Cancer Stem Cells and Prostate Cancer: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evidence Synthesis
2.1. Prostate Cancer Stem Cells Origin and Phenotype
2.2. PCSC Molecular Pathways and Metabolism
2.2.1. Wnt Pathway
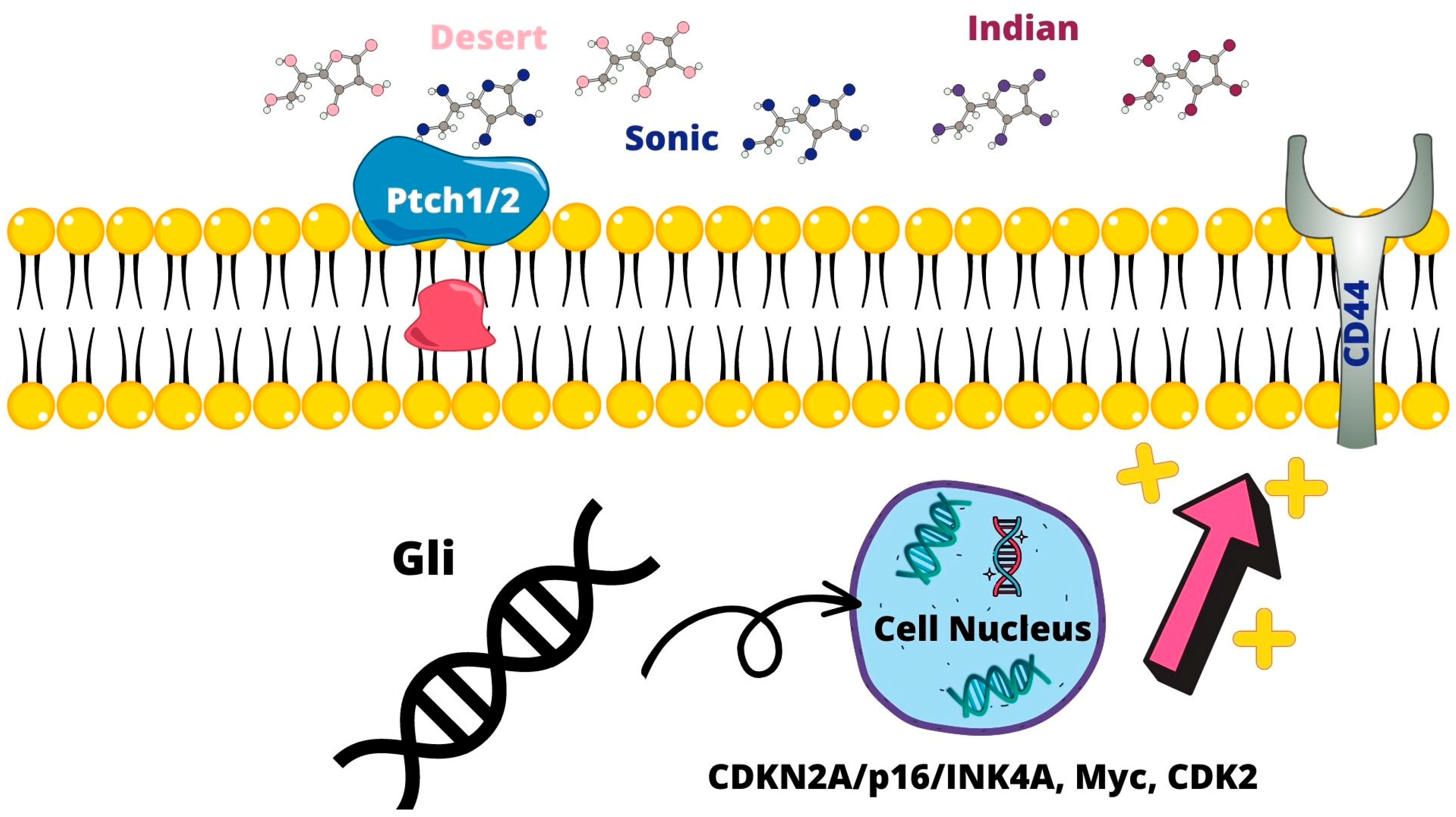
2.2.2. Sonic Hedgehog Pathway
2.2.3. Notch Signaling Pathway
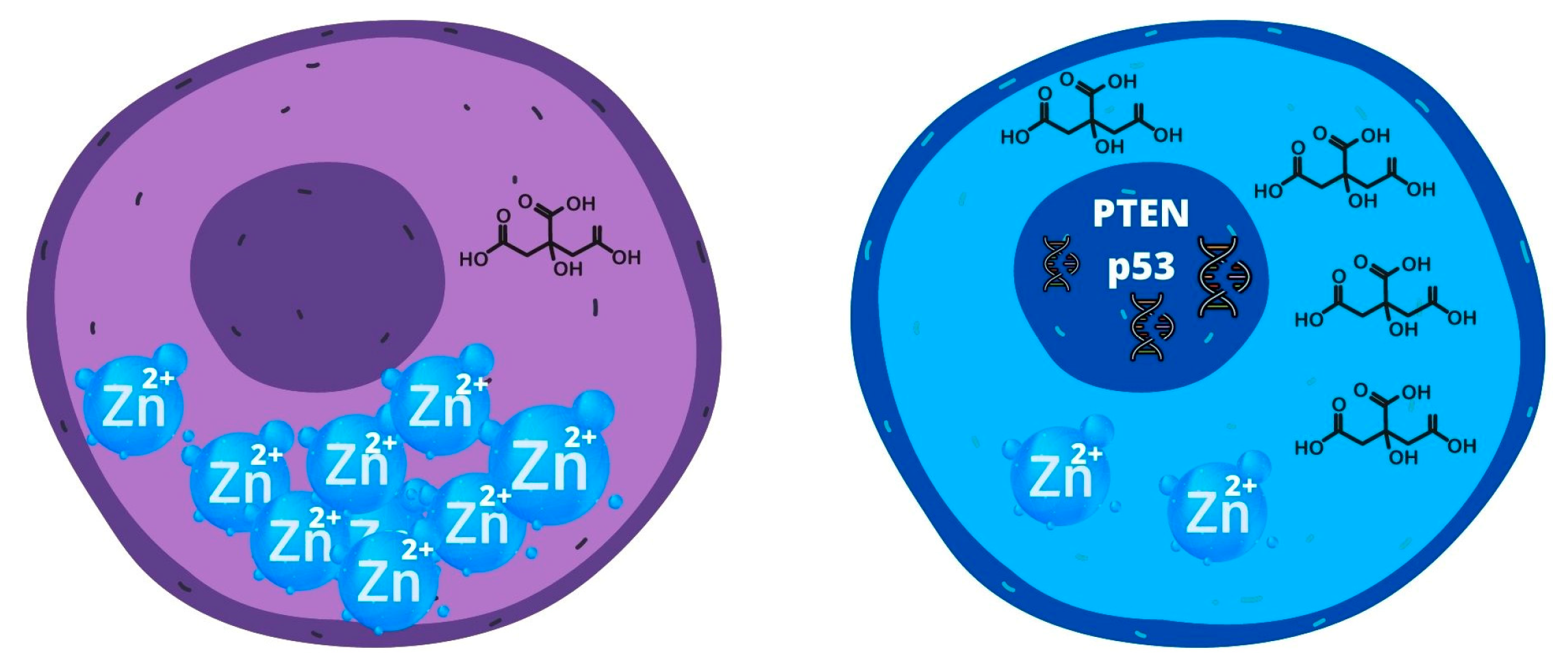
2.2.4. Metabolism of PCSC
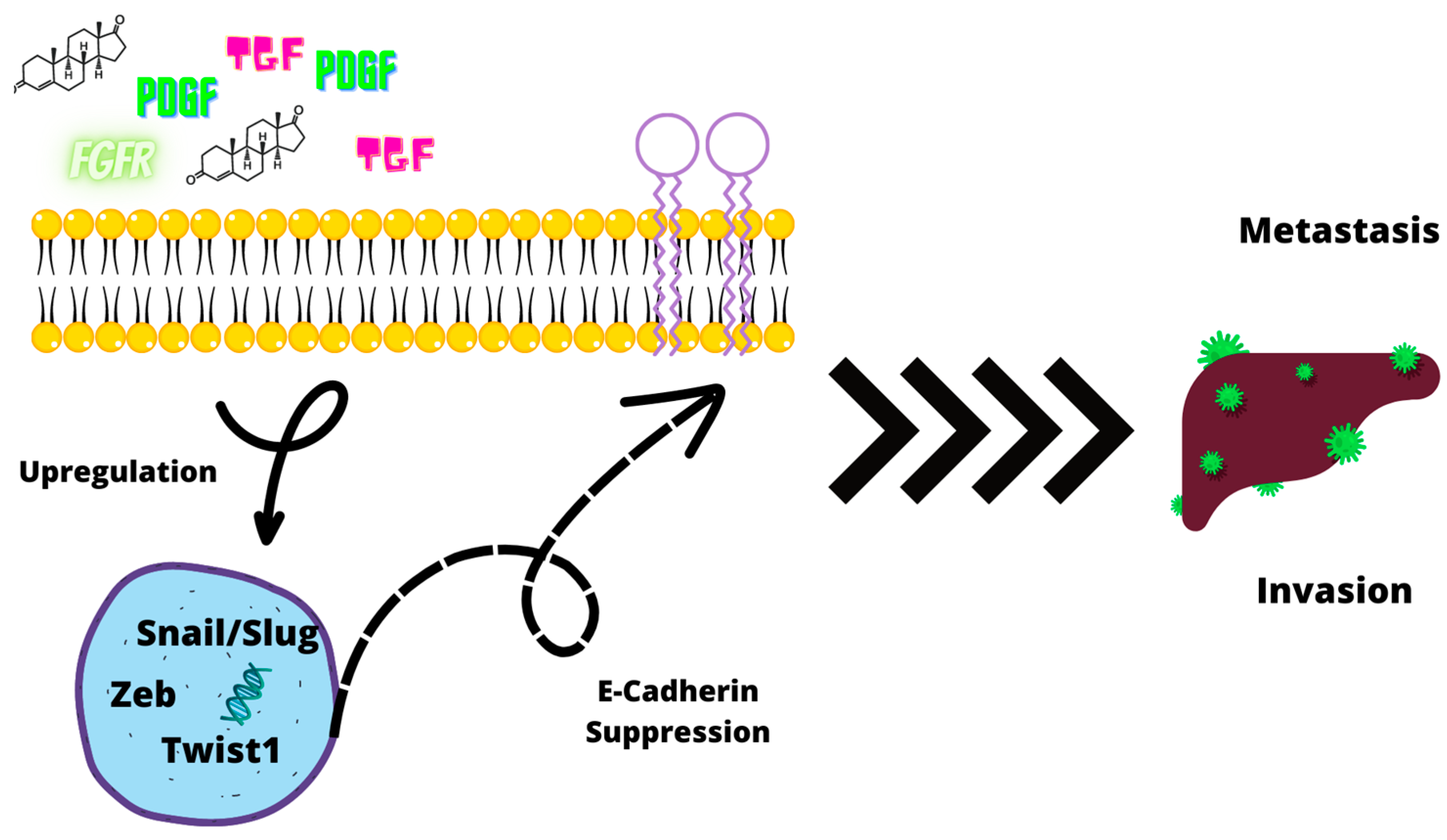
2.3. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and CSC Correlation
2.3.1. Loss of E-Cadherin Expression
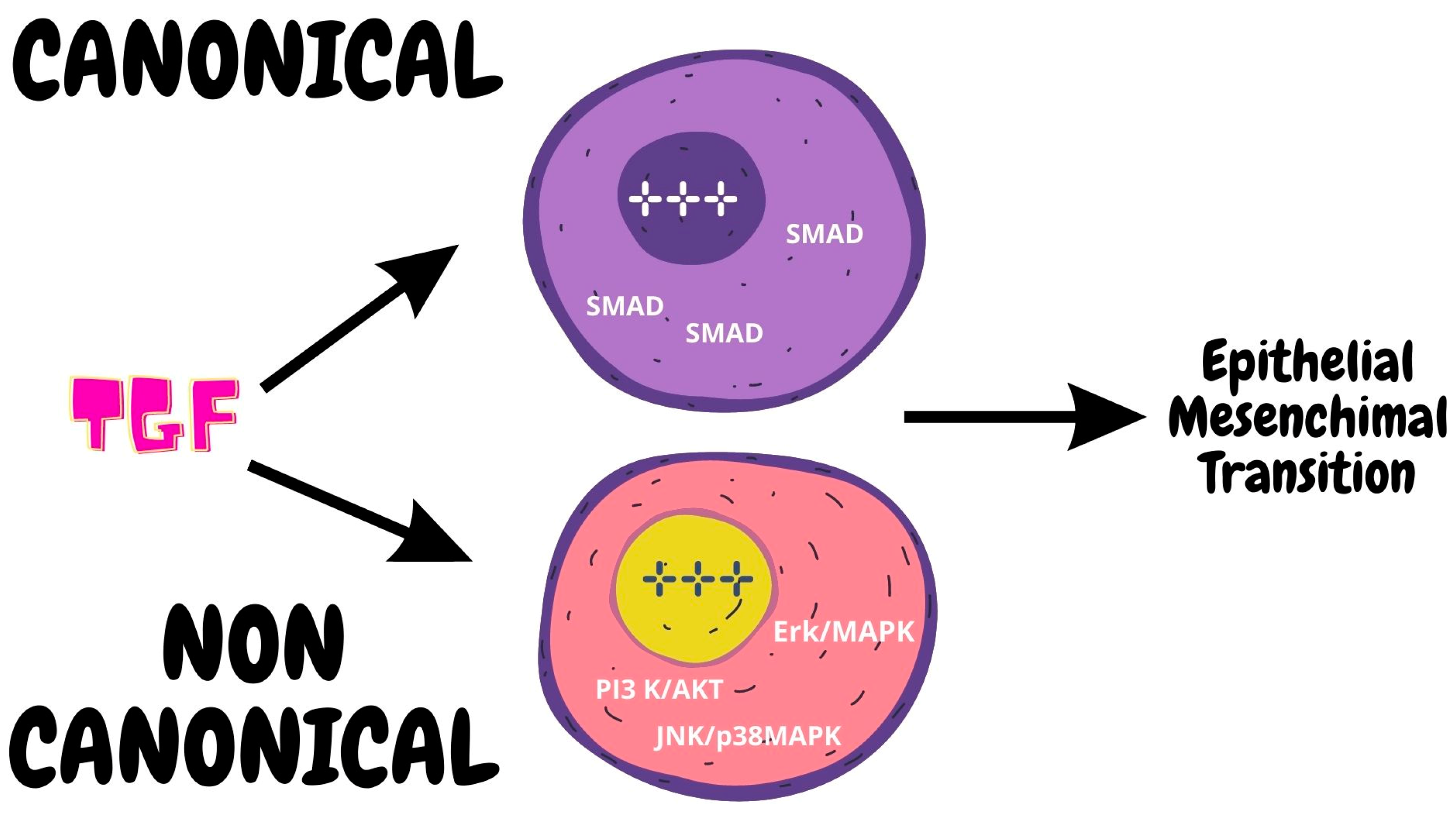
2.3.2. Role of TGF-β
2.3.3. Role of CD44
2.4. MicroRNA and CSC
2.5. MicroRNA and PCa
2.6. CSC Treatment
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandaglia, G.; Leni, R.; Bray, F.; Fleshner, N.; Freedland, S.J.; Kibel, A.; Stattin, P.; Van Poppel, H.; La Vecchia, C. Epidemiology and Prevention of Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culp, M.B.B.; Soerjomataram, I.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A. Recent Global Patterns in Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; Bellmunt, J.; Bolla, M.; Briers, E.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fossati, N.; Gross, T.; Henry, A.M.; Joniau, S.; et al. EAU–ESTRO–SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Natl. Cent. Biotechnol. Inf. 2016, 71, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Lombardo, R.; Tema, G.; Cancrini, F.; Russo, G.I.; Chacon, R.; Garcia-Cruz, E.; Ribal, M.J.; Morgia, G.; Alcaraz, A.; et al. Mobile Phone Apps for the Prediction of Prostate Cancer: External Validation of the Coral and Rotterdam Apps. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Lombardo, R.; Tema, G.; Alkhatatbeh, H.; Gandaglia, G.; Briganti, A.; Tubaro, A. External Validation of Chun, PCPT, ERSPC, Kawakami, and Karakiewicz Nomograms in the Prediction of Prostate Cancer: A Single Center Cohort-Study. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2018, 36, 364.e1–364.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.M.; Gleadle, J.M.; O’Callaghan, M.; Vasilev, K.; MacGregor, M. Prostate Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review of Urinary Biosensors. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stultz, J.; Fong, L. How to Turn up the Heat on the Cold Immune Microenvironment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 697–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorko, N.A.; Ryan, C.J. Novel Immune Engagers and Cellular Therapies for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Do We Take a BiTe or Ride BiKEs, TriKEs, and CARs? Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Tang, P.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, S.; Lan, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Genetic Profiling of Hormone-Sensitive and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancers and Identification of Genetic Mutations Prone to Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 26, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi Tesiye, M.; Abrishami Kia, Z.; Rajabi-Maham, H. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Prostate Cancer: A Concise Review of Therapeutic Potentials and Biological Aspects. Stem Cell Res. 2022, 63, 102864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.T.; Berry, P.A.; Hyde, C.; Stower, M.J.; Maitland, N.J. Prospective Identification of Tumorigenic Prostate Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10946–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.S.; Kerr, B.A. Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Markers Drive Progression, Therapeutic Resistance, and Bone Metastasis. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 8629234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cable, J.; Pei, D.; Reid, L.M.; Wang, X.W.; Bhatia, S.; Karras, P.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Grompe, M.; Lathia, J.D.; Song, E.; et al. Cancer Stem Cells: Advances in Biology and Clinical Translation-a Keystone Symposia Report. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1506, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, I.; Gratzke, C.; Wolf, P. Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: Clinical Aspects and Targeted Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 935715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchuck, J.E.; Viscuse, P.V.; Beltran, H.; Aparicio, A. Clinical Considerations for the Management of Androgen Indifferent Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denunzio, C.; Presicce, F.; Giacinti, S.; Bassanelli, M.; Tubaro, A. Castration-Resistance Prostate Cancer: What Is in the Pipeline? Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2018, 70, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Lombardo, R.; Tema, G.; Voglino, O.; Sica, A.; Baldassarri, V.; Nacchia, A.; Iacovelli, R.; Bracarda, S.; Tubaro, A. Adverse Events Related to Abiraterone and Enzalutamide Treatment: Analysis of the EudraVigilance Database and Meta-Analysis of Registrational Phase III Studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, S.; Skvortsova, I.I.; Tang, D.G.; Dubrovska, A. Concise Review: Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: Current Understanding. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 1457–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Liu, X.; Laffin, B.; Chen, X.; Choy, G.; Jeter, C.R.; Calhoun-Davis, T.; Li, H.; Palapattu, G.S.; Pang, S.; et al. The PSA(-/Lo) Prostate Cancer Cell Population Harbors Self-Renewing Long-Term Tumor-Propagating Cells That Resist Castration. Cell Stem. Cell 2012, 10, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Xu, P.; Huang, P.; Liu, C. A Convenient and Effective Strategy for the Enrichment of Tumor-Initiating Cell Properties in Prostate Cancer Cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11973–11981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, E.M.; Kawasaki, B.T.; Klarmann, G.J.; Thomas, S.B.; Farrar, W.L. CD44+ CD24 (−) Prostate Cells Are Early Cancer Progenitor/Stem Cells That Provide a Model for Patients with Poor Prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekhar, V.K.; Studer, L.; Gerald, W.; Socci, N.D.; Scher, H.I. Tumour-Initiating Stem-like Cells in Human Prostate Cancer Exhibit Increased NF-ΚB Signalling. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampayo, R.G.; Bissell, M.J. Cancer Stem Cells in Breast and Prostate: Fact or Fiction? Adv. Cancer Res. 2019, 144, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebe, N.; Harris, P.J.; Warren, R.Q.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting Cancer Stem Cells by Inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog Pathways. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Salm, S.N.; Coetzee, S.; Xiong, X.; Burger, P.E.; Shapiro, E.; Lepor, H.; Moscatelli, D.; Wilson, E.L. Proximal Prostatic Stem Cells Are Programmed to Regenerate a Proximal-Distal Ductal Axis. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moad, M.; Hannezo, E.; Buczacki, S.J.; Wilson, L.; El-Sherif, A.; Sims, D.; Pickard, R.; Wright, N.A.; Williamson, S.C.; Turnbull, D.M.; et al. Multipotent Basal Stem Cells, Maintained in Localized Proximal Niches, Support Directed Long-Ranging Epithelial Flows in Human Prostates. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, N.J.; Frame, F.M.; Polson, E.S.; Lewis, J.L.; Collins, A.T. Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: Do They Have a Basal or Luminal Phenotype? Horm. Cancer 2011, 2, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Shen, M.M. Prostate Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Boysen, G.; Barbieri, C.E.; Bryant, H.E.; Castro, E.; Nelson, P.S.; Olmos, D.; Pritchard, C.C.; Rubin, M.A.; de Bono, J.S. DNA Repair in Prostate Cancer: Biology and Clinical Implications. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.A.; Fraser, M.; Livingstone, J.; Espiritu, S.M.G.; Thorne, H.; Huang, V.; Lo, W.; Shiah, Y.J.; Yamaguchi, T.N.; Sliwinski, A.; et al. Germline BRCA2 Mutations Drive Prostate Cancers with Distinct Evolutionary Trajectories. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, E.S.; Lewis, J.L.; Celik, H.; Mann, V.M.; Stower, M.J.; Simms, M.S.; Rodrigues, G.; Collins, A.T.; Maitland, N.J. Monoallelic Expression of TMPRSS2/ERG in Prostate Cancer Stem Cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, L.K.; Frame, F.M.; Maitland, N.J. Stem Cells and the Role of ETS Transcription Factors in the Differentiation Hierarchy of Normal and Malignant Prostate Epithelium. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 166, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Nandi, A.K.; Li, X.; Bieberich, C.J. NKX-3.1 Interacts with Prostate-Derived Ets Factor and Regulates the Activity of the PSA Promoter. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.J.; Lo, U.G.; Hsieh, J.T. The Regulatory Pathways Leading to Stem-like Cells Underlie Prostate Cancer Progression. Asian J. Androl. 2019, 21, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Ji, Z.; Cheng, C.; Li, L.; Fang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhu, H.H.; et al. WNT/β-Catenin Directs Self-Renewal Symmetric Cell Division of HTERThigh Prostate Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2534–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, I.; Prowse, D.M. WNT Signaling Regulates Self-Renewal and Differentiation of Prostate Cancer Cells with Stem Cell Characteristics. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, I.S.; Chang, K.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Ke, J.Y.; Lu, P.J.; Lee, K.H.; Yeh, S.D.; Hong, T.M.; Chen, Y.L. MicroRNA-320 Suppresses the Stem Cell-like Characteristics of Prostate Cancer Cells by Downregulating the Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunich, S.M.; Valdovinos, M.; Douglas, T.; Walterhouse, D.; Iannaccone, P.; Lamm, M.L.G. Osteoblast-Secreted Collagen Upregulates Paracrine Sonic Hedgehog Signaling by Prostate Cancer Cells and Enhances Osteoblast Differentiation. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Chen, B.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Tsao, Z.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chang, C.P.; Yang, C.R.; Lin, D.P.C. Hedgehog Overexpression Leads to the Formation of Prostate Cancer Stem Cells with Metastatic Property Irrespective of Androgen Receptor Expression in the Mouse Model. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, J.L. Castration-Recurrent Prostate Cancer Is Not Androgen-Independent. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 617, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.; Laakso, M.; Ovaska, K.; Mirtti, T.; Lundin, J.; Rannikko, A.; Sankila, A.; Turunen, J.P.; Lundin, M.; Konsti, J.; et al. Dual Role of FoxA1 in Androgen Receptor Binding to Chromatin, Androgen Signalling and Prostate Cancer. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3962–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.M.; Abate-Shen, C. Molecular Genetics of Prostate Cancer: New Prospects for Old Challenges. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1967–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Ni, J.; Hao, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Li, Y. Targeting PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer Radioresistance. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Domenech, J.; Vidal, S.J.; Rodriguez-Bravo, V.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Quinn, S.A.; Rodriguez-Barrueco, R.; Bonal, D.M.; Charytonowicz, E.; Gladoun, N.; de la Iglesia-Vicente, J.; et al. Suppression of Acquired Docetaxel Resistance in Prostate Cancer through Depletion of Notch- and Hedgehog-Dependent Tumor-Initiating Cells. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanos, T.; Corn, P.G.; Thompson, T.C. Prostate Cancer Progression after Androgen Deprivation Therapy: Mechanisms of Castrate Resistance and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5501–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Jiang, R.; Linn, D.E.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Kong, X.; Melamed, J.; Tepper, C.G.; et al. A Novel Androgen Receptor Splice Variant Is Up-Regulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Promotes Androgen Depletion-Resistant Growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycielska, M.E.; Patel, A.; Rizaner, N.; Mazurek, M.P.; Keun, H.; Patel, A.; Ganapathy, V.; Djamgoz, M.B.A. Citrate Transport and Metabolism in Mammalian Cells: Prostate Epithelial Cells and Prostate Cancer. Bioessays 2009, 31, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.B.; Feng, P.; Milon, B.; Desouki, M.M.; Singh, K.K.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Bagasra, O.; Costello, L.C. HZIP1 Zinc Uptake Transporter down Regulation and Zinc Depletion in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2005, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, H.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Chang, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; You, M.J.; et al. Hexokinase 2-Mediated Warburg Effect Is Required for PTEN- and P53-Deficiency-Driven Prostate Cancer Growth. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pértega-Gomes, N.; Vizcaíno, J.R.; Attig, J.; Jurmeister, S.; Lopes, C.; Baltazar, F. A Lactate Shuttle System between Tumour and Stromal Cells Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V.; Le, A.; Gao, P. MYC-Induced Cancer Cell Energy Metabolism and Therapeutic Opportunities. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6479–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.A.; Lin, C.; Rajapakshe, K.; Dong, J.; Shi, Y.; Tsouko, E.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Jasso, D.; Dawood, W.; Coarfa, C.; et al. Glutamine Transporters Are Targets of Multiple Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nupponen, N.N.; Kakkola, L.; Koivisto, P.; Visakorpi, T. Genetic Alterations in Hormone-Refractory Recurrent Prostate Carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, L.A.; Farfán, N.M.; Castellón, E.A.; Contreras, H.R. SNAIL Transcription Factor Increases the Motility and Invasive Capacity of Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Subramanyam, D.; Blelloch, R.; Derynck, R. Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal and Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transitions by MicroRNAs. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Kyprianou, N. Role of Androgens and the Androgen Receptor in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, M.; Kyprianou, N. Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition Regulators in Prostate Cancer: Androgens and Beyond. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 166, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadil, J.; Bitzer, M.; Liang, D.; Yang, Y.C.; Massimi, A.; Kneitz, S.; Piek, E.; Böttinger, E.P. Genetic Programs of Epithelial Cell Plasticity Directed by Transforming Growth Factor-Beta. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6686–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Generates Cells with Properties of Stem Cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Liu, H. Overview of Cancer Stem Cells and Stemness for Community Oncologists. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, G.; Liu, B.; Ye, B.; Du, Y.; Gao, G.; Tian, Y.; He, L.; et al. LncBRM Initiates YAP1 Signalling Activation to Drive Self-Renewal of Liver Cancer Stem Cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.; Pauklin, S. Epigenetic Regulation of Cancer Stem Cell Formation and Maintenance. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.T.; Weng, C.C.; Hsiao, P.J.; Chen, L.H.; Kuo, T.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Kuo, K.K.; Cheng, K.H. Stem Cell Marker Nestin Is Critical for TGF-Β1-Mediated Tumor Progression in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Kelnar, K.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Calhoun-Davis, T.; Li, H.; Patrawala, L.; Yan, H.; Jeter, C.; Honorio, S.; et al. The MicroRNA MiR-34a Inhibits Prostate Cancer Stem Cells and Metastasis by Directly Repressing CD44. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coradduzza, D.; Cruciani, S.; Arru, C.; Garroni, G.; Pashchenko, A.; Jedea, M.; Zappavigna, S.; Caraglia, M.; Amler, E.; Carru, C.; et al. Role of MiRNA-145, 148, and 185 and Stem Cells in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Hwang, C.I.; Corney, D.C.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Jiang, L.; Öner, G.M.; Munroe, R.J.; Schimenti, J.C.; Hermeking, H.; Nikitin, A.Y. MiR-34 Cooperates with P53 in Suppression of Prostate Cancer by Joint Regulation of Stem Cell Compartment. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, B.A.; Valera, V.A.; Pinto, P.A.; Merino, M.J. Comprehensive MicroRNA Profiling of Prostate Cancer. J. Cancer 2013, 4, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Liu, H.; Chen, A.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, X.; Huang, J. MiR-148-3p and MiR-152-3p Synergistically Regulate Prostate Cancer Progression via Repressing KLF4. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 17228–17239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arámbula-Meraz, E.; Bergez-Hernández, F.; Leal-León, E.; Romo-Martínez, E.; Picos-Cárdenas, V.; Luque-Ortega, F.; Romero-Quintana, J.; Alvarez-Arrazola, M.; García-Magallanes, N. Expression of MiR-148b-3p Is Correlated with Overexpression of Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2020, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostadrahimi, S.; Fayaz, S.; Parvizhamidi, M.; Abedi-Valugerdi, M.; Hassan, M.; Kadivar, M.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L.; Asgari, M.; Shahrokh, H.; Abolhasani, M.; et al. Downregulation of MiR-1266-5P, MiR-185-5P and MiR-30c-2 in Prostatic Cancer Tissue and Cell Lines. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8157–8164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, H.; Thomsen, A.R.; Haldrup, C.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Høyer, S.; Borre, M.; Mouritzen, P.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Sørensen, K.D. Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Classifiers for Prostate Cancer Identified by Genome-Wide MicroRNA Profiling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30760–30771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—MicroRNAs with a Role in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, N.G.; Miller, A.; Titus, M.A.; Huss, W.J. The Efflux Transporter ABCG2 Maintains Prostate Stem Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlind, M.P.; Hsieh, A.C. PI3K-AKT-MTOR Signaling in Prostate Cancer Progression and Androgen Deprivation Therapy Resistance. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Hao, J.; Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. Acquisition of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes Is Associated with Activation of the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Pathway in Prostate Cancer Radioresistance. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Pathways for Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corn, P.G. The Tumor Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer: Elucidating Molecular Pathways for Therapy Development. Cancer Manag. Res. 2012, 4, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antigen | Function | Role |
|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | Transporter | Chemoresistance |
| ABCg2 | Transporter | Chemoresistance, CSC maintenance |
| ALDH | Aldheyde dehydrogenase | Radioresistance, self-renewal, tumorigenicity |
| AR-7 | Transcriprion factor | EMT, stemness |
| CD117 | Signaling, proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, migration | CSC maintenance, sphere formation, proliferation, migration, invasion |
| CD133 | Currently unknown | Thepetic resistance, self-renewal, tumorigenicity |
| CD44 | Signaling, Adhesion | Self-renewal, invasion |
| E-Cadherin | Adhesion, epithelial morphogenesis | Sphere formation |
| EpCAM | Adhesion, epithelial morphogenesis | CSC maintenance |
| TG2 | Transferase | EMT, chemoresistance |
| MicroRNA | Function on PCSC | Function on EMT | Targeting EMT-TF | Targeting EMT Pathway | Targeting EMT-CSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | / | Inhibition | Slug, Twist1 | / | / |
| miR-18a | Progression | / | / | / | / |
| miR-21 | Invasiveness, CRPC | Promotion | / | BTG2, TGFβ | / |
| miR-23a-3p | / | Promotion | E-cadherin | / | / |
| miR-23b | / | Inhibition | / | Src kinase, Akt | / |
| miR-25 | Progression | / | / | / | / |
| miR-29b | / | Inhibition | / | MMP2 | / |
| miR-30 | / | Inhibition | / | ERG | / |
| miR-32 | Anti-apoptotic | Promotion | / | BTG2 | / |
| miR-34a | / | Inhibition | / | LEF1 | / |
| miR-34b | / | Inhibition | / | Akt | / |
| miR-100 | / | Inhibition | / | Aug-02 | / |
| miR-106 | Progression | / | / | / | / |
| miR-124 | / | Inhibition | Slug | / | / |
| miR-125b | Proliferation | / | / | / | / |
| miR-141 | CRPC | / | / | / | / |
| miR-145 | / | Inhibition | ZEB2, HEF1 | / | Zeb2 |
| miR-154 | / | Inhibition | / | HMGA2, SMAD7 | / |
| miR-186 | / | Inhibition | Twist1 | / | |
| miR-195 | / | Inhibition | / | FGF2, HMGA1, RPS6KB | / |
| miR-200 | / | Inhibition | Zeb1, Zeb2, Slug | / | Notch1 |
| miR-203 | / | Inhibition | Zeb2, Bmi1, Survivin CKAP2, LASP1, WASF1, ASAP1 mRNAs | / | / |
| miR-205 | / | Inhibition | Zeb2, Protein Kinase Cε | / | Zeb2, Protein Kinase Cε |
| miR-221 | Proliferation, invasion | / | / | / | / |
| miR-222 | Proliferation, invasion | / | / | / | / |
| miR-223 | / | Inhibition | / | ITGA3, ITGB1 | / |
| miR-301a | / | Promotion | / | p63 | / |
| miR-331-3p | / | Promotion | / | NRP2, NACC1 | / |
| miR-375 | Diagnosis | / | / | / | / |
| miR-379 | / | Promotion | / | FOXF2 | / |
| miR-573 | / | Inhibition | / | FGFR1 | / |
| miR-4534 | Tumorigenesis | / | / | / | / |
| Pathway | Drugs | |
|---|---|---|
| Hh pathway |
|
|
| Wnt pathway |
|
|
| Notch pathway |
|
|
| NFkB pathway |
|
|
| PI3K/mTOR |
| |
| EMT transformation |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Salhi, Y.; Sequi, M.B.; Valenzi, F.M.; Fuschi, A.; Martoccia, A.; Suraci, P.P.; Carbone, A.; Tema, G.; Lombardo, R.; Cicione, A.; et al. Cancer Stem Cells and Prostate Cancer: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097746
Al Salhi Y, Sequi MB, Valenzi FM, Fuschi A, Martoccia A, Suraci PP, Carbone A, Tema G, Lombardo R, Cicione A, et al. Cancer Stem Cells and Prostate Cancer: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097746
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Salhi, Yazan, Manfredi Bruno Sequi, Fabio Maria Valenzi, Andrea Fuschi, Alessia Martoccia, Paolo Pietro Suraci, Antonio Carbone, Giorgia Tema, Riccardo Lombardo, Antonio Cicione, and et al. 2023. "Cancer Stem Cells and Prostate Cancer: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097746
APA StyleAl Salhi, Y., Sequi, M. B., Valenzi, F. M., Fuschi, A., Martoccia, A., Suraci, P. P., Carbone, A., Tema, G., Lombardo, R., Cicione, A., Pastore, A. L., & De Nunzio, C. (2023). Cancer Stem Cells and Prostate Cancer: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097746







