Fusion-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Technogenic-Waste-Derived Zeolites and Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mercury (II) Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
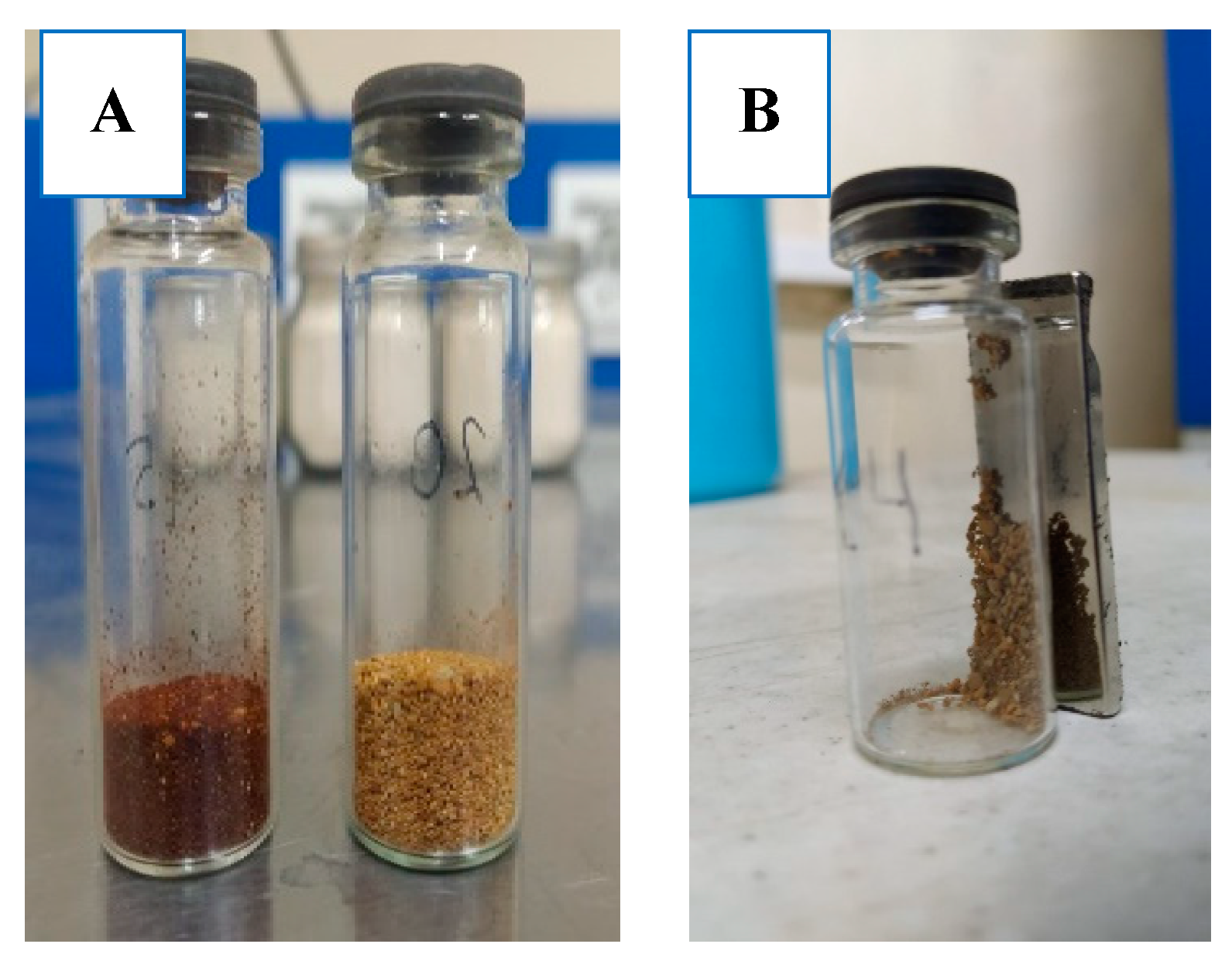
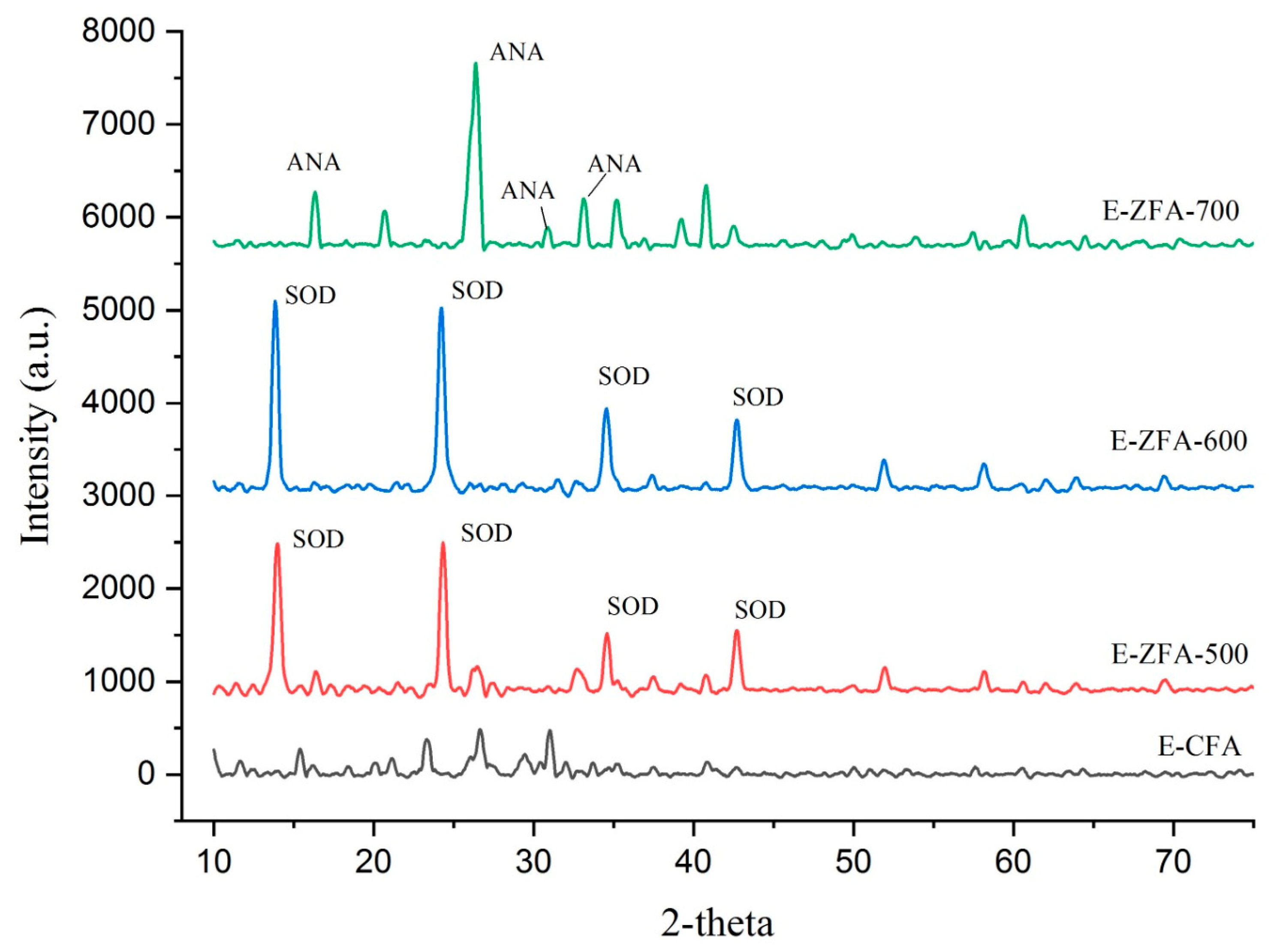
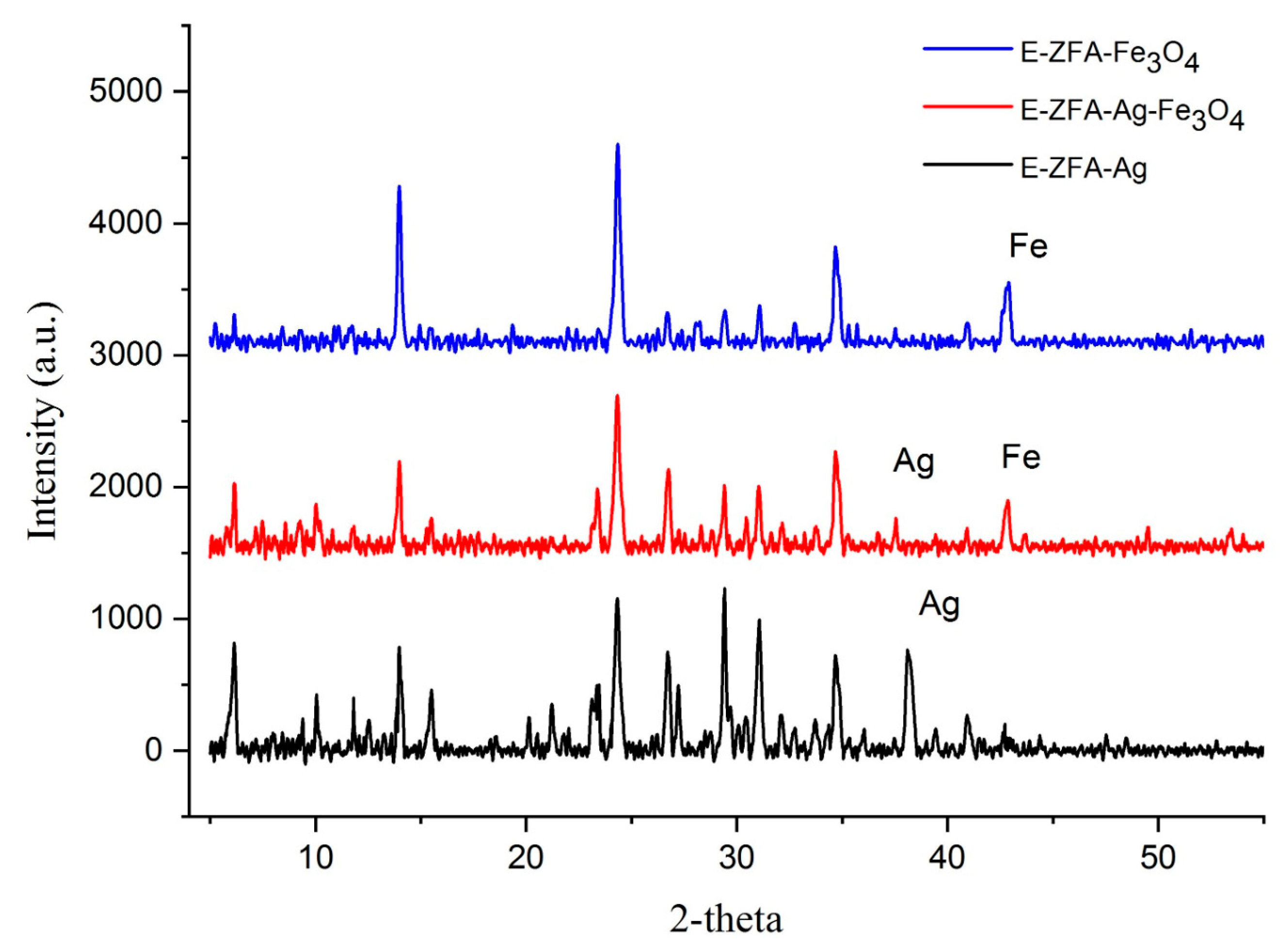
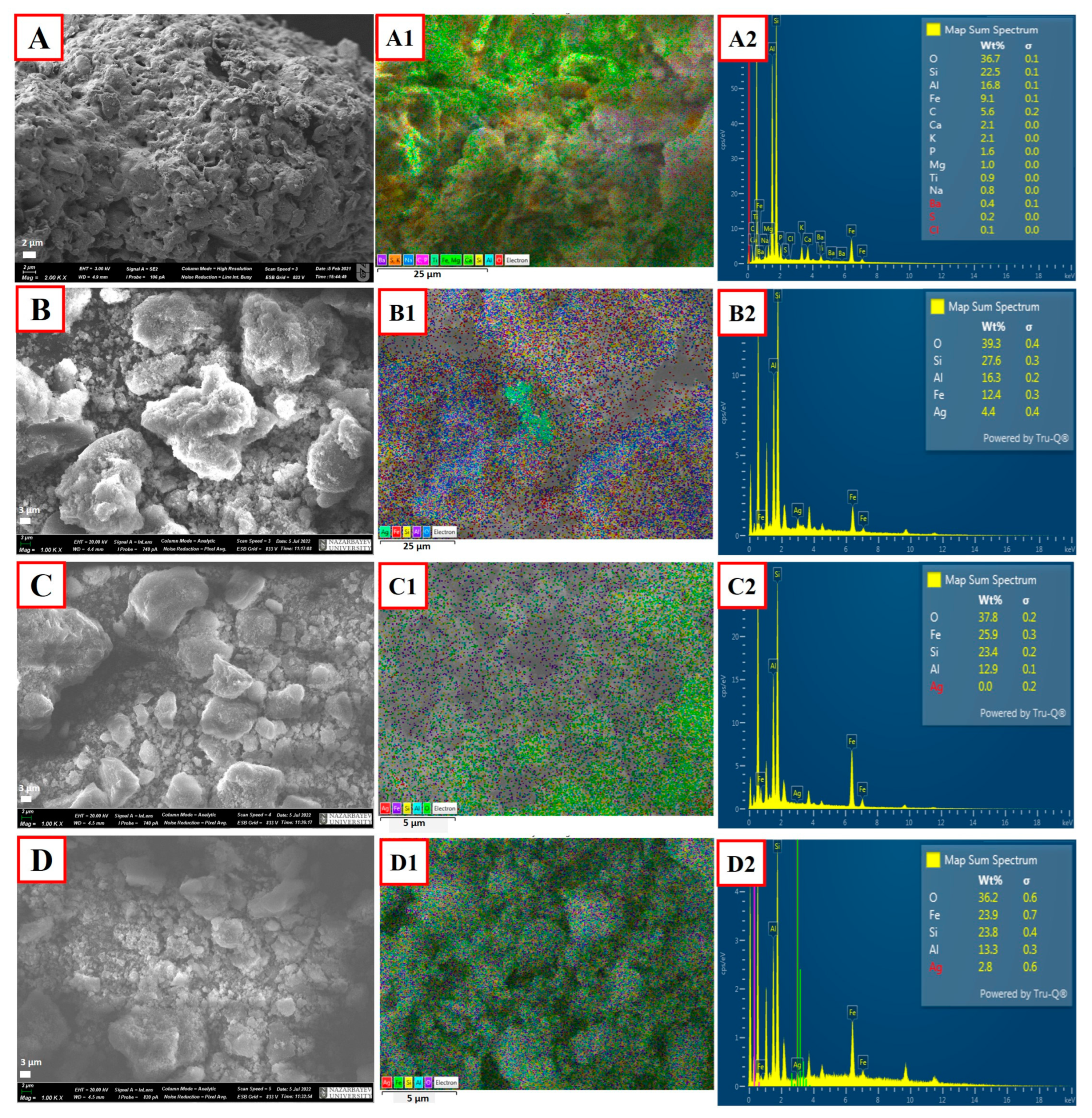
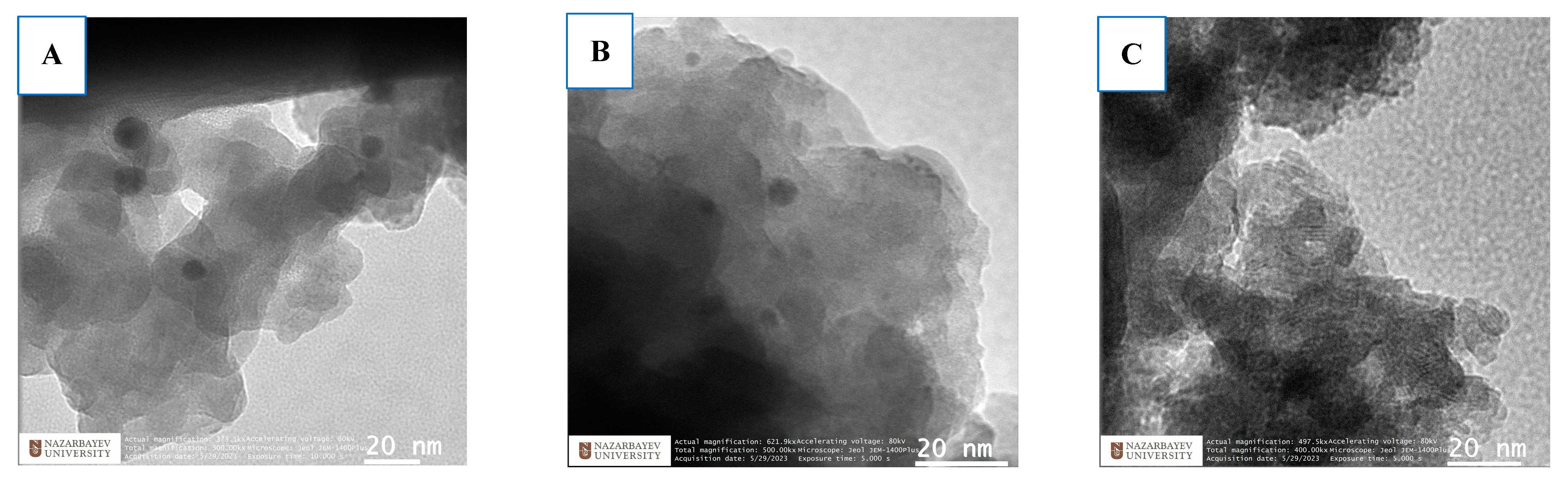
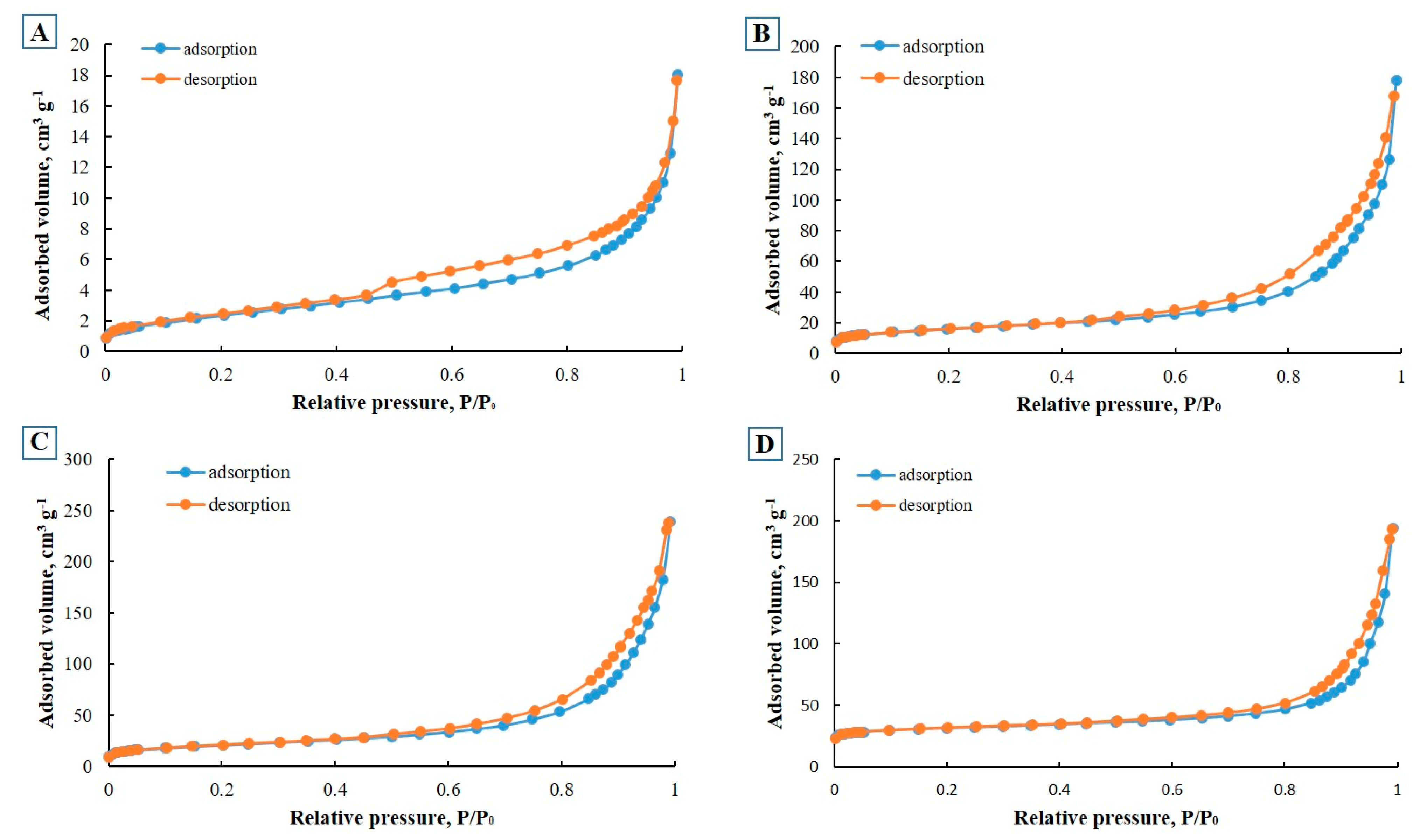
2.1. Characterization
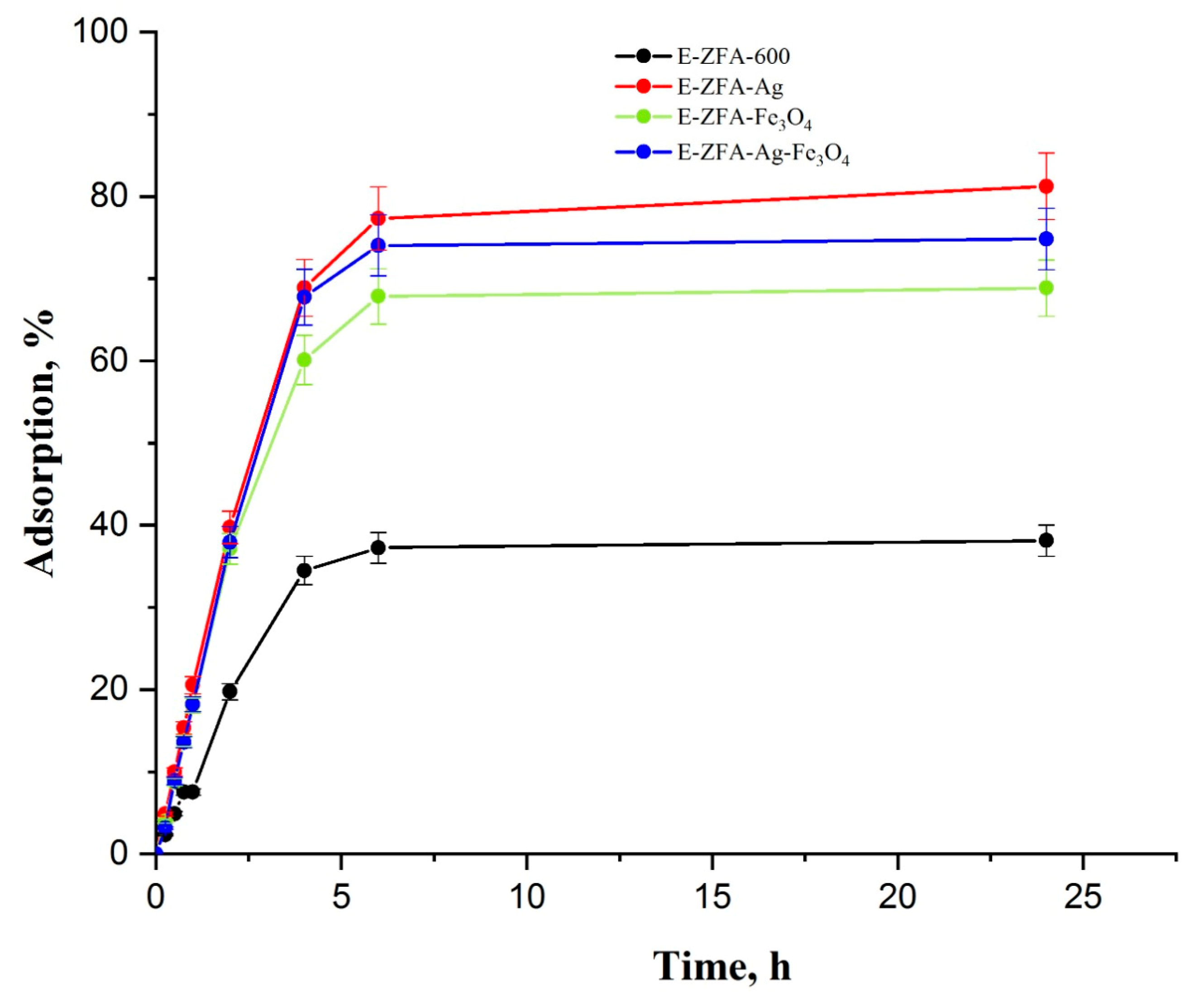
2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
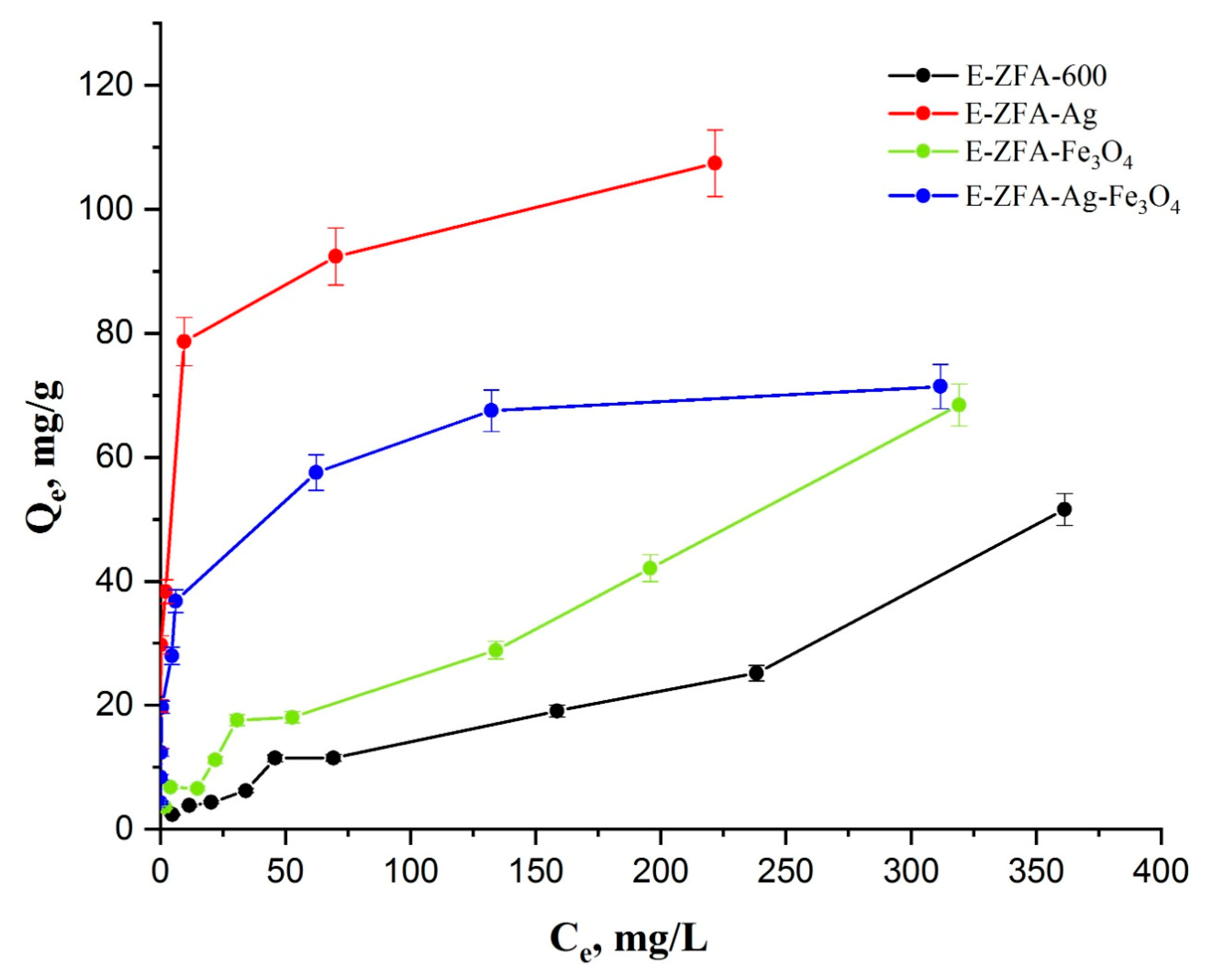
2.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Zeolite
3.3. Synthesis of Nanocomposites
3.3.1. Magnetite NP-Impregnated Zeolitic Nanocomposites
3.3.2. Silver NP-Impregnated Zeolitic Nanocomposites
3.3.3. Silver-Magnetite NP-Impregnated Zeolitic Nanocomposites
3.4. Characterization of Materials
3.5. Batch Adsorption Kinetics
3.6. Batch Adsorption Isotherm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yurekli, Y. Removal of heavy metals in wastewater by using zeolite nano-particles impregnated polysulfone membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Daman, R.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P. Chemosphere Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Arya, R.K. Removal of Mercury(II) from aqueous solution: A review of recent work. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorifuji, T.; Tsuda, T.; Kashima, S.; Takao, S.; Harada, M. Long-term exposure to methylmercury and its effects on hypertension in Minamata. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulter, M.A. Minamata convention on mercury. Int. Leg. Mater. 2016, 55, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esdaile, L.J.; Chalker, J.M. The mercury problem in artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6905–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, H.H.; Perrez, F.X. The Minamata convention: A comprehensive response to a global problem. Rev. Eur. Comp. Int. Environ. Law 2014, 23, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Azat, S.; Tauanov, Z.; Mikhalovsky, S.V. Functionalization of biosourced silica and surface reactions with mercury in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 129745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, D.; Cao, Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Tack, F.M.G.G.; Rinklebe, J.; O’Connor, D. Remediation of mercury contaminated soil, water, and air: A review of emerging materials and innovative technologies. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franus, W. Characterization of X-type zeolite prepared from coal fly ash. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Qu, R.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W.; Song, H.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, X. Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash for the removal of harmful gaseous pollutants: A review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1127–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, F.P.X.; Moreno, N.; Umana, J.C.; Alastuey, A.; Hernandez, E.; Lopez-Soler, A. Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash: An overview. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Guo, F.; Shao, Z.; Wu, J. Zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash produced by a gasification process for Ni2+ removal from water. Minerals 2018, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, Y. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by zeolite synthesized from fly ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-B.; Ye, J.-J.; Liu, Z.-H.; Qiu, Y.-Q. Microwave digestion and alkali fusion assisted hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite from coal fly ash for enhanced adsorption of Cd(II) in aqueous solution. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Guo, F.; Wu, J.; Dai, B. Synthesis of zeolite Na-P1 from coal fl y ash produced by gasification and its application as adsorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from water. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yao, B.; Xia, Y.; Huang, H.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, W. Coal fly ash derived zeolite for highly efficient removal of Ni2+ in waste water. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycheva, S.; Zgureva, D.; Miteva, S.; Marinov, I.; Behunová, D.M.; Trendafilova, I.; Popova, M.; Václaviková, M. Studies on the potential of nonmodified and metal of heavy metals and catalytic degradation of organics for waste water recovery. Processes 2020, 8, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ji, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, C.; Yang, K.; Xu, M. Chemosphere removal of Pb(II) from wastewater using Al2O3-NaA zeolite composite hollow fiber membranes synthesized from solid waste coal fly ash. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauanov, Z.; Lee, J.; Inglezakis, V.J. Mercury reduction and chemisorption on the surface of synthetic zeolite silver nanocomposites: Equilibrium studies and mechanisms. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauanov, Z.; Abylgazina, L.; Spitas, C.; Itskos, G.; Inglezakis, V. Mineralogical, microstructural and thermal characterization of coal fly ash produced from Kazakhstani power plants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 230, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauanov, Z.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Inglezakis, V.J. Synthetic coal fly ash-derived zeolites doped with silver nanoparticles for mercury (II) removal from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauanov, Z.; Shah, D.; Itskos, G.; Inglezakis, V. Optimized production of coal fly ash derived synthetic zeolites for mercury removal from wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 230, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G. A new approach for the classification of coal fly ashes based on their origin, composition, properties, and behaviour. Fuel 2007, 86, 1490–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C. State-of-the-art applications of fly ash from coal and biomass: A focus on zeolite synthesis processes and issues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 65, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visa, M.; Chelaru, A.M. Hydrothermally modified fly ash for heavy metals and dyes removal in advanced wastewater treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 303, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, W.; Wdowin, M.; Franus, M. Synthesis and characterization of zeolites prepared from industrial fly ash. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5721–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.N.; Daghigh, A.A.; Abrishamkar, M. Phase transformation of zeolite P to Y and analcime zeolites due to changing the time and temperature. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 2013, 428216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yen, W.; Chen, H.; Dung, W. Phase transition pathway of hydrothermal zeolite synthesis. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2021, 48, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkowski, A.; Franus, W.; Beran, E.; Czímerová, A. Properties and potential applications of zeolitic materials produced from fly ash using simple method of synthesis. Powder Technol. 2006, 166, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowin, M.; Franus, M.; Panek, R.; Badura, L.; Franus, W. The conversion technology of fly ash into zeolites. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy. 2014, 16, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Ju, F.; Han, L.; Chang, L.; Bao, W. Supercritical hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash for mercury removal from coal derived gas. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 136, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attari, M.; Bukhari, S.S.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S. A low-cost adsorbent from coal fly ash for mercury removal from industrial wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Kurbanova, A.; Molkenova, A.; Zorpas, A.A. Magnetic Fe3O4-ago nanocomposites for effective mercury removal from water. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katok, K.V.; Whitby, R.L.D.; Fukuda, T.; Maekawa, T.; Bezverkhyy, I.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Cundy, A.B. Hyperstoichiometric interaction between silver and mercury at the nanoscale. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2632–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katok, K.V.; Whitby, R.L.D.; Fayon, F.; Bonnamy, S.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Cundy, A.B. Synthesis and application of hydride silica composites for rapid and facile removal of aqueous mercury. ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 4126–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarna, D.; Baran, P.; Kunecki, P.; Panek, R.; Żmuda, R.; Wdowin, M. Synthetic zeolites as potential sorbents of mercury from wastewater occurring during wet FGD processes of flue gas. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanardakani, S.; Jafari, A.; Zandipak, R.; Meidanchi, A. Removal of heavy metal (Hg(II) and Cr(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions using Fe2O3@SiO2 thin films as a novel adsorbent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 120, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I Solids J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Maleki, A.; Najafi, F.; Gharibi, F.; McKay, G.; Gupta, V.K.; Puttaiah, S.H.; Marzban, N. Heavy metal adsorption using PAMAM/CNT nanocomposite from aqueous solution in batch and continuous fixed bed systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Synthetic Zeolite Type | * Tf °C | * tf [h] | * Tc [°C] | * tc [h] | Additional Synthesis Step | NaOH:CFA Ratio | Heavy Metals | Conc. [mg/L] | Removal [%] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite X | 550 | 1.5 | 90 | 15 | Hydrothermal treatment | 2:1 | Ni2+ | 20 | 90 | [15] |
| Sodalite | 550 | 1 | 105 | 24 | Hydrothermal treatment | 2:1 | Pb2+ Cu2+ Mn2+ | 1.8 7.5 5.7 | 93 95 78 | [16] |
| Zeolite | 450 | 4 | 90 | 12 | Microwave digestion | 5:1 | Cd2+ | 20 | 98 | [17] |
| Zeolite Na-P1 | 550 | 2 | 100 | 12 | Hydrothermal treatment | 1:1 | Cr3+ | 100 | - | [18] |
| Zeolite A | 650 | 2 | 100 | 24 | Hydrothermal treatment | 1:1 | Ni2+ | 200 | 94 | [19] |
| Zeolite Na-X | 550 | - | 90 105 | 4 1 | Hydrothermal treatment | 2:1 | Cd2+ Pb2+ | 50 100 | - | [20] |
| Al2O3-NaA zeolite | 600 | 2 | RT | 12 | Hydrothermal treatment | 1:0.7 | Pb2+ | 50 | 99 | [21] |
| Elements | E-CFA | E-ZFA-500 | E-ZFA-600 | E-ZFA-700 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | - | 9.369 ± 0.128 | 9.978 ± 0.163 | 6.326 ± 0.162 |
| Na | - | 2.455 ± 0.076 | 2.138 ± 0.058 | 1.505 ± 0.045 |
| Mg | 0.140 ± 0.009 | 0.232 ± 0.002 | 0.167 ± 0.023 | 0.162 ± 0.028 |
| Al | 14.165 ± 0.046 | 14.632 ± 0.245 | 14.024 ± 0.245 | 12.934 ± 0.845 |
| Si | 46.954 ± 0.519 | 31.150 ± 0.845 | 31.471 ± 0.724 | 34.190 ± 0.923 |
| P | 0.941 ± 0.012 | 1.536 ± 0.063 | 1.637 ± 0.102 | 1.874 ± 0.148 |
| S | 0.274 ± 0.004 | 0.361 ± 0.086 | 0.359 ± 0.054 | 0.047 ± 0.004 |
| Cl | 0.747 ± 0.024 | 0.713± 0.094 | 0.626 ± 0.073 | 0.107 ± 0.012 |
| K | 1.567 ± 0.126 | 0.377 ± 0.068 | 0.293 ± 0.028 | 1.081 ± 0.145 |
| Ca | 6.499 ± 0.175 | 8.398 ± 0.284 | 8.216 ± 0.438 | 8.147 ± 0.628 |
| Fe | 22.275 ± 0.481 | 24.370 ± 0.172 | 24.537 ± 0.984 | 26.627 ± 0.823 |
| Elements | E-ZFA-Ag | E-ZFA-Fe3O4 | E-ZFA-Ag-Fe3O4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 1.982 ± 0.109 | 1.341 ± 0.359 | 1.796 ± 0.157 |
| Al | 5.476 ± 0.358 | 6.355 ± 0.823 | 6.285 ± 0.643 |
| Si | 12.623 ± 0.636 | 12.424 ± 1.344 | 13.203 ± 0.823 |
| K | 0.302 ± 0.018 | 0.113 ± 0.012 | 0.201 ± 0.009 |
| Ca | 2.629 ± 0.110 | 2.308 ± 0.228 | 2.718 ± 0.196 |
| Ti | 0.771 ± 0.017 | 0.678 ± 0.018 | 0.794 ± 0.037 |
| Mn | 0.954 ± 0.048 | 0.113 ± 0.002 | 0.107 ± 0.004 |
| Fe | 6.002 ± 0.227 | 11.552 ± 1.018 | 8.760 ± 0.182 |
| Ag | 2.318 ± 0.365 | - | 1.259 ± 0.596 |
| Other * |
| Sample Name | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Size (nm) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Micropore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-CFA | 8.7 | 1.9 | 0.027 | 0.003 |
| E-ZFA-600 | 74.9 | 4.8 | 0.076 | 0.023 |
| E-ZFA-Fe3O4 | 48.6 | 1.0 | 0.015 | 0.013 |
| E-ZFA-Ag | 128.7 | 0.6 | 0.092 | 0.061 |
| E-ZFA-Ag-Fe3O4 | 86.9 | 0.7 | 0.057 | 0.036 |
| Adsorbent Type | Adsorption Capacity [mg/g] | pH Range | Initial Concentration [mg/L] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-ZFA-600 | 51.5 | 2.5 | 490 | This work |
| E-ZFA-Ag | 107.4 | 2.5 | 490 | This work |
| E-ZFA-Fe3O4 | 68.4 | 2.5 | 490 | This work |
| E-ZFA-Ag-Fe3O4 | 71.4 | 2.5 | 490 | This work |
| CFA-derived zeolite | 0.3 | 2.5 | 10 | [35] |
| Fe3O4-Ag0 nanocomposite | 71.3 | 6.5 | 200 | [36] |
| CFA-derived zeolite | 5.1 | 5-6 | 575 | [39] |
| Ag-doped CFA-derived zeolite | 5.0 | 5-6 | 575 | [39] |
| Fe2O3@SiO2 thin films | 126.0 | 7.0 | 336 | [40] |
| Experimental | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax, mg/g | qmax, mg/g | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 | ||
| E-ZFA-600 | 51.5 | 35.2 | 0.0086 | 0.8639 | 1.4684 | 1.4521 | 0.9631 | |
| E-ZFA-Fe3O4 | 68.4 | 48.3 | 0.0168 | 0.8399 | 1.8646 | 2.4005 | 0.9424 | |
| E-ZFA-Ag | 107.4 | 107.5 | 0.3298 | 0.9976 | 4.6970 | 39.884 | 0.9471 | |
| E-ZFA-Ag-Fe3O4 | 71.4 | 71.9 | 0.1601 | 0.9981 | 4.1425 | 20.247 | 0.9677 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suleimenova, M.; Zharylkan, S.; Mekenova, M.; Mutushev, A.; Azat, S.; Tolepova, A.; Baimenov, A.; Satayeva, A.; Tauanov, Z. Fusion-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Technogenic-Waste-Derived Zeolites and Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mercury (II) Adsorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411317
Suleimenova M, Zharylkan S, Mekenova M, Mutushev A, Azat S, Tolepova A, Baimenov A, Satayeva A, Tauanov Z. Fusion-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Technogenic-Waste-Derived Zeolites and Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mercury (II) Adsorption. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411317
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuleimenova, Madina, Saule Zharylkan, Meruyert Mekenova, Alibek Mutushev, Seytkhan Azat, Aidana Tolepova, Alzhan Baimenov, Aliya Satayeva, and Zhandos Tauanov. 2023. "Fusion-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Technogenic-Waste-Derived Zeolites and Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mercury (II) Adsorption" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411317
APA StyleSuleimenova, M., Zharylkan, S., Mekenova, M., Mutushev, A., Azat, S., Tolepova, A., Baimenov, A., Satayeva, A., & Tauanov, Z. (2023). Fusion-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Technogenic-Waste-Derived Zeolites and Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mercury (II) Adsorption. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411317







