A Novel Wall-Associated Kinase TaWAK-5D600 Positively Participates in Defense against Sharp Eyespot and Fusarium Crown Rot in Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
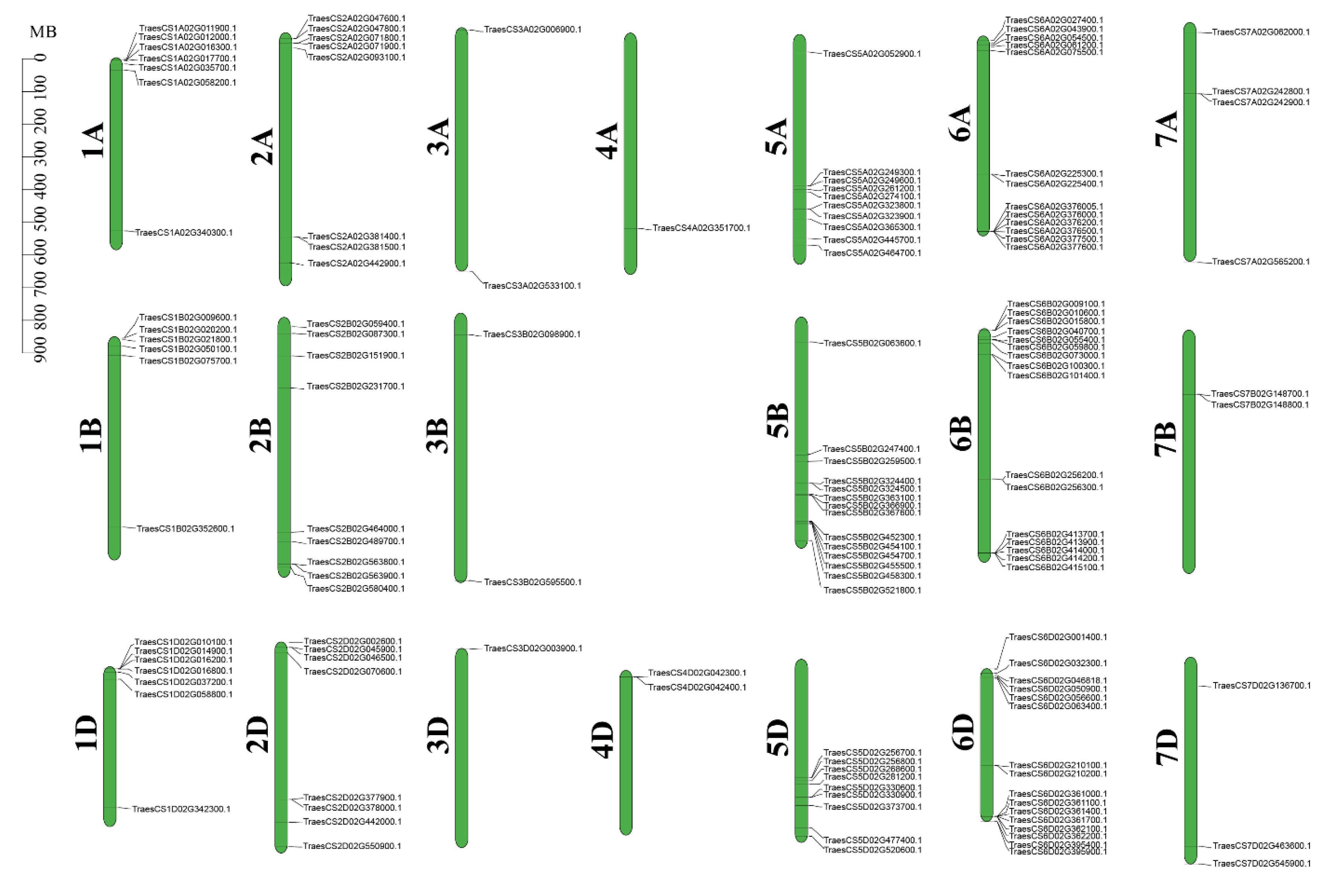
2.1. Identification of Typical WAK Family Genes in Wheat
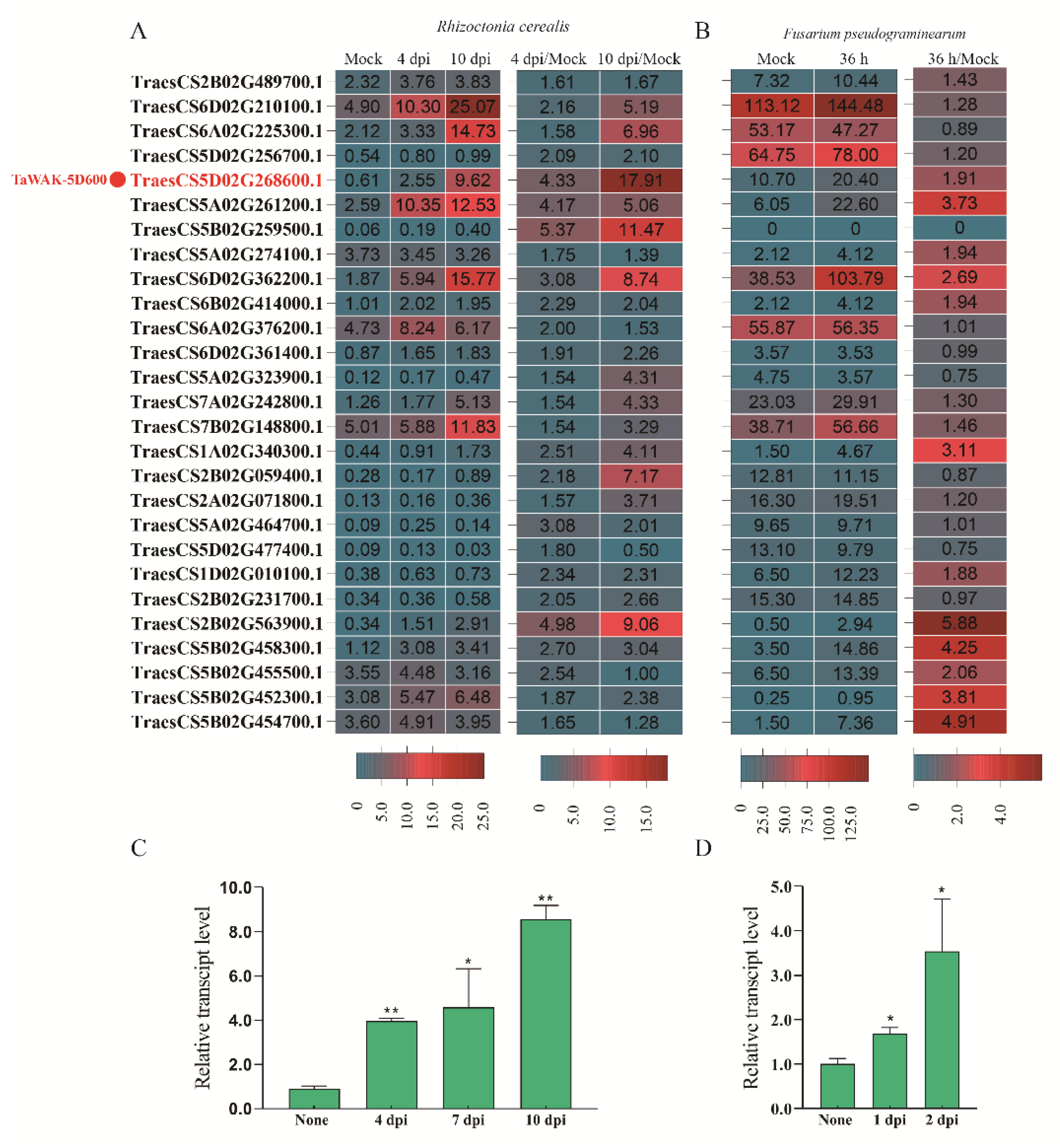
2.2. TaWAK-5D600 Are Involved in Wheat Responses against R. cerealis and F. pseudograminearum
2.3. Phylogenetic and Sequence Analyses, and Sub-Cellular Localization of TaWAK-5D600
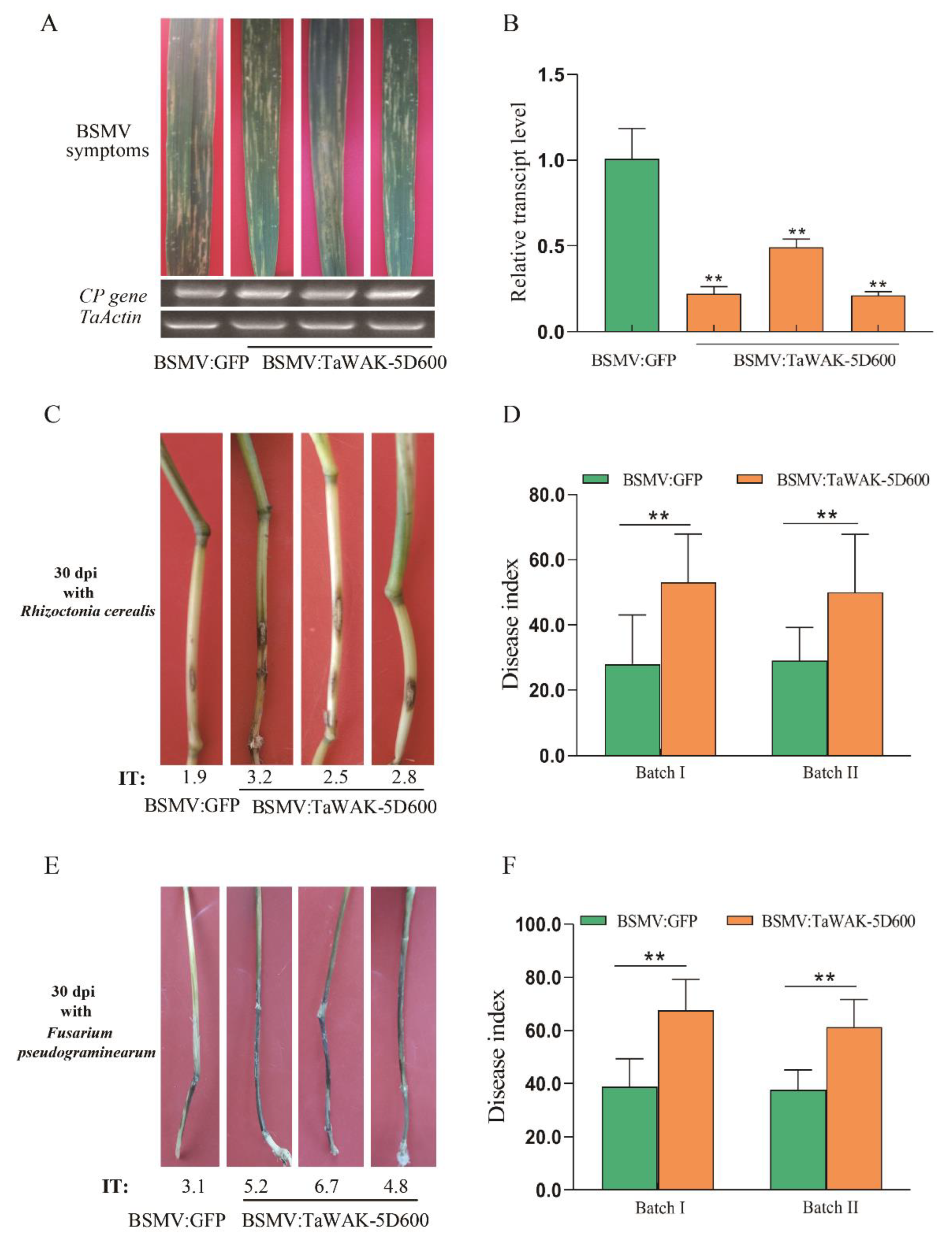
2.4. TaWAK-5D600 Is Required for Wheat Defense against R. cerealis and F. pseudograminearum
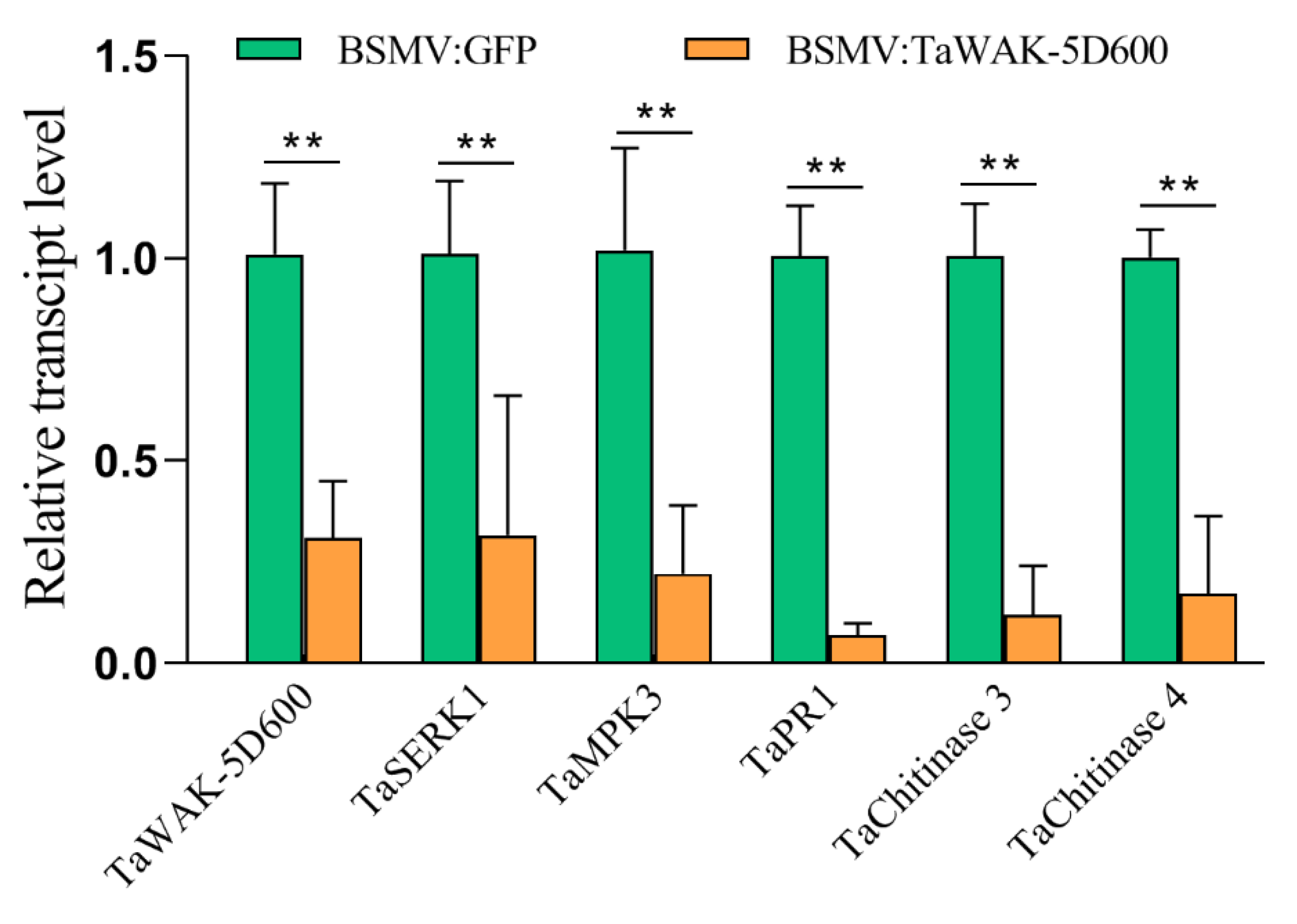
2.5. TaWAK-5D600 Positively Regulated Expression of Several Defense-Related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plants and Fungal Materials
4.2. Identification of WAK Gene Family Members in Wheat
4.3. Phylogenetic, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motifs Analysis
4.4. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
4.5. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
4.6. Subcellular Localization of TaWAK-5D600
4.7. VIGS and Assessment for Wheat Resistance to R. cerealis and F. pseudograminearum
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC). Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 2018, 361, 661. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.S.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z. The escalating threat of Rhizoctonia cerealis, the causal agent of sharp eyespot in wheat. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.L.; Yuan, H.X.; Fu, B.; Xing, X.P.; Sun, B.J.; Tang, W.H. First report of Fusarium pseudograminearum causing crown rot of wheat in Henan, China. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.H.; Du, Z.Y.; Quan, W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Che, M.Z.; Mang, Z.; Zhang, Z.J. Mapping of QTL conferring resistance to sharp eyespot (Rhizoctonia cerealis) in bread wheat at the adult plant growth stage. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazan, K.; Gardiner, D.M. Fusarium crown rot caused by Fusarium pseudograminearum in cereal crops: Recent progress and future prospects. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley, R.W.; Yan, H. Variability of fusarium crown rot tolerances among cultivars of spring and winter wheat. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.J.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, R.H.; Zang, S.J.; Bie, T.D.; Jiang, Z.N.; Gao, D.; Zhang, B. Quantitative trait loci responsible for sharp eyespot resistance in common wheat CI12633. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pan, Y.B.; Singh, P.K.; He, X.Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, S.; Chen, F. Investigation and genome-wide association study for Fusarium crown rot resistance in Chinese common wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verica, J.A.; He, Z.H. The cell wall-associated kinase (WAK) and WAK-like kinase gene family. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohorn, B.D.; Kohorn, S.L. The cell wall-associated kinases, WAKs, as pectin receptors. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, C.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Kanyuka, K. WAKsing plant immunity, waning diseases. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutus, A.; Sicilia, F.; Macone, A.; Cervone, F.; De Lorenzo, G. A domain swap approach reveals a role of the plant wall-associated kinase 1 (WAK1) as a receptor of oligogalacturonides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9452–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, P.; Mun, B.G.; Imran, Q.M.; Hussain, A.; Lee, S.U.; Loake, G.; Yun, B.W. Differential expression of AtWAKL10 in response to nitric oxide suggests a putative role in biotic and abiotic stress responses. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, A.C.; Ausubel, F.M. Resistance to fusarium oxysporum 1, a dominant Arabidopsis disease-resistance gene, is not race specific. Genetics 2005, 171, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, S.; Scheuermann, D.; Krattinger, S.G.; Kessel, B.; Wicker, T.; Herren, G.; Breen, J.; Presterl, T.; Ouzunova, M.; Keller, B. The maize disease resistance gene Htn1 against northern corn leaf blight encodes a wall- associated receptor-like kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8780–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Chao, Q.; Zhang, N.; Ye, J.; Tan, G.; Li, B.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Fengler, K.A.; et al. A maize wall-associated kinase confers quantitative resistance to head smut. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, W.; Su, S.; Peng, Y. A novel wall-associated receptor-like protein kinase gene, OsWAK1, plays important roles in rice blast disease resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delteil, A.; Gobbato, E.; Cayrol, B.; Estevan, J.; Michel-Romiti, C.; Dievart, A.; Kroj, T.; Morel, J.B. Several wall-associated kinases participate positively and negatively in basal defense against rice blast fungus. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Xia, F.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. Improvement of multiple agronomic traits by a disease resistance gene via cell wall reinforcement. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintenac, C.; Lee, W.S.; Cambon, F.; Rudd, J.J.; King, R.C.; Marande, W.; Powers, S.J.; Bergès, H.; Phillips, A.L.; Uauy, C. Wheat receptor-kinase-like protein Stb6 controls gene-for-gene resistance to fungal pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochowska-Boguta, M.; Kloc, Y.; Zielezinski, A.; Werecki, P.; Nadolska-Orczyk, A.; Karlowski, W.; Orczyk, W. TaWAK6 encoding wall-associated kinase is involved in wheat resistance to leaf rust similar to adult plant resistance. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wu, T.; Xu, G.; Qi, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z. TaWAK2A-800, a wall-associated kinase, participates positively in resistance to fusarium head blight and sharp eyespot in wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.J.; Zhu, X.L.; Guo, F.L.; Lv, L.J.; Zhang, Z.Y. The wall-associated receptor-like kinase TaWAK7D is required for defense responses to Rhizoctonia cerealis in wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.J.; Guo, F.L.; Lv, L.J.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.F.; Wei, X.N.; Zhang, Z.Y. The wheat wall-associated receptor-like kinase TaWAK-6D mediates broad resistance to two fungal pathogens Fusarium pseudograminearum and Rhizoctonia cerealis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhou, L.; Jamieson, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.X.; Babilonia, K.; Shao, W.; Wu, L.; Mustafa, R.; Amin, I.; et al. The cotton wall-associated kinase GhWAK7A mediates responses to fungal wilt pathogens by complexing with the chitin sensory receptors. Plant Cell 2020, 2, 3978–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, L.F.V.; Christoff, A.P.; de Lima, J.C.; de Ross, B.C.F.; Sachetto-Martins, G.; Margis-Pinheiro, M.; Margis, R. The wall-associated kinase gene family in rice genomes. Plant Sci. 2014, 229, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, D.; Zang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Qu, G. Genome-wide identification, classification, characterization, and expression analysis of the wall-associated jinase family during fruit development and under wound stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Genes 2020, 11, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Li, Z.; Shen, Q.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Zou, C.; Shang, H.; Li, H.; Xiao, G. Genome-wide characterization of the WAK gene family and expression analysis under plant hormone treatment in cotton. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.K.; Aguirre, J.A.; Singh, J. Genome-wide analysis of wall associated kinase (WAK) gene family in barley. Genomics 2021, 113, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; An, Q.; Tu, Q.; Wu, L.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, P.; Yu, L.; et al. Characterization of the WAK gene family reveals genes for FHB resistance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative Toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.; Carere, J.; Fitzgerald, T.; Stiller, J.; Covarelli, L.; Xu, Q.; Gubler, F.; Colgrave, M.L.; Gardiner, D.M.; Manners, J.M. The Fusarium crown rot pathogen Fusarium pseudograminearum triggers a suite of transcriptional and metabolic changes in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kohorn, B.D.; Johansen, S.; Shishido, A.; Todorova, T.; Martinez, R.; Defeo, E.; Obregon, P. Pectin activation of MAP kinase and gene expression is WAK2 dependent. Plant J. 2009, 60, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, H.; Liu, H.; Du, L.; Xu, H.; Xin, Z. Overexpression of TiERF1 enhances resistance to sharp eyespot in transgenic wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4195–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, X.T.; Ni, Z.F.; Hu, Z.R.; Xin, M.M.; Peng, H.; Yao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Guo, W. SnpHub: An easy-to-set-up web server framework for exploring large-scale genomic variation data in the post-genomic era with applications in wheat. GigaScience 2020, 9, giaa060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, A.; Qi, J.; Dou, W.; Qin, X.; Zou, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, S.; He, Y. CsWAKL08, a pathogen-induced wall-associated receptor-like kinase in sweet orange, confers resistance to citrus bacterial canker via ROS control and JA signaling. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkenrider, M.; Sharma, R.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Tsao, L.; Zhang, X.; Chern, M.; Canlas, P.; Zuo, S.; Ronald, P.C. Overexpression of rice wall-associated kinase 25 (OsWAK25) alters resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0147310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.J.; Yu, J.; Yuan, X.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Z.Y. The somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase TaSERK1 participates in the immune response to Rhizoctonia cerealis infection by interacting and phosphorylating the receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase TaRLCK1B in wheat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 15, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.C.; Zhu, X.L.; LÜ, L.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Xu, G.B.; Zhang, Z.Y. The wheat receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase TaRLCK1B is required for host immune response to the necrotrophic pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, k.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Cho, Y.; Sheen, J. Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: A versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, H.; Zhu, X.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Z. A Novel Wall-Associated Kinase TaWAK-5D600 Positively Participates in Defense against Sharp Eyespot and Fusarium Crown Rot in Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055060
Qi H, Zhu X, Shen W, Zhang Z. A Novel Wall-Associated Kinase TaWAK-5D600 Positively Participates in Defense against Sharp Eyespot and Fusarium Crown Rot in Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):5060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055060
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Haijun, Xiuliang Zhu, Wenbiao Shen, and Zengyan Zhang. 2023. "A Novel Wall-Associated Kinase TaWAK-5D600 Positively Participates in Defense against Sharp Eyespot and Fusarium Crown Rot in Wheat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 5060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055060
APA StyleQi, H., Zhu, X., Shen, W., & Zhang, Z. (2023). A Novel Wall-Associated Kinase TaWAK-5D600 Positively Participates in Defense against Sharp Eyespot and Fusarium Crown Rot in Wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 5060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055060







