Interaction between Nanoparticles, Membranes and Proteins: A Surface Plasmon Resonance Study
Abstract
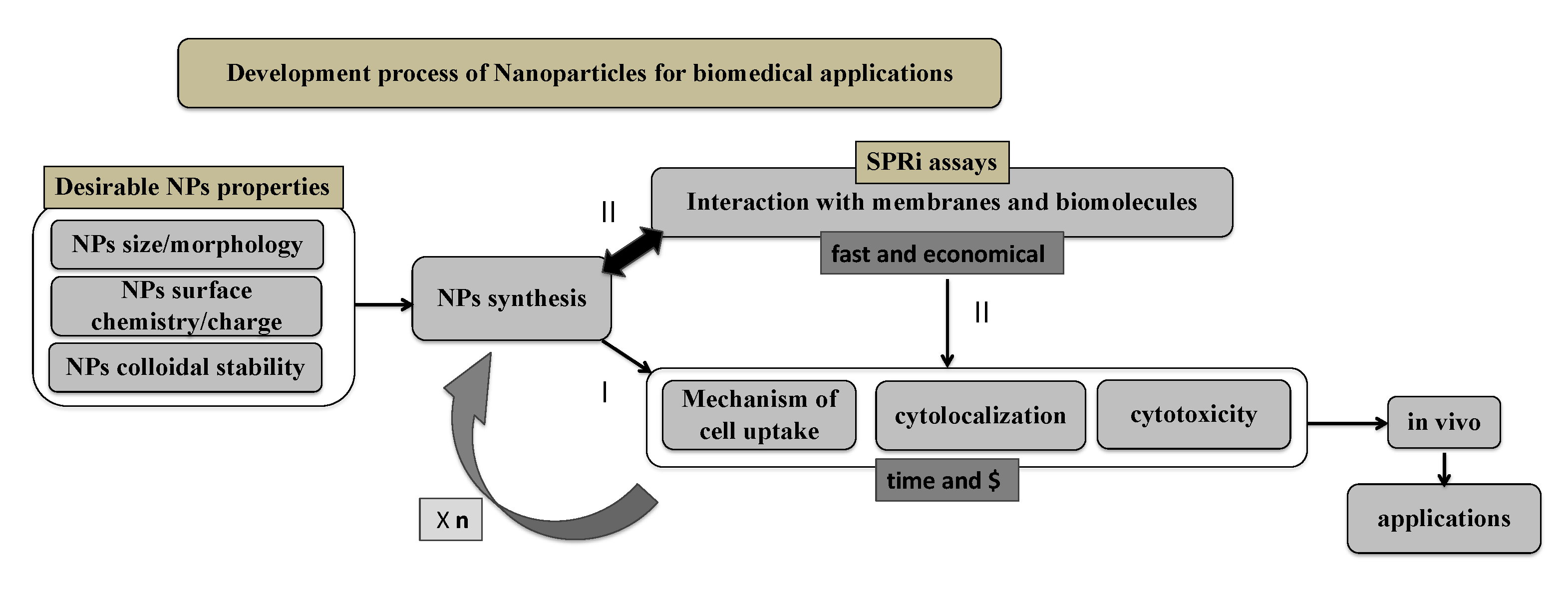
1. Introduction
2. Results
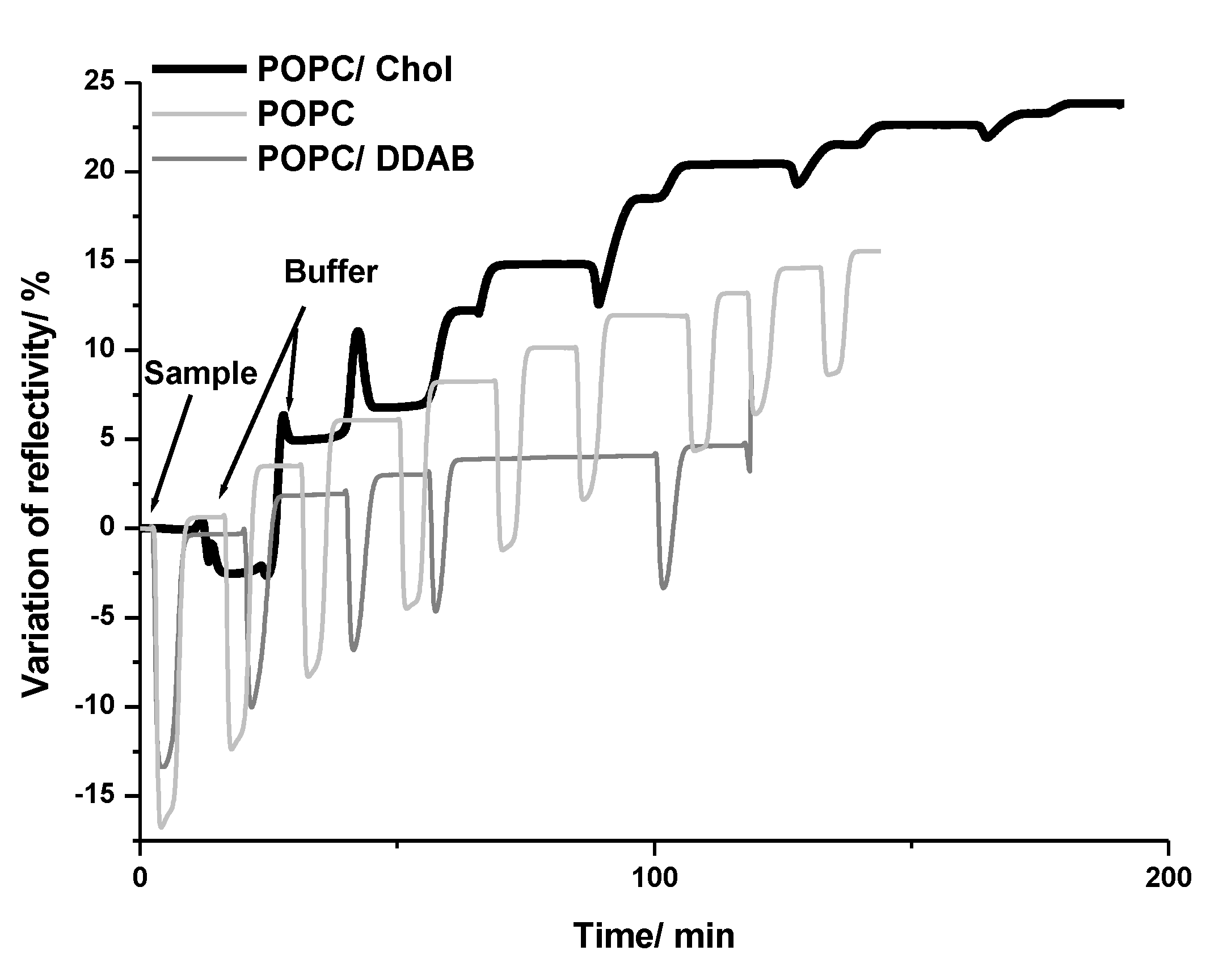
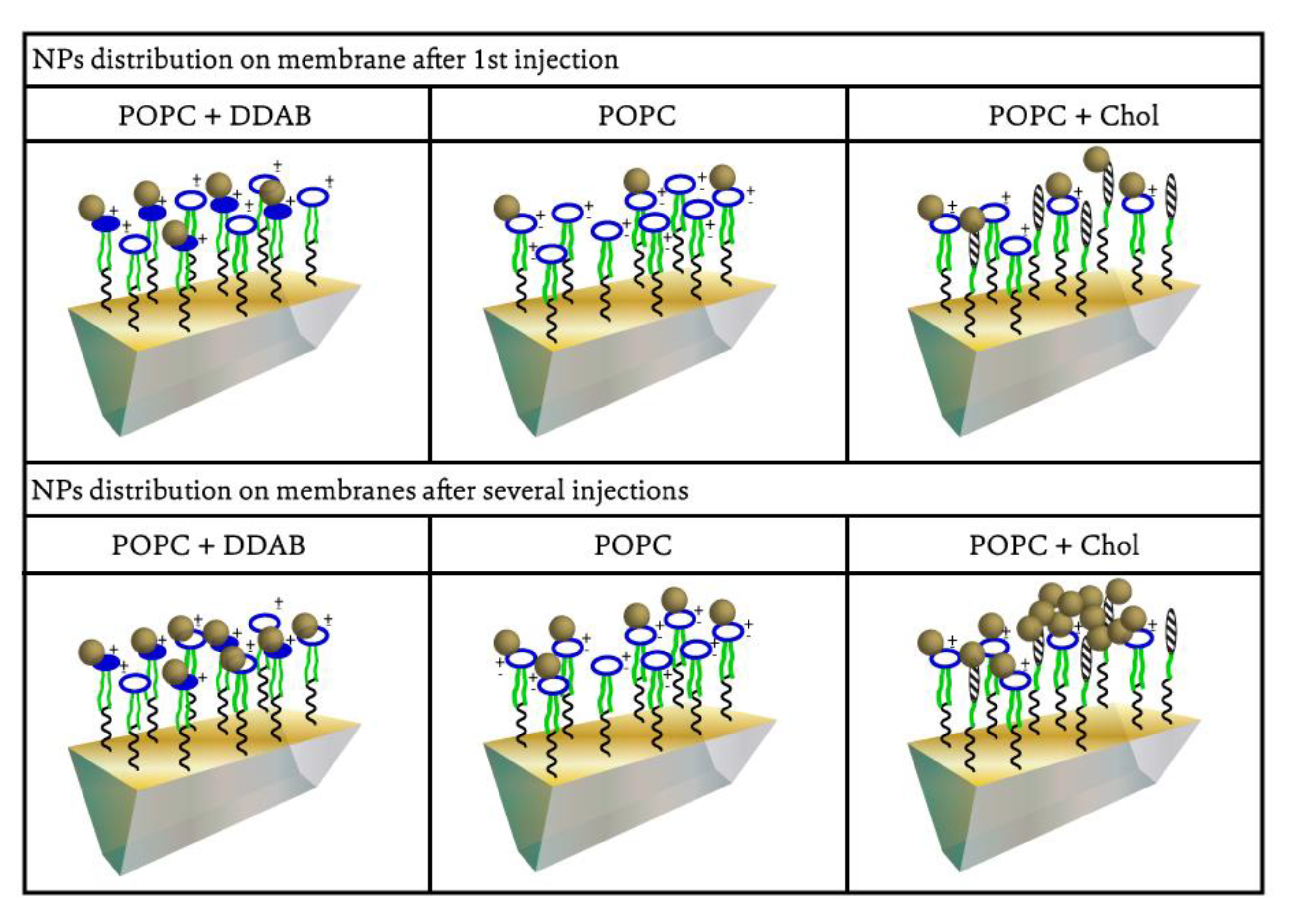
2.1. Gold NPs Interaction with Membrane
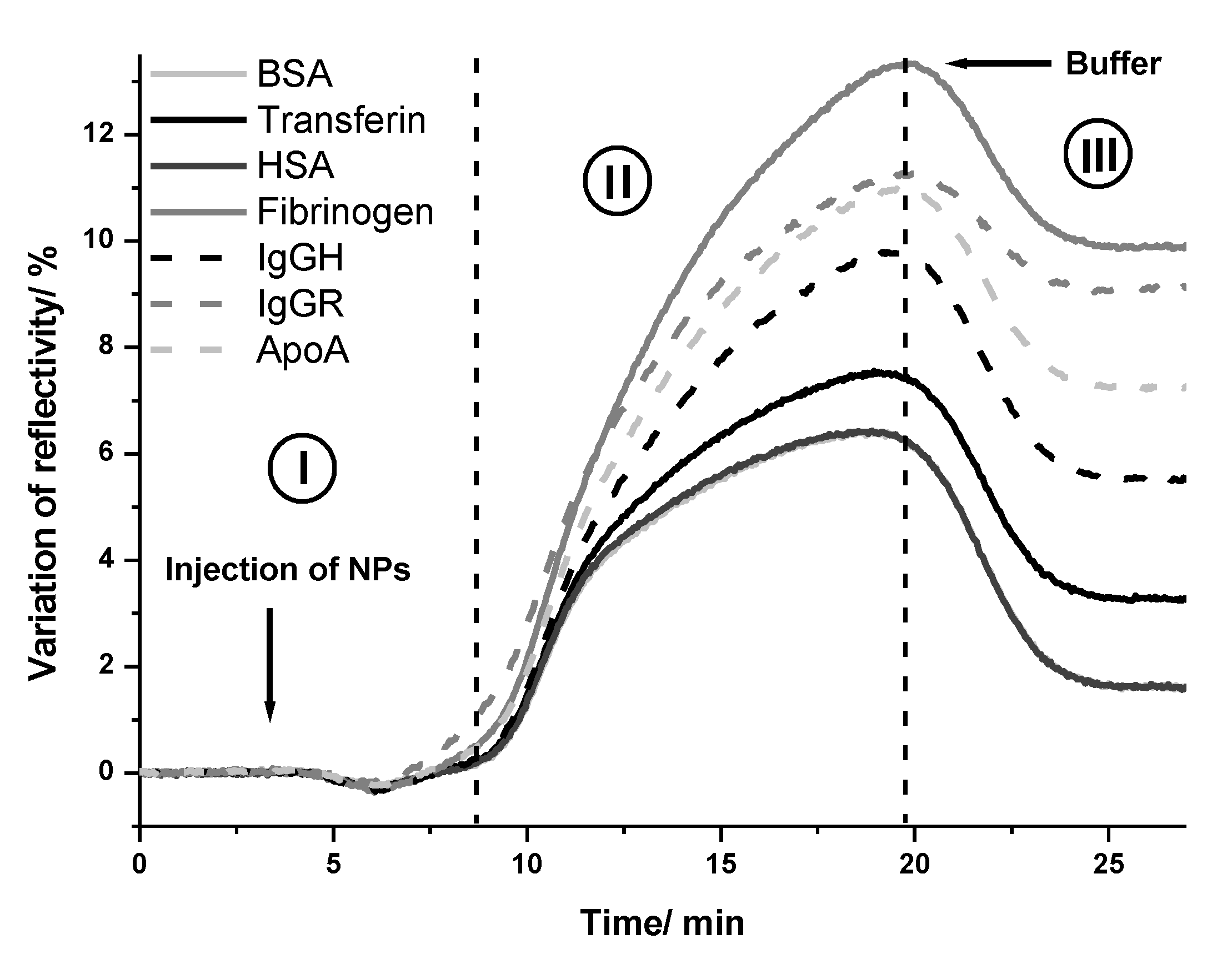
2.2. Interaction of NPs with Proteins
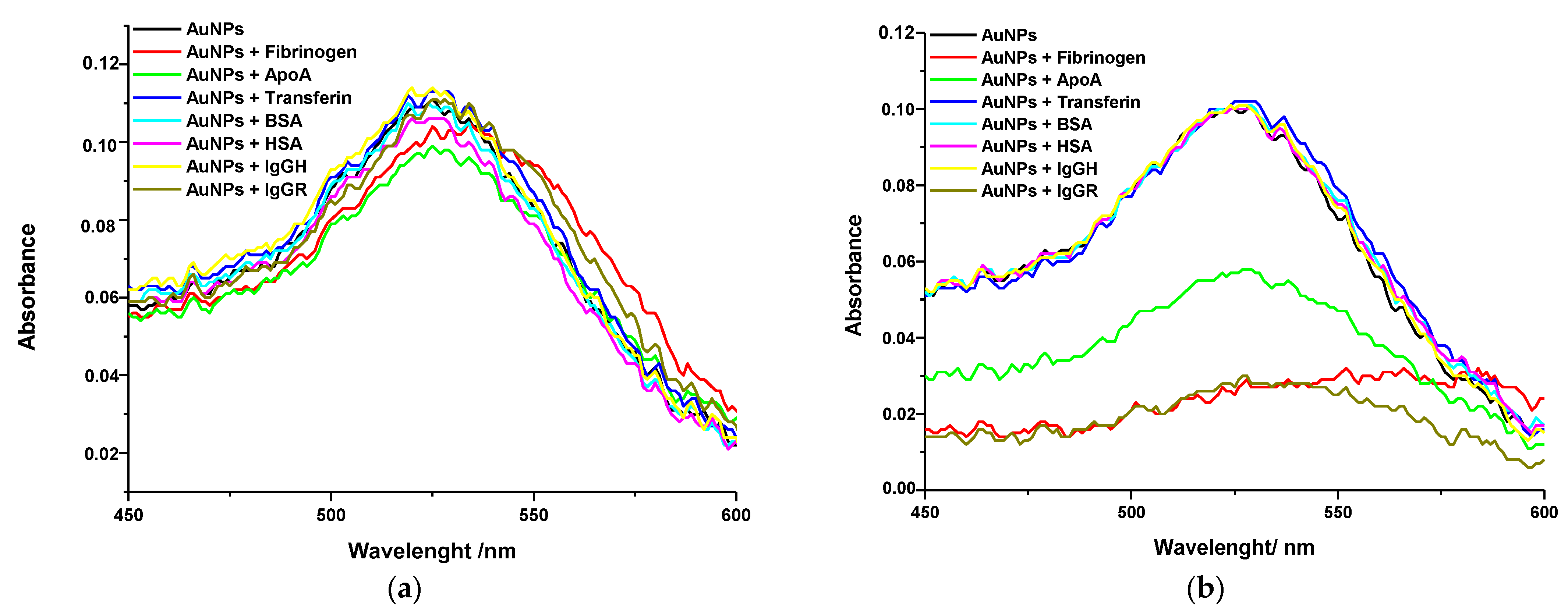
Interaction between Gold NPs and Proteins Studied by Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance
3. Discussion
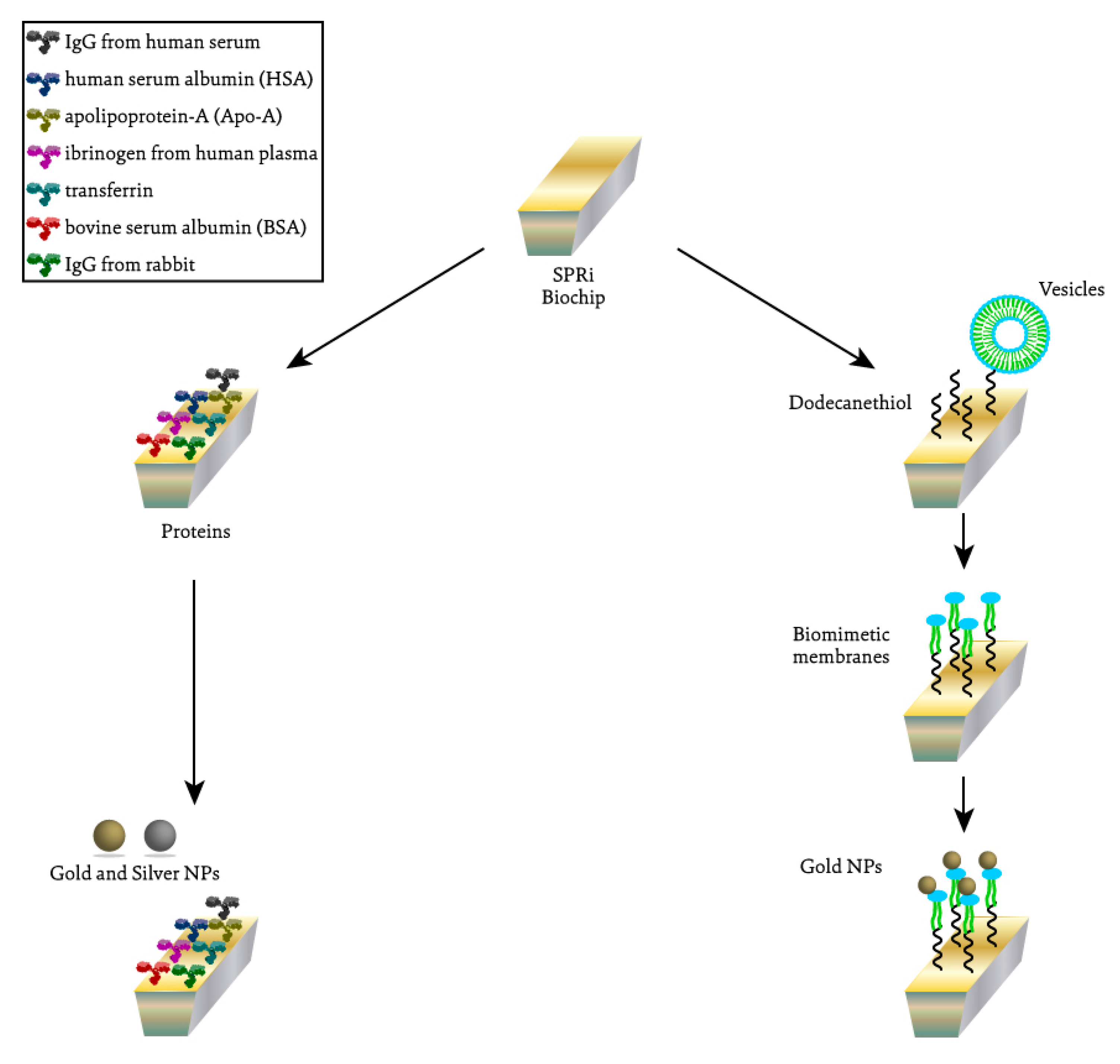
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. SPRi Assay with Membranes
4.1.1. Preparation of the Biochip
4.1.2. Vesicles Preparation
4.1.3. SPRi Assay
4.2. SPRi Assay with Proteins
4.2.1. Preparation of the Protein and Prism
4.2.2. SPRi Experiment Protocol
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, M.R.; Mohamed, Z.J. Dual nanoparticle drug delivery: The future of anticancer therapies? Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Amini, A.M.; He, C.; Lu, B.; Ahmed, T.; Lip, H.; Rauth, A.M.; Wu, X.Y. Importance of integrating nanotechnology with pharmacology and physiology for innovative drug delivery and therapy—An illustration with firsthand examples. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 825–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Liu, F.; Nasr, K.; Misra, P.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Design considerations for tumour-targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, J.L.S.; Abbiati, R.A.; Wientjes, M.G.; Lu, Z. Target site delivery and residence of nanomedicines: Application of quantitative systems pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmeiner, W.H.; Ghosh, S. Nanotechnology for cancer treatment. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2014, 3, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Walkey, C.D.; Olsen, J.B.; Guo, H.; Emili, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Secreted biomolecules alter the biological identity and cellular interactions of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5515–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fetz, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; et al. Rapid formation of plasma protein corona critically affects nanoparticle pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Chan, W.C.W. Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docter, D.; Westmeier, D.; Markiewicz, M.; Stolte, S.; Knauer, S.K.; Stauber, R.H. The nanoparticle biomolecule corona: Lessons learned–challenge accepted? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6094–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lehn, R.C.; Atukorale, P.U.; Carney, R.P.; Yang, Y.; Stellacci, F.; Irvine, D.J.; Alexander-Katz, A. Effect of particle diameter and surface composition on the spontaneous fusion of monolayer-protected gold nanoparticles with lipid bilayers. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4060–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kröger, M.; Liu, W.K. Shape Effect in Cellular Uptake of PEGylated Nanopar-ticles: Comparison between sphere, rod, cube and disk. Analyst 2015, 140, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Dargazany, R.; Alexander-Katz, A. Lipid Flip-Flop and Pore Nucleation on Zwitterionic Bilayers are Asymmetric under Ionic Imbalance. Small 2017, 13, 1603708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hartel, N.; Ren, K.; Graham, N.A.; Malmstadt, N. Effect of protein corona on nanoparticle-plasma membrane and nanoparticle-biomimetic membrane interactions. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Jin, S.; Ma, X.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Kumar, A.; Wang, P.C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Liang, X.-J. Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles as Carriers for Nucleus-Based Gene Therapy Due to Size-Dependent Nuclear Entry. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishmukhametov, I.; Batasheva, S.; Rozhina, E.; Akhatova, F.; Mingaleeva, R.; Rozhin, A.; Fakhrullin, R. DNA/Magnetic Nanoparticles Composite to Attenuate Glass Surface Nanotopography for Enhanced Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation. Polymers 2022, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.L.M.S.; Barbosa, L.; Hurtado, C.R.; Ramos, L.D.P.; Montanheiro, T.L.A.; Oliveira, L.D.; Tada, D.B.; Trichês, E.D.S. Bioglass-based scaffolds coated with silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, processing and antimicrobial activity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.—Part A 2020, 108, 2447–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, P.; Riviere, J.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles determines the biocorona composition impacting cellular uptake, toxicity and gene expression profiles in human endothelial cells. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Tian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, R.; Chai, Z. Towards understanding of nanoparticle–protein corona. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalinardo, M.; Caicci, F.; Cavallini, M.; Gentili, D. Protein Corona Mediated Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast. Small 2018, 14, 1801219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Gao, H. The impact of protein corona on the behavior and targeting capability of nanoparticle-based delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopac, T. Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle—protein interactions and future perspectives: A critical review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francia, V.; Yang, K.; Deville, S.; Reker-Smit, C.; Nelissen, I.; Salvati, A. Corona Composition Can Affect the Mechanisms Cells Use to Internalize Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11107–11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caracciolo, G.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Biological identity of nanoparticles in vivo: Clinical implications of the protein corona. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, S.M.; Rao, C.M.; Ahmad, M.F. Nanoparticle-Protein Interaction: The Significance and Role of Protein Corona. Cell. Mol. Toxicol. Nanoparticles 2018, 1048, 175–198. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkov, V.; Bubis, J.A.; Solovyeva, E.M.; Gorshkov, M.V.; Kjeldsen, F. Protein corona formed on silver nanoparticles in blood plasma is highly selective and resistant to physicochemical changes of the solution. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenheer, R.; Castellanos, E.R.; Nakamoto, M.Y.; Gerner, K.T.; Lampe, A.M.; Wheeler, K.E. Silver nanoparticle protein corona composition compared across engineered particle properties and environmentally relevant reaction conditions. Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 1, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.; García, I.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Martínez-Calvo, M.; Dhanjani, M.; Mascareñas, J.L.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Reversible Control of Protein Corona Formation on Gold Nanoparticles Using Host-Guest Interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 14, 5382–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bicer, E.M.; Pfeffer, P.; Monopoli, M.P.; Dawson, K.A.; Eriksson, J.; Edwards, K.; Lynham, S.; Arno, M.; Behndig, A.F.; et al. Differences in the coronal proteome acquired by particles depositing in the lungs of asthmatic versus healthy humans. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hessler, J.A.; Putchakayala, K.; Panama, B.K.; Khan, D.P.; Hong, S.; Mullen, D.G.; DiMaggio, S.C.; Som, A.; Tew, G.N.; et al. Cationic nanoparticles induce nanoscale disruption in living cell plasma membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 11179–11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y. Penetration of lipid membranes by gold nanoparticles: Insights into cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and their relationship. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5421–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, C.; Schneemilch, M.; Gaisford, S.; Quirke, N. Nanoparticle–membrane interactions. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2018, 13, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Gu, N. Computational investigation of interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: Hydrophobic/hydrophilic effect. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16647–16653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggard, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Using Methods to Quantify Exchange Rates and Affinities of Proteins for Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canovi, M.; Lucchetti, J.; Stravalaci, M.; Re, F.; Moscatelli, D.; Bigini, P.; Salmona, M.; Gobbi, M. Applications of Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) for the characterization of nanoparticles developed for biomedical purposes. Sensors 2012, 12, 16420–16432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavel, P.; Canva, M.; Lecaruyer, P.; Sauer, H.; Taboury, J. Surface plasmon resonance imaging instrumentation and data handling for biochips: Review and perspectives. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Correlation Optics, Chernivtsi, Ukraine, 6–9 September 2006; p. 62540M. [Google Scholar]
- Hommola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkel, L.C.; Bakovic, M. Formation and Regulation of Mitochondrial Membranes. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 2014, 709828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, N.D.; Acar, H.; Wilhelm, S. Concepts of nanoparticle cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and kinetics in nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 68–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francia, V.; Montizaan, D.; Salvati, A. Interactions at the cell membrane and pathways of internalization of nano-sized materials for nanomedicine. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.Y.; van Harmelen, R.J.J.; Norouzi, N.; Offens, F.; Venema, I.M.; Najafi, M.B.H.; Schirhagl, R. Interaction of nanodiamonds with bacteria. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17117–17124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.V.; Gunsolus, I.L.; Qiu, T.A.; Hurley, K.R.; Nyberg, L.H.; Frew, H.; Johnson, K.P.; Vartanian, A.M.; Jacob, L.M.; Lohse, S.E.; et al. Impacts of gold nanoparticle charge and ligand type on surface binding and toxicity to Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5186–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, S.C.; Zhao, G.; Saha, K.; Phillips, R.L.; Li, X.; Miranda, O.R.; Rotello, V.M.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Schmidt-Krey, I.; Bunz, U.H.F. Aggregation and interaction of cationic nanoparticles on bacterial surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6920–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Jiang, X. Small molecule-capped gold nanoparticles as potent antibacterial agents that target gram-negative bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12349–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Pang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, Y. Evaluating the single-molecule interactions between targeted peptides and the receptors on living cell membrane. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17318–17324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Domínguez, S.; Caballero-Mancebo, S.; Marcuello, C.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Medina, M.; Lostao, A. Nanomechanical Study of Enzyme: Coenzyme Complexes: Bipartite Sites in Plastidic Ferredoxin-NADP+ Reductase for the Interaction with NADP+. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Fang, Q. Interaction of gold and silver nanoparticles with human plasma: Analysis of protein corona reveals specific binding patterns. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Ding, T.; Engudar, G.; Wang, Y.; Dykas, M.M.; Liedberg, B.; Kah, J.C.Y.; Venkatesan, T.; Drum, C. Component-Specific Analysis of Plasma Protein Corona Formation on Gold Nanoparticles Using Multiplexed Surface Plasmon Resonance. Small 2016, 12, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Zhan, H.; Chu, Y.; Sun, B. Mechanistic Understanding of the Engineered Nanomaterial-Induced Toxicity on Kidney. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 2954853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peetla, C.; Stine, A.; Labhasetwar, V. Biophysical interactions with model lipid membranes: Applications in drug discovery and drug delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huff, T.B.; Hansen, M.N.; Wei, A.; Cheng, J.X. Gold nanorods mediate tumor cell death by compromising membrane integrity. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3136–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Bothun, G.D. Nanoparticles meet cell membranes: Probing nonspecific interactions using model membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Edwards, L.W.; Fu, X.; Badman, D.L.; Huo, S.; Jin, A.J.; Lu, Q. Effects of gold nanoparticles on lipid packing and membrane pore formation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 263106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formaggio, D.M.D.; de Oliveira Neto, X.A.; Rodrigues, L.D.A.; De Andrade, V.M.; Nunes, B.C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Ferreira, F.G.; Wachesk, C.C.; Camargo, E.R.; Conceição, K.; et al. In vivo toxicity and antimicrobial activity of AuPt bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2019, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Alexander-Katz, A. Cell membranes open ‘doors’ for cationic nanoparticles/biomolecules: Insights into uptake kinetics. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10799–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baowan, D. Penetration of spherical gold nanoparticle into a lipid bilayer. ANZIAM J. 2015, 57, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.W. Study of interactions between polymer nanoparticles and cell membranes at atomistic levels. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.M.; McCusker, C.D.; Yilmaz, T.; Rotello, V.M. Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhashal, A.R.; Roy, S. Effect of gold nanoparticle on structure and fluidity of lipid membrane. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Bielinska, A.U.; Mecke, A.; Keszler, B.; Beals, J.L.; Shi, X.; Balogh, L.; Orr, B.G.; Baker, J.R., Jr.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Interaction of poly(amidoamine) dendrimers with supported lipid bilayers and cells: Hole formation and the relation to transport. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lehn, R.C.; Alexander-Katz, A. Membrane-embedded nanoparticles induce lipid rearrangements similar to those exhibited by biological membrane proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 12586–12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Alwarawrah, M.; Huang, J. Instability of Cholesterol Clusters in Lipid Bilayers and The Cholesterol’s Umbrella Effect. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Q.; Huang, C.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, B.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.-Q. Cooperative transmembrane penetration of nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, D.B.; Suraniti, E.; Rossi, L.M.; Leite, C.A.P.; Oliveira, C.S.; Tumolo, T.C.; Calemczuk, R.; Livache, T.; Baptista, M.S. Effect of lipid coating on the interaction between silica nanoparticles and membranes. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemelaar, S.R.; Nagl, A.; Bigot, F.; Rodríguez-García, M.M.; De Vries, M.P.; Chipaux, M.; Schirhagl, R. The interaction of fluorescent nanodiamond probes with cellular media. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Patri, A.K.; Zheng, J.; Clogston, J.D.; Ayub, N.; Aggarwal, P.; Neun, B.W.; Hall, J.B.; McNeil, S.E. Interaction of colloidal gold nanoparticles with human blood: Effects on particle size and analysis of plasma protein binding profiles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Mesquita, B.; Horvatovich, P.; Salvati, A. Tuning liposome composition to modulate corona formation in human serum and cellular uptake. Acta Biomater. 2020, 106, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, E.W.E.; Bosma, R.; Gao, M.; Bor, J.V.D.; Al Araaj, B.; de Munnik, S.M.; Ma, X.; Leurs, R.; Vischer, H.F. BRET-Based Biosensors to Measure Agonist Efficacies in Histamine H1 Receptor-Mediated G Protein Activation, Signaling and Interactions with GRKs and β-Arrestins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobowska, I.; Becker, F.; Minguzzi, S.; Hansen, K.; Henke, B.; Epalle, N.H.; Beitz, E.; Hannus, S. Fluorescence Cross-Correlation Spectroscopy Yields True Affinity and Binding Kinetics of Plasmodium Lactate Transport Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; de Miguel, R.; Lostao, A. Molecular Recognition of Proteins through Quantitative Force Maps at Single Molecule Level. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Protein | koff (AuNPs)/s−1 | koff (AgNPs)/s−1 | koff (AuNPs) [25] |
|---|---|---|---|
| IgGR | (1.10 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | (1.50 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−3∙s−1 |
| Fibrinogen | (1.40 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | (1.60 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | 2.0 × 10−3∙s−1 |
| ApoA | (1.90 ± 0.02) ×10−3 | (1.40 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | 1.6 × 10−3∙s−1 |
| IgGH | (2.60 ± 0.04) × 10−3 | (1.40 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−3∙s−1 |
| Transferrin | (3.60 ± 0.05) × 10−3 s−1 | (1.50 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | |
| HSA | (5.50 ± 0.01) × 10−3 s−1 | (1.60 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | 1.8 × 10−3 |
| BSA | (5.50 ± 0.01) × 10−3 s−1 | (1.30 ± 0.01) × 10−3 |
| Sample | Immediately | After 4 h | Variation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λmax (nm) | Absorbance | λmax (nm) | Absorbance | Δλmax (nm) | ΔAbsorbance | |
| Gold NPs | ||||||
| Gold NPs | 525 | 0.12 | 528 | 0.12 | 3 | −0.01 |
| NPs + HEPES | 525 | 0.11 | 528 | 0.10 | 3 | −0.01 |
| NPs + Fibr | 534 | 0.10 | 584 | 0.04 | 50 | −0.07 |
| NPs + ApoA | 525 | 0.10 | 529 | 0.06 | 4 | −0.04 |
| NPs + Transf | 529 | 0.11 | 525 | 0.10 | −4 | −0.01 |
| NPs + BSA | 519 | 0.11 | 526 | 0.10 | 7 | −0.01 |
| NPs + IgGH | 520 | 0.11 | 524 | 0.10 | 4 | −0.01 |
| NPs + IgGR | 528 | 0.11 | 529 | 0.09 | 1 | −0.02 |
| Silver NPs | ||||||
| Silver NPs | 431 | 0.09 | 428 | 0.11 | −3 | 0.01 |
| NPs + HEPES | 412 | 0.14 | 430 | 0.10 | 18 | −0.03 |
| NPs + Fibr | 415 | 0.14 | 435 | 0.05 | 20 | −0.09 |
| NPs + ApoA | 389 | 0.15 | 410 | 0.12 | 21 | −0.02 |
| NPs + Transf | 408 | 0.17 | 415 | 0.14 | 7 | −0.03 |
| NPs + BSA | 411 | 0.15 | 430 | 0.09 | 19 | −0.06 |
| NPs + IgGH | 408 | 0.16 | 428 | 0.07 | 20 | −0.09 |
| NPs + IgGR | 408 | 0.14 | 429 | 0.11 | 21 | −0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Macedo, E.F.; Santos, N.S.; Nascimento, L.S.; Mathey, R.; Brenet, S.; de Moura, M.S.; Hou, Y.; Tada, D.B. Interaction between Nanoparticles, Membranes and Proteins: A Surface Plasmon Resonance Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010591
de Macedo EF, Santos NS, Nascimento LS, Mathey R, Brenet S, de Moura MS, Hou Y, Tada DB. Interaction between Nanoparticles, Membranes and Proteins: A Surface Plasmon Resonance Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010591
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Macedo, Erenildo Ferreira, Nivia Salles Santos, Lucca Silva Nascimento, Raphaël Mathey, Sophie Brenet, Matheus Sacilotto de Moura, Yanxia Hou, and Dayane Batista Tada. 2023. "Interaction between Nanoparticles, Membranes and Proteins: A Surface Plasmon Resonance Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010591
APA Stylede Macedo, E. F., Santos, N. S., Nascimento, L. S., Mathey, R., Brenet, S., de Moura, M. S., Hou, Y., & Tada, D. B. (2023). Interaction between Nanoparticles, Membranes and Proteins: A Surface Plasmon Resonance Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010591







