Hypomyelinated vps16 Mutant Zebrafish Exhibit Systemic and Neurodevelopmental Pathologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Zebrafish vps16(-/-) Mutants Exhibit Multiple Systemic Pathologies
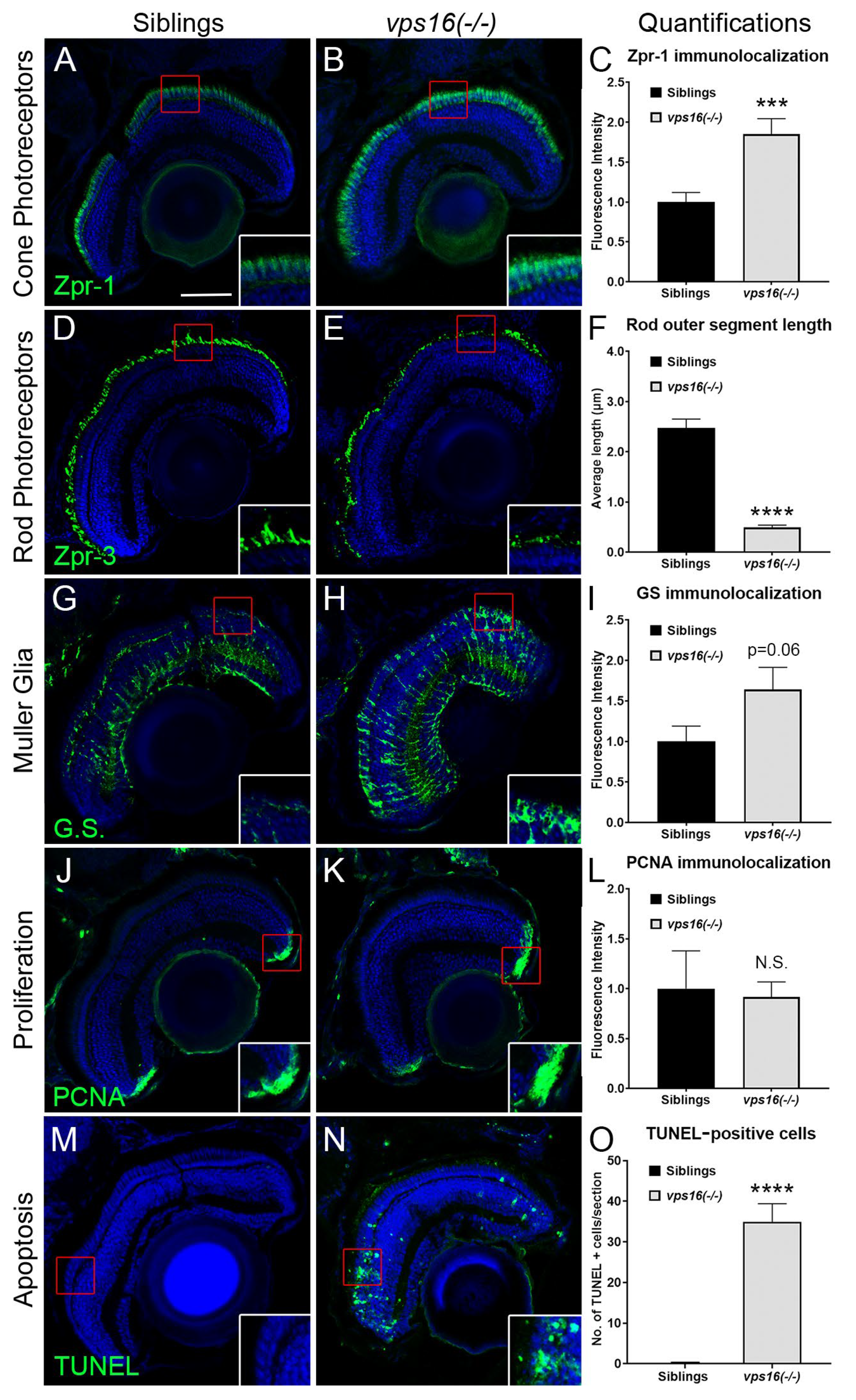
2.2. vps16(-/-) Mutants Show Retinal Pathologies by 7 dpf, including Apoptosis, Rod Photoreceptor Truncation, and Müller Glia (MG) Reactive Gliosis
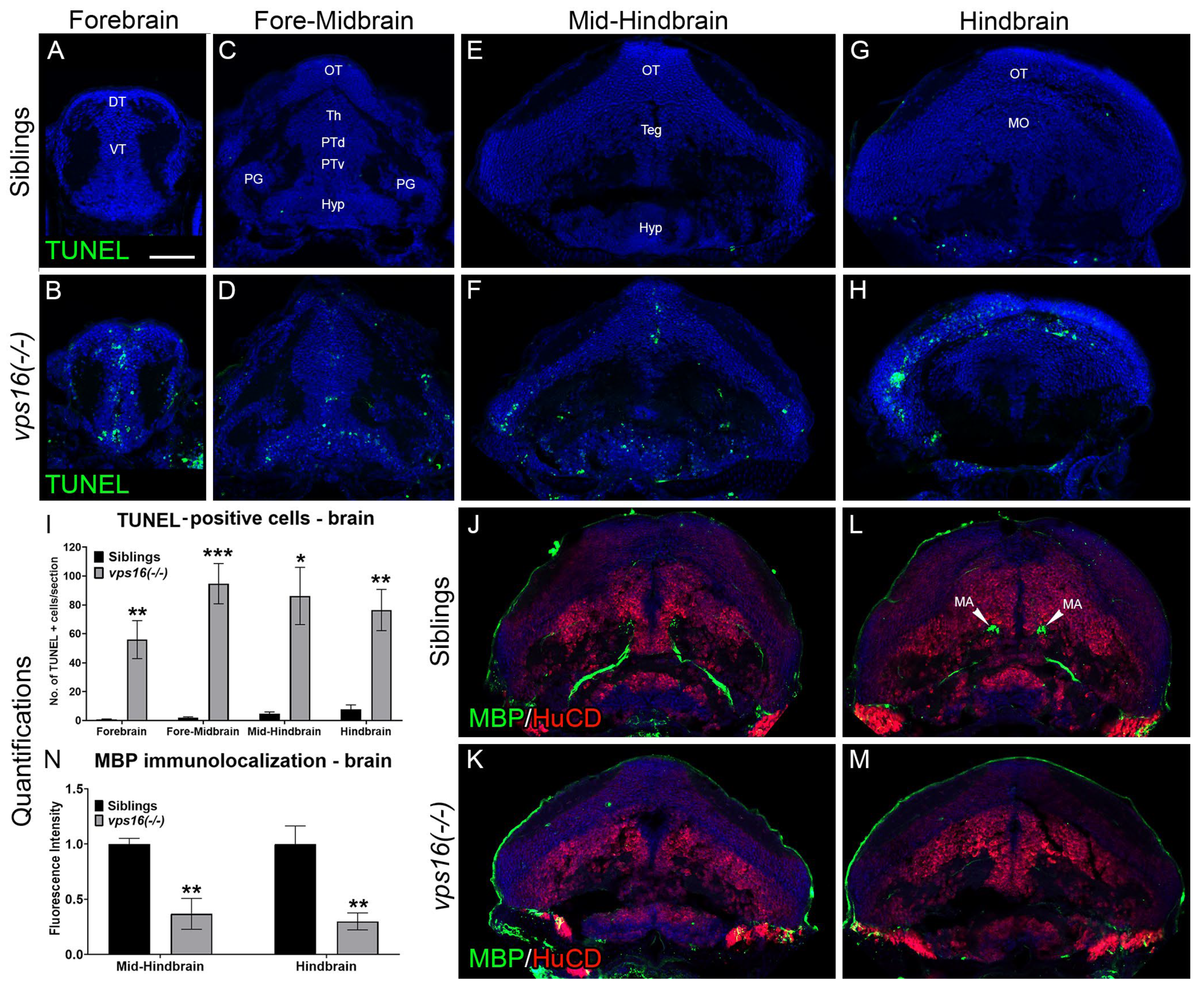
2.3. vps16(-/-) Mutants Exhibit Apoptosis in the CNS and Progressive Hypomyelination
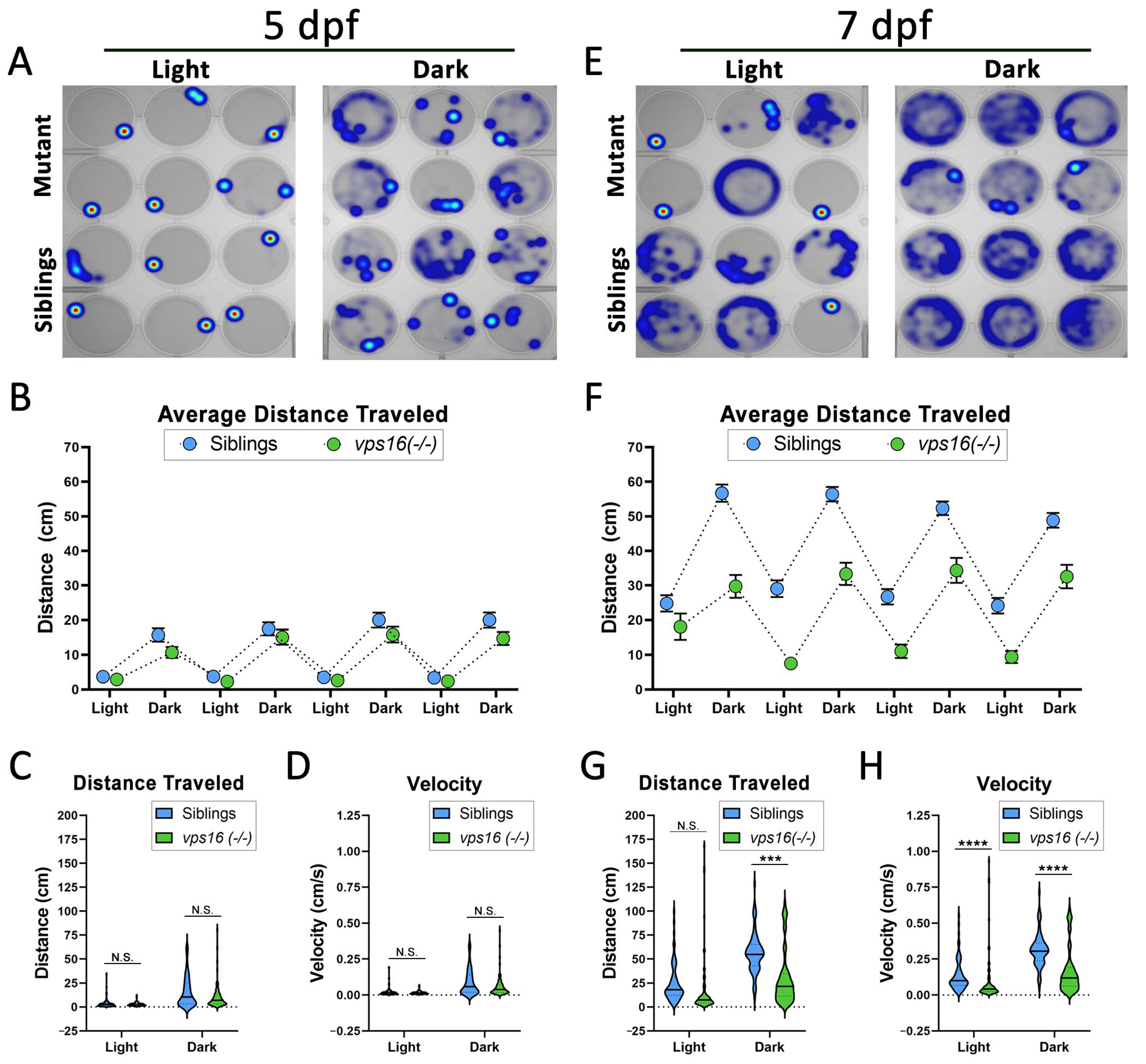
2.4. vps16(-/-) Mutants Show Progressive Loss of Sensorimotor Response to Visual Stimuli
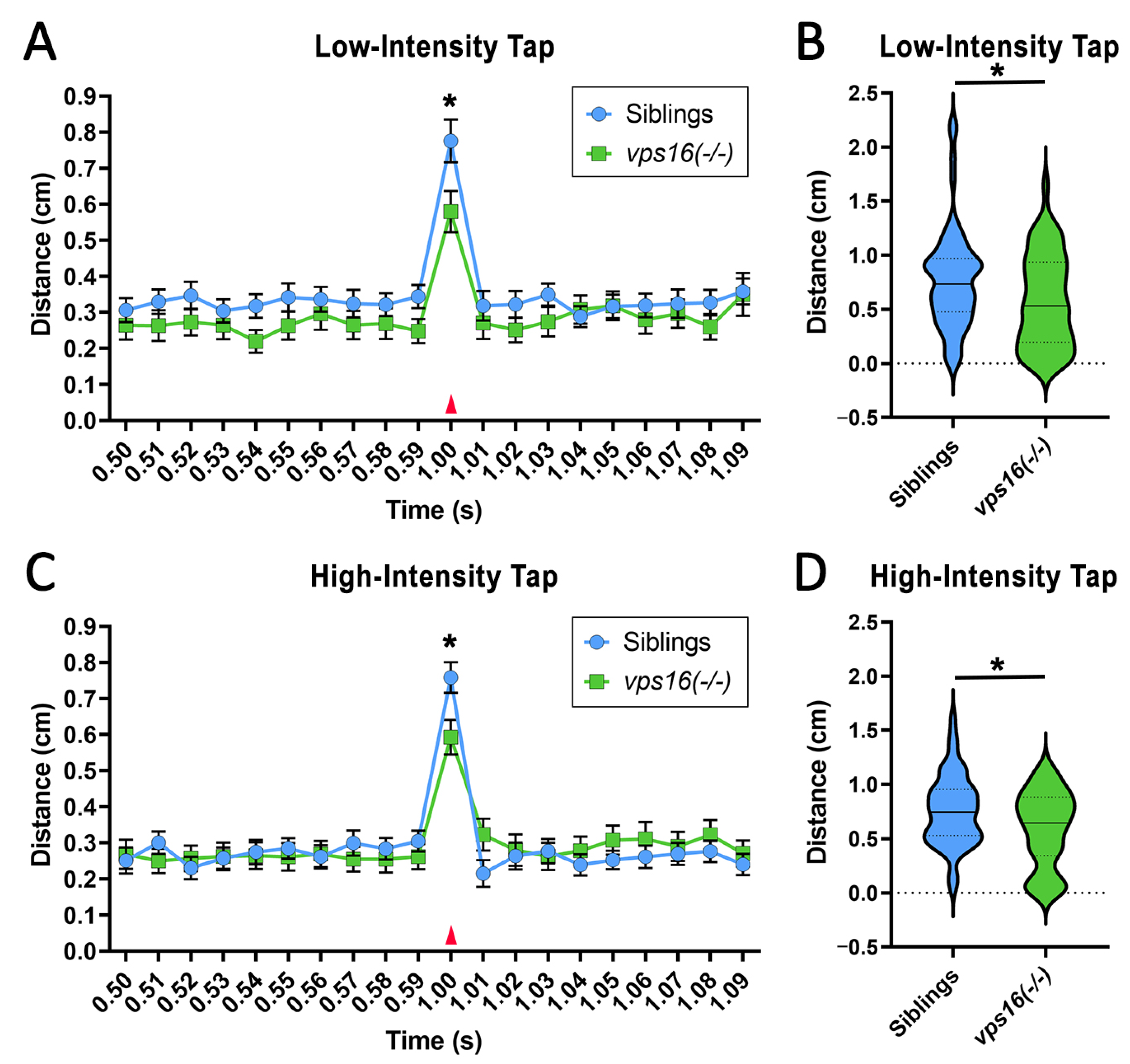
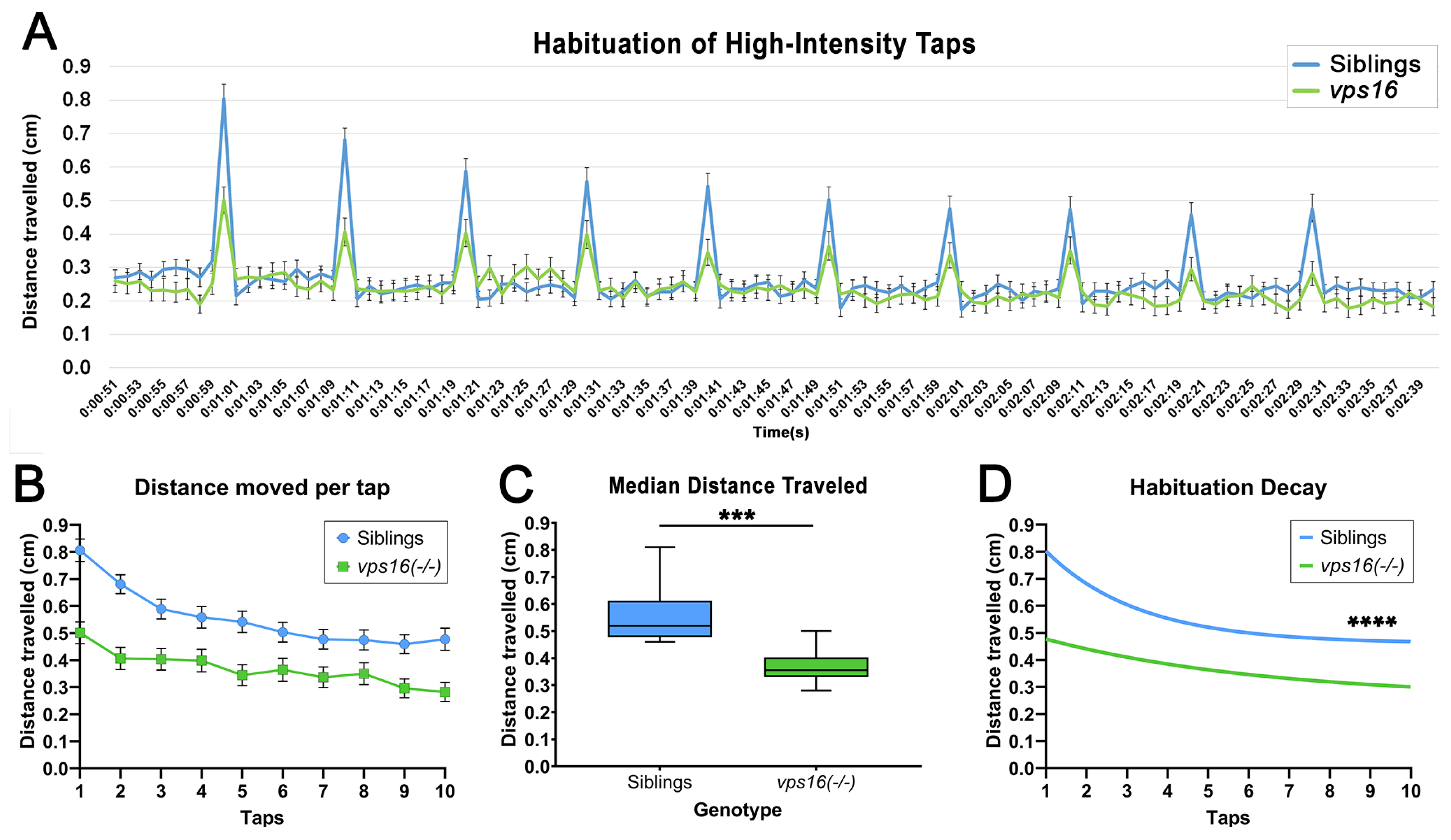
2.5. vps16(-/-) Mutants Show a Lower Sensorimotor Response to an Acoustic/Tap Stimulus but Maintain a Habituation Response to a Series of Multiple-Tap Stimuli
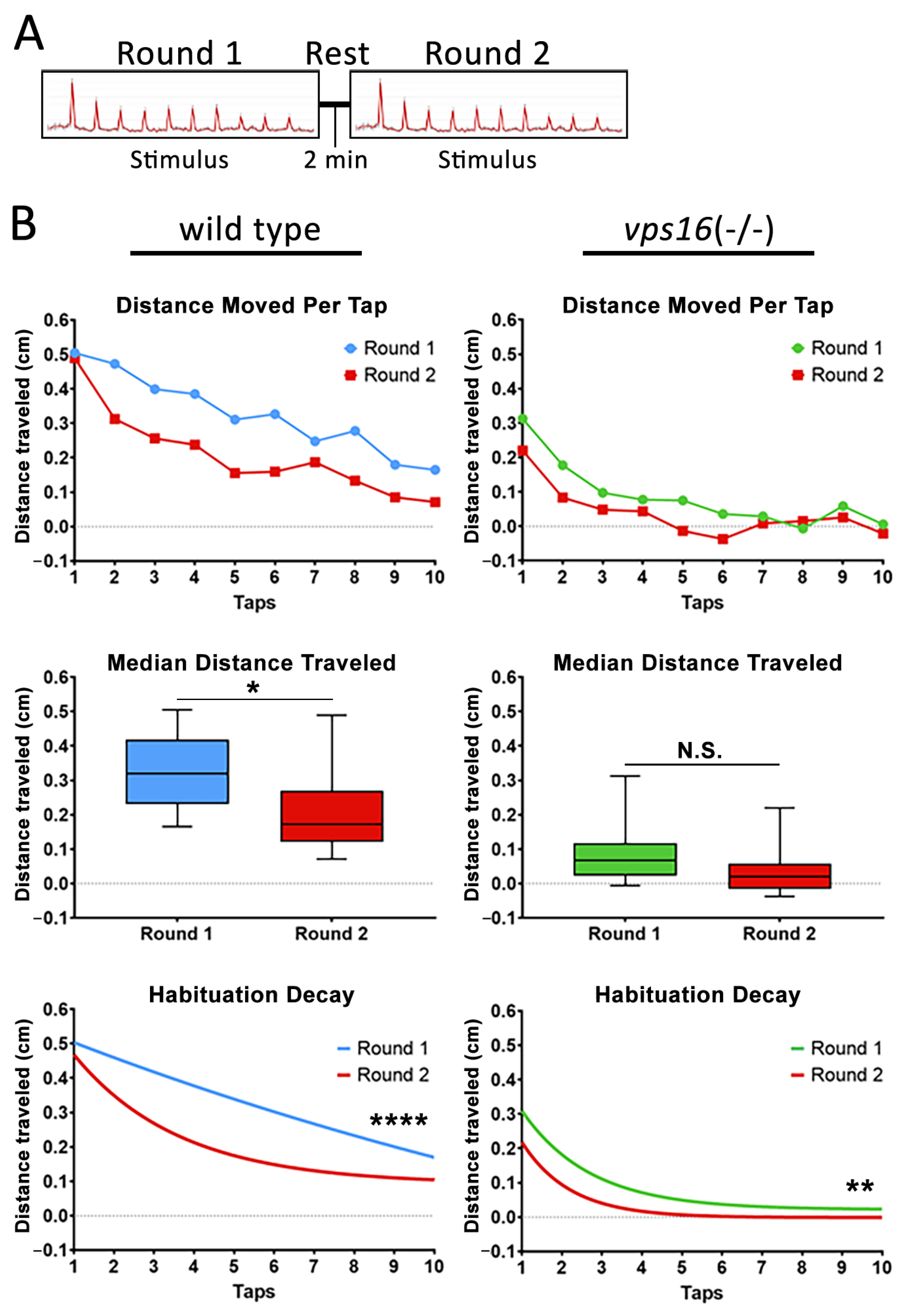
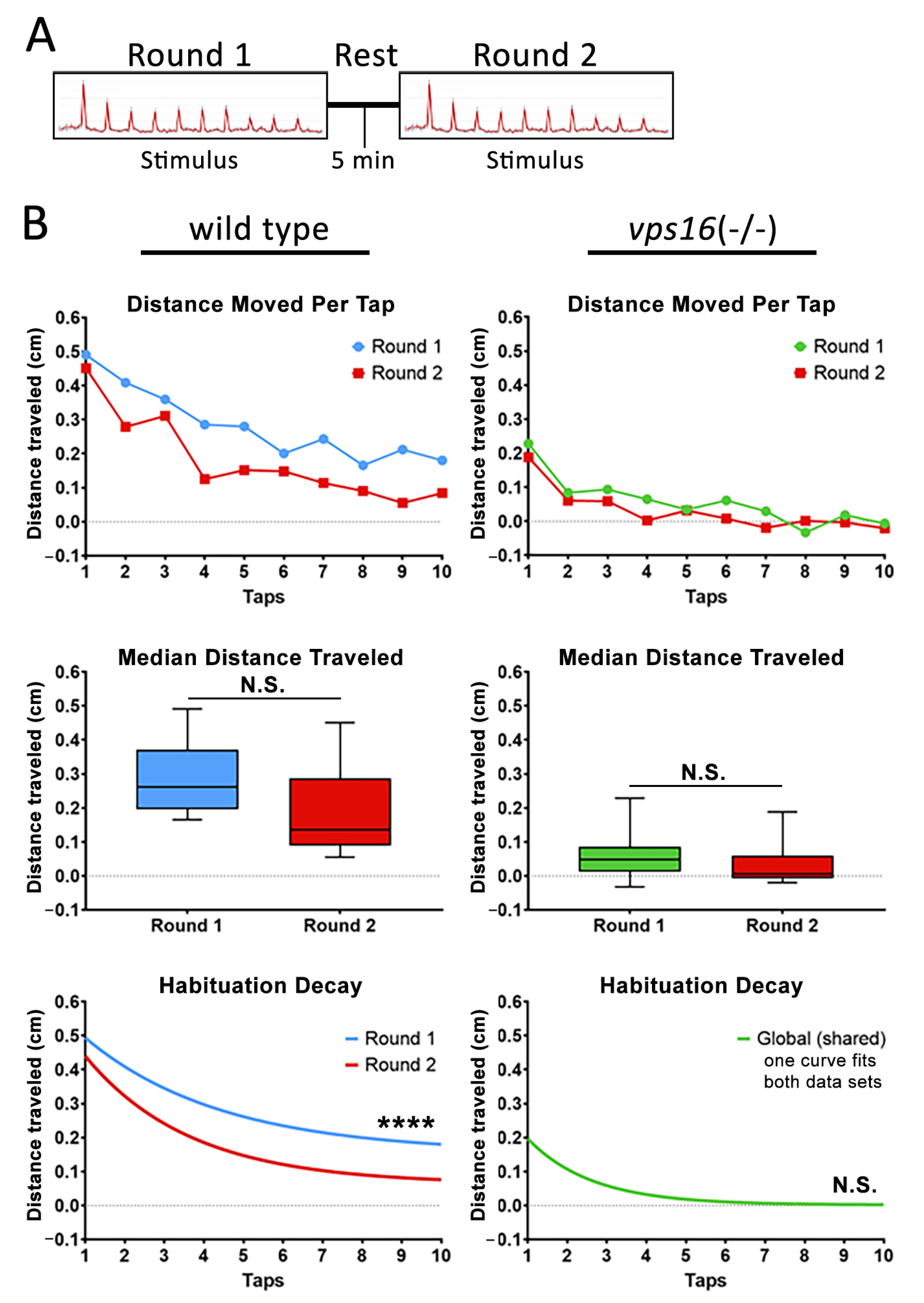
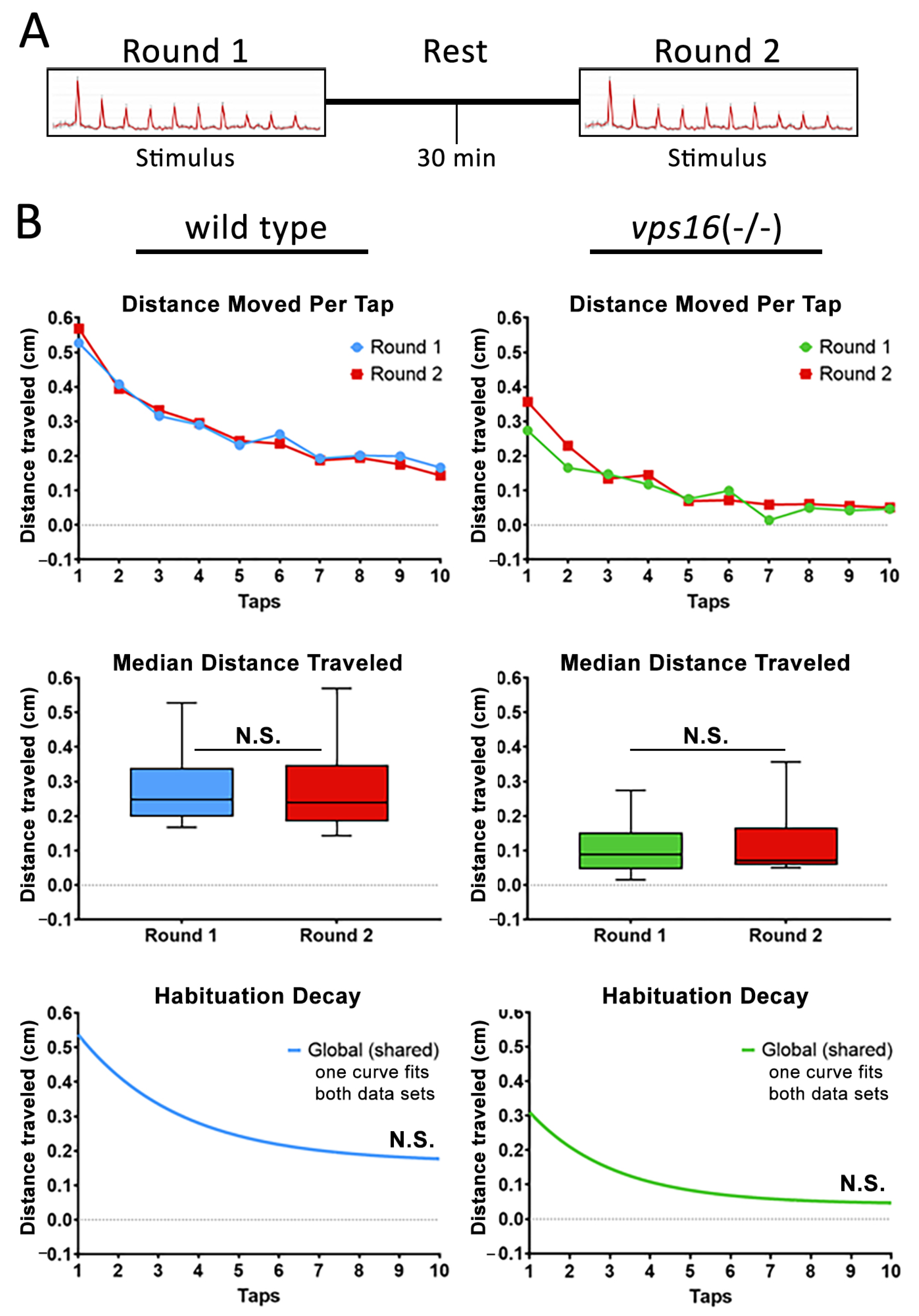
2.6. vps16(-/-) Mutants Show Abnormalities in Intermediate Memory
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zebrafish Lines and Maintenance
4.2. Generation of the vps16(-/-) Mutant Line
4.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
4.4. Wholemount Brightfield Imaging
4.5. Survival Curves
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Analysis
4.8. Confocal Microscopy and Quantification
4.9. Histopathology
4.10. Behavioral Analysis
4.10.1. Light/Dark Paradigm
4.10.2. Single Acoustic/Tap Paradigm
4.10.3. Multiple Acoustic/Tap Habituation Paradigm
4.10.4. Intermediate Memory Paradigm
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huotari, J.; Helenius, A. Endosome maturation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3481–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balderhaar, H.J.; Ungermann, C. CORVET and HOPS tethering complexes-coordinators of endosome and lysosome fusion. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, D.P.; Brett, C.L.; Merz, A.J. Vps-C complexes: Gatekeepers of endolysosomal traffic. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Kramer, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Kominami, E.; Kohsaka, S.; Akazawa, C. Molecular characterization of mammalian homologues of class C Vps proteins that interact with syntaxin-7. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29393–29402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Ueda, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Akazawa, C. Expression of the mammalian homologue of vacuolar protein sorting 16 (Vps16p) in the mouse and rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 355, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Nishimura, T.; Sakamaki, Y.; Itakura, E.; Hatta, T.; Natsume, T.; Mizushima, N. The HOPS complex mediates autophagosome-lysosome fusion through interaction with syntaxin 17. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wartosch, L.; Gunesdogan, U.; Graham, S.C.; Luzio, J.P. Recruitment of VPS33A to HOPS by VPS16 Is Required for Lysosome Fusion with Endosomes and Autophagosomes. Traffic 2015, 16, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, G.; Medina, D.L.; Ballabio, A. The rapidly evolving view of lysosomal storage diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.K.; Kishnani, P.; Wanner, C.; Dong, D.; Bender, J.; Batista, J.L.; Foster, J. Rare lysosomal disease registries: Lessons learned over three decades of real-world evidence. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraguna, M.C.; Musto, F.; Crescitelli, V.; Iascone, M.; Spaccini, L.; Tonduti, D.; Fedeli, T.; Kullmann, G.; Canonico, F.; Cattoni, A.; et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis-Plus Syndrome, a Rapidly Progressive Disease: Favorable Impact of a Very Prolonged Steroid Treatment on the Clinical Course in a Child. Genes 2022, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegrzyn, G.; Pierzynowska, K.; Pavone, L.M. Editorial: Molecular Aspects of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 874267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, M.; Arunkumar, N.; Kubaski, F.; Mason, R.W.; Tadao, O.; Tomatsu, S. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 125, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofou, K.; Meier, K.; Sanderson, L.E.; Kaminski, D.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Samuelsson, E.; Blomqvist, M.; Agholme, L.; Gartner, J.; Muhlhausen, C.; et al. Bi-allelic VPS16 variants limit HOPS/CORVET levels and cause a mucopolysaccharidosis-like disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dursun, A.; Yalnizoglu, D.; Gerdan, O.F.; Yucel-Yilmaz, D.; Sagiroglu, M.S.; Yuksel, B.; Gucer, S.; Sivri, S.; Ozgul, R.K. A probable new syndrome with the storage disease phenotype caused by the VPS33A gene mutation. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2017, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Maksimova, N.; Otomo, T.; Kato, H.; Imai, A.; Asano, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Nojima, S.; Nakaya, A.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Mutation in VPS33A affects metabolism of glycosaminoglycans: A new type of mucopolysaccharidosis with severe systemic symptoms. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, E.V.; Shatunov, A.; Wartosch, L.; Moskvina, A.I.; Nikolaeva, L.E.; Bright, N.A.; Tylee, K.L.; Church, H.J.; Ballabio, A.; Luzio, J.P.; et al. The lysosomal disease caused by mutant VPS33A. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 2514–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, Y.; Kosukcu, C.; Aygun, D.; Akcaboy, M.; Oztek Celebi, F.Z.; Tasci Yildiz, Y.; Sahin, G.; Aytekin, C.; Yuksel, D.; Lay, I.; et al. Homozygous missense VPS16 variant is associated with a novel disease, resembling mucopolysaccharidosis-plus syndrome in two siblings. Clin. Genet. 2021, 100, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Homozygous mutation of VPS16 gene is responsible for an autosomal recessive adolescent-onset primary dystonia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, D.; Zech, M.; Zhao, C.; Barwick, K.E.S.; Burke, D.; Demailly, D.; Kumar, K.R.; Zorzi, G.; Nardocci, N.; Kaiyrzhanov, R.; et al. Loss-of-Function Variants in HOPS Complex Genes VPS16 and VPS41 Cause Early Onset Dystonia Associated with Lysosomal Abnormalities. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Bhatia, K.; Bressman, S.B.; Delong, M.R.; Fahn, S.; Fung, V.S.; Hallett, M.; Jankovic, J.; Jinnah, H.A.; Klein, C.; et al. Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: A consensus update. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, D.; Kurian, M.A. Recent genetic advances in early-onset dystonia. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lachance, V.; Schaffner, A.; Li, X.; Fedick, A.; Kaye, L.E.; Liao, J.; Rosenfeld, J.; Yachelevich, N.; Chu, M.L.; et al. A Founder Mutation in VPS11 Causes an Autosomal Recessive Leukoencephalopathy Linked to Autophagic Defects. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Beek, J.; Jonker, C.; van der Welle, R.; Liv, N.; Klumperman, J. CORVET, CHEVI and HOPS-multisubunit tethers of the endo-lysosomal system in health and disease. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs189134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Ranspach, L.E.; Luo, X.; Cianciolo, L.T.; Fogerty, J.; Perkins, B.D.; Thummel, R. Vision and sensorimotor defects associated with loss of Vps11 function in a zebrafish model of genetic leukoencephalopathy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.L.; Vihtelic, T.S.; denDekker, A.D.; Willer, G.; Luo, X.; Murphy, T.R.; Gregg, R.G.; Hyde, D.R.; Thummel, R. The loss of vacuolar protein sorting 11 (vps11) causes retinal pathogenesis in a vertebrate model of syndromic albinism. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkalj, B.; Quallich, D.; Bessert, D.A.; Kramer, A.C.; Cook, T.A.; Thummel, R. Development and characterization of a chronic photoreceptor degeneration model in adult zebrafish that does not trigger a regenerative response. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 209, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.C.; Gurdziel, K.; Thummel, R. A Comparative Analysis of Gene and Protein Expression Throughout a Full 28-Day Retinal Regeneration Time-Course in Adult Zebrafish. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 741514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranski, A.H.; Kramer, A.C.; Morgan, G.W.; Perez, J.L.; Thummel, R. Characterization of retinal regeneration in adult zebrafish following multiple rounds of phototoxic lesion. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkowski, J.R.; Qin, Z.; Sifuentes, C.J.; Thummel, R.; Soto, C.M.; Moens, C.B.; Raymond, P.A. Retinal regeneration in adult zebrafish requires regulation of TGFbeta signaling. Glia 2013, 61, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.H.; Ravanelli, A.M.; Schwindt, R.; Scott, E.K.; Appel, B. Neuronal activity biases axon selection for myelination In Vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppi, C.; Straumann, D.; Bogli, S.Y. A model-based quantification of startle reflex habituation in larval zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfrini, E.; Cogiamanian, F.; Salani, S.; Straniero, L.; Fagiolari, G.; Garbellini, M.; Carsana, E.; Borellini, L.; Biella, F.; Moggio, M.; et al. A Novel Homozygous VPS11 Variant May Cause Generalized Dystonia. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvardson, S.; Gerhard, F.; Jalas, C.; Lachmann, J.; Golan, D.; Saada, A.; Shaag, A.; Ungermann, C.; Elpeleg, O. Hypomyelination and developmental delay associated with VPS11 mutation in Ashkenazi-Jewish patients. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, M.S.; Heijnen, H.F.; Raposo, G. Lysosome-related organelles: Unusual compartments become mainstream. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulipparacharuvil, S.; Akbar, M.A.; Ray, S.; Sevrioukov, E.A.; Haberman, A.S.; Rohrer, J.; Kramer, H. Drosophila Vps16A is required for trafficking to lysosomes and biogenesis of pigment granules. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3663–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, T.S.; Sinclair, D.A.; Fitzpatrick, K.A.; Singh, M.; Devlin, R.H.; Honda, B.M. The light gene of Drosophila melanogaster encodes a homologue of VPS41, a yeast gene involved in cellular-protein trafficking. Genome 1998, 41, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevrioukov, E.A.; He, J.P.; Moghrabi, N.; Sunio, A.; Kramer, H. A role for the deep orange and carnation eye color genes in lysosomal delivery in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, V.; Krishnan, K.S.; Mayor, S. deep-orange and carnation define distinct stages in late endosomal biogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, E.; Hernandez, F.; Lozano, C.; Castro, M.E.; Navarro, R.E. The zebrafish mutant vps18 as a model for vesicle-traffic related hypopigmentation diseases. Pigment. Cell Res. 2006, 19, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.D. Insights from zebrafish on human pigment cell disease and treatment. Dev. Dyn. 2017, 246, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.A. Development of pigment cells in the zebrafish embryo. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 58, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Collins, J.E.; Andrews, R.M.; Stemple, D.; Gong, Z. Comparative transcriptome analyses indicate molecular homology of zebrafish swimbladder and mammalian lung. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, B.J.; Pack, M. Zebrafish models of human liver development and disease. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S.; et al. Towards a comprehensive catalog of zebrafish behavior 1.0 and beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosamle, C.; Halpern, M.E. Characterization of myelination in the developing zebrafish. Glia 2002, 39, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, M.A.; Jain, R.A.; Liss, L.; Granato, M. Chemical modulation of memory formation in larval zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15468–15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Schier, H. Neuroplasticity in the acoustic startle reflex in larval zebrafish. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2019, 54, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.C.; Pearce, K.C.; Choe, R.C.; Alzagatiti, J.B.; Yeung, A.K.; Bill, B.R.; Glanzman, D.L. Long-term habituation of the C-start escape response in zebrafish larvae. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2016, 134 Pt B, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Inoue, M.; Tanimoto, M.; Kohashi, T.; Oda, Y. Short-term desensitization of fast escape behavior associated with suppression of Mauthner cell activity in larval zebrafish. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 121, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The zebrafish book. In A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banerjee, S.; Bongu, S.; Hughes, S.P.; Gaboury, E.K.; Carver, C.E.; Luo, X.; Bessert, D.A.; Thummel, R. Hypomyelinated vps16 Mutant Zebrafish Exhibit Systemic and Neurodevelopmental Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137260
Banerjee S, Bongu S, Hughes SP, Gaboury EK, Carver CE, Luo X, Bessert DA, Thummel R. Hypomyelinated vps16 Mutant Zebrafish Exhibit Systemic and Neurodevelopmental Pathologies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137260
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanerjee, Shreya, Shivani Bongu, Sydney P. Hughes, Emma K. Gaboury, Chelsea E. Carver, Xixia Luo, Denise A. Bessert, and Ryan Thummel. 2024. "Hypomyelinated vps16 Mutant Zebrafish Exhibit Systemic and Neurodevelopmental Pathologies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137260
APA StyleBanerjee, S., Bongu, S., Hughes, S. P., Gaboury, E. K., Carver, C. E., Luo, X., Bessert, D. A., & Thummel, R. (2024). Hypomyelinated vps16 Mutant Zebrafish Exhibit Systemic and Neurodevelopmental Pathologies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137260





