ABCB1 and ABCC1 Function during TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Relationship between Multidrug Resistance and Tumor Progression
Abstract
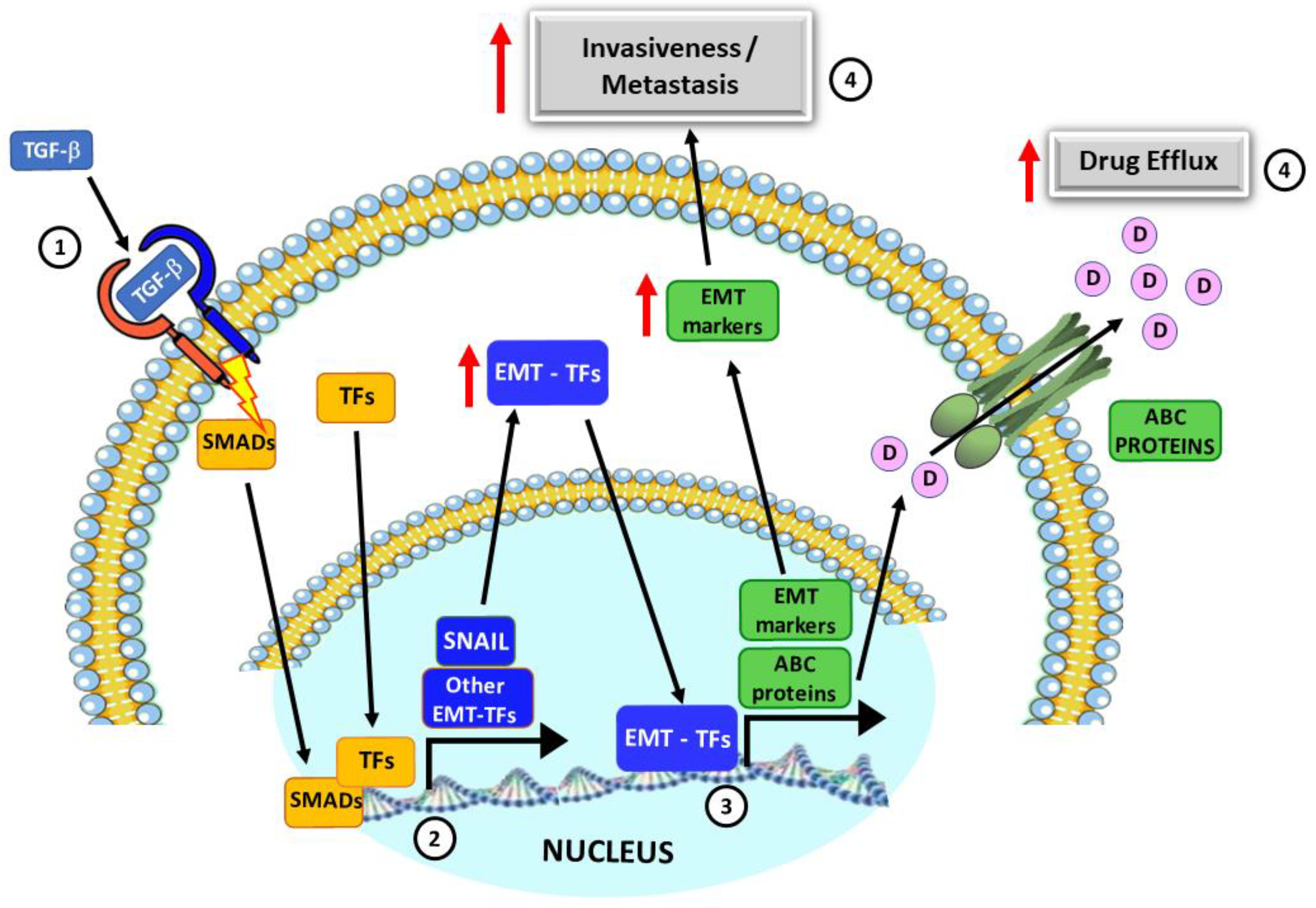
1. Introduction
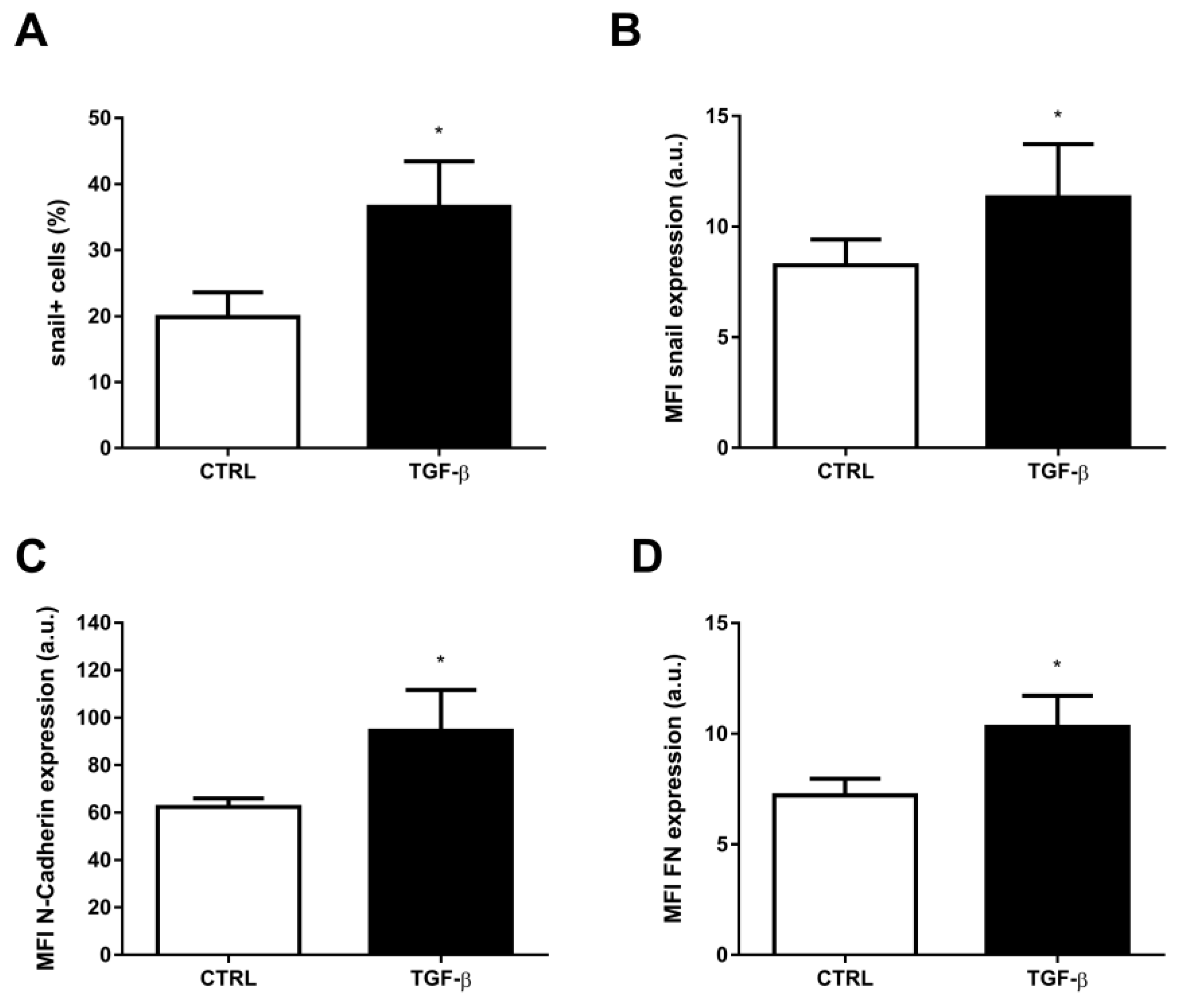
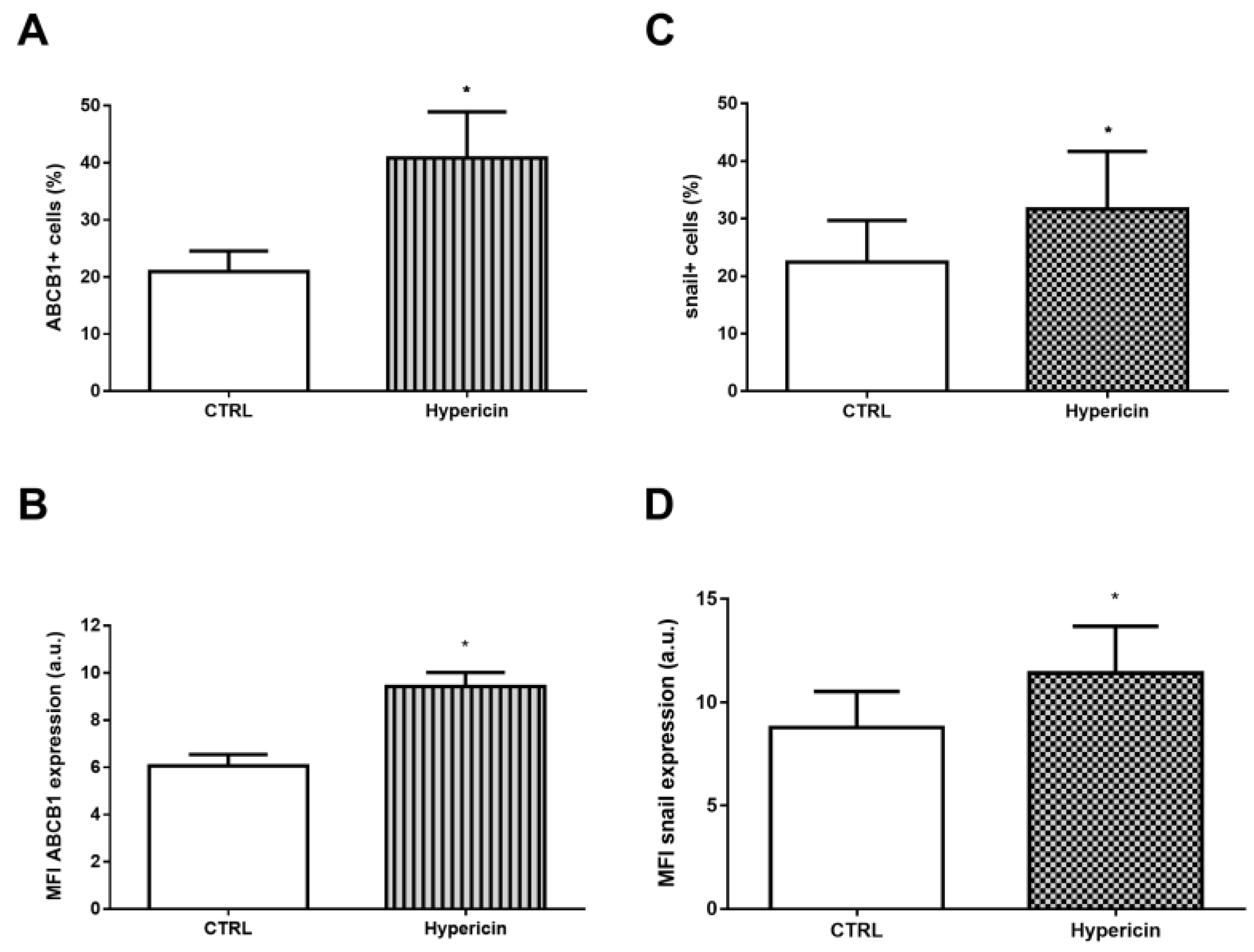
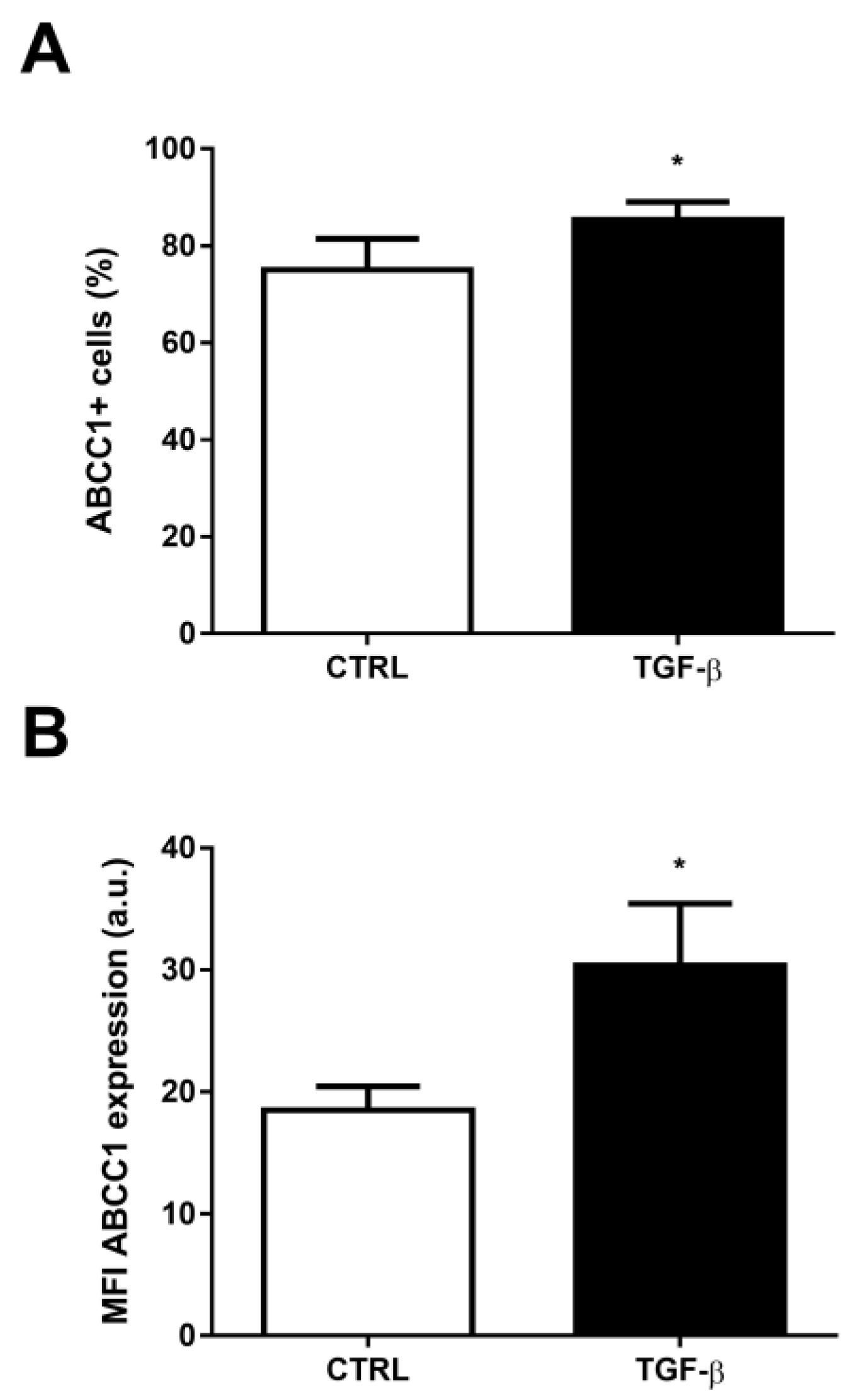
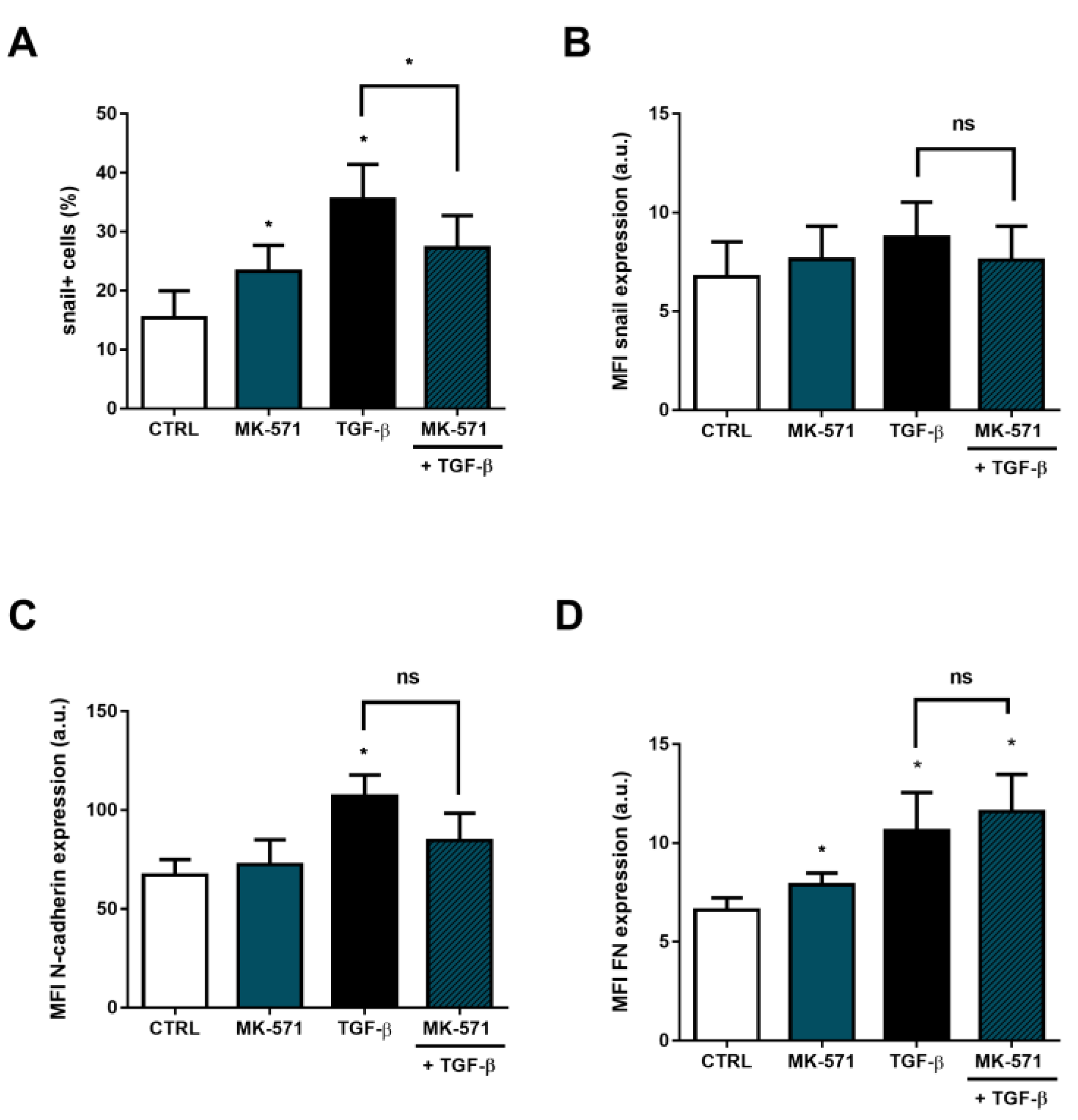
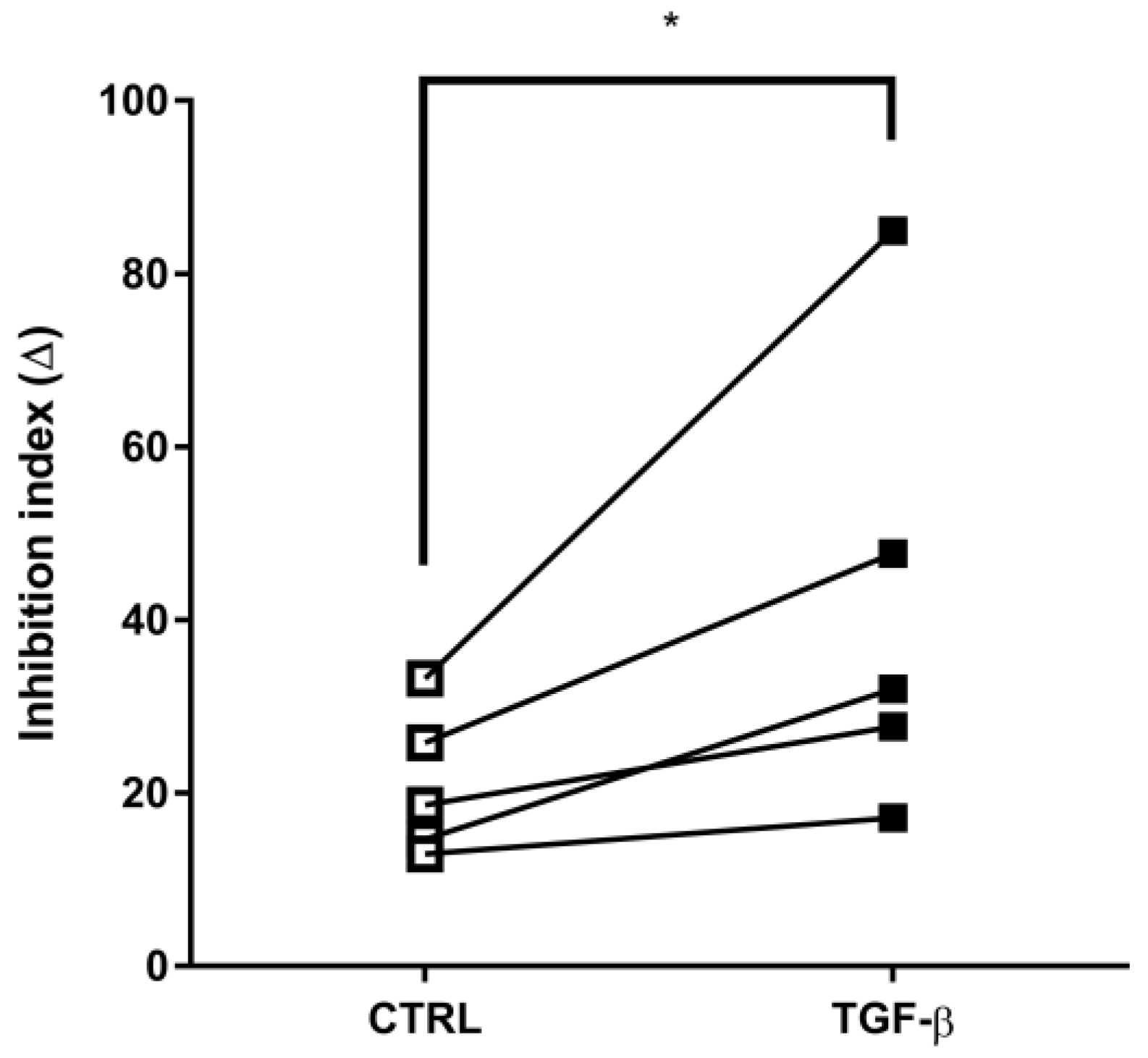
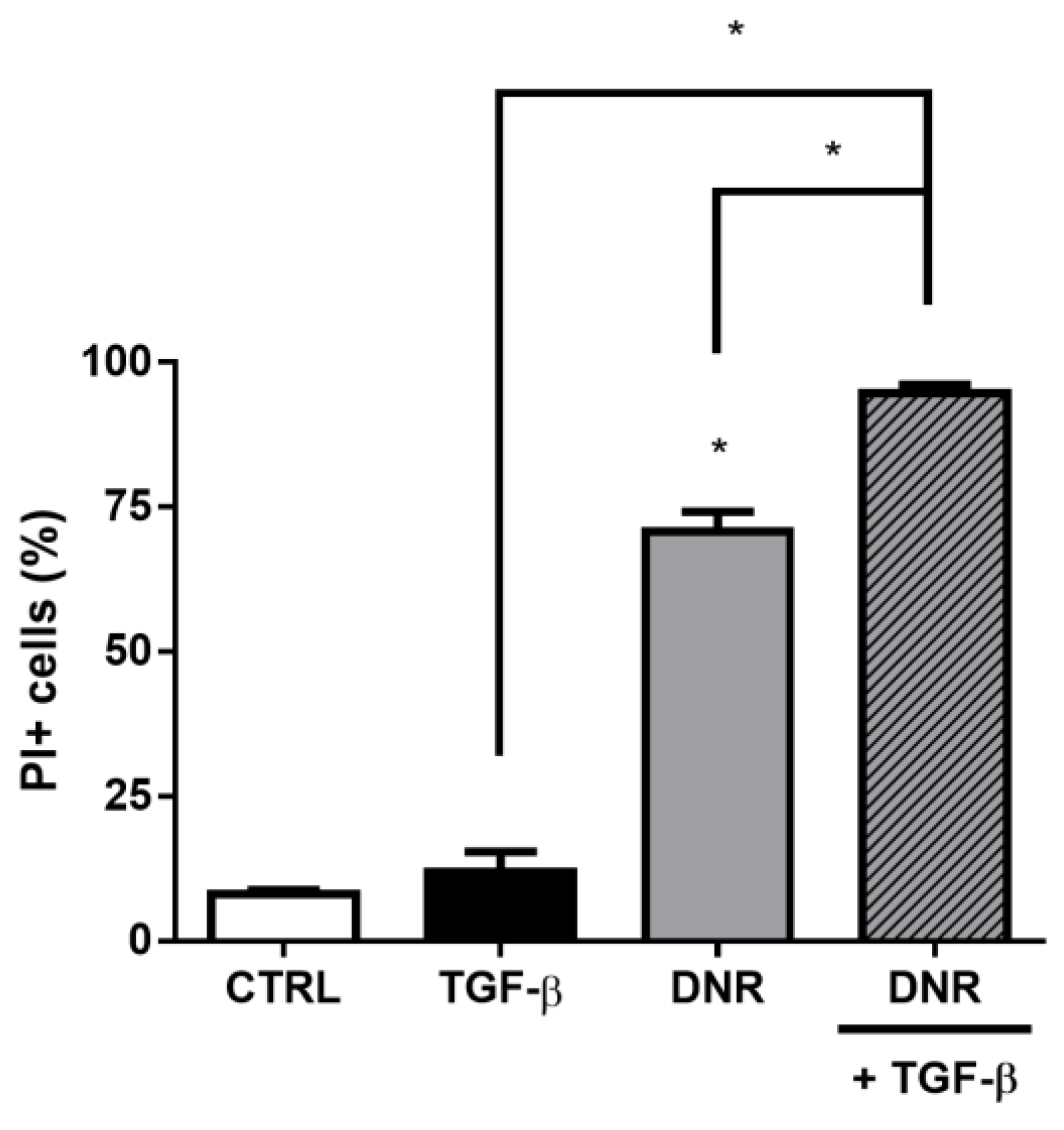
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Subculture
4.2. Induction of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
4.3. Induction of ABCB1 Transporter Expression
4.4. Antibody Labeling
4.5. ABCB1 and ABCC1-Mediated Efflux Assay
4.6. Assessment of Cellular Viability
4.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ABCB1 | subfamily B, member 1 |
| ABCC1 | subfamily C, member 1 |
| CSC | cancer stem cells |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| FN | fibronectin |
| GSH | reduced glutathione |
| GSSG | oxidized glutathione |
| MDR | multidrug resistance |
| MFI | median fluorescence intensities |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SP | side population |
References
- INCA. O Que é Cancer? Available online: https://www.gov.br/inca/pt-br/assuntos/cancer/o-que-e-cancer/o-que-e-cancer (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ritchie, H.S.; Spooner, F.; Roser, M. Causes of Death. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/causes-of-death (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Globocan. Cancer Fact Sheets. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriithi, W.; Macharia, L.W.; Heming, C.P.; Echevarria, J.L.; Nyachieo, A.; Filho, P.N.; Neto, V.M. ABC transporters and the hallmarks of cancer: Roles in cancer aggressiveness beyond multidrug resistance. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Annilo, T. Evolution of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily in vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet 2005, 6, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ling, V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 455, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.P.; Bhardwaj, G.; Gerlach, J.H.; Mackie, J.E.; Grant, C.E.; Almquist, K.C.; Stewart, A.J.; Kurz, E.U.; Duncan, A.M.; Deeley, R.G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science 1992, 258, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, E.M.; Deeley, R.G.; Cole, S.P. Multidrug resistance proteins: Role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2005, 204, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.P. Targeting multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1, ABCC1): Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaut, F.; Tsuruo, T.; Hamada, H.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Willingham, M.C. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7735–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Vilas-Boas, V.; Carmo, H.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carvalho, F.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Remiao, F. Modulation of P-glycoprotein efflux pump: Induction and activation as a therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 149, 1–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, K.M.; Haber, M.; Fletcher, J.I. Targeting multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1)-expressing cancers: Beyond pharmacological inhibition. Drug Resist. Update 2021, 59, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, S.; Gorgi Valokala, M.; Mosaffa, F.; Zirak, M.R.; Zamani, P.; Behravan, J. Crosstalk in cancer resistance and metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 132, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, J.S.D.; Santos, M.; da Costa, K.M.; Freire-de-Lima, C.G.; Morrot, A.; Previato, J.O.; Previato, L.M.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Freire-de-Lima, L. Increased Expression of the Pathological O-glycosylated Form of Oncofetal Fibronectin in the Multidrug Resistance Phenotype of Cancer Cells. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2023, 118, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Panda, C.K.; Nandi, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A. An insight into metastasis: Random or evolving paradigms? Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, V.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chikkaputtaiah, C.; Hazra, S.; Pal, M. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A study from a structure, dynamics, and functional perspective. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 14535–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelford, C.B.; Dagnino, L.; Di Guglielmo, G.M. Transforming growth factor-beta in tumour development. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 991612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrallo-Gimeno, A.; Nieto, M.A. The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: Implications in development and cancer. Development 2005, 132, 3151–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasarathy, A.; Phadke, D.; Mav, D.; Shah, R.R.; Wade, P.A. The transcription factors Snail and Slug activate the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturi, V.; Enroth, S.; Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. Genome-wide binding of transcription factor ZEB1 in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 7113–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheeva, S.A.; Mikheev, A.M.; Petit, A.; Beyer, R.; Oxford, R.G.; Khorasani, L.; Maxwell, J.P.; Glackin, C.A.; Wakimoto, H.; Gonzalez-Herrero, I.; et al. TWIST1 promotes invasion through mesenchymal change in human glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, A.K.; Wilgenbus, P.; Dahl, U.; Semb, H.; Christofori, G. A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from adenoma to carcinoma. Nature 1998, 392, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, A.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Rodrigo, I.; Locascio, A.; Blanco, M.J.; del Barrio, M.G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufhold, S.; Bonavida, B. Central role of Snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer: A target for therapeutic intervention. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire-de-Lima, L.; Gelfenbeyn, K.; Ding, Y.; Mandel, U.; Clausen, H.; Handa, K.; Hakomori, S.I. Involvement of O-glycosylation defining oncofetal fibronectin in epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17690–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo-Saito, C.; Shirako, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Kawakami, Y. Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ao, X.; Chen, Z. Knockdown of Snail, a novel zinc finger transcription factor, via RNA interference increases A549 cell sensitivity to cisplatin via JNK/mitochondrial pathway. Lung Cancer 2008, 62, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslehurst, A.M.; Koti, M.; Dharsee, M.; Nuin, P.; Evans, K.; Geraci, J.; Childs, T.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Weberpals, J.; et al. EMT transcription factors snail and slug directly contribute to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurrey, N.K.; Jalgaonkar, S.P.; Joglekar, A.V.; Ghanate, A.D.; Chaskar, P.D.; Doiphode, R.Y.; Bapat, S.A. Snail and slug mediate radioresistance and chemoresistance by antagonizing p53-mediated apoptosis and acquiring a stem-like phenotype in ovarian cancer cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, T.; Zhao, G.; Zha, Y.; Yang, M. Expression of snail in pancreatic cancer promotes metastasis and chemoresistance. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 141, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, S.M.; Fu, S.; Mao, X.; Yopp, A.; Gunn, M.D.; Randolph, G.J.; Bromberg, J.S. FTY720 stimulates multidrug transporter- and cysteinyl leukotriene-dependent T cell chemotaxis to lymph nodes. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunk, C.E.; Pappas, J.J.; Lye, P.; Kibschull, M.; Javam, M.; Bloise, E.; Lye, S.J.; Szyf, M.; Matthews, S.G. P-Glycoprotein (P-gp)/ABCB1 plays a functional role in extravillous trophoblast (EVT) invasion and is decreased in the pre-eclamptic placenta. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5378–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landreville, S.; Agapova, O.A.; Kneass, Z.T.; Salesse, C.; Harbour, J.W. ABCB1 identifies a subpopulation of uveal melanoma cells with high metastatic propensity. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2011, 24, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Q.; Xu, J.D.; Wang, W.J.; Cao, X.X.; Chen, Q.; Tang, F.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, X.P.; Xu, Z.D. Twist1-mediated adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluesener, H.J.; Meyermann, R. Spontaneous multidrug transport in human glioma cells is regulated by transforming growth factors type beta. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 81, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohgu, S.; Yamauchi, A.; Takata, F.; Naito, M.; Tsuruo, T.; Higuchi, S.; Sawada, Y.; Kataoka, Y. Transforming growth factor-beta1 upregulates the tight junction and P-glycoprotein of brain microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 24, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques da Fonseca, L.; Jacques da Silva, L.R.; Santos Dos Reis, J.; Rodrigues da Costa Santos, M.A.; de Sousa Chaves, V.; Monteiro da Costa, K.; Sa-Diniz, J.N.; Freire de Lima, C.G.; Morrot, A.; Nunes Franklim, T.; et al. Piperine Inhibits TGF-beta Signaling Pathways and Disrupts EMT-Related Events in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Medicines 2020, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, C.E.; Tsokos, M.; Bates, S.E.; Fojo, A.T. Increased mdr-1/P-glycoprotein expression after treatment of human colon carcinoma cells with P-glycoprotein antagonists. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 2946–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderle, P.; Niederer, E.; Rubas, W.; Hilgendorf, C.; Spahn-Langguth, H.; Wunderli-Allenspach, H.; Merkle, H.P.; Langguth, P. P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated efflux in Caco-2 cell monolayers: The influence of culturing conditions and drug exposure on P-gp expression levels. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, H. From the Photosensitizer Hypericin to the Photoreceptor Stentorin—The Chemistry of Phenanthroperylene Quinones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1999, 38, 3116–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perloff, M.D.; von Moltke, L.L.; Stormer, E.; Shader, R.I.; Greenblatt, D.J. Saint John’s wort: An in vitro analysis of P-glycoprotein induction due to extended exposure. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.; Palmeira, A.; Carmo, H.; Barbosa, D.J.; Gameiro, M.; Gomes, A.; Paiva, A.M.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.; Bastos Mde, L.; et al. P-glycoprotein induction in Caco-2 cells by newly synthetized thioxanthones prevents paraquat cytotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1783–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.J.; Barecki-Roach, M.; Johnson, W.W. Quantitative characterization of direct P-glycoprotein inhibition by St John’s wort constituents hypericin and hyperforin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, G.; Jaffrezou, J.P. Signaling pathways activated by daunorubicin. Blood 2001, 98, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Wang, L.L.; Di, Y.M.; Xue, C.C.; Duan, W.; Li, C.G.; Li, Y. Substrates and inhibitors of human multidrug resistance associated proteins and the implications in drug development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1981–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Seike, M.; Noro, R.; Kunugi, S.; Kubota, K.; Gemma, A. Prognostic significance of ABCB1 in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, D.H.; Storer, L.C.D.; Liu, J.F.; Jackson, H.K.; Kilday, J.P.; Grundy, R.G.; Kerr, I.D.; Coyle, B. A role for ABCB1 in prognosis, invasion and drug resistance in ependymoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, P.; Wang, X. Expression levels of MRP1, GST-pi, and GSK3beta in ovarian cancer and the relationship with drug resistance and prognosis of patients. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, F.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Lactate-induced MRP1 expression contributes to metabolism-based etoposide resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2020, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivnan, A.; Zakaria, Z.; O’Leary, C.; Kogel, D.; Pokorny, J.L.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Prehn, J.H. Inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) improves chemotherapy drug response in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.Z.; Chan, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, C.D.; Wang, L.H. Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.F.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, C.J.; Huang, M.S.; Liu, Y.P. Reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition contributes to the regain of drug sensitivity in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. PloS ONE 2017, 12, e0180383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.M.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.B.; Deng, S.H.; Han, R.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Xu, Y. The PAX6-ZEB2 axis promotes metastasis and cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer through PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Fonseca, L.M.; da Silva, V.A.; da Costa, K.M.; Dos Reis, J.S.; Previato, J.O.; Previato, L.M.; Freire-de-Lima, L. Resistance to cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells: Effects on the glycophenotype and epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers. Glycoconj. J. 2022, 39, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Ohnuma, S.; Lee, J.W.; An, X.; Dai, C.L.; Lu, Q.S.; Singh, S.; Yang, D.H.; Talele, T.T.; et al. The phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor vardenafil is a potent inhibitor of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein transporter. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e19329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, A.; Dayan, G.; Conseil, G.; Steinfels, E.; Krell, T.; Trompier, D.; Baubichon-Cortay, H.; Jault, J. P-glycoprotein-mediated resistance to chemotherapy in cancer cells: Using recombinant cytosolic domains to establish structure-function relationships. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1999, 32, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, F.; Chen, H. PCAT1/miR-129/ABCB1 axis confers chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Biosci. 2020, 25, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.M.; Zhang, F.; Tao, W.P.; Ye, J.J.; Ge, W. Twist mediates an aggressive phenotype in human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flens, M.J.; Zaman, G.J.; van der Valk, P.; Izquierdo, M.A.; Schroeijers, A.B.; Scheffer, G.L.; van der Groep, P.; de Haas, M.; Meijer, C.J.; Scheper, R.J. Tissue distribution of the multidrug resistance protein. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Schrenk, D.; Baus, P.R.; Ermel, N.; Klein, C.; Vorderstemann, B.; Kauffmann, H.M. Up-regulation of transporters of the MRP family by drugs and toxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 120, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, C.; Maruyama, M.; Fujishita, T.; Dohkan, J.; Oda, H.; Shinoda, K.; Yamada, T.; Miyabayashi, K.; Hayashi, R.; Kawagishi, Y.; et al. Doxorubicin induces expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 in human small cell lung cancer cell lines by the c-jun N-terminal kinase pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Stephens, M.A.; Pathak, H.; Rangarajan, A. Transcription factors that mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition lead to multidrug resistance by upregulating ABC transporters. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.F.; Widder, J.D.; McNally, J.S.; McCann, L.; Jones, D.P.; Harrison, D.G. The role of the multidrug resistance protein-1 in modulation of endothelial cell oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ju, M.K.; Jeon, H.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, C.H.; Park, H.G.; Han, S.I.; Kang, H.S. Reactive oxygen species induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition, glycolytic switch, and mitochondrial repression through the Dlx-2/Snail signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.P.; Deeley, R.G. Transport of glutathione and glutathione conjugates by MRP1. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, R.; Lorendeau, D.; Khonkarn, R.; Dury, L.; Peres, B.; Boumendjel, A.; Cortay, J.C.; Falson, P.; Chaptal, V.; Baubichon-Cortay, H. Molecular analysis of the massive GSH transport mechanism mediated by the human Multidrug Resistant Protein 1/ABCC1. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.; Luo, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C. Oct-4 and Nanog promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10803–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, H.; Liao, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.W. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway reverses multi-drug resistance and EMT in Oct4(+)/Nanog(+) NSCLC cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Raj, R.R.; Mohan, G.; Padmaja, K.P.; Maliekal, T.T. Reporters of Cancer Stem Cells as a Tool for Drug Discovery. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 669250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayle, A.; Luo, M.; Jeong, M.; Goodell, M.A. Flow cytometry analysis of murine hematopoietic stem cells. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2013, 83, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challen, G.A.; Little, M.H. A side order of stem cells: The SP phenotype. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.C.; Schroder, H.D.; Jensen, C.H. Non-cultured adipose-derived CD45- side population cells are enriched for progenitors that give rise to myofibres in vivo. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2951–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Maruyama, T.; Gargett, C.E.; Miyazaki, K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Okano, H.; Tanaka, M. Endometrial side population cells: Potential adult stem/progenitor cells in endometrium. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.V.; Wang, T.; Maki, C.B.; Pascual, M.; Izadyar, F. Adipose stem cell side population in the mouse. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2009, 3, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, L.; Arnautou, P.; Trignol, A.; Segot, A.; Farge, T.; Desterke, C.; Soave, S.; Clay, D.; Raffoux, E.; Sarry, J.E.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells confer chemoresistance to myeloid leukemia blasts through Side Population functionality and ABC transporter activation. Haematologica 2020, 105, 987–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Costa, K.M.; Freire-de-Lima, L.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Previato, J.O.; Mendonça-Previato, L.; Valente, R.d.C. ABCB1 and ABCC1 Function during TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Relationship between Multidrug Resistance and Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076046
da Costa KM, Freire-de-Lima L, da Fonseca LM, Previato JO, Mendonça-Previato L, Valente RdC. ABCB1 and ABCC1 Function during TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Relationship between Multidrug Resistance and Tumor Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076046
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Costa, Kelli Monteiro, Leonardo Freire-de-Lima, Leonardo Marques da Fonseca, José Osvaldo Previato, Lucia Mendonça-Previato, and Raphael do Carmo Valente. 2023. "ABCB1 and ABCC1 Function during TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Relationship between Multidrug Resistance and Tumor Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076046
APA Styleda Costa, K. M., Freire-de-Lima, L., da Fonseca, L. M., Previato, J. O., Mendonça-Previato, L., & Valente, R. d. C. (2023). ABCB1 and ABCC1 Function during TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Relationship between Multidrug Resistance and Tumor Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076046






