Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
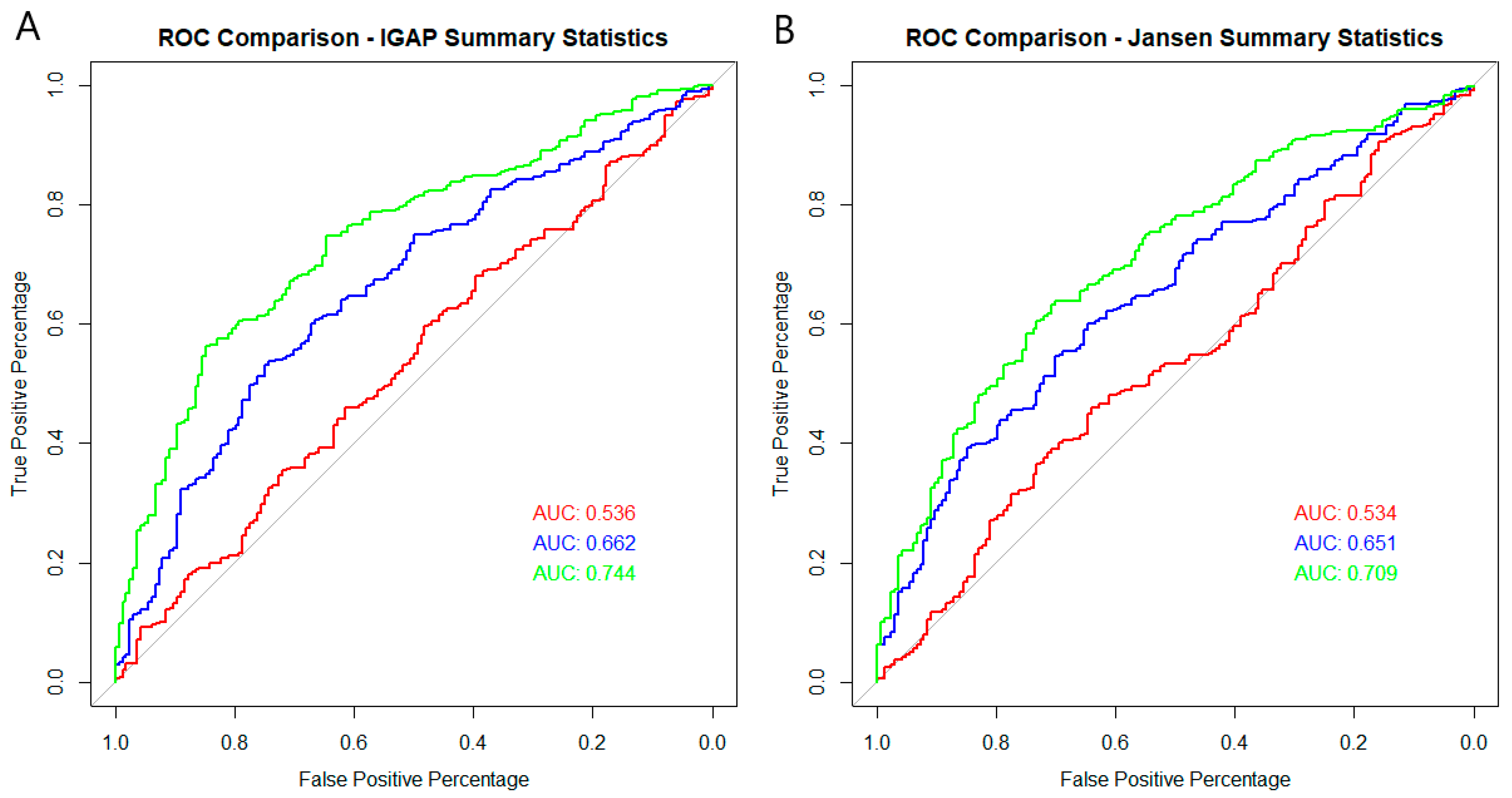
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, W.W.; Luis, C.A.; Kashuba, A.; Luis, M.; Harwood, D.G.; Loewenstein, D.; Waters, C.; Jimison, P.; Shepherd, E.; Sevush, S.; et al. Relative Frequencies of Alzheimer Disease, Lewy Body, Vascular and Frontotemporal Dementia, and Hippocampal Sclerosis in the State of Florida Brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2002, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatz, M.; Reynolds, C.A.; Fratiglioni, L.; Johansson, B.; Mortimer, J.A.; Berg, S.; Fiske, A.; Pedersen, N.L. Role of Genes and Environments for Explaining Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, R.; Hill, M.; Williams, J. The Multiplex Model of the Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Zimmer, J.A.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Ardayfio, P.; Sparks, J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shcherbinin, S.; Wang, H.; Nery, E.S.M.; et al. Donanemab in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease: The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.R.J.R.; Mistry, S.; Muskett, N.; Escott-Price, V.; Brookes, K. From Polygenic Scores to Precision Medicine in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 74, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, T.W.; Katzourou, I.K.; Stevenson-Hoare, J.O.; Bracher-Smith, M.R.; Ivanov, D.K.; Escott-Price, V. Machine Learning for the Life-Time Risk Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, A.C.J.W. Validity of Polygenic Risk Scores: Are We Measuring What We Think We Are? Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, R143–R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecile, A.; Janssens, J.W.; Joyner, M.J. Polygenic Risk Scores That Predict Common Diseases Using Millions of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms: Is More, Better? Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, F.K.; Tonk, E.C.M.; Janssens, A.C.J.W. Evaluation of Polygenic Risk Models Using Multiple Performance Measures: A Critical Assessment of Discordant Results. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Gallagher, E.; Koska, K.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Morgan, K.; Thomas, A.; Brookes, K.J. Genome-Wide Association Findings from the Brains for Dementia Research Cohort. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.-C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; Jun, G.; DeStefano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; et al. Meta-Analysis of 74,046 Individuals Identifies 11 New Susceptibility Loci for Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.M.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.K.; Hägg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies New Loci and Functional Pathways Influencing Alzheimer’s Disease Risk. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Küçükali, F.; Jansen, I.E.; Kleineidam, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Campos-Martin, R.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; et al. New Insights into the Genetic Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, R.; Van Der Lee, S.J.J.; Naj, A.C.C.; Bellenguez, C.; Badarinarayan, N.; Jakobsdottir, J.; Kunkle, B.W.W.; Boland, A.; Raybould, R.; Bis, J.C.C.; et al. Rare Coding Variants in PLCG2, ABI3, and TREM2 Implicate Microglial-Mediated Innate Immunity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, L.; Ueno, L.; Du, L.; Jonkers, M.; Yates, J.R.; Vogt, P.K. The Butterfly Effect in Cancer: A Single Base Mutation Can Remodel the Cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desi, N.; Tay, Y. The Butterfly Effect of RNA Alterations on Transcriptomic Equilibrium. Cells 2019, 8, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Romero, M.; Glymour, M.M.; Hayes-Larson, E.; Mayeda, E.R.; Graff, R.E.; Brenowitz, W.D.; Ackley, S.F.; Witte, J.S.; Kobayashi, L.C. Association Between Alzheimer Disease and Cancer With Evaluation of Study Biases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K.; Soosaipillai, A.; Sando, S.B.; Lauridsen, C.; Berge, G.; Møller, I.; Grøntvedt, G.R.; Bråthen, G.; Begcevic, I.; Moussaud, S.; et al. Assessment of Kallikrein 6 as a Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, S.; Kousiappa, I.; Stavrou, M.; Sargiannidou, I.; Georgiou, E.; Papacostas, S.S.; Kleopa, K.A. Altered Expression of Glial Gap Junction Proteins Cx43, Cx30, and Cx47 in the 5XFAD Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 582934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Hassan, R.; Adam, I.; Bansal, R.; Broersen, K. A Review of Oxidative Stress Products and Related Genes in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 83, 977–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, K.; Pedersen, T.L.; Seyfried, N.T.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; Hales, C.M.; Dammer, E.B.; Blach, C.; Louie, G.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; et al. Association of Plasma and CSF Cytochrome P450, Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase, and Ethanolamide Metabolism with Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarparast, M.; Dattmore, D.; Alan, J.; Lee, K.S.S. Cytochrome P450 Metabolism of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Neurodegeneration. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, K.J.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Thomas, A.; Morgan, K. An Alternative Method of SNP Inclusion to Develop a Generalized Polygenic Risk Score Analysis across Alzheimer’s Disease Cohorts. Front. Dement. 2023, 2, 1120206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, J.S.; Bonham, L.W.; Sears, R.L.; Klein, E.; Karydas, A.; Kramer, J.H.; Miller, B.L.; Coppola, G. Decision Tree Analysis of Genetic Risk for Clinically Heterogeneous Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleegers, K.; Bettens, K.; De Roeck, A.; Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Cuyvers, E.; Verheijen, J.; Struyfs, H.; Van Dongen, J.; Vermeulen, S.; Engelborghs, S.; et al. A 22-Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Score Correlates with Family History, Onset Age, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Abeta42. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escott-Price, V.; Sims, R.; Bannister, C.; Harold, D.; Vronskaya, M.; Majounie, E.; Badarinarayan, N.; Morgan, K.; Passmore, P.; Holmes, C.; et al. Common Polygenic Variation Enhances Risk Prediction for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 2015, 138, 3673–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonenko, G.; Baker, E.; Stevenson-Hoare, J.; Sierksma, A.; Fiers, M.; Williams, J.; de Strooper, B.; Escott-Price, V. Identifying Individuals with High Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Polygenic Risk Scores. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosto, G.; Bird, T.D.; Tsuang, D.; Bennett, D.A.; Boeve, B.F.; Cruchaga, C.; Faber, K.; Foroud, T.M.; Farlow, M.; Goate, A.M.; et al. Polygenic Risk Scores in Familial Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escott-Price, V.; Myers, A.J.; Huentelman, M.; Hardy, J. Polygenic Risk Score Analysis of Pathologically Confirmed Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escott-Price, V.; Myers, A.; Huentelman, M.; Shoai, M.; Hardy, J.; Hardy, J. Polygenic Risk Score Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease in Cases without APOE4 or APOE2 Alleles. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. JPAD 2019, 6, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigorta, U.M.; Denson, L.A.; Hyams, J.S.; Mondal, K.; Prince, J.; Walters, T.D.; Griffiths, A.; Noe, J.D.; Crandall, W.V.; Rosh, J.R.; et al. Transcriptional Risk Scores Link GWAS to EQTL and Predict Complications in Crohn’s Disease HHS Public Access Author Manuscript. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pividori, M.; Manichaikul, A.; Palmer, A.A.; Cox, N.J.; Wheeler, H.E.; Im, H.K. Polygenic Transcriptome Risk Scores (PTRS) Can Improve Portability of Polygenic Risk Scores across Ancestries. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pain, O.; Glanville, K.P.; Hagenaars, S.; Selzam, S.; Fürtjes, A.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Rimfeld, K.; Breen, G.; Folkersen, L.; Lewis, C.M. Imputed Gene Expression Risk Scores: A Functionally Informed Component of Polygenic Risk. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.T.; Costello, H.; Hayes, G.M. Brains for Dementia Research: Evolution in a Longitudinal Brain Donation Cohort to Maximize Current and Future Value. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, S.; Patel, T.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Sang, F.; Francis, P.T.; Morgan, K.; Brookes, K.J. Observations of Extensive Gene Expression Differences in the Cerebellum and Potential Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabalin, A.A. Gene Expression Matrix EQTL: Ultra Fast EQTL Analysis via Large Matrix Operations. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. PROC: An Open-Source Package for R and S+ to Analyze and Compare ROC Curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| eQTLs | eQTLs Plus APOE | eQTLs in DE Genes | eQTLs in DE Genes Plus APOE | rs429358 & rs7412 Only | Best Model Using Thresholding without APOE Region | Best Model Using Thresholding Plus APOE Isoform SNPs | Best Model Using Thresholding with APOE Region | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGAP | # SNPs | 17,865 | 17,867 | 1614 | 1616 | 2 | 29 | 31 | 56 |
| Logisitic Regression p value | 9.22 × 10−6 | 1.52 × 10−8 | 0.184 | 3.18 × 10−8 | 6.89 × 10−15 | 6.73 × 10−5 | 2.61 × 10−16 | 9.20 × 10−18 | |
| Area Under the Curve | 0.6144 | 0.6508 | 0.5357 | 0.6616 | 0.7082 | 0.6078 | 0.7442 | 0.7633 | |
| Jansen | # SNPs | 34,894 | 34,896 | 3116 | 3118 | 2 | 62 | 64 | 164 |
| Logisitic Regression p value | 1.02 × 10−6 | 2.51 × 10−9 | 0.264 | 7.72 × 10−8 | 2.1 × 10−14 | 0.0002 | 1.93 × 10−12 | 3.72 × 10−16 | |
| Area Under the Curve | 0.6417 | 0.6738 | 0.5335 | 0.6511 | 0.7083 | 0.6033 | 0.7089 | 0.7543 | |
| Bellenguez | # SNPs | 30,863 | - | 2759 | - | - | 70,674 | - | - |
| Logisitic Regression p value | 1.76 × 10−5 | - | 0.03 | - | - | 2.73 × 10−11 | - | - | |
| Area Under the Curve | 0.6241 | - | 0.5586 | - | - | 0.6865 | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brookes, K.J. Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799
Brookes KJ. Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(16):12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrookes, Keeley J. 2023. "Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 16: 12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799
APA StyleBrookes, K. J. (2023). Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(16), 12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799





