1. Introduction
The evasion of apoptosis, which leads to cancer initiation and progression as well as its resistance to treatment, is considered a hallmark of cancer [
1]. Therefore, induction of apoptosis in cancer cells represents the principal goal of anticancer therapy. Both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways can be activated in response to most anticancer strategies currently used, such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy [
2]. In this matter, the knowledge of aberrant apoptotic machinery in cancer cells is of key importance to enhance the efficacy of therapy. As shown by numerous studies, one of the most common strategies that cancer cells employ to evade apoptosis is overexpression of pro-survival members of the BCL-2 protein family [
3]. These proteins, namely BCL-2, BCL-XL, BCL-w, MCL-1 and BFL-1/A1, are essential regulators of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. They function to counteract the activity of pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family members, such as BAX/BAK multidomain proteins and BH3-only proteins, thereby preventing mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), which leads to caspase cascade activation and apoptosis [
4].
Overexpression of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins was reported in various solid tumors and hematological malignancies [
5]. Considering the latter, a number of studies have linked de-regulation of these anti-apoptotic proteins with pathogenesis and treatment failure in acute and chronic leukemias of myeloid origin [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Importantly, during myelopoiesis, several factors influence the survival, proliferation and differentiation of myeloid cells, in part by regulating the expression of BCL-2 family proteins. Members of the BCL-2 family function as critical nodes in complex regulatory networks, which make ultimate life/death decisions within a cell. Although BCL-2 family proteins do not have a direct role in myeloid cell proliferation and differentiation programs, they can either allow these programs to proceed or prevent them. Through such effects, the BCL-2 family proteins maintain cellular homeostasis [
10]. Therefore, any alteration in the expression of its members disturbs the proper balance between cell death and cell survival signals and contributes to leukemogenesis [
10].
Among leukemias, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common malignancy diagnosed in the adult population and accounts for about 80% of all cases [
11]. It still remains a disease with poor clinical prognosis due to high incidence of relapses and low 5-year survival rate (40–50%) [
11]. Intensive studies aimed to determine the molecular pathways of leukemogenesis recognized AML as a heterogenous disease, which results from a complex network of cytogenetic aberrations and molecular mutations [
12,
13]. As a result, in AML, excessive cell proliferation accompanied with a differentiation block and inhibition of apoptosis leads to the accumulation of abnormal myeloid precursor cells [
13]. Moreover, the heterogeneity of AML is a key determinant of disease progression and poor treatment response. For the past 40 years, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and chemotherapy based on anthracyclines and cytarabine remained the main treatments for AML. However, in 2017, there was a breakthrough, and new therapeutics were approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the US, including targeted drugs, such as FLT3 inhibitor midostaurin, IDH2 inhibitor enasidenib and venetoclax, which belongs to the class of small-molecule BCL-2 inhibitors [
14].
BCL-2 inhibitors, named BH3 mimetics, were designed to specifically block anti-apoptotic proteins from the BCL-2 family by binding to their hydrophobic groove and preventing their ability to inhibit pro-apoptotic family members. These agents can act as apoptosis inducers and/or sensitizers in cancer cells [
15]. Thus far, a number of BH-3 mimetics with different specificities have been synthetized. ABT-737 and its orally available analog ABT-263 were one of the first BCL-2 inhibitors designed to bind with high affinity to BCL-2, BCL-XL and BCL-w [
15]. ABT-737 induced apoptosis as a single agent in AML-derived cell lines in primary blasts and in AML stem cells and was effective at reducing the leukemia burden in vivo in a xenograft model of AML [
16]. Moreover, BH3 profiling demonstrated myeloblast sensitivity to ABT-737 and its dependence on BCL-2 in the mitochondria [
17], which prompted the development of a highly specific inhibitor of BCL-2 protein, ABT-199 (venetoclax). This BH3 mimetic induced apoptosis in multiple AML cell lines at nanomolar concentrations and inhibited leukemia progression in an in vivo murine AML xenograft model [
18]. However, consequent studies revealed that cancer cells can acquire resistance to ABT-737 and ABT-199, which is partially mediated by the up-regulation of MCL-1, another member of the BCL-2 family. It was shown that high MCL-1 expression and BCL-2 phosphorylation markedly reduced the ability of ABT-737 to induce apoptosis [
16], whereas up-regulation of MCL-1 and BCL-XL was found to be responsible for the resistance of myeloid leukemia cell lines to ABT-199 [
19]. The increased MCL-1 protein expression was found to occur through transcriptional or post-transcriptional mechanisms [
20,
21]. Given the latter, MCL-1 can be phosphorylated at Thr163 by the ERK1/2 protein, thus increasing its stability and enhancing its anti-apoptotic activity [
22]. Importantly, in addition to regulating the activity of anti-apoptotic proteins from the BCL-2 family, ERK/MAPK signaling pathway can provide an anti-apoptotic effect by up-regulating the expression of these proteins [
21,
22].
As MCL-1 is critical for the sustained survival and expansion of mouse as well as human AML cells [
20], targeting the intrinsic apoptotic pathway through MCL-1 antagonism is a rational strategy to restore apoptosis in AML cells. Recently, a new specific small-molecule inhibitor of MCL-1, namely S63845, has been synthetized [
23]. This agent has been shown to inhibit MCL-1 with a Ki < 1.2 nM and Kd of 0.19 nM with no concurrent binding to either BCL-2 or BCL-XL (Ki > 10,000 nM) [
24]. Its pro-apoptotic activity has been observed in a number of hematological malignancies, including multiple myeloma, lymphoma and AML-derived cell lines in vitro and in vivo [
24]. S63845 selectively killed cancer cells, which relied on MCL-1 for survival, by activating the BAX/BAK-dependent mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, confirming its on-target effects [
23]. Moreover, the high efficacy of the combination of S63845 with other anticancer drugs, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, cytarabine or docetaxel, was shown in hematological malignances as well as in solid tumors [
23,
25,
26]. Recently, MIK665 (S64315) derived from S63845 has been introduced to clinical trials for hematological malignancies (NCT04629443, NCT02979366, NCT02992483, NCT04702425).
Considering all the above data, in this study, the antileukemic effects of an MCL-1 inhibitor, S63845, were examined in human AML cell lines when used as a single agent or in combination with BCL-2/BCL-XL inhibitor, ABT-737. Two AML cell lines, which differ with respect to their maturation level, were used in the study: HL-60 acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturation (FAB-M2) and human myeloblastic leukemia ML-1 (FAB-M5). These AML cell lines have been accepted as model systems for hematopoietic cell proliferation, differentiation and death studies. Given that AML is a disease associated with impaired cell differentiation and apoptosis, the impact of S63845 and ABT-737 on the induction of these processes was determined. Furthermore, as the expression of the MCL-1 protein is regulated by MAPK/ERK signaling, we also investigated the effects of MAPK pathway inhibition on the sensitivity of AML cells to S63845. Our in vitro data show that S63845 exerts cytotoxic effects on leukemic cells, and its anti-AML efficacy is enhanced by simultaneous targeting of BCL2/BCL-XL. Moreover, we demonstrate that the sensitivity of AML cells to S63845 can be increased by the inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway. Importantly, in the present study, we show for the first time that a combined application of S63845 and ABT-737 or MAPK inhibitor promotes not only apoptosis but also differentiation of human AML HL-60 and ML-1 cells.
3. Discussion
Targeted therapy has gained much interest in cancer treatment since the introduction of the first targeted drugs in oncology, such as all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) [
30] and BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, imatinib, which has been the mainstay of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) therapy for decades [
31]. In the past 20 years, there has been a significant increase in FDA-approved targeted drugs for cancer treatment. Nevertheless, their development is still challenging. In this context, the discovery of therapeutic targets is of key importance. The recognition of the pivotal role played by anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins in cancer development and treatment resistance made them a relevant target for anticancer therapy [
32]. Indeed, venetoclax, the first BCL-2 inhibitor approved by the FDA, is a mild and efficient drug for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia, especially when combined with other anticancer agents [
33]. However, the responses to venetoclax in various leukemia subtypes can differ significantly. Failures of BCL-2 inhibition may rely on the survival dependence of cancer cells on numerous other anti-apoptotic proteins. Brunelle et al. [
34] compared the function of MCL-1 and BCL-2 in cancer cell survival using mouse leukemia models based on Eμ-Myc expression, where either BCL-2 or MCL-1 were required for leukemia maintenance. It was shown that leukemias are dependent on the continuous function of either MCL-1 or BCL-2 for survival. Accumulating evidence has indicated the critical pro-survival role of MCL-1 in hematological malignancies, making this protein an important target in leukemia therapy [
20]. In line with this, herein, we utilized two myeloid leukemia cell lines to study the antileukemic efficacy of a novel MCL-1 inhibitor, S63845. This study showed that it exerts potent antileukemic activity and synergizes with BCL-2/BCL-XL inhibitor ABT-737 to induce apoptosis and differentiation in AML cells. Moreover, it was found that the pro-apoptotic and pro-differentiating activity of S63845 in AML cells might be enhanced by the inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway.
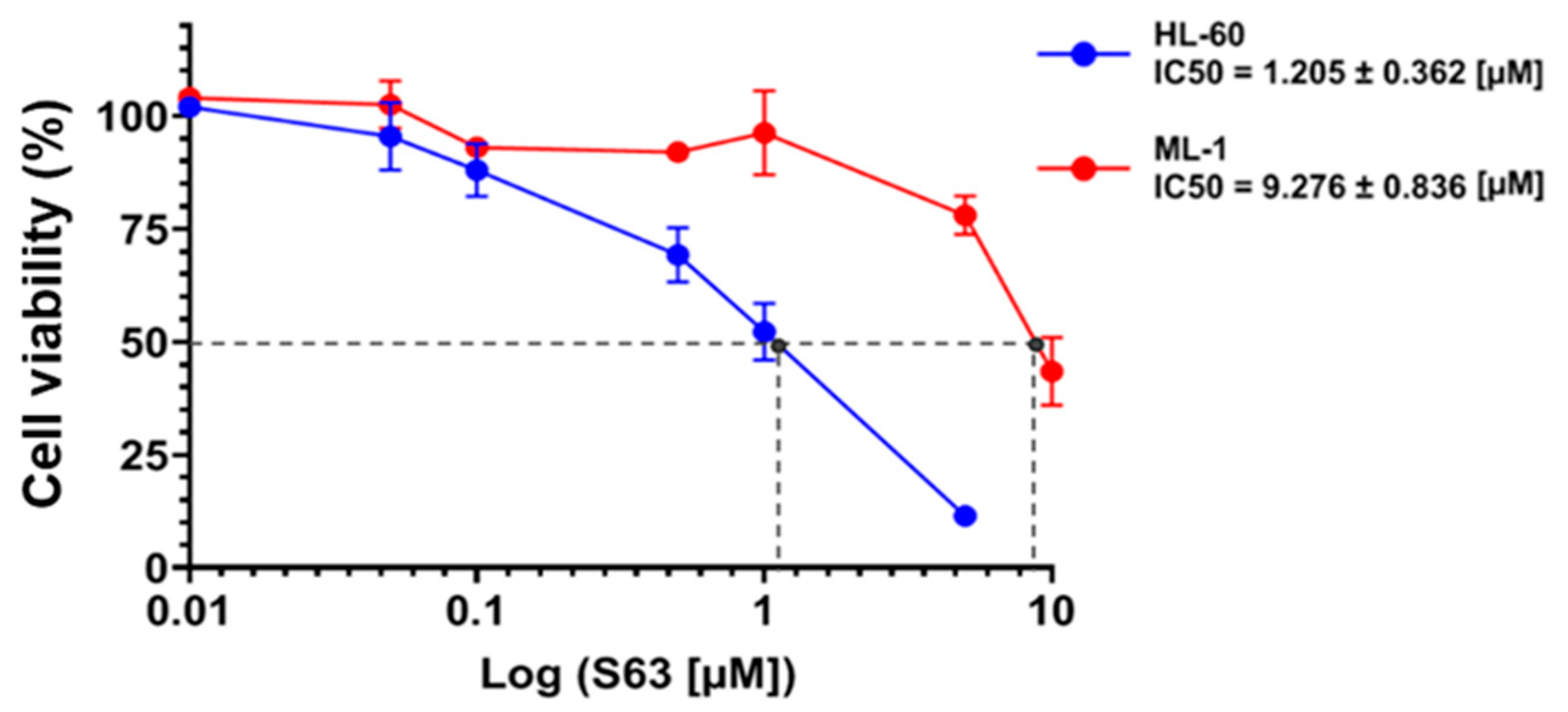
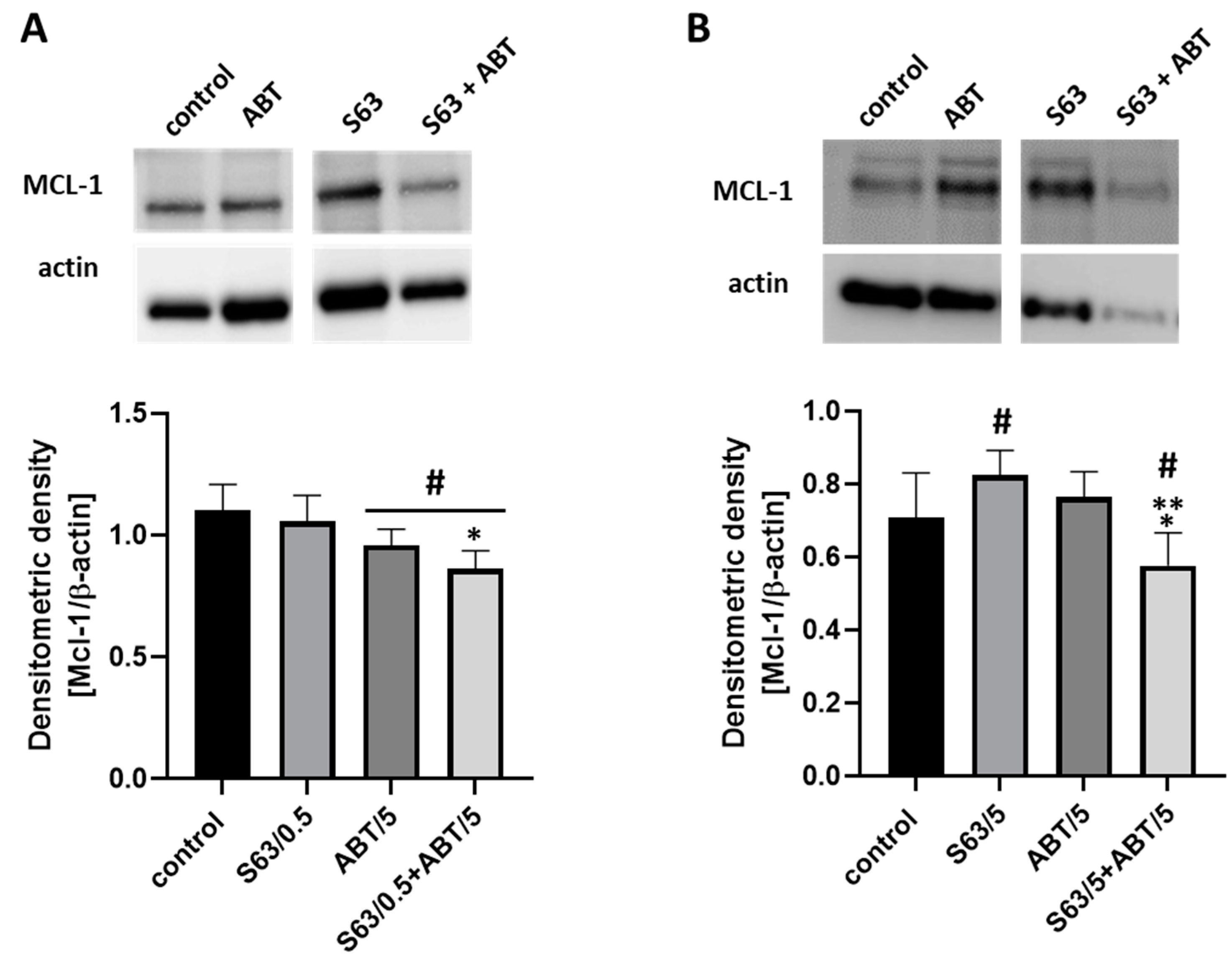
The results of the present as well as previous studies demonstrated that S63845, used as a single agent, decreased AML cell viability and count in a concentration- and cell-line-dependent manner [
23,
35]. In terms of cell viability, it was shown that among a panel of cancer cell lines derived from hematologic malignancies and solid tumors, the MCL-1 inhibitor appeared to be the most potent in AML and multiple myeloma, showing IC50 values of <1 µM [
23]. However, the IC50 value of S63845 for both AML cell lines tested in the present study was above 1 µM, indicating their resistance to the MCL-1 inhibitor. As shown by Western blot analysis, both HL-60 and ML-1 cells expressed MCL-1 at a comparable level, and S63845 was able to enhance the level of this protein. Interestingly, in ML-1 cells, two isoforms of MCL-1 were noticed at the 24 h time point. As shown by numerous studies in humans, Mcl-1 mRNA may undergo alternative splicing to produce two isoforms of protein with opposite functions. The long variant, MCL-1L (40 kDa), acts as an anti-apoptotic factor and is traditionally referred to as MCL-1, whereas the short variant, MCL-1S (32 kDa), displays pro-apoptotic features [
24]. Splicing dysregulation of MCL-1 may lead to resistance toward apoptosis and is observed in various types of cancers [
24]. Given that two isoforms were seen in ML-1 cells but not in HL-60 cells, this may indicate the important role of mRNA splicing in ML-1 cell survival and response to treatment. Further detailed mechanistic studies are required to resolve this issue. Importantly, inhibition of the MCL-1 protein by a specific inhibitor did not always result in a reduction in its level. No changes in the expression of MCL-1 were found in the sensitive AML cell line MV4-11 treated with S63845 [
36]. Interestingly, MCL-1 inhibitor can cause an increase in total MCL-1 protein level, which was observed in difficult-to-treat melanoma cells [
37], and it was also found in the present study in ML-1 cells treated with S63845. In previous studies, this was hypothesized to be due to the compound displacement of NOXA, a BH3 protein involved in MCL-1 turnover. Indeed, it was shown by the numerous studies that the mechanism of S63845 action in cancer cells is correlated with the release of pro-apoptotic proteins, such as NOXA, BAK and BIM, upon S63845 binding to the MCL-1 protein [
38]. On the other hand, sensitivity to S63845 was correlated with diminished expression of other anti-apoptotic proteins in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells [
39], melanoma [
37] and myeloma cells [
40]. In particular, MCL-1 inhibition may lead to BCL-XL overexpression in cancer cells as a compensatory survival adaptation. In line with this, in the present study, we explored the effects of combined treatment covering both MCL-1 and BCL2/BCL-XL inhibition.
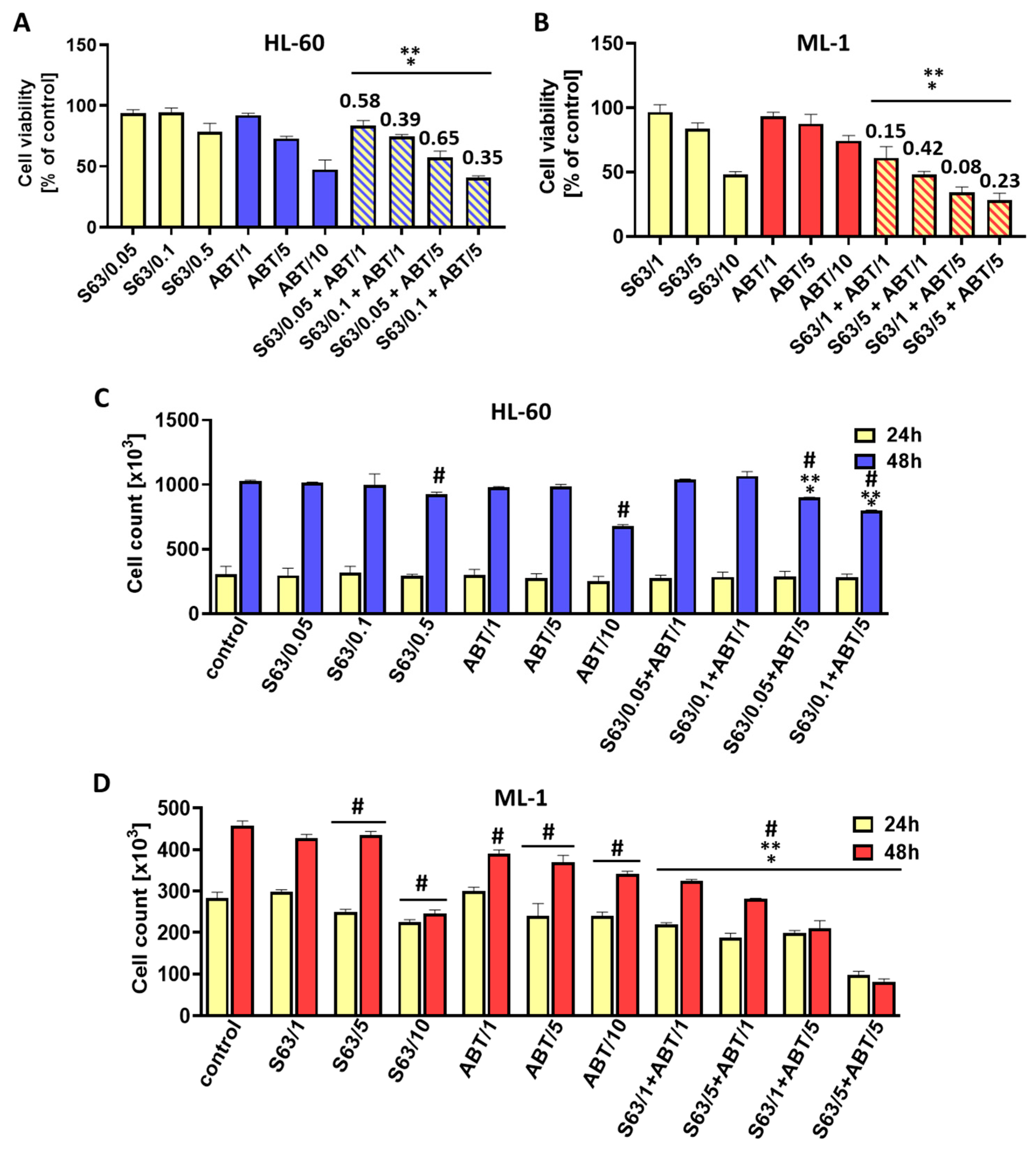
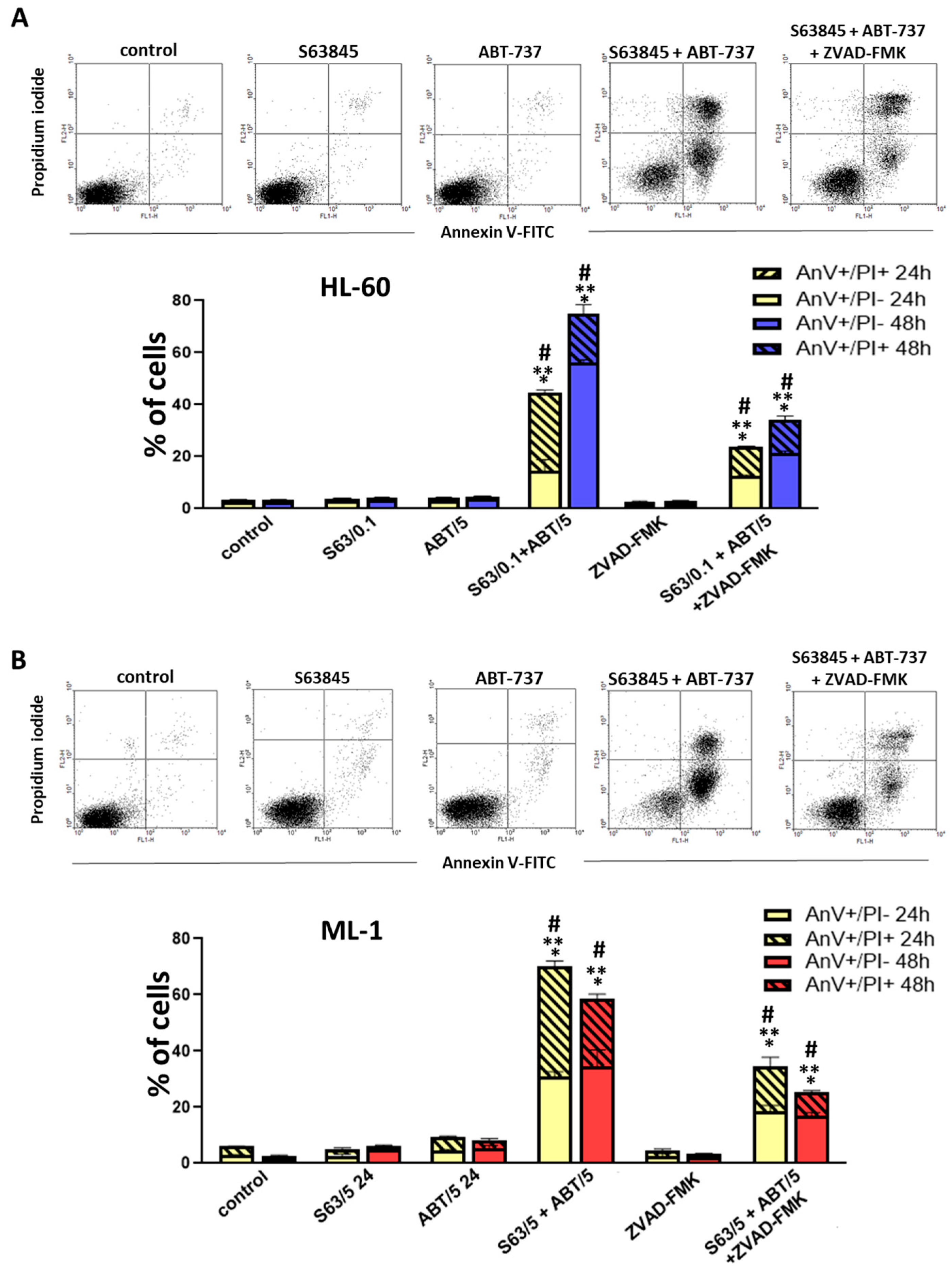
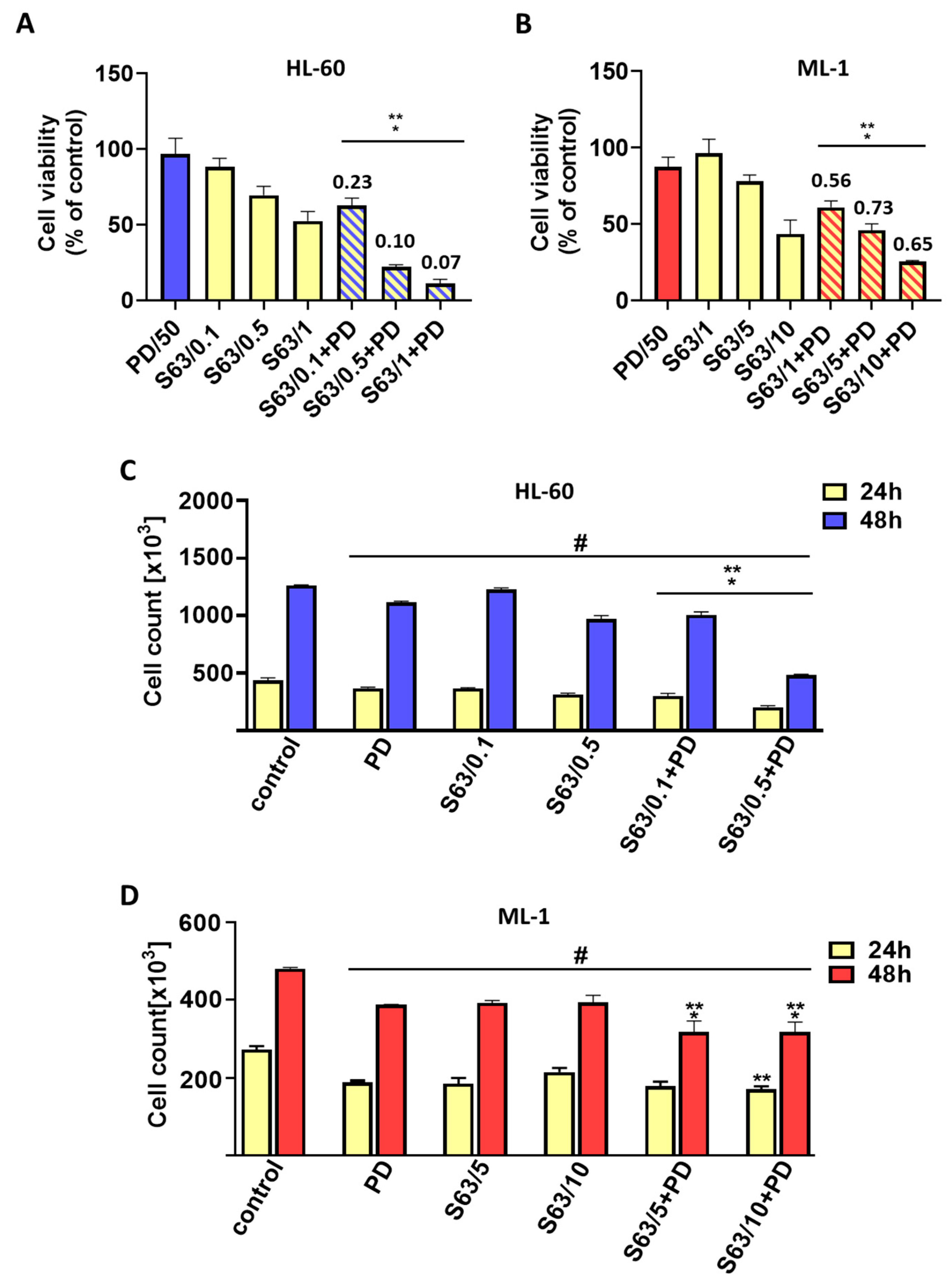
Our data indicate that treatment of AML cells with a combination of S63845 and ABT-737, a well-defined BCL-2/BCL-XL inhibitor, resulted in more effective cell killing compared to single-agent treatment. The analysis of the combination index clearly showed a strong synergism of the S63845 and ABT-737 interaction. We found a pronounced reduction in cell viability and count as well as an increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells, as shown by the annexin V/propidium iodide assay and morphological examination. Importantly, the use of ZVAD-FMK, a pan-caspase inhibitor, markedly diminished apoptosis triggered by the combined treatment, indicating that the antileukemic effect of S63845 and ABT-737 applied in combination might primarily stem from the activation of the apoptotic pathway. In addition, S63845 together with ABT-737 was able to reduce the MCL-1 protein level. The high pro-apoptotic efficacy of MCL-1 and BCL-2/BCL-XL co-inhibition was also found in previous studies concerning hematological malignancies and solid tumors [
37,
41]. Decreased viability of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas in response to ABT-737 was shown to be further reduced in combinations with S63845 [
39]. The use of S63845 with ABT-263, an orally available analog of ABT-737, induced apoptosis in melanoma cells with high potency, both in vitro and in vivo [
37]. Of note, the combination of S63845 with either selective BCL-2 or BCL-XL inhibitor also resulted in synergistic reduction in cervical cancer cell growth and invasion [
41], increased apoptotic response in AML cell lines and primary samples [
36], and exerted profound synergistic activity against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells (T-ALL) in vitro and in vivo in a T-ALL zebrafish embryos model [
42]. Taken together, the results of the present study as well as previous investigations clearly show the high potency of combined inhibition of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members in cancer cells. Of note, co-inhibition with BCL-2 inhibitors requires lower concentrations of them compared to the doses needed to assess their pro-apoptotic activity in the single-agent treatments. In this way, the therapeutic index of BCL-2 inhibitors can be enhanced with concomitant decrease in potential adverse effects. For example, ABT-737 and ABT-263 by themselves cause dose-dependent thrombocytopenia as a result of BCL-XL inhibition. By lowering the dosage of BCL-XL inhibitors, this side effect of their use is expected to be markedly decreased.
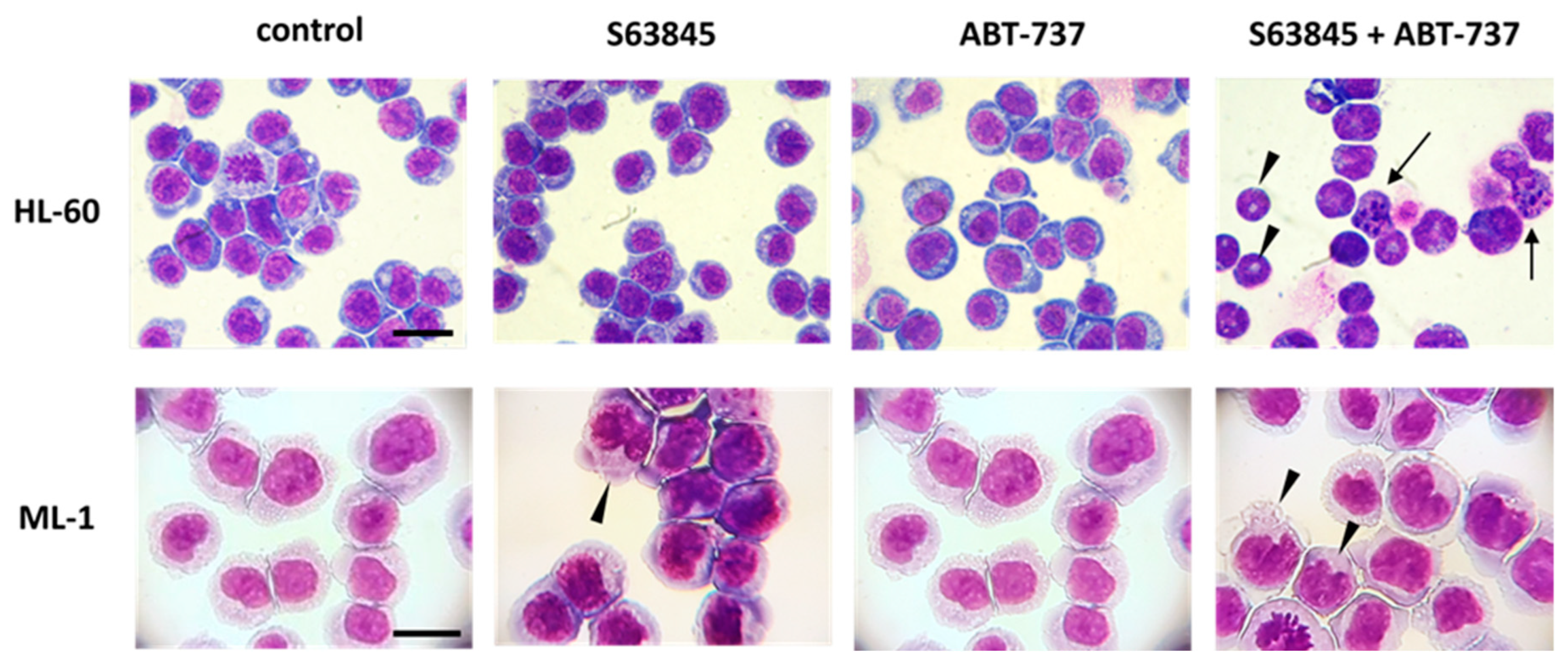
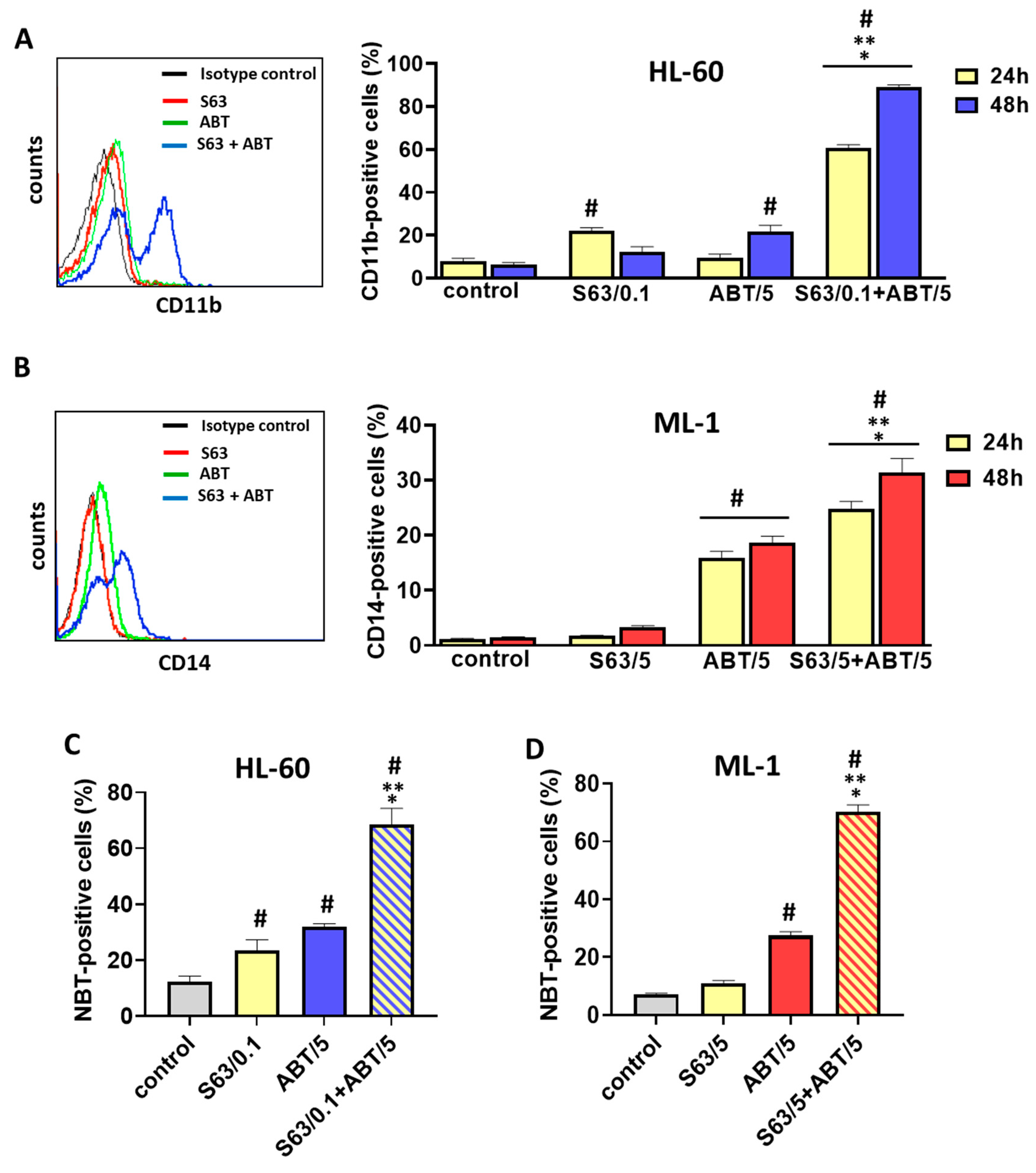
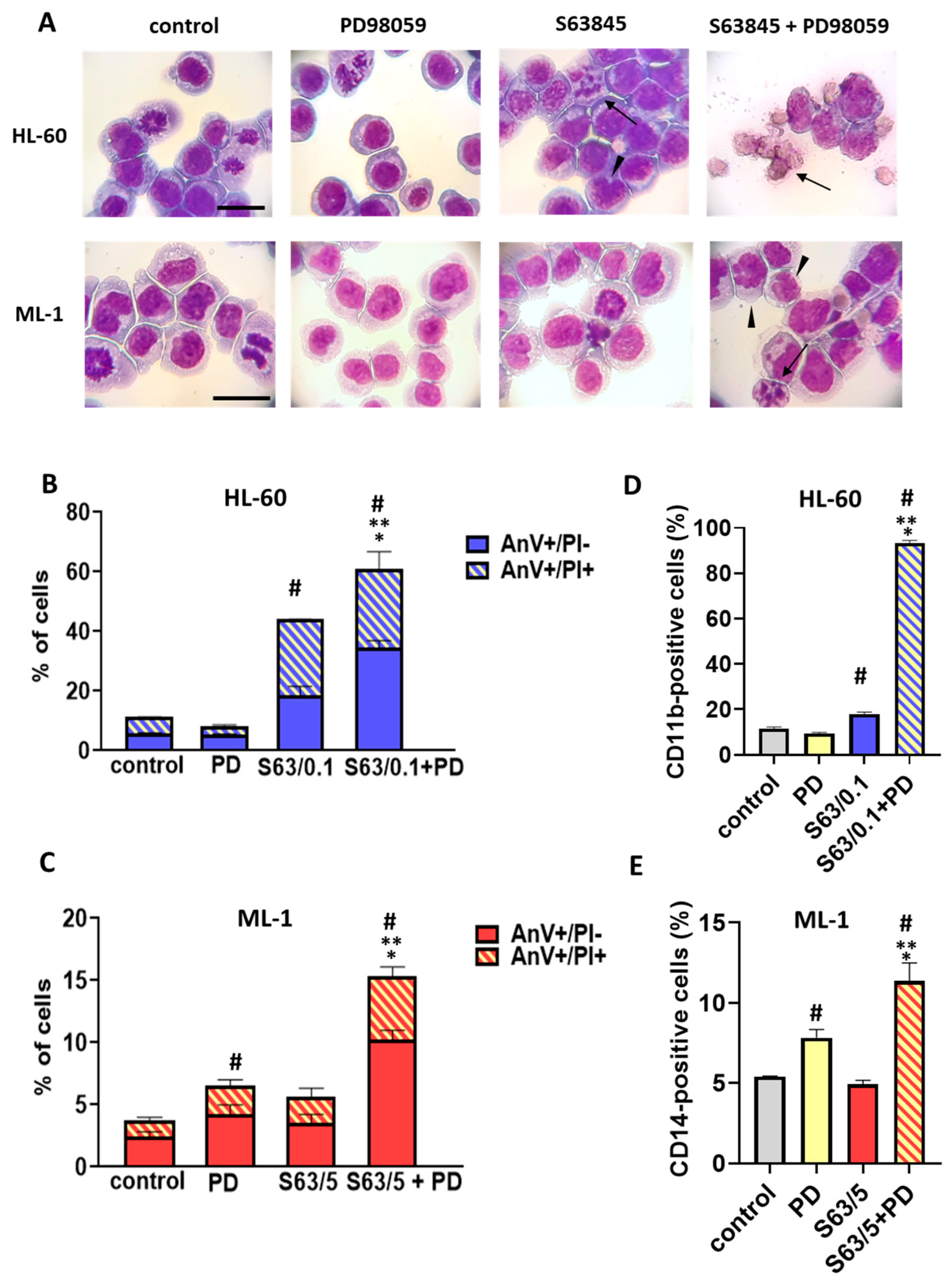
In addition to the above observations of pronounced pro-apoptotic activity of S63845 and ABT-737 combinational treatment of AML cells, we report for the first time the pro-differentiating impact of this treatment. HL-60 and ML-1 cells exposed to S63845 in combination with ABT-737 acquired a phenotype characteristic of more mature myeloid cells, such as unique morphology, the ability to perform oxidative burst and higher expression of a specific differentiation marker. In particular, HL-60 cells displayed a morphology of granulocytic lineage cells with enhanced expression of CD11b, whereas the expression of CD14 and morphology of ML-1 cells indicated their monocytic differentiation. Previous studies have demonstrated that the BCL-2 protein family is crucial for both controlled myelopoiesis and homeostasis of mature myeloid cells. Interestingly, during differentiation, AML cells undergo a number of marked changes in apoptosis-related genes, among which a down-regulation of the BCL-2 protein appears to be a part of the differentiation pathway and may serve to facilitate the apoptotic response [
43]. It was shown that differentiation and consequent apoptosis of HL-60 cells in response to ATRA treatment was accompanied by bcl-2-mRNA instability [
44]. In contrast, MCL-1 is crucial for the survival of myeloid precursor cells and their successful maturation into granulocytes [
45]. A conditional knockout of MCL-1 in the myeloid lineage led to disturbed neutrophil differentiation with an increase in immature precursors’ number and a general deficit of mature granulocytes [
45]. On the other hand, differentiation into monocytes is not disturbed by the down-regulation of MCL-1, showing increased expression of BCL-2 and BCL-XL [
45]. In the present study, among the two cell lines tested, ML-1 cells in particular differentiated in response to ABT-737 alone, whereas both AML cell lines showed clear features of differentiation after combined treatment with S63845 and ABT-737. Based on this observation, it can be assumed that induction of AML cell differentiation and consequent apoptosis may be achieved by simultaneous inhibition of both MCL-1 and BCL-2 proteins. In the previous study, regarding the pro-differentiating mechanisms of ATRA in NB4 and HL-60 cells, it was shown that ATRA increased the level of MCL-1 protein, while BCL-2 expression was decreased. Inhibition of MCL-1 appeared to accelerate the apoptosis of the ATRA-differentiated AML cells [
46]. In line with this, additional experiments are needed to firmly establish the role of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins in differentiation of AML cells induced by combined treatment with S63845 and ABT-737. Nevertheless, it is clear now that the close relationships between the processes mediating apoptosis and differentiation are fundamental to leukemia and are thus important for the development of an effective targeted therapy.
When considering the enhancement of S63845 antileukemic activity, the MAPK signaling pathway is also of importance. This pathway is associated with an apoptosis-resistant phenotype due to the anti-apoptotic function of MAPK signaling. It was found that in primary AML cells, MAPK is constitutively active and promotes leukemic cell growth [
5]. With regard to the MCL-1 protein, the activation of the MAPK pathway leads to its increased stability and higher levels [
47]. Simultaneous up-regulation of the BCL2 ratio and activation of the MAPK pathway act synergistically to enhance leukemic cell survival. Therefore, in the present study, in relation to the antileukemic effects of S63845, we also report that inhibition of the MAPK pathway can enhance the pro-apoptotic as well as pro-differentiating activity of this MCL-1 inhibitor in AML cells. We found a strong synergism of the S63845 and PD98059 combination, which was confirmed by combination index analysis. A synergistic effect of combined ERK1/2 and MCL-1 inhibition was also seen in rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines [
48]. Moreover, the sensitivity of AML cells to co-treatment with S63845 and MEK inhibitor trametinib was greater in leukemic cells with elevated MCL-1 and MEK levels [
47]. Interestingly, previous mechanistic studies revealed that the ERK1/2 signaling pathway is activated in response to venetoclax treatment, which contributes to an acquired resistance phenotype [
49]. The observed response of cancer cells to the combinational treatment with BCL-2 and MAPK inhibitors may be related to the phenomenon of cancer cell dependence on a specific oncogene to sustain growth and survival. In this way, the inhibition of this specific oncogene/pathway seemed to be sufficient to inhibit the neoplastic phenotype. Importantly, as shown in the present study, the inhibition of MAPK phosphorylation may occur in the first hours after cell exposure to the MAPK inhibitor.
In conclusion, our study reveals that targeting different anti-apoptotic proteins from the BCL-2 family simultaneously by specific inhibitors leads to profound reduction in AML cell growth and, equally important, their differentiation. The observed pro-apoptotic and pro-differentiating activity of S63845 enhanced by the combination with BCL-2/BAX or MAPK inhibitors provides the rationale for further studies regarding the use of this strategy in AML therapy.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
S63845, ABT-737 and ZVAD-FMK were purchased from Selleck Chemicals (Munich, Germany). BCL-2 inhibitors were dissolved in DMSO and stored as 5 mM stock solutions at −20 °C. RPMI 1640 medium, fetal calf serum and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) were obtained from GIBCO BRL Life Technologies (Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Antibiotic antimycotic solution (AAS), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), Nitroblue tetrazolium, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, PD98059 were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). PrestoBlue™ Cell Viability reagent was acquired from Invitrogen (Life Technologies, Eugene, OR, USA). FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I, propidium iodide (PI)/RNase staining buffer, anti CD11b and anti-CD-14 were obtained from BD Biosciences (BD Biosciences, San Diego, CA, USA). CellEvent™ Caspase 3/7 Green Flow Cytometry Assay kit was purchased from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR, USA). The Hemacolor® Rapid Staining kit was obtained from Merck Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany). RIPA lysis buffer and Halt™ Protease Inhibitor Cocktail were obtained from ThermoScientific (Rockford, IL, USA). The antibody against MCL-1 (cat. #4572), pMAPK (cat. #9101), MAPK (cat. #9102), β-actin (cat. #4970) and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (cat. #7074) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). WesternBright Sirius Western blotting HRP substrate was acquired from Advansta (Menlo Park, CA, USA).
4.2. AML Cell Culture and Treatment
Human acute myeloid leukemia cell lines HL-60 (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) and ML-1 (ECACC, Salisbury, UK) were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mM L-glutamine and AAS containing 20 units of penicillin, 20 mg streptomycin and 0.05 mg amphotericin B. The cells were passaged every 2–3 days. The cells grew exponentially at 37 °C in an atmosphere of 5% CO
2 in air (HERAcell incubator, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Leukemic cells were seeded in 12-, 24- or 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 10
5 cells/mL prior to performing the experiments. For cell viability analysis, HL-60 and ML-1 cells were treated with S63845 at a concentration range of 0.01–10 µM. For subsequent experiments, adequate S63845 concentrations were chosen for each cell line based on the results of the cell viability assay. The concentrations of ABT-737 were chosen based on previous studies [
27]. The BH3 mimetic concentrations were physiologically relevant and could potentially be achieved in vivo. Leukemia cells were treated with a single inhibitor or simultaneous combination of S63845 and ABT-737 for 24 h or 48 h. The control treatments consisted of untreated and DMSO-treated HL-60 and ML-1 cells. The final concentration of DMSO did not influence the analyzed parameters, and no significant differences in cell response to this diluent were observed; therefore, the data obtained from DMSO-treated cells were considered as control. To study the effects of S63845 in combination with MAPK inhibitor, the cells were pretreated with 50 µM of PD98059 for 1 h, then treated with S63845 for an additional 24 h or 48 h. In some experiments, AML cells were pre-incubated with a pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK for 1 h.
4.3. Analysis of AML Cell Viability and Count
Cell viability was assessed using the PrestoBlue reagent (PB) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. After 48 h exposure of HL-60 and ML-1 cells to BCL-2 and/or MAPK inhibitors, 11 μL of PB solution was added to the wells containing 100 μL of cell suspension, and the plate was incubated in darkness for 60 min at 37 °C. The fluorescence of resorufin was measured using TECAN Infinite F200 PRO plate reader with excitation and emission wavelengths set at 535 nm and 595 nm, respectively. Cell viability was expressed as a percentage relative to control. The IC50 (half-maximal inhibitory concentration) values for S63845 were calculated from the concentration–response curves.
The number of HL-60 and ML-1 cells was analyzed using a Z2 Coulter counter (Beckman Coulter, INC, Fullerton, CA, USA), as previously described in detail [
50]. The cell counts were determined at a range of 476–2432 fL using Z2 AccuComp software version 3.0 (Beckman Coulter INC, USA).
4.4. Morphological Observation of AML Cells
To assess the morphology changes in HL-60 and ML-1 cells, staining using Hemacolor was performed. Briefly, approximately 1 × 105 cells were resuspended in 0.2 mL PBS. The cell suspension was added to the cytospin chamber and centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 6 min at 4 °C. After air drying, the prepared cytospins were fixed in methanol for 15 min at room temperature. Then, each slide was stained with the Hemacolor® Rapid Staining Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cellular morphology was analyzed using a light microscope under 100× magnification (AXIO Scope.A1 microscope, Carl Zeiss Microscopy, Oberkochen, Germany).
4.5. Annexin V-FITC/PI Assay
To determine the induction of apoptosis, dual staining of HL-60 and ML-1 cells with fluoresceinated annexin V (annexin V-FITC) and propidium iodide (PI) was performed using FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I. After 24 h and 48 h of cell incubation with the tested agents, the cells were harvested and then washed twice with cold PBS. The cell pellets were resuspended in 100 μL of binding buffer and 5 µL of annexin V-FITC, and 5 μL of PI staining solution was added to the cell suspension. Cells were incubated in the dark for 15 min at room temperature. Following the incubation, 400 μL of the binding buffer was added to each tube, and cells were analyzed using the FACS Calibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). Two-parameter fluorescence dot plots were generated by analyzing at least 1 × 104 cells. The percentages of annexin V positive/PI negative cells and annexin V positive/PI positive cells were determined using WinMDI software version 2.8.
4.6. Nitroblue Tetrazolium Assay
Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) was used to estimate intracellular O2− as a measure of differentiation of HL-60 and ML-1 cells. For this assay, AML cells were seeded in a 96-well plate in a 100 µL final volume of cell suspension. At the indicated time point, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) at a final concentration of 100 nM was added to each well to stimulate the cells. After cell incubation with PMA at 37 °C for 60 min, 10 μL of NBT solution (10 mg/mL) was added to each well, and the cells were further incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. Following the incubation period, the cytospin slides were prepared. A light microscope was used to identify NBT-positive cells, which contained intracellular blue formazan deposits. A total of 200 cells on each slide were counted, and the percentage of NBT-positive cells was calculated for each group.
4.7. Flow Cytometric Detection of CD11b and CD14 Expression
Quantitative immunofluorescence measurements were performed to determine the expression of myeloid differentiation markers CD11b and CD14 on HL-60 and ML-1 cells, respectively. AML cells were centrifuged, washed and resuspended in 100 μL of PBS. Then, 5 μL of either APC-conjugated CD11b antibody or FITC-conjugated anti-human CD14 antibody was added to the suspension, followed by incubation in the dark for 30 min at room temperature. After the incubation period, 400 μL of PBS was added to each tube, and the cells were centrifuged. Finally, the cells were resuspended in 500 μL of PBS and measured in the FACSCalibur flow cytometer. One-parameter fluorescence histograms were generated by analyzing at least 1 × 104 cells in each sample. The percentages of CD11b-positive cells and CD14-positive cells were determined using BD CellQuest Pro software.
4.8. Preparation of Cell Lysates and Western Blot Analysis
Whole cell lysates were prepared using the RIPA lysis buffer supplemented with protease inhibitors. HL-60 and ML-1 cells were washed with ice-cold PBS, lysed on ice for 15 min and cleared by centrifugation at 15,000× g at 4 °C for 15 min. The protein content was determined via Bradford protein assay using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. Proteins (30 μg from each experimental group) were separated by Mini-PROTEAN® TGX™ gels (Cat. No. 456–1093; BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) using SDS-PAGE (BioRad Mini-PROTEAN II Electrophoresis Cell), followed by transferring them to PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked in 5% BSA/TBST and probed with anti-MCL-1 primary antibody (1:1000 in blocking buffer) at 4 °C overnight. Next, the membranes were incubated with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody diluted to 1:1000. The bands were detected by chemiluminescence using the WesternBright Sirius Western blotting HRP substrate (Advansta, Menlo Park, CA, USA), visualized using a ChemiDoc-It Imaging System (UVP, LLC, Cambridge, UK) and quantified using ImageJ analysis software (US National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The blots were then stripped and probed for anti-β-actin used as an internal control for the samples.
4.9. Statistical Analysis and Calculation of Synergy
The obtained results were confirmed by three independent experiments, and in the case of cell viability and count analysis, each experiment was performed in triplicate and duplicate, respectively. All data are shown as the mean value ±the standard deviation (SD). STATISTICA 10 software (StatSoft, Kraków, Poland) was used to perform statistical analyses. The statistical significance of the data was evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s honestly significant difference multiple range test. A
p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The agent interactions were analyzed using CompuSyn software version 1.0 (ComboSyn Inc., Paramus, NJ, USA). The combination index (CI) values were calculated according to the Chou and Talalay mathematical model for drug interactions [
51]. CI < 1.0 represents synergy, CI = 1.0 indicates an additive effect, whereas CI > 1.0 implies antagonism.