Micro RNA Dysregulation in Keratinocyte Carcinomas: Clinical Evidence, Functional Impact, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. MicroRNA Dysregulation in cSCC
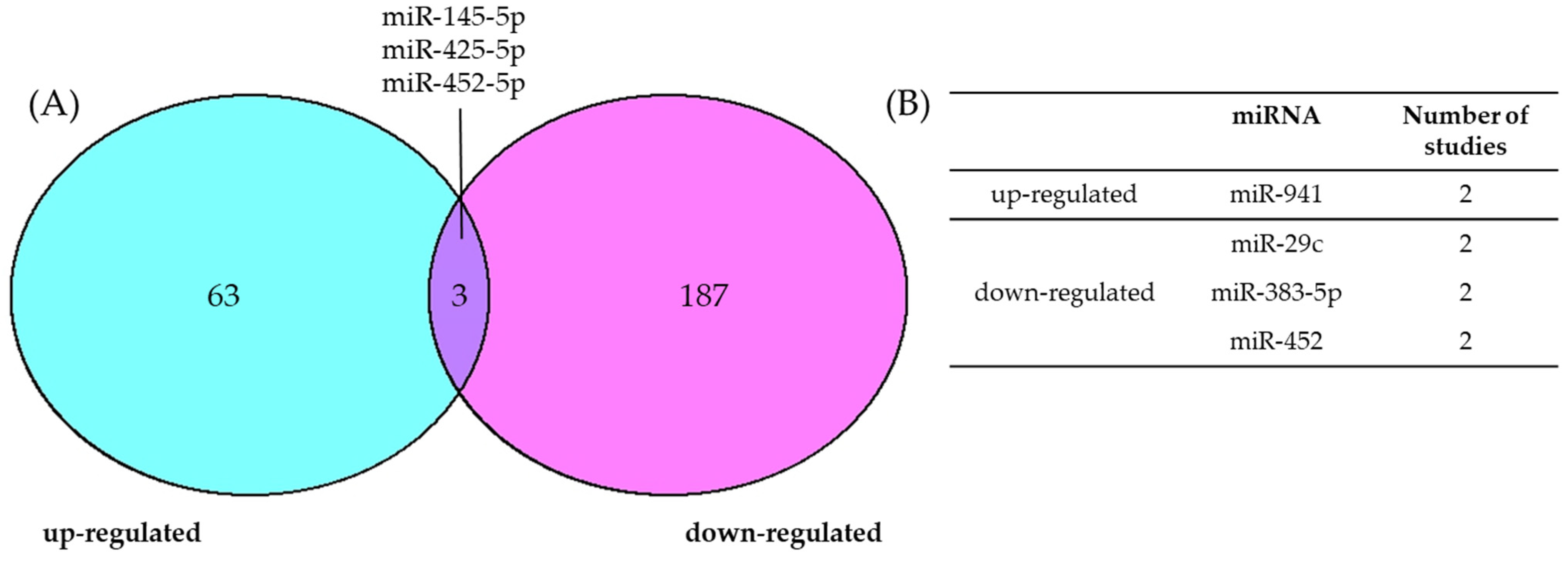
3.1. Consensus of Dysregulated miRNAs in cSCC
3.2. Experimentally Validated miRNAs in cSCC
| miRNA | Tissue Comparison | Cell or Animal Model | Validated Target | Functional Effect of the miRNA | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-10a | cSCC vs. HS | A431 | SDC1 | Proliferation ↑ Migration, invasion ↑ | [56] |
| miR-10b | cSCC (RDEB and non-RDEB) vs. HS | RDEB-SCC1/2/62 SCC13 A431 WT18SCC | DIAPH2 | Spheroid formation ↑ Migration ↓ CSC phenotype ↑ | [57] |
| miR-22 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 COLO-16 Xenograft | FOSB PAD2 | Migration ↑ EMT, stemness ↑ Spheroid formation ↑ Tumor formation, growth, and metastasis ↑ Wnt/ β-catenin signaling ↑ | [58] |
| miR-31 | cSCC vs. HS/ AK | UT-SCC-7 | nd | Motility ↑ Migration, invasion ↑ Colony formation ↑ | [29] |
| miR-31-3p | cSCC/IEC/AK vs. HS | COLO-16 SCC9 SCC-25 | nd | Viability ↑ Colony formation ↑ | [59] |
| miR-135b | cSCC vs. HS | PM1 MET1 MET4 | LZTS1 | Migration, invasion ↑ | [60] |
| miR-186 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCL-1 | RETREG1 | Proliferation ↑ Apoptosis ↓ | [61] |
| cSCC vs. HS | A431 | APAF1 | Apoptosis ↓ Autophagy ↓ Migration, invasion ↑ Colony formation ↑ Cell cycle progression ↑ Proliferation ↑ | [62] | |
| miR-217 | cSCC vs. HS | SCC13 | PTRF | Proliferation ↑ Cell cycle progression ↑ Invasion ↑ | [63] |
| miR-221 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCC13 | PTEN | Viability ↑ Colony formation ↑ Akt signaling ↑ | [64] |
| miR-320a | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCL-1 Xenograft | ATG2B | Autophagy ↓ Apoptosis ↓ Tumor growth ↑ Proliferation ↑ | [65] |
| miR-346 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 | SRCIN1 | Proliferation ↑ Migration ↑ | [66] |
| miR-365 | cSCC vs. HS | HaCaT A431 Xenograft | nd | Tumorigenicity ↑ Tumor growth ↑ Colony formation ↑ Migration, invasion ↑ Apoptosis ↓ | [67] |
| cSCC vs. HS | A431 HSC-1 Xenograft | NFIB | Tumor formation and growth ↑ | [68] | |
| miR-486-3p | cSCC vs. HS | HSC-5 HSC-1 Xenograft | FLOT2 | Tumor growth ↑ Viability, proliferation ↑ Migration ↑ | [69] |
| miR-664 | cSCC vs. HS | HSC-5 HSC-1 Xenograft | IRF2 | Tumorigenicity ↑ Migration, invasion ↑ Proliferation ↑ | [70] |
| miR-675 | cSCC vs. HS | HaCaT SCL-1 A431 | TP53 H19 | Proliferation ↑ Migration, invasion ↑ Apoptosis ↓ EMT ↑ | [71] |
| miR-766 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCL-1 Xenograft | PDCD5 | Apoptosis ↓ Migration, invasion ↑ Proliferation ↑ MMP2/9 expression ↑ Tumor growth ↑ | [72] |
| miR-7150 | cSCC/IEC/AK vs. HS | COLO-16 SCC-9 | nd | Viability ↑ Colony formation ↑ | [59] |
| miRNA | Tissue Comparison | Cell or Animal Model | Validated Target | Functional Effect of the miRNA | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-23b | cSCC vs. HS/ AK | UT-SCC7 UT-SCC12a Xenograft | RRAS2 | Angiogenesis ↓ Colony formation ↓ Spheroid formation ↓ Tumor growth and proliferation ↓ | [73] |
| miR-31-5p | cSCC/IEC/AK vs. HS | COLO-16 SCC-9 | nd | Colony formation ↓ | [59] |
| miR-34a-5p | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCL-1 | SIRT6 | Proliferation ↓ Colony formation ↓ Migration ↓ Apoptosis ↑ | [74] |
| miR-124 | cSCC vs. HS | DJM-1 | nd | ERK signaling ↓ Proliferation ↓ | [75] |
| miR-125b | cSCC vs. HS/ AK | UT-SCC-7 A431 | MMP13 | Growth ↓ Colony formation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ | [38] |
| cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCC13 SCL-1 | STAT3 | Viability ↓ Cell cycle progression ↓ Apoptosis via Bcl2 ↑ | [42] | |
| miR-130a | cSCC vs. HS/ AK | UT-SCC-7 A431 Xenograft | ACVR1 | HRAS/MAPK signaling ↓ Tumor growth ↓ Tumor sphere formation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ SMAD1 signaling ↓ | [76] |
| miR-138-5p | cSCC vs. HS | A431 Xenograft | EZH2 | Autophagy ↓ Apoptosis ↑ Viability ↓ STAT/VERFR2 signaling ↓ Tumor growth ↓ | [77] |
| miR-148a | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCL-1 Xenograft | MAP3K4 MAP3K9 | Colony formation ↓ Proliferation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ EMT ↓ MAPK signaling ↓ Tumor growth ↓ | [78] |
| miR-181a | cSCC vs. HS | SCC13 Xenograft | KRAS | Tumor growth ↓ Viability ↓ ERK signaling ↓ | [79] |
| miR-199a | cSCC vs. HS | A431 | CD44 | Proliferation ↓ Invasion ↓ MMP2/9 expression ↓ | [80] |
| miR-203 | cSCC vs. HS | UT-SCC7 A431 Xenograft | MYC | Cell cycle progression ↓ Colony formation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ Angiogenesis ↓ Tumor growth and angiogenesis ↓ | [43] |
| miR-203a-3p | cSCC vs. HS | SCL-1 | APC | APC/ β-catenin signaling ↓ Proliferation ↓ Colony formation ↓ | [81] |
| miR-204 | cSCC vs. AK | HaCaT | PTPN11 | FGF-STAT3 signaling ↑ EGF-MAPK signaling ↓ | [82] |
| miR-211-5p | cSCC vs. HS | IC4 IC18 | TP63 | Differentiation ↑ EMT ↓ Proliferation ↓ | [83] |
| miR-214 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCC13 | BCL2 VEGFA | Viability ↓ Proliferation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ Apoptosis ↑ Wnt/ β-catenin signaling ↓ | [84] |
| cSCC vs. HS | DJM-1 | nd | ERK signaling ↓ Proliferation ↓ | [75] | |
| miR-340 | cSCC vs. HS | A431 Sa3 | RHOA | Proliferation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ | [85] |
| miR-342-3p | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCC13 | NEAT1 | Proliferation ↓ Colony formation ↓ PI3K signaling ↓ | [86] |
| cSCC vs. HS | SCC13 | SCARNA2 | Proliferation ↓ Cell cycle progression ↓ Invasion ↓ | [87] | |
| miR-361-5p | cSCC vs. HS | HaCaT A431 | VEGFA | VEGFA levels ↓ | [88] |
| miR-497 | cSCC vs. HS/AK | SCLII MET1 | SERPINE1 | Growth ↓ Migration ↓ EMT ↓ | [89] |
| cSCC vs. HS | A431 HSC-5 | FAM114A2 | Viability ↓ Cell cycle progression ↓ | [90] | |
| miR-1193 | cSCC vs. HS | SCC13 COLO-16 Xenograft | MAP3K9 | Viability ↓ Colony formation ↓ Migration, invasion ↓ Lactate production ↓ Glucose consumption ↓ Tumor growth ↓ | [91] |
| miR-1238-3p | cSCC vs. HS | A431 SCL-1 Xenograft | FOXG1 | Migration, invasion ↓ Proliferation ↓ Cell cycle progression ↓ Viability ↓ Apoptosis ↑ Tumor growth ↓ | [92] |
3.3. Differential Expression of MicroRNAs during the Clinical Progression of cSCC
4. miRNA Dysregulation in BCC
4.1. Consensus of Dysregulated miRNAs in BCC
4.2. Experimentally Validated miRNAs in BCC
5. Clinical Applications of miRNAs in KCs
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciążyńska, M.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Lange, D.; Lewandowski, B.; Reich, A.; Sławińska, M.; Pabianek, M.; Szczepaniak, K.; Hankiewicz, A.; Ułańska, M.; et al. The incidence and clinical analysis of non-melanoma skin cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didona, D.; Paolino, G.; Bottoni, U.; Cantisani, C. Non Melanoma Skin Cancer Pathogenesis Overview. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fania, L.; Didona, D.; Di Pietro, F.R.; Verkhovskaia, S.; Morese, R.; Paolino, G.; Donati, M.; Ricci, F.; Coco, V.; Ricci, F.; et al. Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dika, E.; Scarfì, F.; Ferracin, M.; Broseghini, E.; Marcelli, E.; Bortolani, B.; Campione, E.; Riefolo, M.; Ricci, C.; Lambertini, M. Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya-Grosjean, L.; Couvé-Privat, S. Sonic hedgehog signaling in basal cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2005, 225, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocka, P.M.; Galka-Marciniak, P.; Urbanek-Trzeciak, M.O.; M-Thirusenthilarasan, I.; Szostak, N.; Philips, A.; Susok, L.; Sand, M.; Kozlowski, P. Profile of Basal Cell Carcinoma Mutations and Copy Number Alterations-Focus on Gene-Associated Noncoding Variants. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 752579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, A.S.; Ashford, B.; Strbenac, D.; Mitchell, J.; Lee, J.; Mueller, S.A.; Minaei, E.; Perry, J.R.; Ch’ng, S.; Iyer, N.G.; et al. Whole genome analysis reveals the genomic complexity in metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 919118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.R.; Genenger, B.; Thind, A.S.; Ashford, B.; Ranson, M. PIK Your Poison: The Effects of Combining PI3K and CDK Inhibitors against Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro. Cancers 2024, 16, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genenger, B.; Perry, J.R.; Ashford, B.; Ranson, M. A tEMTing target? Clinical and experimental evidence for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (a scoping systematic review). Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cives, M.; Mannavola, F.; Lospalluti, L.; Sergi, M.C.; Cazzato, G.; Filoni, E.; Cavallo, F.; Giudice, G.; Stucci, L.S.; Porta, C.; et al. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: Biological and Clinical Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Román, M.; Padilla-Gutiérrez, J.R.; Valle, Y.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Valdés-Alvarado, E. Non-melanoma skin cancer: A genetic update and future perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, M.; Mohan, M. MicroRNAs: History, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, K.; Sivasankar, V. MicroRNAs-Biology and clinical applications. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Pathol. 2014, 18, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikova, O.; Baranova, A.; Skoblov, M. Comprehensive Analysis of Human microRNA–mRNA Interactome. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranwal, S.; Alahari, S.K. miRNA control of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Abd-Aziz, N.; Khalid, K.; Poh, C.L.; Naidu, R. miRNA: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Trials and Tribulations of MicroRNA Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Li, A.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, K. Plasma specific miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabortty, A.; Patton, D.J.; Smith, B.F.; Agarwal, P. miRNAs: Potential as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Cancer. Genes 2023, 14, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, S. Non-coding RNAs in skin cancers: Biological roles and molecular mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 934396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, M.P.; Sinha, R.; Mukhtar, M.S.; Athar, M. Epigenetic regulation in the pathogenesis of non-melanoma skin cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Z. The role of miRNAs in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konicke, K.; López-Luna, A.; Muñoz-Carrillo, J.L.; Servín-González, L.S.; Flores-de la Torre, A.; Olasz, E.; Lazarova, Z. The microRNA landscape of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sancha, N.; Corchado-Cobos, R.; Pérez-Losada, J.; Cañueto, J. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruegger, C.; Kempf, W.; Spoerri, I.; Arnold, A.W.; Itin, P.H.; Burger, B. MicroRNA expression differs in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and healthy skin of immunocompetent individuals. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Landén, N.X.; Meisgen, F.; Lohcharoenkal, W.; Ståhle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNA-31 Is Overexpressed in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Regulates Cell Motility and Colony Formation Ability of Tumor Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Zhou, Y.; Lian, X.; Tu, Y. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting RhoTBT1. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Figueras, M.T.; Carrato, C.; Saenz-Sardà, X.; Musulén, E.; Fuente, M.J.; Puig, L. MicroRNA31 and MMP-1 contribute to the differentiated pathway of invasion -with enhanced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition- in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 314, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. miR-31: A crucial overseer of tumor metastasis and other emerging roles. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, S.; Asai, S.; Seki, N.; Minemura, C.; Kinoshita, T.; Goto, Y.; Kikkawa, N.; Moriya, S.; Kasamatsu, A.; Hanazawa, T.; et al. Identification of Tumor Suppressive Genes Regulated by miR-31-5p and miR-31-3p in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wu, W.; Ying, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, S. MicroRNA-31: A pivotal oncogenic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, A.F.; Khalifa, A.S.; Eed, E.M.; Banjer, H.J.; Shami, A.A.; Askary, A.E.; Elsawy, W.H. Role of MicroRNA-31 (miR-31) in Breast Carcinoma Diagnosis and Prognosis. In Vivo 2022, 36, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-w.; Ming, X.-l.; Rong, Y.; Huang, C.-q.; Weng, H.; Chen, H.; Bian, J.-m.; Wang, F.-b. Diagnostic Value Investigation and Bioinformatics Analysis of miR-31 in Patients with Lymph Node Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 9740475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Kao, S.Y.; Tu, H.F.; Tsai, M.M.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. Increase of microRNA miR-31 level in plasma could be a potential marker of oral cancer. Oral. Dis. 2010, 16, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, L.; Meisgen, F.; Harada, M.; Heilborn, J.; Homey, B.; Grandér, D.; Ståhle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNA-125b Down-regulates Matrix Metallopeptidase 13 and Inhibits Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29899–29908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, A.N.; Fisher, M.D.; Amborski, G.; Allain, D.C.; Klee, V.; Peters, S.B.; Kang, S.; Toland, A.E. MicroRNA Expression Profiling of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising in Different Sites. Otolaryngol.–Head. Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojadinovic, O.; Ramirez, H.; Pastar, I.; Gordon, K.A.; Stone, R.; Choudhary, S.; Badiavas, E.; Nouri, K.; Tomic-Canic, M. MiR-21 and miR-205 are induced in invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Sánchez, D.; Arriaga-Canon, C.; Pedroza-Torres, A.; De La Rosa-Velázquez, I.A.; González-Barrios, R.; Contreras-Espinosa, L.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Fragoso-Ontiveros, V.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; et al. The Promising Role of miR-21 as a Cancer Biomarker and Its Importance in RNA-Based Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, N.; Yao, C.; Miao, G. MicroRNA-125b exerts antitumor functions in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the STAT3 pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohcharoenkal, W.; Harada, M.; Lovén, J.; Meisgen, F.; Landén, N.X.; Zhang, L.; Lapins, J.; Mahapatra, K.D.; Shi, H.; Nissinen, L.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Inversely Correlates with Differentiation Grade, Targets c-MYC, and Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in cSCC. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, Y. The Emerging Roles of miR-125b in Cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandarillas, A.; Watt, F.M. c-Myc promotes differentiation of human epidermal stem cells. Genes. Dev. 1997, 11, 2869–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, A.; Frye, M.; Herold, S.; Benitah, S.A.; Braun, K.; Samans, B.; Watt, F.M.; Elsässer, H.P.; Eilers, M. Myc regulates keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation via complex formation with Miz1. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfer, A.; Ramaswamy, S. MYC and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, M.; Li, Y.; Felsher, D.W. MYC activation is a hallmark of cancer initiation and maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Precazzini, F.; Detassis, S.; Imperatori, A.S.; Denti, M.A.; Campomenosi, P. Measurements Methods for the Development of MicroRNA-Based Tests for Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, T.; Heinemann, I.U. Bringing MicroRNAs to Light: Methods for MicroRNA Quantification and Visualization in Live Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 619583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Karlsson, M.; Marionnet, C.; Bernerd, F.; Gueniche, A.; Rawadi, C.E.l.; Ståhle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Breton, L.; Pivarcsi, A. Identification of chronological and photoageing-associated microRNAs in human skin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, K.; Zhao, H.; Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Xu, J. Analysis of the expression profile of miRNAs related to skin photoaging in the GEO database. Chin. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 5, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Yang, W.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Cui, Q.; Zhou, Y. Identification and Analysis of Human Sex-biased MicroRNAs. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, S.; Gangemi, S.; Murdaca, G.; Allegra, A. Gender Differences and miRNAs Expression in Cancer: Implications on Prognosis and Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geusau, A.; Borik-Heil, L.; Skalicky, S.; Mildner, M.; Grillari, J.; Hackl, M.; Sunder-Plassmann, R. Dysregulation of tissue and serum microRNAs in organ transplant recipients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. Health Sci. Rep. 2020, 3, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, G. Downregulation of miR-10a inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting Syndecan-1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, M.; Zauner, R.; Ablinger, M.; Piñón-Hofbauer, J.; Guttmann-Gruber, C.; Reisenberger, M.; Lettner, T.; Niklas, N.; Proell, J.; Sajinovic, M.; et al. A cancer stem cell-like phenotype is associated with miR-10b expression in aggressive squamous cell carcinomas. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Zhang, P.; Wen, L.; Jia, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, L. miR-22 promotes stem cell traits via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5799–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, A.; Tom, L.N.; Melati-Rad, A.; Yamada, M.; Hammerlindl, S.; Jagirdar, K.; Prow, T.W.; Soyer, H.P.; Stark, M.S. MicroRNA expression profiling of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and precursor lesions. Ski. Health Dis. 2024, 4, e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasz, E.B.; Seline, L.N.; Schock, A.M.; Duncan, N.E.; Lopez, A.; Lazar, J.; Flister, M.J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, P.; Sokumbi, O.; et al. MicroRNA-135b Regulates Leucine Zipper Tumor Suppressor 1 in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Ai, P.; He, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, T. MicroRNA-186 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RETREG1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Shen, R.; Yan, Y.; Deng, L. miR-186 promotes tumor growth in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting apoptotic protease activating factor-1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4010–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Zhang, M.; Long, F.; Yu, N.; Zeng, A.; Wang, X. MiR-217 promotes cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting PTRF. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.-H.; Zhou, F.; Shi, C.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, C.-K.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-S.; Gao, S.-F. miRNA-221 promotes cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting PTEN. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Jiang, Z.; Luan, Z.; Qiu, D. Crocin exerts anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects on cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via miR-320a/ATG2B. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 4569–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Pan, W.; Lin, X.; Hu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, G.; Qiu, Y.; Chang, L.; Hua, C.; et al. MicroRNA-346 functions as an oncogene in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, W.; Ma, S.; Cao, H.; Peng, X.; Guo, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, L.; Guo, L.; Wan, M.; et al. A novel onco-miR-365 induces cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ou, C.; Ding, Z. miR-365 Promotes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC) through Targeting Nuclear Factor I/B (NFIB). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, K.; Lu, S.; Chen, F.; Zhou, M.; Zhen, P. MicroRNA-486–3p promotes the proliferation and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing flotillin-2. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 105, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, C.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L.; Ding, Z. MicroRNA-664 functions as an oncogene in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (cSCC) via suppressing interferon regulatory factor 2. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 94, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Deng, D.; Yao, Z. Roles of the H19/microRNA-675 axis in the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shi, L.; Ding, Y.; Luan, J.; Shan, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S. MicroRNA-766 Promotes The Proliferation, Migration And Invasion, And Inhibits The Apoptosis Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells By Targeting PDCD5. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Mahapatra, K.D.; Elton, J.; Li, C.; Fernando, W.; Lohcharoenkal, W.; Lapins, J.; Homey, B.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNA-23b Plays a Tumor-Suppressive Role in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Targets Ras-Related Protein RRAS2. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yuan, M.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, D.; Miao, X.; Shi, J. MiR-34a-5p suppresses cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting SIRT6. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, K.; Jinnin, M.; Etoh, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimozono, N.; Fukushima, S.; Masuguchi, S.; Maruo, K.; Inoue, Y.; Ishihara, T.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-124/-214 in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma mediates abnormal cell proliferation via the induction of ERK. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohcharoenkal, W.; Li, C.; Das Mahapatra, K.; Lapins, J.; Homey, B.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MiR-130a Acts as a Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Regulates the Activity of the BMP/SMAD Pathway by Suppressing ACVR1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S. lncRNA HCP5 acts as a ceRNA to regulate EZH2 by sponging miR-138-5p in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Li, W.; Zhao, T.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Role of miR-148a in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by repression of MAPK pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 583, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, J.; Dziunycz, P.J.; Dzung, A.; Lefort, K.; Falke, M.; Denzler, R.; Freiberger, S.N.; Iotzova-Weiss, G.; Kuzmanov, A.; Levesque, M.P.; et al. miR-181a decelerates proliferation in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the proto-oncogene KRAS. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Zhou, J.D.; He, Q.Y.; Yin, Z.Q.; Cao, K.; Luo, C.Q. MiR-199a inhibits the ability of proliferation and migration by regulating CD44-Ezrin signaling in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7131–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Gu, D.; Feng, J.; Li, C. Effect of Hsa-miRNA-203a-3p on proliferation of skin squamous cell carcinoma-1 human skin squamous cell cancer cells by targeting adenomatous polyposis coli using magnetic nanoparticles. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll, A.; Salgado, R.; Espinet, B.; Díaz-Lagares, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, E.; Andrades, E.; Sandoval, J.; Esteller, M.; Pujol, R.M.; Hernández-Muñoz, I. MiR-204 silencing in intraepithelial to invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.J.; Patel, A.; Purdie, K.J.; Wang, J.; Rizvi, H.; Hufbauer, M.; Ostano, P.; Akgül, B.; Chiorino, G.; Harwood, C.A.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of iASPP-p63 Feedback Loop in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1658–1671.e1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, D.; Zhang, X.; Shao, X.; Hu, G. microRNA-214 Prevents Traits of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma via VEGFA and Bcl-2. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820980098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Jian, Q.; Xue, K.; Huang, M.; Chi, S.; Li, C.; Li, C. MicroRNA-340 inhibits squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by downregulating RhoA. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 92, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Ji, J. LncRNA NEAT1 Targets miR-342-3p/CUL4B to Inhibit the Proliferation of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8145129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jia, M.; Wen, C.; He, A.; Ma, Z. Long non-coding RNA SCARNA2 induces cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression via modulating miR-342-3p expression. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitz, A.; Imig, J.; Dziunycz, P.J.; Primorac, A.; Galgano, A.; Hofbauer, G.F.L.; Gerber, A.P.; Detmar, M. The Expression Levels of MicroRNA-361-5p and Its Target VEGFA Are Inversely Correlated in Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, A.; Barzilai, A.; Gur-Wahnon, D.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Glassberg, S.; Meningher, T.; Elharar, E.; Masalha, M.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Tabibian-Keissar, H.; et al. Alterations of microRNAs throughout the malignant evolution of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: The role of miR-497 in epithelial to mesenchymal transition of keratinocytes. Oncogene 2018, 37, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.H.; Gu, X.L.; Zhou, X.T.; Ma, M.; Lou, C.X. miR-497 promotes the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through FAM114A2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7348–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gan, Q.; Gan, C. Circular RNA circSEC24A Promotes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Regulating miR-1193/MAP3K9 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kong, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Jiang, M.; Sun, W.; Xu, S. CircRNA circ_0067772 aggravates the malignant progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-1238-3p/FOXG1 axis. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riolo, G.; Cantara, S.; Marzocchi, C.; Ricci, C. miRNA Targets: From Prediction Tools to Experimental Validation. Methods Protoc. 2020, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Di, K.; Fan, B.; Wu, J.; Gu, X.; Sun, Y.; Khan, A.; Li, P.; Li, Z. MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles: Sorting mechanisms, diagnostic value, isolation, and detection technology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 948959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, L.T.; Gong, J.; Pham, T.T.; Kim, Y.; Le, M.T.N. microRNA exchange via extracellular vesicles in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, M.; Takahashi, H.; Dragomir, M.P.; Lindemann, A.; Gleber-Netto, F.O.; Pickering, C.R.; Anfossi, S.; Osman, A.A.; Cai, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Loss of p53 drives neuron reprogramming in head and neck cancer. Nature 2020, 578, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.T.-L.; Shen, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-C.; Chen, C.-B.; Ma, K.S.-K. Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overmiller, A.M.; Pierluissi, J.A.; Wermuth, P.J.; Sauma, S.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.; Tuluc, M.; Luginbuhl, A.; Curry, J.; Harshyne, L.A.; Wahl, J.K., 3rd; et al. Desmoglein 2 modulates extracellular vesicle release from squamous cell carcinoma keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genenger, B.; McAlary, L.; Perry, J.R.; Ashford, B.; Ranson, M. Protocol for the generation and automated confocal imaging of whole multi-cellular tumor spheroids. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.; Perry, J.R.; Ashford, B.; Ranson, M. Ex vivo therapeutic screening of metastatic cSCC: A review of methodological considerations for clinical implementation. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratushny, V.; Gober, M.D.; Hick, R.; Ridky, T.W.; Seykora, J.T. From keratinocyte to cancer: The pathogenesis and modeling of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.R.; Mladkova, N.; Gulati, A.; Hamoudi, R.; Purdie, K.; Cerio, R.; Leigh, I.; Proby, C.; Harwood, C.A. Key differences identified between actinic keratosis and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by transcriptome profiling. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Ridgway, R.A.; Cammareri, P.; Treanor-Taylor, M.; Bailey, U.-M.; Schoenherr, C.; Bone, M.; Schreyer, D.; Purdie, K.; Thomson, J.; et al. Driver gene combinations dictate cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma disease continuum progression. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañueto, J.; Cardeñoso-Álvarez, E.; García-Hernández, J.L.; Galindo-Villardón, P.; Vicente-Galindo, P.; Vicente-Villardón, J.L.; Alonso-López, D.; De Las Rivas, J.; Valero, J.; Moyano-Sanz, E.; et al. MicroRNA (miR)-203 and miR-205 expression patterns identify subgroups of prognosis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Eryani, L.; Waigel, S.; Tyagi, A.; Peremarti, J.; Jenkins, S.F.; Damodaran, C.; States, J.C. Differentially Expressed mRNA Targets of Differentially Expressed miRNAs Predict Changes in the TP53 Axis and Carcinogenesis-Related Pathways in Human Keratinocytes Chronically Exposed to Arsenic. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2018, 162, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.S.; Toon, C.W.; Harish, V. The prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. ANZ J. Surg. 2023, 93, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.; Ngwenya, S.; Molaudzi, M.; Molepo, J.; Adeola, H.; Magangane, P. The clinicopathological and microrna expression signature associated with lymphovascular invasion in squamous cell carcinoma: A basic descriptive study. Health Sci. Rep. 2022, 5, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, J.; Skeeles, L.E.; Allain, D.C.; Kent, M.N.; Peters, S.B.; Nagarajan, P.; Yu, L.; Teknos, T.N.; Olencki, T.; Toland, A.E. MicroRNA expression profiling in metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tincknell, G.; Piper, A.-K.; Aghmesheh, M.; Becker, T.; Vine, K.L.; Brungs, D.; Ranson, M. Experimental and Clinical Evidence Supports the Use of Urokinase Plasminogen Activation System Components as Clinically Relevant Biomarkers in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Buckley, B.; Ranson, M. The Urokinase Plasminogen Activation System in Pancreatic Cancer: Prospective Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zheng, X.; Guo, H.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, M.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; Yang, D.; et al. Serum Exosomal miR-941 as a promising Oncogenic Biomarker for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 5329–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surapaneni, S.K.; Bhat, Z.R.; Tikoo, K. MicroRNA-941 regulates the proliferation of breast cancer cells by altering histone H3 Ser 10 phosphorylation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fateme Karimi Dermani, I.D. Saeideh Gholamzadeh Khoei. MicroRNA-452: A double-edged sword in multiple human cancers. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 1189–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.; Lai, K.; Yan, L.; Xie, S.; Qiu, X.; Xiao, S.; Wei, S. miR-18a expression in basal cell carcinoma and regulatory mechanism on autophagy through mTOR pathway. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Lovén, J.; Xu, N.; Meisgen, F.; Wei, T.; Brodin, P.; Jaks, V.; Kasper, M.; Shimokawa, T.; Harada, M.; et al. MicroRNA-203 functions as a tumor suppressor in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Jiang, P. MicroRNA-451a acts as tumor suppressor in cutaneous basal cell carcinoma. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Purdie, K.J.; Wang, J.; Harwood, C.A.; Proby, C.M.; Pourreyron, C.; Mladkova, N.; Nagano, A.; Dhayade, S.; Athineos, D.; et al. A Unique Panel of Patient-Derived Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Provides a Preclinical Pathway for Therapeutic Testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, G.J.; Wang, J.; Nagano, A.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Purdie, K.J.; Taylor, R.G.; Sherwood, V.; Thomson, J.; Hogan, S.; Spender, L.C.; et al. The genomic landscape of cutaneous SCC reveals drivers and a novel azathioprine associated mutational signature. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolitz, E.; Lucas, E.; Hosler, G.A.; Kim, J.; Hammer, S.; Lewis, C.; Xu, L.; Day, A.T.; Mauskar, M.; Lea, J.S.; et al. Human Papillomavirus–Positive and –Negative Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma Are Biologically but Not Clinically Distinct. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1280–1290.e1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietanen, S.; Grénman, S.; Syrjänen, K.; Lappalainen, K.; Kauppinen, J.; Carey, T.; Syrjänen, S. Human papillomavirus in vulvar and vaginal carcinoma cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, L.; Ni, L. Association of miR-203 Expression with Prognostic Value in Patients with Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Surg. 2023, 36, 2285780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Kong, M.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, M.; Zhang, X. Prognostic significance of miR-203 and ZEB1 expression in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4810–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panoutsopoulou, K.; Avgeris, M.; Mavridis, K.; Dreyer, T.; Dorn, J.; Obermayr, E.; Reinthaller, A.; Michaelidou, K.; Mahner, S.; Vergote, I.; et al. miR-203 is an independent molecular predictor of prognosis and treatment outcome in ovarian cancer: A multi-institutional study. Carcinogenesis 2019, 41, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakimoto, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kamiguchi, H.; Ochiai, E.; Osawa, M. MicroRNA Stability in FFPE Tissue Samples: Dependence on GC Content. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balci, S.; Ayaz, L.; Gorur, A.; Yildirim Yaroglu, H.; Akbayir, S.; Dogruer Unal, N.; Bulut, B.; Tursen, U.; Tamer, L. microRNA profiling for early detection of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamas, T.; Raduly, L.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Dinu, C.; Botan, E.; Bumbu, B.; Tamas, A.; Stoia, S.; Leucuta, D.C.; Bran, S.; et al. The Role of miRNA-221 and miRNA-34a in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer of the Head and Neck Region. Genes 2023, 14, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| miRNA | Tissue Comparison | Cell or Animal Model | Validated Target | Functional Effect | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| up | miR-18a | BCC vs. HS | A431 | nd | Proliferation ↑ Migration ↑ Cell cycle progression ↑ Apoptosis ↓ Autophagy ↓ | [114] |
| down | miR-203 | BCC vs. HS | Primary human keratinocytes K5tTA/TREGLI1 mice | JUN | Proliferation ↓ Cell cycle progression ↓ Tumor growth ↓ | [115] |
| miR-451a | BCC vs. HS | TE 354.T Primary epidermal keratinocytes | TBX1 | Proliferation ↓ Cell cycle progression ↓ | [116] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conley, J.; Genenger, B.; Ashford, B.; Ranson, M. Micro RNA Dysregulation in Keratinocyte Carcinomas: Clinical Evidence, Functional Impact, and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158493
Conley J, Genenger B, Ashford B, Ranson M. Micro RNA Dysregulation in Keratinocyte Carcinomas: Clinical Evidence, Functional Impact, and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158493
Chicago/Turabian StyleConley, Jessica, Benjamin Genenger, Bruce Ashford, and Marie Ranson. 2024. "Micro RNA Dysregulation in Keratinocyte Carcinomas: Clinical Evidence, Functional Impact, and Future Directions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158493
APA StyleConley, J., Genenger, B., Ashford, B., & Ranson, M. (2024). Micro RNA Dysregulation in Keratinocyte Carcinomas: Clinical Evidence, Functional Impact, and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158493





