Semaphorins and Their Roles in Breast Cancer: Implications for Therapy Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
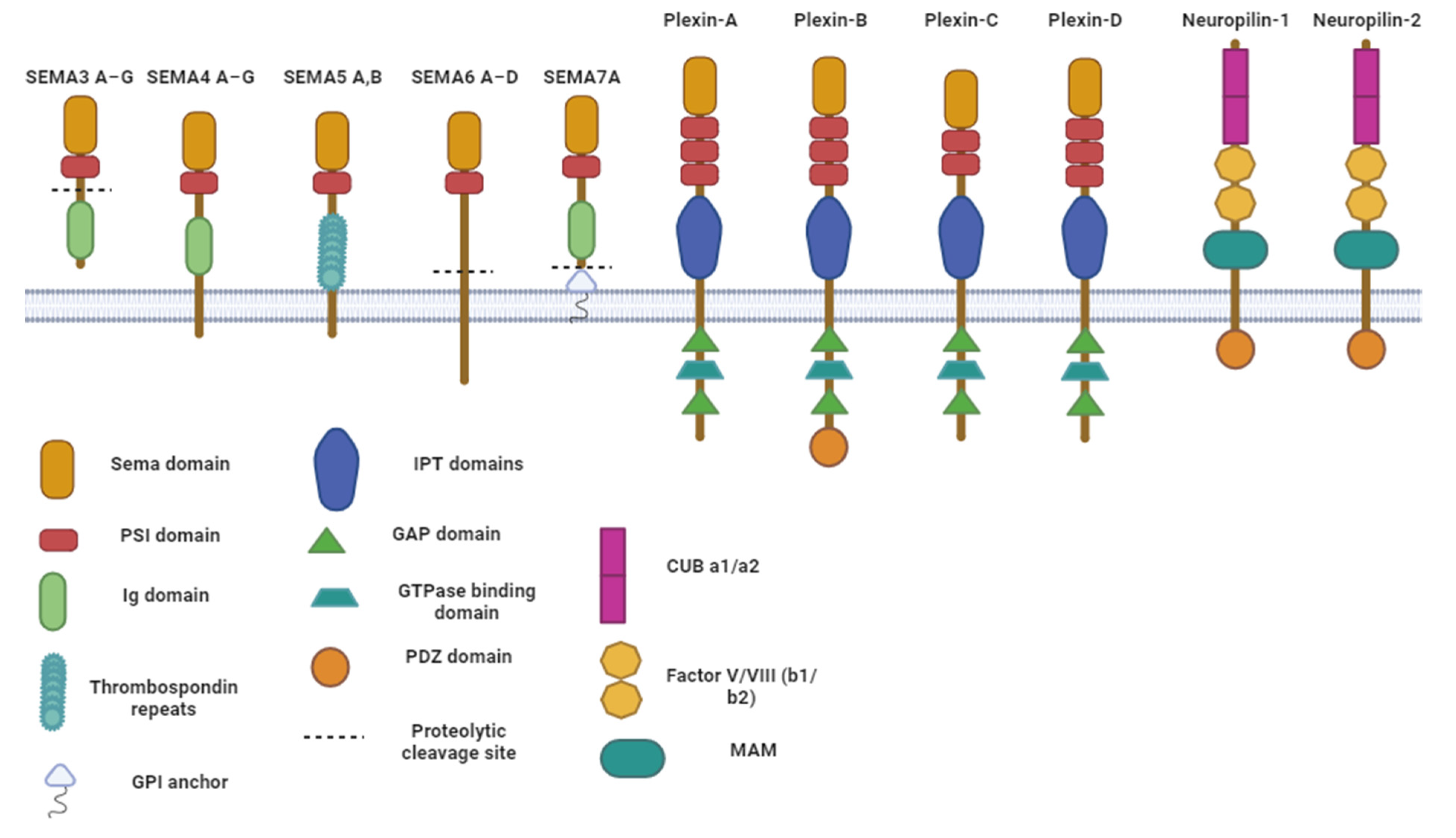
2. Semaphorins
3. SEMA3A
4. SEMA3B and SEMA3F
5. SEMA3C
6. SEMA3E
7. SEMA4A
8. SEMA4B
9. SEMA4C
10. SEMA4D
11. SEMA6D
12. SEMA7A
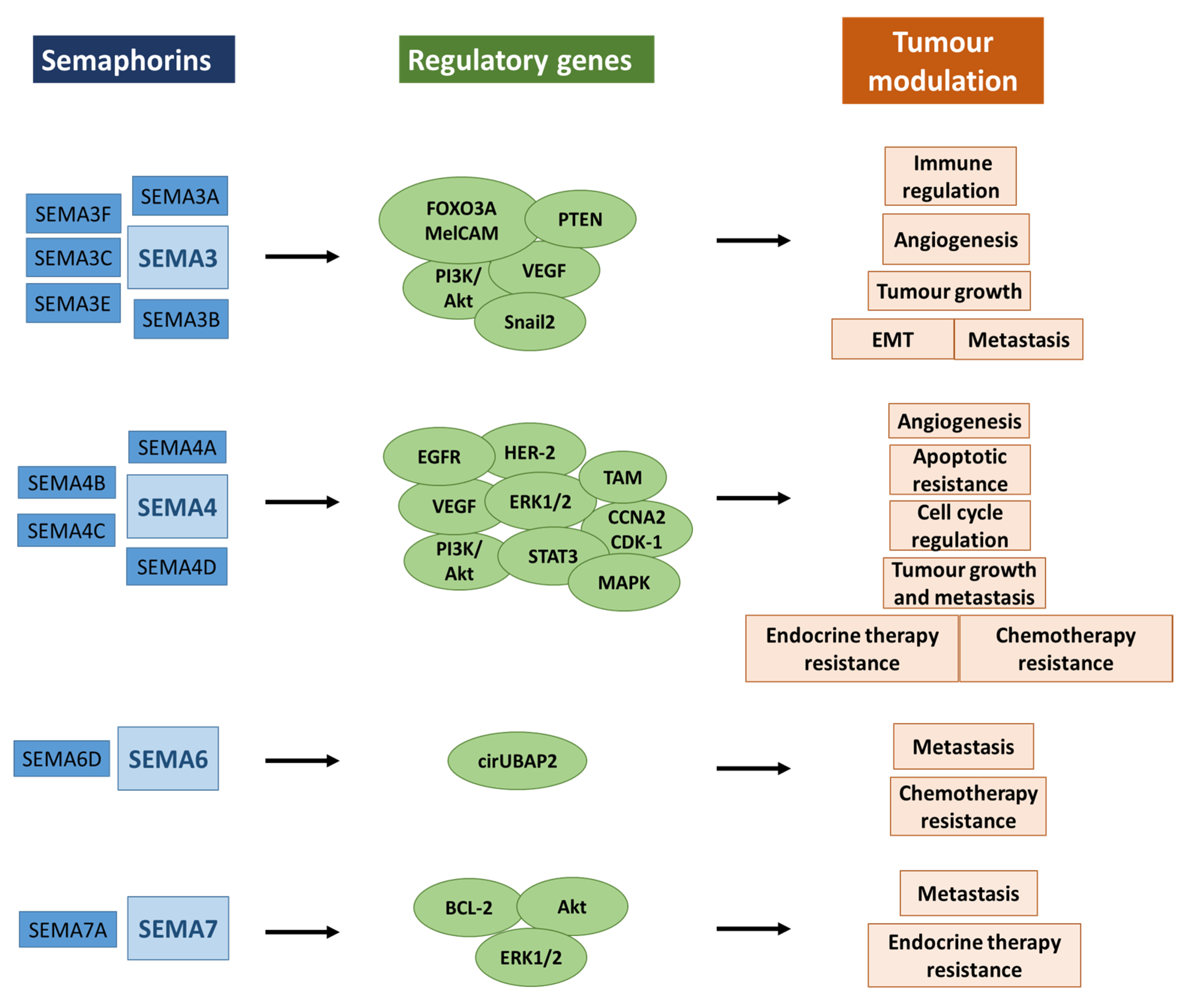
13. Therapy Resistance across Breast Cancer and Other Malignancies
- SEMA3A
- 2.
- SEMA3B, SEMA3E and SEMA3F
| Semaphorins | Drug Response—Breast Cancer | Drug Response—Other Cancers | Clinical Trials |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEMA3A | - | Chemosensitisation with sunitinib in pancreatic cancer [55] | |
| Chemoresistance to androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer [56] | |||
| SEMA3B | - | Chemoresistance to cisplatin in endometrial cancer [58] | |
| SEMA3C | - | Chemoresistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer [30] | |
| SEMA3E | - | Chemoresistance to cisplatin, carboplatin, adriamycin, mitomycin C, etoposide in ovarian cancer | |
| Radioresistance to UV, X-ray radiation in ovarian cancer [59] | |||
| SEMA3F | - | Chemosensitisation to 5-FU in prostate cancer [24] | |
| SEMA4A | - | Improves efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody in NSCLC [61] | |
| SEMA4C | Endocrine therapy resistance [43] | Chemoresistance to cisplatin in cervical cancer [62] | |
| Chemotherapy resistance to paclitaxel [45] | |||
| SEMA4D | Risk of bone metastasis [47] | Chemoresistance to 5-FU in colorectal cancer [63] | Pipinemab NCT05378464—Breast cancer NCT05102721—Pancreatic cancer NCT03320330—Refractory solid cancers in young patients |
| SEMA6D | Chemosensitisation to epirubicin [49] | Chemoresistance to cisplatin in osteosarcoma [64] | |
| SEMA7A | Endocrine therapy and Palbociclib resistance [53] Paclitaxel resistance [52] | Chemoresistance to TKIs in lung cancer [65] |
- 3.
- SEMA4A, SEMA4C and SEMA4D
- 4.
- SEMA6D
- 5.
- SEMA7A
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CRUK. Breast Cancer Statistics. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/breast-cancer (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- McCarthy, A.M.; Friebel-Klingner, T.; Ehsan, S.; He, W.; Welch, M.; Chen, J.; Kontos, D.; Domchek, S.M.; Conant, E.F.; Semine, A.; et al. Relationship of established risk factors with breast cancer subtypes. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 6456–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidelines, N. Early and Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Diagnosis and Management. 2018. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng101 (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Hu, S.; Zhu, L. Semaphorins and Their Receptors: From Axonal Guidance to Atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, C.; Grande, F.; Granieri, M.C.; Colombo, B.; De Bartolo, A.; Giordano, F.; Rago, V.; Amodio, N.; Tota, B.; Cerra, M.C.; et al. The chromogranin A(1-373) fragment reveals how a single change in the protein sequence exerts strong cardioregulatory effects by engaging neuropilin-1. Acta Physiol. 2021, 231, e13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carulli, D.; de Winter, F.; Verhaagen, J. Semaphorins in Adult Nervous System Plasticity and Disease. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2021, 13, 672891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrantonio, R.; You, H.; Tamagnone, L. Semaphorins as emerging clinical biomarkers and therapeutic targets in cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3262–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, G.; Romano, A.; Sirabella, R.; Serafini, S.; Maier, T.J.; Matrone, C. An increase in Semaphorin 3A biases the axonal direction and induces an aberrant dendritic arborization in an in vitro model of human neural progenitor differentiation. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallerius, M.; Wallmann, T.; Bartish, M.; Östling, J.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Tobin, N.P.; Nygren, E.; Pangigadde, P.; Pellegrini, P.; Squadrito, M.L.; et al. Guidance Molecule SEMA3A Restricts Tumor Growth by Differentially Regulating the Proliferation of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3166–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendrowicz, E.; Sas, Z.; Bremer, E.; Rygiel, T.P. The Role of Macrophages in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hunborg, P.; Varvares, M.A.; Hoft, D.F.; Hsueh, E.C.; et al. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells have opposing roles in breast cancer progression and outcome. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17462–17478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Thorat, D.; Soundararajan, G.; Pradhan, S.J.; Chakraborty, G.; Lohite, K.; Karnik, S.; Kundu, G.C. Semaphorin 3A upregulates FOXO 3a-dependent MelCAM expression leading to attenuation of breast tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroki, T.; Trapasso, F.; Yendamuri, S.; Matsuyama, A.; Alder, H.; Williams, N.N.; Kaiser, L.R.; Croce, C.M. Allelic loss on chromosome 3p21.3 and promoter hypermethylation of semaphorin 3B in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3352–3355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, Y.; Sekido, Y.; Kondo, M.; Gao, B.; Yokota, J.; Roche, J.; Drabkin, H.; Lerman, M.I.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D. Inhibition of lung cancer cell growth and induction of apoptosis after reexpression of 3p21.3 candidate tumor suppressor gene SEMA3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13954–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, P.; Wang, C.Y.; Chou, J.; Hagerling, C.; Gonzalez Velozo, H.; Ruderisch, A.; Yu, Y.; Lai, M.D.; Werb, Z. GATA3 targets semaphorin 3B in mammary epithelial cells to suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5567–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, H.; Hedayati, E.; Lindström, A.; Shabo, I. GATA-3 expression in breast cancer is related to intratumoral M2 macrophage infiltration and tumor differentiation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorana, F.; Motta, G.; Pavone, G.; Motta, L.; Stella, S.; Vitale, S.R.; Manzella, L.; Vigneri, P. AKT Inhibitors: New Weapons in the Fight against Breast Cancer? Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 662232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Rivera, E.; Ran, S.; Brekken, R.A.; Minna, J.D. Semaphorin 3B inhibits the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway through neuropilin-1 in lung and breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8295–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-da-Cruz, D.A.; Brignier, A.C.; Asnafi, V.; Baleydier, F.; Messias, C.V.; Lepelletier, Y.; Bedjaoui, N.; Renand, A.; Smaniotto, S.; Canioni, D.; et al. Semaphorin 3F and neuropilin-2 control the migration of human T-cell precursors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasarre, P.; Kusy, S.; Constantin, B.; Castellani, V.; Drabkin, H.A.; Bagnard, D.; Roche, J. Semaphorin SEMA3F has a repulsing activity on breast cancer cells and inhibits E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.; Ho, S.-M.; Syed, V. Hormonal Regulation and Distinct Functions of Semaphorin-3B and Semaphorin-3F in Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.F.; Satherley, L.K.; Davies, E.L.; Ye, L.; Jiang, W.G. Expression of Semaphorin 3C in Breast Cancer and its Impact on Adhesion and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Ma, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Lv, R.; Zhou, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; et al. Semaphorin 3F induces colorectal cancer cell chemosensitivity by promoting P27 nuclear export. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 899927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, N.M.; Jaradat, S.K.; Al-Shami, K.M.; Alkhalifa, A.E. Targeting Angiogenesis in Breast Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives of Novel Anti-Angiogenic Approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 838133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Rivera, E.; Ran, S.; Thorpe, P.; Minna, J.D. Semaphorin 3B (SEMA3B) induces apoptosis in lung and breast cancer, whereas VEGF165 antagonizes this effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11432–11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, R.; Horiuchi, A.; Kikuchi, N.; Ohira, S.; Ota, M.; Katsuyama, Y.; Konishi, I. Expression of semaphorins, vascular endothelial growth factor, and their common receptor neuropilins and alleic loss of semaphorin locus in epithelial ovarian neoplasms: Increased ratio of vascular endothelial growth factor to semaphorin is a poor prognostic factor in ovarian carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yu, J.S. Semaphorin 3C and Its Receptors in Cancer and Cancer Stem-Like Cells. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Healy, Z.; Vergani, P.; Hunter, K.; Brown, N.J.; Reed, M.W.; Staton, C.A. The relationship between semaphorin 3C and microvessel density in the progression of breast and oral neoplasia. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.H.F.; Tam, K.J.; Jiao, I.Z.F.; Ong, C.J. Semaphorin 3C as a Therapeutic Target in Prostate and Other Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchino, J.; Hocine, M.; Amoureux, M.C.; Gibert, B.; Bernet, A.; Royet, A.; Treilleux, I.; Lécine, P.; Borg, J.P.; Mehlen, P.; et al. Semaphorin 3E suppresses tumor cell death triggered by the plexin D1 dependence receptor in metastatic breast cancers. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casazza, A.; Finisguerra, V.; Capparuccia, L.; Camperi, A.; Swiercz, J.M.; Rizzolio, S.; Rolny, C.; Christensen, C.; Bertotti, A.; Sarotto, I.; et al. Sema3E-Plexin D1 signaling drives human cancer cell invasiveness and metastatic spreading in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. Expression of EMT-related genes in lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer: A TCGA-based study. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, K.; Haraguchi, N.; Nishimura, J.; Yasueda, A.; Fujino, S.; Ogino, T.; Takahashi, H.; Miyoshi, N.; Uemura, M.; Matsuda, C.; et al. PLXND1/SEMA3E Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Partly via the PI3K/AKT-Signaling Pathway and Induces Heterogenity in Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7435–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J. The expression and clinical significance of sema4a in triple negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2020, 4, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Tian, W.; Wang, F.; Lv, X.; Wang, M.; Sun, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Han, M. Sema4A Responds to Hypoxia and Is Involved in Breast Cancer Progression. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranthaman, P.; Veerappapillai, S. Design of a potential Sema4A-based multi-epitope vaccine to combat triple-negative breast cancer: An immunoinformatic approach. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Pan, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, R. Semaphorin 4B promotes tumor progression and associates with immune infiltrates in lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Lu, S. SEMA4B inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jian, W.; Luo, Q.; Fang, L. CircSEMA4B inhibits the progression of breast cancer by encoding a novel protein SEMA4B-211aa and regulating AKT phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Fang, T.; et al. Serum semaphorin 4C as a diagnostic biomarker in breast cancer: A multicenter retrospective study. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Li, X. Effect of microrna-138 on epithelial-Mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting semaphorin 4C. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10117–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrapu, S.; Pupo, E.; Franzolin, G.; Lanzetti, L.; Tamagnone, L. Sema4C/PlexinB2 signaling controls breast cancer cell growth, hormonal dependence and tumorigenic potential. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, S.; Ma, Q.; Wei, J.; Wu, M.; et al. Semaphorin 4C Promotes Macrophage Recruitment and Angiogenesis in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z. MiR-125b regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting Sema4C in paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3268–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi-Koga, T.; Shinohara, M.; Komatsu, N.; Bito, H.; Kodama, T.; Friedel, R.H.; Takayanagi, H. Suppression of bone formation by osteoclastic expression of semaphorin 4D. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Buhamrah, A.; Schneider, A.; Lin, Y.L.; Zhou, H.; Bugshan, A.; Basile, J.R. Semaphorin 4D Promotes Skeletal Metastasis in Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunyuz, Z.E.; Sahi-Ilhan, E.; Kucukkose, C.; Ipekgil, D.; Tok, G.; Mese, G.; Ozcivici, E.; Yalcin-Ozuysal, O. SEMA6D Differentially Regulates Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Breast Cell Lines. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 15769–15778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, D.E.; Allinson, L.M.; Al Amri, W.S.; Poulter, J.A.; Pramanik, A.; Thorne, J.L.; Verghese, E.T.; Hughes, T.A. MiR-195 and Its Target SEMA6D Regulate Chemoresponse in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiao, K. SEMA6D Expression and Patient Survival in Breast Invasive Carcinoma. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2015, 2015, 539721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.A.; Nelson, A.C.; Gurule, N.J.; Futscher, B.W.; Lyons, T.R. Semaphorin 7a exerts pleiotropic effects to promote breast tumor progression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5170–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, T.R.; Elder, A.M.; Lyons, T.R. Anoikis resistance in mammary epithelial cells is mediated by semaphorin 7a. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, L.S.; Wyatt, G.L.; Rutherford, T.R.; Richer, J.K.; Porter, W.W.; Lyons, T.R. Hormonal Regulation of Semaphorin 7a in ER+ Breast Cancer Drives Therapeutic Resistance. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, V.F.; Hu, J.; Young, C.; Maggard, J.; Parris, H.J.; Gao, D.; Lyons, T.R. Semaphorin 7a is a biomarker for recurrence in postpartum breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, F.; Capano, S.; Regano, D.; Zentilin, L.; Giacca, M.; Casanovas, O.; Bussolino, F.; Serini, G.; Giraudo, E. Semaphorin 3A overcomes cancer hypoxia and metastatic dissemination induced by antiangiogenic treatment in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1832–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Dai, L.; Han, S.; Xing, N.; Ren, S. SEMA3A-mediated crosstalk between prostate cancer cells and tumor-associated macrophages promotes androgen deprivation therapy resistance. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Cho, H.J.; Sa, J.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.; Yoon, Y.; Nam, D.H. Anti-SEMA3A Antibody: A Novel Therapeutic Agent to Suppress Glioblastoma Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peszek, W.; Kras, P.; Grabarek, B.O.; Boroń, D.; Oplawski, M. Cisplatin Changes Expression of SEMA3B in Endometrial Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Endo, R.; Gotoh, M.; Hirohashi, S. Identification of semaphorin E as a non-MDR drug resistance gene of human cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14713–14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casazza, A.; Kigel, B.; Maione, F.; Capparuccia, L.; Kessler, O.; Giraudo, E.; Mazzone, M.; Neufeld, G.; Tamagnone, L. Tumour growth inhibition and anti-metastatic activity of a mutated furin-resistant Semaphorin 3E isoform. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Koyama, S.; Masuhiro, K.; Hirai, T.; Uenami, T.; Inoue, T.; Osa, A.; Machiyama, H.; Watanabe, G.; Sax, N.; et al. Tumor-derived semaphorin 4A improves PD-1-blocking antibody efficacy by enhancing CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity and proliferation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade0718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, M. Sema4C mediates EMT inducing chemotherapeutic resistance of miR-31-3p in cervical cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, G.; Rezaeepoor, M.; Mohammadi, C.; Solgi, G.; Najafi, R. Inhibition of semaphorin 4D enhances chemosensitivity by increasing 5-fluorouracile-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7017–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Qu, F. CircUBAP2 promotes SEMA6D expression to enhance the cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma through sponging miR-506-3p by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Mol. Histol. 2020, 51, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinehara, Y.; Nagatomo, I.; Koyama, S.; Ito, D.; Nojima, S.; Kurebayashi, R.; Nakanishi, Y.; Suga, Y.; Nishijima-Futami, Y.; Osa, A.; et al. Semaphorin 7A promotes EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e123093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuazo-Gaztelu, I.; Pàez-Ribes, M.; Carrasco, P.; Martín, L.; Soler, A.; Martínez-Lozano, M.; Pons, R.; Llena, J.; Palomero, L.; Graupera, M.; et al. Antitumor Effects of Anti-Semaphorin 4D Antibody Unravel a Novel Proinvasive Mechanism of Vascular-Targeting Agents. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5328–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aiyappa-Maudsley, R.; McLoughlin, L.F.V.; Hughes, T.A. Semaphorins and Their Roles in Breast Cancer: Implications for Therapy Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713093
Aiyappa-Maudsley R, McLoughlin LFV, Hughes TA. Semaphorins and Their Roles in Breast Cancer: Implications for Therapy Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713093
Chicago/Turabian StyleAiyappa-Maudsley, Radhika, Louis F. V. McLoughlin, and Thomas A. Hughes. 2023. "Semaphorins and Their Roles in Breast Cancer: Implications for Therapy Resistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713093
APA StyleAiyappa-Maudsley, R., McLoughlin, L. F. V., & Hughes, T. A. (2023). Semaphorins and Their Roles in Breast Cancer: Implications for Therapy Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713093







