In Silico Identification and In Vitro Evaluation of New ABCG2 Transporter Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
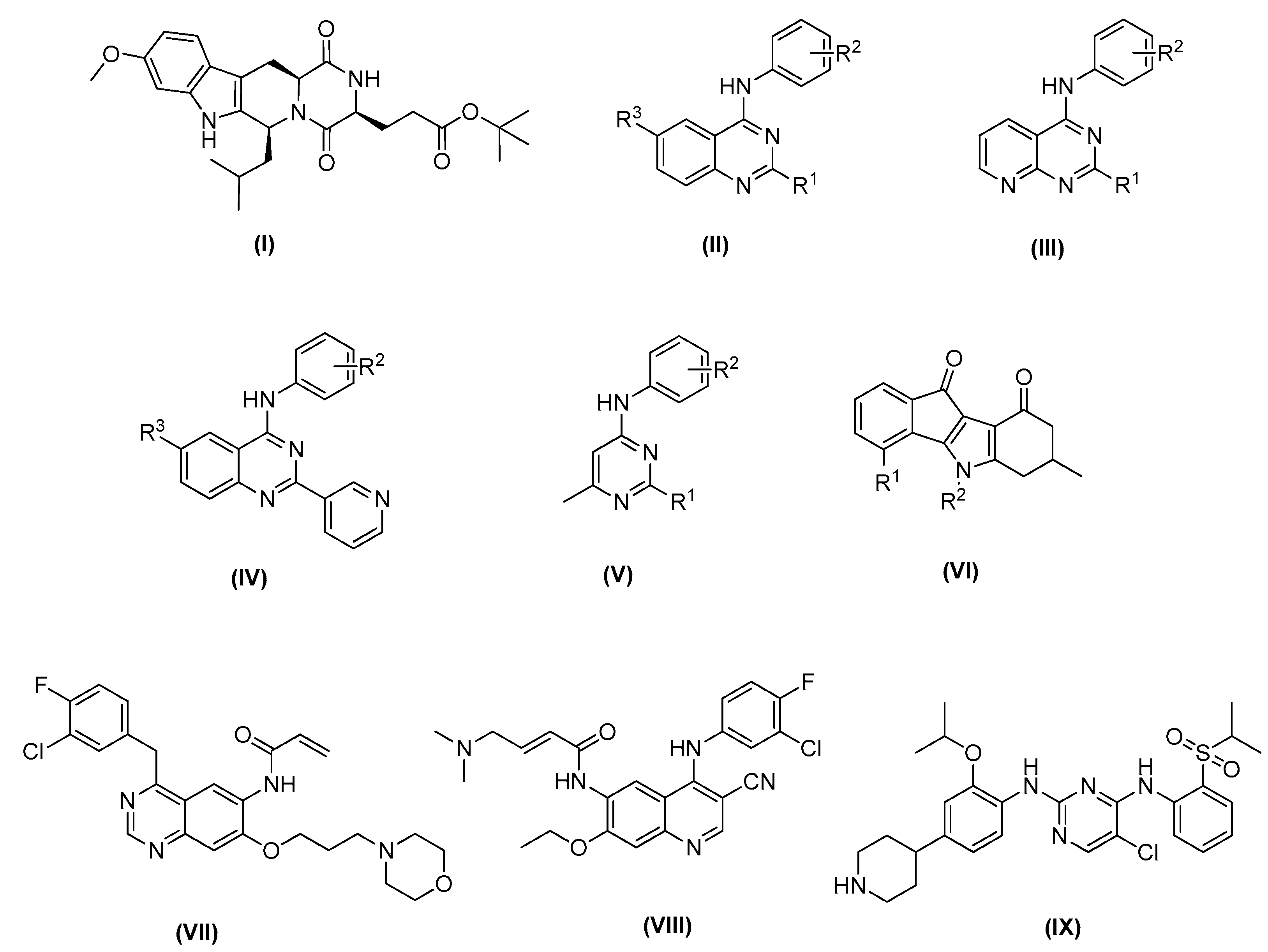
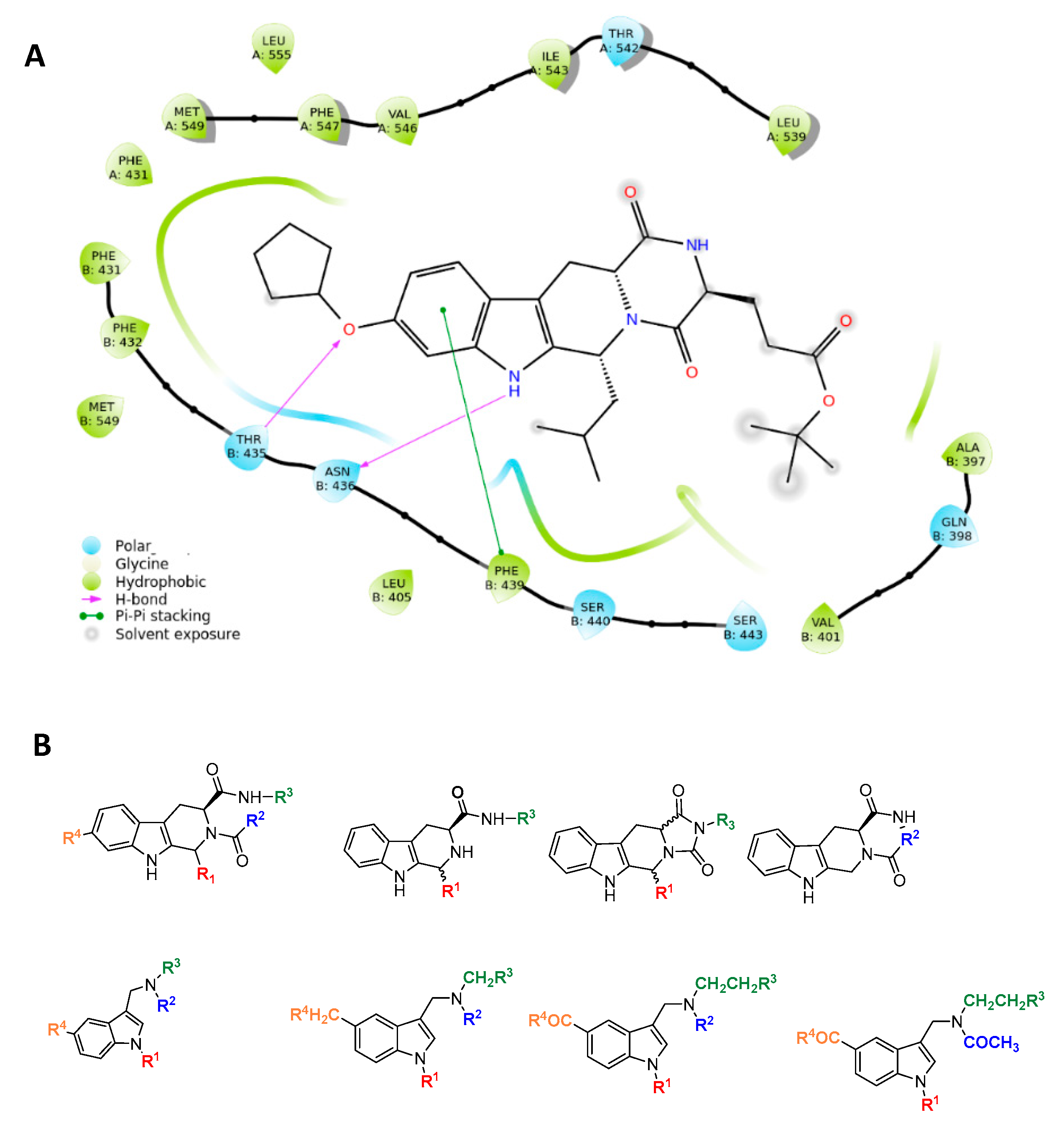
2.1. In-Silico Analysis
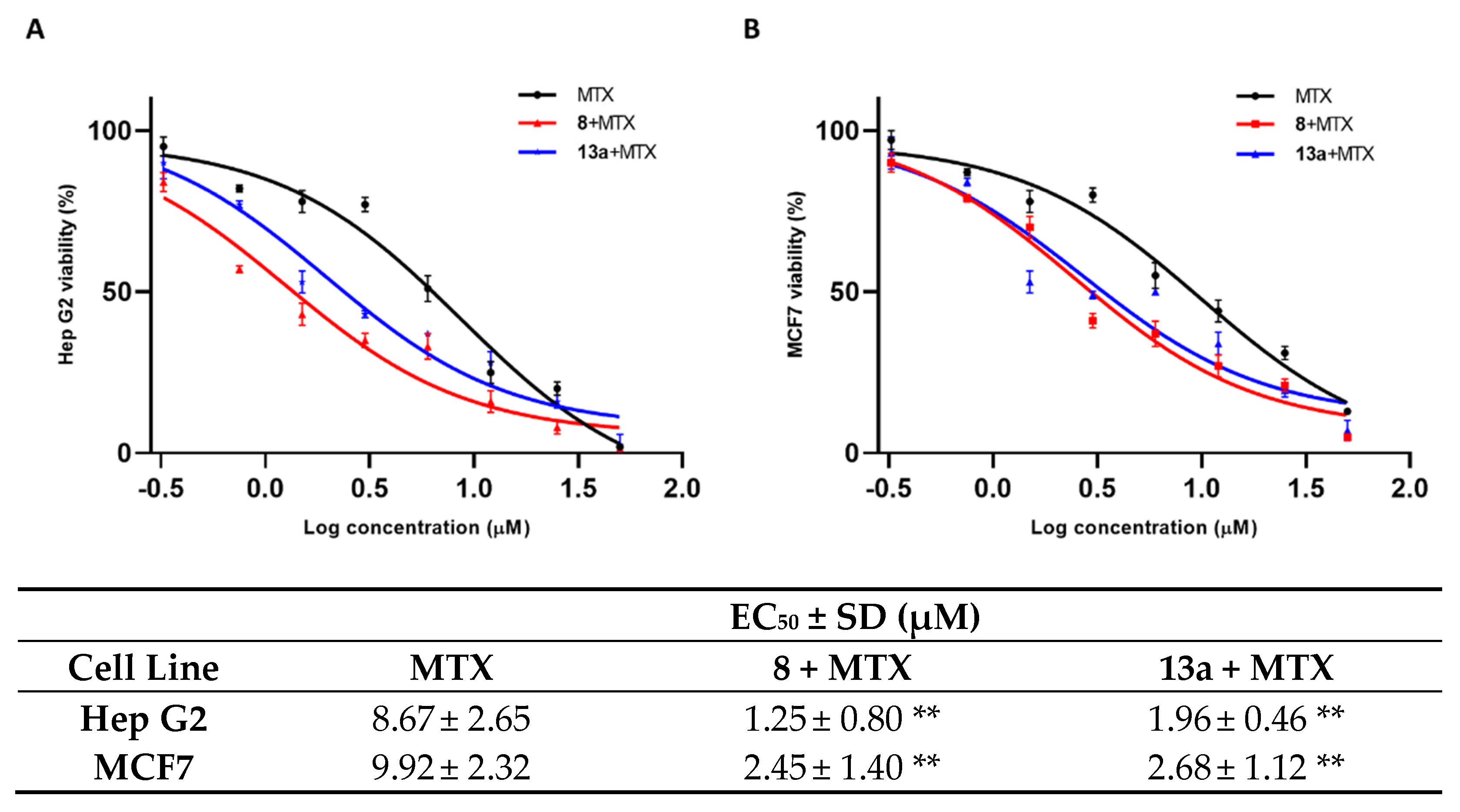
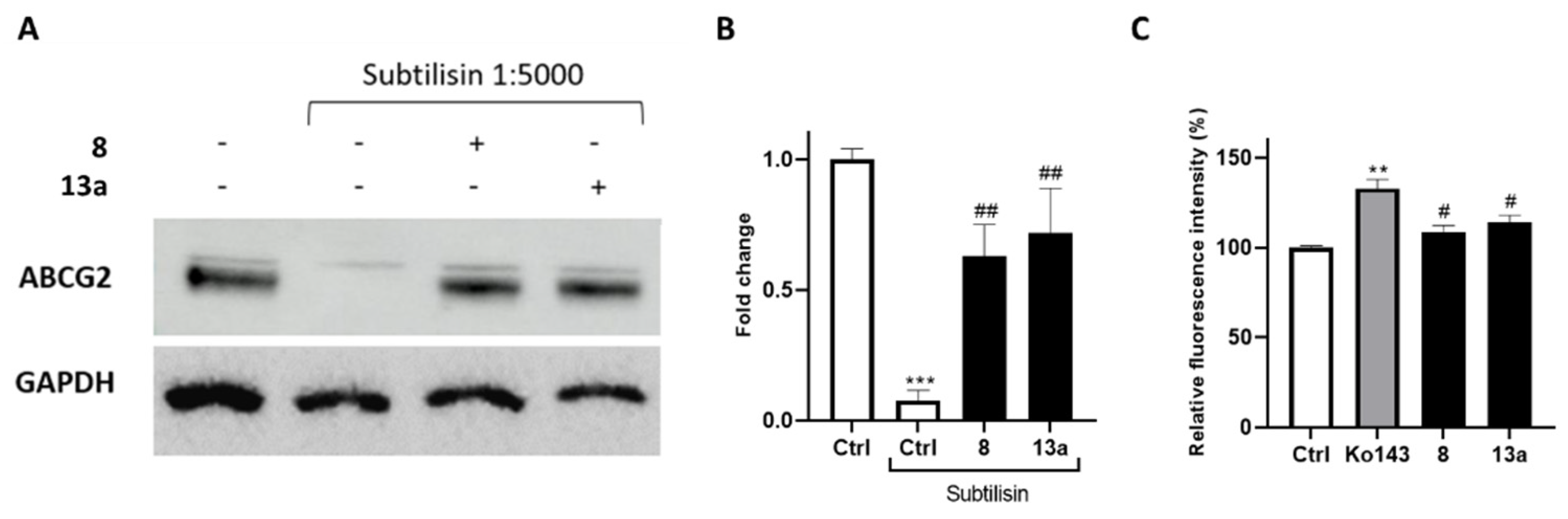
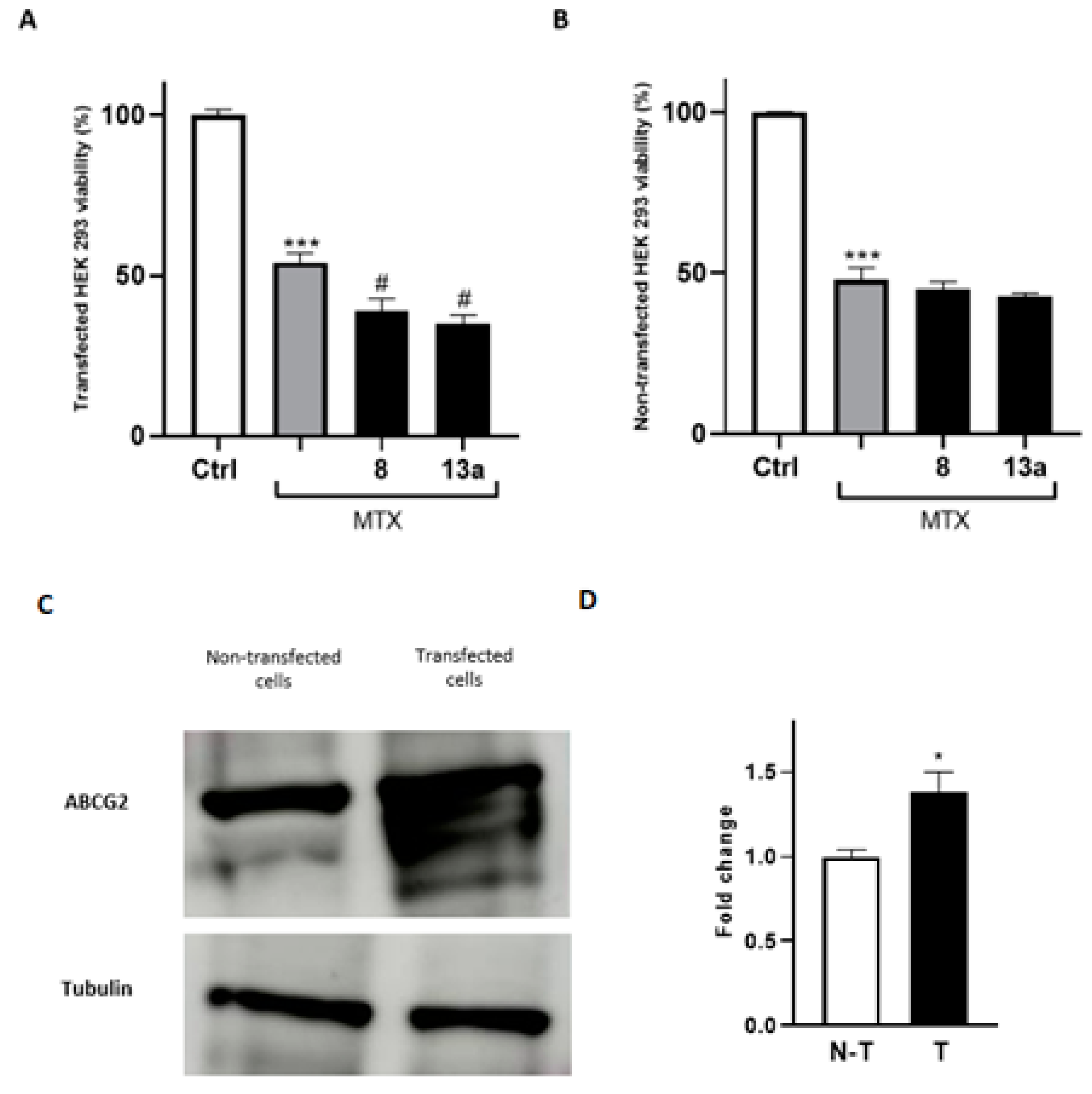
2.2. Biological Investigation
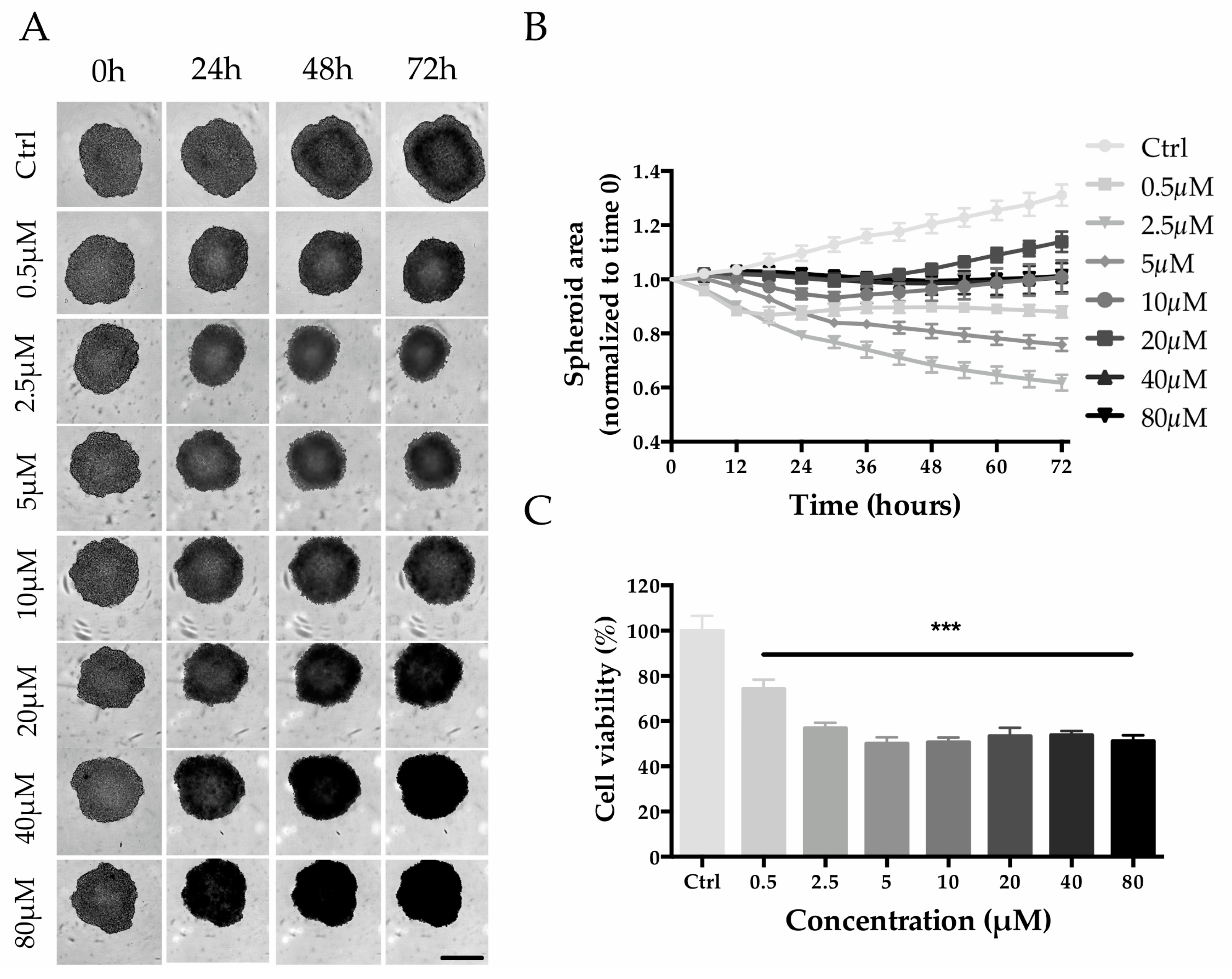
2.3. HepG2 Spheroid Production and Mitoxantrone Treatment
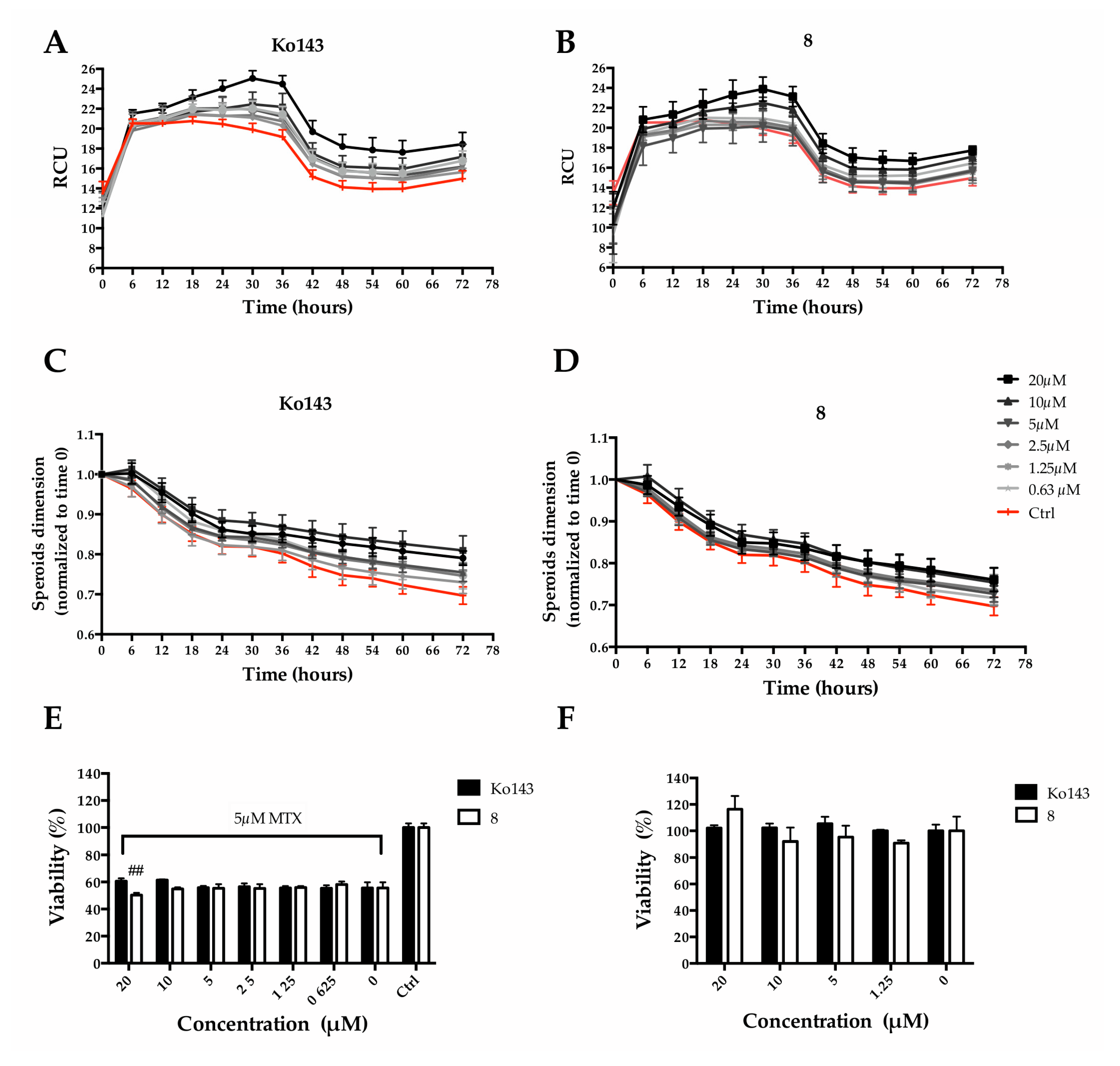
2.4. Effect of the Inhibitor (8) on MTX Uptake in HepG2 Spheroids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Computational Details
4.2. Chemistry
4.3. 2D Cell Cultures and Transfection
4.4. 2D Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Hoechst 33,342 Accumulation Assay
4.6. Mitoxantrone and Inhibitor Treatment on 2D Cell Cultures
4.7. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS) and Target Identification
4.8. Selectivity Assay
4.9. Spheroids Generation
4.10. Mitoxantrone and Inhibitor Treatment
4.11. 3D Cell Viability Assay
4.12. HEK293 Transfection and Mass Cell Analysis for Gene Expression Confirmation
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug Resistance in Cancer: An Overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, T.H.; Ruoff, H.J.; Volm, M. Intrinsic and acquired drug resistance in malignant tumors. The main reason for therapeutic failure. Arzneimittelforschung 2008, 58, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The Different Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance: A Brief Review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meads, M.B.; Gatenby, R.A.; Dalton, W.S. Environment-mediated drug resistance: a major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahreddine, H.; Borden, K.L.B. Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhlaoui, I.; Vahdati, S.; Maalej, E.; Chabchoub, F.; Wiese, M.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Ismaili, l. Synthesis and biological assessment of new pyrimidopyrimidines as inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 116, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yauch, R.L.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.P.; Alicke, B.; Januario, T.; Ahn, C.P.; Holcomb, T.; Pujara, K.; Stinson, J.; Callahan, C.A.; Tang, T.; et al. Smoothened Mutation Confers Resistance to a Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor in Medulloblastoma. Science 2009, 326, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaraju, V.L.; Damaraju, S.; Young, J.D.; Baldwin, S.A.; Mackey, J.; Sawyer, M.B.; Cass, C.E. Nucleoside anticancer drugs: the role of nucleoside transporters in resistance to cancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7524–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP–dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano-Pinto, P.; Jansen, J.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Masereeuw, R. The importance of breast cancer resistance protein to the kidneys excretory function and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2017, 30, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Gupta, P.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist. Updat. 2015, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, D.; Sell, W.; Voigt, A.; Hermann, J.; Zintl, F.; Sauerbrey, A. BCRP gene expression is associated with a poor response to remission induction therapy in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.K.W.; Poon, D.C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, F.; Lin, G.; Fu, L. Pelitinib (EKB-569) targets the up-regulation of ABCB1 and ABCG2 induced by hyperthermia to eradicate lung cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4089–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, J.-H.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Han, H.-S. Breast cancer resistance protein expression is associated with early recurrence and decreased survival in resectable pancreatic cancer patients. Pathol. Int. 2012, 62, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Eno, M.L.; Ahn, E.H.; Shahzad, M.M.K.; Im, D.D.; Rosenshein, N.B.; Sood, A.K. Multidrug Resistance Gene (MDR-1) and Risk of Brain Metastasis in Epithelial Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Peritoneal Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 34, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlichman, C.; Boerner, S.A.; Hallgren, C.G.; Spieker, R.; Wang, X.Y.; James, C.D.; Scheffer, G.L.; Maliepaard, M.; Ross, D.D.; Bible, K.C.; et al. The HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor CI1033 enhances cytotoxicity of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin and topotecan by inhibiting breast cancer resistance protein-mediated drug efflux. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Allikmets, R.; Schriml, L.M.; Hutchinson, A.; Romano-Spica, V.; Dean, M. A human placenta-specific ATP-binding cassette gene (ABCP) on chromosome 4q22 that is involved in multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5337–5339. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, K.; Mickley, L.; Litman, T.; Zhan, Z.; Robey, R.; Cristensen, B.; Brangi, M.; Greenberger, L.; Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; et al. Molecular cloning of cDNAs which are highly overexpressed in mitoxantrone-resistant cells: demonstration of homology to ABC transport genes. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, L.A.; Yang, W.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Krogmann, T.; Gao, Y.; Rishi, A.K.; Ross, D.D. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15665–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Bikadi, Z.; F. Rosenberg, M.; Mao, Q. Structure and Function of the Human Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, F.; Miura, M.; Fujioka, Y.; Abumiya, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, S.; Yoshioka, T.; Kameoka, Y.; Takahashi, N. The BCRP inhibitor febuxostat enhances the effect of nilotinib by regulation of intracellular concentration. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 113, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, H.-M.; Lee, C.-Y.; Ee, P.L.R.; Go, M.-L. Dimethoxyaurones: Potent inhibitors of ABCG2 (breast cancer resistance protein). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 35, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-X.; Zhao, T.-Q.; Gong, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.-Y.; Liu, H.-M. Pyrimidine: A promising scaffold for optimization to develop the inhibitors of ABC transporters. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 200, 112458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, E.; Moréno, A.; Altounian, N.; Philouze, C.; Pérès, B.; Thomas, A.; Renaudet, O.; Falson, P.; Boumendjel, A. Chromones bearing amino acid residues: Easily accessible and potent inhibitors of the breast cancer resistance protein ABCG2. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 202, 112503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabindran, S.K.; He, H.; Singh, M.; Brown, E.; Collins, K.I.; Annable, T.; Greenberger, L.M. Reversal of a novel multidrug resistance mechanism in human colon carcinoma cells by fumitremorgin C. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5850–5858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.D.; van Loevezijn, A.; Lakhai, J.M.; van der Valk, M.; van Tellingen, O.; Reid, G.; Schellens, J.H.; Koomen, G.J.; Schinkel, A.H. Potent and specific inhibition of the breast cancer resistance protein multidrug transporter in vitro and in mouse intestine by a novel analogue of fumitremorgin C. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran, S.K.; Ross, D.D.; Doyle, L.A.; Yang, W.; Greenberger, L.M. Fumitremorgin C reverses multidrug resistance in cells transfected with the breast cancer resistance protein. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Krapf, M.K.; Gallus, J.; Namasivayam, V.; Wiese, M. 2,4,6-Substituted Quinazolines with Extraordinary Inhibitory Potency toward ABCG2. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7952–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapf, M.K.; Gallus, J.; Vahdati, S.; Wiese, M. New Inhibitors of Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (ABCG2) Containing a 2,4-Disubstituted Pyridopyrimidine Scaffold. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3389–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapf, M.K.; Gallus, J.; Wiese, M. 4-Anilino-2-pyridylquinazolines and -pyrimidines as Highly Potent and Nontoxic Inhibitors of Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (ABCG2). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4474–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabor Gozzi, G.; Bouaziz, Z.; Winter, E.; Daflon-Yunes, N.; Aichele, D.; Nacereddine, A.; Marminon, C.; Valdameri, G.; Zeinyeh, W.; Bollacke, A.; et al. Converting Potent Indeno[1,2-b]indole Inhibitors of Protein Kinase CK2 into Selective Inhibitors of the Breast Cancer Resistance Protein ABCG2. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 58, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbermann, K.; Li, J.; Namasivayam, V.; Stefan, S.M.; Wiese, M. Rational drug design of 6-substituted 4-anilino-2-phenylpyrimidines for exploration of novel ABCG2 binding site. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 212, 113045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Xu, M.; To, K.K.W.; Li, Q.; Fu, L. Effect of ceritinib (LDK378) on enhancement of chemotherapeutic agents in ABCB1 and ABCG2 overexpressing cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44643–44659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.M.; Manolaridis, I.; Kowal, J.; Zechner, M.; Taylor, N.M.I.; Bause, M.; Bauer, S.; Bartholomaeus, R.; Bernhardt, G.; Koenig, B.; et al. Structural basis of small-molecule inhibition of human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertamino, A.; Ostacolo, C.; Medina, A.; Di Sarno, V.; Lauro, G.; Ciaglia, T.; Vestuto, V.; Pepe, G.; Basilicata, M.G.; Musella, S.; et al. Exploration of TRPM8 Binding Sites by β-Carboline-Based Antagonists and Their In Vitro Characterization and In Vivo Analgesic Activities. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9672–9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostacolo, C.; Di Sarno, V.; Lauro, G.; Pepe, G.; Musella, S.; Ciaglia, T.; Vestuto, V.; Autore, G.; Bifulco, G.; Marzocco, S.; et al. Identification of an indol-based multi-target kinase inhibitor through phenotype screening and target fishing using inverse virtual screening approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Del Gaudio, F.; Johansson, C.; Riccio, R.; Oppermann, U.; Di Micco, S. Virtual Fragment Screening Identification of a Quinoline-5,8-dicarboxylic Acid Derivative as a Selective JMJD3 Inhibitor. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Forte, G.; Terracciano, S.; Russo, A.; Sala, M.; Scala, M.C.; Johansson, C.; Oppermann, U.; Riccio, R.; Bruno, I.; et al. Identification of the 2-Benzoxazol-2-yl-phenol Scaffold as New Hit for JMJD3 Inhibition. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Rahimova, R.; Sala, M.; Scala, M.C.; Vivenzio, G.; Musella, S.; Andrei, G.; Remans, K.; Mammri, L.; Snoeck, R.; et al. Rational design of the zonulin inhibitor AT1001 derivatives as potential anti SARS-CoV-2. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 244, 114857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, F.; Ren, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z. Suppression of ABCG2 inhibits cancer cell proliferation. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boussac, H.; Orbán, T.I.; Várady, G.; Tihanyi, B.; Bacquet, C.; Brózik, A.; Váradi, A.; Sarkadi, B.; Arányi, T. Stimulus-induced expression of the ABCG2 multidrug transporter in HepG2 hepatocarcinoma model cells involves the ERK1/2 cascade and alternative promoters. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, S.C.; Wiese, M. HM30181 Derivatives as Novel Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP/ABCG2). J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3910–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollo, Z.; Homolya, L.; Hegedus, T.; Muller, M.; Szakacs, G.; Jakab, K.; Antal, F.; Sarkadi, B. Parallel functional and immunological detection of human multidrug resistance proteins, P-glycoprotein and MRP1. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 2981–2987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, I.V.; Szabó, E.; Türk, D.; Telbisz, Á.; Kucsma, N.; Horváth, T.; Szakács, G.; Homolya, L.; Sarkadi, B.; Várady, G. A new fluorescent dye accumulation assay for parallel measurements of the ABCG2, ABCB1 and ABCC1 multidrug transporter functions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190629. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, K.; Shibo, L.; Xiao, Z.; Longerich, T.; Buchler, M.W.; Schemmer, P. Correlation of gene expression of ATP-binding cassette protein and tyrosine kinase signaling pathway in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Hoffmann, K.; Xiao, Z.; Jin, N.; Galli, U.; Mohr, E.; Büchler, M.W.; Schemmer, P. MEK inhibition induced downregulation of MRP1 and MRP3 expression in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-M.; Shu, C.; Chen, J.-J.; Sodani, K.; Wang, J.; Bhatnagar, J.; Lan, P.; Ruan, Z.-X.; Xiao, Z.-J.; Ambudkar, S.V.; et al. BBA, a Derivative of 23-Hydroxybetulinic Acid, Potently Reverses ABCB1-Mediated Drug Resistance in Vitro and in Vivo. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, D.H.; Guragossian, N.; Zattoni, I.F.; Moure, V.R.; Rego, F.G.d.M.; Lusvarghi, S.; Moulenat, T.; Belhani, B.; Picheth, G.; Bouacida, S.; et al. Mechanistic basis of breast cancer resistance protein inhibition by new indeno[1,2-b]indoles. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, L.D.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Lu, S.; Shukla, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Pike, V.W.; Mulder, J.; Gottesman, M.M.; Innis, R.B.; Hall, M.D. The Inhibitor Ko143 Is Not Specific for ABCG2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 354, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A Force Field Providing Broad Coverage of Drug-like Small Molecules and Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, W.C.; Tempczyk, A.; Hawley, R.C.; Hendrickson, T. Semianalytical treatment of solvation for molecular mechanics and dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 112, 6127–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LigPrep. Schrödinger Release 2017-1; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. -Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein Preparation Wizard. Schrödinger Release 2017-1: Schrödinger Suite 2017-1; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein−Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Masullo, M.; Bandak, A.F.; Berger, J.M.; Riccio, R.; Piacente, S.; Bifulco, G. Garcinol and Related Polyisoprenylated Benzophenones as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors: Biochemical and Molecular Modeling Studies. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2768–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Terracciano, S.; Cantone, V.; Fischer, K.; Koeberle, A.; Foglia, A.; Riccio, R.; Werz, O.; Bruno, I.; Bifulco, G. Discovery of new potent molecular entities able to inhibit mPGES-1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Terracciano, S.; Pierri, M.; Cantone, V.; Liening, S.; König, S.; Garscha, U.; Hofstetter, R.K.; Koeberle, A.; Werz, O.; et al. Identification of 2,4-Dinitro-Biphenyl-Based Compounds as MAPEG Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karászi, É.; Jakab, K.; Homolya, L.; Szakács, G.; Holló, Z.; Telek, B.; Kiss, A.; Rejtô, L.; Nahajevszky, S.; Sarkadi, B.; et al. Calcein assay for multidrug resistance reliably predicts therapy response and survival rate in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 112, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novizio, N.; Belvedere, R.; Morretta, E.; Tomasini, R.; Monti, M.C.; Morello, S.; Petrella, A. Role of Intracellular and Extracellular Annexin A1 in MIA PaCa-2 Spheroids Formation and Drug Sensitivity. Cancers 2022, 14, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebersold, R.; Goodlett, D.R. Mass Spectrometry in Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertamino, A.; Lauro, G.; Ostacolo, C.; Di Sarno, V.; Musella, S.; Ciaglia, T.; Campiglia, P.; Bifulco, G.; Gomez-Monterrey, I.M. Ring-Fused Cyclic Aminals from Tetrahydro-β-carboline-Based Dipeptide Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 12014–12027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| EC50 ± SD (µM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Hep G2 | MCF7 | MCF 10A |
| 8 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 13a | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 30 | 28.21 ± 3.17 | 33.25 ± 2.63 | 36.12 ± 5.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Micco, S.; Di Sarno, V.; Rossi, M.; Vestuto, V.; Konno, T.; Novi, S.; Tecce, M.F.; Napolitano, V.; Ciaglia, T.; Vitale, A.; et al. In Silico Identification and In Vitro Evaluation of New ABCG2 Transporter Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010725
Di Micco S, Di Sarno V, Rossi M, Vestuto V, Konno T, Novi S, Tecce MF, Napolitano V, Ciaglia T, Vitale A, et al. In Silico Identification and In Vitro Evaluation of New ABCG2 Transporter Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010725
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Micco, Simone, Veronica Di Sarno, Martina Rossi, Vincenzo Vestuto, Takumi Konno, Sara Novi, Mario Felice Tecce, Valeria Napolitano, Tania Ciaglia, Andrea Vitale, and et al. 2023. "In Silico Identification and In Vitro Evaluation of New ABCG2 Transporter Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010725
APA StyleDi Micco, S., Di Sarno, V., Rossi, M., Vestuto, V., Konno, T., Novi, S., Tecce, M. F., Napolitano, V., Ciaglia, T., Vitale, A., Gomez-Monterrey, I. M., Bifulco, G., Bertamino, A., Ostacolo, C., Blasi, P., Fasano, A., Campiglia, P., & Musella, S. (2023). In Silico Identification and In Vitro Evaluation of New ABCG2 Transporter Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010725













