Influence of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Processes and Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Enrichment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Differential Expression of BTK-p80 and BTK-p65 Isoforms in Tumors of HNSCC Patients
2.2. Morphological Changes in Two-Dimensional Cultivated Tumor Cells from HNSCC after Treatment with BTK Inhibitor Are Associated with EMT Processes
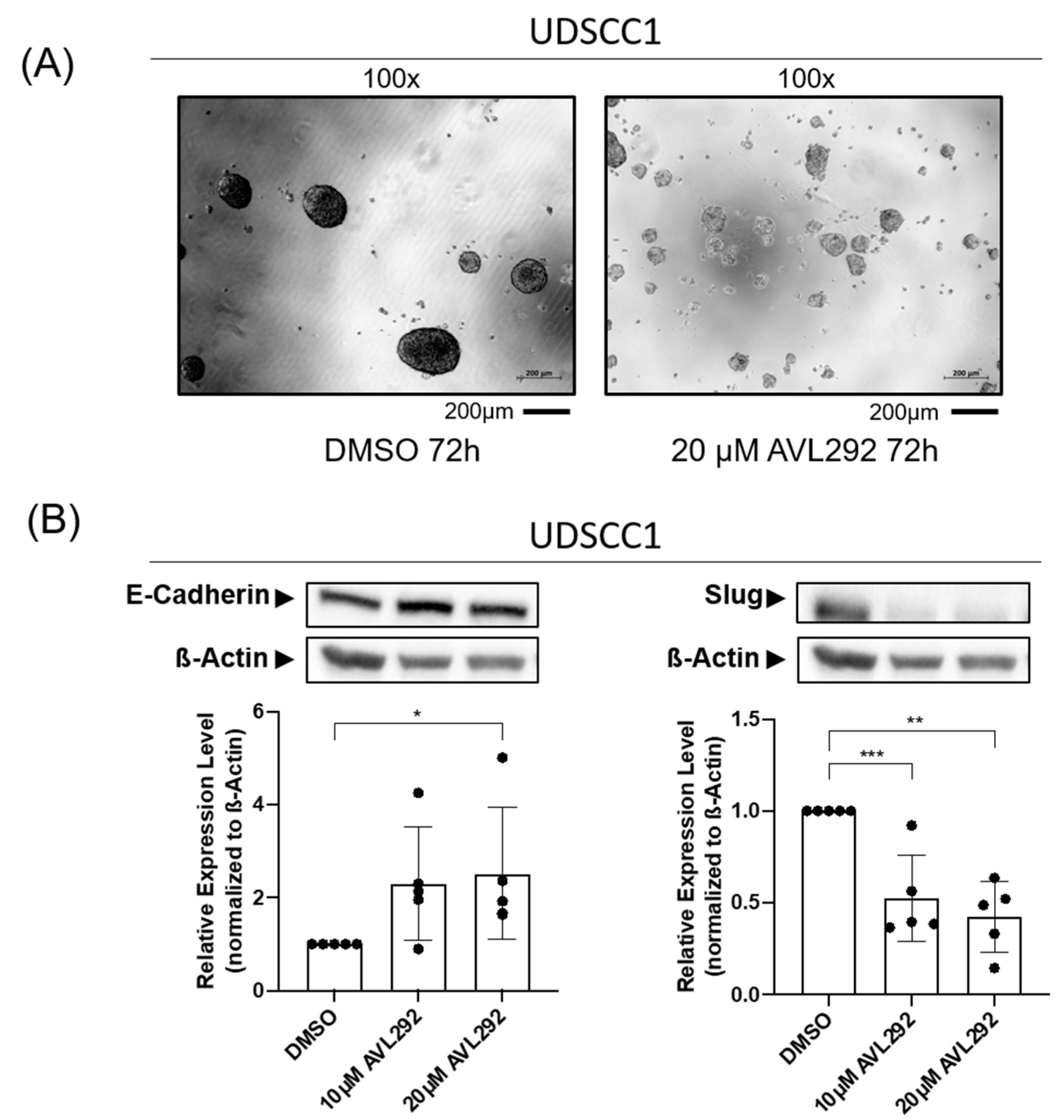
2.3. Morphological Changes in Three-Dimension Cultures of HNSCC after Treatment with BTK Inhibitor Are Associated with EMT Processes
2.4. Influence of BTK Inhibition on CTC Enrichment
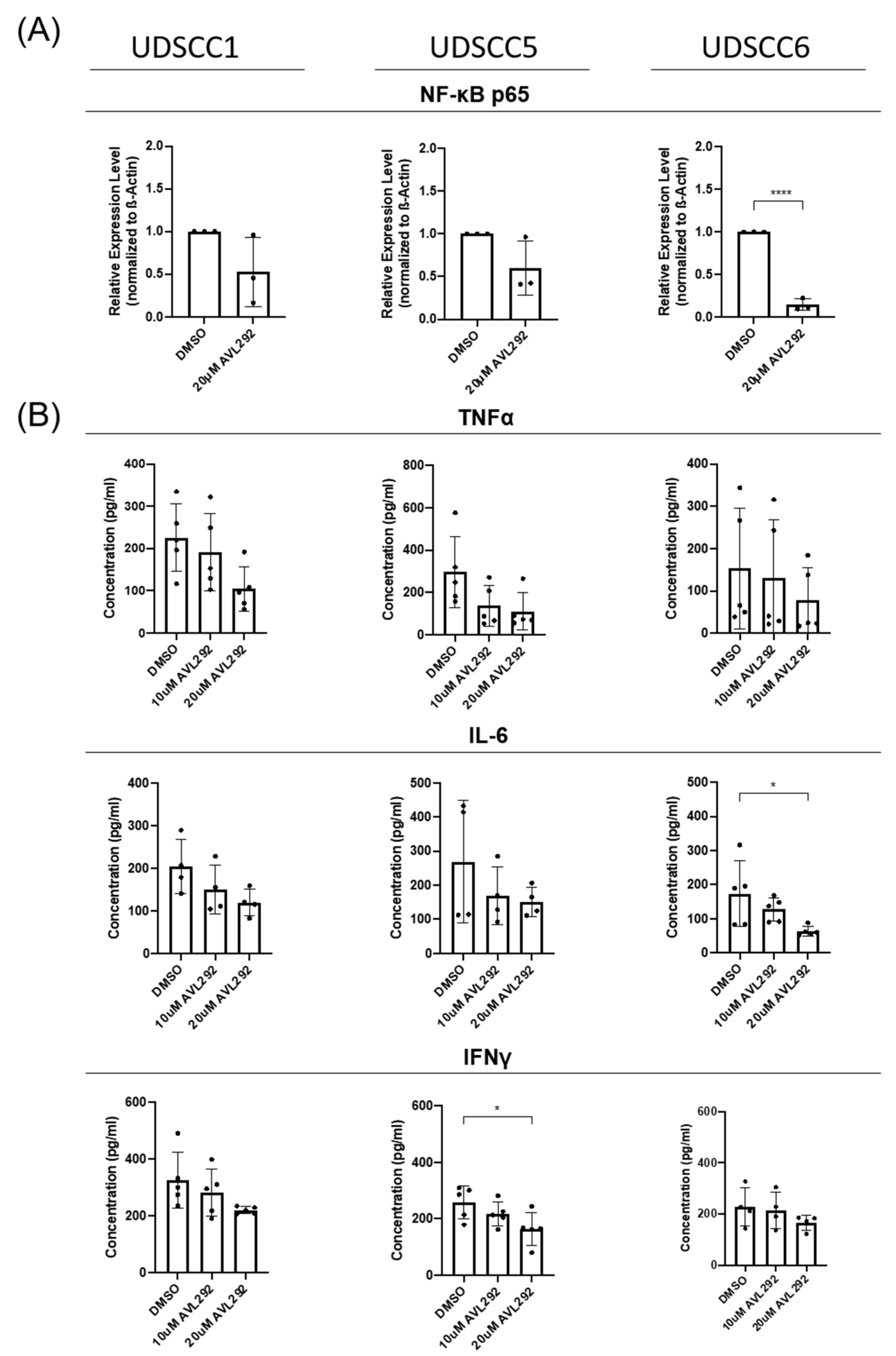
2.5. BTK Inhibition Influences the NF-κB Pathway and Cytokine Release from Tumor Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Immunohistochemical Staining of Tissue Microarrays and Scoring of BTK Expression
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture
4.3. Drug
4.4. Sphere Formation Assay
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and Analysis
4.8. ELISA
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 26, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Burtness, B. Treating Head and Neck Cancer in the Age of Immunotherapy: A 2023 Update; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 83, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wartmann, T.; Jauch, K.W.; et al. Targeting cancer stem cells and their niche: Perspectives for future therapeutic targets and strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Alonci, A.; Penna, G.; Innao, V.; Gerace, D.; Rotondo, F.; Musolino, C. The cancer stem cell hypothesis: A guide to potential molecular targets. Cancer Investig. 2014, 32, 470–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, V.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, I.; Ambati, R.; Gundamaraju, R. Exploring the Crosstalk between Inflammation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9918379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Saleh, A.; Si, H.; Lee, S.; Guven-Maiorov, E.; Keskin, O.; Gursoy, A.; et al. Head and neck cancers promote an inflammatory transcriptome through coactivation of classic and alternative NF-κB pathways. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loercher, A.; Lee, T.L.; Ricker, J.L.; Howard, A.; Geoghegen, J.; Chen, Z.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Sitcheran, R.; Chuang, E.Y.; Mitchell, J.B.; et al. Nuclear factor-κB is an important modulator of the altered gene expression profile and malignant phenotype in squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6511–6523, Erratum in Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8130–8132. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, E.L.; Chen, Z.; Van Waes, C. Regulation of nfκb signalling by ubiquitination: A potential therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma? Cancers 2020, 12, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.T.; Ricker, J.L.; Chen, Z.; Van Waes, C. Role of activated nuclear factor-κB in the pathogenesis and therapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck—Allen—2007—Head & Neck—Wiley Online Library.pdf. Haed Neck 2007, 10, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrey, F.G.; Dong, G.; Sunwoo, J.; Chen, Z.; Wolf, J.S.; Crowl-Bancroft, C.V.; Mukaida, N.; Van Waes, C. Constitutive Activation of Transcription Factors NF-jB, AP-1, and NF-IL6 in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines that Express Pro-in¯ammatory and Pro-angiogenic Cytokines. Mol. Carcinog. 1999, 26, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal Singh, S.; Dammeijer, F.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, S.; Rawlings, D.J.; Witte, O.N. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in immunodeficiency. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1994, 6, 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler, K.; Sindrilaru, A.; Terszowski, G.; Kokai, E.; Feyerabend, T.B.; Bullinger, L.; Rodewald, H.-R.; Brunner, C. Neutrophil development and function critically depend on Bruton tyrosine kinase in a mouse model of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Blood 2011, 117, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmeier, W.; Abramova, A.; Schebesta, A. Tec family kinases: Regulation of FcεRI-mediated mast-cell activation. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.N.R.; Bittner, Z.; Liu, X.; Dang, T.-M.; Radsak, M.P.; Brunner, C. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase: An emerging key player in innate immunity. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprulu, A.D.; Ellmeier, W. The role of Tec family kinases in mononuclear phagocytes. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 29, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, P. Inhibitors targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in cancers: Drug development advances. Leukemia 2021, 35, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eifert, C.; Wang, X.; Kokabee, L.; Kourtidis, A.; Jain, R.; Gerdes, M.G.; Conklin, D.S. A novel Isoform of the B cell Tyrosine Kinase BTK Protects Breast cancer Cells from Apoptosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassilli, E.; Pisano, F.; Cialdella, A.; Bonomo, S.; Missaglia, C.; Cerrito, M.G.; Masiero, L.; Ianzano, L.; Giordano, F.; Cicirelli, V.; et al. A novel oncogenic BTK isoform is overexpressed in colon cancers and required for RAS-mediated transformation. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4368–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.; Vaira, V.; Cortinovis, D.; Bonomo, S.; Goedmakers, J.; Brena, F.; Cialdella, A.; Ianzano, L.; Forno, I.; Cerrito, M.G.; et al. P65BTK is a novel potential actionable target in KRAS-mutated/EGFR-wild type lung adenocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Chen, X.Y.; Ji, K.W.; Tao, F. Targeting Btk with ibrutinib inhibit gastric carcinoma cells growth. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3003–3012. [Google Scholar]
- Kokabee, L.; Wang, X.; Sevinsky, C.J.; Wang, W.L.W.; Cheu, L.; Chittur, S.V.; Karimipoor, M.; Tenniswood, M.; Conklin, D.S. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a potential therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, R.; Bhardwaj, G.; Yang, J.C.; Changou, C.; Ma, A.-H.; Mazloom, A.; Chintapalli, S.; Xiao, K.; Xiao, W.; et al. Targeting Btk/Etk of prostate cancer cells by a novel dual inhibitor. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Su, Y.-K.; Lin, C.-M.; Chao, T.-Y.; Huang, S.-P.; Huynh, T.-T.; Jan, H.-J.; Whang-Peng, J.; Chiou, J.-F.; Wu, A.T.H.; et al. Preclinical investigation of ibrutinib, a Bruton’s kinase tyrosine (Btk) inhibitor, in suppressing glioma tumorigenesis and stem cell phenotypes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69961–69975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Hong, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, P.; Gu, A.; Guo, X.; Zhao, P. Ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, exhibits antitumoral activity and induces autophagy in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucha, M.A.; Wu, A.T.H.; Lee, W.; Wang, L.; Lin, W.; Yuan, C.; Yeh, C. Bruton’ s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor ibrutinib suppresses stem-like traits in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13255–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Huang, C.M.; Hsieh, M.S.; Huang, T.Y.; Huang, C.S.; Hsu, T.N.; Huang, M.S.; Lee, W.H.; Yeh, C.T.; et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic strategy for chemoresistant oral squamous cell carcinoma and potential suppression of cancer stemness. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzler, A.C.; Strobel, H.; Kors, T.A.; Ezi, J.; Lesakova, K.; Pscheid, R.; Azoitei, N.; Sporleder, J.; Staufenberg, A.; Drees, R.; et al. BTK Isoforms p80 and p65 Are Expressed in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) and Involved in Tumor Progression. Cancers 2023, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uckun, F.M.; Venkatachalam, T. Targeting Solid Tumors With BTK Inhibitors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 650414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Chen, L.; Wei, X. Inflammatory cytokines in cancer: Comprehensive understanding and clinical progress in gene therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.L.; Lu, H.; Soutto, M.; Bhat, N.; Chen, Z.; Peng, D.; Gomaa, A.; Wang, J.B.; Xie, J.W.; Li, P.; et al. Multivalent tyrosine kinase inhibition promotes T cell recruitment to immune-desert gastric cancers by restricting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via tumour-intrinsic IFN-γ signalling. Gut 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, D.; Ju, H.; Ma, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Deng, J.; et al. Stabilization of Slug by NF-κB is Essential for TNF-α-Induced Migration and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikatan, N.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Bamodu, O.A.; Hsiao, M.; Hsu, W.M.; Haryana, S.M.; Sutaryo; Chao, T.Y.; Yeh, C.T. Aberrantly expressed Bruton’s tyrosine kinase preferentially drives metastatic and stem cell-like phenotypes in neuroblastoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, X. E-cadherin expression and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Evidence from 19 published investigations. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinke, H.; Pan, M.; Akyol, M.; Zhou, J.; Shi, E.; Kranz, G.; Libl, D.; Quadt, T.; Simon, F.; Canis, M.; et al. SLUG-related partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a transcriptomic prognosticator of head and neck cancer survival. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chiu, S.C.; Cho, D.Y.; Lee, L.M.; Wen, Y.C.; Whang-Peng, J.; Hsiao, C.H.; Shih, P.H. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine Kinase suppresses cancer stemness and promotes carboplatin-induced cytotoxicity against bladder cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 6093–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.S.; Cirillo, N. The molecular markers of cancer stem cells in head and neck tumors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Chen, K.H.; Huang, P.I.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiou, G.Y.; Lo, W.L.; Tseng, L.M.; Hsu, H.S.; Chang, K.W.; Chiou, S.H. Cucurbitacin I suppressed stem-like property and enhanced radiation-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous carcinoma-derived CD44 +ALDH1+ cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2879–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.; Gunduz, E.; Tamagawa, S.; Enomoto, K.; Hotomi, M. Identification and chemoresistance of cancer stem cells in HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Dong, Z.; Vodopyanov, D.; Imai, A.; Helman, J.I.; Prince, M.E.; Wicha, M.S.; Nör, J.E. Endothelial cell-initiated signaling promotes the survival and self-renewal of cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9969–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavyraki, M.; Porter, R.K. Evidence of a role for interleukin-6 in anoikis resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Chung, I.; Wong, W.F.; Masamune, A.; Sim, M.S.; Looi, C.Y. Paracrine IL-6 signaling mediates the effects of pancreatic stellate cells on epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Stat3/Nrf2 pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, B.; Datta, J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, K.; Li, W.Y. IL-6 promotes cancer stemness and oncogenicity in U2OS and MG-63 osteosarcoma cells by upregulating the OPN-STAT3 pathway. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6511–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, B.; de Souza, F.C.; Mota de Souza Lima, I.; dos Santos Schiavinato, J.L.; Corveloni, A.C.; Thomé, C.H.; Araújo Silva, W.; Faça, V.M.; Covas, D.T.; Zago, M.A.; et al. A High-Content Screening Approach to Identify MicroRNAs Against Head and Neck Cancer Cell Survival and EMT in an Inflammatory Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beziaud, L.; Young, C.M.; Alonso, A.M.; Norkin, M.; Minafra, A.R.; Huelsken, J. IFNγ-induced stem-like state of cancer cells as a driver of metastatic progression following immunotherapy. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 818–831.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocher, A.M.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Interferon-γ: Teammate or opponent in the tumour microenvironment? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, L.; He, Q.; Ye, B.; Wu, L.; Huang, X.; et al. High PD-L1 expression associates with low T-cadherin expression and poor prognosis in human papillomavirus-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2023, 45, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Petro, J.B.; Rahman, S.M.; Ballard, D.W.; Khan, W.N. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is required for activation of IkappaB kinase and nuclear factor kappaB in response to B cell receptor engagement. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm 2021, 2, 618–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.L.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Clare, S.E.; Morimiya, A.; Badve, S.; Nakshatri, H. NF-kappaB re-presses E-cadherin expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2. Oncogene 2007, 26, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leichtle, F.; Betzler, A.C.; Eizenberger, C.; Lesakova, K.; Ezić, J.; Drees, R.; Greve, J.; Schuler, P.J.; Laban, S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; et al. Influence of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Processes and Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Enrichment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713133
Leichtle F, Betzler AC, Eizenberger C, Lesakova K, Ezić J, Drees R, Greve J, Schuler PJ, Laban S, Hoffmann TK, et al. Influence of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Processes and Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Enrichment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeichtle, Franziska, Annika C. Betzler, Carlotta Eizenberger, Kristina Lesakova, Jasmin Ezić, Robert Drees, Jens Greve, Patrick J. Schuler, Simon Laban, Thomas K. Hoffmann, and et al. 2023. "Influence of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Processes and Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Enrichment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713133
APA StyleLeichtle, F., Betzler, A. C., Eizenberger, C., Lesakova, K., Ezić, J., Drees, R., Greve, J., Schuler, P. J., Laban, S., Hoffmann, T. K., Cordes, N., Lavitrano, M., Grassilli, E., & Brunner, C. (2023). Influence of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) on Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Processes and Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) Enrichment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713133







