A Predictive Model of Adaptive Resistance to BRAF/MEK Inhibitors in Melanoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
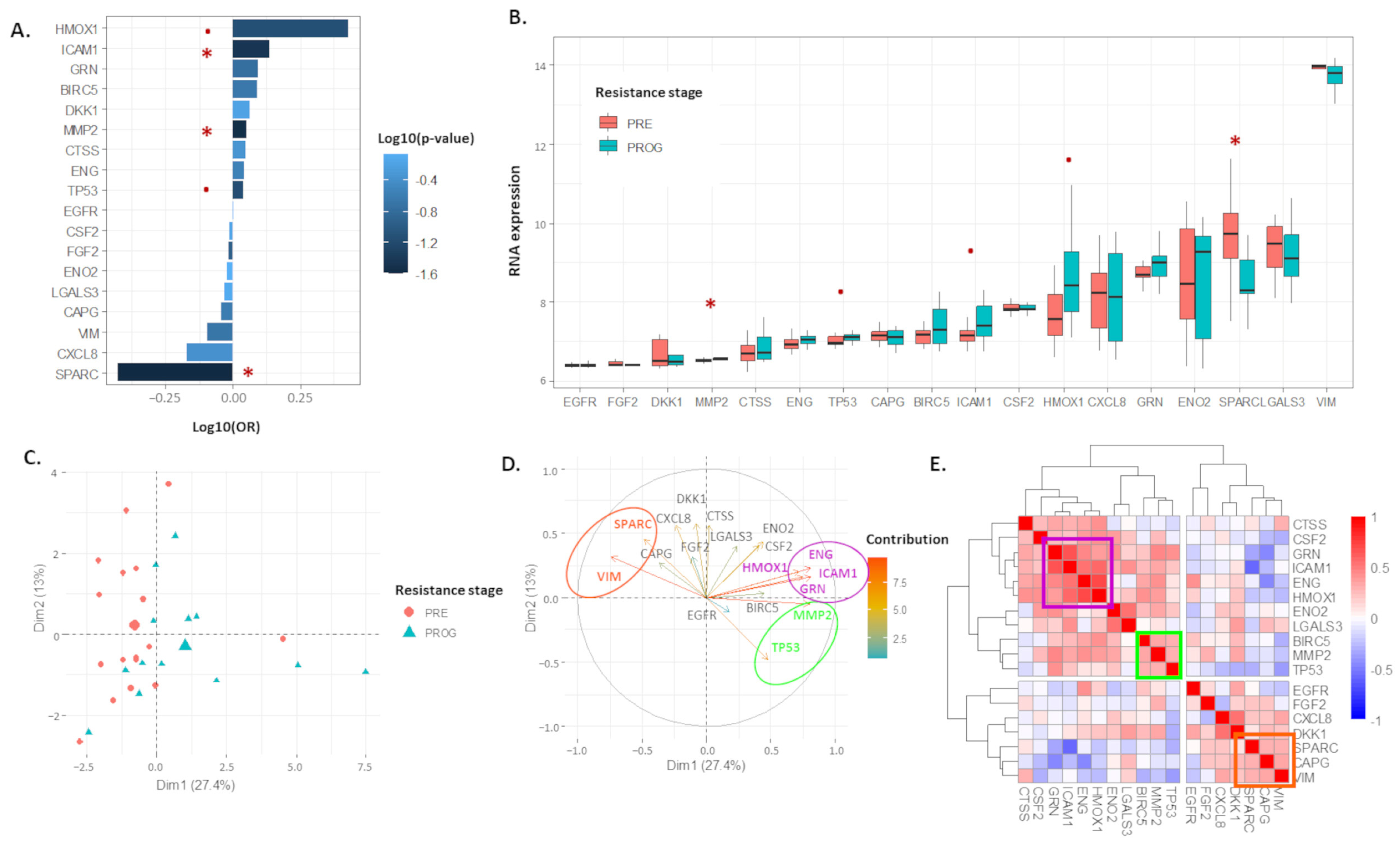
2.1. The 18 Proteomic Panel Is Deregulated in the Resistant Human Melanoma Model
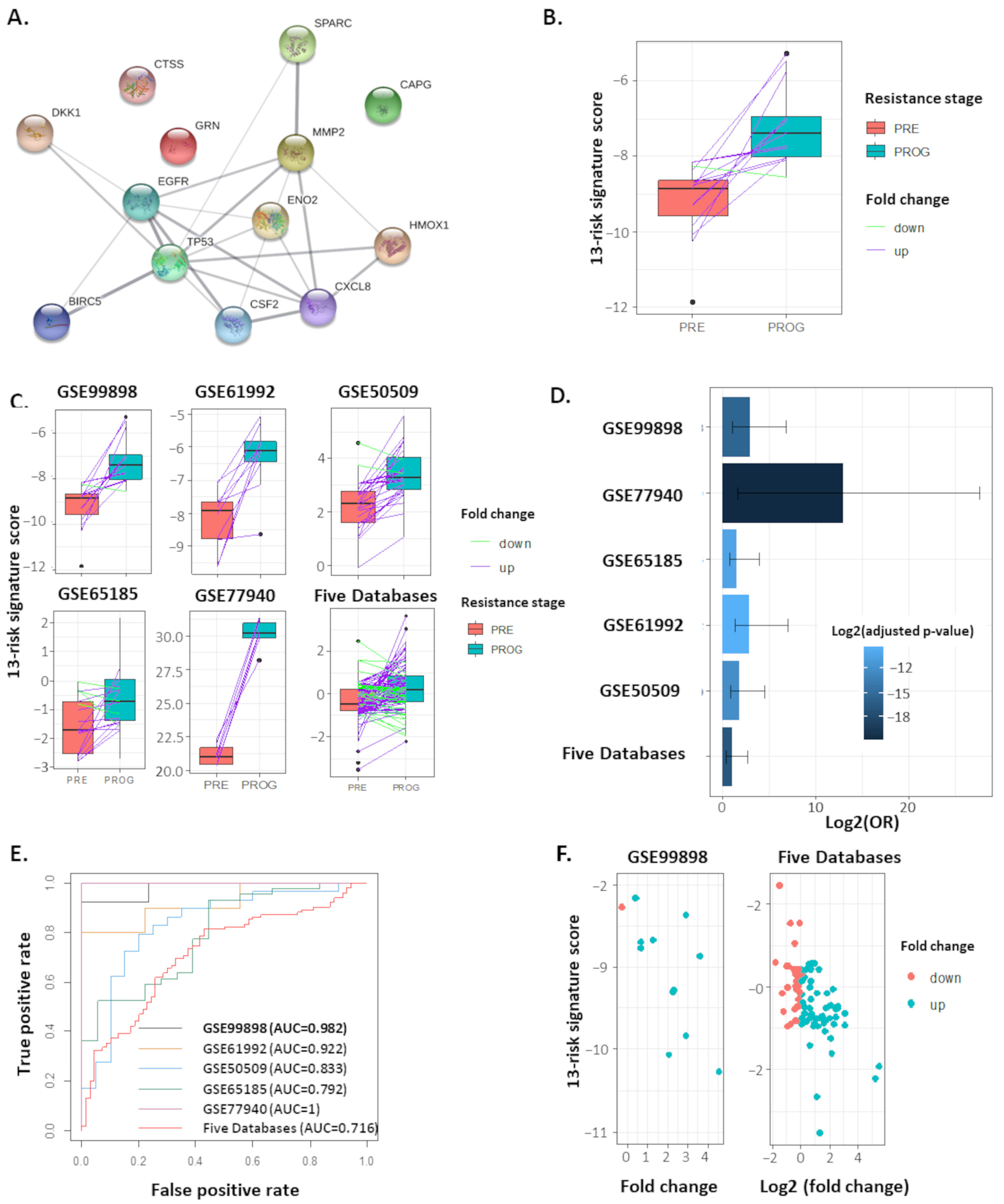
2.2. The 13-Risk Panel Predicts the Resistance Stage
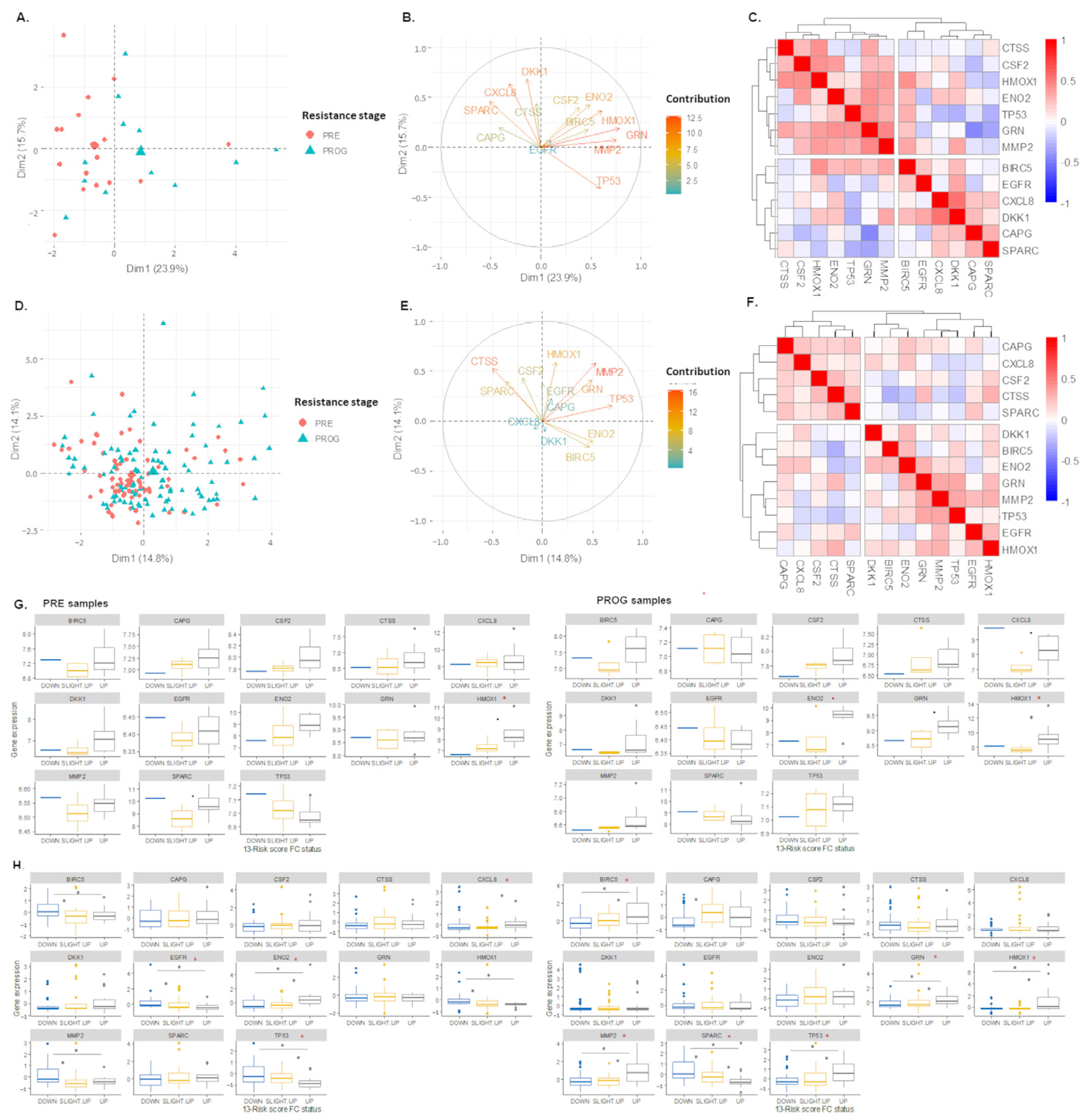
2.3. The 13-Risk Score Is Highly Differentiated according to the Resistance Stage
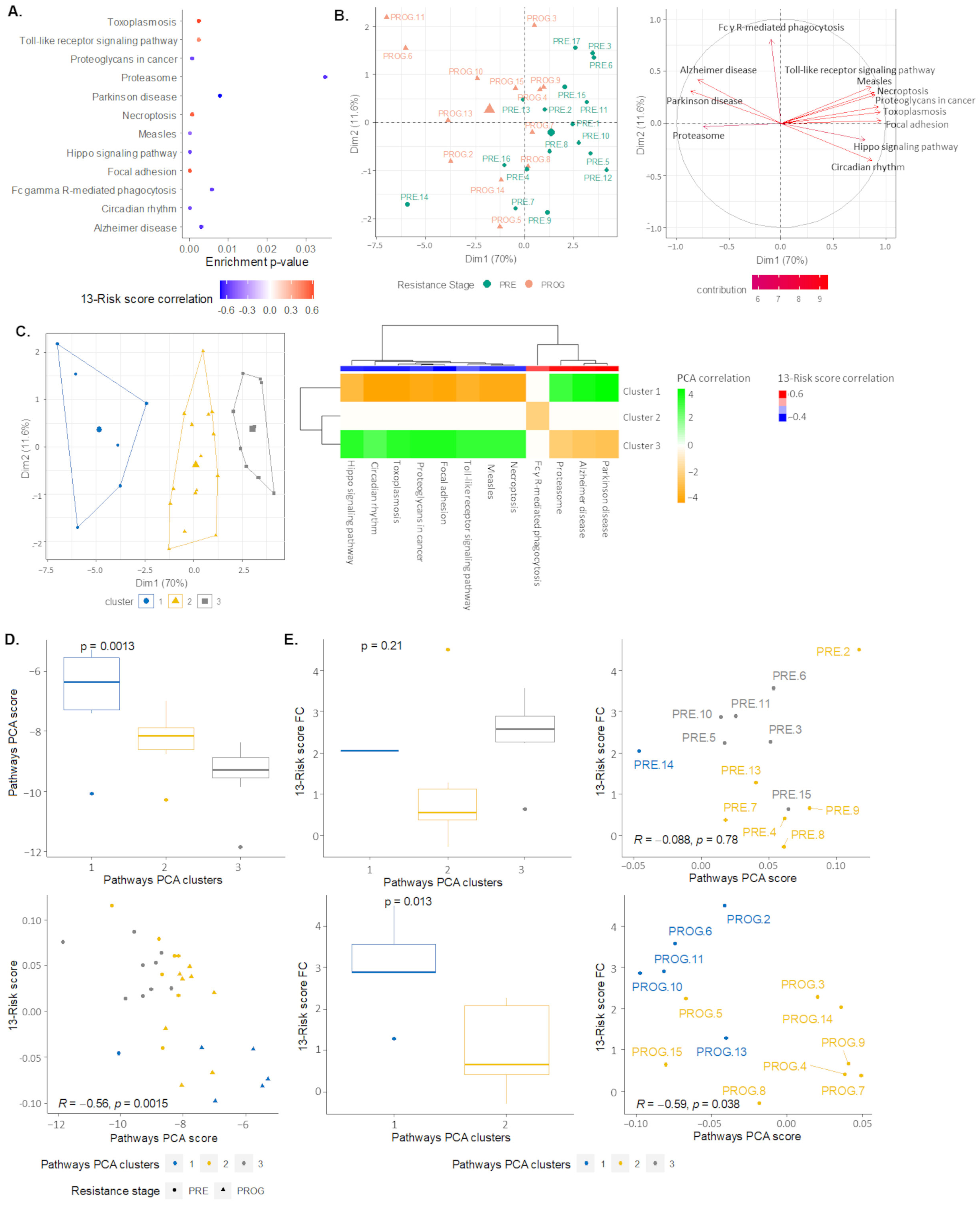
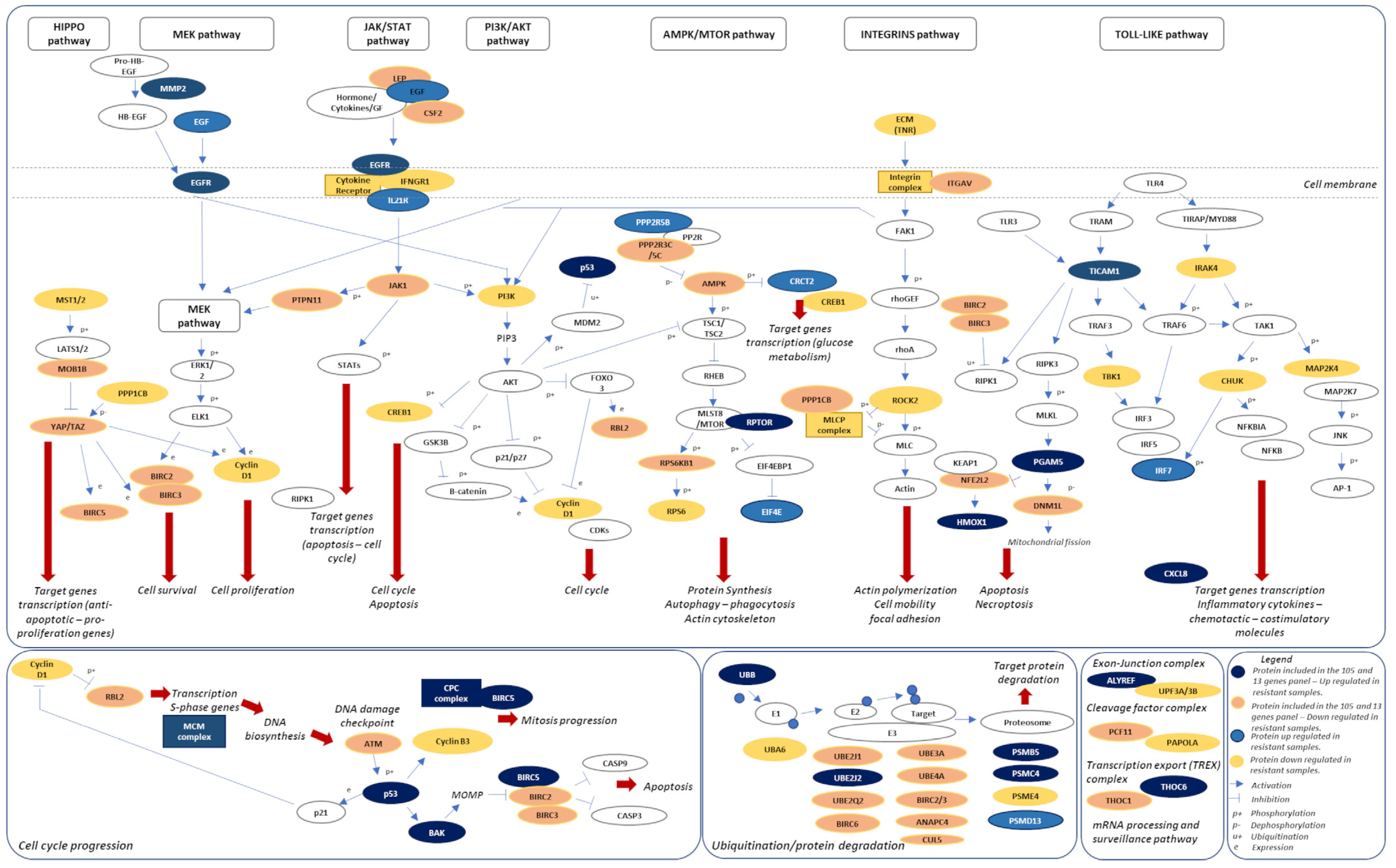
2.4. Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Sensitivity
2.5. Pathways Score Distribution according to the 13-Risk Score
2.6. The 105. Genes Involved in the Resistance-Related Pathways
2.7. A Novel Model of Therapeutic Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Datasets
4.2. The 13-Risk Panel Establishment and 13-Risk Score Calculation
4.3. KEGG Pathways Enrichment Analyses
4.4. Protein-Protein Interaction Network
4.5. Statistical Tests and Plots Design
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Vaccarella, S.; Meheus, F.; Cust, A.E.; de Vries, E.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Cutaneous Melanoma in 2020 and Projections to 2040. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, R.J.; van der Westhuizen, A.; Bowden, N.A. Metastatic melanoma treatment: Combining old and new therapies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 98, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozar, I.; Margue, C.; Rothengatter, S.; Haan, C.; Kreis, S. Many ways to resistance: How melanoma cells evade targeted therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayan, C.A.Y.; Lopez, A.T.; Gartrell, R.D.; Komatsubara, K.M.; Bogardus, M.; Rao, N.; Saenger, Y.M. The Role of Oncolytic Viruses in the Treatment of Melanoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellrich, F.F.; Schmitz, M.; Beissert, S.; Meier, F. Anti-PD-1 and Novel Combinations in the Treatment of Melanoma—An Update. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, M.; Botticelli, A.; Visconti, I.C.; Angeletti, D.; Fiore, M.; Marchetti, P.; Lambiase, A.; De Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A. Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 9235638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, M.; Pouyssegur, J. Targeting the ERK signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Dackiw, A.P.; Xing, M. Inhibitory effects of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor CI-1040 on the proliferation and tumor growth of thyroid cancer cells with BRAF or RAS mutations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4686–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Trink, E.; Bojdani, E.; Ning, G.; Xing, M. The Akt-Specific Inhibitor MK2206 Selectively Inhibits Thyroid Cancer Cells Harboring Mutations That Can Activate the PI3K/Akt Pathway. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E577–E585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Thakur, M.; Salangsang, F.; Landman, A.S.; Sellers, W.R.; Pryer, N.K.; Levesque, M.P.; Dummer, R.; McMahon, M.; Stuart, D.D. Modelling vemurafenib resistance in melanoma reveals a strategy to forestall drug resistance. Nature 2013, 494, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Thakur, M.; Stuart, D.D. The Evolution of Melanoma Resistance Reveals Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6106–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidsky, M.; Antoun, G.; Speicher, P.; Adams, B.; Turley, R.; Augustine, C.; Tyler, D.; Ali-Osman, F. Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Hyperactivation and Enhanced NRAS Expression Drive Acquired Vemurafenib Resistance in V600E BRAF Melanoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27714–27726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarian, R.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Lee, M.-K.; Attar, N.; Sazegar, H.; et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010, 468, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trunzer, K.; Pavlick, A.C.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Kim, K.B.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Effects and Mechanisms of Resistance to Vemurafenib in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, M.L.; Sztiller-Sikorska, M.; Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Czyz, M. Dissecting Mechanisms of Melanoma Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors Revealed Genetic and Non-Genetic Patient- and Drug-Specific Alterations and Remarkable Phenotypic Plasticity. Cells 2020, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Hugo, W.; Kong, X.; Hong, A.; Koya, R.C.; Moriceau, G.; Chodon, T.; Guo, R.; Johnson, D.B.; Dahlman, K.B.; et al. Acquired Resistance and Clonal Evolution in Melanoma during BRAF Inhibitor Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Moriceau, G.; Kong, X.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, H.; Koya, R.C.; Lo, R.S. Melanoma whole-exome sequencing identifies (V600E)B-RAF amplification-mediated acquired B-RAF inhibitor resistance. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauf, J.A.; Luckett, K.A.; Chen, K.-Y.; Voza, F.; Socci, N.D.; Ghossein, R.; Fagin, J.A. Hgf/Met activation mediates resistance to BRAF inhibition in murine anaplastic thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, W.; Shi, H.; Sun, L.; Piva, M.; Song, C.; Kong, X.; Moriceau, G.; Hong, A.; Dahlman, K.B.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Non-genomic and Immune Evolution of Melanoma Acquiring MAPKi Resistance. Cell 2015, 162, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharia, Y.; Monga, V.; Swami, U.; Bossler, A.D.; Freesmeier, M.; Frees, M.; Khan, M.; Frydenlund, N.; Srikantha, R.; Vanneste, M.; et al. Targeting epigenetics for treatment of BRAF mutated metastatic melanoma with decitabine in combination with vemurafenib: A phase lb study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89182–89193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, A. Tumor heterogeneity and plasticity as elusive drivers for resistance to MAPK pathway inhibition in melanoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2951–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerfaoui, M.; Toraih, E.; Ruiz, E.; Errami, Y.; Attia, A.S.; Krzysztof, M.; Kandil, E. Nuclear Localization of BRAF(V600E) Is Associated with HMOX-1 Upregulation and Aggressive Behavior of Melanoma Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Lu, M.; Jung, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Yu, L.; Onuchic, J.N.; Kaipparettu, B.A.; Levine, H. Elucidating cancer metabolic plasticity by coupling gene regulation with metabolic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3909–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, H.B.; Keenan, J.E.; Piantadosi, C.A. Mitochondrial quality-control dysregulation in conditional HO-1(-/-) mice. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e89676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, T.D.; Boddu, R.; Guo, L.; Tisher, C.C.; Traylor, A.M.; Patel, B.; Joseph, R.; Prabhu, S.D.; Suliman, H.B.; Piantadosi, C.A.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 regulates mitochondrial quality control in the heart. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 1, e85817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.; Zielke, S.; Michaelis, J.B.; Linder, B.; Warnsmann, V.; Rakel, S.; Osiewacz, H.D.; Fulda, S.; Mittelbronn, M.; Münch, C.; et al. AT 101 induces early mitochondrial dysfunction and HMOX1 (heme oxygenase 1) to trigger mitophagic cell death in glioma cells. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1693–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Luo, L.; Guo, C.-Y.; Goto, S.; Urata, Y.; Shao, J.-H.; Li, T.-S. Doxorubicin-induced mitophagy contributes to drug resistance in cancer stem cells from HCT8 human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.-I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative Stress Sensor Keap1 Functions as an Adaptor for Cul3-Based E3 Ligase to Regulate Proteasomal Degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Sohn, H.Y.; Koh, Y.H.; Jo, C. TFEB activates Nrf2 by repressing its E3 ubiquitin ligase DCAF11 and promoting phosphorylation of p62. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, S.P.; Altieri, D.C. Survivin at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs223826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhao, W.; Qin, S.; Chu, Q.; Wu, K. EGFR-TKIs resistance via EGFR-independent signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Youle, R.J. The Role of Mitochondria in Apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradner, J.E.; Hnisz, D.; Young, R.A. Transcriptional Addiction in Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- East, M.P.; Johnson, G.L. Adaptive chromatin remodeling and transcriptional changes of the functional kinome in tumor cells in response to targeted kinase inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Hou, W.; Xu, C. JUND-dependent up-regulation of HMOX1 is associated with cisplatin resistance in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Biochem. 2020, 168, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, M.; Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; et al. HIF1A Alleviates compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived stem cells via upregulating autophagy. Autophagy 2021, 17, 3338–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Diao, W.; Deng, G.; Li, Q.; Wu, C. HMOX1 Attenuates the Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib via Modulating the Expression of ABC Transporters. Int. J. Genom. 2022, 2022, 9451557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.A.; Brekken, R.A. SPARC: A matricellular regulator of tumorigenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 3, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Chan, A.P.; Tai, I.T. A Peptide of SPARC Interferes with the Interaction between Caspase8 and Bcl2 to Resensitize Chemoresistant Tumors and Enhance Their Regression In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26390, Correction in PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, S.; Hu, J.; Yue, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, G.; et al. SPARC enhances 5-FU chemosensitivity in gastric cancer by modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 558, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, I.T.; Dai, M.; Owen, D.A.; Chen, L.B. Genome-wide expression analysis of therapy-resistant tumors reveals SPARC as a novel target for cancer therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.J.; Tai, I.T. A Novel Interaction between Procaspase 8 and SPARC Enhances Apoptosis and Potentiates Chemotherapy Sensitivity in Colorectal Cancers. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34457–34467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavand, H.; Rawson, R.V.; Pupo, G.M.; Yang, J.Y.H.; Menzies, A.M.; Carlino, M.S.; Kefford, R.F.; Howle, J.R.; Saw, R.P.; Thompson, J.F.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and Immune Escape in Melanoma Resistance to MAPK Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6054–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Fung, C.; Menzies, A.M.; Pupo, G.M.; Carlino, M.S.; Hyman, J.; Shahheydari, H.; Tembe, V.; Thompson, J.F.; Saw, R.P.; et al. Increased MAPK reactivation in early resistance to dabrafenib/trametinib combination therapy of BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, Y.V.; Rizos, H.; Chen, G.; Deng, W.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Davies, M.A. Inhibition of mTORC1/2 overcomes resistance to MAPK pathway inhibitors mediated by PGC1alpha and oxidative phosphorylation in melanoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7037–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, N.; Van Allen, E.M.; Treacy, D.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Rosenberg, M.; Goetz, E.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltz, S.M.; Greene, C.S.; Taroni, J.N. Cross-platform normalization enables machine learning model training on microarray and RNA-seq data simultaneously. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulgen, E.; Ozisik, O.; Sezerman, O.U. pathfindR: An R Package for Comprehensive Identification of Enriched Pathways in Omics Data Through Active Subnetworks. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R. pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. 2019. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/pheatmap/ (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]


| HO-1/HMOX1 |
|---|
| Endoglin/CD105 |
| CXCL8/IL8 |
| CTSS |
| GRN |
| LGALS3 |
| BIRC5 |
| GM-CSF |
| ICAM-1 |
| DKK-1 |
| SPARC/BM-40 |
| CAPG |
| P53 |
| FGF2 |
| ENO2 |
| MMP2 |
| EGFR |
| VIM |
| Classifier Markers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PPV | NPV | AUC | |
| ENG | 0.636 | 0.684 | 0.633 |
| HMOX1 | 0.700 | 0.700 | 0.706 |
| ICAM1 | 0.778 | 0.714 | 0.697 |
| GRN | 0.778 | 0.714 | 0.674 |
| VIM | 0.667 | 0.722 | 0.624 |
| TP53 | 0.600 | 0.733 | 0.683 |
| MMP2 | 0.750 | 0.778 | 0.796 |
| SPARC | 0.769 | 0.824 | 0.76 |
| FGF2 | 0.520 | 1.000 | 0.615 |
| BIRC5 | 0.750 | 0.682 | 0.606 |
| CTSS | 0.522 | 0.857 | 0.593 |
| CAPG | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.588 |
| CXCL8 | 0.800 | 0.640 | 0.579 |
| DKK1 | 0.500 | 0.833 | 0.552 |
| LGALS3 | 0.529 | 0.692 | 0.548 |
| ENO2 | 0.625 | 0.636 | 0.511 |
| CSF2 | 0.464 | 1.000 | 0.507 |
| EGFR | 0.464 | 1.000 | 0.498 |
| Kruskal-Wallis Test | Linear Regression | Classifier Markers | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | OR | 95%CI OR | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC | 95%CI AUC | |
| GSE99898 | 8.30 × 10−6 | 4.26 × 10−5 | 7.38 | 3.58–15.19 | 8.70× 10−6 | 2.10 × 10−5 | 0.923 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.944 | 0.982 | 0.943–1.021 |
| GSE61992 | 1.92 × 10−3 | 6.55 × 10−3 | 7.29 | 2.96–17.95 | 4.60 × 10−4 | 1.67 × 10−3 | 0.800 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.818 | 0.922 | 0.797–1.047 |
| GSE50509 | 8.64 × 10−5 | 2.53 × 10−4 | 3.53 | 2.00–6.25 | 7.43 × 10−5 | 2.34 × 10−4 | 0.793 | 0.800 | 0.852 | 0.727 | 0.833 | 0.709–0.957 |
| GSE65185 | 3.40 × 10−4 | 1.07 × 10−3 | 2.94 | 1.70–5.09 | 2.80 × 10−4 | 8.21 × 10−4 | 0.932 | 0.556 | 0.837 | 0.769 | 0.792 | 0.67–0.913 |
| GSE77940 | 3.95 × 10−3 | 2.05 × 10−2 | 8163.08 | 2632–25310 | 2.40 × 10−8 | 4.91 × 10−7 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1 | 1−1 |
| FiveDataBase | 1.47 × 10−6 | 3.76 × 10−6 | 2.11 | 1.56–2.86 | 3.37 | 8.63 × 10−6 | 0.814 | 0.571 | 0.735 | 0.678 | 0.716 | 0.639–0.794 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz, E.M.; Alhassan, S.A.; Errami, Y.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Fang, J.S.; Wang, G.; Brooks, M.A.; Abi-Rached, J.A.; Kandil, E.; Zerfaoui, M. A Predictive Model of Adaptive Resistance to BRAF/MEK Inhibitors in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098407
Ruiz EM, Alhassan SA, Errami Y, Abd Elmageed ZY, Fang JS, Wang G, Brooks MA, Abi-Rached JA, Kandil E, Zerfaoui M. A Predictive Model of Adaptive Resistance to BRAF/MEK Inhibitors in Melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):8407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098407
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz, Emmanuelle M., Solomon A. Alhassan, Youssef Errami, Zakaria Y. Abd Elmageed, Jennifer S. Fang, Guangdi Wang, Margaret A. Brooks, Joe A. Abi-Rached, Emad Kandil, and Mourad Zerfaoui. 2023. "A Predictive Model of Adaptive Resistance to BRAF/MEK Inhibitors in Melanoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 8407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098407
APA StyleRuiz, E. M., Alhassan, S. A., Errami, Y., Abd Elmageed, Z. Y., Fang, J. S., Wang, G., Brooks, M. A., Abi-Rached, J. A., Kandil, E., & Zerfaoui, M. (2023). A Predictive Model of Adaptive Resistance to BRAF/MEK Inhibitors in Melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 8407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098407







