Advances in Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Spinal Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biology of Platelets
2.1. Platelet Activation and Secretion
2.2. Platelet Extracellular Vesicles
2.3. PRP
3. PRP Classification
4. Basic Studies
4.1. Basic Studies on PRP for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration (Table 2)
4.2. Basic Studies of PRP in Other Spine Research Areas (Table 2)
| Research Area | Experiment Type | Author (Year) | Agent | Target | Species | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVD | In vitro | Akeda et al. (2006) [38] | Porcine PRP | IVD cells | Porcine | cell proliferation↑ collagen synthesis↑ proteoglycan accumulation↑ |
| Chen et al. (2006) [39] | Human PRP | NP cells | Human | cell proliferation↑ collagen synthesis↑ proteoglycan accumulation↑ | ||
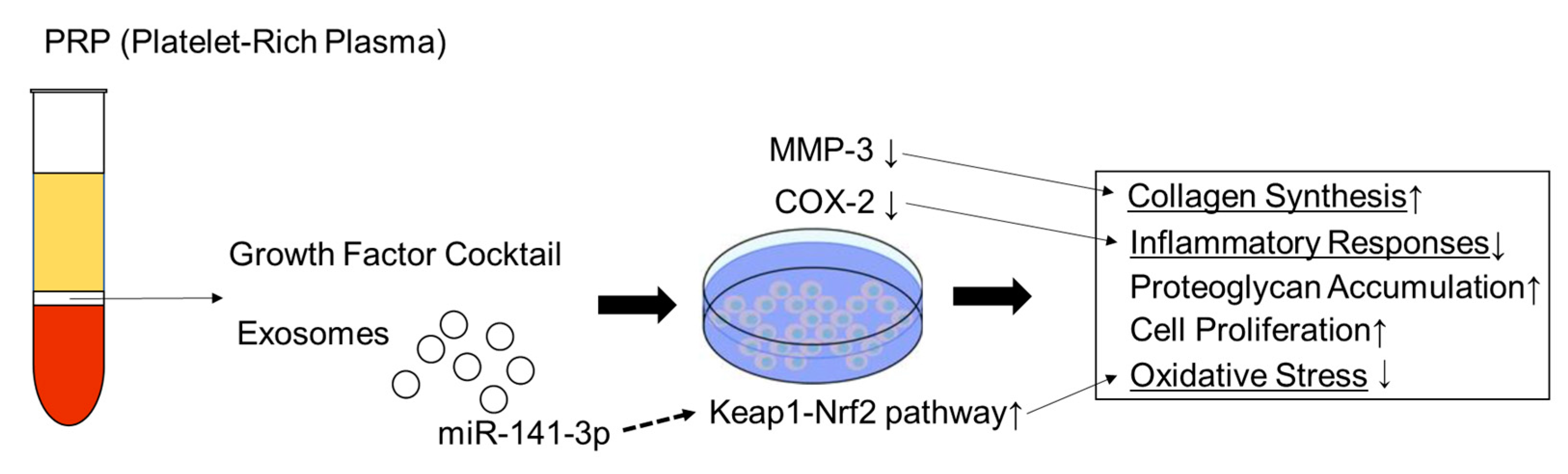
| Kim et al. (2014) [40] | Human PRP | NP cells | Human | matrix metalloproteinase-3 ↓ cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)↓ | ||
| Xu et al. (2021) [41] | PRP-derived exosomes | NP cells IVD degeneration | Mice | exosomal miR-141-3p↑ Keap1-NF-E2-related factor 2 pathway↑ | ||
| Qian et al. (2022) [42] | Rat PRP and PRP-derived exosomes | NP cells IVD degeneration | Rat | inflammatory responses↓ IL-1β secretion↓ | ||
| In vivo | Nagae et al. (2007) [44] | Rabbit PRP | IVD degeneration/needle puncture | Rabbit | IVD degeneration↓ | |
| Obata et al. (2012) [45] | Rabbit PRP | IVD degeneration/needle puncture | Rabbit | IVD degeneration↓ | ||
| Chen et al. (2009) [46] | Porcine MSC and/or PRP | IVD degeneration/chymopapain | Porcine | IVD degeneration↓ | ||
| Gullung et al. (2011) [47] | PRP | IVD degeneration/needle puncture | Rat | IVD degeneration↓ | ||
| Spinal fusion | In vitro | Kinoshita et al. (2020) [54] | Rodent fresh or freeze-dried PRP | Osteoblast | Human | osteoblast proliferation↑ |
| In vivo | Kamoda et al. (2012) [51] | Rat PRP | Interbody fusion | Rat | bone union↑ | |
| Kamoda et al. (2013) [53] | Rat PRP | Posterolateral fusion | Rat | bone union↑ | ||
| Cinotti et al. (2013) [52] | Rabbit PRP | Posterolateral fusion | Rabbit | bone union→ | ||
| Li et al. (2004) [49] | Carbon fiber cage loaded with bioceramics and platelet-rich plasma | Interbody fusion | Porcine | bone union→ | ||
| Scholz et al. (2010) [50] | Cages augmented with mineralized collagen and PRP | Interbody fusion | Sheep | bone union→ | ||
| Spinal cord | In vivo | Salarinia et al. (2017) [55] | Rat PRP | Spinal cord injury | Rat | nerve regeneration↑ |
| Chen et al. (2018) [56] | n.d. | Spinal cord injury | Rat | locomotor recovery with neuronal regeneration | ||
| Salarinia et al. (2020) [57] | Rat PRP and MSC | Spinal cord injury | Rat | synergistic effects in spinal cord injury | ||
| Behroozi et al. (2021) [58] | Human umbilical cord blood-derived PRP | Spinal cord injury | Rat | neuropathic pain↓ | ||
| Behroozi et al. (2022) [59] | Human umbilical cord blood-derived PRP | Spinal cord injury | Rat | motor function recovery and axonal regeneration |
5. Clinical Studies
5.1. Clinical Application of PRP for Intradiscal Therapy
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Disease | Number of Subjects | PRP Classification | PRP Isolation Method | Outcomes | Follow Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuakli-Wosornu et al. (2016) [60] | RCT | DLBP | 47 (29 PRP, 18 control) | 1A | Kit | FRI, NRS, SF-36, modified NASS outcome questionnaire | 12 months | 5 |
| Levi et al. (2016) [66] | Prospective cohort study | DLBP | 22 | 1A | Kit | VAS, ODI | 6 months | 4 |
| Akeda at al. (2017) [63] | Prospective cohort study | DLBP | 14 | 4B | Manual | VAS, RDQ, X-ray, MRI | 10 months | 4 |
| Cheng J (2019) [69] | Retrospective cohort study | DLBP | 29 | 1A | Kit | NRS, SF-36 | 6.57 years | 4 |
| Wu TJ (2020) [72] | Case reports | DLBP | 2 | 3B | Kit | VAS | 3 months | 3 |
| Jain D (2020) [65] | Prospective cohort study | DLBP | 25 | 3B | Kit | NRS, ODI | 6 months | 4 |
| Akeda K at al. (2022) [64] | RCT | DLBP | 15 | 4B | Manual | VAS, ODI, RDQ, Radiographic measurements, MRI | 12 months | 4 |
| Jiang Y (2022) [61] | Prospective cohort study | LDH (TELD) | 108 | n.d. | Kit | VAS, ODI, MRI | 12 months | 5 |
| Akeda K at al. (2022) [68] | Retrospective cohort study | DLBP | 11 | 4B | Manual | VAS, RDQ, Radiographic measurements | 5.9 years | 4 |
| Lutz C at al. (2022) [73] | Retrospective cohort study | DLBP | 37 | 1A/3A | Kit | NRS, FRI, NASS patient satisfaction index | 18 months | 4 |
| Lam et al. (2022) [62] | Case reports | CLBP | 1 | 3- | n.d. | NRS, NDI | 9 months | 3 |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [67] | Prospective cohort study | DLBP | 31 | 3B | Kit | SF-36, FRI, NRS | 48 week | 4 |
| Kawabata et al. (2023) [70] | Case reports | DLBP | 2 | 1B | Kit | VAS, ODI, RDQ, Radiographic measurements, MRI | 25 weeks | 3 |
5.2. Clinical Application of PRP for Spinal Fusion Surgery
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Surgical Procedure | Number of Subjects (PRP/Control) | PRP Classification | PRP Isolation Method | Outcomes | Follow Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weiner and Walker (2003) [74] | Retrospective cohort study | PLF | 32/27 | 2A | Kit | Bone fusion rate | 24 months | 1 |
| Hee et al. (2003) [80] | Prospective cohort study | TLIF | 23/111 | 2B | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 25 months [24–27] | 2 |
| Castro et al. (2004) [85] | Prospective cohort study | TLIF | 22/62 | 2B | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 34 ± 2 months | 3 |
| Carreon et al. (2005) [86] | Retrospective cohort study | PLF | 76/76 | 2- | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 32 months [24–48] | 2 |
| Jenis et al. (2006) [81] | Prospective cohort study | anterior spinal fusion (interbody) | 15/22 | 2- | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 25.7 months [6–40] | 2 |
| Feiz-Erfan et al. (2007) [75] | RCT | ACDF | 42/39 | 2A | Kit | Bone fusion rate | 24 months | 2 |
| Tsai et al. (2009) [82] | RCT | PLF | 34/33 | n.d. | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 28.5 months [24–34.9] | 2 |
| Hartmann et al. (2010) [83] | Retrospective cohort study | anterior spinal fusion (interbody) | 15/20 | 2- | Kit | Bone fusion rate, bone density | 8.3 months [4–15] | 5 |
| Acebal-Cortina et al. (2011) [78] | Nonrandomized study | PLF | 67/40 | n.d. | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 24 months | 1 |
| Landi et al. (2011) [87] | Prospective cohort study | PLF | 14/14 | 2A | Kit | Bone fusion rate, bone density | 6 months | 3 |
| Sys el al. (2011) [79] | RCT | PLIF | 19/19 | 2A | Kit | Bone fusion rate | 12 months | 2 |
| Tarantino et al. (2014) [88] | Prospective cohort study | PLF | 20/20 | 2- | Kit | Bone fusion rate, bone density | 12 months | 5 |
| Vadalà et al. (2016) [89] | Nonrandomized study | PLF | 10/10 | 2- | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 12 months | 5 |
| Rezende et al. (2017) [90] | RCT | PLF | 20/20 | 4- | Manual | Bone fusion rate | 6 months | 2 |
| Imagama et al. (2017) [77] | Prospective cohort study | PLF | 29/29 | 4A | Manual | Bone fusion area | 12 months | 5 |
| Kubota et al. (2018) [84] | Retrospective cohort study | TLIF | 11/9 | 4A | Manual | Duration of bone fusion, and bone fusion rate | 24 months | 5 |
| Kubota et al. (2019) [76] | RCT | PLF | 25/25 | 4A | Manual | Duration of bone fusion, bone fusion rate, and bone fusion area | 24 months | 5 |
5.3. Clinical Application of PRP for Intraarticular Therapy of Facet or Sacroiliac Joint Pain
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Disease | Number of Subjects | PRP Classification | PRP Isolation Method | Outcomes | Follow Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al. (2016) [91] | Case series | Facet joint syndrome | 19 | 1B | Manual | Pain VAS, RDQ, ODI, Modified MacNab criteria | 3 months | 4 |
| Kirchner et al. (2016) [93] | Case series | LBP | 86 | 4B | Kit | VAS | 6 months | 4 |
| Wu et al. (2017) [92] | RCT | Facet joint syndrome | 46 | 1B | Manual | Pain VAS, RDQ, ODI, Modified MacNab criteria | 6 months | 5 |
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Disease | Number of Subjects | PRP Classification | PRP Isolation Method | Outcomes | Follow Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navani et al. (2016) [94] | Case series | chronic SIJ pain | 10 | n.d. | Manual | VAS, SF-36 | 12 months | 3 |
| Singla et al. (2017) [95] | RCT | chronic low back pain | 40 | 3 | Manual | VAS, MODQ, SF-12 | 3 months | 5 |
| Ko et al. (2017) [99] | Case reports | SIJ pain | 4 | 1A | Kit | SFM, NRS, and ODI | 48 months | 4 |
| Eldin et al. (2019) [97] | Non-RCT | SIJ dysfunction pain | PRF 124 PRP 62 | PRF 1 PRP 2 | Kit | VAS | 6 months | 4 |
| Wallace et al. (2020) [100] | Case series | SIJ dysfunction pain | 50 | 1A | Kit | ODI, NRS | 6 months | 4 |
| Broadhead et al. (2020) [98] | Case reports | SIJ dysfunction pain | 1 | 1A | Kit | NRS, ODI | 12 months | 4 |
| Chen et al. (2022) [96] | RCT | SIJ pain | 26 | 1- | Kit | NRS, ODI | 6 months | 4 |
5.4. Clinical Application of PRP for Epidural Therapy
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Disease | Number of Subjects | PRP Classification | PRP Isolation Method | Outcomes | Follow Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirchner et al. (2016) [93] | Retrospective cohort study | LBP w/or w/o radicular pain | 86 | 4B | Kit | VAS for LBP | 6 months | 4 |
| Bhatia et al. (2016) [107] | Case series | LBP w/or w/o radicular pain | 10 | n.d. | Manual | VAS, ODI, SLRT | 3 months | 3 |
| Rawson et al. (2020) [108] | Case series | radicular pain | 2 | 1A | Manual | Pain | 3–6 months | 3 |
| Bise et al. (2020) [104] | Prospective cohort study | radicular pain | 60 (Steroid 30-PRP30) | 3B | Manual | NRS for leg pain, ODI | 6 weeks | 4 |
| Ruiz-Lopez et al. (2020) [102] | RCT | LBP w/or w/o radicular pain | 50 (Steroid 25-PRP25) | 1- | Manual | VAS for LBP, SF-36 | 6 months | 5 |
| Machado et al. (2021) [106] | Prospective cohort study | LBP w/or w/o radicular pain | 46 | 3B | Manual | VAS for LBP, RDQ, NASS Satisfaction | 52 weeks | 4 |
| Kirchner et al. (2021) [101] | Retrospective cohort study | Cervical and low back pain | 65 (18 Cervical and 47 LBP) | 4B | Kit | NRS for neck and LBP, COMI, ODI | 5 months [1–24] | 4 |
| Xu et al. (2021) [103] | RCT | LBP w/radicular pain | 124 (Steroid 68-PRP64) | n.d. | Manual | VAS, ODI, SF-36 and etc | 12 months | 4 |
| Barbieri et al. (2022) [105] | Prospective cohort study | LBP w/or w/o radicular pain | 30 | 4- | Kit | VAS for LBP and leg pain, ODI, PGIC | 6 months | 2 |
| Yalçın Demirci et al. (2022) [109] | Retrospective cohort study | Radicular pain | 62 (Steroid 31-PRP31) | n.d. | Manual | VAS, ODI | 35.7 months | 4 |
| Le et al. (2023) [110] | Prospective cohort study | LBP w/radicular pain | 25 | n.d. | Manual | VAS, ODI, SLRT | 12 months | 4 |
5.5. Clinical Application of PRP for Spinal Cord Injury
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Last, A.R.; Hulbert, K. Chronic low back pain: Evaluation and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 79, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Takeshita, K.; Inoue, G.; Sekiguchi, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hoshino, M.; Kaito, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Minetama, M.; Orita, S.; et al. Watanabe, and team Structured abstract preparation. Japanese Orthopaedic Association (Joa) Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis, 2021—Secondary Publication. J. Orthop. Sci. 2023, 48, 46–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Bridwell, K.H.; Lenke, L.G.; Rhim, S.; Cheh, G. Pseudarthrosis in Long Adult Spinal Deformity Instrumentation and Fusion to the Sacrum: Prevalence and Risk Factor Analysis of 144 Cases. Spine 2006, 31, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmeler, S.; Ding, S.; Rando, T.A.; Trounson, A. Translational strategies and challenges in regenerative medicine. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, P.; Fiz, N.; Beitia, M.; Owston, H.E.; Delgado, D.; Jones, E.; Sánchez, M. Effect of Combined Intraosseous and Intraarticular Infiltrations of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on Subchondral Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Patients with Hip Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.H.R.; Reddy, R.; Babu, N.C.; Ashok, G. Stem-cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma in regenerative medicines: A review on pros and cons of the technologies. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2018, 22, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Anitua, E.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Prado, R.; Orive, G.; Padilla, S. Platelet-rich plasma, a source of autologous growth factors and biomimetic scaffold for peripheral nerve regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsousou, J.; Ali, A.; Willett, K.; Harrison, P. The role of platelet-rich plasma in tissue regeneration. Platelets 2012, 24, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Tuan, R.S. Biology of platelet-rich plasma and its clinical application in cartilage repair. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 16, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeda, K.; Yamada, J.; Linn, E.T.; Sudo, A.; Masuda, K. Platelet-rich plasma in the management of chronic low back pain: A critical review. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaumenhaft, R.; Sharda, A. Platelet Secretion. In Platelets; Michelson, A.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 349–370. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, D.M.; Heijnen, H.F.; Horne, M.K.; White, J.G.; Gahl, W.A. Proteomic Analysis of Platelet Alpha-Granules Using Mass Spectrometry. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: Microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppinger, J.A.; Cagney, G.; Toomey, S.; Kislinger, T.; Belton, O.; McRedmond, J.P.; Cahill, D.J.; Emili, A.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Maguire, P.B. Characterization of the proteins released from activated platelets leads to localization of novel platelet proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Blood 2004, 103, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T. Platelets, Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Thromb. Haemost 2011, 105 (Suppl. S1), S13–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, B.A.; Vales, O. The release of vesicles from platelets following adhesion to vessel walls in vitro. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1972, 53, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P. The Nature and Significance of Platelet Products in Human Plasma. Br. J. Haematol. 1967, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.C.; Guo, S.C.; Zhang, C.Q. Platelet-derived Extracellular Vesicles: An Emerging Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Rodeo, S.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Orthopaedic Surgery: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2017, 5, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.; Grimalt, R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2018, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, S.; Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Hara, T.; Ogawa, T.; Mitsui, T.; Kusumoto, K. Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: A comparison of seven commercial separation systems. J. Artif. Organs 2014, 17, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppley, B.L.; Pietrzak, W.S.; Blanton, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Review of Biology and Applications in Plastic Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 147e–159e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, J.M.; Russell, R.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The PAW Classification System. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo, C.; Roffi, A.; Grigolo, B.; Mariani, E.; Pratelli, L.; Merli, G.; Kon, E.; Marcacci, M.; Filardo, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The Choice of Activation Method Affects the Release of Bioactive Molecules. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6591717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Ortega-Mata, D.; Tamez-Mata, Y.; Olivo, C.A.A.; Vilchez-Cavazos, F. Comparison of the clinical effectiveness of activated and non-activated platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Calabrese, C.; De Angelis, B.; Dionisi, L.; Pizzicannella, J.; Kothari, A.; De Fazio, D.; Garcovich, S. Impact of the Different Preparation Methods to Obtain Autologous Non-Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma (A-PRP) and Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma (Aa-Prp) in Plastic Surgery: Wound Healing and Hair Regrowth Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.A.; Murray, I.R.; Chu, C.R.; Muschler, G.F.; Rodeo, S.A.; Piuzzi, N.S. Classification systems for platelet-rich plasma. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101-B, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wang, S.-Z.; Ma, L.-Y.; Yu, J.-B.; Guo, Y.-D.; Wang, C. The Differential Effects of Leukocyte-Containing and Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma on Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implications for the Clinical Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 7162084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gu, Y.; Ran, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zeng, M.; Heng, B.C.; Chen, X.; Yin, Z.; Chen, W.; et al. Intratendon Delivery of Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Healing Compared with Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma in a Rabbit Achilles Tendinopathy Model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Laprade, R.F.; Harmon, K.G.; Filardo, G.; Kon, E.; Della Villa, S.; Bahr, R.; Moksnes, H.; Torgalsen, T.; Lee, J.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Patellar Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Leukocyte-Rich PRP or Leukocyte-Poor PRP Versus Saline. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, K.; Wedderkopp, N. Platelet-rich plasma (Prp) treatment of noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy in a two case series: No significant difference in effect between leukocyte-rich and leukocyte-poor PRP. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2019, 11, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerlikaya, M.; Çalış, H.T.; Sütbeyaz, S.T.; Sayan, H.; Ibiş, N.; Koç, A.; Karakükçü, C. Comparison of Effects of Leukocyte-Rich and Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma on Pain and Functionality in Patients with Lateral Epicondylitis. Arch. Rheumatol. 2018, 33, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Del Corso, M.; Diss, A.; Mouhyi, J.; Charrier, J.B. Three-Dimensional Architecture and Cell Composition of a Choukroun's Platelet-Rich Fibrin Clot and Membrane. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Harmon, K.; Woodall, J.; Vieira, A. Sports Medicine Applications of Platelet Rich Plasma. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeda, K.; An, H.S.; Pichika, R.; Attawia, M.; Thonar, E.J.-M.A.; Lenz, M.E.; Uchida, A.; Masuda, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Stimulates the Extracellular Matrix Metabolism of Porcine Nucleus Pulposus and Anulus Fibrosus Cells Cultured in Alginate Beads. Spine 2006, 31, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Lo, W.C.; Lee, J.J.; Su, C.H.; Lin, C.T.; Liu, H.Y.; Lin, T.W.; Lin, W.C.; Huang, T.Y.; Deng, W.P. Tissue-Engineered Intervertebral Disc and Chondrogenesis Using Human Nucleus Pulposus Regulated through Tgf-Beta1 in Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 209, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Yeom, J.S.; Koh, Y.G.; Yeo, J.E.; Kang, K.T.; Kang, Y.M.; Chang, B.S.; Lee, C.K. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Nucleus Pulposus Cells with Response of Tnf-Alpha and Il-1. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xie, G.; Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, W. Platelet-Rich Plasma Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Delivering Mir-141-3p-Containing Exosomes. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Su, G.; Shu, X.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, Q. Platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes attenuate intervertebral disc degeneration by promoting NLRP3 autophagic degradation in macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujel, B.; Shin, H.E.; Choi, D.J.; Han, I. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration: Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, M.; Ikeda, T.; Mikami, Y.; Hase, H.; Ozawa, H.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Sakamoto, H.; Tabata, Y.; Kawata, M.; Kubo, T. Intervertebral Disc Regeneration Using Platelet-Rich Plasma and Biodegradable Gelatin Hydrogel Microspheres. Tissue Eng. 2006, 13, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, S.; Akeda, K.; Imanishi, T.; Masuda, K.; Bae, W.; Morimoto, R.; Asanuma, Y.; Kasai, Y.; Uchida, A.; Sudo, A. Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma-releasate on intervertebral disc degeneration in the rabbit anular puncture model: A preclinical study. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 14, R241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Lo, W.C.; Wu, S.C.; Chi, C.H.; Chang, H.Y.; Hsiao, S.H.; Wu, C.H.; Chiu, W.T.; Chen, B.J.; et al. Intervertebral disc regeneration in an ex vivo culture system using mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5523–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullung, G.B.; Woodall, W.B.; A Tucci, M.; James, J.; A Black, D.; A McGuire, R. Platelet-rich plasma effects on degenerative disc disease: Analysis of histology and imaging in an animal model. Evidence-Based Spine-Care J. 2011, 2, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Q. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Retarding Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: A Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7919201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zou, X.; Xue, Q.; Egund, N.; Lind, M.; Bunger, C. Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Carbon Fiber Cage Loaded with Bioceramics and Platelet-Rich Plasma. An Experimental Study on Pigs. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.; Schleicher, P.; Eindorf, T.; Friedersdorff, F.; Gelinsky, M.; König, U.; Sewing, A.; Haas, N.P.; Kandziora, F. Cages Augmented with Mineralized Collagen and Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Osteoconductive/Inductive Combination for Interbody Fusion. Spine 2010, 35, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoda, H.; Yamashita, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Miyagi, M.; Arai, G.; Suzuki, M.; Eguchi, Y.; Orita, S.; Sakuma, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Hydroxyapatite for Lumbar Interbody Fusion Promoted Bone Formation and Decreased an Inflammatory Pain Neuropeptide in Rats. Spine 2012, 37, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, G.; Corsi, A.; Sacchetti, B.; Riminucci, M.; Bianco, P.; Giannicola, G. Bone Ingrowth and Vascular Supply in Experimental Spinal Fusion with Platelet-Rich Plasma. Spine 2013, 38, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoda, H.; Ohtori, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Miyagi, M.; Arai, G.; Suzuki, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Kubota, G.; Orita, S.; et al. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion in a Rat Model. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 95, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Orita, S.; Inage, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Shiga, Y.; Abe, K.; Inoue, M.; Norimoto, M.; Umimura, T.; Ishii, T.; et al. Freeze-Dried Platelet-Rich Plasma Induces Osteoblast Proliferation via Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarinia, R.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Alamdari, D.H.; Hoseini, S.J.; Mafinezhad, A.; Hosseini, M. Platelet rich plasma: Effective treatment for repairing of spinal cord injury in rat. Acta Orthop. Et Traumatol. Turc. 2017, 51, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.F.; Sung, C.S.; Wen, Z.H.; Chen, C.H.; Feng, C.W.; Hung, H.C.; Yang, S.N.; Tsui, K.H.; Chen, W.F. Therapeutic Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Rat Spinal Cord Injuries. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarinia, R.; Hosseini, M.; Mohamadi, Y.; Ghorbani, A.; Alamdari, D.H.; Mafinezhad, A.; Sadeghnia, H. Combined use of platelet-rich plasma and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells shows a synergistic effect in experimental spinal cord injury. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 110, 101870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozi, Z.; Ramezani, F.; Janzadeh, A.; Rahimi, B.; Nasirinezhad, F. Platelet-rich plasma in umbilical cord blood reduces neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury by altering the expression of Atp receptors. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 228, 113186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behroozi, Z.; Ramezani, F.; Nasirinezhad, F. Human umbilical cord blood-derived platelet -rich plasma: A new window for motor function recovery and axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 252, 113840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuakli-Wosornu, Y.A.; Terry, A.; Boachie-Adjei, K.; Harrison, J.R.; Gribbin, C.K.; LaSalle, E.E.; Nguyen, J.T.; Solomon, J.L.; Lutz, G.E. Lumbar Intradiskal Platelet-Rich Plasma (Prp) Injections: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Study. PM R 2016, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zuo, R.; Yuan, S.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Ma, M.; Li, D.; Hai, Y. Transforaminal Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy with versus without Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Prospective Cohort Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 6181478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.H.S.; Hung, C.Y.; Wu, T.J.; Chen, W.H.; Ng, T.K.T.; Lin, J.A.; Wu, Y.T.; Lai, W.W. Novel Ultrasound-Guided Cervical Intervertebral Disc Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Cervicodiscogenic Pain: A Case Report and Technical Note. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeda, K.; Ohishi, K.; Masuda, K.; Bae, W.C.; Takegami, N.; Yamada, J.; Nakamura, T.; Sakakibara, T.; Kasai, Y.; Sudo, A. Intradiscal Injection of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate to Treat Discogenic Low Back Pain: A Preliminary Clinical Trial. Asian Spine J. 2017, 11, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeda, K.; Ohishi, K.; Takegami, N.; Sudo, T.; Yamada, J.; Fujiwara, T.; Niimi, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Ogura, T.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate versus Corticosteroid for the Treatment of Discogenic Low Back Pain: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Goyal, T.; Verma, N.; Paswan, A.K.; Dubey, R.K. Intradiscal Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Discogenic Low Back Pain and Correlation with Platelet Concentration: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, D.; Horn, S.; Tyszko, S.; Levin, J.; Hecht-Leavitt, C.; Walko, E. Intradiscal Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain: Preliminary Results from a Prospective Trial. Pain Med. 2015, 17, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Gong, Q.; Chen, J.; Wan, L. Intradiscal Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Discogenic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9563693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeda, K.; Takegami, N.; Yamada, J.; Fujiwara, T.; Ohishi, K.; Tamaru, S.; Sudo, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma-Releasate (Prpr) for the Treatment of Discogenic Low Back Pain Patients: Long-Term Follow-Up Survey. Medicina 2022, 58, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Santiago, K.; Nguyen, J.T.; Solomon, J.L.; E Lutz, G. Treatment of symptomatic degenerative intervertebral discs with autologous platelet-rich plasma: Follow-up at 5–9 years. Regen. Med. 2019, 14, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, S.; Hachiya, K.; Nagai, S.; Takeda, H.; Rashid, M.Z.M.; Ikeda, D.; Kawano, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Ohno, Y.; Fujita, N. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Administration on the Intervertebral Disc in Low Back Pain Patients with Modic Type 1 Change: Report of Two Cases. Medicina 2023, 59, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mera, Y.; Teraguchi, M.; Hashizume, H.; Oka, H.; Muraki, S.; Akune, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Tamai, H.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Association between types of Modic changes in the lumbar region and low back pain in a large cohort: The Wakayama spine study. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 30, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.J.; Hung, C.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Lam, S.; Clark, T.B.; Chang, K.V. Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Intradiscal Injection for Discogenic Pain: Technical Innovation and Presentation of Two Cases. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, C.; Cheng, J.; Prysak, M.; Zukofsky, T.; Rothman, R.; Lutz, G. Clinical outcomes following intradiscal injections of higher-concentration platelet-rich plasma in patients with chronic lumbar discogenic pain. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, B.K.; Walker, M. Efficacy of Autologous Growth Factors in Lumbar Intertransverse Fusions. Spine 2003, 28, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feiz-Erfan, I.; Harrigan, M.; Sonntag, V.K.; Harrington, T.R. Effect of Autologous Platelet Gel on Early and Late Graft Fusion in Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2007, 7, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, G.; Kamoda, H.; Orita, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Inage, K.; Sainoh, T.; Sato, J.; Ito, M.; et al. Platelet-rich plasma enhances bone union in posterolateral lumbar fusion: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Spine J. 2019, 19, e34–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagama, S.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Hida, T.; Ito, K.; Tsushima, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Morozumi, M.; et al. Efficacy of Early Fusion with Local Bone Graft and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery Followed Over 10 Years. Glob. Spine J. 2017, 7, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebal-Cortina, G.; Suárez-Suárez, M.A.; García-Menéndez, C.; Moro-Barrero, L.; Iglesias-Colao, R.; Torres-Pérez, A. Evaluation of autologous platelet concentrate for intertransverse lumbar fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sys, J.; Weyler, J.; Van Der Zijden, T.; Parizel, P.; Michielsen, J. Platelet-rich plasma in mono-segmental posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, H.T.; Majd, M.E.; Holt, R.T.; Myers, L. Do Autologous Growth Factors Enhance Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion? Eur. Spine J. 2003, 12, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenis, L.G.; Banco, R.J.; Kwon, B. A prospective study of Autologous Growth Factors (Agf) in lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2006, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Hsu, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, M.-J.; Chen, H.-T. Using the Growth Factors-enriched Platelet Glue in Spinal Fusion and its Efficiency. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2009, 22, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, E.K.; Heintel, T.M.; Morrison, R.H.; Weckbach, A. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on the anterior fusion in spinal injuries: A qualitative and quantitative analysis using computer tomography. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2009, 130, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, G.; Kamoda, H.; Orita, S.; Inage, K.; Ito, M.; Yamashita, M.; Furuya, T.; Akazawa, T.; Shiga, Y.; Ohtori, S. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Bone Fusion in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2018, 12, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.P., Jr. Role of Activated Growth Factors in Lumbar Spinal Fusions. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2004, 17, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreon, L.Y.; Glassman, S.D.; Anekstein, Y.; Puno, R.M. Platelet Gel (AGF) Fails to Increase Fusion Rates in Instrumented Posterolateral Fusions. Spine 2005, 30, E243–E246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, A.; Tarantino, R.; Marotta, N.; Ruggeri, A.G.; Domenicucci, M.; Giudice, L.; Martini, S.; Rastelli, M.; Ferrazza, G.; De Luca, N.; et al. The use of platelet gel in postero-lateral fusion: Preliminary results in a series of 14 cases. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, R.; Donnarumma, P.; Mancarella, C.; Rullo, M.; Ferrazza, G.; Barrella, G.; Martini, S.; Delfini, R. Posterolateral Arthrodesis in Lumbar Spine Surgery Using Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma and Cancellous Bone Substitute: An Osteoinductive and Osteoconductive Effect. Glob. Spine J. 2014, 4, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadalà, G.; Di Martino, A.; Russo, F.; Tirindelli, M.C.; De Felice, L.; Agostini, F.; Papalia, R.; Denaro, V. Autologous bone marrow concentrate combined with platelet-rich plasma enhance bone allograft potential to induce spinal fusion. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, C.F.; Azevedo, D.D.P.; Lourenço, R.B.; Duarte, J.F.; Cardoso, I.M.; Júnior, C.J. Evaluation of the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in the bone consolidation of patients submitted to lumbar arthrodesis. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2017, 52, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Du, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Q. A New Technique for the Treatment of Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome Using Intra-articular Injection with Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma. Pain Physician 2016, 19, 617–625. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, W.; Lv, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, R.; Du, Z.; Zhang, G.; et al. A Prospective Study Comparing Platelet-Rich Plasma and Local Anesthetic (La)/Corticosteroid in Intra-Articular Injection for the Treatment of Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome. Pain Pract. 2017, 17, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, F.; Anitua, E. Intradiscal and intra articular facet infiltrations with plasma rich in growth factors reduce pain in patients with chronic low back pain. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2016, 7, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Navani, A.; Li, G.; Chrystal, J. Platelet Rich Plasma in Musculoskeletal Pathology: A Necessary Rescue or a Lost Cause? Pain Physician 2017, 20, E345–E356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, V.; Batra, Y.K.; Bharti, N.; Goni, V.G.; Marwaha, N. Steroid vs. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Ultrasound-Guided Sacroiliac Joint Injection for Chronic Low Back Pain. Pain Pract. 2016, 17, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.S.; Solberg, J.; Smith, C.; Chi, M.; Lowder, R.; Christolias, G.; Singh, J.R. Intra-Articular Platelet Rich Plasma Vs Corticosteroid Injections for Sacroiliac Joint Pain: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Clinical Trial. Pain Med. 2022, 23, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohi Eldin, M.; Sorour, O.O.; Hassan, A.S.A.; Baraka, M.A.F.A.H.; Ahmed, M.F. Percutaneous injection of autologous platelet-rich fibrin versus platelet-rich plasma in sacroiliac joint dysfunction: An applied comparative study. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2019, 32, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhead, D.Y.; Douglas, H.E.; Wallace, L.M.B.; Wallace, P.J.; Tamura, S.; Morgan, K.C.; E Hemler, D. Use of Ultrasound-Guided Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection of the Sacroiliac Joint as a Treatment for Chronic Low Back Pain. Mil. Med. 2019, 185, e1312–e1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.D.; Mindra, S.; Lawson, G.E.; Whitmore, S.; Arseneau, L. Case series of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for sacroiliac joint dysfunction. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2017, 30, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, P.; Wallace, L.B.; Tamura, S.; Prochnio, K.; Morgan, K.; Hemler, D. Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in Relieving Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 99, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, F.; Milani, I.; Martinez, A.; Kirchner-Bossi, N.; Prado, R.; Padilla, S.; Anitua, E. Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (Prgf) in the Treatment of Cervical and Lumbar Back Pain: A Retrospective Observational Clinical Study. Pain Physician 2021, 24, E649–E660. [Google Scholar]
- Ricardo, R.-L.; Tsai, Y.-C. A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Pilot Study Comparing Leucocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma and Corticosteroid in Caudal Epidural Injection for Complex Chronic Degenerative Spinal Pain. Pain Pract. 2020, 20, 639–646. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, X.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Fan, S.; Ma, C. Ultrasound-Guided Transforaminal Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma Compared with Steroid in Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Study. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 5558138. [Google Scholar]
- Bise, S.; Dallaudiere, B.; Pesquer, L.; Pedram, M.; Meyer, P.; Antoun, M.B.; Hocquelet, A.; Silvestre, A. Comparison of interlaminar CT-guided epidural platelet-rich plasma versus steroid injection in patients with lumbar radicular pain. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Colombini, A.; Stogicza, A.; de Girolamo, L. Effectiveness of plasma rich in growth factors in the management of chronic spinal pain: A case series of 32 patients. Regen. Med. 2022, 17, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, E.S.; Ambach, M.A.; Caldas, J.M.; Wei, J.J.; Bredemeier, M. Personalized multitarget biologic injection in the spine: Prospective case series of multitarget platelet-rich plasma for low back pain. Regen. Med. 2022, 17, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, R.; Chopra, G. Efficacy of Platelet Rich Plasma Via Lumbar Epidural Route in Chronic Prolapsed Intervertebral Disc Patients-a Pilot Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, Uc05–Uc07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, B. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Epidural Platelet Lysate: Novel Treatment for Lumbar Disk Herniation. J. Am. Osteopat. Assoc. 2020, 120, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, Y.D. The Retrospective Analysis of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Corticosteroid Injection under Epiduroscopic Guidance for Radiculopathy in Operated or Unoperated Patients for Lumbar Disc Herniation. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 68, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Le, V.T.; Dao, L.T.N.; Nguyen, A.M. Transforaminal injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma for lumbar disc herniation: A single-center prospective study in Vietnam. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadi, J.A.; Elzein, S.M.; Beery, P.; Spalding, M.C.; Pershing, M. Combined administration of platelet rich plasma and autologous bone marrow aspirate concentrate for spinal cord injury: A descriptive case series. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisch, L.; Brachtl, G.; Hochmann, S.; Andrade, A.C.; Oeller, M.; Ebner-Peking, P.; Schallmoser, K.; Strunk, D. Improving Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Megakaryocyte Differentiation and Platelet Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Eto, K. Ex vivo generation of platelet products from human iPS cells. Inflamm. Regen. 2020, 40, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Factor | Examples |
|---|---|
| Adhesive proteins | Von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen, fibronectin, vitronectin, thrombospondin-1 and -2, laminin-8 |
| Clotting factors and inhibitors | Factor V/Va, factor XI, multimerin, protein S, high-molecular-weight kininogen, protease nexin-1 and -2, tissue factor pathway inhibitor, protein C inhibitor |
| Fibrinolytic factors and inhibitors | Plasminogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA), α2-antiplasmin, histidine-rich glycoprotein, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI,) α2-macroglobulin |
| Proteases and antiproteases | Metalloproteinases (MMP)-1, -2, -4, -9, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS) 10, -13, TIMPs 1–4, platelet inhibitor of FIX, C1 inhibitor, α1-antitrypsin |
| Growth and mitogenic factors | transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-β1, -β2, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) -A, -B, and -C, epithelial growth factor (EGF), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) -A, -C, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-2, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), bone morphometric protein (BMP)-2, -4, -6, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), signal peptide, CUB domain and EGF-like domain containing 1 (SCUBE1), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) |
| Chemokines, cytokines and others | Interleukin (IL)-1, RANTES (CCL5), IL-8 (CXCL8), macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α (CCL3), MIP-2 (CXCL2), LIX (CXCL6) GRO-α (CXCL1), ENA-78 (CXCL5), stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α (CXCL12), MCP-1 (CCL2), MCP-3 (CCL7), platelet factor 4 (PF4) (CXCL4), pro-platelet basic protein (PBP), β-thromboglobulin (β-TG), neutrophil activating protein-2 (NAP-2), connective-tissue activating peptide III T(CXCL7), thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) (CCL17), angiopoietin-1, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), interleukin-6 soluble receptor (IL-6sR), bone sialoprotein, dickkopf-1, osteoprotegerin |
| Others | Chondroitin 4-sulfate, albumin, immunoglobulins G and M, amyloid β-protein precursor, disabled-2, complement factor H, bile salt-dependent lipase (BSDL), semaphorin 3A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawabata, S.; Akeda, K.; Yamada, J.; Takegami, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujita, N.; Sudo, A. Advances in Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Spinal Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087677
Kawabata S, Akeda K, Yamada J, Takegami N, Fujiwara T, Fujita N, Sudo A. Advances in Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Spinal Diseases: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087677
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawabata, Soya, Koji Akeda, Junichi Yamada, Norihiko Takegami, Tatsuhiko Fujiwara, Nobuyuki Fujita, and Akihiro Sudo. 2023. "Advances in Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Spinal Diseases: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087677
APA StyleKawabata, S., Akeda, K., Yamada, J., Takegami, N., Fujiwara, T., Fujita, N., & Sudo, A. (2023). Advances in Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment for Spinal Diseases: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087677








