The Functional Role of Myogenin in Cardiomyoblast H9c2 Cells Treated with High Glucose and Palmitic Acid: Insights into No-Rejection Heart Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
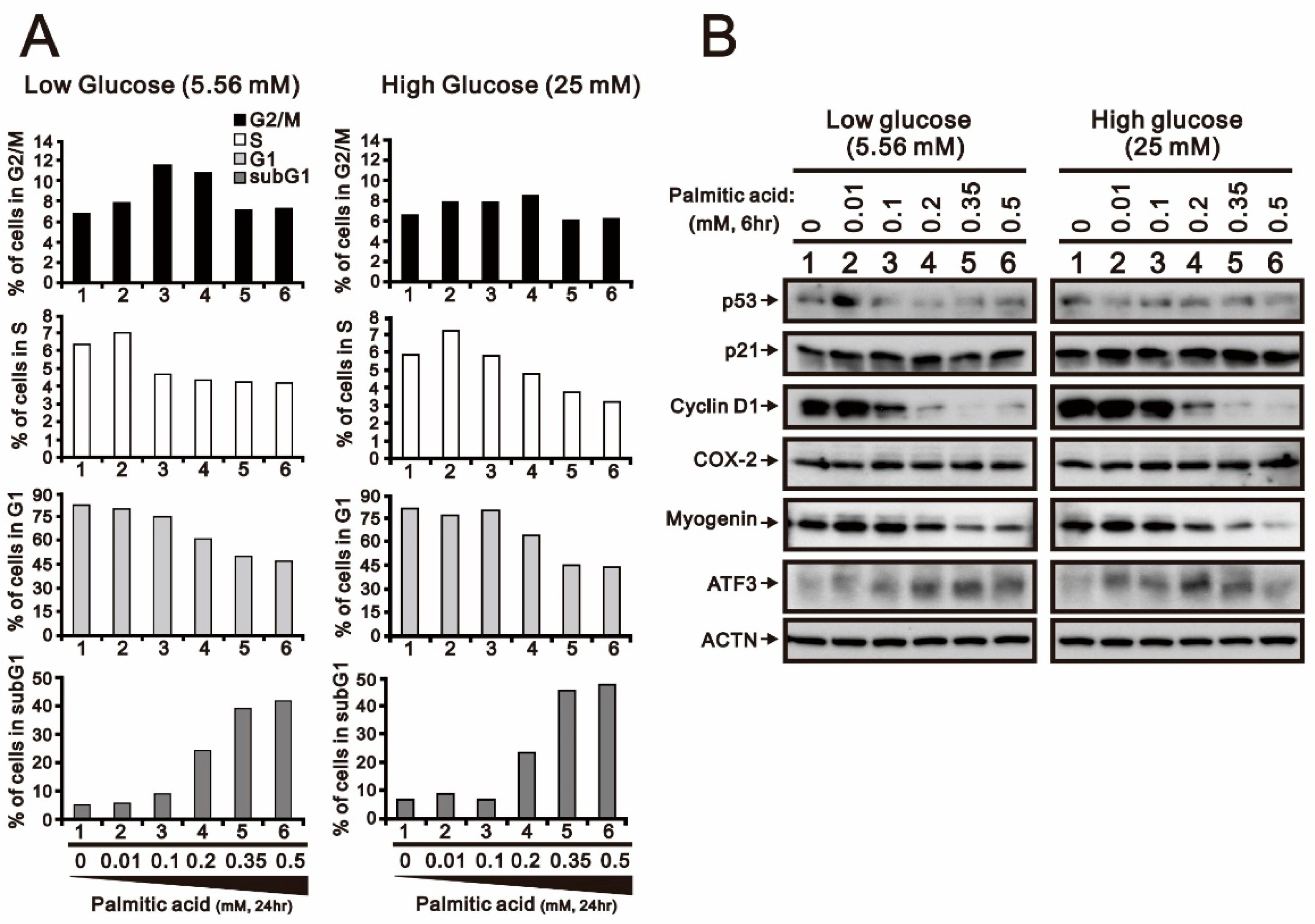
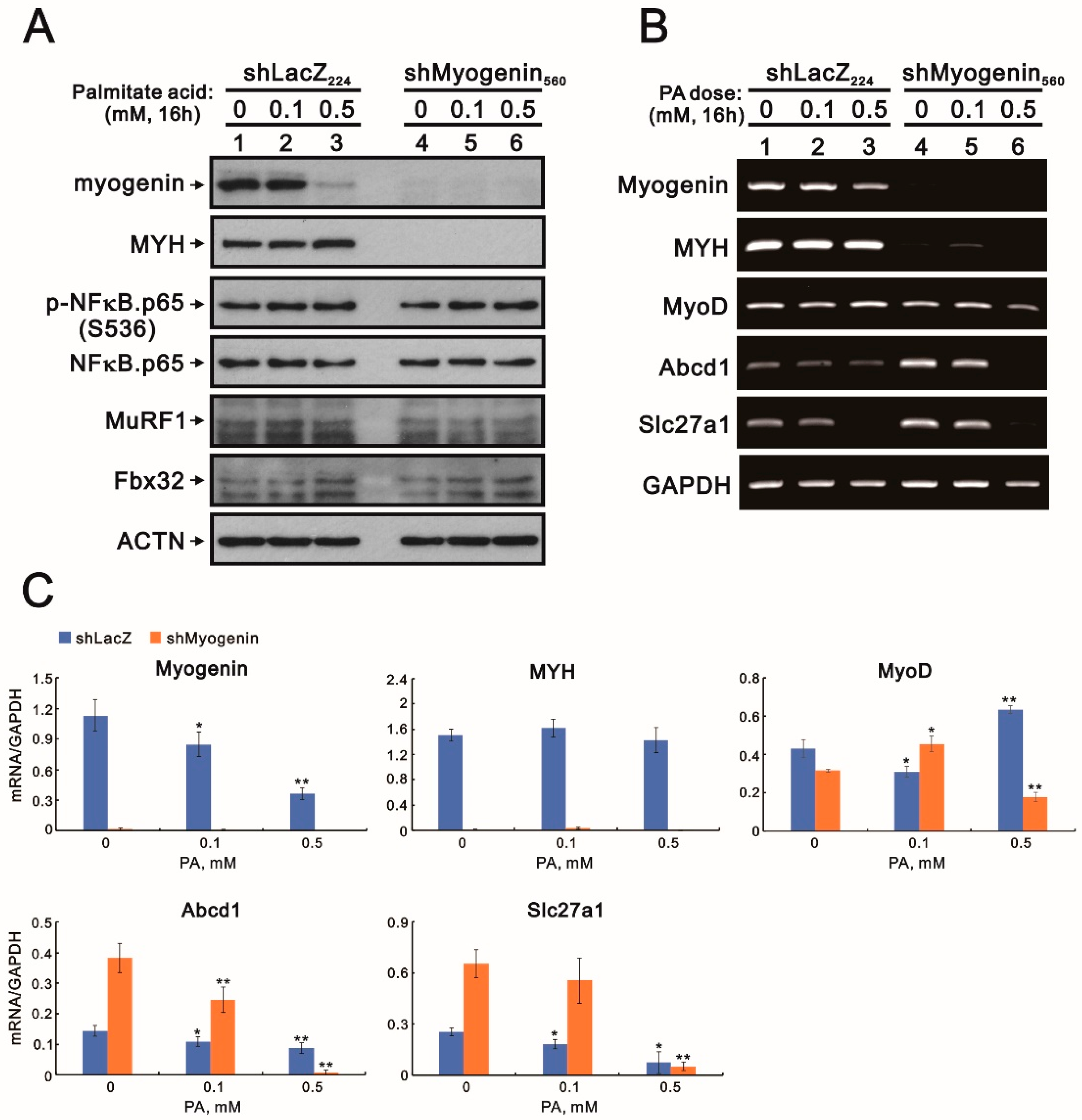
2.1. The Effects of Palmitic Acid Were Examined in H9c2 Cells Cultured with and without Glucose
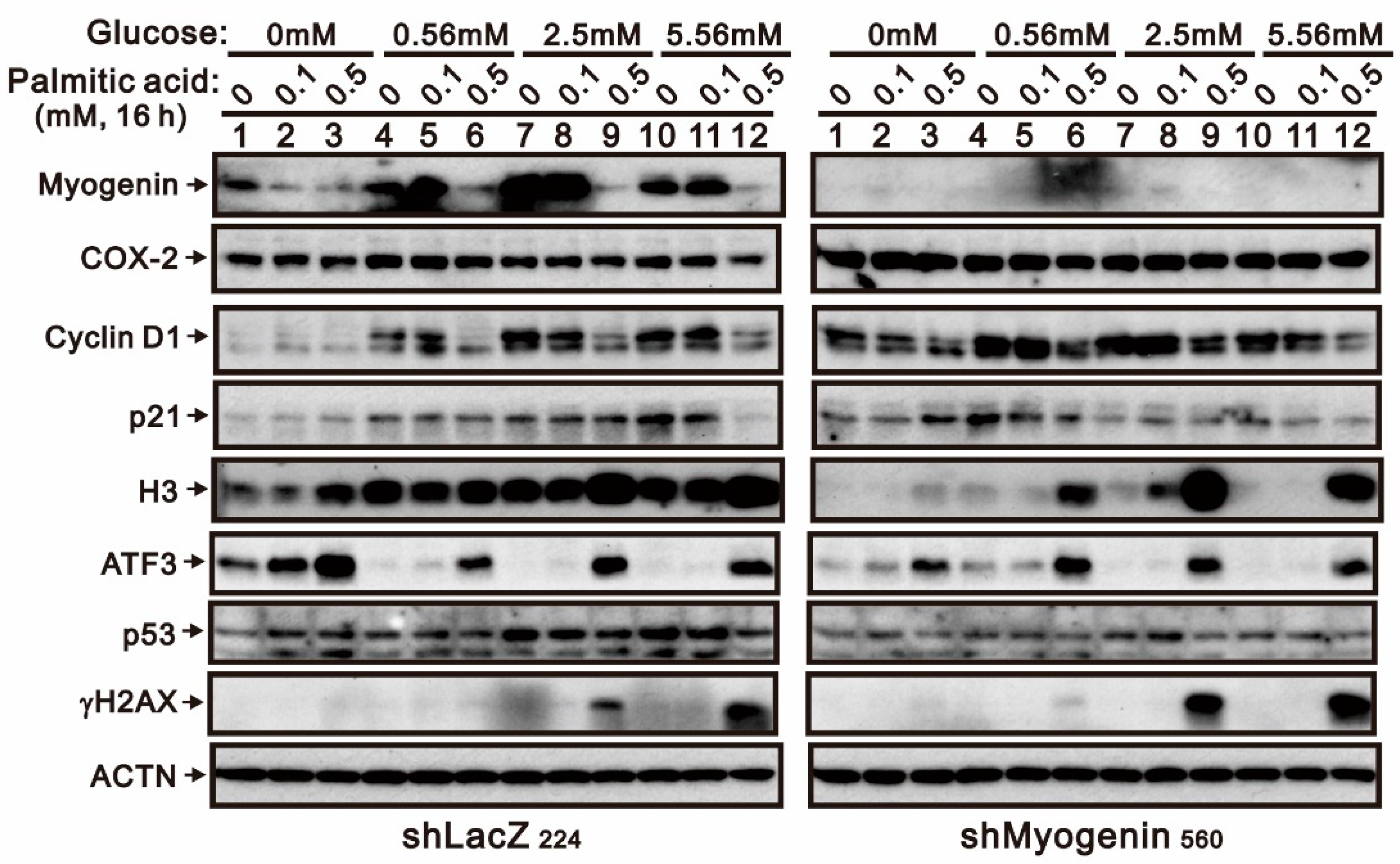
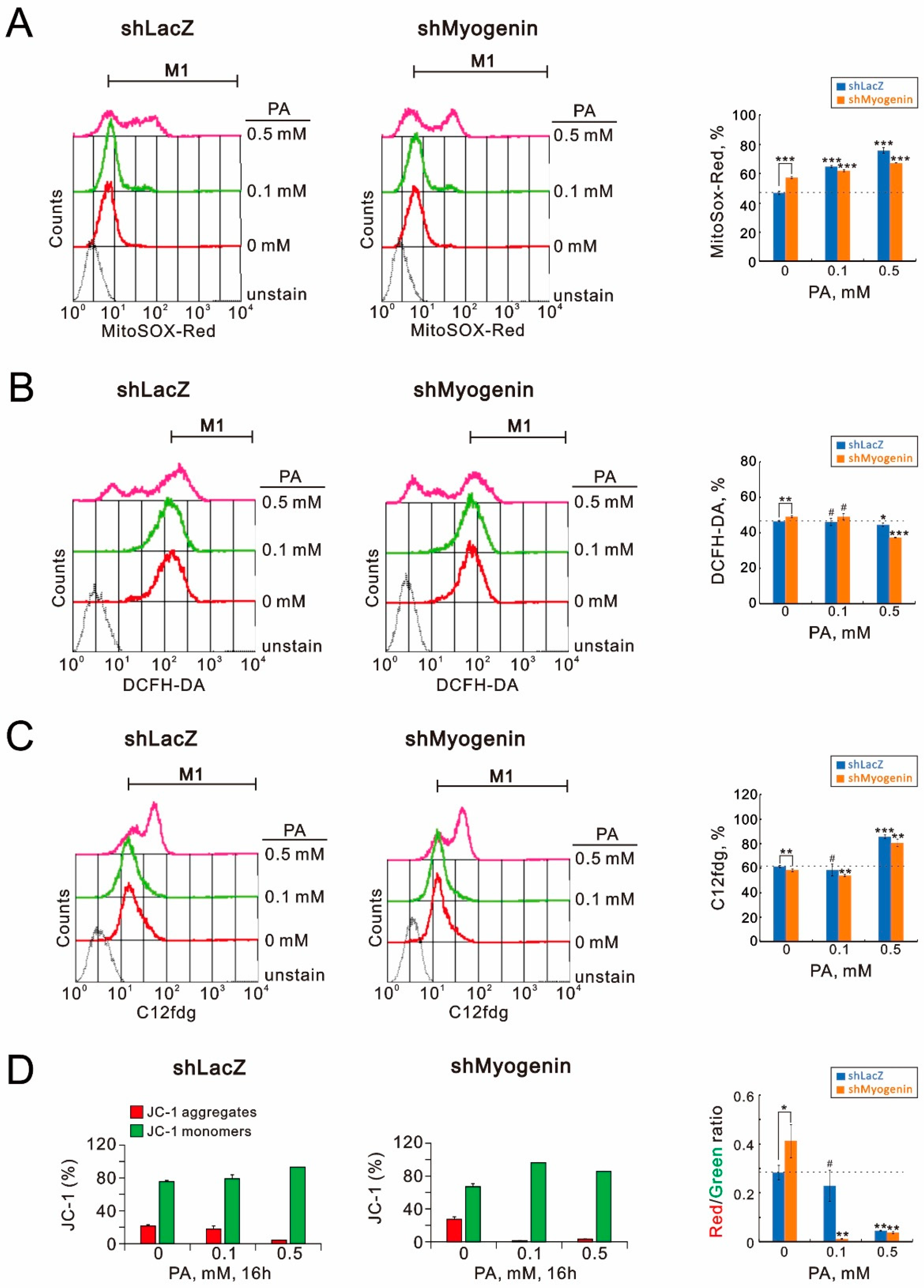
2.2. Evaluating the Functional Roles of Myogenin in Palmitic-Acid-Treated H9c2 Cells
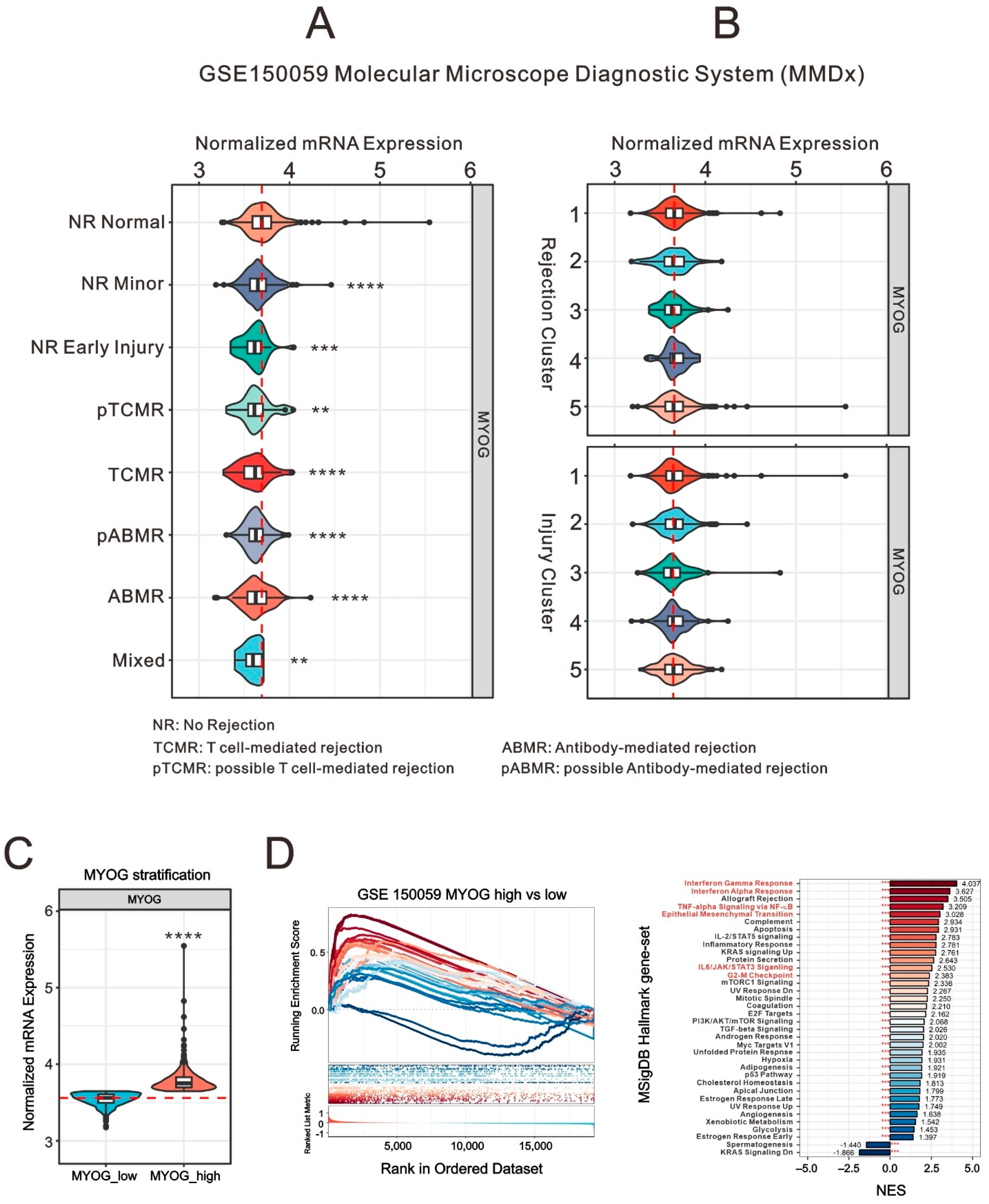
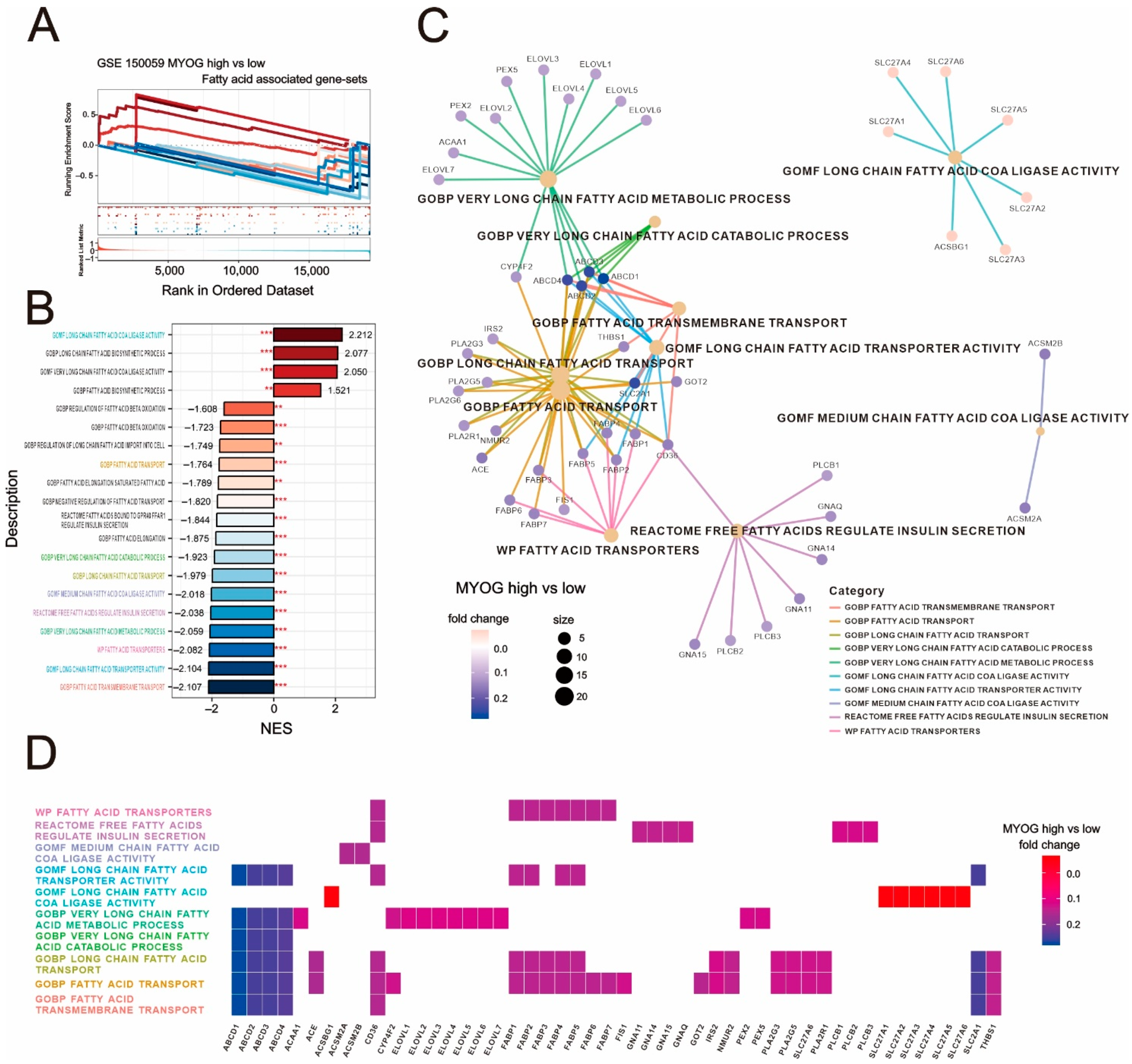
2.3. Evaluating the Clinical Role of Myogenin in Myocardial Tissue: Insights from GSE150059 Myocardial Tissue Sample Database
2.4. Unraveling the Complexities of Fatty-Acid-Related Gene Expression in Myogenin-High Cardiovascular Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Chemicals
4.2. Western Blot Analysis
4.3. Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.4. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis
4.5. Gene Silencing
4.6. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of MYOG Expression and Fatty-Acid-Related Genes in GSE150059 Samples
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sithara, T.; Drosatos, K. Metabolic Complications in Cardiac Aging. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 669497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Sadoshima, J. Cardiomyopathy in obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 2977–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deedwania, P.; Acharya, T. Cardiovascular Protection with Anti-hyperglycemic Agents. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2019, 19, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heileson, J.L. Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: A narrative review. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Appel, L.J.; Vadiveloo, M.; Hu, F.B.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Rebholz, C.M.; Sacks, F.M.; Thorndike, A.N.; Van Horn, L.; Wylie-Rosett, J. 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, e472–e487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, P.M.; Keogh, J.B. A systematic review of the effect of dietary saturated and polyunsaturated fat on heart disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 1060–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, G.; Murru, E.; Banni, S.; Manca, C. Palmitic Acid: Physiological Role, Metabolism and Nutritional Implications. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murru, E.; Manca, C.; Carta, G.; Banni, S. Impact of Dietary Palmitic Acid on Lipid Metabolism. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 861664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Endo, J.; Kataoka, M.; Matsuhashi, T.; Katsumata, Y.; Shirakawa, K.; Isobe, S.; Moriyama, H.; Goto, S.; Shimanaka, Y.; et al. Palmitate induces cardiomyocyte death via inositol requiring enzyme-1 (IRE1)-mediated signaling independent of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fan, Z.; Liu, S.; Fang, W. Palmitic acid, but not high-glucose, induced myocardial apoptosis is alleviated by N-acetylcysteine due to attenuated mitochondrial-derived ROS accumulation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, B.W.; Brandt, B.L. Properties of a clonal muscle cell line from rat heart. Exp. Cell Res. 1976, 98, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.; Pupier, S.; Mornet, D.; Kitzmann, M.; Nargeot, J.; Lory, P. Modulation of L-type calcium channel expression during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of H9C2 cardiac cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29063–29070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hescheler, J.; Meyer, R.; Plant, S.; Krautwurst, D.; Rosenthal, W.; Schultz, G. Morphological, biochemical, and electrophysiological characterization of a clonal cell (H9c2) line from rat heart. Circ. Res. 1991, 69, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson-Bick, D.L.; Buja, L.M.; McMillin, J.B. Palmitate-mediated alterations in the fatty acid metabolism of rat neonatal cardiac myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2000, 32, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauw, B.; Schiaffino, S.; Reggiani, C. Mechanisms modulating skeletal muscle phenotype. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1645–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, K.; Yang, J.; Eisenberg, C.A.; Eisenberg, L.M. 5-azacytidine promotes the transdifferentiation of cardiac cells to skeletal myocytes. Cell. Reprogram. 2014, 16, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, P.; Qiu, H.; Qiu, B.; Yi, W.; Tu, W.; Lin, B.; Sun, D.; Zeng, R.; Huang, M.; et al. Myogenin suppresses apoptosis induced by angiotensin II in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 552, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, M.A.; Jaenisch, R. The MyoD family of transcription factors and skeletal myogenesis. Bioessays 1995, 17, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, J.M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, E.G.; Brun, C.E.; Rudnicki, M.A. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroyiannopoulos, N.P.; Nicolaou, P.; Anayasa, M.; Uney, J.B.; Phylactou, L.A. Down-regulation of myogenin can reverse terminal muscle cell differentiation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, V.; Walsh, K. Myogenin expression, cell cycle withdrawal, and phenotypic differentiation are temporally separable events that precede cell fusion upon myogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 132, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Pereyra, A.; Zhang, T.; Messi, M.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Herenu, C.; Kuan, P.F.; Delbono, O. The Cavbeta1a subunit regulates gene expression and suppresses myogenin in muscle progenitor cells. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 205, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A.; Mastroyiannopoulos, N.P.; Uney, J.B.; Phylactou, L.A. miR-186 inhibits muscle cell differentiation through myogenin regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3923–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroyiannopoulos, N.P.; Antoniou, A.A.; Koutsoulidou, A.; Uney, J.B.; Phylactou, L.A. Twist reverses muscle cell differentiation through transcriptional down-regulation of myogenin. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33, e00083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Pan, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, F.; Shan, H.; Luo, X.; Bai, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. MicroRNA-328 contributes to adverse electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2010, 122, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Giessen, K.; Di-Marco, S.; Clair, E.; Gallouzi, I.E. RNAi-mediated HuR depletion leads to the inhibition of muscle cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47119–47128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Huang, S.M.; Ho, C.L.; Yen, L.C.; Huang, C.J.; Lin, W.S.; Chan, J.Y. The regulatory mechanisms of myogenin expression in doxorubicin-treated rat cardiomyocytes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37443–37457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.E.; Brunet, A. FOXO transcription factors: Key regulators of cellular quality control. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; Mora, C.; Pintado, C.; Mazuecos, L.; Fernandez, A.; Lopez, V.; Andres, A.; Gallardo, N. The nutrient sensing pathways FoxO1/3 and mTOR in the heart are coordinately regulated by central leptin through PPARbeta/delta. Implications in cardiac remodeling. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.H.; Liu, S.T.; Huang, S.M.; Salter, D.M.; Lee, H.S.; Hsu, Y.J. High phosphate induces skeletal muscle atrophy and suppresses myogenic differentiation by increasing oxidative stress and activating Nrf2 signaling. Aging 2020, 12, 21446–21468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.D.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.Y.; Tong, Y.Q.; Dai, W. Palmitate induces H9c2 cell apoptosis by increasing reactive oxygen species generation and activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X.; Xia, T.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, R.; Wu, T. Palmitic Acid, A Critical Metabolite, Aggravates Cellular Senescence Through Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 809157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorelli, S.; Passos, J.F. Reactive Oxygen Species Detection in Senescent Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1896, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Halloran, P.F.; Madill-Thomsen, K.S. The Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System: Assessment of Rejection and Injury in Heart Transplant Biopsies. Transplantation 2023, 107, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, F.; Testa, G.; Liguori, I.; Papillo, M.; Flocco, V.; Panicara, V.; Galizia, G.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Cacciatore, F.; et al. Sarcopenia and Heart Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganassi, M.; Badodi, S.; Wanders, K.; Zammit, P.S.; Hughes, S.M. Myogenin is an essential regulator of adult myofibre growth and muscle stem cell homeostasis. Elife 2020, 9, e60445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Broz, D.K.; Noderer, W.L.; Ferreira, J.P.; Overton, K.W.; Spencer, S.L.; Meyer, T.; Tapscott, S.J.; Attardi, L.D.; Wang, C.L. p53 suppresses muscle differentiation at the myogenin step in response to genotoxic stress. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.L.; So, K.K.; He, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Yao, M.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; et al. MyoD- and FoxO3-mediated hotspot interaction orchestrates super-enhancer activity during myogenic differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 8785–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, S.T.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Xing, S.S.; Shen, C.C.; Wang, X.X.; Yue, Y.X.; Song, J.; Chen, M.; et al. TNF alpha inhibits myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells through NF-kappaB activation and impairment of IGF-1 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Sugihara, H.; Watanabe, M.; Sawayama, H.; Iwatsuki, M.; Baba, Y.; Okabe, H.; Hidaka, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Miyake, K.; et al. Macrophage-derived reactive oxygen species suppress miR-328 targeting CD44 in cancer cells and promote redox adaptation. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, T.; Toyono, T.; Inoue, A.; Matsubara, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Kokabu, S. Factors Regulating or Regulated by Myogenic Regulatory Factors in Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species in living systems: Source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, 14S–22S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarse, K.; Ristow, M. Mitochondrial ROS signals prevent excessive immune response. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 588–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagatsuma, A.; Sakuma, K. Mitochondria as a potential regulator of myogenesis. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 593267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.R.; Xu, D.; Williams, B.R. ATF3 transcription factor and its emerging roles in immunity and cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Activating transcription factor 3, glucolipid metabolism, and metabolic diseases. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 14, mjac067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.K.; Liu, S.T.; Wu, Z.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Huang, S.M. Mechanisms of Cisplatin in Combination with Repurposed Drugs against Human Endometrial Carcinoma Cells. Life 2021, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Liu, S.T.; Chen, G.S.; Lee, S.P.; Huang, S.M. Differential Cytotoxicity Mechanisms of Copper Complexed with Disulfiram in Oral Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.C.; Wu, Z.S.; Chen, J.L.; Wu, Z.F.; Lai, H.C.; Huang, Y.H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Involved in the Cytotoxicity of Tramadol in Human Endometrial Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (Forward) | Primer Sequence (Reverse) |
|---|---|---|
| Troponin I | 5′-GCAAAAGTCACCAAGAACATC-3′ | 5′-GCGCCAGTCTCCCACCTCCCGG-3′ |
| Myogenin | 5′-CTACCTTCCTGTCCACCTTC-3′ | 5′-CTCCAGTGCATTGCCCCACT-3′ |
| MYH | 5′GCCTCATCCACACCAAGAAGA-3′ | 5′-TCCACCAGATCCTGCAATCTC-3′ |
| Myo D1 | 5′-CAGCGGGCACCACCAG-3′ | 5′-ATGCTGGACAGGCAGTC-3′ |
| p53 | 5′-GCAACTATGGCTTCCACCTG-3′ | 5′-CACGAACCTCAAAGCTGTCC-3′ |
| p21 | 5′-GCTGTCTCCAGGAGGCCCG-3′ | 5′-GCTGGTCTGCCTCCGTTTTCG-3′ |
| Cyclin D1 | 5′-ATGGAACACCAGCTCCTGTG-3′ | 5′-CTTAGAGGCCACGAACATGC-3′ |
| ATF3 | 5′-GAGGATTTTGCTAACCTGAC-3′ | 5′-TAGCTCTGCAATGTTCCTTC-3′ |
| COX-2 | 5′-GTCTCTCATCTGCAATAATGTG-3′ | 5′-ATCTGTGTGGGTACAAATTTG-3′ |
| FASN | 5′-TGAGCCTCATGCGCCTGGAC-3′ | 5′-CGCACCTCCTTGGCAAACAC-3′ |
| Abcd1 | 5′-TCCTGTCTGTGTATGTTGCCC-3′ | 5′-GGAGAGAAGGCTCGAAGCAC-3′ |
| Slc27a1 | 5′-CAAGGTCAACGAGGACACGA-3′ | 5′-ACAGCCACTCCATACACAGC-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-CTTCATTGACCTCAACTAC-3′ | 5′-GCCATCCACAGTCTTCTG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, P.-S.; Liu, S.-T.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Tsai, C.-S. The Functional Role of Myogenin in Cardiomyoblast H9c2 Cells Treated with High Glucose and Palmitic Acid: Insights into No-Rejection Heart Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713031
Hsu P-S, Liu S-T, Chiu Y-L, Tsai C-S. The Functional Role of Myogenin in Cardiomyoblast H9c2 Cells Treated with High Glucose and Palmitic Acid: Insights into No-Rejection Heart Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713031
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Po-Shun, Shu-Ting Liu, Yi-Lin Chiu, and Chien-Sung Tsai. 2023. "The Functional Role of Myogenin in Cardiomyoblast H9c2 Cells Treated with High Glucose and Palmitic Acid: Insights into No-Rejection Heart Transplantation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713031
APA StyleHsu, P.-S., Liu, S.-T., Chiu, Y.-L., & Tsai, C.-S. (2023). The Functional Role of Myogenin in Cardiomyoblast H9c2 Cells Treated with High Glucose and Palmitic Acid: Insights into No-Rejection Heart Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713031





