Propolis Ethanolic Extract Attenuates D-gal-induced C2C12 Cell Injury by Modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and p38/p53 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
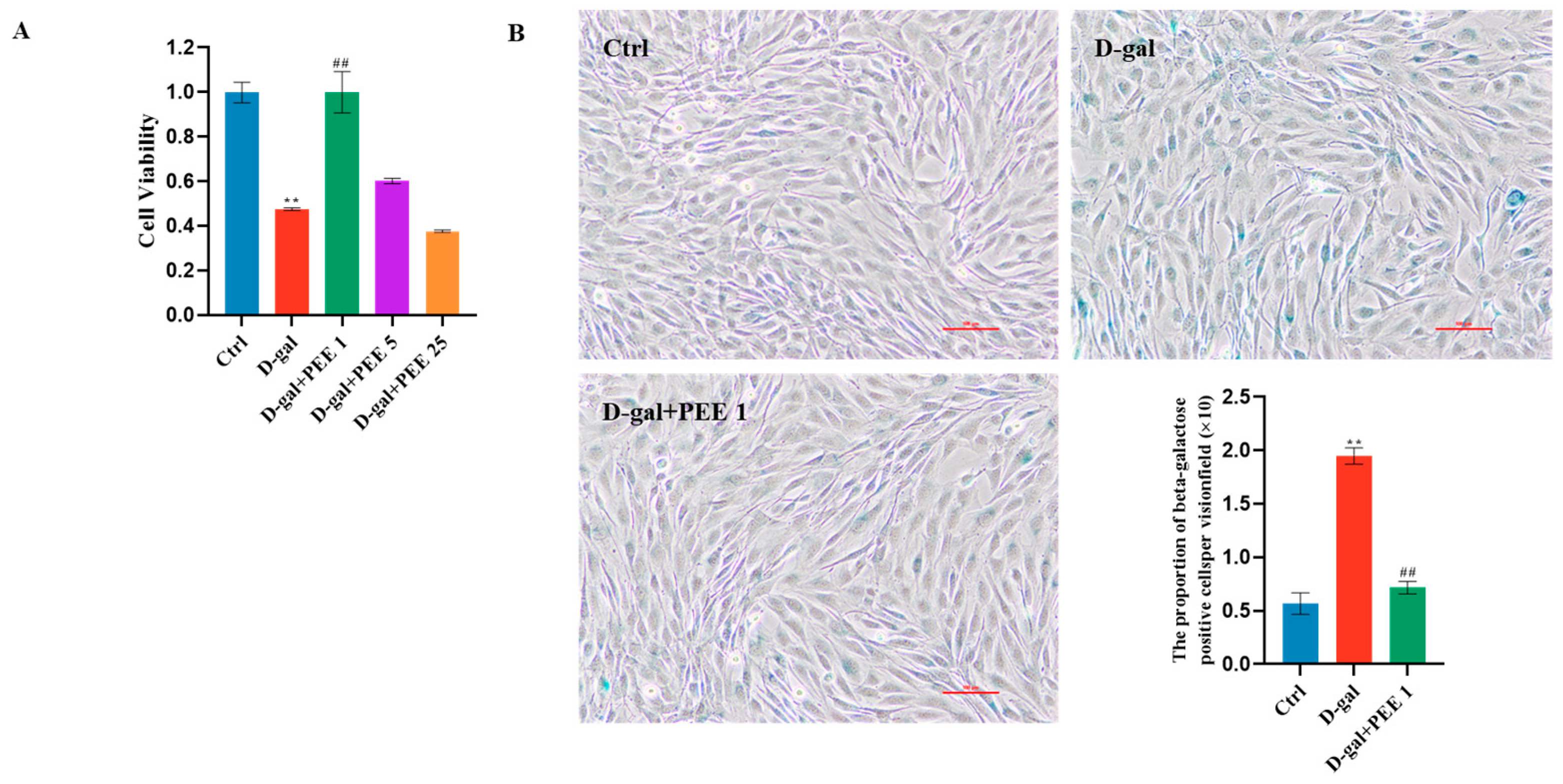
2.1. Effect of PEE on D-Gal-Induced C2C12 Cell Viability and Senescence
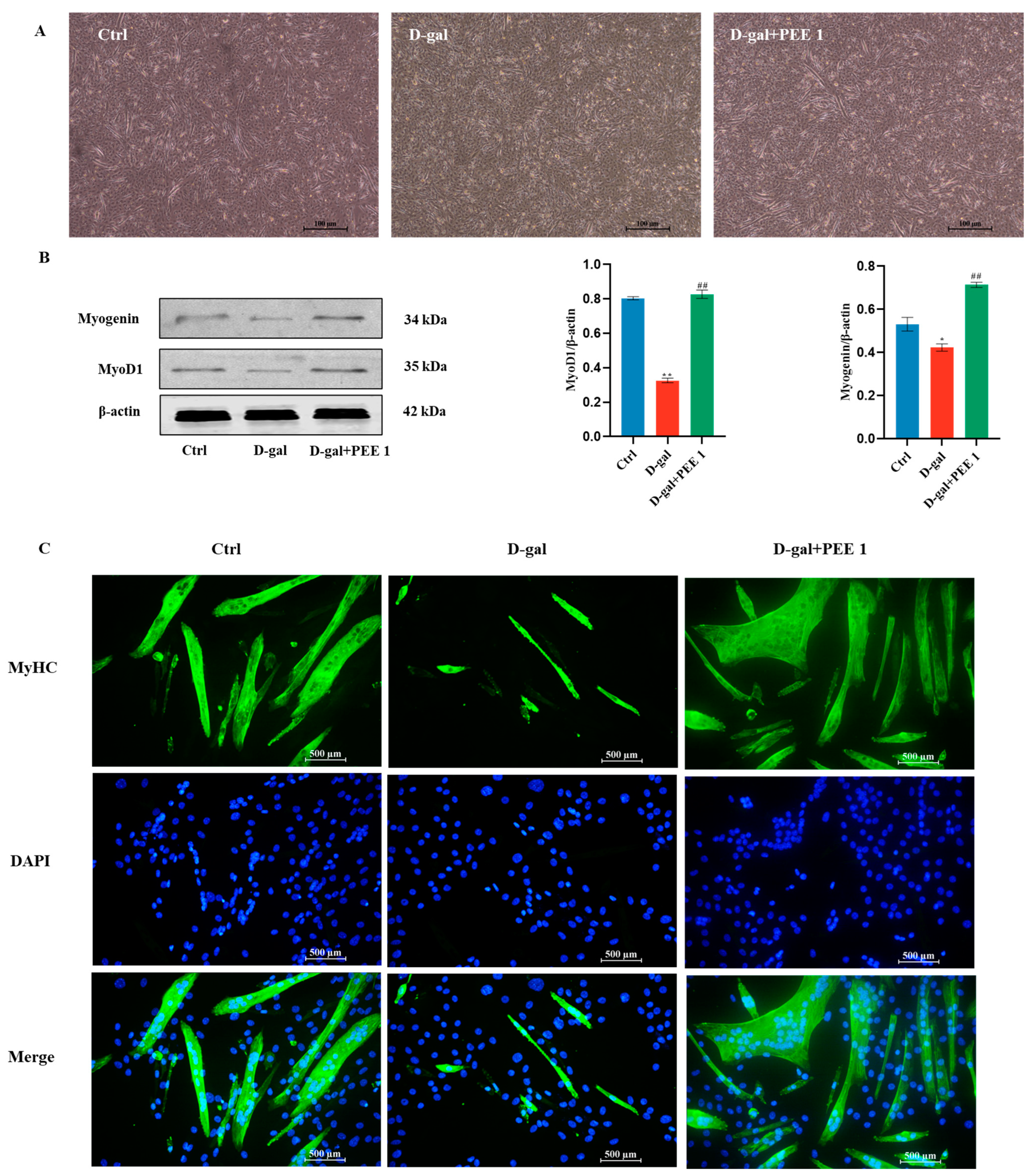
2.2. Effect of PEE on Differentiation Ability of D-Gal-Treated C2C12 Cells
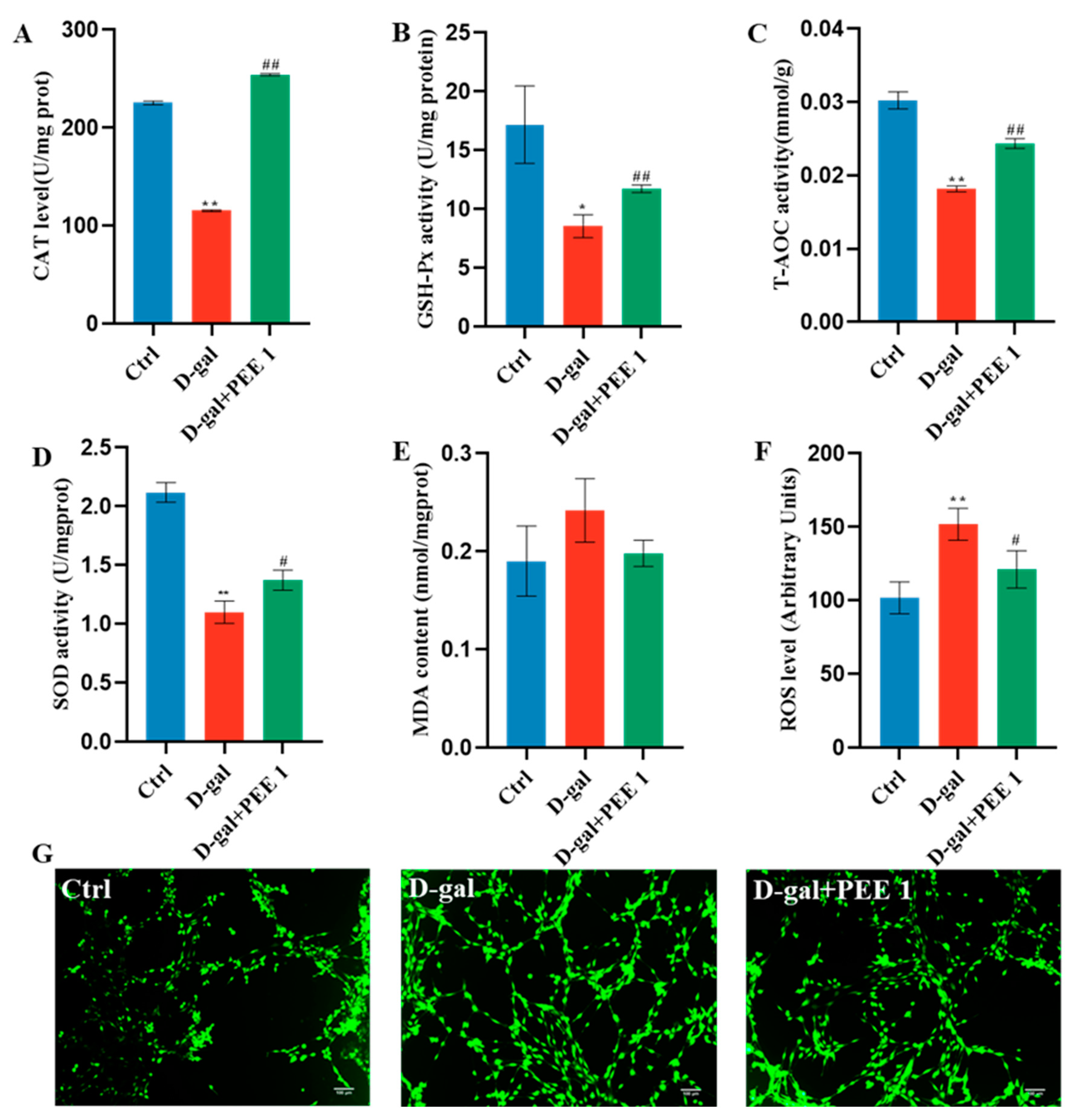
2.3. PEE Reduces Oxidative Stress in D-Gal-Treated C2C12 Cells
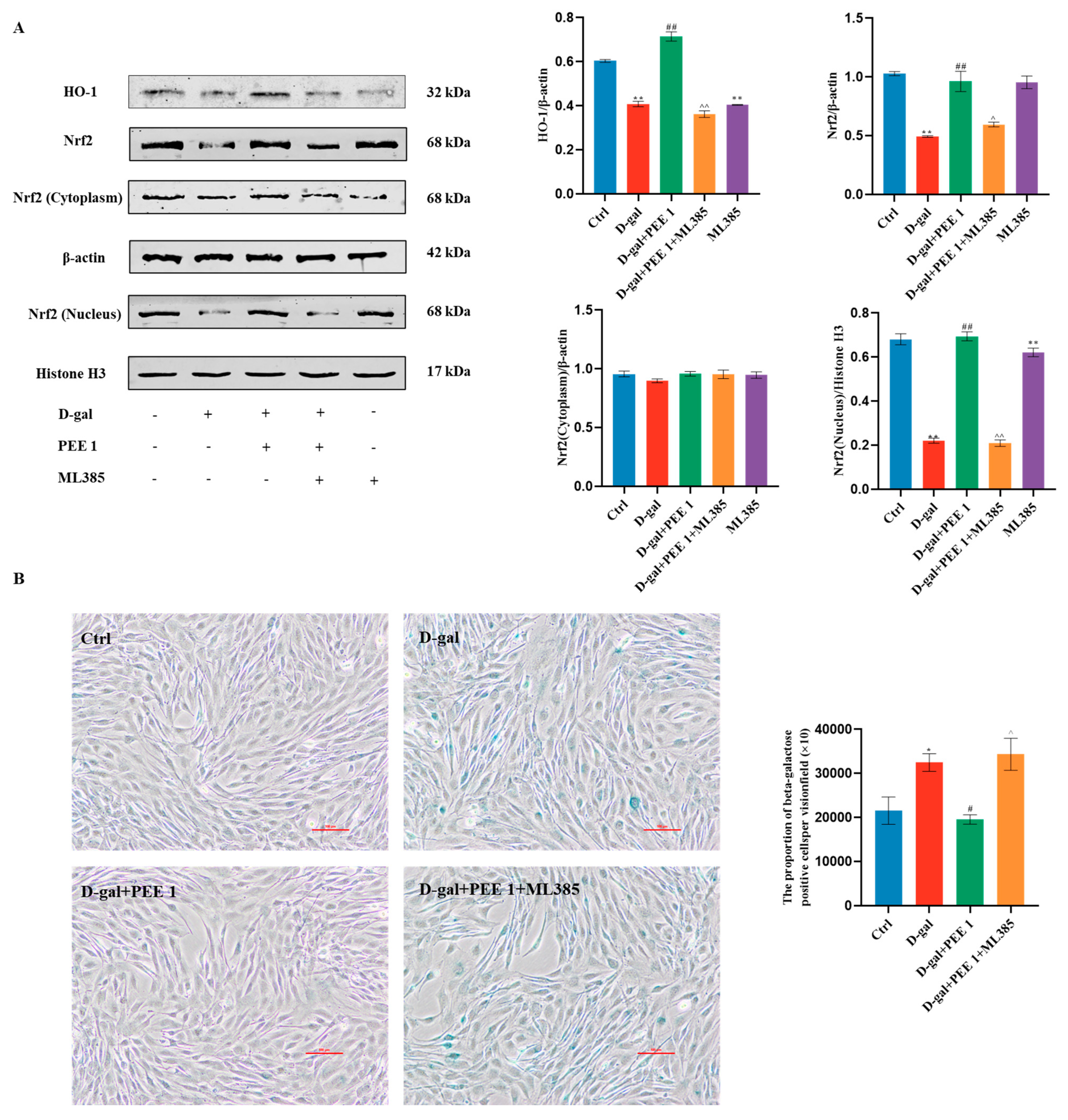
2.4. PEE Attenuates D-Gal-Induced C2C12 Cell Injury by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway
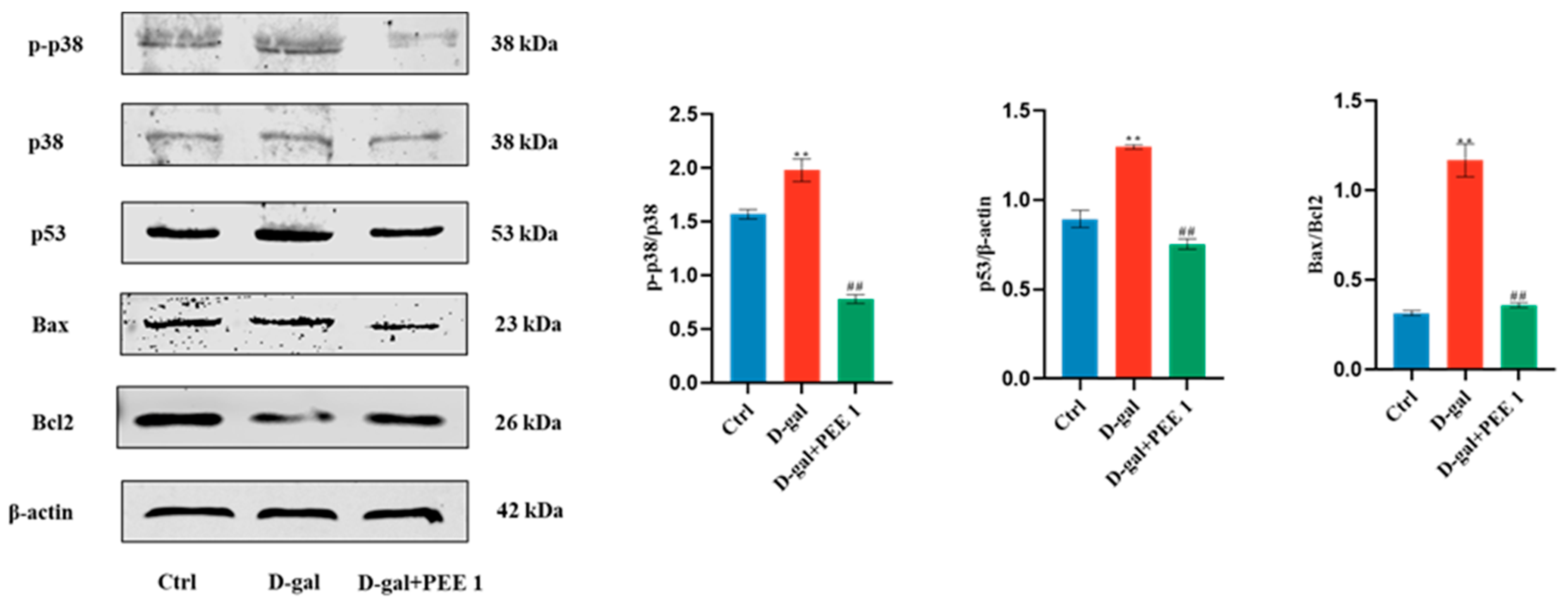
2.5. PEE Inhibits D-Gal-Induced Apoptosis in C2C12 Cells through p38/p53 Pathway
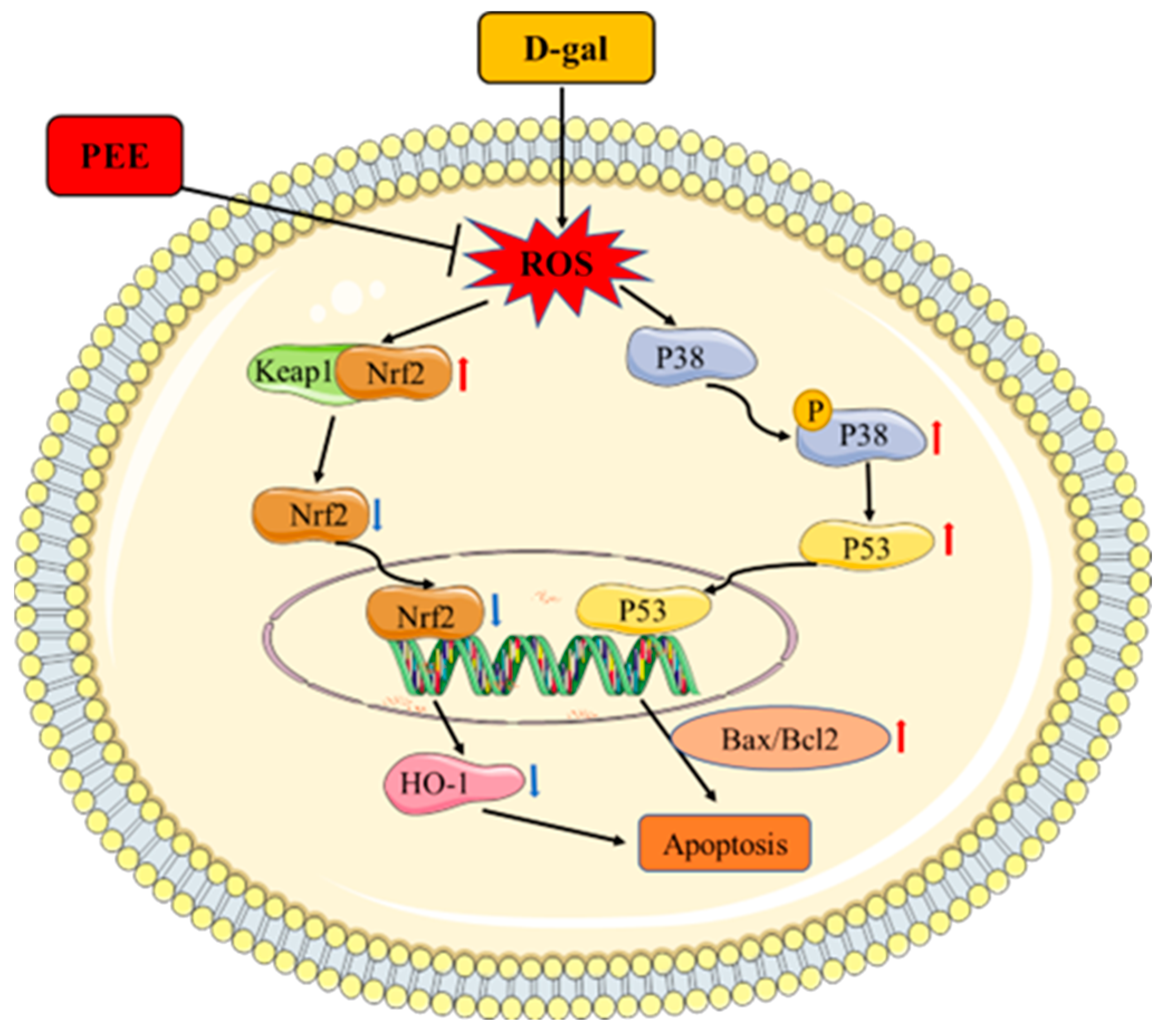
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. CCK-8 Assay for Cell Viability
4.4. SA-β-Gal Staining
4.5. Determination of Antioxidant Activity in C2C12 Cells
4.6. Measurement of ROS Content
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKendry, J.; Currier, B.S.; Lim, C.; Mcleod, J.C.; Thomas, A.C.; Phillips, S.M. Nutritional supplements to support resistance exercise in countering the sarcopenia of aging. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Yadav, S.S.; Singh, S.; Dabur, R. Natural products: Potential therapeutic agents to prevent skeletal muscle atrophy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 925, 174995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.M.; Al-Zougbi, A.; Bodine, S.C.; Adams, C.M. Skeletal muscle atrophy: Discovery of mechanisms and potential therapies. Physiology 2019, 34, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haus, J.M.; Carrithers, J.A.; Trappe, S.W.; Trappe, T.A. Collagen, cross-linking, and advanced glycation end products in aging human skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Yang, R.S.; Sheu, M.L.; Chan, D.C.; Yang, T.H.; Tsai, K.S.; Chiang, C.K.; Liu, S.H. Advanced glycation end-products induce skeletal muscle atrophy and dysfunction in diabetic mice via a RAGE-mediated, AMPK-down-regulated, Akt pathway. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Apitherapy for Age-Related Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction (Sarcopenia): A Review on the Effects of Royal Jelly, Propolis, and Bee Pollen. Foods 2020, 9, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Bao, M.; Li, D.; Li, Y.M. Advanced glycation in D-galactose induced mouse aging model. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1999, 108, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Mokhosoev, I.M.; Mel’nikova, T.I.; Porozov, Y.B.; Terentiev, A.A. Oxidative stress and advanced lipoxidation and glycation end products (ALEs and AGEs) in aging and age-related diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3085756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossena, S.; Marino, A. Cellular oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Jing, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yong, J.; Wang, Y. The positive effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 upon the hematopoietic microenvironment in a D-Galactose-induced aged rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Lin, Q.; Cai, J.; Tang, L.; Liang, Y. Active Peptide KF-8 from Rice Bran Attenuates Oxidative Stress in a Mouse Model of Aging Induced by d-Galactose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12271–12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, W.; Liao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Guo, A.; Yu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J. MICU3 regulates mitochondrial Ca2+-dependent antioxidant response in skeletal muscle aging. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Wu, T.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Ota, T.; Fu, Z. Protective effects of astaxanthin on a combination of D-galactose and jet lag-induced aging model in mice. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Zheng, L.; Guo, H.; Jiang, Y. Metabolomics reveals that alcohol extract of propolis alleviates D-gal-induced skeletal muscle senescence in mice. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, N. Ampelopsin attenuates the atrophy of skeletal muscle from d-gal-induced aging rats through activating AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling cascade. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.Y.; Al-Salami, H.; Dass, C.R. C2C12 cell model: Its role in understanding of insulin resistance at the molecular level and pharmaceutical development at the preclinical stage. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1667–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, V.D.; Punch, V.G.; Kawabe, Y.-i.; Jones, A.E.; Palidwor, G.A.; Porter, C.J.; Cross, J.W.; Carvajal, J.J.; Kockx, C.E.; van IJcken, W.F. Transcriptional dominance of Pax7 in adult myogenesis is due to high-affinity recognition of homeodomain motifs. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanou, N.; Gailly, P. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and regeneration: Interplay between the myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) pathways. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4117–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ning, Z.; Ye, Z.; Li, Q.X.; Hu, C.; Wang, C. Mdfi promotes C2C12 cell differentiation and positively modulates fast-to-slow-twitch muscle fiber transformation. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 605875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Inoue, R.; Inoue, H.; Suzuki, N. Preparation and antioxidant properties of water extract of propolis. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonska, M.; Bronikowska, J.; Pietsz, G.; Czuba, Z.; Scheller, S.; Krol, W. Effects of ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) and its flavones on inducible gene expression in J774A. 1 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisard, S.; Le Ray, A.-M.; Gatto, J.; Aumond, M.-C.; Blanchard, P.; Derbré, S.; Flurin, C.; Richomme, P. Chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-AGEs activities of a French poplar type propolis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisard, S.; Shahali, Y.; Aumond, M.C.; Derbré, S.; Blanchard, P.; Dadar, M.; Le Ray, A.M.; Richomme, P. Anti-AGE activity of poplar-type propolis: Mechanism of action of main phenolic compounds. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 55, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzioni, D.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Fantone, S.; Tossetta, G. NRF2 modulation in TRAMP mice: An in vivo model of prostate cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Montanari, E.; Marzioni, D.; Goteri, G. Role of NRF2 in Ovarian Cancer. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Marzioni, D. Natural and synthetic compounds in Ovarian Cancer: A focus on NRF2/KEAP1 pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Marzioni, D. Targeting the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway in cervical and endometrial cancers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 941, 175503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, H. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids from Propolis via Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways. Foods 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Shi, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z. Non-esterified fatty acids activate the ROS–p38–p53/Nrf2 signaling pathway to induce bovine hepatocyte apoptosis in vitro. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-N.; Fan, Z.; Lyu, A.-K.; Wu, J.; Guo, A.; Yang, Y.-F.; Chen, J.-L.; Xiao, Q. Effect of sarcolipin-mediated cell transdifferentiation in sarcopenia-associated skeletal muscle fibrosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 389, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustogiannis, A.; Philippou, A.; Taso, O.; Zevolis, E.; Pappa, M.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Koutsilieris, M. The effects of muscle cell aging on myogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, Y.; Jia, P.; Han, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Zheng, Y. Early-senescent bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote C2C12 cell myogenic differentiation by preventing the nuclear translocation of FOXO3. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Morton, A.B.; Ahn, B.; Smuder, A.J. Redox control of skeletal muscle atrophy. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 98, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia, E.; Soto, V.; Ortiz-Vega, K.M.; Zarco-Márquez, G.; Molina-Jijón, E.; Cristóbal-García, M.; Santamaría, J.; García-Niño, W.R.; Correa, F.; Zazueta, C. Curcumin induces Nrf2 nuclear translocation and prevents glomerular hypertension, hyperfiltration, oxidant stress, and the decrease in antioxidant enzymes in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 269039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępkowski, T.M.; Kruszewski, M.K. Molecular cross-talk between the NRF2/KEAP1 signaling pathway, autophagy, and apoptosis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, M.; Jiao, D.; Yao, B.; Xu, K.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Long, M. Astaxanthin protects ochratoxin a-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in the heart via the Nrf2 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 7639109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Guo, M.; Xu, S. TBBPA induces inflammation, apoptosis, and necrosis of skeletal muscle in mice through the ROS/Nrf2/TNF-α signaling pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 317, 120745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, M.; Hong, J.; Atieno, N.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Davidson, C.J.; Abu-Rmaileh, N.; Richardson, R.S.; Gomes, A.V.; Hoidal, J.R.; Rajasekaran, N.S. Nrf2 deficiency promotes apoptosis and impairs PAX7/MyoD expression in aging skeletal muscle cells. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 71, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, D.; Yu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Song, L. hPMSCs protects against D-galactose-induced oxidative damage of CD4+ T cells through activating Akt-mediated Nrf2 antioxidant signaling. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Kee, H.J.; Bai, L.; Kim, M.-K.; Kee, S.-J.; Jeong, M.H. Selective HDAC8 inhibition attenuates isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis via p38 MAPK pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 677757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Li, L. Non-esterified fatty acid-induced reactive oxygen species mediated granulosa cells apoptosis is regulated by nrf2/p53 signaling pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Bian, H.-J.; Bao, J.-K. Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human melanoma A375 cells through a mitochondria-mediated ROS–p38–p53 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2009, 275, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, X.; Li, Q.; Sawaya, A.; Le Leu, R.K.; Conlon, M.A.; Wu, L.; Hu, F. Propolis from Different Geographic Origins Decreases Intestinal Inflammation and Bacteroides spp. Populations in a Model of DSS-Induced Colitis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Ping, S.; Ma, Q.; Chen, X.; Xuan, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, F. Anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol extracts of Chinese propolis and buds from poplar (Populus× canadensis). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibodies | Cat No. | Company | Source | Dilution Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | l102 | Bioworld Technology, Inc, Nanjing, China | Rabbit | 1:20,000 |
| HO-1 | A1346 | ABclonal Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| Nrf-2 | A1820 | ABclonal Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| Histone H3 | A2348 | ABclonal Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| Myogenin | A17427 | ABclonal Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| Bcl-2 | WL01556 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | Rabbit | 1:500 |
| Bax | WL01637 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | Rabbit | 1:500 |
| p38 | WL00764 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | Rabbit | 1:500 |
| p-p38 | WLP1576 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | Rabbit | 1:500 |
| p53 | WL01919 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | Rabbit | 1:500 |
| MyoD1 | WL04662 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | Rabbit | 1:500 |
| MHC | MF20 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Iowa City, IA, USA | Mouse | 1:20 |
| IgG H&L/FITC | bs-0296G-FITC | Bioss Antibodies, Beijing, China | Goat | 1:100 |
| IRDye®800CW | C926-32211 | LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA | Goat | 1:20,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, S.; Zhao, H.; Guo, H.; Feng, W.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, Y. Propolis Ethanolic Extract Attenuates D-gal-induced C2C12 Cell Injury by Modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and p38/p53 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076408
Tian S, Zhao H, Guo H, Feng W, Jiang C, Jiang Y. Propolis Ethanolic Extract Attenuates D-gal-induced C2C12 Cell Injury by Modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and p38/p53 Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076408
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Songhao, Huiting Zhao, Hongru Guo, Wei Feng, Conglin Jiang, and Yusuo Jiang. 2023. "Propolis Ethanolic Extract Attenuates D-gal-induced C2C12 Cell Injury by Modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and p38/p53 Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076408
APA StyleTian, S., Zhao, H., Guo, H., Feng, W., Jiang, C., & Jiang, Y. (2023). Propolis Ethanolic Extract Attenuates D-gal-induced C2C12 Cell Injury by Modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and p38/p53 Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076408






