Oncogenic BRAF and p53 Interplay in Melanoma Cells and the Effects of the HDAC Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
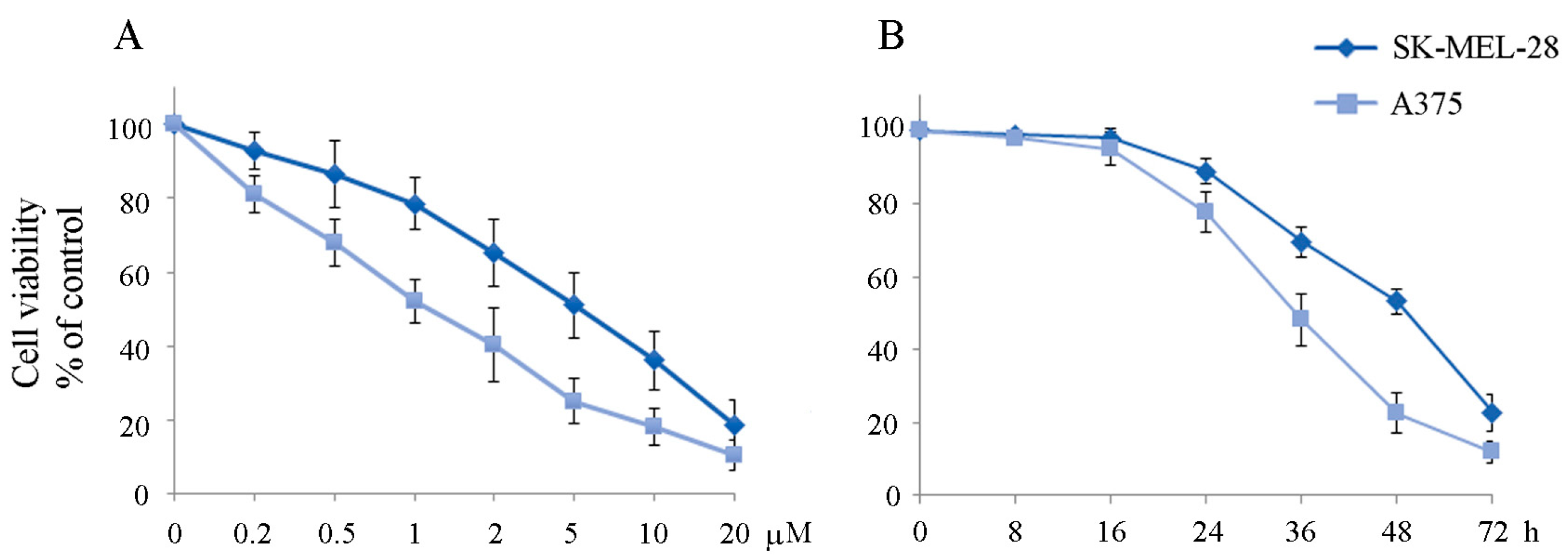
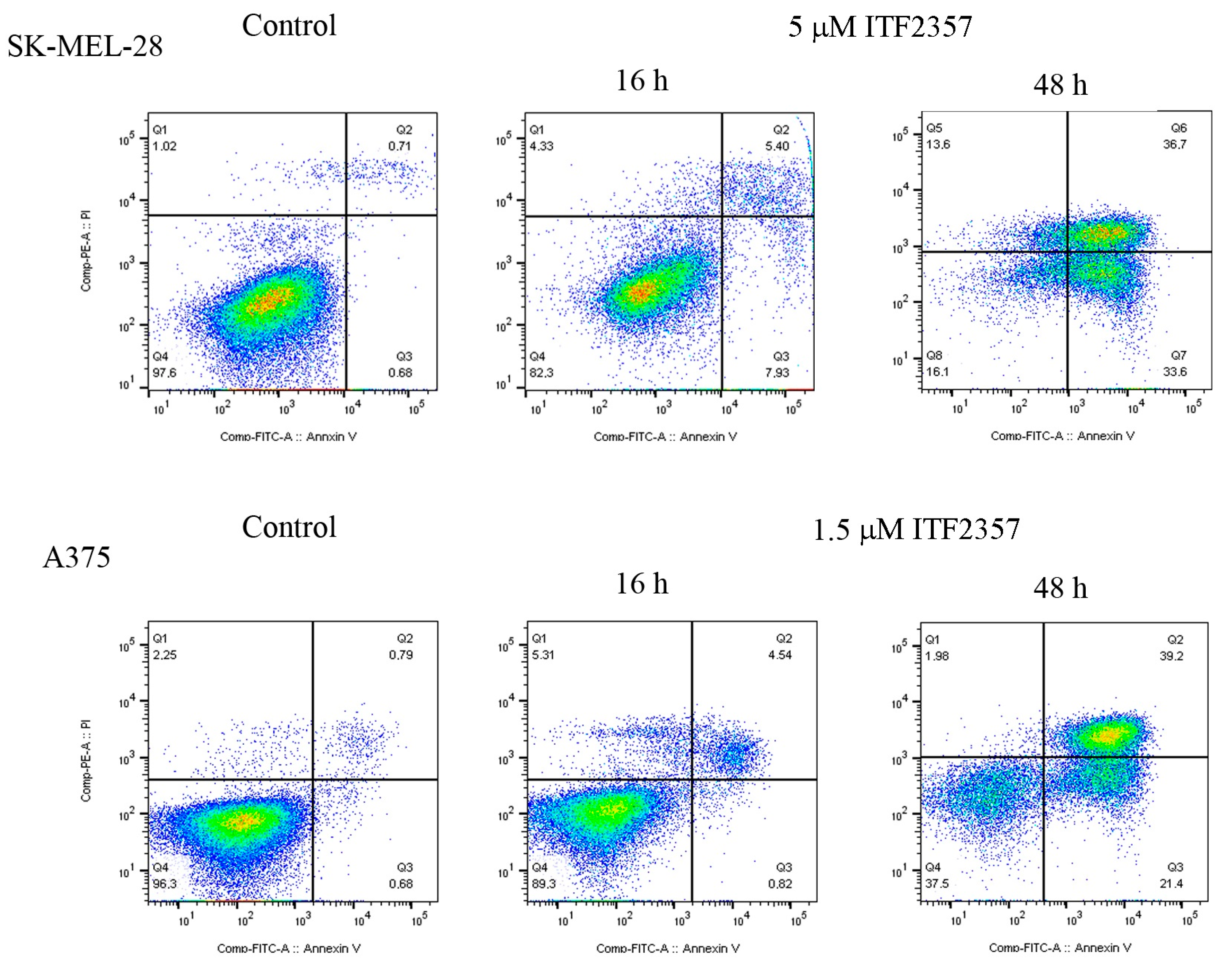
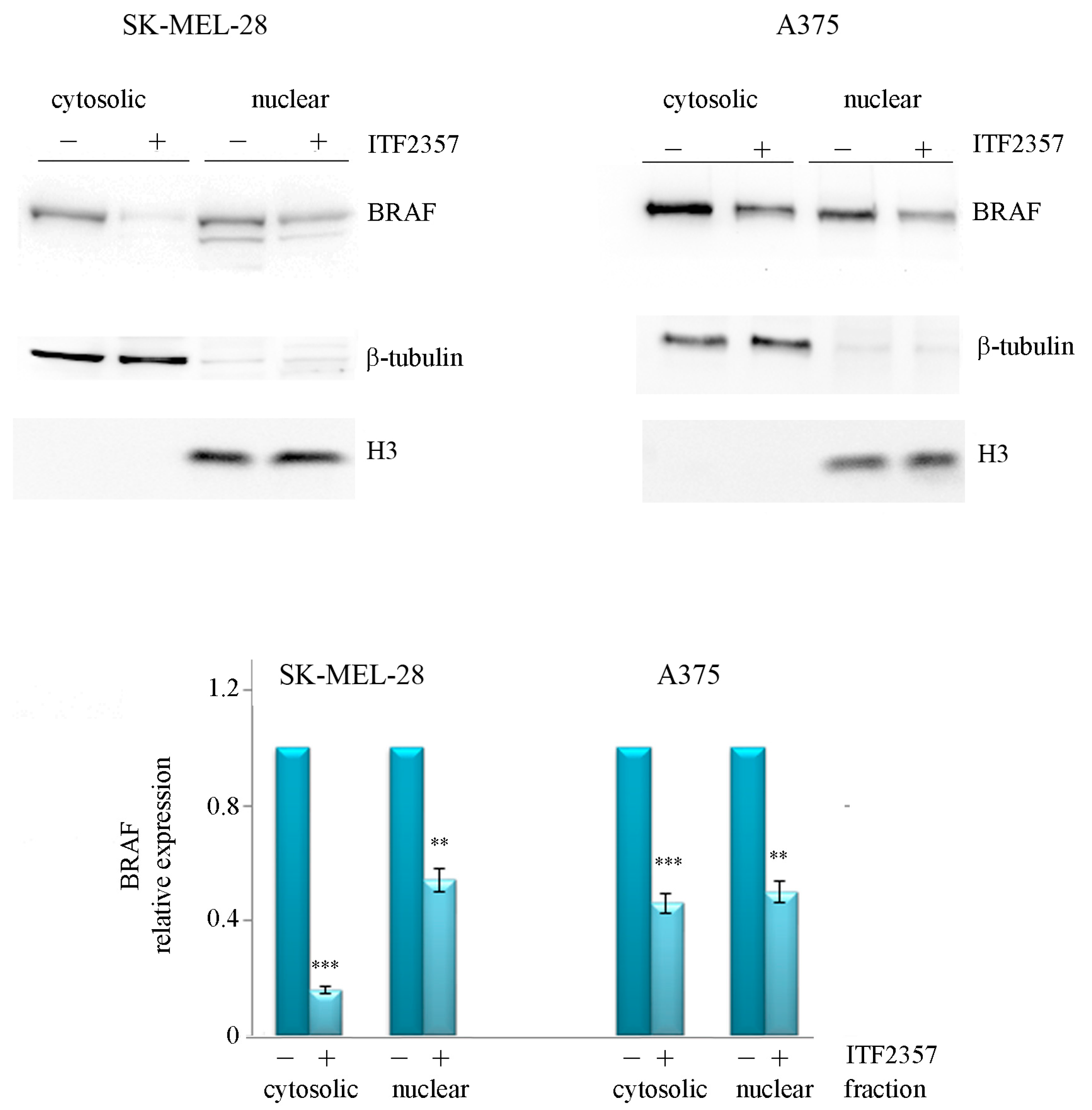
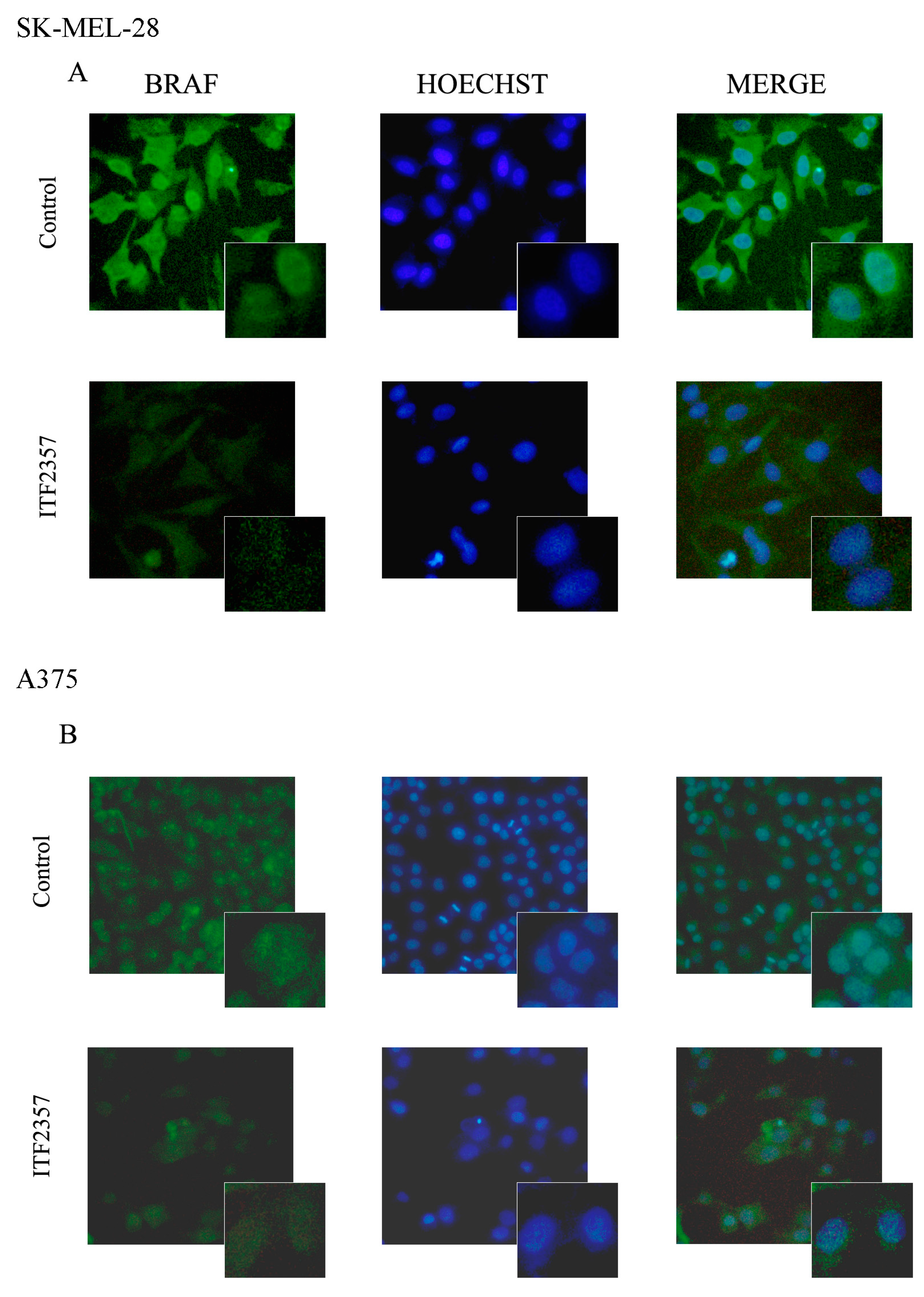
2.1. The Apoptotic Effect of IT2357 and BRAF Localisation in SK-MEL-28 and A375 Melanoma Cells
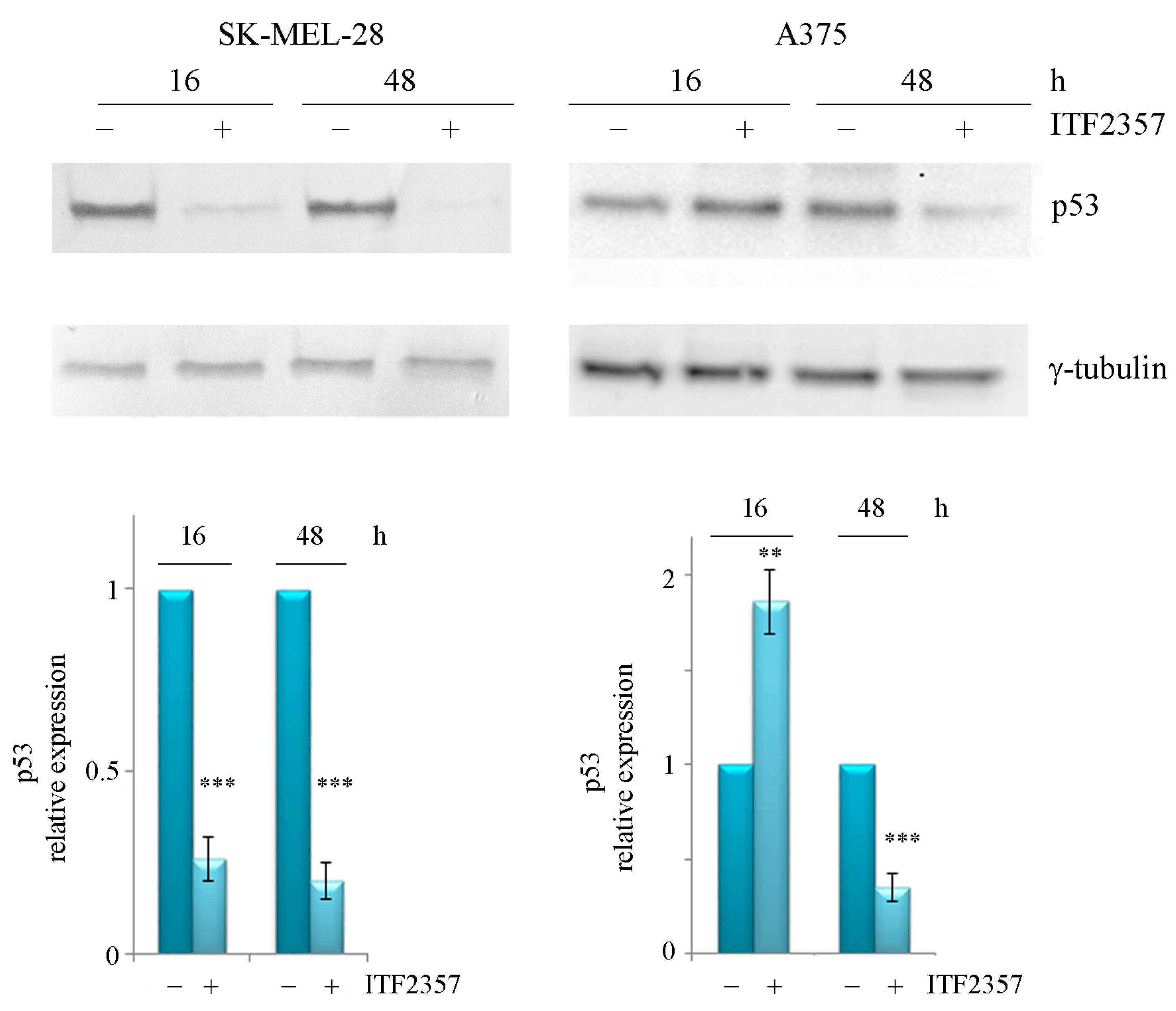
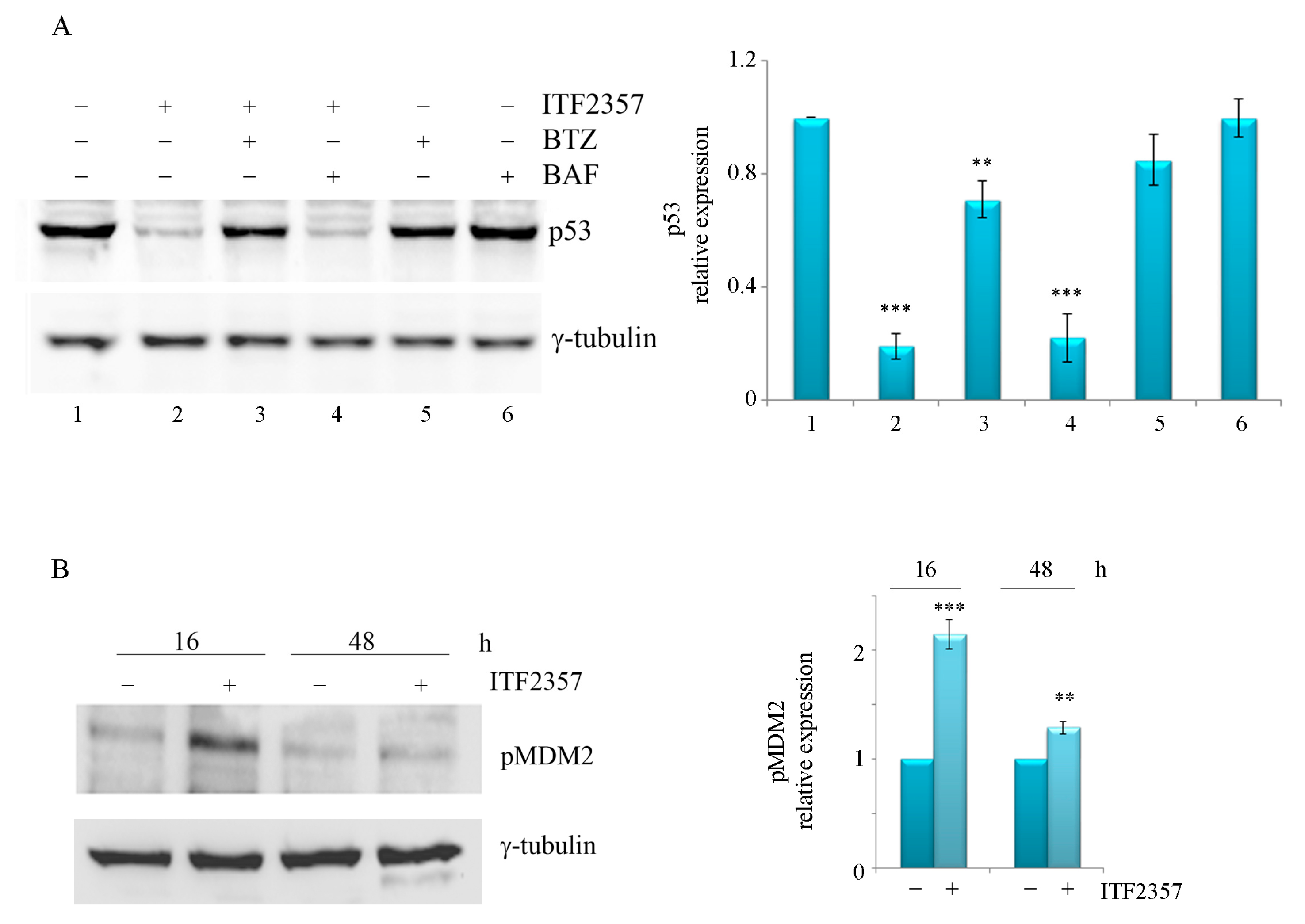
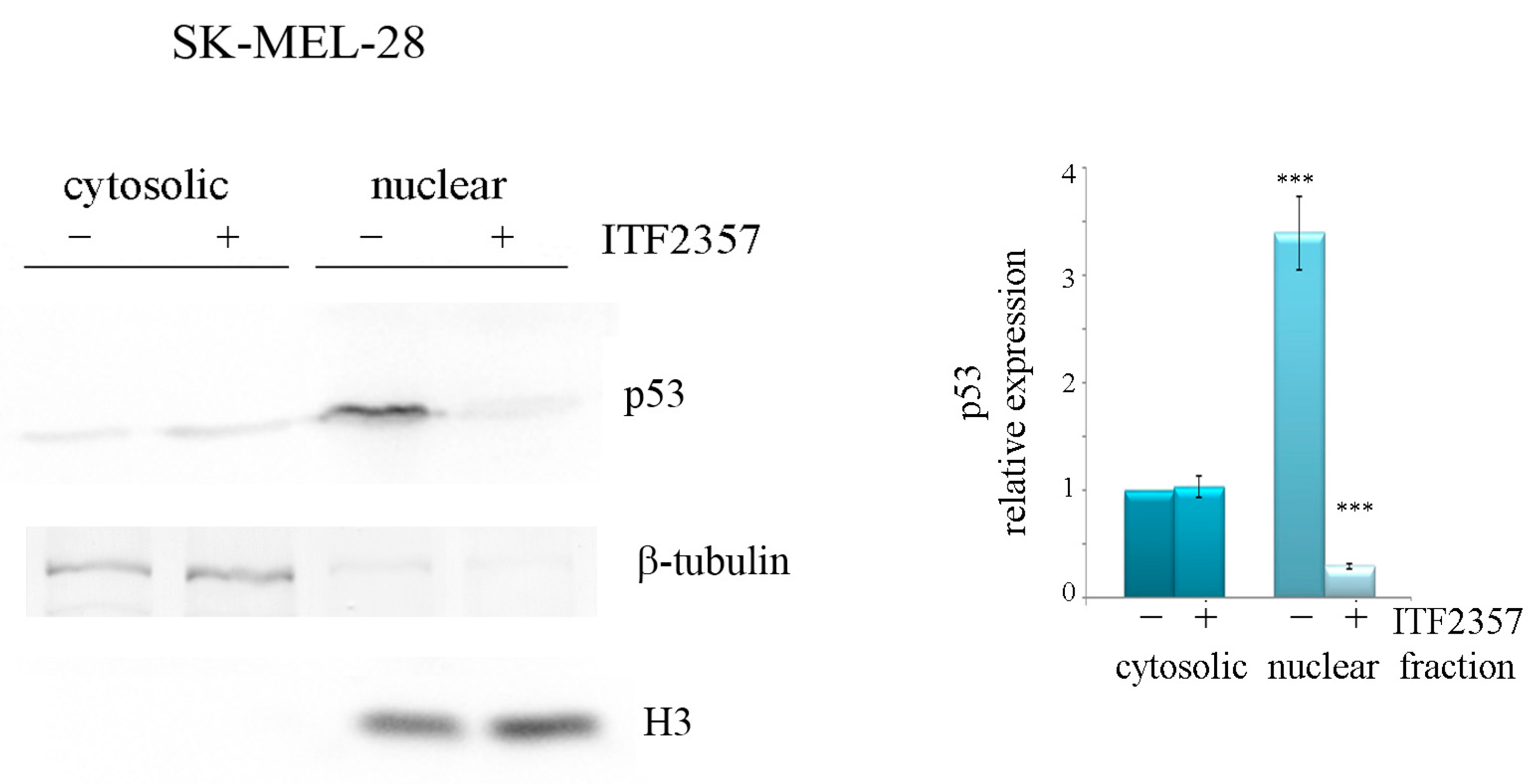
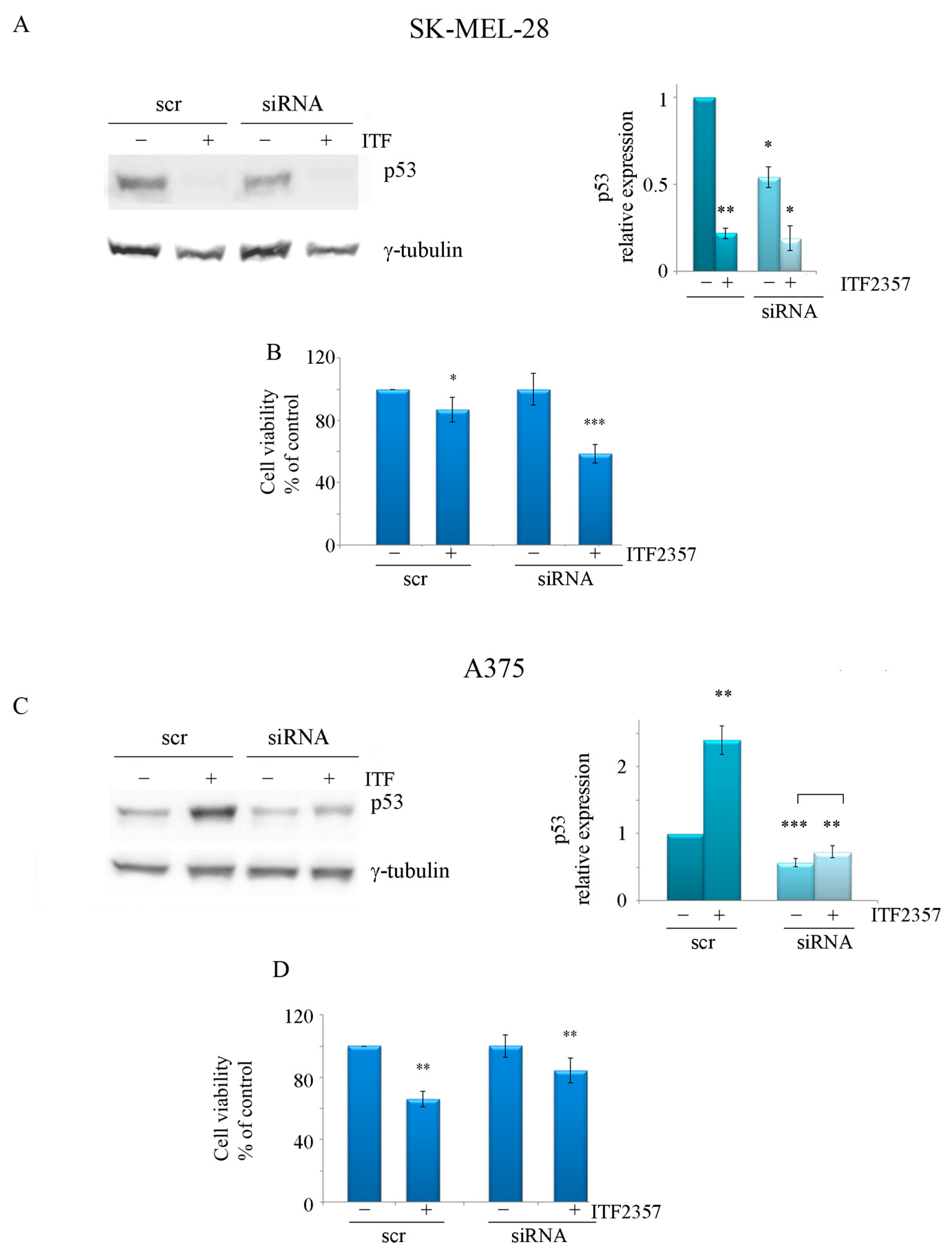
2.2. ITF2357 Differently Affects p53 in SK-MEL-28 and A375 Melanoma Cells
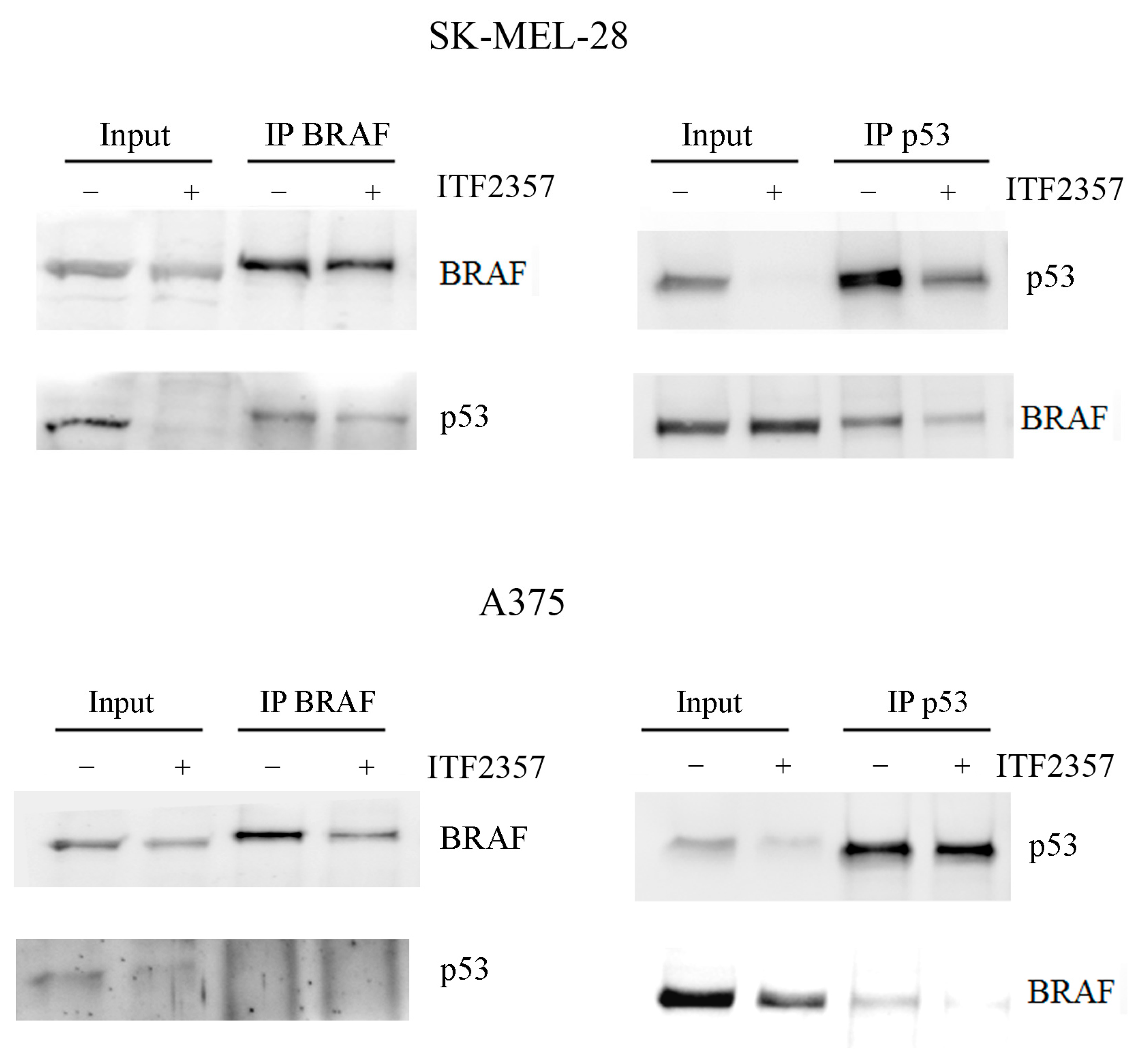
2.3. Oncogenic BRAF Interacts with Oncogenic p53 in Melanoma Cells
2.4. The ITF2357 Response in Melanoma Cells Is Dependent on p53 Status
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Cell Cultures
3.3. Annexin V-FITC/PI Staining
3.4. Extraction of Cytosolic and Nuclear Fraction
3.5. Immunofluorescence Analysis
3.6. Immunoprecipitation Analysis
3.7. P53 siRNA Transfection
3.8. Evaluation of Cell Viability
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Shang, Y.P.; Chen, H.-Y.; Li, J. Histone deacetylases function as novel potential therapeutic targets for cancer: Histone deacetylases. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dorfman, R.G.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhao, S.; Yao, Y.; et al. Histone deacetylase 3 overexpression in human cholangiocarcinoma and promotion of cell growth via apoptosis inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhou, B.Y.; Chu, Y.; Huo, J.R.; Tan, Y.Y.; Liu, D.L. Histone deacetylase 6 is overexpressed and promotes tumor growth of colon cancer through regulation of the MAPK/ERK signal pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alseksek, R.K.; Ramadan, W.S.; Saleh, E.; El-Awady, R. The Role of HDACs in the Response of Cancer Cells to Cellular Stress and the Potential for Therapeutic Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Q.; Hao, J.J.; Zhang, Z.; Hsu, I.; Liu, Y.I.; Tao, Z.; Lewi, K.; Metwalli, A.R.; Agarwal, P.K. Histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced cell death in bladder cancer is associated with chromatin modification and modifying protein expression: A proteomic approach. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2591–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liang, Q.; Shen, K.; Ma, L.; An, N.; Deng, W.; Fei, Z.; Liu, J. A novel class I histone deacetylase inhibitor, I-7ab, induces apoptosis and arrests cell cycle progression in human colorectal cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 71, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; De Martino, V.; Di Giuseppe, L.; Battafarano, G.; Di Gregorio, J.; Terreri, S.; Marampon, F.; Minisola, S.; Del Fattore, A. Anti-proliferative, pro-apototic and anti-migratory properties of HDAC inhibitor PXD-101 on osteosarcoma cell lines. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 734, 109489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marampon, F.; Leoni, F.; Mancini, A.; Pietrantoni, I.; Codenotti, S.; Letizia, F.; Megiorni, F.; Porro, G.; Galbiati, E.; Pozzi, P.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 (givinostat) reverts transformed phenotype and counteracts stemness in in vitro and in vivo models of human glioblastoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiarol, L.; Bigogno, C.; Sesana, S.; Kravicz, M.; Viale, F.; Pozzi, E.; Monza, L.; Carozzi, V.A.; Meregalli, C.; Valtorta, S.; et al. Givinostat-Liposomes: Anti-Tumor Effect on 2D and 3D Glioblastoma Models and Pharmacokinetics. Cancers 2022, 14, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, A.M.; Sarno, J.; Trentin, L.; Vieri, M.; Fazio, G.; Bardini, M.; Bugarin, C.; Fossati, G.; Davis, K.L.; Gaipa, G.; et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat (ITF2357) exhibits potent anti-tumor activity against CRLF2-rearranged BCP-ALL. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Xu, F.; Bai, W.; Zhao, T.; Hong, J.; Zuo, W. HDAC inhibitor ITF2357 reduces resistance of mutant-KRAS non-small cell lung cancer to pemetrexed through a HDAC2/miR-130a-3p-dependent mechanism. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganai, S.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat: The small-molecule with promising activity against therapeutically challenging haematological malignancies. J. Chemother. 2016, 28, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaldi, A.; Iurlo, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Martino, B.; Guarini, A.; Ruggeri, M.; von Bubnoff, N.; De Muro, M.; McMullin, M.F.; Luciani, S.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of givinostat in polycythemia vera: 4-year mean follow up of three phase 1/2 studies and a compassionate use program. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celesia, A.; Notaro, A.; Franzò, M.; Lauricella, M.; D’Anneo, A.; Carlisi, D.; Giuliano, M.; Emanuele, S. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat) Targets Oncogenic BRAF in Melanoma Cells and Promotes a Switch from Pro-Survival Autophagy to Apoptosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, I.; Tanda, E.T.; Spagnolo, F.; Andreotti, V.; Bruno, W.; Ghiorzo, P. The Current State of Molecular Testing in the BRAF-Mutated Melanoma Landscape. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Morton, D.L.; Hoon, D.S.B. Incidence of BRAF Oncogene Mutation and Clinical Relevance for Primary Cutaneous Melanomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerhorst, J.A.; Greene, V.R.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Warneke, C.L.; Johnson, M.M.; Cooke, C.P.; Wang, L.E.; Prieto, V.G.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Wei, Q.; et al. Clinical Correlates of NRAS and BRAF Mutations in Primary Human Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugdahl, E.; Kalvenes, M.B.; Puntervoll, H.E.; Ladstein, R.G.; Akslen, L.A. BRAF-V600E expression in primary nodular melanoma is associated with aggressive tumour features and reduced survival. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zhou, E.; Cheng, C. AB-Raf V600E gene signature for melanoma predicts prognosis and reveals sensitivity to targeted therapies. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zablocka, T.; Kreismane, M.; Pjanova, D.; Isajevs, S. Effects of BRAF V600E and NRAS mutational status on the progression-free survival and clinicopathological characteristics of patients with melanoma. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzotto, D.; Englmaier, L.; Villunger, A. At a Crossroads to Cancer: How p53-Induced Cell Fate Decisions Secure Genome Integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. putting p53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimovich, B.; Merle, N.; Neumann, M.; Elmshäuser, S.; Nist, A.; Mernberger, M.; Kazdal, D.; Stenzinger, A.; Timofeev, O.; Stiewe, T. p53 partial loss-of-function mutations sensitize to chemotherapy. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, M.; Riscal, R.; Arena, G.; Linares, L.K.; Le Cam, L. Metabolic functions of the tumor suppressor p53: Implications in normal physiology, metabolic disorders, and cancer. Mol. Metabolism. 2020, 33, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Jiang, C.; Tse, P.; Achacoso, N.; Alexeeff, S.; Solorzano, A.V.; Chung, E.; Hu, W.; Truong, T.G.; Arora, A.; et al. TP53 Gain-of-Function and Non–Gain-of-Function Mutations Are Differentially Associated With Sidedness-Dependent Prognosis in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, T.; Hu, W.; Feng, Z. Gain-of-function mutant p53 in cancer progression and therapy. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.; Bei, J.X.; Li, B.; Liang, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, X. Mutant p53 in Cancer Progression and Targeted Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 595187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, J.B.; Raimundo, L.; Calheiros, J.; Carvalho, C.; Barcherini, V.; Lima, N.R.; Gomes, C.; Almeida, M.I.; Alves, M.G.; Costa, J.L.; et al. Targeting p53 for Melanoma Treatment: Counteracting Tumour Proliferation, Dissemination and Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery-Kiejda, K.A.; Bowden, N.A.; Croft, A.J.; Scurr, L.L.; Kairupan, C.F.; Ashton, K.A.; Talseth-Palmer, B.A.; Rizos, H.; Zhang, X.D.; Scott, R.J.; et al. P53 in human melanoma fails to regulate target genes associated with apoptosis and the cell cycle and may contribute to proliferation. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, P.; Kublo, L.; Stewart-Ornstein, J. p53 Promotes Cytokine Expression in Melanoma to Regulate Drug Resistance and Migration. Cells 2022, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadijan, A.; Precazzini, F.; Hanžić, N.; Radić, M.; Gavioli, N.; Vlašić, I.; Ozretić, P.; Pinto, L.; Škreblin, L.; Barban, G.; et al. Altered Expression of Shorter p53 Family Isoforms Can Impact Melanoma Aggressiveness. Cancers 2021, 13, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschos, S.J.; Sandhu, S.; Lewis, K.D.; Sullivan, R.J.; Puzanov, I.; Johnson, D.B.; Henary, H.A.; Wong, H.; Upreti, V.V.; Long, G.V.; et al. Targeting wild-type TP53 using AMG 232 in combination with MAPK inhibition in Metastatic Melanoma; a phase 1 study. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrakovcic, M.; Kleinheinz, J.; Fröhlich, L.F. p53 at the Crossroads between Different Types of HDAC Inhibitor-Mediated Cancer Cell Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, S.J.; Gunatilake, D.; Beaumont, K.A.; Sharp, D.M.; Tiffen, J.C.; Heinemann, A.; Weninger, W.; Haass, N.K.; Wilmott, J.S.; Madore, J.; et al. HDAC inhibitors restore BRAF-inhibitor sensitivity by altering PI3K and survival signalling in a subset of melanoma: HDACi restore BRAFi sensitivity in melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1926–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, U.; Wang, Z.; Pei, S.; Ou, Y.; Hu, P.; Liu, W.; Song, J. ACY-1215 accelerates vemurafenib induced cell death of BRAF-mutant melanoma cells via induction of ER stress and inhibition of ERK activation. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikediobi, O.N.; Davies, H.; Bignell, G.; Edkins, S.; Stevens, C.; O’Meara, S.; Santarius, T.; Avis, T.; Barthorpe, S.; Brackenbury, L.; et al. Mutation analysis of 24 known cancer genes in the NCI-60 cell line set. Mol. Cancer Therapeut. 2006, 5, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, Z.S.; Ralph, A.C.L.; Calcagno, D.Q.; dos Santos Barbosa, G.; do Nascimento Pedrosa, T.; Antony, L.P.; Smith, M.D.A.C.; de Lucas Chazin, E.; Vasconcelos, T.R.A.; Montenegro, R.C.; et al. Anticancer potential of benzothiazolic derivative (E)-2-((2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)-4-nitrophenol against melanoma cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 50, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Moore, R.F.; Tsumagari, K.; Lee, M.M.; Sholl, A.B.; Friedlander, P.; Al-Qurayshi, Z.; Hassan, M.; Wang, A.R.; Boulares, H.A.; et al. Prognostic Role of BRAFV600E Cellular Localization in Melanoma. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2018, 226, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerfaoui, M.; Dokunmu, T.M.; Toraih, E.A.; Rezk, B.M.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Kandil, E. New Insights into the Link between Melanoma and Thyroid Cancer: Role of Nucleocytoplasmic Trafficking. Cells 2021, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappetta, G.; Basile, A.; Arra, C.; Califano, D.; Pasquinelli, R.; Barbieri, A.; De Simone, V.; Rea, D.; Giudice, A.; Pezzullo, L.; et al. BAG3 Down-Modulation Reduces Anaplastic Thyroid Tumor Growth by Enhancing Proteasome-Mediated Degradation of BRAF Protein. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E115–E120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Localized Proteasomal Degradation: From the Nucleus to Cell Periphery. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Singh, J.; Verma, S.R. Targeting Y220C mutated p53 by Foeniculum vulgare-derived phytochemicals as cancer therapeutics. J. Mol. Model. 2023, 29, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Meng, F.; Wu, S.; Zhou, P.; Ge, R.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, D.; Xie, S. Selective degradation of the p53-R175H oncogenic hotspot mutant by an RNA aptamer-based PROTAC. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Iwakuma, T. Drugs Targeting p53 Mutations with FDA Approval and in Clinical Trials. Cancers 2023, 15, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zeng, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Huang, W. F-Box Protein 43, Stabilized by N6-Methyladenosine Methylation, Enhances Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Growth and Invasion via Promoting p53 Degradation in a Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme E2 C-Dependent Manner. Cancers 2023, 15, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.M.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, W.Y.; Wu, H.A.; Chen, W.L.; Chang, Y.F.; Chou, C.W.; Tzeng, C.C.; Chen, Y.L.; et al. Loss of IKKβ activity increases p53 stability and p21 expression leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckbach, D.; Bauer, J.; Pflugfelder, A.; Meier, F.; Busch, C.; Eigentler, T.K.; Capper, D.; Von Deimling, A.; Mittelbronn, M.; Perner, S.; et al. Survival According to BRAF-V600 Tumor Mutations—An Analysis of 437 Patients with Primary Melanoma. Haass NK, editor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.R.; Fane, M.E.; Alicea, G.M.; Basu, S.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Marino, G.E.; Douglass, S.M.; Kaur, A.; Ecker, B.L.; Gnanapradeepan, K.; et al. Paradoxical Role for Wild-Type p53 in Driving Therapy Resistance in Melanoma. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 633–644.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, E.E.; Widlund, H.R.; Kutok, J.L.; Kopani, K.R.; Amatruda, J.F.; Murphey, R.D.; Berghmans, S.; Mayhall, E.A.; Traver, D.; Fletcher, C.D.; et al. BRAF Mutations Are Sufficient to Promote Nevi Formation and Cooperate with p53 in the Genesis of Melanoma. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuda, Y.; Okada, Y.; Hattori, K.; Heissig, B. YO2 Induces Melanoma Cell Apoptosis through p53-Mediated LRP1 Downregulation. Cancers 2022, 15, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitolli, C.; Wang, Y.; Mancini, M.; Shi, Y.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. Do Mutations Turn p53 into an Oncogene? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, A.; Rotter, V. Oncogenic Mutations of the p53 Tumor Suppressor: The Demons of the Guardian of the Genome. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6788–6793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vlašić, I.; Horvat, A.; Tadijan, A.; Slade, N. p53 Family in Resistance to Targeted Therapy of Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Q.; Ji, Y.; Yang, J.; Shen, J.; Peng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Kong, X.; Ma, W.; et al. Targeting KRAS-mutant stomach/colorectal tumors by disrupting the ERK2-p53 complex. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Xu, H.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Trichostatin a Promotes the Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma Cells through p53 Signaling Pathway Activation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dai, J.; Zong, G.; Xiao, J.; Guo, X.; Dai, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wan, R. Restoration of p53 acetylation by HDAC inhibition permits the necrosis/apoptosis switch of pancreatic ainar cell during experimental pancreatitis in mice. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 21988–21998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauricella, M.; D’Anneo, A.; Giuliano, M.; Calvaruso, G.; Emanuele, S.; Vento, R.; Tesoriere, G. Induction of apoptosis in human osteosarcoma Saos-2 cells by the proteasome inhibitor MG132 and the protective effect of pRb. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Lai, E.M. Protein–Protein Interactions: Co-Immunoprecipitation. In Bacterial Protein Secretion Systems [Internet]; Methods in Molecular Biology; Journet, L., Cascales, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1615, pp. 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuele, S.; Notaro, A.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Maggio, A.; Lauricella, M.; D’Anneo, A.; Cernigliaro, C.; Calvaruso, G.; Giuliano, M. Sicilian Litchi Fruit Extracts Induce Autophagy versus Apoptosis Switch in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, M.; Pellerito, C.; Celesia, A.; Fiore, T.; Emanuele, S. Tributyltin(IV) Butyrate: A Novel Epigenetic Modifier with ER Stress- and Apoptosis-Inducing Properties in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celesia, A.; Morana, O.; Fiore, T.; Pellerito, C.; D’Anneo, A.; Lauricella, M.; Carlisi, D.; De Blasio, A.; Calvaruso, G.; Giuliano, M.; et al. ROS-Dependent ER Stress and Autophagy Mediate the Anti-Tumor Effects of Tributyltin (IV) Ferulate in Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celesia, A.; Fiore, T.; Di Liberto, D.; Giuliano, M.; Pellerito, C.; Emanuele, S. Bortezomib potentiates the antitumor effect of tributyltin(IV) ferulate in colon cancer cells exacerbating ER stress and promoting apoptosis. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 537, 120929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Celesia, A.; Franzò, M.; Di Liberto, D.; Lauricella, M.; Carlisi, D.; D’Anneo, A.; Notaro, A.; Allegra, M.; Giuliano, M.; Emanuele, S. Oncogenic BRAF and p53 Interplay in Melanoma Cells and the Effects of the HDAC Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119148
Celesia A, Franzò M, Di Liberto D, Lauricella M, Carlisi D, D’Anneo A, Notaro A, Allegra M, Giuliano M, Emanuele S. Oncogenic BRAF and p53 Interplay in Melanoma Cells and the Effects of the HDAC Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119148
Chicago/Turabian StyleCelesia, Adriana, Marzia Franzò, Diana Di Liberto, Marianna Lauricella, Daniela Carlisi, Antonella D’Anneo, Antonietta Notaro, Mario Allegra, Michela Giuliano, and Sonia Emanuele. 2023. "Oncogenic BRAF and p53 Interplay in Melanoma Cells and the Effects of the HDAC Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119148
APA StyleCelesia, A., Franzò, M., Di Liberto, D., Lauricella, M., Carlisi, D., D’Anneo, A., Notaro, A., Allegra, M., Giuliano, M., & Emanuele, S. (2023). Oncogenic BRAF and p53 Interplay in Melanoma Cells and the Effects of the HDAC Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119148











