.; Chong, S.Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Soon, J.L.; Liang, M.C.; Wong, Y.P.; Huang, N.; et al. Regulation of Blood Pressure by Targeting Ca(V)1.2-Galectin-1 Protein Interaction. Circulation 2018, 138, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Huang, D.J.; Baloche, V.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.X.; Li, B.W.; Zhao, X.R.; He, J.; Mai, H.Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; et al. Galectin-9 promotes a suppressive microenvironment in human cancer by enhancing STING degradation. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, P.; Hagan, S.; Heathcote, L.; Sheridan, C.M.; Groenewald, C.P.; Grierson, I.; Wong, D.; Paraoan, L. Pathobiology of epiretinal and subretinal membranes: Possible roles for the matricellular proteins thrombospondin 1 and osteonectin (SPARC). Eye 2002, 16, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Lei, H.; Samad, A.; Basavanthappa, S.; Maberley, D.; Matsubara, J.; Kazlauskas, A. PDGF receptors are activated in human epiretinal membranes. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 88, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, G.; Cui, J.; Matsubara, J.A.; Kazlauskas, A.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Lei, H. PDGFRβ plays an essential role in patient vitreous-stimulated contraction of retinal pigment epithelial cells from epiretinal membranes. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 197, 108116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alge-Priglinger, C.S.; Andre, S.; Kreutzer, T.C.; Deeg, C.A.; Kampik, A.; Kernt, M.; Schoffl, H.; Priglinger, S.G.; Gabius, H.J. Inhibition of human retinal pigment epithelial cell attachment, spreading, and migration by the human lectin galectin-1. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alge, C.S.; Priglinger, S.G.; Neubauer, A.S.; Kampik, A.; Zillig, M.; Bloemendal, H.; Welge-Lussen, U. Retinal pigment epithelium is protected against apoptosis by alphaB-crystallin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar]
- Hillenmayer, A.; Wertheimer, C.M.; Geerlof, A.; Eibl, K.H.; Priglinger, S.; Priglinger, C.; Ohlmann, A. Galectin-1 and -3 in high amounts inhibit angiogenic properties of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priglinger, C.S.; Szober, C.M.; Priglinger, S.G.; Merl, J.; Euler, K.N.; Kernt, M.; Gondi, G.; Behler, J.; Geerlof, A.; Kampik, A.; et al. Galectin-3 induces clustering of CD147 and integrin-β1 transmembrane glycoprotein receptors on the RPE cell surface. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bizzotto, M.; Ostermaier, A.; Liesenhoff, C.; Ma, W.; Geerlof, A.; Priglinger, S.G.; Priglinger, C.S.; Ohlmann, A. Galectin-1 Attenuates PDGF-Mediated AKT Signaling in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179267
Bizzotto M, Ostermaier A, Liesenhoff C, Ma W, Geerlof A, Priglinger SG, Priglinger CS, Ohlmann A. Galectin-1 Attenuates PDGF-Mediated AKT Signaling in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179267
Chicago/Turabian StyleBizzotto, Martina, Annabella Ostermaier, Caspar Liesenhoff, Wenxiu Ma, Arie Geerlof, Siegfried G. Priglinger, Claudia S. Priglinger, and Andreas Ohlmann. 2024. "Galectin-1 Attenuates PDGF-Mediated AKT Signaling in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179267
APA StyleBizzotto, M., Ostermaier, A., Liesenhoff, C., Ma, W., Geerlof, A., Priglinger, S. G., Priglinger, C. S., & Ohlmann, A. (2024). Galectin-1 Attenuates PDGF-Mediated AKT Signaling in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179267





