COVID-19 in Children: Molecular Profile and Pathological Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
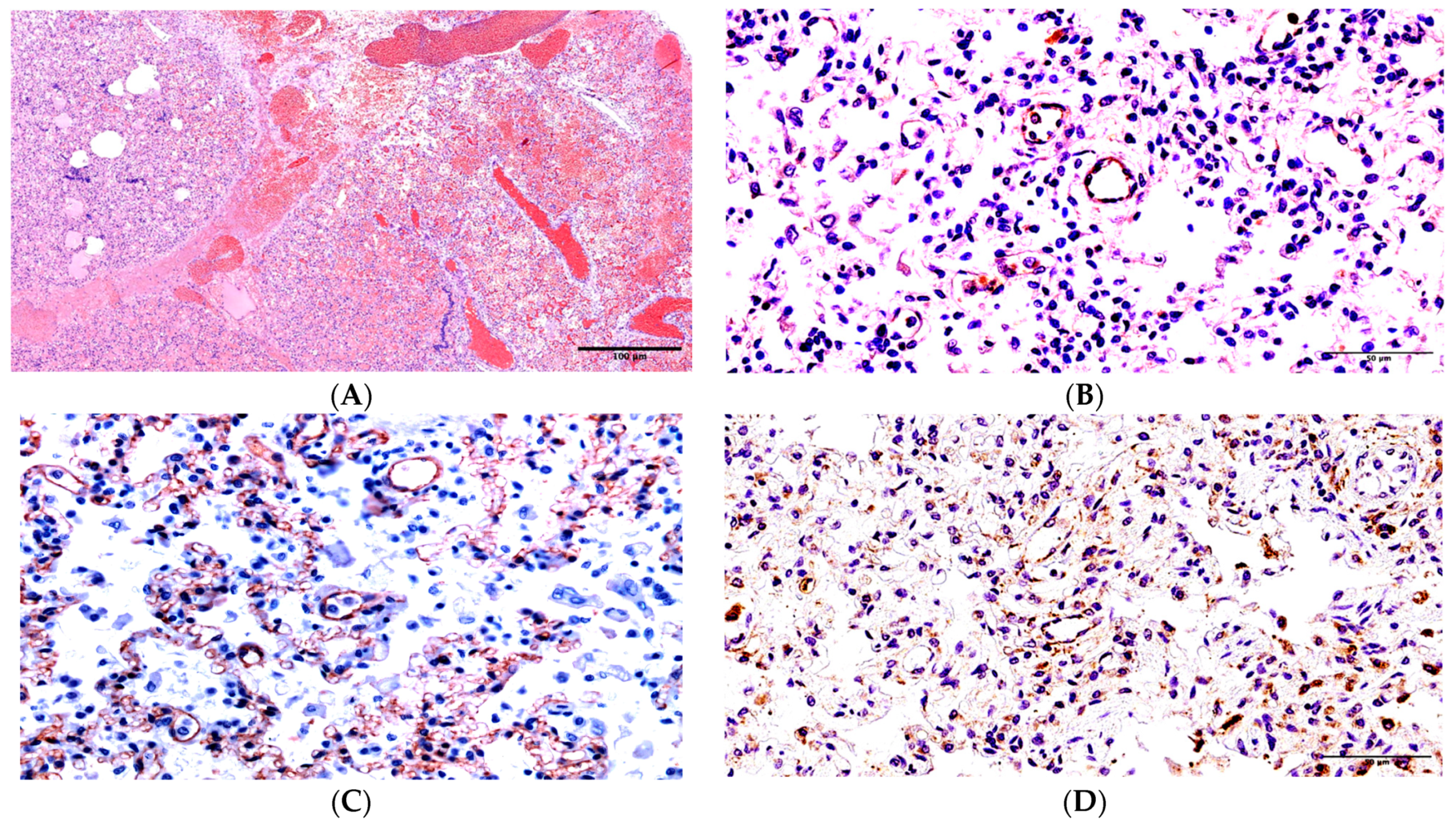
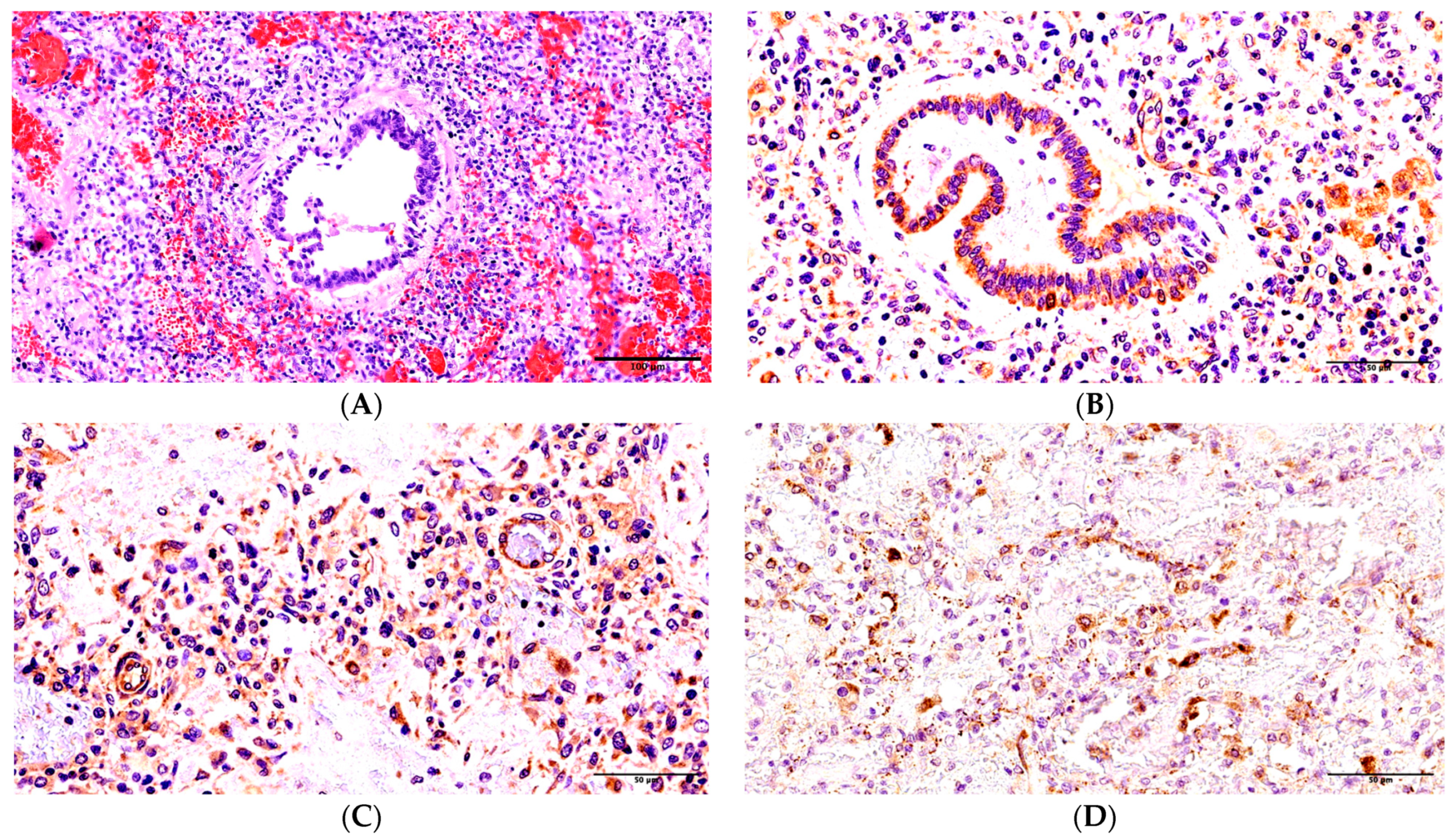
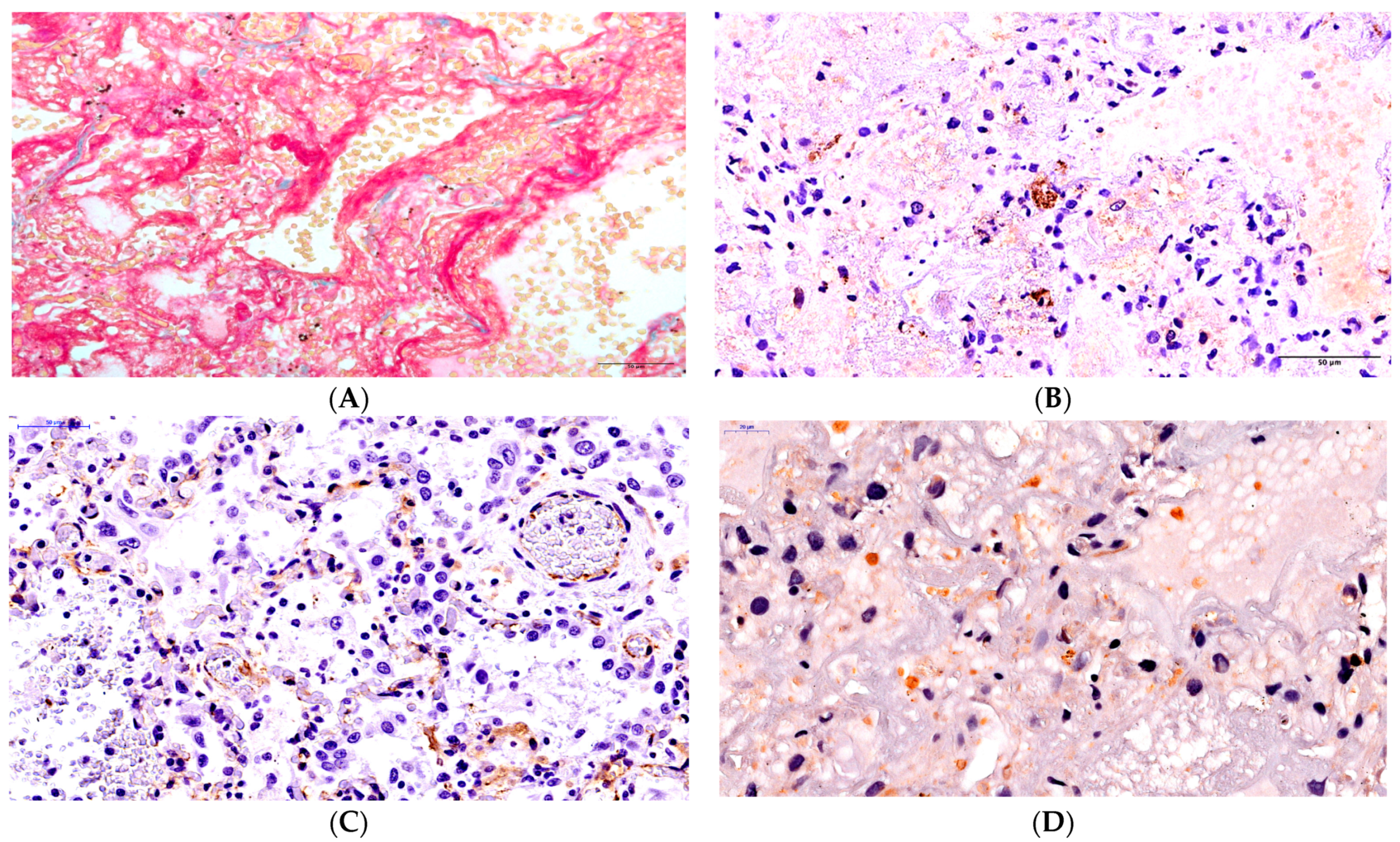
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, L.F.; Dallagnol, C.A.; Moulepes, T.H.; Hirota, C.Y.; Kutsmi, P.; dos Santos, L.V.; Pirich, C.L.; Picheth, G.F. Oxygen therapy alternatives in COVID-19: From classical to nanomedicine. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying-Hao, P.; Rui-Han, L.; Hai-Dong, Z.; Qiu-Hua, C.; Yuan-Yuan, G.; Yu-Shan, Y.; Hai-Qi, Z.; Hua, J. Different effects of vaccine on VST in critical and non-critical COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study of 363 cases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiani, L.; Mancino, E.; Matera, L.; Nenna, R.; Pierangeli, A.; Scagnolari, C.; Midulla, F. Will children reveal their secret? The coronavirus dilemma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.D.; Esposito, E.; Cristiani, L.; Mancino, E.; Nenna, R.; Cortis, E.; Midulla, F. Covid-19 in children: A brief overview after three months experience. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 35, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskov, A.N.; Lobzin, Y.V.; Rychkova, S.V.; Babachenko, I.V.; Fedorov, V.V.; Ulukhanova, L.U.; Pochinyaeva, L.M. Course of a new coronavirus infection in children: Some aspects of monitoring and analysis of mortality. J. Infectology 2020, 12, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrusak, O.; Kalina, T.; Wolf, J.; Balduzzi, A.; Provenzi, M.; Rizzari, C.; Rives, S.; del Pozo Carlavilla, M.; Alonso, M.E.; Domínguez-Pinilla, N.; et al. Flash survey on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infections in paediatric patients on anticancer treatment. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Taxy, J.; Angst, D.B.; Mangurten, H.H. Autopsies in Children: Are they still useful? Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1998, 152, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bryce, C.; Grimes, Z.; Pujadas, E.; Ahuja, S.; Beasley, M.B.; Albrecht, R.; Hernandez, T.; Stock, A.; Zhao, Z.; AlRasheed, M.R.; et al. Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: The Mount Sinai COVID-19 autopsy experience. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsana, L.; Sonzogni, A.; Nasr, A.; Rossi, R.S.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Zerbi, P.; Rech, R.; Colombo, R.; Antinori, S.; Corbellino, M.; et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: A two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edler, C.; Schröder, A.S.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Fitzek, A.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Klein, A.; Langenwalder, F.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Meißner, K.; et al. Dying with SARS-CoV-2 infection—An autopsy study of the first consecutive 80 cases in Hamburg, Germany. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2020, 134, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.E.; Akmatbekov, A.; Harbert, J.L.; Li, G.; Brown, J.Q.; Heide, R.S.V. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: An autopsy series from New Orleans. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, R.B.; Ritter, J.M.; Matkovic, E.; Gary, J.; Bollweg, B.C.; Bullock, H.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Silva-Flannery, L.; Seixas, J.N.; Reagan-Steiner, S.; et al. Pathology and Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with Fatal Coronavirus Disease, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Li, X.; Huang, B.; Su, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.J.; Chen, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, S.H.; Nie, X.; et al. Pathological changes of fatal coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the lungs: Report of 10 cases by postmortem needle autopsy. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020, 49, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maiese, A.; Manetti, A.C.; La Russa, R.; Di Paolo, M.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. Autopsy findings in COVID-19-related deaths: A literature review. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2021, 17, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borczuk, A.C.; Salvatore, S.P.; Seshan, S.V.; Patel, S.S.; Bussel, J.B.; Mostyka, M.; Elsoukkary, S.; He, B.; Del Vecchio, C.; Fortarezza, F.; et al. COVID-19 pulmonary pathology: A multi-institutional autopsy cohort from Italy and New York City. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2156–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Michele, S.; Sun, Y.; Yilmaz, M.M.; Katsyv, I.; Salvatore, M.; Dzierba, A.L.; Marboe, C.C.; Brodie, D.; Patel, N.M.; Garcia, C.K.; et al. Forty Postmortem Examinations in COVID-19 Patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsoukkary, S.S.; Mostyka, M.; Dillard, A.; Berman, D.R.; Ma, L.X.; Chadburn, A.; Yantiss, R.K.; Jessurun, J.; Seshan, S.V.; Borczuk, A.C.; et al. Autopsy Findings in 32 Patients with COVID-19: A Single-Institution Experience. Pathobiology 2020, 88, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlang, L.-A.; Mohl, B.-P.; Blaurock, C.; Harder, S.; Breithaupt, A.; Merkel, O.M.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; Popp, A. SARS-CoV-2 induced changes in the glycosylation pattern in the respiratory tract of Golden Syrian hamsters. Acta Histochem. 2023, 125, 152077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashefski, J.F.; Cagle, P.T.; Farver, C.F.; Fraire, A.E. (Eds.) Dail and Hammar’s Pulmonary Pathology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 426–475. [Google Scholar]
- Dorward, D.A.; Russell, C.D.; Um, I.H.; Elshani, M.; Armstrong, S.D.; Penrice-Randal, R.; Millar, T.; Lerpiniere, C.E.B.; Tagliavini, G.; Hartley, C.S.; et al. Tissue-Specific Immunopathology in Fatal COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, K.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, A.G. Clinico-Pathogenesis of COVID-19 in children. Indian J. Biochem. AND Biophys. 2020, 57, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Control of COVID-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzankov, A.; Jonigk, D. Unlocking the lockdown of science and demystifying COVID-19: How autopsies contribute to our understanding of a deadly pandemic. Virchows Arch. 2020, 477, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Han, K.; Blair, R.; Kenst, K.; Qin, Z.; Upcin, B.; Wörsdörfer, P.; Midkiff, C.C.; Mudd, J.; Belyaeva, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infects Endothelial Cells In Vivo and In Vitro. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 701278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menter, T.; Haslbauer, J.D.; Nienhold, R.; Savic, S.; Hopfer, H.; Deigendesch, N.; Frank, S.; Turek, D.; Willi, N.; Pargger, H.; et al. Post-mortem examination of COVID19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings of lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction. Histopathology 2020, 77, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilosi, M.; Poletti, V.; Ravaglia, C.; Rossi, G.; Dubini, A.; Piciucchi, S.; Pedica, F.; Bronte, V.; Pizzolo, G.; Martignoni, G.; et al. The pathogenic role of epithelial and endothelial cells in early-phase COVID-19 pneumonia: Victims and partners in crime. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. Cell Pyroptosis, a Potential Pathogenic Mechanism of 2019-nCoV Infection. 2020. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3527420 (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Goldsmith, C.S.; Miller, S.E.; Martines, R.B.; Bullock, H.A.; Zaki, S.R. Electron microscopy of SARS-CoV-2: A challenging task. Lancet 2020, 395, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Mentzer, S.J.; Jonigk, D. Visualization of SARS-CoV-2 in the Lung. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2689–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, M.; Hoton, D.; Marot, L.; Herman, A. Chilblains and COVID-19: Why SARS-CoV-2 endothelial infection is questioned. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, I.-M.; Padera, R.F.; Solomon, I.H.; Kanjilal, S.; Hammer, M.M.; Hornick, J.L.; Sholl, L.M. In situ detection of SARS-CoV-2 in lungs and airways of patients with COVID-19. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, N.N.; Zinserling, V.A.; Semenova, N.Y. Case of lethal outcome of an infant due to COVID-19. J. Infectology 2021, 13, 142–148. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Author Correction: Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.J.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, C.S.; Tatti, K.M.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rollin, P.E.; Comer, J.A.; Lee, W.W.; Rota, P.A.; Bankamp, B.; Bellini, W.J.; Zaki, S.R. Ultrastructural Characterization of SARS Coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Müller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasyrov, R.A.; Sidorova, N.A.; Melnikova, V.F.; Fedotova, E.P. Morphological and Immunohistochemical Features of Placental Damage in Cases of Perinatal Death: Institutional Experience with Emphasis on Viral Etiology. Ann. Clin. Lab Sci. 2020, 50, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, D.; Mironova, E.; Polyakova, V.; Evsyukova, I.; Osetrov, M.; Kvetnoy, I.; Nasyrov, R. Sudden infant death syndrome: Melatonin, serotonin, and CD34 factor as possible diagnostic markers and prophylactic targets. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinod, K.; Wagner, D.D. Thrombosis: Tangled up in NETs. Blood 2014, 123, 2768–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernick, N. CD95. PathologyOutlines.com Website. 2021. Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd95.html (accessed on 1 September 2013).
- Fritsch, M.; Günther, S.D.; Schwarzer, R.; Albert, M.-C.; Schorn, F.; Werthenbach, J.P.; Schiffmann, L.M.; Stair, N.; Stocks, H.; Seeger, J.M.; et al. Caspase-8 is the molecular switch for apoptosis, necroptosis and pyroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Li, H.; Ye, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z.-L.; Zhou, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 triggers inflammatory responses and cell death through caspase-8 activation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, A.J.; Anderson, T.; Celermajer, D.S.; Creager, M.A.; Deanfield, J.; Ganz, P.; Hamburg, N.M.; Lüscher, T.F.; Shechter, M.; Taddei, S.; et al. The Assessment of Endothelial Function: From research into clinical practice. Circulation 2012, 126, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösmüller, H.; Traxler, S.; Bitzer, M.; Häberle, H.; Raiser, W.; Nann, D.; Frauenfeld, L.; Vogelsberg, A.; Klingel, K.; Fend, F. The evolution of pulmonary pathology in fatal COVID-19 disease: An autopsy study with clinical correlation. Virchows Arch. 2020, 477, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D., Jr.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient | Age | Duration of the Disease | Comorbid Conditions | Results of Laboratory Investigations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferritin (mkg/L) n = 15.00–120.00 | D-Dimer (ng/mL) n = 0–250.0 | C-Reactive Protein (mg/L) n = 0–5.80 | ||||
| 1. Girl E. | 1 year, 7 months | 6 days | Acute myeloblastic leukemia, M4 variant with eosinophilia, CD19 co-expression, CBFB-inv [16] gene reorganization, and neuroleucosis | 1654.7 (2 days of the disease) 3775.1 (4–5 days of the disease) | 4158.0 (1 day of the disease) 5160.0 (4–5 days of the disease) | 157.8 (1 day of the disease) 277.5 (2 days of the disease) 226.3 (4–5 days of the disease) |
| 2. Boy M. | 1 year, 5 months | 20 days | Hydrocephaly | 714.60 (16 days of the disease) 391.4 (20 days of the disease) | 81.0 (15 days of the disease) 1174.0 (19 days of the disease) 11009.0 (20 days of the disease) | 9.6 (13 days of the disease) 69.30 (18 days of the disease) 59.1 (20 days of the disease) |
| 3. Boy X. | 12 years, 7 months | 50 days | Acute lymphoblastic, leukemia, B II immunological variant, and condition after bone marrow transplantation | 3091.1 (1 week of the disease) 3840.7 (18–26 days of the disease) 8947.1 (29–30 days of the disease) 10,899.3 (44 days of the disease) | 387.0 (29–30 days of the disease) 2292.0 (44 days of the disease) | 27.0 (18–26 days of the disease) 45.1 (29–30 days of the disease) 298.0 (31–37 days of the disease) >320.0 (44 days of the disease) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasyrov, R.A.; Ivanov, D.O.; Krasnogorskaya, O.L.; Timchenko, V.N.; Fedotova, E.P.; Chepelev, A.S.; Galichina, V.A.; Sidorova, N.A.; Anichkov, N.M. COVID-19 in Children: Molecular Profile and Pathological Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316750
Nasyrov RA, Ivanov DO, Krasnogorskaya OL, Timchenko VN, Fedotova EP, Chepelev AS, Galichina VA, Sidorova NA, Anichkov NM. COVID-19 in Children: Molecular Profile and Pathological Features. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316750
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasyrov, Ruslan A., Dmitry O. Ivanov, Olga L. Krasnogorskaya, Vladimir N. Timchenko, Elena P. Fedotova, Alexander S. Chepelev, Veronika A. Galichina, Nadezhda A. Sidorova, and Nikolai M. Anichkov. 2023. "COVID-19 in Children: Molecular Profile and Pathological Features" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316750
APA StyleNasyrov, R. A., Ivanov, D. O., Krasnogorskaya, O. L., Timchenko, V. N., Fedotova, E. P., Chepelev, A. S., Galichina, V. A., Sidorova, N. A., & Anichkov, N. M. (2023). COVID-19 in Children: Molecular Profile and Pathological Features. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316750





