A New Derivative of Retro-2 Displays Antiviral Activity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
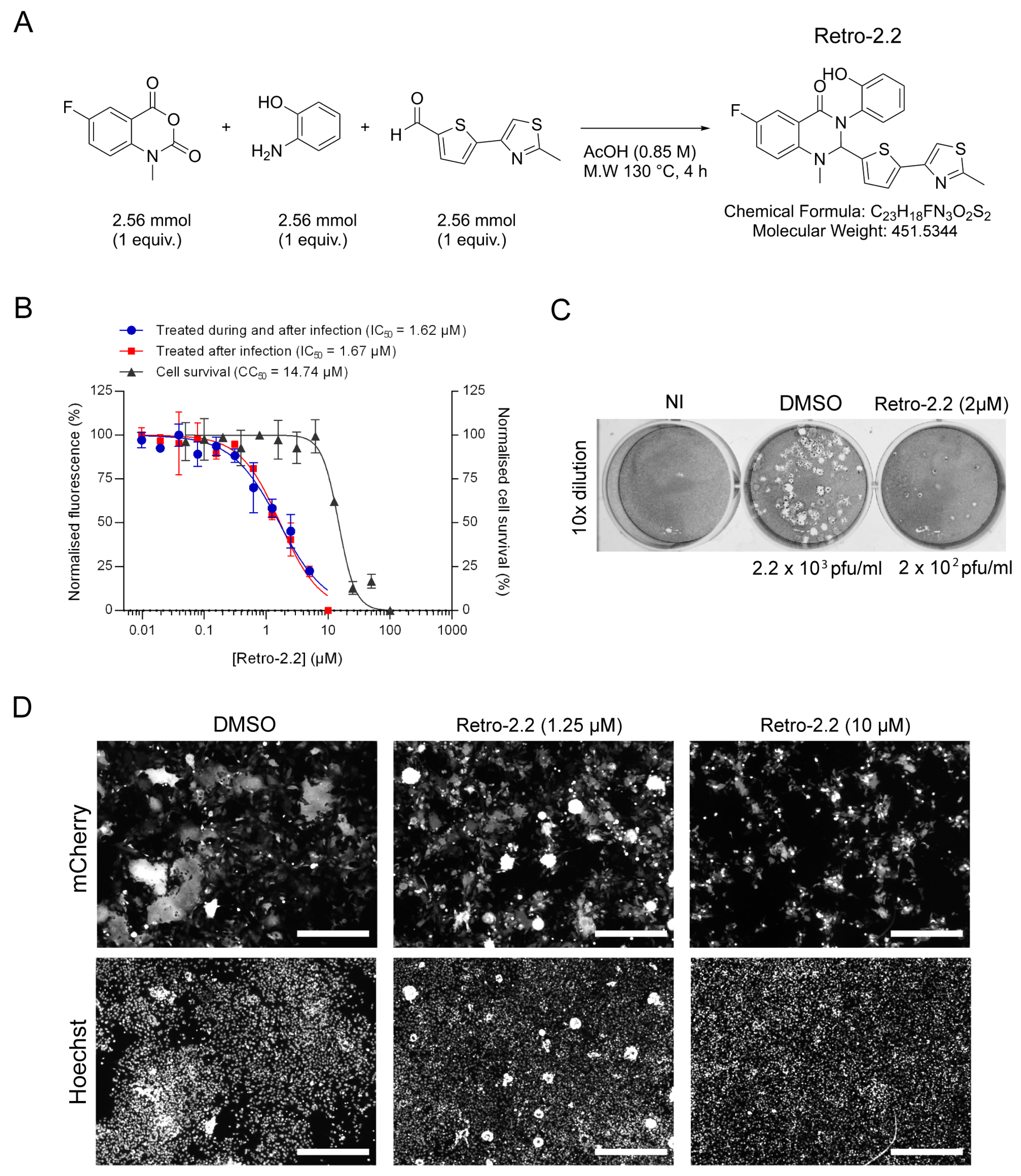
2.1. Retro-2.2 Antiviral Activity against hRSV
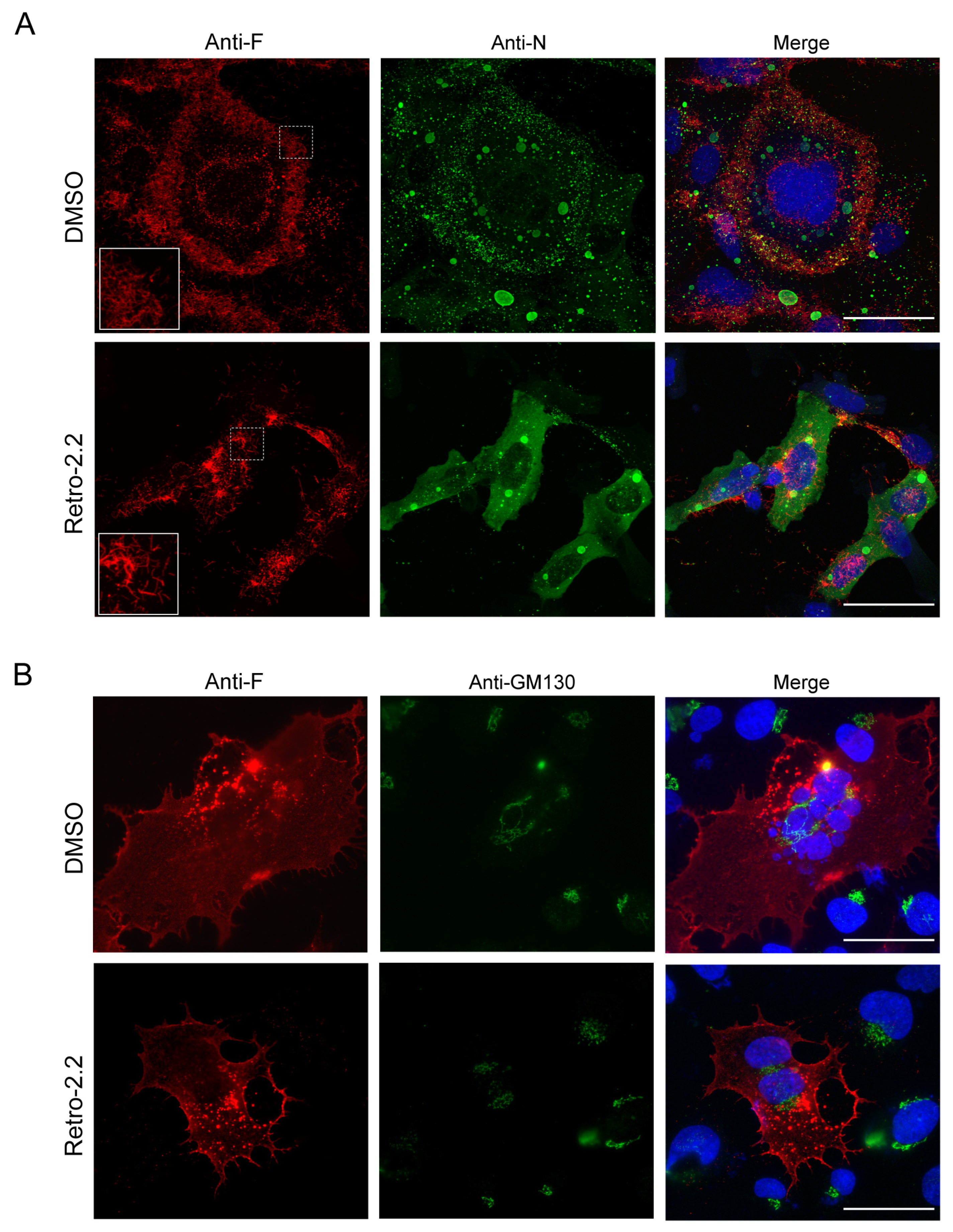
2.2. Retro-2.2 Effect on the Formation of IBs and Virions Assembly in hRSV-Infected Cells
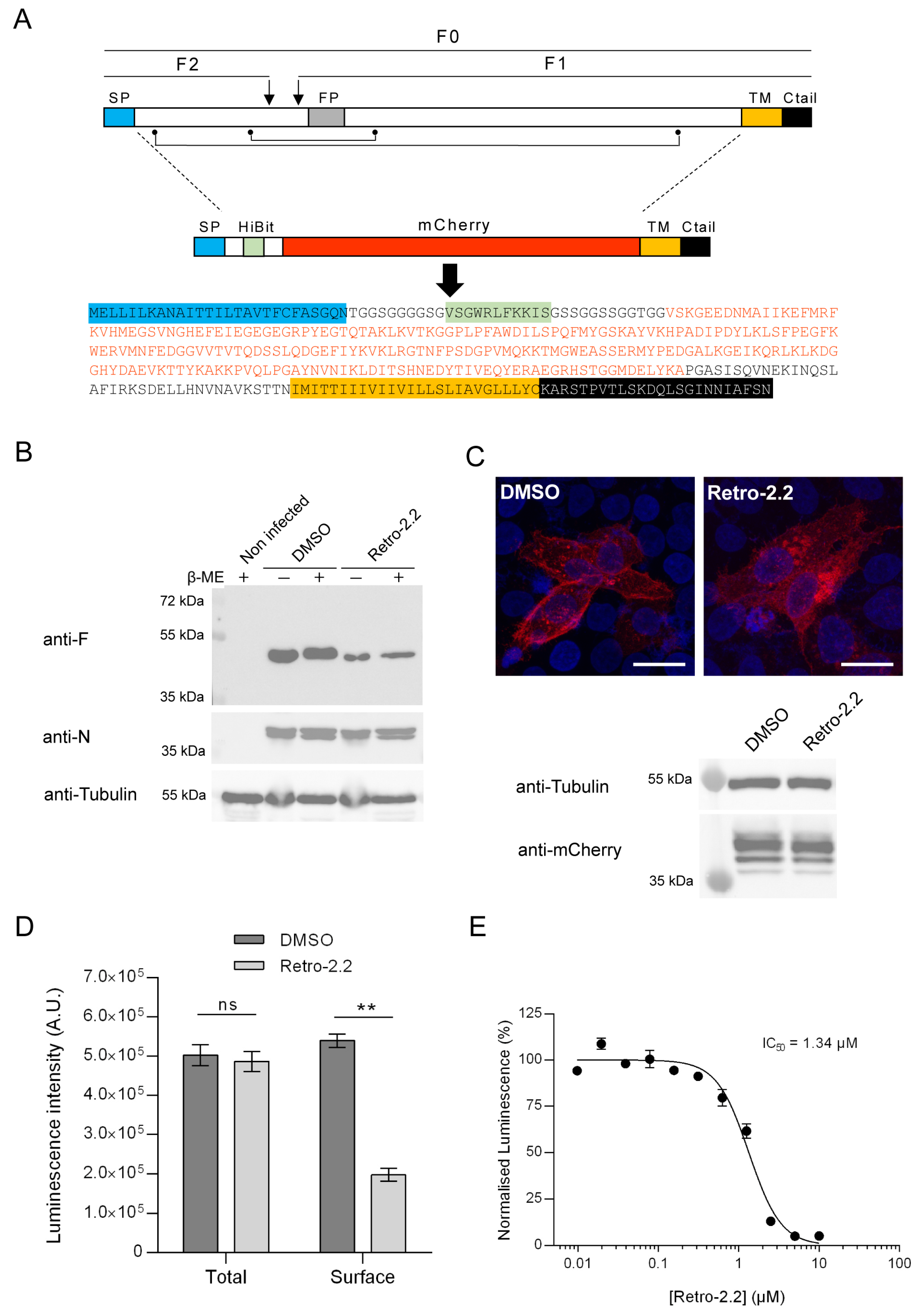
2.3. Retro-2.2 Affects the Trafficking of the F Protein to the Plasma Membrane
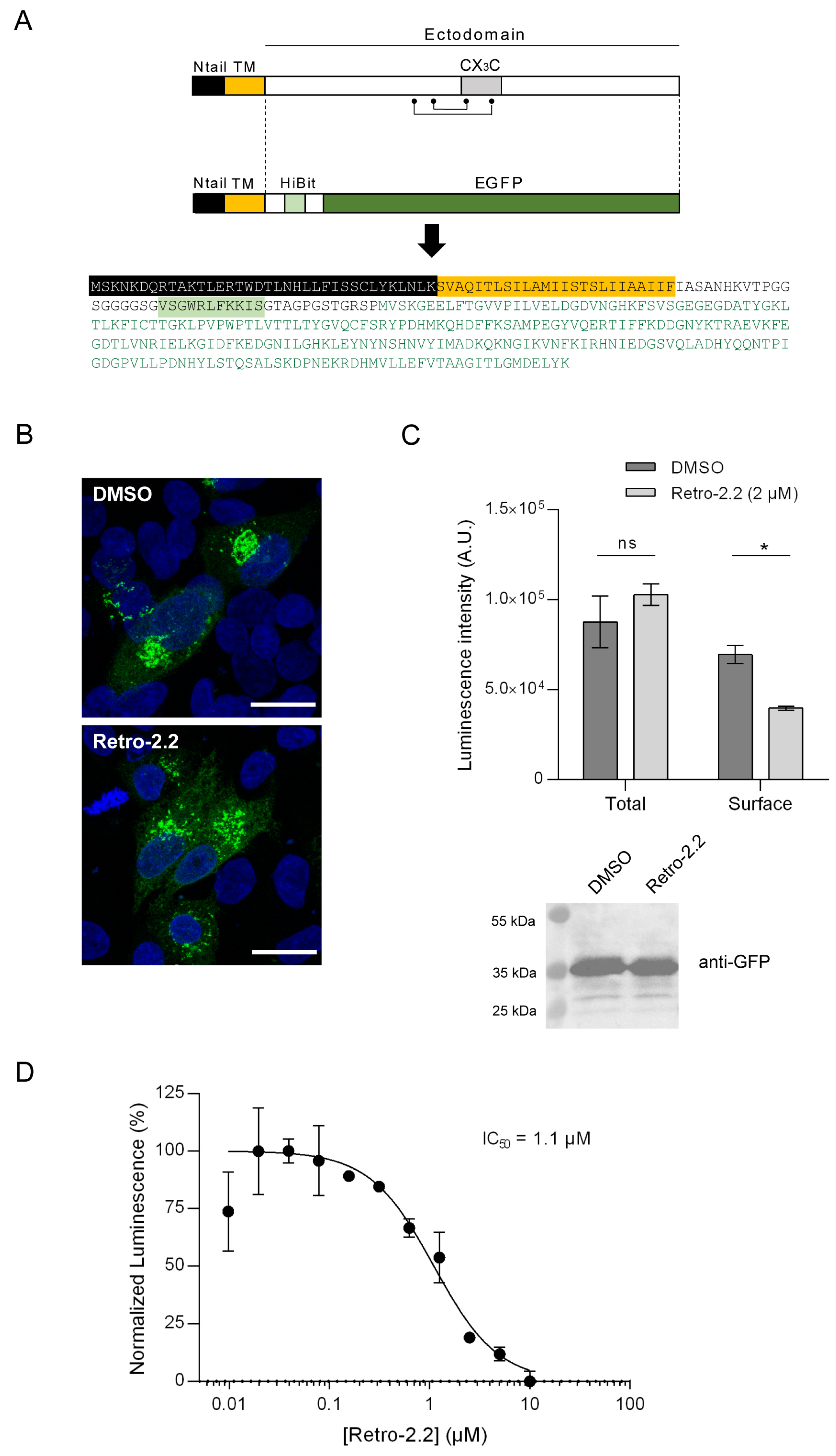
2.4. Impact of Retro-2.2 on the G Glycoprotein Trafficking to the Plasma Membrane
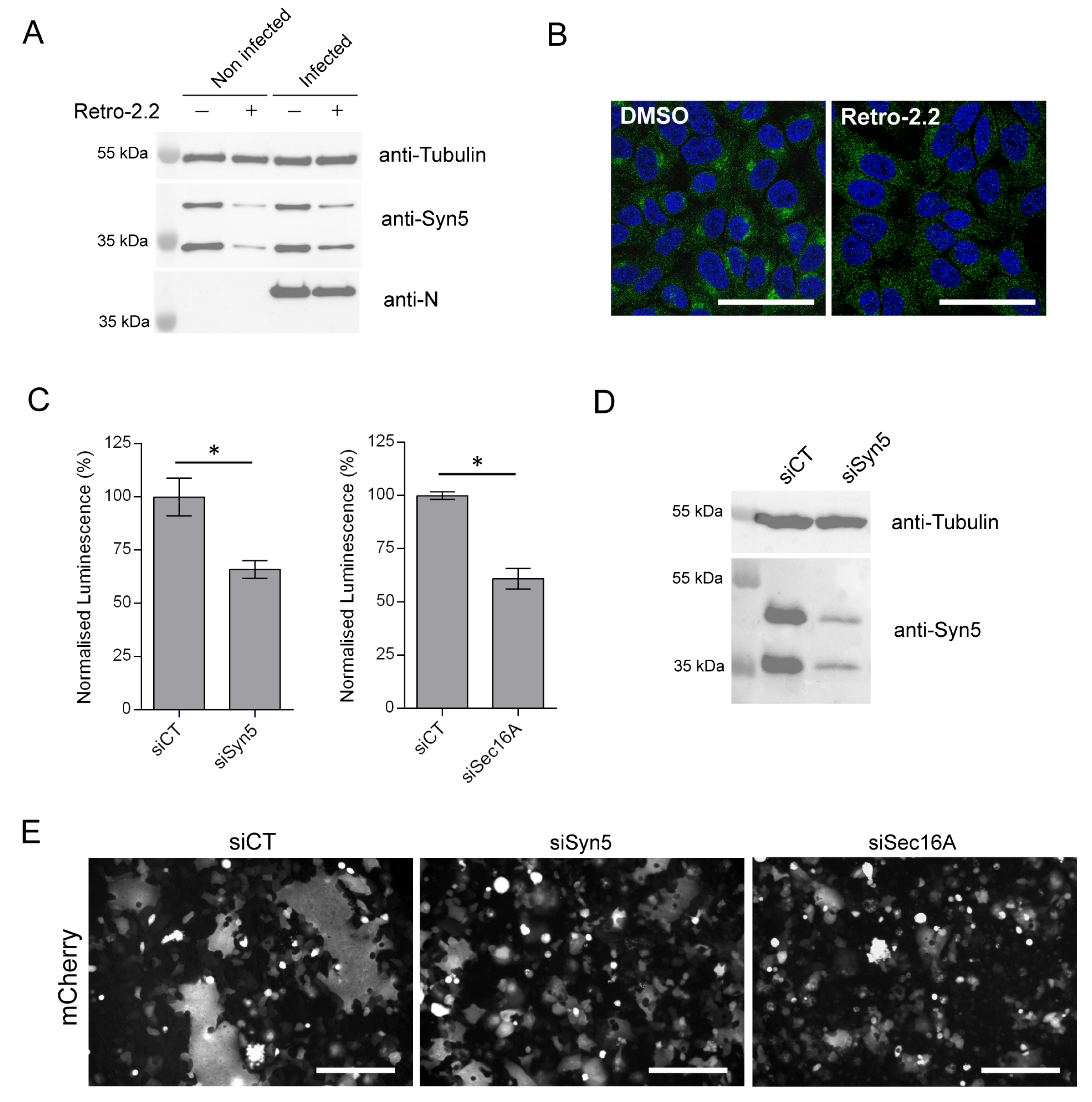
2.5. Down-Expression of Syntaxin-5 and Sec16A Impair hRSV Replication and Syncytia Formation
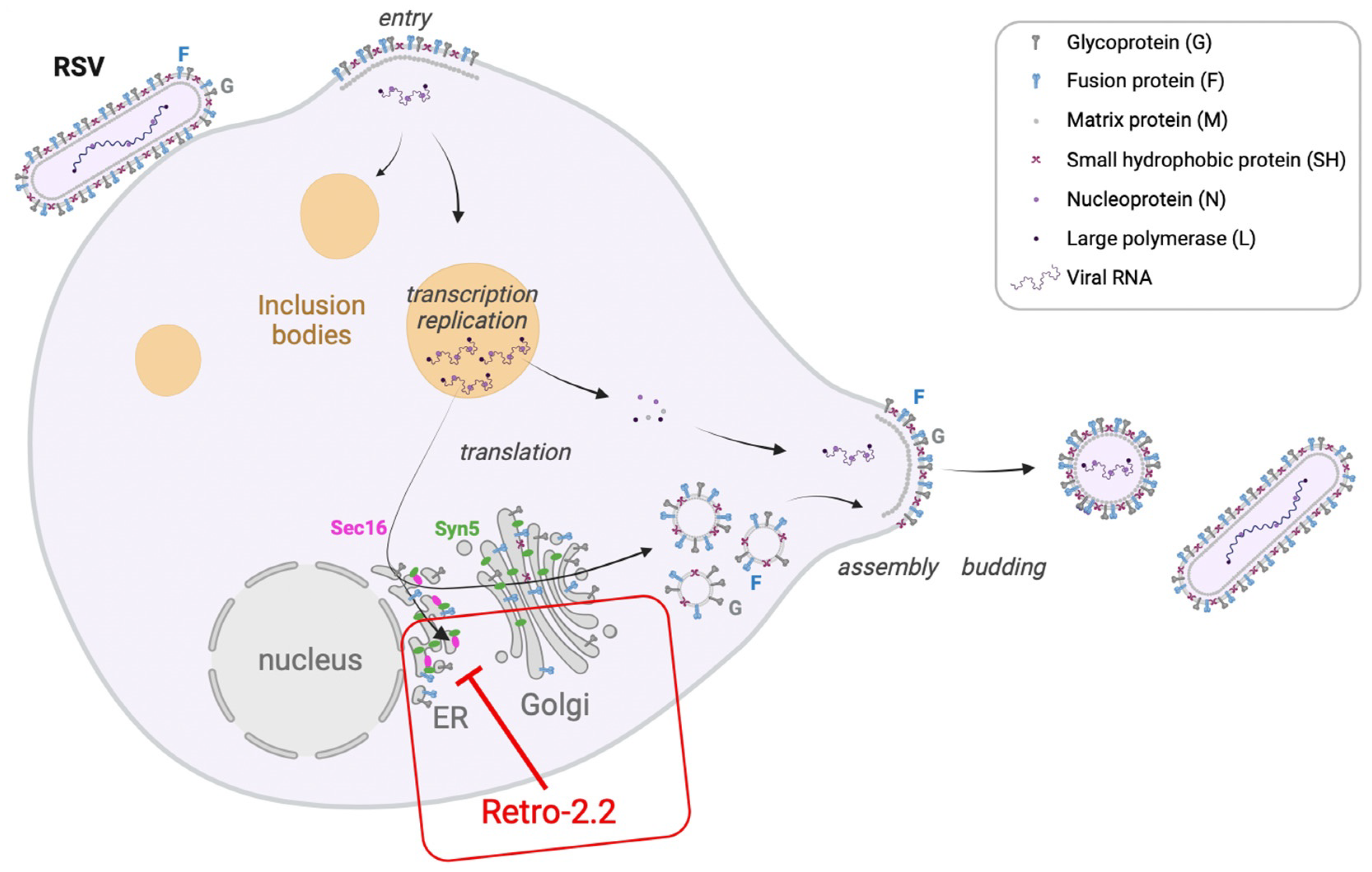
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Retro-2.2 Compound Synthesis
4.3. Viruses and Titration by Plaque Formation Assay
4.4. Plasmids
4.5. Antibodies
4.6. Antiviral and Cytotoxic Activity Assays
4.7. siRNA Experiments
4.8. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Immunofluorescence
4.10. HiBit Luminescence Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.M.; Caballero, M.T.; Feikin, D.R.; Gill, C.J.; Madhi, S.A.; Omer, S.B.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pneumonia Etiology Research for Child Health (PERCH) Study Group. Causes of severe pneumonia requiring hospital admission in children without HIV infection from Africa and Asia: The PERCH multi-country case-control study. Lancet 2019, 394, 757–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Finelli, L.; Saiman, L.; Wang, C.; Choi, Y.; Patel, J. Respiratory Syncytial Virus-associated Acute Otitis Media in Infants and Children. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2020, 9, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Ooi, Y.; Zaw, E.M.; Utjesanovic, N.; Campbell, H.; Cunningham, S.; Bont, L.; Nair, H.; Investigators, R. Association Between Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Acute Lower Respiratory Infection in Early Life and Recurrent Wheeze and Asthma in Later Childhood. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222 (Suppl. S7), S628–S633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busack, B.; Shorr, A.F. Going Viral-RSV as the Neglected Adult Respiratory Virus. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Ison, M.G.; Langley, J.M.; Lee, D.G.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Martinon-Torres, F.; Schwarz, T.F.; van Zyl-Smit, R.N.; Campora, L.; Dezutter, N.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Protein Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Perez Marc, G.; Zareba, A.M.; Falsey, A.R.; Jiang, Q.; Patton, M.; Polack, F.P.; Llapur, C.; Doreski, P.A.; Ilangovan, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Bivalent RSV Prefusion F Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, B.; Madhi, S.A.; Munjal, I.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Pahud, B.A.; Llapur, C.; Baker, J.; Perez Marc, G.; Radley, D.; Shittu, E.; et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cummins, C.; Bayliss, S.; Sandercock, J.; Burls, A. Immunoprophylaxis against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with palivizumab in children: A systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2008, 12, iii, ix–x, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinquier, D.; Crepey, P.; Tissieres, P.; Vabret, A.; Roze, J.C.; Dubos, F.; Cahn-Sellem, F.; Javouhey, E.; Cohen, R.; Weil-Olivier, C. Preventing Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Children in France: A Narrative Review of the Importance of a Reinforced Partnership Between Parents, Healthcare Professionals, and Public Health Authorities. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.P.; Yuan, Y.; Takas, T.; Domachowske, J.B.; Madhi, S.A.; Manzoni, P.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Esser, M.T.; Khan, A.A.; Dubovsky, F.; et al. Single-Dose Nirsevimab for Prevention of RSV in Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammitt, L.L.; Dagan, R.; Yuan, Y.; Baca Cots, M.; Bosheva, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Muller, W.J.; Zar, H.J.; Brooks, D.; Grenham, A.; et al. Nirsevimab for Prevention of RSV in Healthy Late-Preterm and Term Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.L.; Crowe, J.E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Metapneumovirus. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1601–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Afonso, C.L.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Banyai, K.; Bao, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briand, F.X.; Briese, T.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: Update 2016. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasakumar, N.; Ogra, P.L.; Flanagan, T.D. Characteristics of fusion of respiratory syncytial virus with HEp-2 cells as measured by R18 fluorescence dequenching assay. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4063–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyzaniak, M.A.; Zumstein, M.T.; Gerez, J.A.; Picotti, P.; Helenius, A. Host cell entry of respiratory syncytial virus involves macropinocytosis followed by proteolytic activation of the F protein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.S.; Schnell, M.J.; Buonocore, L.; Rose, J.K. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus expressing respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) glycoproteins: RSV fusion protein can mediate infection and cell fusion. Virology 1999, 254, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, A.; Scagnolari, C.; Antonelli, G. Respiratory syncytial virus. Minerva Pediatr. 2018, 70, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.; Fearns, R.; Graham, B.S. Respiratory syncytial virus: Virology, reverse genetics, and pathogenesis of disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, J.; Garcia-Barreno, B.; Vivo, A.; Melero, J.A. Cytoplasmic inclusions of respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells: Formation of inclusion bodies in transfected cells that coexpress the nucleoprotein, the phosphoprotein, and the 22K protein. Virology 1993, 195, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincheval, V.; Lelek, M.; Gault, E.; Bouillier, C.; Sitterlin, D.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Galloux, M.; Zimmer, C.; Eleouet, J.F.; Rameix-Welti, M.A. Functional organization of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in cells infected by respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVincenzo, J.P.; Whitley, R.J.; Mackman, R.L.; Scaglioni-Weinlich, C.; Harrison, L.; Farrell, E.; McBride, S.; Lambkin-Williams, R.; Jordan, R.; Xin, Y.; et al. Oral GS-5806 activity in a respiratory syncytial virus challenge study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detalle, L.; Stohr, T.; Palomo, C.; Piedra, P.A.; Gilbert, B.E.; Mas, V.; Millar, A.; Power, U.F.; Stortelers, C.; Allosery, K.; et al. Generation and Characterization of ALX-0171, a Potent Novel Therapeutic Nanobody for the Treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.; Rusch, S.; DeVincenzo, J.; Kim, Y.I.; Harrison, L.; Meals, E.A.; Boyers, A.; Fok-Seang, J.; Huntjens, D.; Lounis, N.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Oral JNJ-53718678 in Healthy Adult Volunteers Challenged With Respiratory Syncytial Virus: A Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockerill, G.S. JNJ-5371678, Defining a Role for Fusion Inhibitors in the Treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8043–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stechmann, B.; Bai, S.K.; Gobbo, E.; Lopez, R.; Merer, G.; Pinchard, S.; Panigai, L.; Tenza, D.; Raposo, G.; Beaumelle, B.; et al. Inhibition of retrograde transport protects mice from lethal ricin challenge. Cell 2010, 141, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.D.; Carney, D.W.; Derdowski, A.; Lipovsky, A.; Gee, G.V.; O’Hara, B.; Williard, P.; DiMaio, D.; Sello, J.K.; Atwood, W.J. A retrograde trafficking inhibitor of ricin and Shiga-like toxins inhibits infection of cells by human and monkey polyomaviruses. mBio 2013, 4, e00729-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, S.; Jin, G.; Desai, D.; Amin, S.; Shwetank; Lauver, M.D.; Lukacher, A.E. Inhibition of Retrograde Transport Limits Polyomavirus Infection In Vivo. mSphere 2017, 2, e00494-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasure, T.; Nelson, C.D.S. Inhibition of JC polyomavirus infectivity by the retrograde transport inhibitor Retro-2.1. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Noel, R.; Goudet, A.; Hinsinger, K.; Michau, A.; Pons, V.; Abdelkafi, H.; Secher, T.; Shima, A.; Shtanko, O.; et al. Inhibitors of retrograde trafficking active against ricin and Shiga toxins also protect cells from several viruses, Leishmania and Chlamydiales. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 267, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, G.; Weisberg, A.S.; Americo, J.L.; Moss, B. Retrograde Transport from Early Endosomes to the trans-Golgi Network Enables Membrane Wrapping and Egress of Vaccinia Virus Virions. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8891–8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtanko, O.; Sakurai, Y.; Reyes, A.N.; Noel, R.; Cintrat, J.C.; Gillet, D.; Barbier, J.; Davey, R.A. Retro-2 and its dihydroquinazolinone derivatives inhibit filovirus infection. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holwerda, M.; V’Kovski, P.; Wider, M.; Thiel, V.; Dijkman, R. Identification of an Antiviral Compound from the Pandemic Response Box that Efficiently Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameix-Welti, M.A.; Le Goffic, R.; Herve, P.L.; Sourimant, J.; Remot, A.; Riffault, S.; Yu, Q.; Galloux, M.; Gault, E.; Eleouet, J.F. Visualizing the replication of respiratory syncytial virus in cells and in living mice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.L.; Mottet, G. Post-translational processing and oligomerization of the fusion glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72 Pt 12, 3095–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, G.; Pedersen, L.O.; Birkeslund, H.H. Cleavage of the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein is required for its surface expression: Role of furin. Virus Res. 2000, 68, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S.; Ray, W.C.; Peeples, M.E. Structure and function of respiratory syncytial virus surface glycoproteins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Oh-Hashi, K.; Furuta, E.; Fujimura, K.; Hirata, Y. Application of a novel HiBiT peptide tag for monitoring ATF4 protein expression in Neuro2a cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 12, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Y.; Zhu, Q.C.; Liang, J.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Liu, D.X.; Fung, T.S. Development of HiBiT-Tagged Recombinant Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus for Efficient in vitro and in vivo Viral Quantification. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Q.; Rong, L.; Du, R. Development of an HiBiT-tagged reporter H3N2 influenza A virus and its utility as an antiviral screening platform. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, D.A.; Baradaran, K.; McIntosh, K.; Patterson, J.L. Appearance of a soluble form of the G protein of respiratory syncytial virus in fluids of infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68 Pt 6, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukreyev, A.; Yang, L.; Fricke, J.; Cheng, L.; Ward, J.M.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L. The secreted form of respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein helps the virus evade antibody-mediated restriction of replication by acting as an antigen decoy and through effects on Fc receptor-bearing leukocytes. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12191–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karron, R.A.; Buonagurio, D.A.; Georgiu, A.F.; Whitehead, S.S.; Adamus, J.E.; Clements-Mann, M.L.; Harris, D.O.; Randolph, V.B.; Udem, S.A.; Murphy, B.R.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) SH and G proteins are not essential for viral replication in vitro: Clinical evaluation and molecular characterization of a cold-passaged, attenuated RSV subgroup B mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13961–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, A.; Rathjen, S.J.; Daniela Garcia-Castillo, M.; Bachert, C.; Couhert, A.; Tepshi, L.; Pichard, S.; Martinez, J.; Munier, M.; Sierocki, R.; et al. Functional dissection of the retrograde Shiga toxin trafficking inhibitor Retro-2. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K.; Wakana, Y.; Noda, C.; Arasaki, K.; Furuno, A.; Tagaya, M. Contribution of the long form of syntaxin 5 to the organization of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125 Pt 23, 5658–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cox, R.; Plemper, R.K. The paramyxovirus polymerase complex as a target for next-generation anti-paramyxovirus therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearns, R.; Deval, J. New antiviral approaches for respiratory syncytial virus and other mononegaviruses: Inhibiting the RNA polymerase. Antivir. Res. 2016, 134, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockerill, G.S.; Good, J.A.D.; Mathews, N. State of the Art in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Drug Discovery and Development. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3206–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wu, Y.; Bi, J.; Lu, X.; Hou, A.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, B.; Kong, W.; Barbier, J.; Cintrat, J.C.; et al. Antiviral effects of Retro-2(cycl) and Retro-2.1 against Enterovirus 71 in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2017, 144, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinck, R.; Nguyen, L.A.; Munier, M.; Caramelle, L.; Karpman, D.; Barbier, J.; Pruvost, A.; Cintrat, J.C.; Gillet, D. In Vivo Sustained Release of the Retrograde Transport Inhibitor Retro-2.1 Formulated in a Thermosensitive Hydrogel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotard, A.L.; Shaikh, F.Y.; Lee, S.; Yan, D.; Teng, M.N.; Plemper, R.K.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Moore, M.L. A stabilized respiratory syncytial virus reverse genetics system amenable to recombination-mediated mutagenesis. Virology 2012, 434, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloux, M.; Tarus, B.; Blazevic, I.; Fix, J.; Duquerroy, S.; Eleouet, J.F. Characterization of a viral phosphoprotein binding site on the surface of the respiratory syncytial nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8375–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Rouzic, A.; Fix, J.; Vinck, R.; Kappler-Gratias, S.; Volmer, R.; Gallardo, F.; Eléouët, J.-F.; Keck, M.; Cintrat, J.-C.; Barbier, J.; et al. A New Derivative of Retro-2 Displays Antiviral Activity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010415
Le Rouzic A, Fix J, Vinck R, Kappler-Gratias S, Volmer R, Gallardo F, Eléouët J-F, Keck M, Cintrat J-C, Barbier J, et al. A New Derivative of Retro-2 Displays Antiviral Activity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010415
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Rouzic, Adrien, Jenna Fix, Robin Vinck, Sandrine Kappler-Gratias, Romain Volmer, Franck Gallardo, Jean-François Eléouët, Mathilde Keck, Jean-Christophe Cintrat, Julien Barbier, and et al. 2024. "A New Derivative of Retro-2 Displays Antiviral Activity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010415
APA StyleLe Rouzic, A., Fix, J., Vinck, R., Kappler-Gratias, S., Volmer, R., Gallardo, F., Eléouët, J.-F., Keck, M., Cintrat, J.-C., Barbier, J., Gillet, D., & Galloux, M. (2024). A New Derivative of Retro-2 Displays Antiviral Activity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010415








