Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Are the Major Class of HIV Antiretroviral Therapeutics That Induce Neuropathic Pain in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
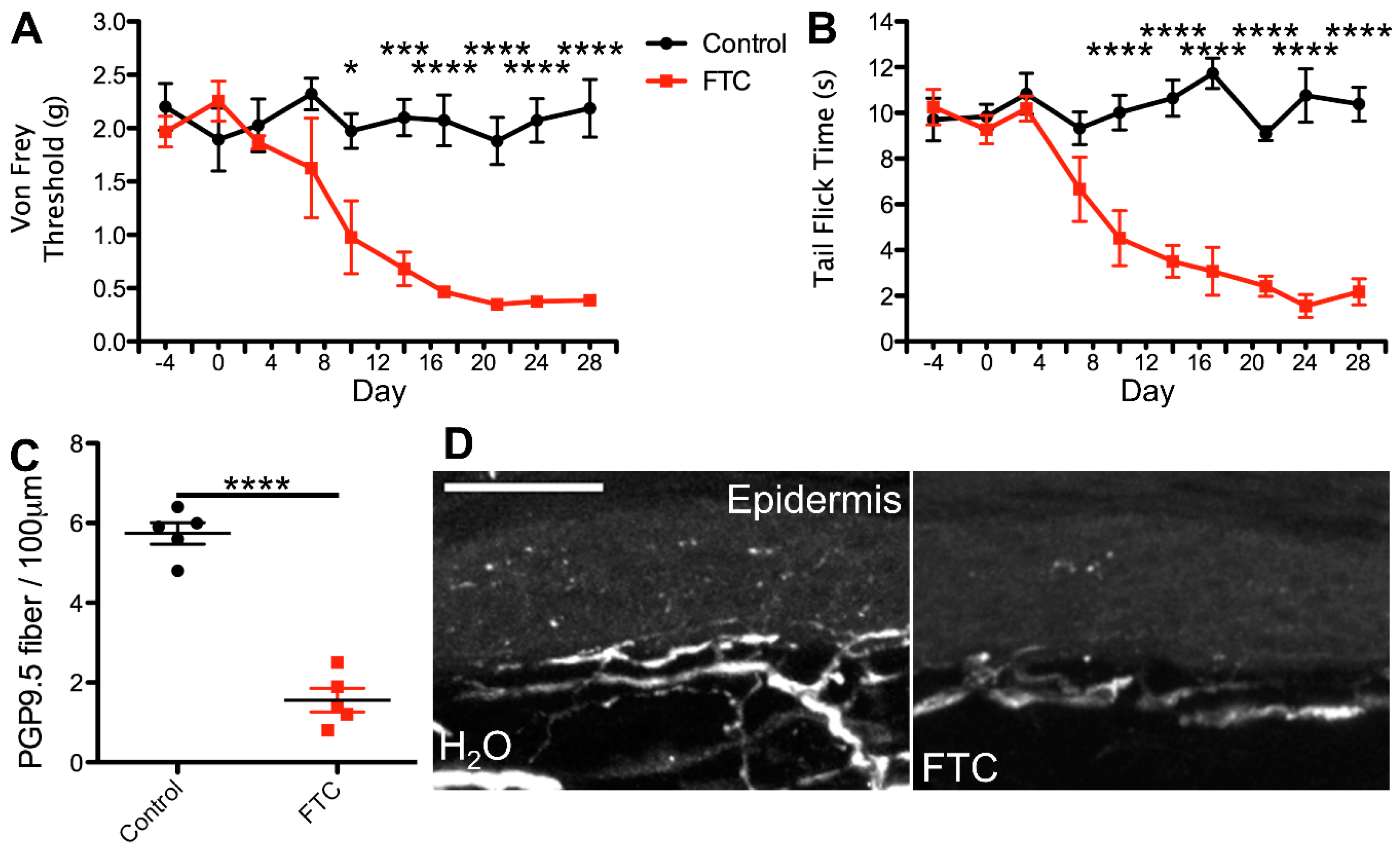
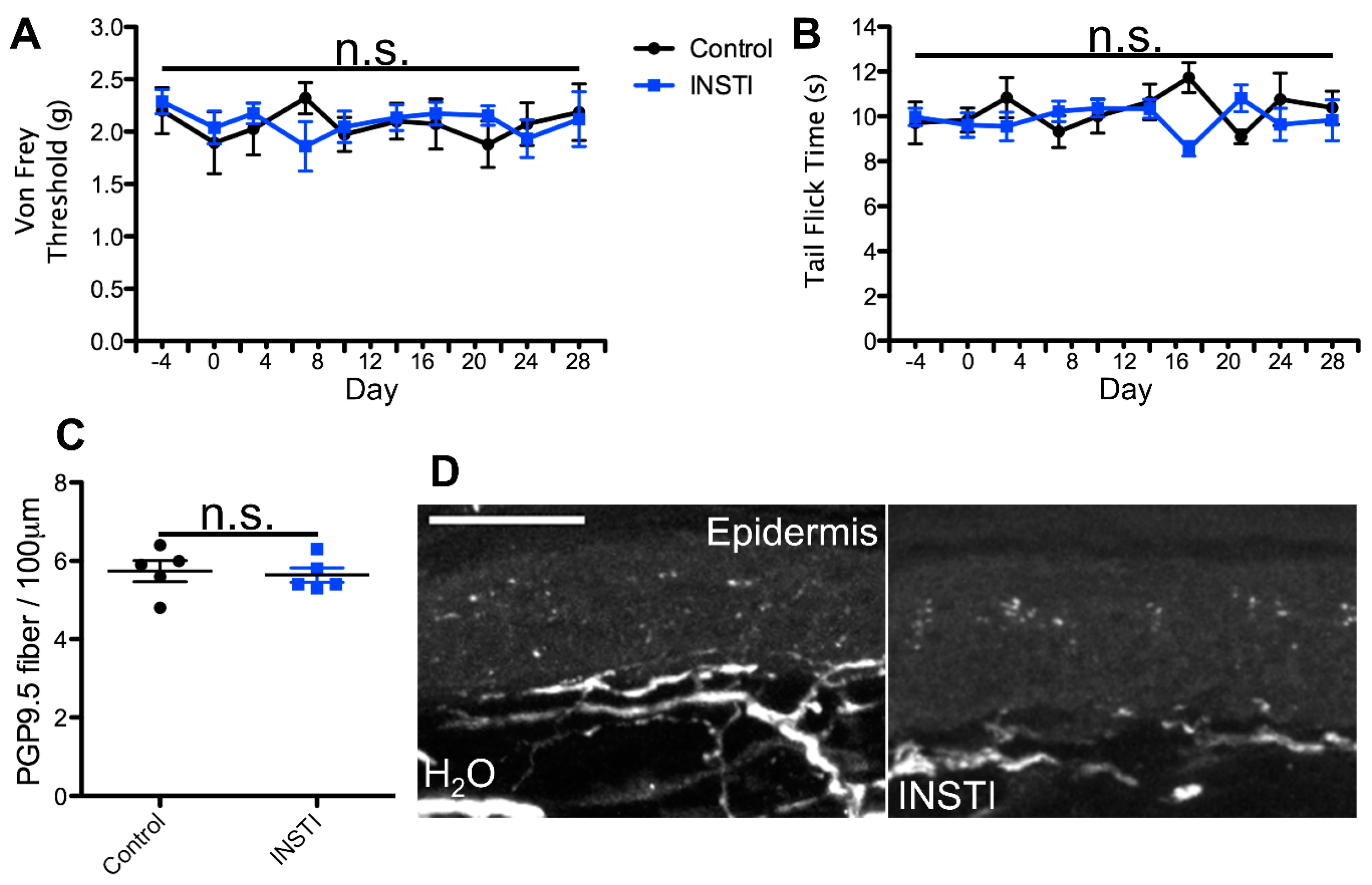
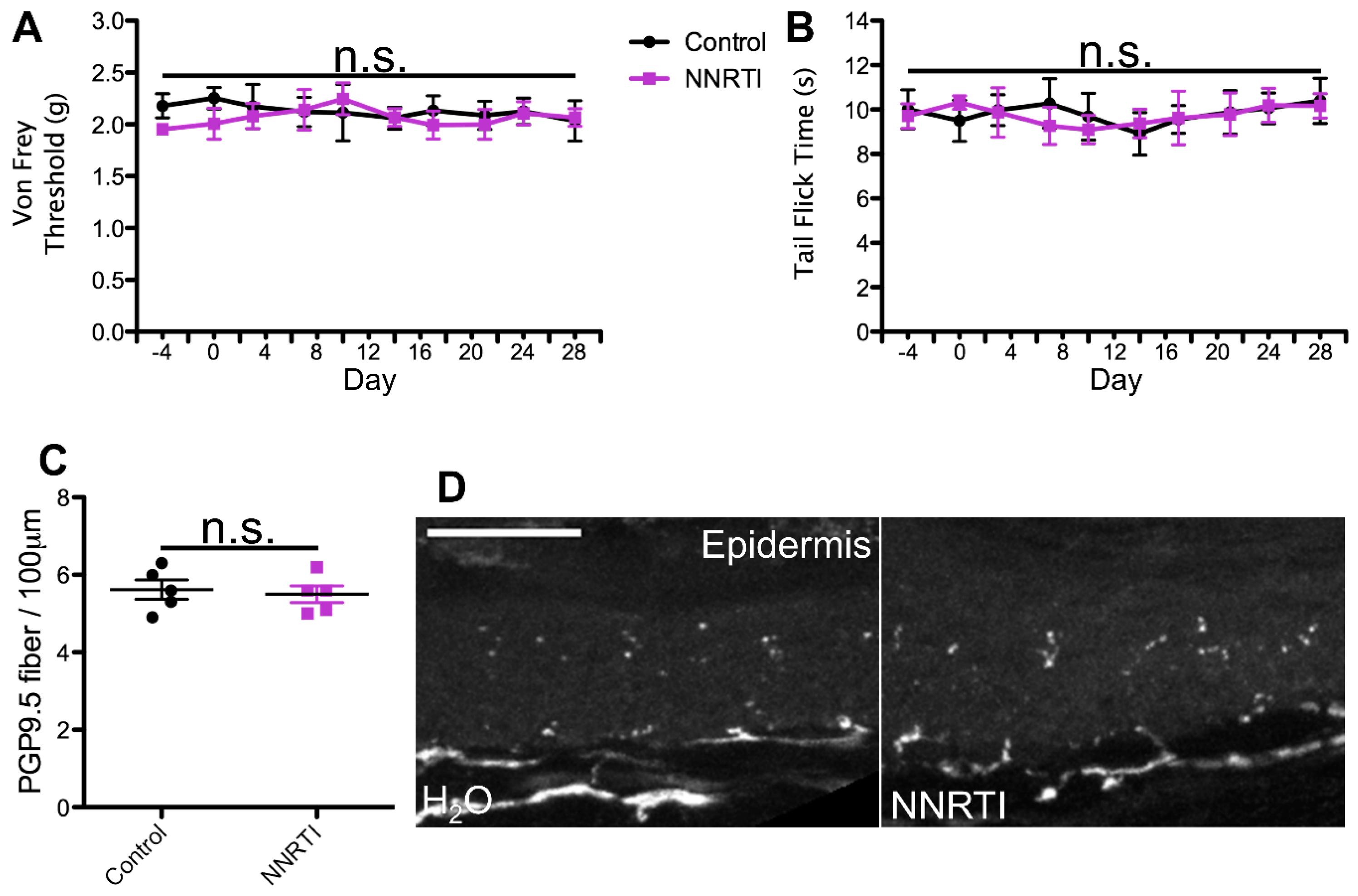
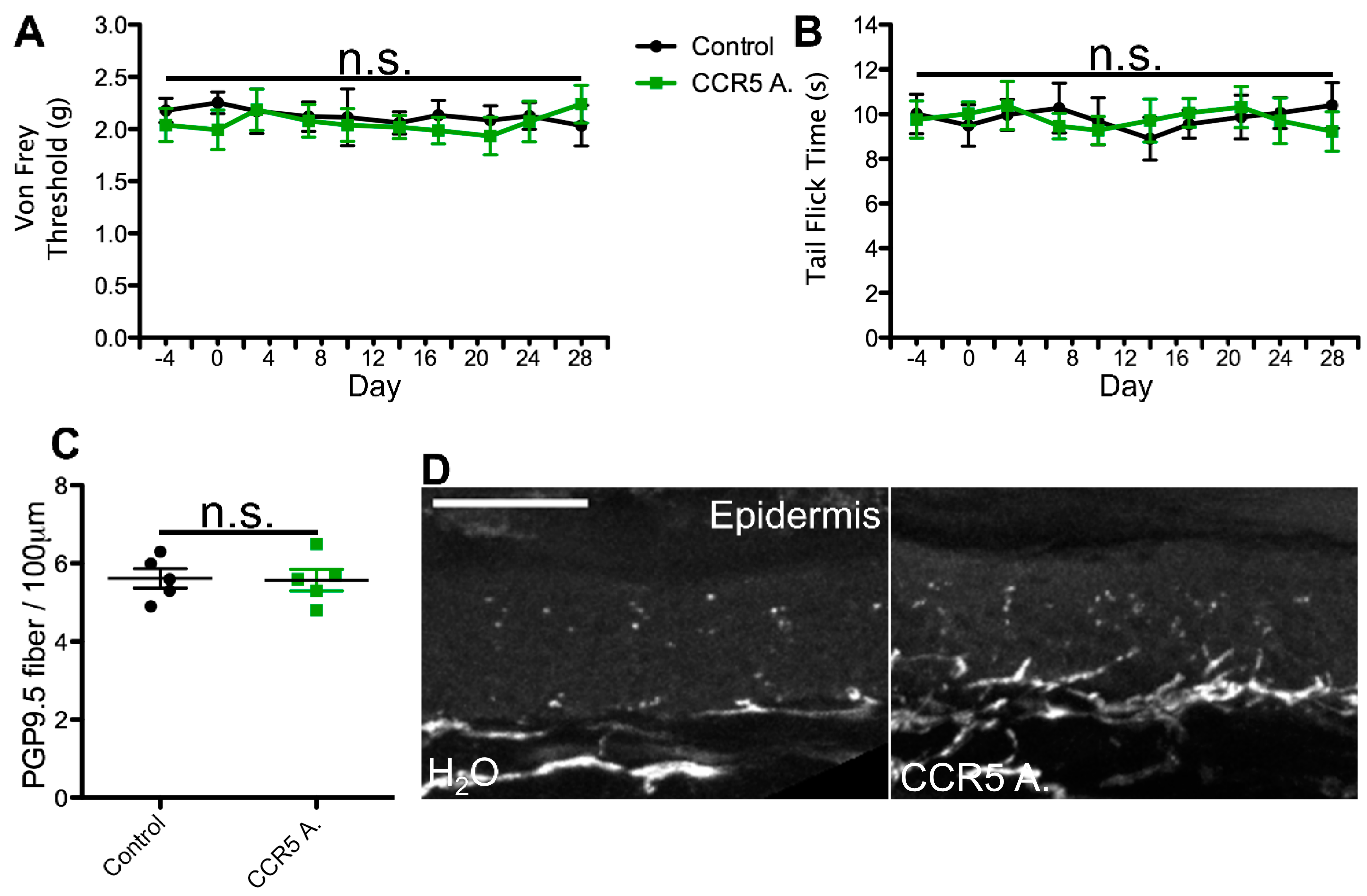
2.1. cART Induces Mechanical Nociception Changes
2.2. Thermal Nociception Sensitization Induced by cART
2.3. Epidermal Denervation Induced by cART
3. Discussion
3.1. Ingestion of cART
3.2. Neurotoxicity of cART
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Mouse Thermal Nociception
4.3. Mouse Mechanical Nociception
4.4. Mouse Treatment
4.5. Mouse Dissection, Imaging, and Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saag, M.S.; Benson, C.A.; Gandhi, R.T.; Hoy, J.F.; Landovitz, R.J.; Mugavero, M.J.; Sax, P.E.; Smith, D.M.; Thompson, M.A.; Buchbinder, S.P.; et al. Antiretroviral Drugs for Treatment and Prevention of HIV Infection in Adults. JAMA 2018, 320, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, R.K.; Franklin, D.R.; Ellis, R.J.; McCutchan, J.A.; Letendre, S.L.; Leblanc, S.; Corkran, S.H.; Duarte, N.A.; Clifford, D.B.; Woods, S.P.; et al. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders before and during the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: Differences in rates, nature, and predictors. J. Neurovirol. 2011, 17, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, E.A.; Wang, A.K.; Simpson, D.M. HIV-associated peripheral neuropathy: Epidemiology, pathophysiology and treatment. Drugs 2000, 59, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chandran, A.; Jansen, J.P. Epidemiology of HIV-related neuropathy: A systematic literature review. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacktor, N. The epidemiology of human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurological disease in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J. Neurovirol. 2002, 8 (Suppl. S2), 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.R.; Ellis, R.J.; Chen, H.; Yeh, T.; Lee, A.J.; Schifitto, G.; Wu, K.; Bosch, R.J.; McArthur, J.C.; Simpson, D.M.; et al. Peripheral neuropathy in HIV: Prevalence and risk factors. AIDS 2011, 25, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.M.; Kitch, D.; Evans, S.R.; McArthur, J.C.; Asmuth, D.M.; Cohen, B.; Goodkin, K.; Gerschenson, M.; So, Y.; Marra, C.M.; et al. HIV neuropathy natural history cohort study: Assessment measures and risk factors. Neurology 2006, 66, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamoto, B.K.; McMurtray, A.; Davis, J.; Valcour, V.; Watters, M.R.; Shiramizu, B.; Chow, D.C.; Kallianpur, K.; Shikuma, C.M. Incident neuropathy in HIV-infected patients on HAART. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2010, 26, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Gangwani, M.R.; Chaudhari, N.S.; Glazyrin, A.; Bhat, H.K.; Kumar, A. Neurotoxicity in the Post-HAART Era: Caution for the Antiretroviral Therapeutics. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 30, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, J.S.; Nagalli, S. Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, B.; Li, Z.; Nath, A. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and human immunodeficiency virus proteins cause axonal injury in human dorsal root ganglia cultures. J. Neurovirol. 2007, 13, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Geng, M.; Tang, S.-J.; Zhang, W.; Shu, J. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) induce proinflammatory cytokines in the CNS via Wnt5a signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, P.; Westby, M.; Dobbs, S.; Griffin, P.; Irvine, B.; Macartney, M.; Mori, J.; Rickett, G.; Smith-Burchnell, C.; Napier, C.; et al. Maraviroc (UK-427,857), a potent, orally bioavailable, and selective small-molecule inhibitor of chemokine receptor CCR5 with broad-spectrum anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4721–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, V.; Keating, G.M.; Plosker, G. Enfuvirtide: A review of its use in the management of HIV infection. Drugs 2005, 65, 1139–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, C.L.; Duncan, A.J.; Mackie, K.F.; Wesselingh, S.L.; Brew, B.J. A report on the effect of commencing enfuvirtide on peripheral neuropathy. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2008, 24, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emu, B.; Fessel, J.; Schrader, S.; Kumar, P.; Richmond, G.; Win, S.; Weinheimer, S.; Marsolais, C.; Lewis, S. Phase 3 Study of Ibalizumab for Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Rawal, R.K.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Structure Based Drug Design: Clinically Relevant HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 2664–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teppler, H.; Brown, D.D.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Sklar, P.; Wan, H.; Xu, X.; Lievano, F.; Lehman, H.P.; Mast, T.C.; Nguyen, B.-Y.T. Long-term safety from the raltegravir clinical development program. Curr. HIV Res. 2011, 9, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettiplace, A.; Stainsby, C.; Winston, A.; Givens, N.; Puccini, S.; Vannappagari, V.; Hsu, R.; Fusco, J.; Quercia, R.; Aboud, M.; et al. Psychiatric Symptoms in Patients Receiving Dolutegravir. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 74, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas-García, A.; Polo, M.; Alegre, F.; Funes, H.A.; Martínez, E.; Apostolova, N.; Esplugues, J.V. Lack of mitochondrial toxicity of darunavir, raltegravir and rilpivirine in neurons and hepatocytes: A comparison with efavirenz. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2995–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latronico, T.; Pati, I.; Ciavarella, R.; Fasano, A.; Mengoni, F.; Lichtner, M.; Vullo, V.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Liuzzi, G.M. In vitro effect of antiretroviral drugs on cultured primary astrocytes: Analysis of neurotoxicity and matrix metalloproteinase inhibition. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Woldstad, C.J.; Fang, M.; Bade, A.N.; McMillan, J.; Edagwa, B.; Boska, M.D.; Gendelman, H.E.; Siuzdak, G. Nanoformulated Antiretroviral Therapy Attenuates Brain Metabolic Oxidative Stress. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Y. HIV protease inhibitors: A review of molecular selectivity and toxicity. HIVAIDS 2015, 7, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.K.; Monnerie, H.; Mannell, M.V.; Gannon, P.J.; Espinoza, C.A.; Erickson, M.A.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Gelman, B.B.; Briand, L.A.; Pierce, R.C.; et al. Altered Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Myelin Maintenance: The Role of Antiretrovirals in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 1093–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Knight, A.G.; Losso, B.Y.; Ingram, D.K.; Keller, J.N.; Bruce-Keller, A.J. Brain injury caused by HIV protease inhibitors: Role of lipodystrophy and insulin resistance. Antivir. Res. 2012, 95, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, J.A.; Jones, G.; Worthington, C.; Krentz, H.B.; Keppler, O.T.; Hoke, A.; Gill, M.J.; Power, C. Sensory neuropathy in human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients: Protease inhibitor-mediated neurotoxicity. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J.; Marquie-Beck, J.; Delaney, P.; Alexander, T.; Clifford, D.B.; McArthur, J.C.; Simpson, D.M.; Ake, C.; Collier, A.C.; Gelman, B.B.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors and risk for peripheral neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastone, J.A.; Decker, C.F. New-onset diabetes mellitus associated with use of protease inhibitor. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 127, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlese, J.F.; Qazi, N.A.; Gazzard, B.G.; Nelson, M.R. Nevirapine-induced neuropsychiatric complications, a class effect of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors? AIDS 2002, 16, 1840–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, M.E.J.; Mistry, K.; Reid, S. Drug points: Neuropsychiatric complications of nevirapine treatment. BMJ 2002, 324, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, G.; de Nocker, D.; von Giesen, H.-J.; Nolting, T. Neuropsychiatric side effects of efavirenz therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2007, 6, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenedi, C.A.; Goforth, H.W. A systematic review of the psychiatric side-effects of efavirenz. AIDS Behav. 2011, 15, 1803–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, N.; Funes, H.A.; Blas-Garcia, A.; Galindo, M.J.; Alvarez, A.; Esplugues, J.V. Efavirenz and the CNS: What we already know and questions that need to be answered. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2693–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Myint, A.-M.; Steinbusch, H.; Leonard, B.E. Efavirenz induces depressive-like behaviour, increased stress response and changes in the immune response in rats. Neuroimmunomodulation 2005, 12, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienstock, R.J.; Copeland, W.C. Molecular insights into NRTI inhibition and mitochondrial toxicity revealed from a structural model of the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase. Mitochondrion 2004, 4, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Shi, Y.; Guo, K.; Tang, S.-J. Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) Induce Pathological Pain through Wnt5a-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Aging Mice. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. Peripheral neuropathy and antiretroviral drugs. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2001, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Semino-Mora, C.; Leon-Monzon, M. Mitochondrial alterations with mitochondrial DNA depletion in the nerves of AIDS patients with peripheral neuropathy induced by 2′3′-dideoxycytidine (ddC). Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2001, 81, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.R.; Arezzo, J.C.; Schaumburg, H.H.; Skowron, G.; Merigan, T.; Bozzette, S.; Richman, D.; Soo, W. 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine (ddC) toxic neuropathy: A study of 52 patients. Neurology 1993, 43, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, S.M. NNRTIs-a new class of drugs for HIV. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 45, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Birari, V.; Sinha, S. Small Conformational Changes Underlie Evolution of Resistance to NNRTI in HIV Reverse Transcriptase. Biophys. J. 2020, 118, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, A.M.; Heverling, H.; Pham, P.A.; Stolbach, A. A review of the toxicity of HIV medications. J. Med. Toxicol. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Pezzotti, P.; Boucher, C.; Döring, M.; Incardona, F.; Kaiser, R.; Lengauer, T.; Pfeifer, N.; Schülter, E.; Vandamme, A.-M.; et al. Clinical use, efficacy, and durability of maraviroc for antiretroviral therapy in routine care: A European survey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; De Clercq, E.; Li, G. Clinical significance of chemokine receptor antagonists. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, P.; Walmsley, S. Reassessment of enfuvirtide’s role in the management of HIV-1 infection. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 2349–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccari, M.V.; Mogle, B.T.; Sidman, E.F.; Mastro, K.A.; Asiago-Reddy, E.; Kufel, W.D. Ibalizumab, a Novel Monoclonal Antibody for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1 Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00110-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Ibalizumab: A Review in Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1 Infection. Drugs 2020, 80, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazuda, D.J.; Felock, P.; Witmer, M.; Wolfe, A.; Stillmock, K.; Grobler, J.A.; Espeseth, A.; Gabryelski, L.; Schleif, W.; Blau, C.; et al. Inhibitors of strand transfer that prevent integration and inhibit HIV-1 replication in cells. Science 2000, 287, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.J.; Squires, K.E. Integrase inhibitors: A novel class of antiretroviral agents. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, C.; Descamps, D. Resistance to HIV Integrase Inhibitors: About R263K and E157Q Mutations. Viruses 2018, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, A.N. Multifaceted HIV integrase functionalities and therapeutic strategies for their inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15137–15157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.N.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Buko, A.M.; Denissen, J.F. Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of the HIV-1 protease inhibitor ritonavir (ABT-538) in human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 277, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Rublein, J.C.; Eron, J.J.; Butts, J.D.; Raasch, R.H. Discontinuation rates for protease inhibitor regimens containing ritonavir 600 mg versus ritonavir 400 mg plus saquinavir 400 mg. Ann. Pharmacother. 1999, 33, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arminio Monforte, A.; Lepri, A.C.; Rezza, G.; Pezzotti, P.; Antinori, A.; Phillips, A.N.; Angarano, G.; Colangeli, V.; De Luca, A.; Ippolito, G.; et al. Insights into the reasons for discontinuation of the first highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) regimen in a cohort of antiretroviral naïve patients. I.CO.N.A. Study Group. Italian Cohort of Antiretroviral-Naïve Patients. AIDS 2000, 14, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.; Cooper, D.A. Adverse effects of antiretroviral therapy. Lancet 2000, 356, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.T.; Cole, S.R.; Li, X.; Kingsley, L.A.; Palella, F.J.; Riddler, S.A.; Visscher, B.R.; Margolick, J.B.; Dobs, A.S. Antiretroviral therapy and the prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus in the multicenter AIDS cohort study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, N.M.; João Correia, M.; Miranda, J.P.; Cipriano, M.; Serpa, J.; Matilde Marques, M.; Monteiro, E.C.; Antunes, A.M.M.; Diogo, L.N.; Pereira, S.A. Unmasking efavirenz neurotoxicity: Time matters to the underlying mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 105, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiseman, J.L.; Yetter, R.A.; Fredrickson, T.N.; Shapiro, S.G.; MacAuley, C.; Bilello, J.A. Effect of 3′azidothymidine administered in drinking water or by continuous infusion on the development of MAIDS. Antiviral Res. 1991, 16, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Asunción, J.G.; del Olmo, M.L.; Sastre, J.; Pallardó, F.V.; Viña, J. Zidovudine (AZT) causes an oxidation of mitochondrial DNA in mouse liver. Hepatology 1999, 29, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirkof, P.; Durst, M.; Klopfleisch, R.; Palme, R.; Thöne-Reineke, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Schmidt-Bleek, K.; Lang, A. Administration of Tramadol or Buprenorphine via the drinking water for post-operative analgesia in a mouse-osteotomy model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polydefkis, M.; Yiannoutsos, C.T.; Cohen, B.A.; Hollander, H.; Schifitto, G.; Clifford, D.B.; Simpson, D.M.; Katzenstein, D.; Shriver, S.; Hauer, P.; et al. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density in HIV-associated sensory neuropathy. Neurology 2002, 58, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, N.; Oriowo, M.A.; Masocha, W. Antihyperalgesic Activities of Endocannabinoids in a Mouse Model of Antiretroviral-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, E.; Khajah, M.A.; Masocha, W. β-Caryophyllene, a CB2-Receptor-Selective Phytocannabinoid, Suppresses Mechanical Allodynia in a Mouse Model of Antiretroviral-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Molecules 2019, 25, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.D.; Manassero, G.; Vercelli, A.; Herdegen, T.; Galeotti, N. The isoform-specific functions of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in a mouse model of antiretroviral-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 880, 173161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinsky, R.M.; Yarchoan, R.; Dalakas, M.; Broder, S. Reversible axonal neuropathy from the treatment of AIDS and related disorders with 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine (ddC). Muscle Nerve 1989, 12, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieu, L.; Boomhower, B.; George, O. Hot Water Tail Immersion Test. 2020. Available online: https://protocols.io/view/hot-water-tail-immersion-test-bhxbj7in (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Polydefkis, M. Skin biopsy findings predict development of symptomatic neuropathy in patients with HIV. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, M.; Katsarava, Z.; Esser, S.; Sommer, C.; He, L.; Selter, L.; Yoon, M.-S.; Kaube, H.; Diener, H.-C.; Maschke, M. Correlation of epidermal nerve fiber density with pain-related evoked potentials in HIV neuropathy. Pain 2008, 138, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.G.; Kamerman, P.R. Colocalization of pain and reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density in individuals with HIV-associated sensory neuropathy. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanman, T.; Letendre, S.; Ma, Q.; Bang, A.; Ellis, R. CNS Neurotoxicity of Antiretrovirals. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyns, T.; De Boever, S.; Schauvliege, S.; Gasthuys, F.; Meissonnier, G.; Oswald, I.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Influence of administration route on the biotransformation of amoxicillin in the pig. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 32, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Perez, R.; Hernandez, A.; Tejada, P.; Arteta, M.; Ramos, J.T. Factors and Mechanisms for Pharmacokinetic Differences between Pediatric Population and Adults. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, H.C.; Stanescu, I.; Frampton, C.; Salem, I.I.; Beasley, C.P.H.; Robson, R. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Ibuprofen and Paracetamol after Intravenous and Oral Administration. Clin. Drug Investig. 2015, 35, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Richter, O.; Lemke, L.; Haliduola, H.; Fuhr, R.; Koernicke, T.; Schuck, E.; Velinova, M.; Skerjanec, A.; Poetzl, J.; Jauch-Lembach, J. GP2017, an adalimumab biosimilar: Pharmacokinetic similarity to its reference medicine and pharmacokinetics comparison of different administration methods. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shoyaib, A.; Archie, S.R.; Karamyan, V.T. Intraperitoneal Route of Drug Administration: Should it Be Used in Experimental Animal Studies? Pharm. Res. 2019, 37, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Three Different Administration Routes for Topotecan Hydrochloride in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagga, A.A.; Gupta, V. Drug Absorption. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rathbun, R.C.; Rossi, D.R. Low-dose ritonavir for protease inhibitor pharmacokinetic enhancement. Ann. Pharmacother. 2002, 36, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Calvo, M.; Pheby, T.; Bennett, D.L.; Rice, A.S. A rodent model of HIV protease inhibitor indinavir induced peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2017, 158, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, A.L.; Lee, R.N.; Panvelker, N.; Li, J.; Harowitz, J.; Jordan-Sciutto, K.L.; Akay-Espinoza, C. Differential Effects of Antiretroviral Drugs on Neurons In Vitro: Roles for Oxidative Stress and Integrated Stress Response. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letendre, S.L.; Mills, A.M.; Tashima, K.T.; Thomas, D.A.; Min, S.S.; Chen, S.; Song, I.H.; Piscitelli, S.C.; extended ING116070 study team. ING116070: A study of the pharmacokinetics and antiviral activity of dolutegravir in cerebrospinal fluid in HIV-1-infected, antiretroviral therapy-naive subjects. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2014, 59, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Kwiatkowski, K.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Mika, J. Maraviroc reduces neuropathic pain through polarization of microglia and astroglia—Evidence from in vivo and in vitro studies. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyseng-Williamson, K.A.; Reynolds, N.A.; Plosker, G.L. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: A review of its use in the management of HIV infection. Drugs 2005, 65, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, P.; Wadley, A.L.; Cherry, C.L.; Karstaedt, A.S.; Kamerman, P.R. Clinical diagnosis of sensory neuropathy in HIV patients treated with tenofovir: A 6-month follow-up study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2019, 24, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Nathans, J. Flat Mount Imaging of Mouse Skin and Its Application to the Analysis of Hair Follicle Patterning and Sensory Axon Morphology. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2014, 88, 51749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.B.; Valdes, V.J.; Cohen, I.; Pothula, V.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, D.; Ezhkova, E. Dissection of Merkel cell formation in hairy and glabrous skin reveals a common requirement for FGFR2-mediated signalling. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzberg, U.; Sagen, J. Peripheral nerve exposure to HIV viral envelope protein gp120 induces neuropathic pain and spinal gliosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 116, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.B.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.; Gelman, B.B.; Lisinicchia, J.G.; Carlton, S.M.; Ferguson, M.R.; Tan, A.; et al. Gp120 in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus-associated pain. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodarski, R.; Bagdas, D.; Paris, J.J.; Pheby, T.; Toma, W.; Xu, R.; Damaj, M.I.; Knapp, P.E.; Rice, A.S.C.; Hauser, K.F. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fibre density, glial activation, and sensory changes in HIV type-1 Tat-expressing female mice: Involvement of Tat during early stages of HIV-associated painful sensory neuropathy. Pain Rep. 2018, 3, e654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdas, D.; Paris, J.J.; Carper, M.; Wodarski, R.; Rice, A.S.C.; Knapp, P.E.; Hauser, K.F.; Damaj, M.I. Conditional expression of HIV-1 tat in the mouse alters the onset and progression of tonic, inflammatory and neuropathic hypersensitivity in a sex-dependent manner. Eur. J. Pain 2020, 24, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yuan, S.; Tang, S.-J. Morphine and HIV-1 gp120 cooperatively promote pathogenesis in the spinal pain neural circuit. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, C.L.; Affandi, J.S.; Imran, D.; Yunihastuti, E.; Smyth, K.; Vanar, S.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Price, P. Age and height predict neuropathy risk in patients with HIV prescribed stavudine. Neurology 2009, 73, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, M.; Simpson, D.M. HIV neuropathy. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.T.; Boubour, A.; Saylor, D.; Das, M.; Bearden, D.R.; Birbeck, G.L. Global HIV neurology: A comprehensive review. AIDS 2019, 33, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bush, K.; Wairkar, Y.; Tang, S.-J. Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Are the Major Class of HIV Antiretroviral Therapeutics That Induce Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169059
Bush K, Wairkar Y, Tang S-J. Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Are the Major Class of HIV Antiretroviral Therapeutics That Induce Neuropathic Pain in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169059
Chicago/Turabian StyleBush, Keegan, Yogesh Wairkar, and Shao-Jun Tang. 2024. "Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Are the Major Class of HIV Antiretroviral Therapeutics That Induce Neuropathic Pain in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169059
APA StyleBush, K., Wairkar, Y., & Tang, S.-J. (2024). Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Are the Major Class of HIV Antiretroviral Therapeutics That Induce Neuropathic Pain in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169059





