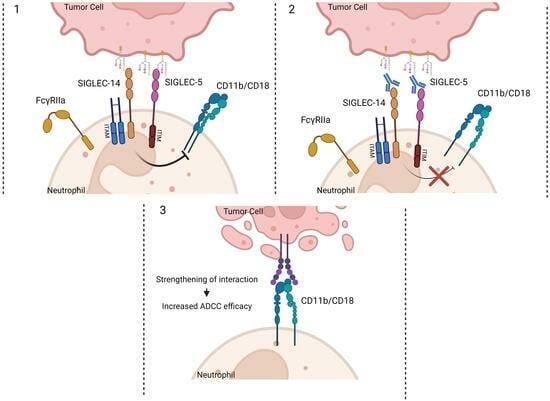
SIGLEC-5/14 Inhibits CD11b/CD18 Integrin Activation and Neutrophil-Mediated Tumor Cell Cytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
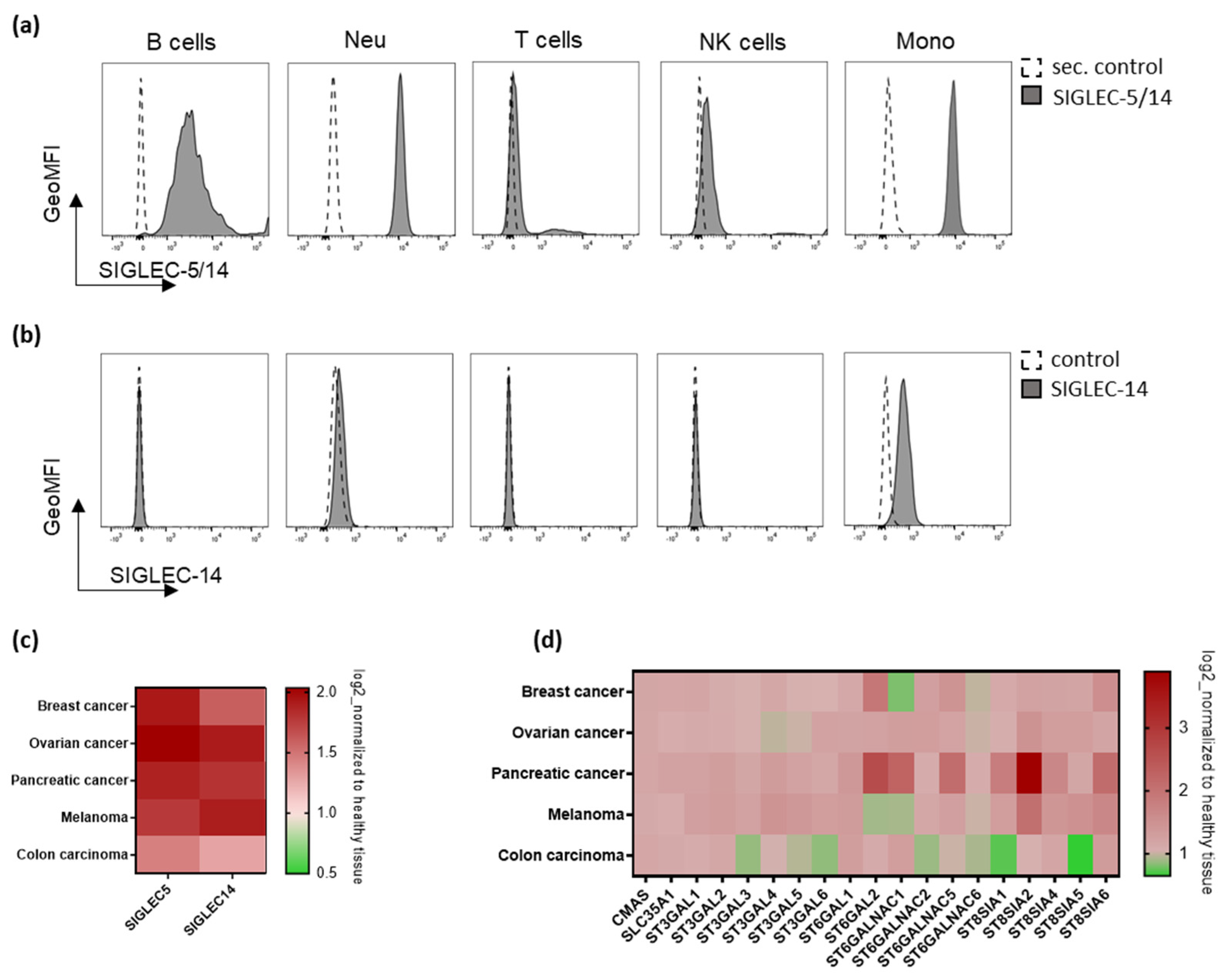
2.1. Immune Receptors SIGLEC-5 and SIGLEC-14, and Genes Involved in Sialic Acid Metabolism Are Present in Human Solid Tumors
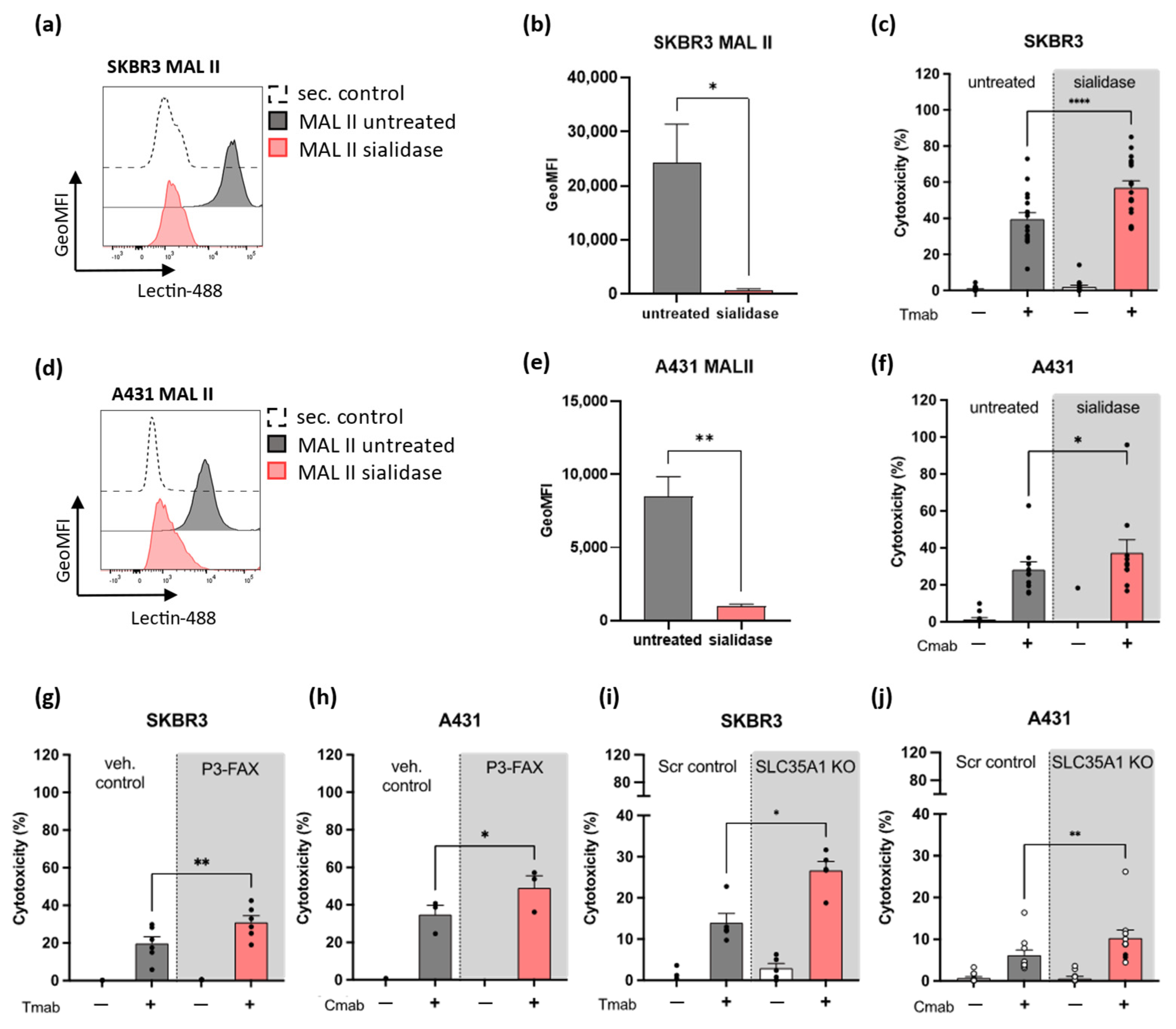
2.2. Decreased Sialic Acid Expression on SKBR3 or A431 Solid Tumor Cells Enhances Neutrophil ADCC
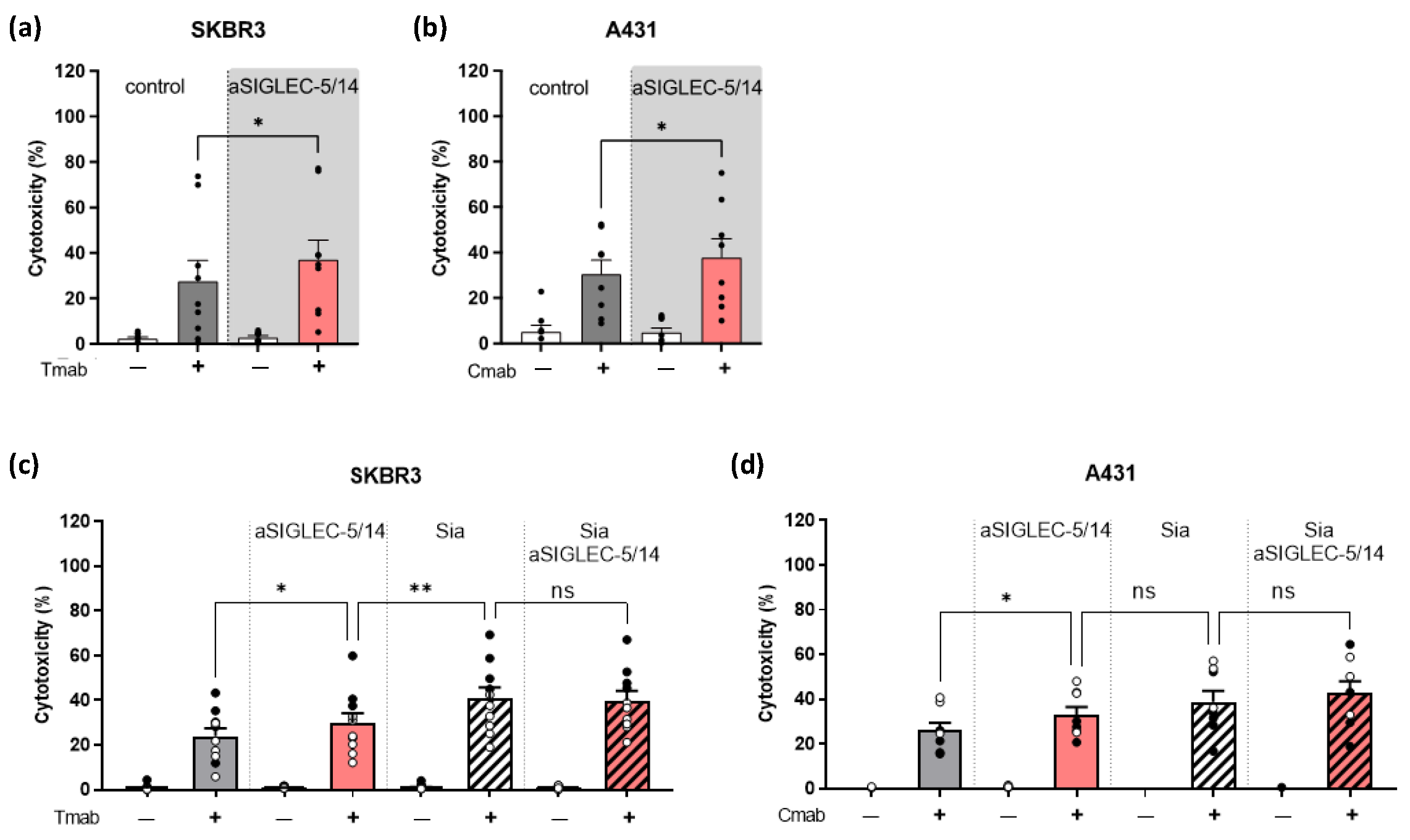
2.3. Inhibition of Sialic Acid Interaction with SIGLEC-5/14 Enhances Neutrophil ADCC of Solid Tumor Cells
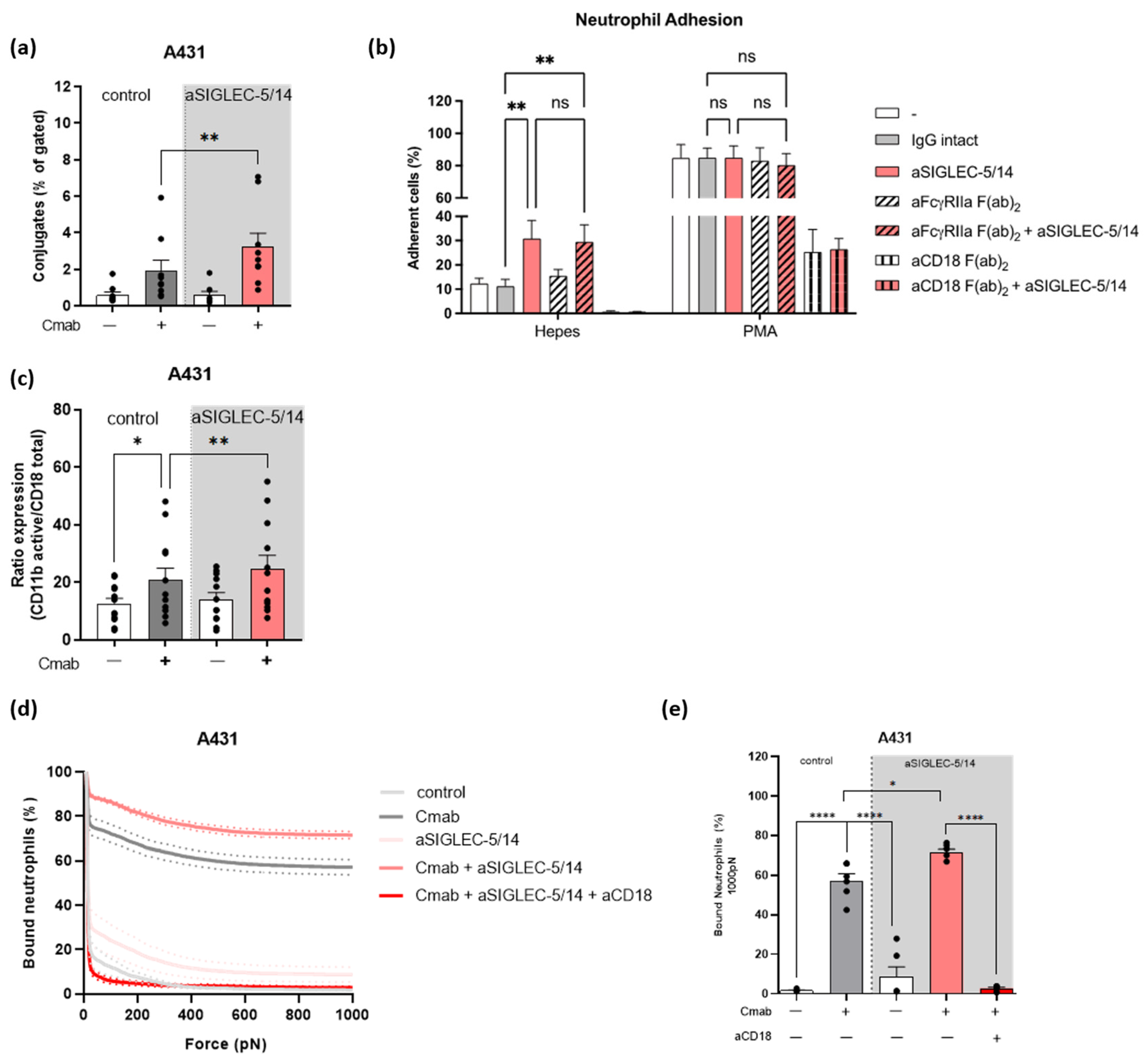
2.4. Sialic Acid-SIGLEC-5/14 Interaction Regulates Neutrophil Conjugate Formation and Trogocytosis by Preventing the High Affinity Conformation of CD11b/CD18
2.5. Sialic Acid-SIGLEC-5/14 Interactions Restrict Neutrophil-Tumor Cell Interactions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Neutrophil Isolation
4.2. Cell Culture and Modifications
4.3. Reagents and Antibodies
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Assay (ADCC)
4.6. Trogocytosis Assay Using Flow Cytometry
4.7. Adhesion Assay
4.8. Conjugate Formation Assay Using Image Stream
4.9. Flow Cytometry for Detection of CD11b-CD18 Activity
4.10. Neutrophil Binding Avidity Assay
4.11. Human Tumor RNA-Sequencing Analysis
4.12. Statistics and Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Want, M.Y.; Bashir, Z.; Najar, R.A. T Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer: Approaches and Strategies. Vaccines 2023, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilard, C.; Ancion, M.; Delvenne, P.; Jerusalem, G.; Hubert, P.; Herfs, M. Cancer immunotherapy: It’s time to better predict patients’ response. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, O.; Cornen, S.; Daëron, M.; Morel, Y.; Medzhitov, R.; Vivier, E. Harnessing innate immunity in cancer therapy. Nature 2019, 574, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.; Hammond, S.A.; Oberst, M.; Wilkinson, R.W. The role of Fc gamma receptors in the activity of immunomodulatory antibodies for cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, M.; Binnewies, M.; Boldajipour, B.; Nelson, A.; Pollock, J.; Erle, D.; Barczak, A.; Rosenblum, M.; Daud, A.; Barber, D.; et al. Dissecting the tumor myeloid compartment reveals rare activating antigen presenting cells, critical for T cell immunity. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereiter, S.; Balmaña, M.; Campos, D.; Gomes, J.; Reis, C.A. Glycosylation in the Era of Cancer-Targeted Therapy: Where Are We Heading? Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.; Mandal, A.; Joshi, A.; Jain, N.; Srivastava, R.S.; Singh, S.; Khattri, A. Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Potential Targets for Cancer Treatment. Diseases 2022, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picco, G.; Julien, S.; Brockhausen, I.; Beatson, R.; Antonopoulos, A.; Haslam, S.; Mandel, U.; Dell, A.; Pinder, S.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; et al. Over-expression of ST3Gal-I promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchell, J.; Poulsom, R.; Hanby, A.; Whitehouse, C.; Cooper, L.; Clausen, H.; Miles, D.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. An α2,3 sialyltransferase (ST3Gal I) is elevated in primary breast carcinomas. Glycobiology 1999, 9, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, S.T.; Ogrodzinski, M.P.; Ross, C.; Hunter, K.W.; Lunt, S.Y. Sialic acid metabolism: A key player in breast cancer metastasis revealed by metabolomics. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, M.M.; Esko, J.D. The sweet and sour of cancer: Glycans as novel therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAuley, M.S.; Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C. Siglec-mediated regulation of immune cell function in disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.Y.; Qi, L.L.; Kang, F.B.; Wang, L. The intriguing roles of Siglec family members in the tumor microenvironment. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C.; Varki, A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bärenwaldt, A.; Läubli, H. The sialoglycan-Siglec glyco-immune checkpoint–a target for improving innate and adaptive anti-cancer immunity. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Wall, S.; Santegoets, K.C.M.; van Houtum, E.J.H.; Büll, C.; Adema, G.J. Sialoglycans and Siglecs Can Shape the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Elkabets, M.; Perlmutter, M.; Porgador, A.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N.; Lichtenstein, R.G. Sialylation of 3-Methylcholanthrene–Induced Fibrosarcoma Determines Antitumor Immune Responses during Immunoediting. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5869–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, J.E.; Canham, S.M.; Bertozzi, C.R. Glycocalyx Engineering Reveals a Siglec-Based Mechanism for NK Cell Immunoevasion. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läubli, H.; Pearce, O.M.T.; Schwarz, F.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Deng, L.; Stanczak, M.A.; Deng, L.; Verhagen, A.; Secrest, P.; Lusk, C.; et al. Engagement of myelomonocytic Siglecs by tumor-associated ligands modulates the innate immune response to cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14211–14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkal, A.A.; Brewer, R.E.; Markovic, M.; Kowarsky, M.; Barkal, S.A.; Zaro, B.W.; Krishnan, V.; Hatakeyama, J.; Dorigo, O.; Barkal, L.J.; et al. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 572, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theruvath, J.; Menard, M.; Smith, B.A.; Linde, M.H.; Coles, G.L.; Dalton, G.N.; Wu, W.; Kiru, L.; Delaidelli, A.; Sotillo, E.; et al. Anti-GD2 synergizes with CD47 blockade to mediate tumor eradication. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Gao, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L. Shaping Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages In Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, B.H.; Giridharan, T.; Suzuki, S.; Khan, A.N.H.; Zsiros, E.; Emmons, T.R.; Yaffe, M.B.; Gankema, A.A.F.; Hoogeboom, M.; Goetschalckx, I.; et al. Neutrophil interactions with T cells, platelets, endothelial cells, and of course tumor cells. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 314, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlung, H.L.; Babes, L.; Zhao, X.W.; van Houdt, M.; Treffers, L.W.; van Rees, D.J.; Franke, K.; Schornagel, K.; Verkuijlen, P.; Janssen, H.; et al. Neutrophils Kill Antibody-Opsonized Cancer Cells by Trogoptosis. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3946–3959.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumaya, C.; Martinez-Sanz, P.; Bouti, P.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Matlung, H.L. Plasticity in Pro- and Anti-tumor Activity of Neutrophils: Shifting the Balance. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouti, P.; Zhao, X.W.; Verkuijlen, P.J.J.H.; Tool, A.T.J.; van Houdt, M.; Köker, N.; Köker, M.Y.; Keskin, O.; Akbayram, S.; van Bruggen, R.; et al. Kindlin3-dependent CD11b/CD18-integrin activation is required for potentiation of neutrophil cytotoxicity by CD47-SIRPa checkpoint disruption. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuravleva, M.A.; Trandem, K.; Sun, P.D. Structural implications of siglec-5 mediated sialo- glycan recognition. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Nicoll, G.; Jones, C.; Crocker, P.R. Siglec-9, a novel sialic acid binding member of the immunoglobulin superfamily expressed broadly on human blood leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22121–22126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhöfft, K.F.; Goldammer, T.; Rebl, A.; Galuska, S.P. Siglecs: A journey through the evolution of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectins. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 86, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angata, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamanaka, M.; Varki, A.; Nakamura, M. Discovery of Siglec-14, a novel sialic acid receptor undergoing concerted evolution with Siglec-5 in primates. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Chan, C.; Jansen, J.H.M.; Bräutigam, M.; Kölling, M.A.; Gehlert, C.L.; Baumann, N.; Mester, S.; Foss, S.; Andersen, J.T.; et al. Disruption of the sialic acid/Siglec-9 axis improves antibody- mediated neutrophil cytotoxicity towards tumor cells. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1178817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, J.C.; Gray, M.A.; Wisnovsky, S.; Ibarlucea-benitez, I.; Nicholas, M.; Ribi, M.K.; Lustig, M.; Errington, W.J.; Bruncsics, B.; Sarkar, C.A. Antibody-lectin chimeras for glyco-immune checkpoint blockade. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoni, A.; Macauley, M.S.; O’Dwyer, M.E. Targeting selectins and their ligands in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouti, P.; Webbers, S.D.S.; Fagerholm, S.C.; Alon, R.; Moser, M.; Matlung, H.L.; Kuijpers, T.W. β2 Integrin Signaling Cascade in Neutrophils: More Than a Single Function. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 619925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wines, B.D.; Trist, H.M.; Esparon, S.; Impey, R.E.; Mackay, G.A.; Andrews, R.K.; Soares da Costa, T.P.; Pietersz, G.A.; Baker, R.I.; Hogarth, P.M. Fc Binding by FcγRIIa Is Essential for Cellular Activation by the Anti-FcγRIIa mAbs 8.26 and 8.2. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Naik, J.; Mansilla-soto, J.; Kefala, D.; Kladis, G.; Nianias, A.; Ruiter, R.; Poels, R.; Sarkar, I.; et al. Combining a CAR and a chimeric costimulatory receptor enhances T cell sensitivity to low antigen density and promotes persistence. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, eabh1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobono, S.; Stecca, B. Aberrant sialylation in cancer: Biomarker and potential target for therapeutic intervention? Cancers 2021, 13, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.; Lustig, M.; Baumann, N.; Valerius, T.; van Tetering, G.; Leusen, J.H.W. Targeting Myeloid Checkpoint Molecules in Combination With Antibody Therapy: A Novel Anti-Cancer Strategy With IgA Antibodies? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, P.R.C.; Saric, A.; Pedram, K.; Bertozzi, C.R.; Grinstein, S.; Freeman, S.A. An Acquired and Endogenous Glycocalyx Forms a Bidirectional “Don’t Eat” and “Don’t Eat Me” Barrier to Phagocytosis. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 77–89.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.W.; Van Beek, E.M.; Schornagel, K.; Van Der Maaden, H.; Van Houdt, M.; Otten, M.A.; Finetti, P.; Van Egmond, M.; Matozaki, T.; Kraal, G.; et al. CD47-signal regulatory protein-α (SIRPα) interactions form a barrier for antibody-mediated tumor cell destruction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18342–18347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, M.A.; Kern, N.; Vale, R.D.; Francisco, S. CD47 ligation repositions the inhibitory receptor SIRPA to suppress integrin activation and phagocytosis Meghan. Immunity 2020, 53, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcutia, V.; Kelm, M.; Fink, D.; Cummings, R.D.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A.; Brazil, J.C. Sialylation regulates neutrophil transepithelial migration, CD11b/CD18 activation, and intestinal mucosal inflammatory function. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e167151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Woods, E.C.; Vukojicic, P.; Bertozzi, C.R. Precision glycocalyx editing as a strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10304–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemskerk, N.; Gruijs, M.; Robin Temming, A.; Heineke, M.H.; Gout, D.Y.; Hellingman, T.; Tuk, C.W.; Winter, P.J.; Lissenberg-Thunnissen, S.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; et al. Augmented antibody-based anticancer therapeutics boost neutrophil cytotoxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysore, V.; Cullere, X.; Mears, J.; Rosetti, F.; Okubo, K.; Liew, P.X.; Zhang, F.; Madera-Salcedo, I.; Rosenbauer, F.; Stone, R.M.; et al. FcγR engagement reprograms neutrophils into antigen cross-presenting cells that elicit acquired anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, S.; Bhojnagarwala, P.S.; O’Brien, S.; Moon, E.K.; Garfall, A.L.; Rao, A.S.; Quatromoni, J.G.; Stephen, T.L.; Litzky, L.; Deshpande, C.; et al. Origin and Role of a Subset of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils with Antigen Presenting Cell Features (Hybrid TANs) in Early- Stage Human Lung Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylaeva, E.; Korschunow, G.; Spyra, I.; Bordbari, S.; Siakaeva, E.; Ozel, I.; Domnich, M.; Squire, A.; Hasenberg, A.; Thangavelu, K.; et al. During early stages of cancer, neutrophils initiate anti-tumor immune responses in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuchkovska, A.; Glanville, D.G.; Scurti, G.M.; Nishimura, M.I.; White, P.; Ulijasz, A.T.; Iwashima, M. Siglec-5 is an inhibitory immune checkpoint molecule for human T cells. Immunology 2022, 166, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santegoets, K.C.M.; Gielen, P.R.; Büll, C.; Schulte, B.M.; Kers-Rebel, E.D.; Küsters, B.; Bossman, S.A.J.F.H.; ter Laan, M.; Wesseling, P.; Adema, G.J. Expression profiling of immune inhibitory Siglecs and their ligands in patients with glioma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.A.; Stanczak, M.A.; Mantuano, N.R.; Xiao, H.; Pijnenborg, J.F.; Malaker, S.A.; Miller, C.L.; Weidenbacher, P.A.; Tanzo, J.T.; Ahn, G.; et al. Targeted glycan degradation potentiates the anticancer immune response in vivo. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läubli, H.; Kawanishi, K.; George Vazhappilly, C.; Matar, R.; Merheb, M.; Sarwar Siddiqui, S. Tools to study and target the Siglec–sialic acid axis in cancer. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6206–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijpers, T.; Tool, A.; van der Schoot, C.; Ginsel, L.; Onderwater, J.; Roos, D.; Verhoeven, A. Membrane surface antigen expression on neutrophils: A reappraisal of the use of surface markers for neutrophil activation. Blood 1991, 78, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijpers, T.; Tool, A.; van der Bijl, I.; de Boer, M.; van Houdt, M.; de Cuyper, I.; Roos, D.; van Alphen, F.; van Leeuwen, K.; Cambridge, E.; et al. Combined immunodeficiency with severe inflammation and allergy caused by ARPC1B deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 273–277.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouti, P.; Blans, C.; Klein, B.J.A.M.; Shome, D.; Nadafi, R.; Van Houdt, M.; Schornagel, K.; Verkuijlen, P.J.J.H.; Roos, V.; Reijmers, R.M.; et al. SIGLEC-5/14 Inhibits CD11b/CD18 Integrin Activation and Neutrophil-Mediated Tumor Cell Cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417141
Bouti P, Blans C, Klein BJAM, Shome D, Nadafi R, Van Houdt M, Schornagel K, Verkuijlen PJJH, Roos V, Reijmers RM, et al. SIGLEC-5/14 Inhibits CD11b/CD18 Integrin Activation and Neutrophil-Mediated Tumor Cell Cytotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417141
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouti, Panagiota, Colin Blans, Bart J. A. M. Klein, Debarati Shome, Reza Nadafi, Michel Van Houdt, Karin Schornagel, Paul J. J. H. Verkuijlen, Virginie Roos, Rogier M. Reijmers, and et al. 2023. "SIGLEC-5/14 Inhibits CD11b/CD18 Integrin Activation and Neutrophil-Mediated Tumor Cell Cytotoxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417141
APA StyleBouti, P., Blans, C., Klein, B. J. A. M., Shome, D., Nadafi, R., Van Houdt, M., Schornagel, K., Verkuijlen, P. J. J. H., Roos, V., Reijmers, R. M., Van Bruggen, R., Kuijpers, T. W., & Matlung, H. L. (2023). SIGLEC-5/14 Inhibits CD11b/CD18 Integrin Activation and Neutrophil-Mediated Tumor Cell Cytotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417141