A Scoping Review on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Small Vessel Disease: Molecular Insights from Human Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
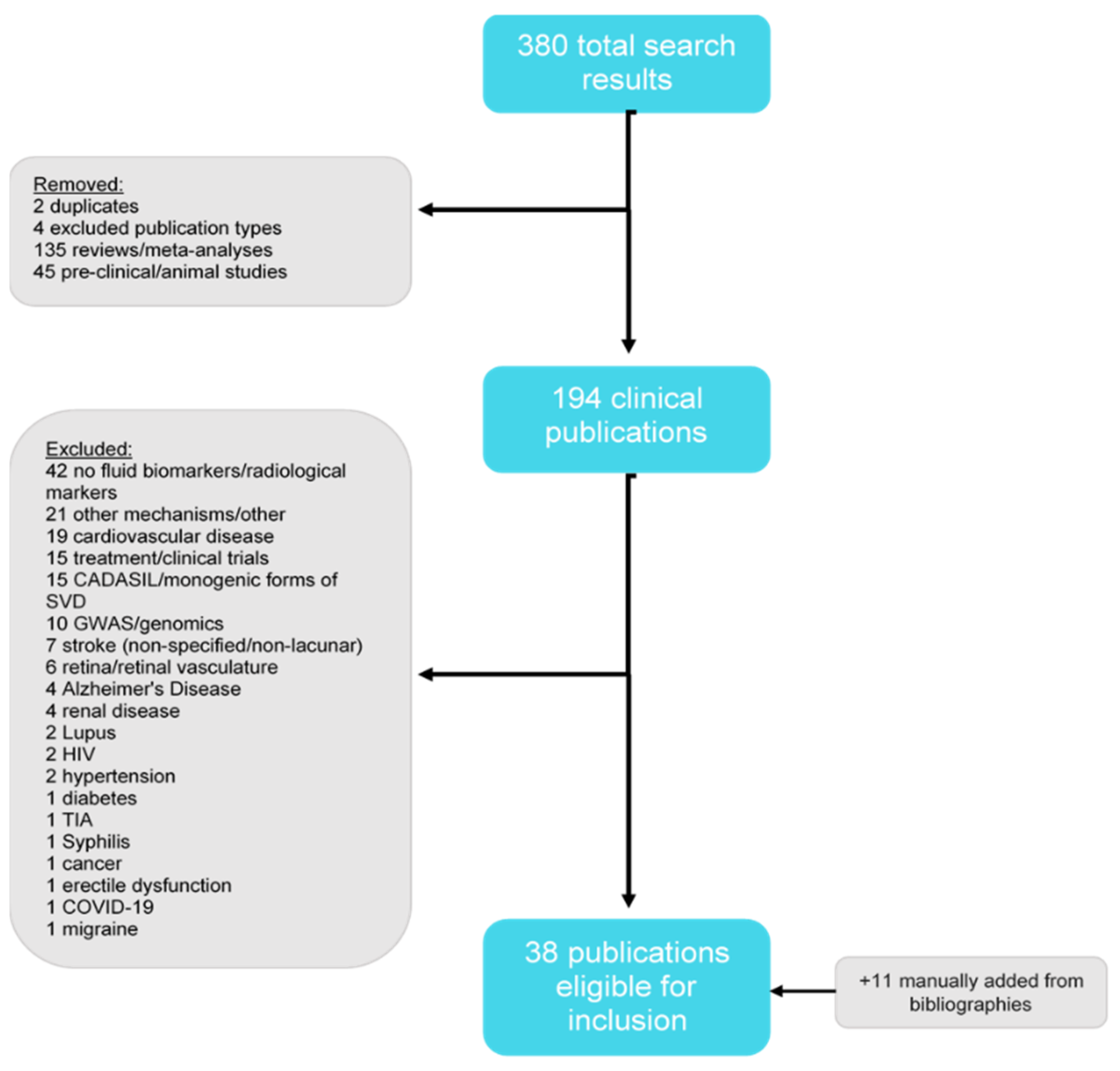
2. Methods
Literature Review
3. Results
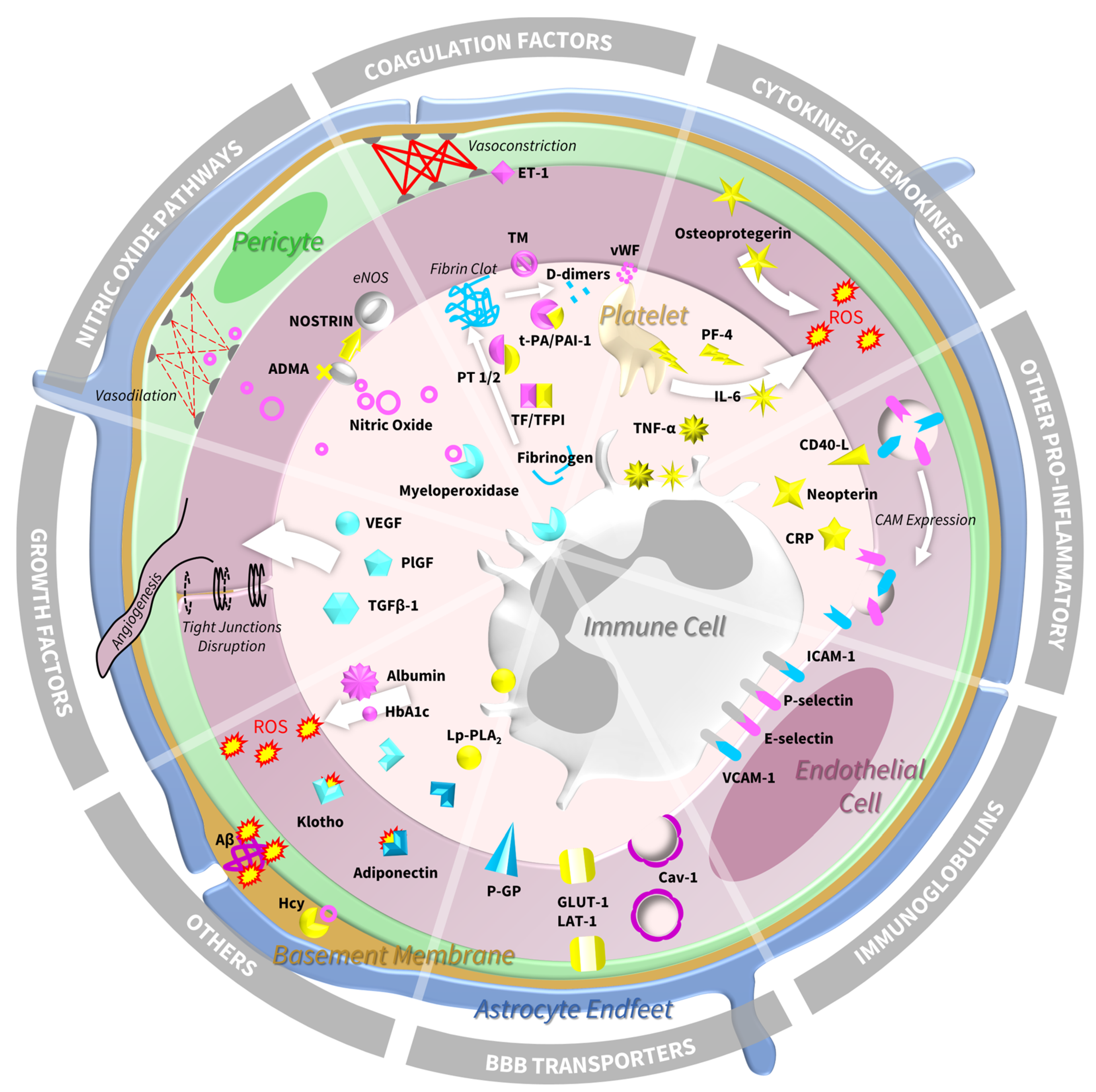
4. Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction and SVD: Molecular Insights from Human Studies
4.1. Immunoglobulin Superfamily—Cell Adhesion Molecules and Selectins
4.2. Blood–Brain Barrier Transporters
4.3. Cytokines and Chemokines
4.3.1. Interleukin-6
4.3.2. Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha and Its Receptors
4.3.3. Osteoprotegerin
4.3.4. Platelet Factor-4
4.4. Other Pro-Inflammatory Markers
4.4.1. C-Reactive Protein
4.4.2. Neopterin
4.4.3. CD40 Ligand
4.5. Coagulation Factors
4.5.1. Von Willebrand Factor
4.5.2. Tissue Factor and Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
4.5.3. Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1
4.5.4. Prothrombin Factors 1 and 2
4.5.5. D-Dimer
4.5.6. Thrombomodulin
4.5.7. Endothelin-1
4.5.8. Fibrinogen
4.6. Growth Factors
4.7. Nitric Oxide Pathways
4.7.1. Nitric Oxide
4.7.2. NOSTRIN
4.7.3. ADMA
4.7.4. Myeloperoxidase
4.8. Other Relevant Biomarkers
4.8.1. Homocysteine
4.8.2. Albumin
4.8.3. Haemoglobin A1c
4.8.4. Amyloid-Beta
4.8.5. Adiponectin
4.8.6. Klotho
4.8.7. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Mass
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
5.1. Implications for Clinical Practice
5.2. Implications for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ADMA | asymmetric dimethylarginine |
| AT1 | angiotensin II type 1 receptor |
| Aβ | amyloid beta |
| β-amyloid1–40 | beta-amyloid1–40 |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| Ca2+ | calcium |
| CADASIL | cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy |
| Cav-1 | caveolin-1 |
| CD40 | CD40 ligand |
| CDR | Clinical Dementia Rating Scale |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| CT | computerised tomography |
| CVR | cerebrovascular reactivity |
| DCE-MRI | dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI |
| DTI | diffusion tensor imaging |
| EDE | endothelial-derived exosome |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| E-selectin | endothelial selectin |
| ET-1 | endothelin-1 |
| GLUT-1 | glucose transporter-1 |
| Hcy | homocysteine |
| HbA1c | haemoglobin A1c |
| ICAM-1 | intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| ICV | intracranial volume |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| K+ | potassium |
| LAT-1 | large neutral amino acid transporter-1 |
| Lp-PLA2 | lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2-mass |
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| NOSTRIN | endothelial nitric oxide synthase traffic inducer |
| PAI-1 | plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PF-4 | platelet factor-4 |
| P-GP | permeability-glycoprotein |
| PlGF | placental growth factor |
| P-selectin | platelet selectin |
| PVS | perivascular spaces |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| sVCAM-1 | soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| SVD | small vessel disease |
| TF | tissue factor |
| TFPI | tissue factor pathway inhibitor |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor- β 1 |
| TM | thrombomodulin |
| TNFR1 | tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 |
| TNFR2 | tumour necrosis factor receptor 2 |
| TNF-α | tumour necrosis factor alpha |
| t-PA | tissue-type plasminogen activator |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| vWF | von Willebrand Factor |
| WMH | white matter hyperintensities |
References
- Hachinski, V.; Einhäupl, K.; Ganten, D.; Alladi, S.; Brayne, C.; Stephan, B.C.; Sweeney, M.D.; Zlokovic, B.; Iturria-Medina, Y.; Iadecola, C. Preventing Dementia by Preventing Stroke: The Berlin Manifesto. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debette, S.; Schilling, S.; Duperron, M.-G.; Larsson, S.C.; Markus, H.S. Clinical Significance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Markers of Vascular Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, U.; Gilmartin, D.; Jochems, A.C.; Knox, L.; Doubal, F.N.; Wardlaw, J.M. Neuropsychiatric Symptoms Associated with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small Vessel Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Benveniste, H.; Williams, A. Cerebral Vascular Dysfunctions Detected in Human Small Vessel Disease and Implications for Preclinical Studies. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Doubal, F.N.; Valdes-Hernandez, M.; Wang, X.; Chappell, F.M.; Shuler, K.; Armitage, P.A.; Carpenter, T.C.; Dennis, M.S. Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Long-Term Clinical and Imaging Outcomes in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Stroke 2013, 44, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeier, B.; Daneman, R.; Ransohoff, R.M. Development, Maintenance and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The Blood–Brain Barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisler, K.; Nelson, A.R.; Montagne, A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Cerebral Blood Flow Regulation and Neurovascular Dysfunction in Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.K. Linking Endothelial Dysfunction with Endothelial Cell Activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longden, T.A.; Hill-Eubanks, D.C.; Nelson, M.T. Ion Channel Networks in the Control of Cerebral Blood Flow. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 492–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluvinage, J.V.; Wyss-Coray, T. Systemic Factors as Mediators of Brain Homeostasis, Ageing and Neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procter, T.V.; Williams, A.; Montagne, A. Interplay between Brain Pericytes and Endothelial Cells in Dementia. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantini, S.; Tran, C.H.T.; Gordon, G.R.; Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A. Impaired Neurovascular Coupling in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Contribution of Astrocyte Dysfunction and Endothelial Impairment to Cognitive Decline. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 94, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, H.; Nedergaard, M. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Glymphopathy? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 72, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, T.; Kerkhofs, D.; Mizuno, T.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Foulquier, S. Vessel-Associated Immune Cells in Cerebrovascular Diseases: From Perivascular Macrophages to Vessel-Associated Microglia. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Regenerating CNS Myelin—From Mechanisms to Experimental Medicines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Hunt, B.J.; O’Sullivan, M.; Parmar, K.; Bamford, J.M.; Briley, D.; Brown, M.M.; Thomas, D.J.; Markus, H.S. Markers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Lacunar Infarction and Ischaemic Leukoaraiosis. Brain 2003, 126 Pt 2, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagne, A.; Barnes, S.R.; Sweeney, M.D.; Halliday, M.R.; Sagare, A.P.; Zhao, Z.; Toga, A.W.; Jacobs, R.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Amezcua, L.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in the Aging Human Hippocampus. Neuron 2015, 85, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, D.A.; Sweeney, M.D.; Montagne, A.; Sagare, A.P.; D’Orazio, L.M.; Pachicano, M.; Sepehrband, F.; Nelson, A.R.; Buennagel, D.P.; Harrington, M.G.; et al. Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown Is an Early Biomarker of Human Cognitive Dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Kisler, K.; Montagne, A.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. The Role of Brain Vasculature in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeuw, F.-E.; Kleine, M.; Frijns, C.J.M.; Fijnheer, R.; Gijn, J.; Kappelle, L.J. Endothelial Cell Activation Is Associated with Cerebral White Matter Lesions in Patients with Cerebrovascular Disease. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2002, 977, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, S.; Marlborough, F.; Doubal, F.; Webb, D.J.; Wardlaw, J. Blood Markers of Coagulation, Fibrinolysis, Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Lacunar Stroke versus Non-Lacunar Stroke and Non-Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 37, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quick, S.; Moss, J.; Rajani, R.M.; Williams, A. A Vessel for Change: Endothelial Dysfunction in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Vitale, G.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. Inflammaging and ‘Garb-Aging’. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golias, C.H.; Tsoutsi, E.; Matziridis, A.; Makridis, P.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. Leukocyte and Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecules in Inflammation Focusing on Inflammatory Heart Disease. In Vivo 2007, 21, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Springer, T.A. Adhesion Receptors of the Immune System. Nature 1990, 346, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, D.; Weiss, G.; Reibnegger, G.; Wachter, H. The Role of Neopterin as a Monitor of Cellular Immune Activation in Transplantation, Inflammatory, Infectious, and Malignant Diseases. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1992, 29, 307–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, S.Y.; Benarroch, A.; Monter-Solans, J.; Edelman, E.R. Monocyte Activation State Regulates Monocyte-Induced Endothelial Proliferation through Met Signaling. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2010, 115, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferretti, M.T.; Merlini, M.; Späni, C.; Gericke, C.; Schweizer, N.; Enzmann, G.; Engelhardt, B.; Kulic, L.; Suter, T.; Nitsch, R.M. T-Cell Brain Infiltration and Immature Antigen-Presenting Cells in Transgenic Models of Alzheimer’s Disease-like Cerebral Amyloidosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 54, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarmann, A.; Nowak, E.; Deiß, A.; van der Pol, S.; Monoranu, C.-M.; Kooij, G.; Müller, N.; van der Valk, P.; Stoll, G.; de Vries, H.E. Soluble VCAM-1 Impairs Human Brain Endothelial Barrier Integrity via Integrin α-4-Transduced Outside-in Signalling. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattsson, N.; Stomrud, E.; Lindberg, O.; Palmqvist, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Hansson, O. CSF Biomarkers of Neuroinflammation and Cerebrovascular Dysfunction in Early Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2018, 91, e867–e877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-W.; Tsai, M.-H.; Chen, N.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Lu, Y.-T.; Lui, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chang, W.-N.; Chang, A.Y.W.; Chang, C.-C. Clinical Significance of Circulating Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 to White Matter Disintegrity in Alzheimer’s Dementia. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhl, R.P.W.; Damoiseaux, J.G.M.C.; Lodder, J.; Theunissen, R.O.M.F.I.H.; Knottnerus, I.L.H.; Staals, J.; Henskens, L.H.G.; Kroon, A.A.; de Leeuw, P.W.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; et al. Vascular Inflammation in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elneihoum, A.M.; Falke, P.; Axelsson, L.; Lundberg, E.; Lindgarde, F.; Ohlsson, K. Leukocyte Activation Detected by Increased Plasma Levels of Inflammatory Mediators in Patients with Ischemic Cerebrovascular Diseases. Stroke 1996, 27, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L. Circulating Markers of Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2003, 169, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yin, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiao, L.; Duan, Z.; Cai, Q.; Liu, D.; et al. Microbleeds in Ischemic Stroke Are Associated with Lower Serum Adiponectin and Higher Soluble E-Selectin Levels. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 334, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallée, P.C.; Labreuche, J.; Faille, D.; Huisse, M.-G.; Nicaise-Roland, P.; Dehoux, M.; Gongora-Rivera, F.; Jaramillo, A.; Brenner, D.; Deplanque, D.; et al. Circulating Markers of Endothelial Dysfunction and Platelet Activation in Patients with Severe Symptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 36, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bodles-Brakhop, A.M.; Barger, S.W. A Role for P-Glycoprotein in Clearance of Alzheimer Amyloid β-Peptide from the Brain. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arba, F.; Giannini, A.; Piccardi, B.; Biagini, S.; Palumbo, V.; Giusti, B.; Nencini, P.; Maria Gori, A.; Nesi, M.; Pracucci, G.; et al. Small Vessel Disease and Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction after Ischaemic Stroke. Eur. Stroke J. 2019, 4, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassbender, K.; Bertsch, T.; Mielke, O.; Mühlhauser, F.; Hennerici, M. Adhesion Molecules in Cerebrovascular Diseases. Evidence for an Inflammatory Endothelial Activation in Cerebral Large- and Small-Vessel Disease. Stroke 1999, 30, 1647–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Wong, K.S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Fu, J.H.; Ding, D.; Hong, Z. Plasma Level of SICAM-1 Is Associated with the Extent of White Matter Lesion among Asymptomatic Elderly Subjects. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-D.; Cao, Y.; Mu, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-M.; Gao, F.; Han, F.; Zhai, F.-F.; Zhou, L.-X.; Ni, J.; Yao, M. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Community-Based Cohort Study. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2022, 7, e001102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoamanesh, A.; Preis, S.R.; Beiser, A.S.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Kase, C.S.; Wolf, P.A.; DeCarli, C.; Romero, J.R.; Seshadri, S. Inflammatory Biomarkers, Cerebral Microbleeds, and Small Vessel Disease: Framingham Heart Study. Neurology 2015, 84, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noz, M.P.; Ter Telgte, A.; Wiegertjes, K.; Tuladhar, A.M.; Kaffa, C.; Kersten, S.; Bekkering, S.; van der Heijden, C.D.C.C.; Hoischen, A.; Joosten, L.A.B.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory Monocyte Phenotype During Acute Progression of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 639361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Cui, Y.; Gong, G.; Chai, Q.; Guo, Y.; et al. Low Carotid Endothelial Shear Stress Associated with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in an Older Population: A Subgroup Analysis of a Population-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Atherosclerosis 2019, 288, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszewski, J.; Piusińska-Macoch, R.; Brodacki, B.; Skrobowska, E.; Stępień, A. IL-6, PF-4, SCD40 L, and Homocysteine Are Associated with the Radiological Progression of Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease: A 2-Year Follow-up Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, M.; Castillo, J.; García, M.M.; Leira, R.; Serena, J.; Chamorro, A.; Dávalos, A. Inflammation-Mediated Damage in Progressing Lacunar Infarctions: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Stroke 2002, 33, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertje, E.C.; Janelidze, S.; van Westen, D.; Cullen, N.; Stomrud, E.; Palmqvist, S.; Hansson, O.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N. Associations Between CSF Markers of Inflammation, White Matter Lesions, and Cognitive Decline in Individuals Without Dementia. Neurology 2023, 100, e1812–e1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.S.; Hunt, B.; Palmer, K.; Enzinger, C.; Schmidt, H.; Schmidt, R. Markers of Endothelial and Hemostatic Activation and Progression of Cerebral White Matter Hyperintensities: Longitudinal Results of the Austrian Stroke Prevention Study. Stroke 2005, 36, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, T.; Kawamura, T.; Umegaki, H.; Mashita, S.; Kanai, A.; Sakakibara, T.; Hotta, N.; Sobue, G. Endothelial and Inflammatory Markers in Relation to Progression of Ischaemic Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease and Cognitive Impairment: A 6-Year Longitudinal Study in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giwa, M.O.; Williams, J.; Elderfield, K.; Jiwa, N.S.; Bridges, L.R.; Kalaria, R.N.; Markus, H.S.; Esiri, M.M.; Hainsworth, A.H. Neuropathologic Evidence of Endothelial Changes in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neurology 2012, 78, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constans, J.; Conri, C. Circulating Markers of Endothelial Function in Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 368, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, F.M.; Casaletto, K.B.; Altendahl, M.; Staffaroni, A.M.; Fletcher, E.; Filshtein, T.J.; Glymour, M.M.; Miller, B.L.; Hinman, J.D.; DeCarli, C.; et al. “Liquid Biopsy” of White Matter Hyperintensity in Functionally Normal Elders. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Yao, J.; Rettberg, J.R.; Chen, S.; Brinton, R.D. Early Decline in Glucose Transport and Metabolism Precedes Shift to Ketogenic System in Female Aging and Alzheimer’s Mouse Brain: Implication for Bioenergetic Intervention. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padowski, J.M.; Pollack, G.M. Influence of Time to Achieve Substrate Distribution Equilibrium between Brain Tissue and Blood on Quantitation of the Blood–Brain Barrier P-Glycoprotein Effect. Brain Res. 2011, 1426, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Ashique, S.; Garg, A.; Rai, V.K.; Dua, K.; Goyal, A.; Bhatt, S. Role of SiRNA-Based Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, R.; Xie, Y.; Ma, M.; Ye, R.; Liu, X. Caveolae: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Targets for Stroke. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-L.; Song, J.-N.; Zhang, M. Role of Caveolin-1 in the Biology of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 25, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, N.; Basi, D.L.; Carlson, M.; Mariash, A.; Hong, Z.; Lehman, U.; Mullegama, S.; Weir, E.K.; Hall, J.L. Increase in GLUT1 in Smooth Muscle Alters Vascular Contractility and Increases Inflammation in Response to Vascular Injury. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.A.; Nishida, Y.; Sagare, A.P.; Rege, S.V.; Bell, R.D.; Perlmutter, D.; Sengillo, J.D.; Hillman, S.; Kong, P.; Nelson, A.R.; et al. GLUT1 Reductions Exacerbate Alzheimer’s Disease Vasculo-Neuronal Dysfunction and Degeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Xiao, L.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Ye, Z.; Hao, Y.; Dai, Q.; Sun, W.; et al. Lower Serum Caveolin-1 Is Associated with Cerebral Microbleeds in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9026787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Castell, J.V.; Andus, T. Interleukin-6 and the Acute Phase Response. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Zhang, H.; Hill, M.A.; Zhang, C.; Park, Y. Interaction of IL-6 and TNF-α Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Mouse Hearts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, S.; Stumpf, M.; Strehlow, K.; Schmid, A.; Schieffer, B.; Böhm, M.; Nickenig, G. Interleukin-6 Induces Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction by Overexpression of the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpato, S.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Balfour, J.; Chaves, P.; Fried, L.P.; Harris, T.B. Cardiovascular Disease, Interleukin-6, and Risk of Mortality in Older Women: The Women’s Health and Aging Study. Circulation 2001, 103, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari, M.; Penninx, B.W.; Newman, A.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nicklas, B.J.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Rubin, S.M.; Ding, J.; Simonsick, E.M.; Harris, T.B. Inflammatory Markers and Onset of Cardiovascular Events: Results from the Health ABC Study. Circulation 2003, 108, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, T.; Kitagawa, K.; Yamagami, H.; Furukado, S.; Hougaku, H.; Hori, M. Relations of Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Interleukin-6 Levels with Silent Brain Infarction. Stroke 2005, 36, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornage, M.; Chiang, Y.A.; O’Meara, E.S.; Psaty, B.M.; Reiner, A.P.; Siscovick, D.S.; Tracy, R.P.; Longstreth Jr, W.T. Biomarkers of Inflammation and MRI-Defined Small Vessel Disease of the Brain: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke 2008, 39, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, S.J.; Doubal, F.N.; Chappell, F.M.; Valdés-Hernández, M.C.; Wang, X.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Plasma Biomarkers of Inflammation, Endothelial Function and Hemostasis in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 40, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszewski, J.; Skrobowska, E.; Piusińska-Macoch, R.; Brodacki, B.; Stępień, A. IL-1α and IL-6 Predict Vascular Events or Death in Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease-Data from the SHEF-CSVD Study. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, A.K.; McClure, L.A.; Zhang, Y.; Luna, J.M.; Del Brutto, O.H.; Benavente, O.R.; Elkind, M.S. Inflammatory Markers and Outcomes after Lacunar Stroke: Levels of Inflammatory Markers in Treatment of Stroke Study. Stroke 2016, 47, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chappell, F.M.; Valdes Hernandez, M.; Lowe, G.; Rumley, A.; Shuler, K.; Doubal, F.; Wardlaw, J.M. Endothelial Function, Inflammation, Thrombosis, and Basal Ganglia Perivascular Spaces in Patients with Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Clark, R.K.; McDonnell, P.C.; Young, P.R.; White, R.F.; Barone, F.C.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Expression in Ischemic Neurons. Stroke 1994, 25, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sairanen, T.; Carpén, O.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; Paetau, A.; Turpeinen, U.; Kaste, M.; Lindsberg, P.J. Evolution of Cerebral Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Production during Human Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2001, 32, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolaki, M.; Armaka, M.; Victoratos, P.; Kollias, G. Cellular Mechanisms of TNF Function in Models of Inflammation and Autoimmunity. TNF Pathophysiol. 2010, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J. TNF-Mediated Inflammatory Disease. J. Pathol. A J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Kastin, A.J. Tumor Necrosis Factor and Stroke: Role of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 83, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchi, A.; Gao, X.; Belmadani, S.; Potter, B.J.; Focardi, M.; Chilian, W.M.; Zhang, C. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Induces Endothelial Dysfunction in the Prediabetic Metabolic Syndrome. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Park, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.P.; Lee, S.; Yang, J.; Dellsperger, K.C.; Zhang, C. Role of TNF-α in Vascular Dysfunction. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynina, L.A.; Zabitova, M.R.; Shabalina, A.A.; Kremneva, E.I.; Akhmetzyanov, B.M.; Gadzhieva, Z.S.; Berdalin, A.B.; Kalashnikova, L.A.; Gnedovskaya, E.V.; Krotenkova, M.V. MRI Types of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Circulating Markers of Vascular Wall Damage. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldiken, B.; Guldiken, S.; Turgut, B.; Turgut, N.; Demir, M.; Celik, Y.; Arikan, E.; Tugrul, A. Serum Osteoprotegerin Levels in Patients with Acute Atherothrombotic Stroke and Lacunar Infarct. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikfalvi, A. Platelet Factor 4: An Inhibitor of Angiogenesis. In Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis; Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 30, pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, P.; Barber, M.; Langhorne, P.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.; Stott, D.J. Associations of Inflammatory and Haemostatic Biomarkers with Poor Outcome in Acute Ischaemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Wang, C.-H.; Li, S.-H.; Dumont, A.S.; Fedak, P.W.; Badiwala, M.V.; Dhillon, B.; Weisel, R.D.; Li, R.-K.; Mickle, D.A. A Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: C-Reactive Protein Attenuates Nitric Oxide Production and Inhibits Angiogenesis. Circulation 2002, 106, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, E.R.F. C-Reactive Protein, Fibrinogen, and Cardiovascular Disease Prediction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimon, L.; Peña, E.; Arderiu, G.; Padró, T.; Slevin, M.; Vilahur, G.; Chiva-Blanch, G. C-Reactive Protein in Atherothrombosis and Angiogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, P.; Hui, R.; Edin, M.L.; Zeldin, D.C.; Wang, D.W. Adeno-Associated Virus–Mediated Human C-Reactive Protein Gene Delivery Causes Endothelial Dysfunction and Hypertension in Rats. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanami, D.; Maemura, K.; Takeda, N.; Harada, T.; Nojiri, T.; Saito, T.; Manabe, I.; Imai, Y.; Nagai, R. C-Reactive Protein Induces VCAM-1 Gene Expression through NF-ΚB Activation in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Atherosclerosis 2006, 185, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Liu, P.; Tan, L.; Yin, C. Exosomal MiRNA-223-3p as Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Cognitive Impairment. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkind, M.S.; Luna, J.M.; McClure, L.A.; Zhang, Y.; Coffey, C.S.; Roldan, A.; Del Brutto, O.H.; Pretell, E.J.; Pettigrew, L.C.; Meyer, B.C. C-Reactive Protein as a Prognostic Marker after Lacunar Stroke: Levels of Inflammatory Markers in the Treatment of Stroke Study. Stroke 2014, 45, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.J.; Prins, N.D.; Vermeer, S.E.; Vrooman, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M.B. C-Reactive Protein and Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease: The Rotterdam Scan Study. Circulation 2005, 112, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.E.; Buchanan, T.A.; Pearson, W.S. C-Reactive Protein and Glycemic Control in Adults with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Haelst, P.L.; Liem, A.; van Boven, A.J.; Veeger, N.J.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; Gans, R.O.; Zijlstra, F. Usefulness of Elevated Neopterin and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Predicting Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Non–Q-Wave Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 92, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, P.; Pacileo, M.; De Rosa, S.; Calabrò, P.; Gargiulo, A.; Angri, V.; Granato-Corigliano, F.; Fiorentino, I.; Prevete, N.; De Palma, R. Neopterin Induces Pro-Atherothrombotic Phenotype in Human Coronary Endothelial Cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, U.; Kiniwa, M.; Wu, C.Y.; Maliszewski, C.; Vezzio, N.; Hakimi, J.; Gately, M.; Delespesse, G. Activated T Cells Induce Interleukin-12 Production by Monocytes via CD40-CD40 Ligand Interaction. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischer, U.M. Von Willebrand Factor, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, P.; Jennewein, C.; Zacharowski, K. Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction: Can They Help Us Deciphering Systemic Inflammation and Sepsis? Biomarkers 2011, 16 (Suppl. S1), S11–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, P.; Hankey, G.J.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Thom, J.; Baker, R.I.; McQuillan, A.; Staton, J.; Yi, Q. Endothelial and Platelet Activation in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Its Etiological Subtypes. Stroke 2003, 34, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, C.V.; Lenting, P.J. Von Willebrand Factor: At the Crossroads of Bleeding and Thrombosis. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Weithauser, A.; Tabaraie, T.; Steffens, D.; Kränkel, N.; Witkowski, M.; Stratmann, B.; Tschoepe, D.; Landmesser, U.; Rauch-Kroehnert, U. Micro–RNA-126 Reduces the Blood Thrombogenicity in Diabetes Mellitus via Targeting of Tissue Factor. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumiya, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Terasaki, T.; Kokawa, T.; Kario, K.; Kato, H. Decreased Plasma Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Activity in Ischemic Stroke Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 74, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, A.E. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor: Multiple Anticoagulant Activities for a Single Protein. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niego, B.; Medcalf, R.L. Plasmin-Dependent Modulation of the Blood–Brain Barrier: A Major Consideration during TPA-Induced Thrombolysis? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Jansson, J.-H.; Boman, K.; Nilsson, T.K.; Stegmayr, B.; Hallmans, G. Tissue Plasminogen Activator, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, and Tissue Plasminogen Activator/Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Complex as Risk Factors for the Development of a First Stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Rai, R.; Khan, S.S.; Eren, M.; Ghosh, A.K. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Is a Marker and a Mediator of Senescence. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hao, H.; Leeper, N.J.; Zhu, L. Thrombotic Regulation from the Endothelial Cell Perspectives. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e90–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynina, L.A.; Gnedovskaya, E.V.; Shabalina, A.A.; Sergeeva, A.N.; Kravchenko, M.A.; Nikolaeva, N.S. Biomarkers and Mechanisms of Early Vascular Damage. Zhurnal Nevrol. Psikhiatrii Im. SS Korsakova 2018, 118, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Kurita, K.; Koyama, S.; Arawaka, S.; Kawanami, T.; Tajima, K.; Daimon, M.; Kato, T. Microalbuminuria Is a Risk Factor for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Community-Based Elderly Subjects. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 255, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folsom, A.R.; Delaney, J.A.; Lutsey, P.L.; Zakai, N.A.; Jenny, N.S.; Polak, J.F.; Cushman, M. Associations of Factor VIIIc, D-Dimer, and Plasmin–Antiplasmin with Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality. Am. J. hematol. 2009, 84, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.M. Thrombomodulin and Its Role in Inflammation. In Seminars in Immunopathology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 34, pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Diwakar, L.; Gowaikar, R.; Chithanathan, K.; Gnanabharathi, B.; Tomar, D.S.; Ravindranath, V. Endothelin-1 Mediated Vasoconstriction Leads to Memory Impairment and Synaptic Dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagne, A.; Nikolakopoulou, A.M.; Zhao, Z.; Sagare, A.P.; Si, G.; Lazic, D.; Barnes, S.R.; Daianu, M.; Ramanathan, A.; Go, A.; et al. Pericyte Degeneration Causes White Matter Dysfunction in the Mouse Central Nervous System. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Iseki, C.; Kawanami, T.; Daimon, M.; Kato, T. Plasma Fibrinogen, Global Cognitive Function, and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Results of a Cross-Sectional Study in Community-Dwelling Japanese Elderly. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peach, C.J.; Mignone, V.W.; Arruda, M.A.; Alcobia, D.C.; Hill, S.J.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Woolard, J. Molecular Pharmacology of VEGF-A Isoforms: Binding and Signalling at VEGFR2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goumans, M.-J.; Liu, Z.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-β Signaling in Vascular Biology and Dysfunction. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Couteur, D.G.; Lakatta, E.G. A Vascular Theory of Aging. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chen, T.T.; Barber, C.L.; Jordan, M.C.; Murdock, J.; Desai, S.; Ferrara, N.; Nagy, A.; Roos, K.P.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Autocrine VEGF Signaling Is Required for Vascular Homeostasis. Cell 2007, 130, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaess, B.M.; Preis, S.R.; Beiser, A.; Sawyer, D.B.; Chen, T.C.; Seshadri, S.; Vasan, R.S. Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events. Heart 2016, 102, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. Pathophysiological Consequences of VEGF-Induced Vascular Permeability. Nature 2005, 437, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Moons, L.; Luttun, A.; Vincenti, V.; Compernolle, V.; De Mol, M.; Wu, Y.; Bono, F.; Devy, L.; Beck, H.; et al. Synergism between Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Placental Growth Factor Contributes to Angiogenesis and Plasma Extravasation in Pathological Conditions. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, D.R.; Galli, S.J.; Dvorak, A.M.; Perruzzi, C.A.; Harvey, V.S.; Dvorak, H.F. Tumor Cells Secrete a Vascular Permeability Factor That Promotes Accumulation of Ascites Fluid. Science 1983, 219, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Koh, S.-H.; Lee, Y.J. Serum VEGF Levels in Acute Ischaemic Strokes Are Correlated with Long-Term Prognosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.R.; Himali, J.J.; Conner, S.C.; DeCarli, C.; Vasan, R.S.; Beiser, A.S.; Seshadri, S.; Maillard, P.; Satizabal, C.L. Circulating Vascular Growth Factors and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Markers of Small Vessel Disease and Atrophy in Middle-Aged Adults. Stroke 2018, 49, 2227–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinman, J.D.; Elahi, F.; Chong, D.; Radabaugh, H.; Ferguson, A.; Maillard, P.; Thompson, J.F.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Sagare, A.; Moghekar, A.; et al. Placental Growth Factor as a Sensitive Biomarker for Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, C. The Gene Encoding Transforming Growth Factor Β1 Confers Risk of Ischemic Stroke and Vascular Dementia. Stroke 2006, 37, 2843–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.G. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Endothelial Cell Dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Pelligrino, D.A.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Lassen, N.A. Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition and Cerebrovascular Regulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Ayyadurai, S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericytes of the Neurovascular Unit: Key Functions and Signaling Pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.A.; Bell, R.D.; Zlokovic, B.V. Central Nervous System Pericytes in Health and Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Opitz, N.; Dedio, J.; Renné, C.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Oess, S. NOSTRIN: A Protein Modulating Nitric Oxide Release and Subcellular Distribution of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 17167–17172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ain, R. Nitric-Oxide Synthase Trafficking Inducer Is a Pleiotropic Regulator of Endothelial Cell Function and Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 6600–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, N.; Deb-Chatterji, M.; Dong, Q.; Kielstein, J.T.; Weissenborn, K.; Worthmann, H. Asymmetric Dimethyarginine as Marker and Mediator in Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15983–16004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallance, P.; Leone, A.; Calver, A.; Collier, J.; Moncada, S. Endogenous Dimethylarginine as an Inhibitor of Nitric Oxide Synthesis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1992, 20, S60-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Fan, Y.; Mu, L.-Y.; Ma, L.; Song, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-N. S100B and ADMA in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Cognitive Dysfunction. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 354, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, U.; Hassan, A.; Vallance, P.; Markus, H.S. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Stroke 2007, 38, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, F.; Cifù, A.; Pessa, M.E.; Domenis, R.; Gigli, G.L.; Sanvilli, N.; Nilo, A.; Garbo, R.; Curcio, F.; Giacomello, R.; et al. ADMA as a Possible Marker of Endothelial Damage. A Study in Young Asymptomatic Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, J.A.; Brennan, M.-L.; Gokce, N.; Mann, S.A.; Goormastic, M.; Shishehbor, M.H.; Penn, M.S.; Keaney, J.F., Jr.; Hazen, S.L. Serum Myeloperoxidase Levels Independently Predict Endothelial Dysfunction in Humans. Circulation 2004, 110, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawakol, A.; Omland, T.; Gerhard, M.; Wu, J.T.; Creager, M.A. Hyperhomocyst (e) Inemia Is Associated with Impaired Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation in Humans. Circulation 1997, 95, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Chook, P.; Lolin, Y.I.; Cheung, A.S.P.; Chan, L.T.; Sun, Y.Y.; Sanderson, J.E.; Metreweli, C.; Celermajer, D.S. Hyperhomocyst (e) Inemia Is a Risk Factor for Arterial Endothelial Dysfunction in Humans. Circulation 1997, 96, 2542–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, H. The Pathophysiological Hypothesis of Homocysteine Thiolactone-Mediated Vascular Disease. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 59 (Suppl. S9), 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, S.B.; Zhang, H.; Lau, C.W.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z. Salidroside Improves Homocysteine-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Reducing Oxidative Stress. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 679635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Sydow, K.; Heistad, D.D.; Lentz, S.R. Plasma Concentration of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, an Endogenous Inhibitor of Nitric Oxide Synthase, Is Elevated in Monkeys with Hyperhomocyst (e) Inemia or Hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, U.; Crossley, C.; Kalra, L.; Rudd, A.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Collinson, P.; Markus, H.S. Homocysteine and Its Relationship to Stroke Subtypes in a UK Black Population: The South London Ethnicity and Stroke Study. Stroke 2008, 39, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloonan, L.; Fitzpatrick, K.M.; Kanakis, A.S.; Furie, K.L.; Rosand, J.; Rost, N.S. Metabolic Determinants of White Matter Hyperintensity Burden in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Su, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, L.; Yao, M.; Zhang, S.; Cui, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, J. Correlation between Total Homocysteine and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Hunt, B.J.; O’Sullivan, M.; Bell, R.; D’Souza, R.; Jeffery, S.; Bamford, J.M.; Markus, H.S. Homocysteine Is a Risk Factor for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease, Acting via Endothelial Dysfunction. Brain 2004, 127 Pt 1, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Teng, Z.; Li, X.; Jin, W.; Lv, P.Y. Homocysteine Is Associated with the Development of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Retrospective Analyses from Neuroimaging and Cognitive Outcomes. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.J.; Barzilay, J.I.; Peterson, D.; Manolio, T.A.; Psaty, B.M.; Kuller, L.; Wexler, J.; Bleyer, A.J.; Cushman, M. The Association of Microalbuminuria with Clinical Cardiovascular Disease and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in the Elderly: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Atherosclerosis 2006, 187, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrinelli, R.; Dell’omo, G.; Catapano, G.; Giampietro, O.; Carmassi, F.; Matteucci, E.; Talarico, L.; Morale, M.; de Negri, F.; di Bello, V. Microalbuminuria and Endothelial Dysfunction in Essential Hypertension. Lancet 1994, 344, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, N.B.; Coull, B.M.; Clark, W.M.; Wynn, M. Microalbuminuria in Ischemic Stroke. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klahr, S. Mechanisms of Progression of Chronic Renal Damage. J. Nephrol. 1999, 12, S53–S62. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, A.L.; Rossetti, H.C.; Peshock, R.M.; Weiner, M.F.; Nakonezny, P.A.; McColl, R.W.; Hulsey, K.M.; Das, S.R.; King, K.S. Urinary Albumin to Creatinine Ratio as Potential Biomarker for Cerebral Microvascular Disease. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2014, 11, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Iseki, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Sato, H.; Arawaka, S.; Kawanami, T.; Kurita, K.; Daimon, M.; Kato, T. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Results of a Cross-Sectional Study in Community-Based Japanese Elderly. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 272, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J.W.; Romundstad, S.; Ellekjær, H.; Janszky, I.; Horn, J. Low Grade Albuminuria as a Risk Factor for Subtypes of Stroke—The HUNT Study in Norway. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low Wang, C.C.; Hess, C.N.; Hiatt, W.R.; Goldfine, A.B. Clinical Update: Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus–Mechanisms, Management, and Clinical Considerations. Circulation 2016, 133, 2459–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, K.; Carlson, G.A.; Iadecola, C. Exogenous Aβ1–40 Reproduces Cerebrovascular Alterations Resulting from Amyloid Precursor Protein Overexpression in Mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000, 20, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, M.; Sobrino, T.; Ois, A.; Millán, M.; Rodríguez-Campello, A.; Pérez de la Ossa, N.; Rodríguez-González, R.; Jiménez-Conde, J.; Cuadrado-Godia, E.; Roquer, J.; et al. Plasma Beta-Amyloid 1-40 Is Associated with the Diffuse Small Vessel Disease Subtype. Stroke 2009, 40, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiopoulos, A.G.; Marinou, K.; Christodoulides, C.; Koutsilieris, M. The Role of Adiponectin in Human Vascular Physiology. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 155, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Hwang, K.-H.; Park, K.-S.; Kong, I.D.; Cha, S.-K. Biological Role of Anti-Aging Protein Klotho. J. Lifestyle Med. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.G.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, D.-R.; Song, T.-J. Plasma Klotho Concentration Is Associated with the Presence, Burden and Progression of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Acute Ischaemic Stroke. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.R.; Preis, S.R.; Beiser, A.S.; DeCarli, C.; Lee, D.Y.; Viswanathan, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Fontes, J.; Au, R.; Pikula, A. Lipoprotein Phospholipase A2 and Cerebral Microbleeds in the Framingham Heart Study. Stroke 2012, 43, 3091–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, C.M.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Bang, H.; Coresh, J.; Folsom, A.R.; Chambless, L.E.; Myerson, M.; Wu, K.K.; Sharrett, A.R.; Boerwinkle, E. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2, High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, and Risk for Incident Ischemic Stroke in Middle-Aged Men and Women in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, F.J.; Ikram, M.K.; Witteman, J.C.; Hofman, A.; De Jong, P.T.; Breteler, M.M. Retinal Vessel Diameters and the Role of Inflammation in Cerebrovascular Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.B.; Moon, Y.; Paik, M.C.; Brown, T.R.; Rabbani, L.; Yoshita, M.; DeCarli, C.; Sacco, R.; Elkind, M.S. Inflammatory Biomarkers of Vascular Risk as Correlates of Leukoariosis. Stroke 2009, 40, 3466–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Chappell, F.M.; Hernandez, M.D.C.V.; Makin, S.D.; Staals, J.; Shuler, K.; Thrippleton, M.J.; Armitage, P.A.; Munoz-Maniega, S.; Heye, A.K. White Matter Hyperin tensity Reduction and Outcomes after Minor Stroke. Neurology 2017, 89, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.M.; Doubal, F.N.; Jackson, C.A.; Chappell, F.M.; Sudlow, C.L.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Counting Cavitating Lacunes Underestimates the Burden of Lacunar Infarction. Stroke 2010, 41, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leijsen, E.M.; Van Uden, I.W.; Ghafoorian, M.; Bergkamp, M.I.; Lohner, V.; Kooijmans, E.C.; van der Holst, H.M.; Tuladhar, A.M.; Norris, D.G.; van Dijk, E.J. Nonlinear Temporal Dynamics of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: The RUN DMC Study. Neurology 2017, 89, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Woodhouse, L.J.; Mhlanga, I.I.; Oatey, K.; Heye, A.K.; Bamford, J.; Cvoro, V.; Doubal, F.N.; England, T.; Hassan, A.; et al. Isosorbide Mononitrate and Cilostazol Treatment in Patients With Symptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: The Lacunar Intervention Trial-2 (LACI-2) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class | Biomarkers | Role in Endothelial (Dys) Function | Relation to SVD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules and selectins | VCAM-1 ICAM-1 P-selectin E-selectin |
|
| [18,22,34,37,38,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,54,70,73] |
| BBB Transporters | GLUT-1 P-GP LAT-1 Cav-1 |
|
| [54,62] |
| Cytokines and chemokines | IL-6 TNF-α/TNFR2 Osteoprotegerin PF-4 |
|
| [43,44,45,47,48,49,68,69,70,71,72,73,81] |
| Other pro-inflammatory markers | CRP Neopterin CD40-L |
|
| [34,38,43,44,47,51,68,69,70,71,72,73,90,91,92] |
| Coagulation factors | vWF TF TFPI t-PA PAI-1 Prothrombin factors 1 and 2 D-dimer TM ET-1 fibrinogen |
|
| [18,38,40,46,50,52,70,71,73,99,108,109,114] |
| Growth factors | VEGF TGF-β1 PlGF |
|
| [40,44,49,81,123,124,125,126] |
| Nitric oxide pathway | NO NOSTRIN ADMA Myeloperoxidase |
|
| [44,46,54,135,136,137] |
| Other relevant biomarkers | Hcy Albumin HbA1c β-amyloid1–40 Adiponectin Klotho Lp-PLA2 |
|
| [37,38,43,44,47,71,90,109,136,144,145,146,147,148,155,158,161,165] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaime Garcia, D.; Chagnot, A.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Montagne, A. A Scoping Review on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Small Vessel Disease: Molecular Insights from Human Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713114
Jaime Garcia D, Chagnot A, Wardlaw JM, Montagne A. A Scoping Review on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Small Vessel Disease: Molecular Insights from Human Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713114
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaime Garcia, Daniela, Audrey Chagnot, Joanna M. Wardlaw, and Axel Montagne. 2023. "A Scoping Review on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Small Vessel Disease: Molecular Insights from Human Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713114
APA StyleJaime Garcia, D., Chagnot, A., Wardlaw, J. M., & Montagne, A. (2023). A Scoping Review on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Small Vessel Disease: Molecular Insights from Human Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713114






