ATP2B3 Inhibition Alleviates Erastin–Induced Ferroptosis in HT-22 Cells through the P62–KEAP1–NRF2–HO-1 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
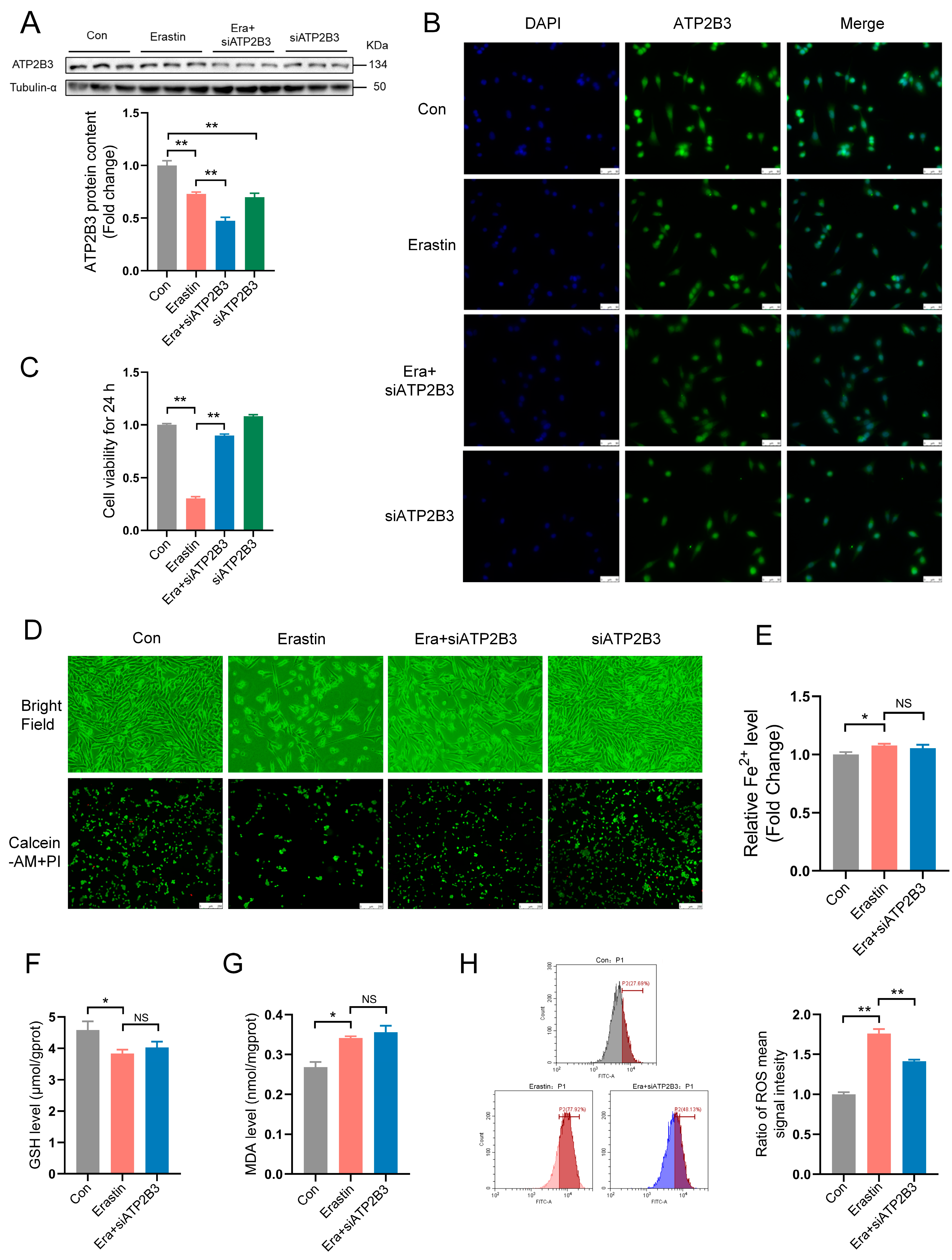
2.1. Erastin Down–Regulates ATP2B3 Protein Level in HT-22 Cells
2.2. ATP2B3 Knockdown Alleviates Ferroptosis in Erastin–Induced HT-22 Cells
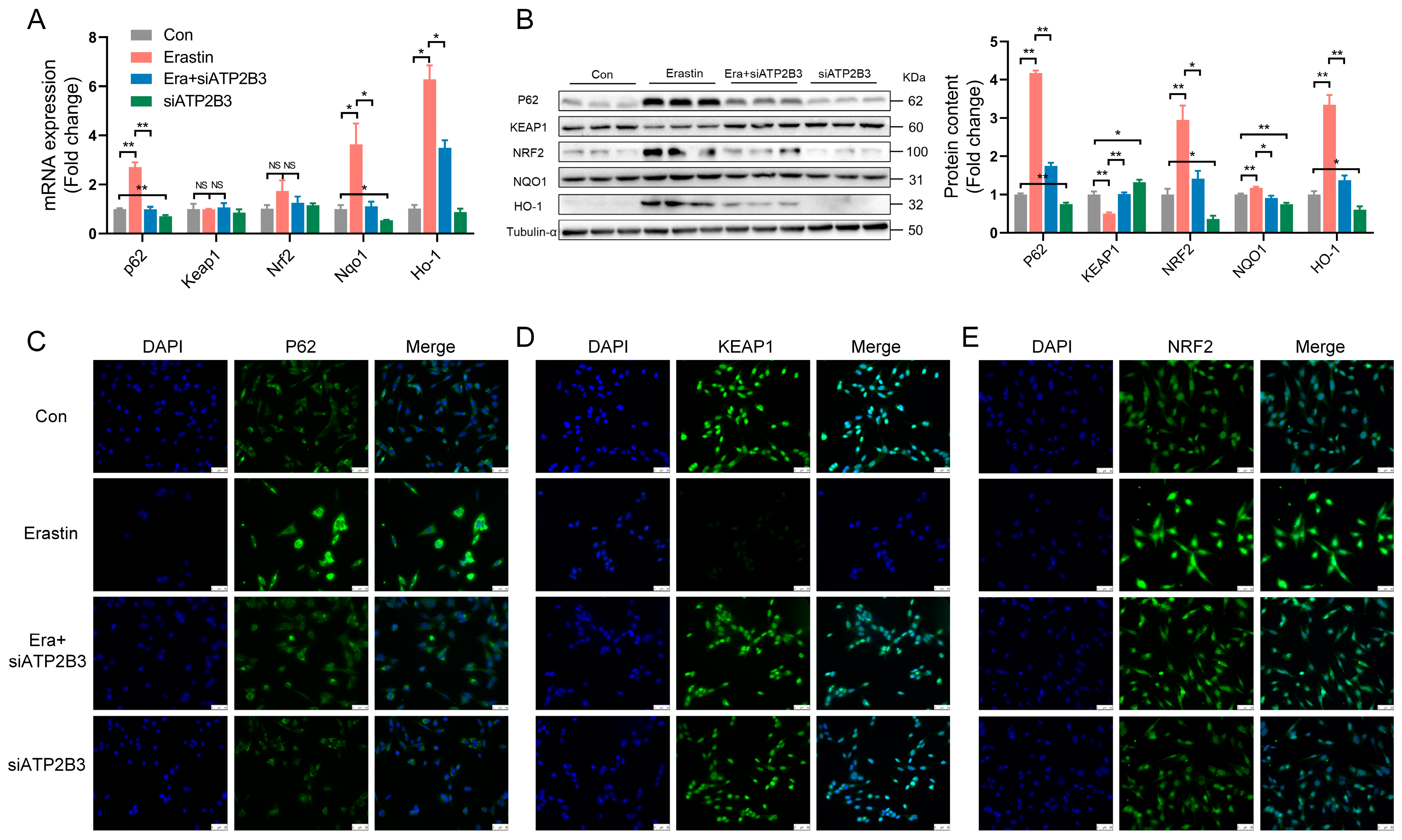
2.3. ATP2B3 Inhibition Regulates Oxidative Stress-Related Genes and Proteins in Erastin–Induced HT-22 Cells
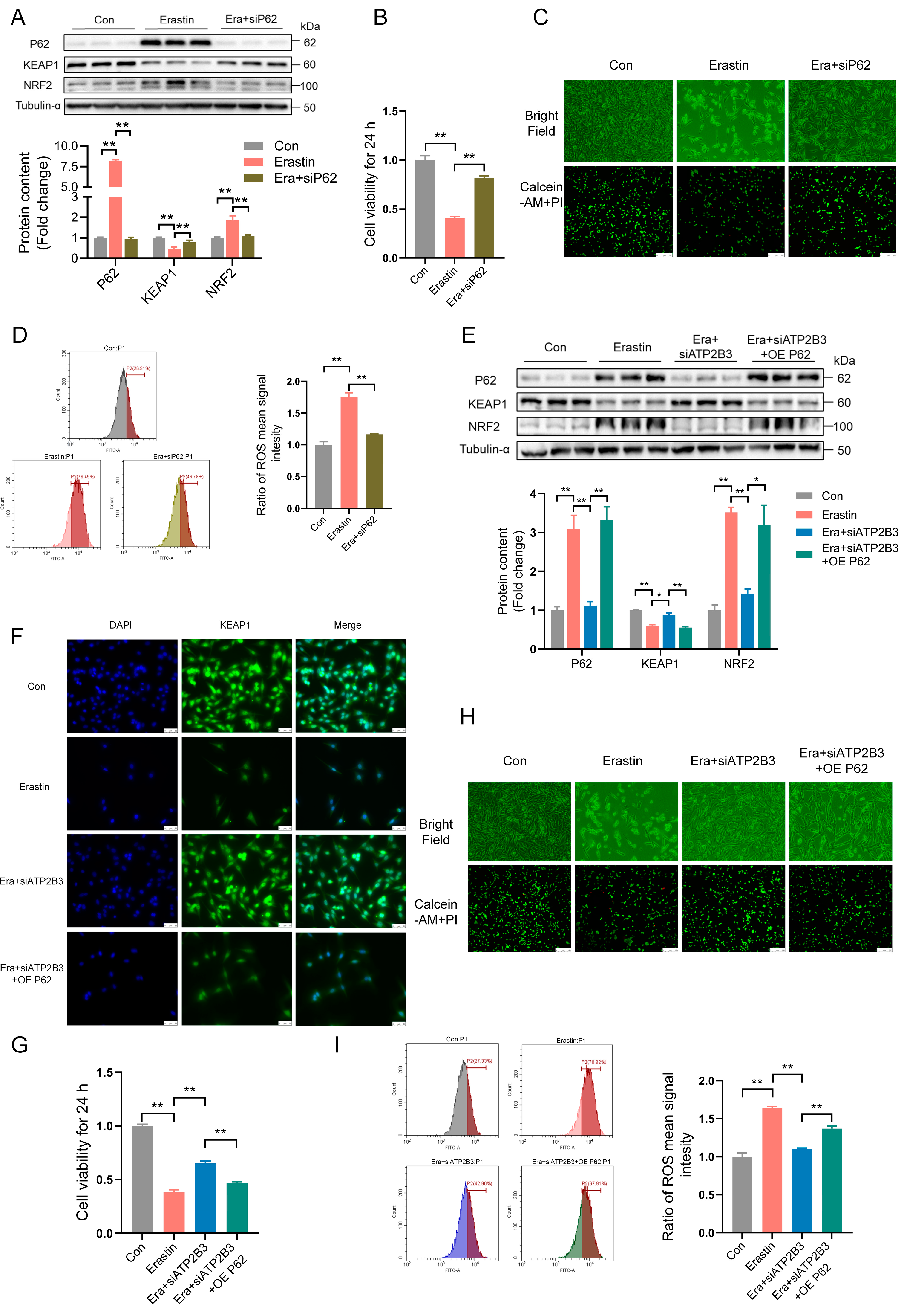
2.4. ATP2B3 Inhibition Mitigates Erastin–Induced HT-22 Ferroptosis via Reducing P62 Protein Expression
2.5. ATP2B3 Inhibition Relieves Erastin–Induced HT-22 Ferroptosis through IncressingKEAP1 Expression
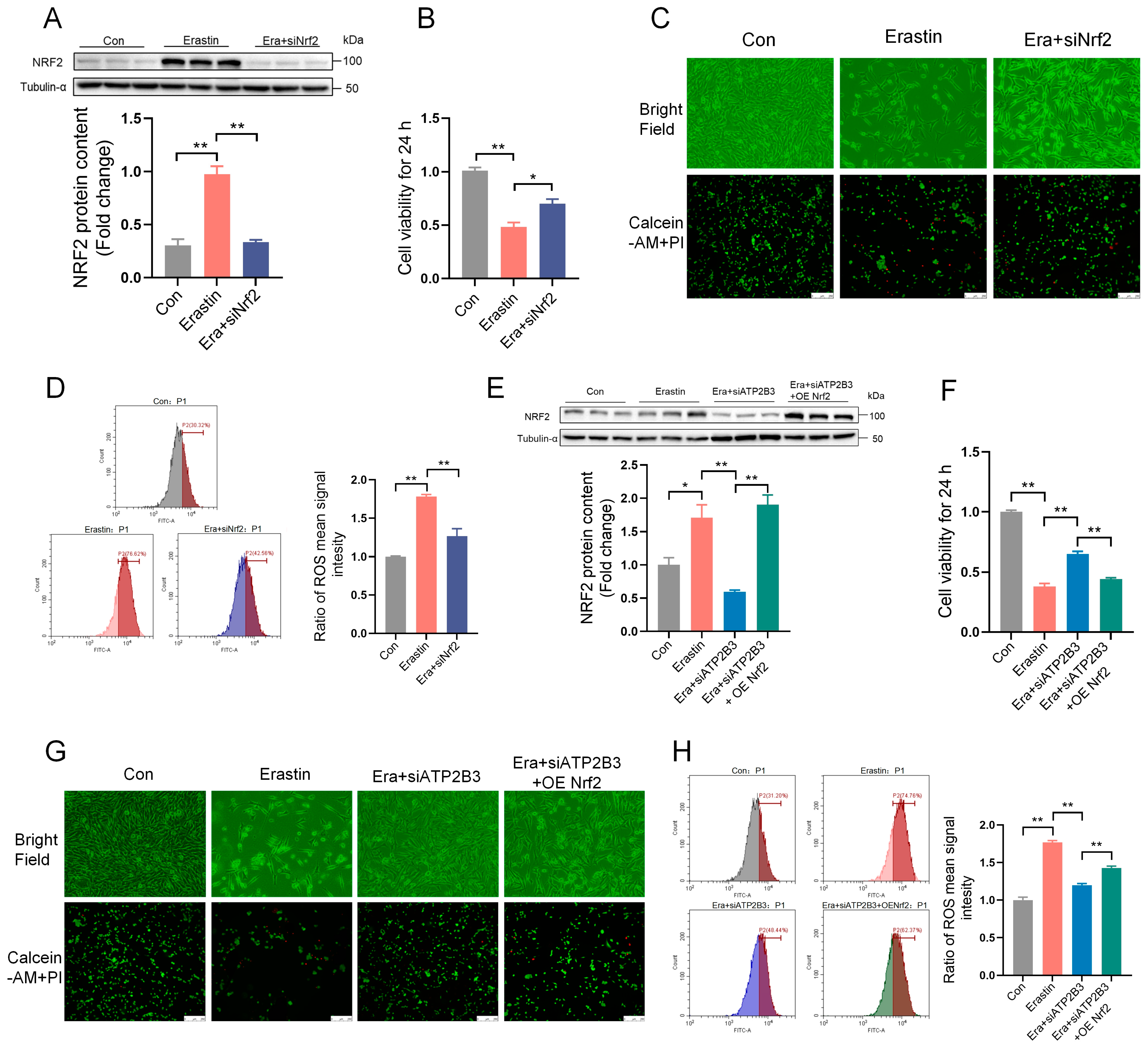
2.6. ATP2B3 Inhibition Alleviates Erastin–Induced HT-22 Ferroptosis through Lowering NRF2 Expression
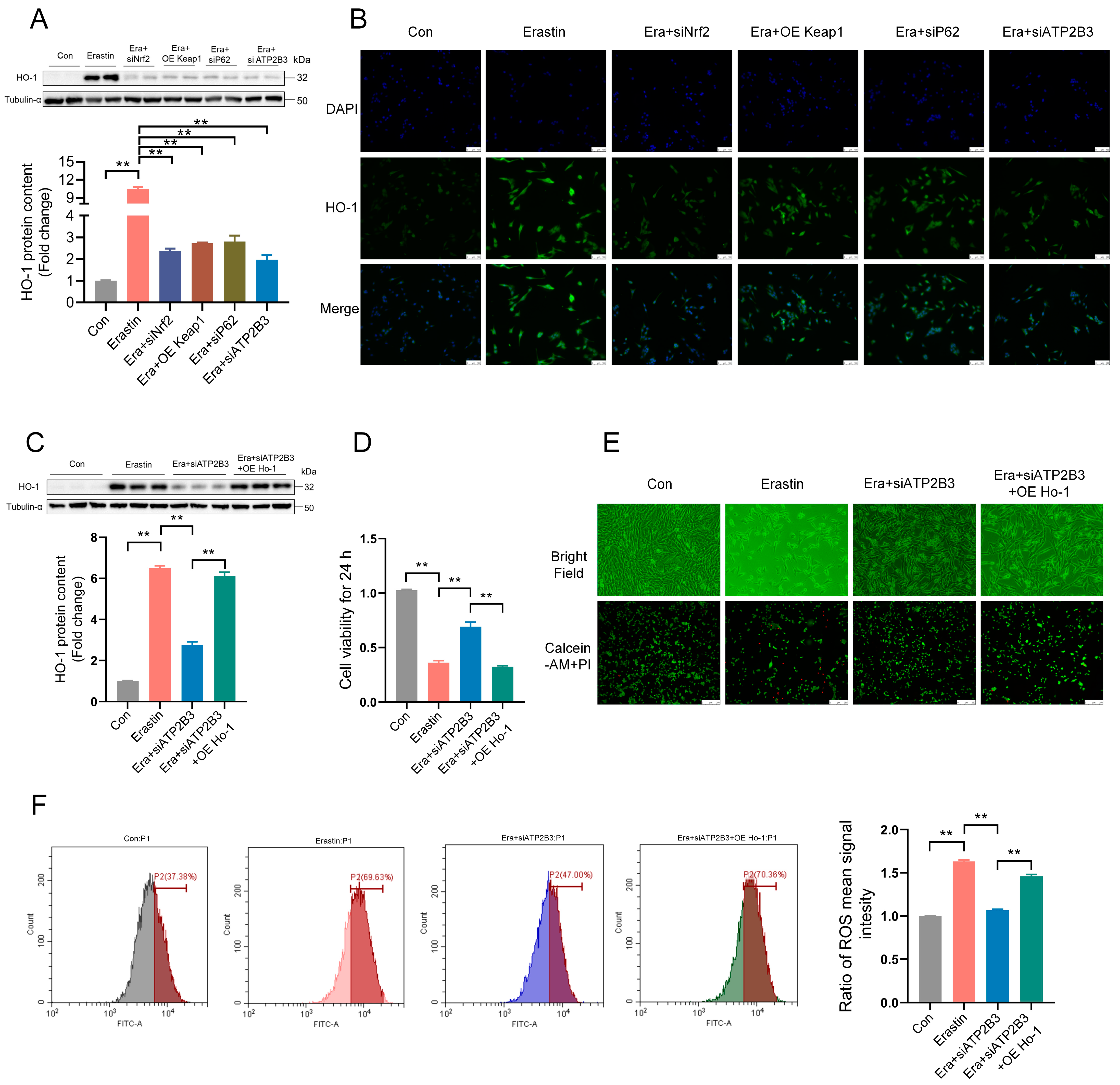
2.7. ATP2B3 Inhibition Mitigates Erastin–Induced HT-22 Ferroptosis through P62−KEAP1−NRF2-HO-1 Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Treatments
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Live/Dead Cell Staining
4.4. Measurement of ROS by Flow Cytometry
4.5. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Glutathione (GSH) Assay
4.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
4.7. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Assay
4.8. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
4.9. Immunofluorescence (IF) Assays
4.10. Fe2+ Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stovner, L.J.; Nichols, E.; Steiner, T.J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Al-Raddadi, R.M.; Ansha, M.G.; Barac, A.; Bensenor, I.M.; Doan, L.P.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 954–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaugler, J.; James, B.; Johnson, T.; Marin, A.; Weuve, J.; Alzheimer’s Association. 2019 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 321–387. [Google Scholar]
- Mastroberardino, P.; Iannicola, C.; Nardacci, R.; Bernassola, F.; De Laurenzi, V.; Melino, G.; Moreno, S.; Pavone, F.; Oliverio, S.; Fesus, L.; et al. ‘Tissue’ transglutaminase ablation reduces neuronal death and prolongs survival in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.D.; Pang, P.; Zhou, X.T.; Hu, F.; Xiong, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.D.; Xie, D.; Hu, Y.Z.; et al. Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1548–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Lu, J.; Hao, X.Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Li, X.R.; Zhao, C.P.; Kuang, W.H.; Chen, D.F.; et al. FTH1 inhibits ferroptosis through ferritinophagy in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1796–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Su, Z.; Kon, N.; Chu, B.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Luo, J.; Stockwell, B.R.; Gu, W. ALOX5-mediated ferroptosis acts as a distinct cell death pathway upon oxidative stress in Huntington’s disease. Genes Dev. 2023, 37, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Jeandriens, J.; Parkes, H.G.; So, P.W. Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, Z.T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, W.S.; Fonseca, R.S.; Chen, L.J.; Na, R.; Ran, Q.T. Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, A.C.; Xiong, M.P. Challenges and opportunities of deferoxamine delivery for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Intracerebral hemorrhage. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, P.; Chen, X.; Guo, C.Y.; Zhang, N.; Ma, B.C. Baicalin and deferoxamine alleviate iron accumulation in different brain regions of Parkinson’s disease rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. Deferoxamine reduces CSF free iron levels following intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2006, 96, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, X.H.; Long, D.X. Nrf2 and ferroptosis: A new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, S.; Pesce, M.; Patruno, A.; Moradi, S.Z.; Iranpanah, A.; Farzaei, M.H.; Sobarzo-Sinchez, E. Attenuation of Nrf2/Keap1/ARE in Alzheimer’s disease by plant secondary metabolites: A mechanistic review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, W.J.; Zheng, X.R.; Liu, Q.L.; Du, Q.; Lai, Y.J.; Liu, S.Q. Eriodictyol ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice by inhibiting ferroptosis via vitamin D receptor-mediated Nrf2 activation. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southon, A.; Szostak, K.; Acevedo, K.M.; Dent, K.A.; Volitakis, I.; Belaidi, A.A.; Barnham, K.J.; Crouch, P.J.; Ayton, S.; Donnelly, P.S.; et al. Cu-II(atsm) inhibits ferroptosis: Implications for treatment of neurodegenerative disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Yang, F.; Li, Q. Post-translational modification of GPX4 is a promising target for treating ferroptosis-related diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 901565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Shao, L.; Li, X.Y. Irisin protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy by suppressing ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2/GPX4 signal axis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 187, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. IJCB 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.Q.; Jiang, Y.A.; Lai, X.X.; Liu, S.J.; Sun, L.T.; Zhou, Z.W. A shortage of FTH induces ROS and sensitizes RAS-proficient neuroblastoma N2A cells to ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.Y.; Park, E.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, S.W. Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin–induced ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24393–24403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.F.; Tuo, Q.Z.; Yin, Q.Z.; Lei, P. The pathological role of ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion-related injury. Zool. Res. 2020, 41, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.L. Identification of ACSL4 as a biomarker and contributor of ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; IngoId, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.; Hayano, M.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.; Tatonetti, N.; Slusher, B.S.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. eLife 2014, 3, e02523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoda, N.; von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; et al. RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.F.; Wang, F.; Wang, T.J.; Jiao, Y. The role of erastin in ferroptosis and its prospects in cancer therapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5429–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Kon, N.; Chen, D.L.; Li, T.Y.; Liu, T.; Jiang, L.; Song, S.J.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Wang, Z.X.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.L.; Chen, Y.X. Melatonin alleviates acute sleep deprivation-induced memory loss in mice by suppressing hippocampal ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 708645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, L.; Dong, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.L.; Li, B.; Dai, R.J. On the role of synthesized hydroxylated chalcones as dual functional amyloid-beta aggregation and ferroptosis inhibitors for potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.F.; Ou, Z.H.; Chen, R.C.; Niu, X.H.; Chen, D.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.L. Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2016, 63, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, P.; Aichinger, B.; Christ, C.; Stindl, J.; Rhayem, Y.; Beuschlein, F.; Warth, R.; Bandulik, S. Cellular pathophysiology of an adrenal adenoma-associated mutant of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase ATP2B3. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, C.; Donoso, P. Crosstalk between calcium and redox signaling: From molecular mechanisms to health implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1275–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, M.O.; Bagirici, F. Blocking of L-type calcium channels protects hippocampal and nigral neurons against iron neurotoxicity the role of L-type calcium channels in iron-induced neurotoxicity. Int. J. Neurosci. 2013, 123, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.G.; Connor, J.R.; Meadowcroft, M.D. The relationship between iron dyshomeostasis and amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease: Two sides of the same coin. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 81, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, M.T.; Hidalgo, C. Noxious iron-calcium connections in neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Wang, N.; Ruan, J.; Cheng, X.; Fan, L.; Zhang, P.; Lu, C.; Hu, Y.; Che, C.; Sun, D.; et al. Enhanced ROS-boosted phototherapy against pancreatic cancer via Nrf2-mediated stress-defense pathway suppression and ferroptosis induction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6404–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wang, C.F. 1,25(OH)(2)D-3 inhibited ferroptosis in zebrafish liver cells (ZFL) by regulating Keap1-Nrf2-GPx4 and NF-kappa B-hepcidin axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Xu, B.; Ren, X.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Yang, C.; Yuan, C.; Li, H.J.; Tong, X.M.; et al. Inhibition of CISD2 promotes ferroptosis through ferritinophagy-mediated ferritin turnover and regulation of p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Lu, J.; Mao, A.K.; Zhang, R.R.; Guan, S. Autophagy inhibition plays a protective role in ferroptosis induced by alcohol via the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9671–9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Jiang, D.L.; Wu, K.J. p62 promotes bladder cancer cell growth by activating KEAP1/NRF2-dependent antioxidative response. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Mimura, J.; Yamamoto, M. Discovery of the negative regulator of Nrf2, Keap1: A historical overview. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.S.; Liang, J.Q.; Zhao, M.N.; Zhang, H.; Jin, X.; Lu, T.; Zheng, Y.S.; Bian, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.C.; Huang, Y.W.; et al. miR-6077 promotes cisplatin/pemetrexed resistance in lung adenocarcinoma via CDKN1A/cell cycle arrest and KEAP1/ferroptosis pathways. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 28, 366–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Huang, M.X.; Yan, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.S.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, B.G. Exosomes derived from baicalin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells alleviate hepatocyte ferroptosis after acute liver injury via the Keap1-NRF2 pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8287227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareghomi, S.; Habibi-Rezaei, M.; Arese, M.; Saso, L.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. Nrf2 Modulation in Breast Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossetta, G.; Marzioni, D. Targeting the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway in cervical and endometrial cancers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 941, 175503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzioni, D.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Fantone, S.; Tossetta, G. NRF2 modulation in TRAMP mice: An in vivo model of prostate cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, O.; Boddu, R.; Traylor, A.; Lever, J.M.; Bolisetty, S.; George, J.F.; Agarwal, A. Heme oxygenase-1 mitigates ferroptosis in renal proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 314, F702–F714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.P.; Hua, S.Y.; Deng, J.W.; Du, Z.; Zhang, D.X.; Liu, Z.F.; Khan, N.U.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Z. Astaxanthin activated the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit ferroptosis, ameliorating acetaminophen-induced liver injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42887–42903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Liu, D.D.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.; Wong, Y.K.; Xia, F.; Zhang, J.Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Tian, Y.; Yang, C.B.; et al. Celastrol induces ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2300–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, S.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Fei, J.M.; Hao, X.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; et al. Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.X.; Wang, H.; Han, D.; Xie, E.J.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.Y.; Gu, S.S.; Gao, F.; Zhu, N.L.; Yin, X.J.; et al. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassannia, B.; Wiernicki, B.; Ingold, I.; Qu, F.; Van Herck, S.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Bayir, H.; Abhari, B.A.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Choi, S.M.; et al. Nano-targeted induction of dual ferroptotic mechanisms eradicates high-risk neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Hsieh, H.C.; Shih, F.S.; Wang, P.W.; Yang, L.X.; Shieh, D.B.; Wang, Y.C. An innovative NRF2 nano-modulator induces lung cancer ferroptosis and elicits an immunostimulatory tumor microenvironment. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7072–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ju, Y.; Dai, X.; Ni, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, H.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Gu, P. HO-1-mediated ferroptosis as a target for protection against retinal pigment epithelium degeneration. Redox Biol. 2021, 43, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yang, C.; Jiang, S.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ma, W. Repeated restraint stress enhances hepatic TFR2 expression and induces hepatic iron accumulation in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 196, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.H.; Chen, Z.J.; Dong, Y.Y.; Ni, Y.D.; Zhao, R.Q.; Ma, W.Q. Chronic corticosterone exposure suppresses copper transport through GR-mediated intestinal CTR1 pathway in mice. Biology 2023, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Zhong, A.; Zhang, D.; Gao, J.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ma, W. ATP2B3 Inhibition Alleviates Erastin–Induced Ferroptosis in HT-22 Cells through the P62–KEAP1–NRF2–HO-1 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119199
Guo S, Zhong A, Zhang D, Gao J, Ni Y, Zhao R, Ma W. ATP2B3 Inhibition Alleviates Erastin–Induced Ferroptosis in HT-22 Cells through the P62–KEAP1–NRF2–HO-1 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119199
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shihui, Aiying Zhong, Dongxu Zhang, Jiang Gao, Yingdong Ni, Ruqian Zhao, and Wenqiang Ma. 2023. "ATP2B3 Inhibition Alleviates Erastin–Induced Ferroptosis in HT-22 Cells through the P62–KEAP1–NRF2–HO-1 Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119199
APA StyleGuo, S., Zhong, A., Zhang, D., Gao, J., Ni, Y., Zhao, R., & Ma, W. (2023). ATP2B3 Inhibition Alleviates Erastin–Induced Ferroptosis in HT-22 Cells through the P62–KEAP1–NRF2–HO-1 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119199






