Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Induces Immunogenic Cell Death Resulting in Maturation of BDCA-1+ Myeloid Dendritic Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
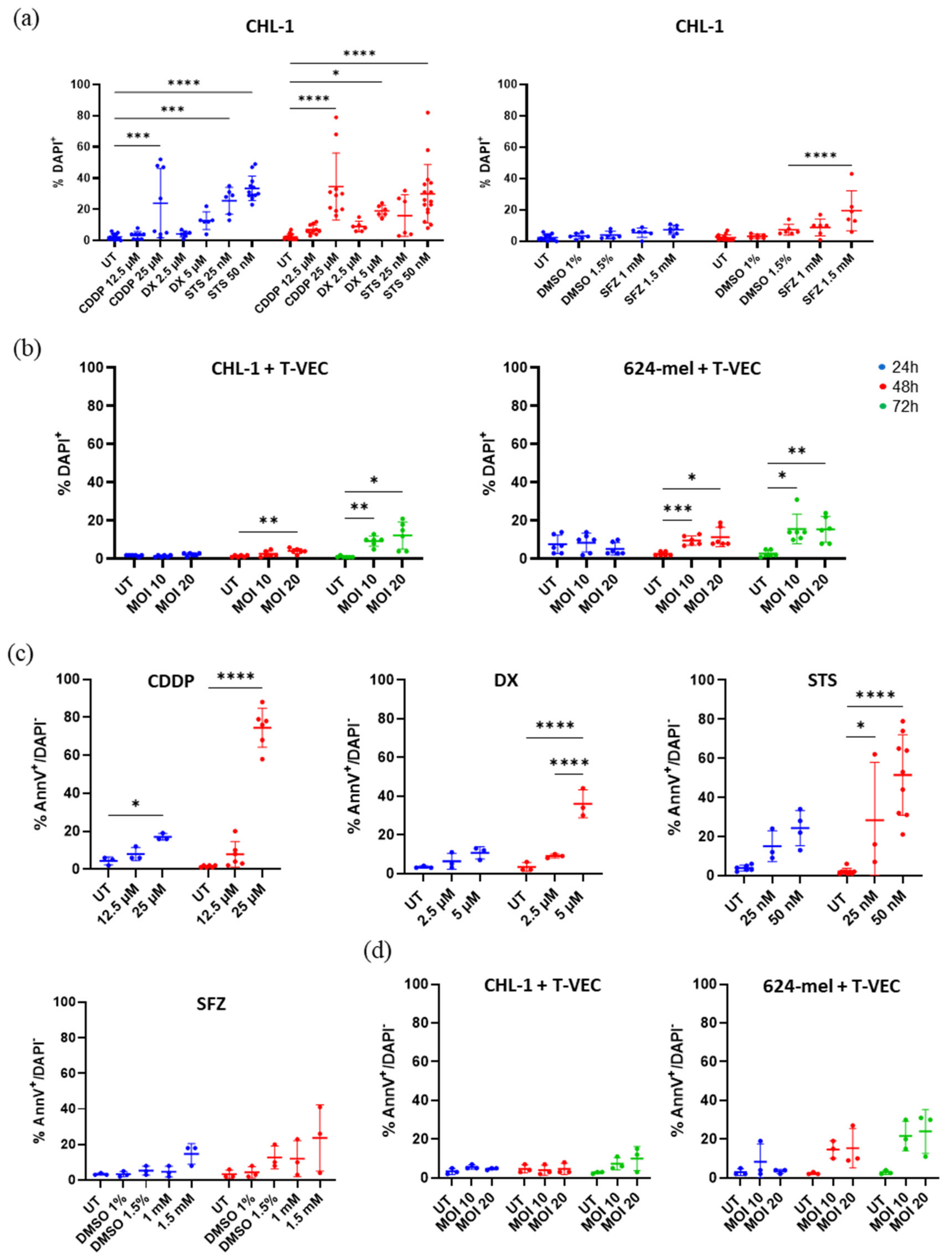
2.1. Screening Method to Identify Appropriate Concentrations of Cell Death Inducing Agents
2.2. Cytocidal Effects of T-VEC Manifest Slower than Chemical Agents
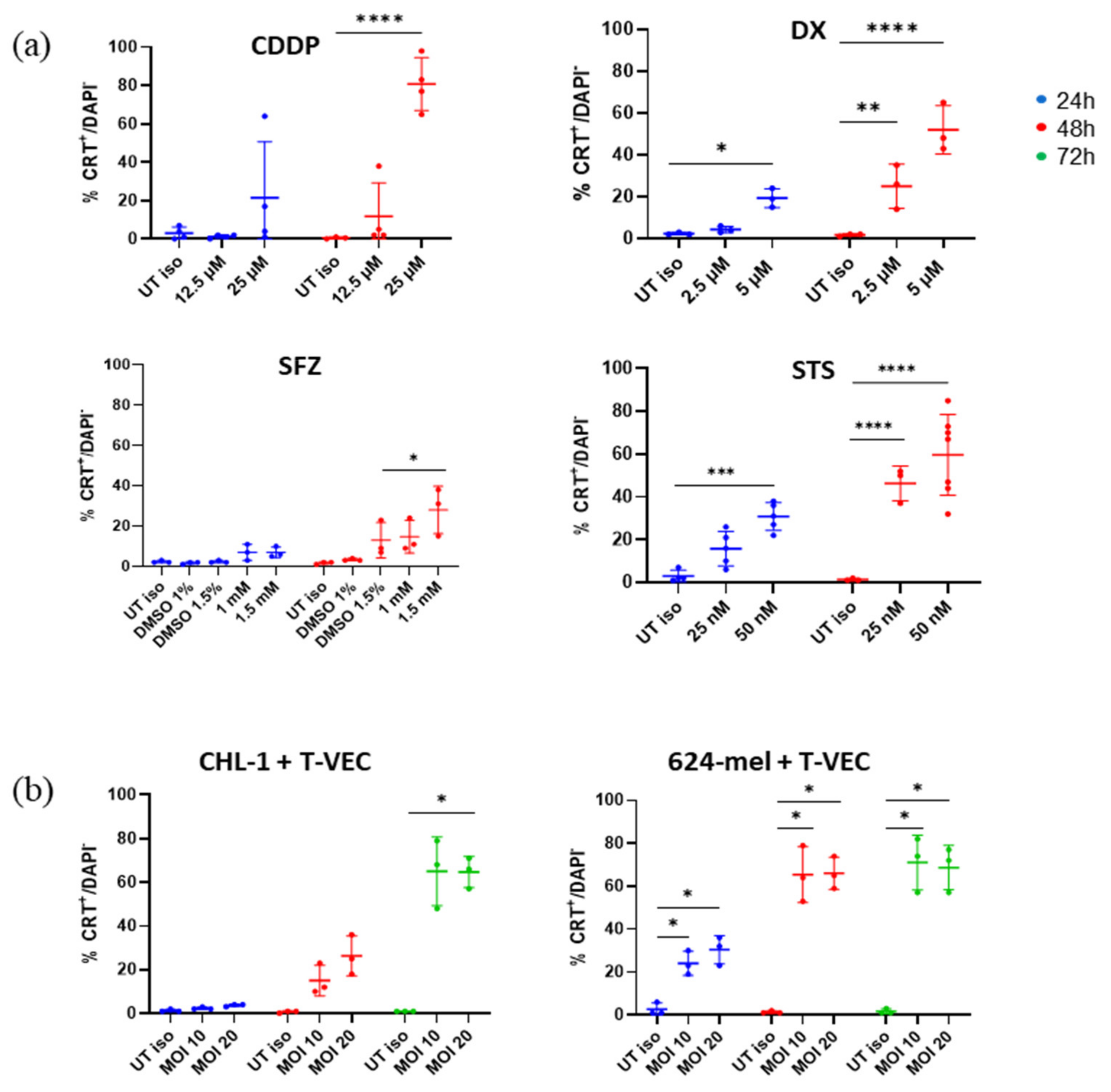
2.3. T-VEC Treatment Triggers Surface CRT Exposure at Comparable Magnitude as Chemical Agents
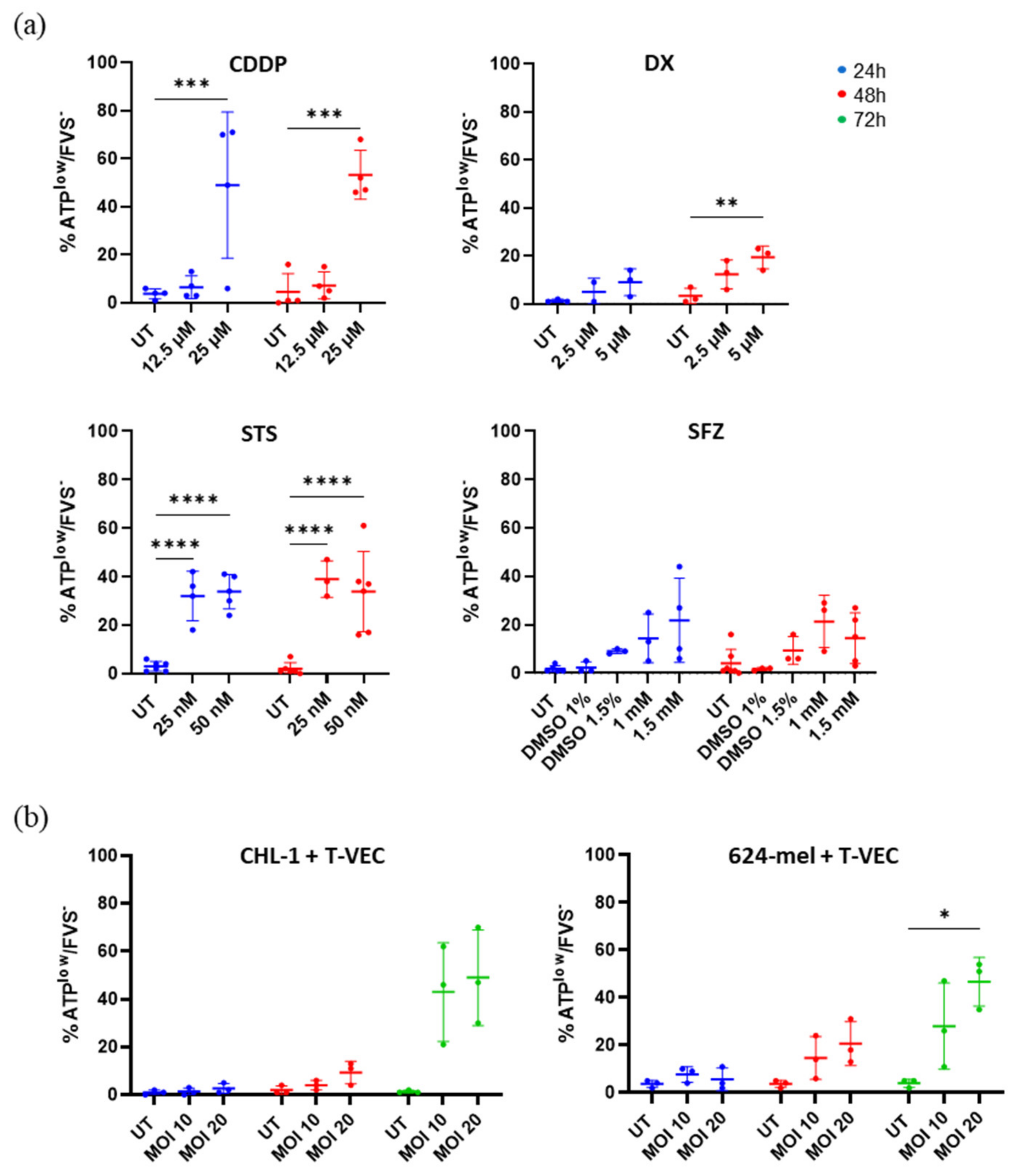
2.4. Treatment with T-VEC and Chemical Agents Causes Release of Vesicular ATP
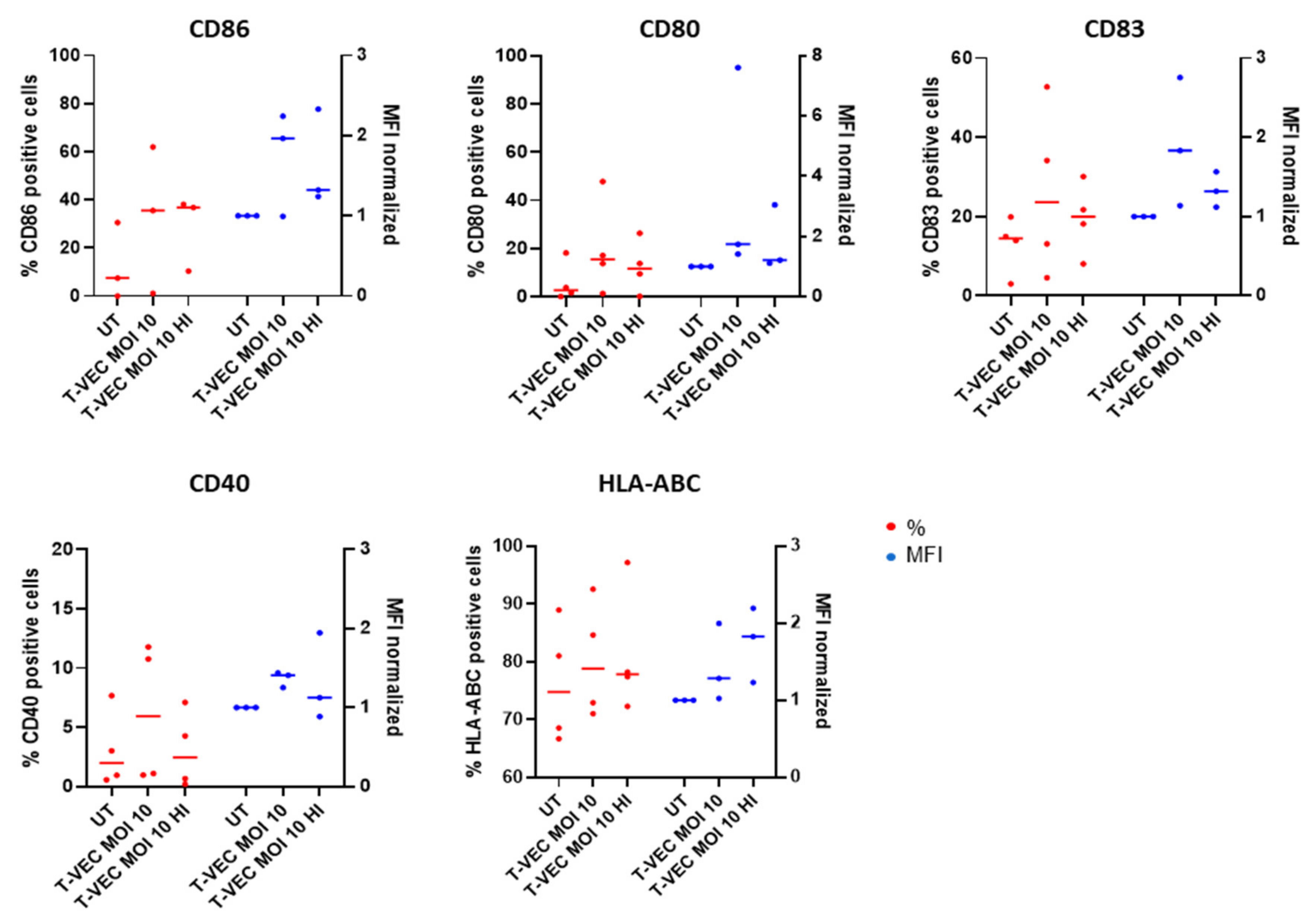
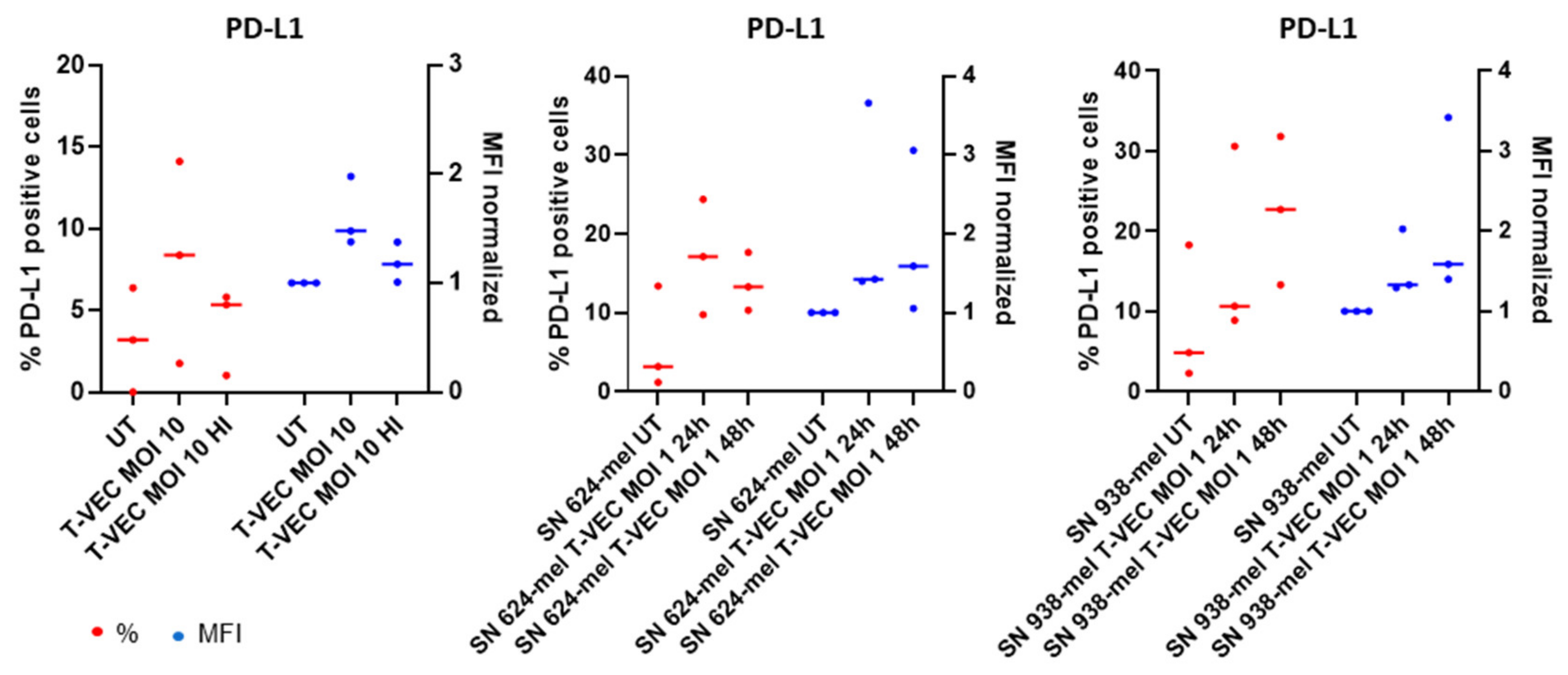
2.5. BDCA-1+ myDCs Mature and Upregulate PD-L1 after Exposure with T-VEC In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Cell Lines
4.2. Induction of (Immunogenic) Cell Death
4.3. Monitoring Cell Proliferation in Real Time Using IncuCyte® Live-Cell Analysis System
4.4. Quantification of Percentage Cell Death Using Flow Cytometry
4.5. Phosphatidylserine Flip-Flop to Outer Membrane Following Induction of Cell Death
4.6. Calreticulin Exposure Following Induction of Cell Death
4.7. ATP Release Following Induction of Cell Death
4.8. Evaluation of BDCA-1+ myDC Maturation in Response to T-VEC Treatment
4.9. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montico, B.; Nigro, A.; Casolaro, V.; Dal Col, J. Immunogenic Apoptosis as a Novel Tool for Anticancer Vaccine Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aaes, T.L.; Kaczmarek, A.; Delvaeye, T.; De Craene, B.; De Koker, S.; Heyndrickx, L.; Delrue, I.; Taminau, J.; Wiernicki, B.; De Groote, P.; et al. Vaccination with Necroptotic Cancer Cells Induces Efficient Anti-tumor Immunity. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krysko, D.V.; Garg, A.D.; Kaczmarek, A.; Krysko, O.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efimova, I.; Catanzaro, E.; Van Der Meeren, L.; Turubanova, V.D.; Hammad, H.; Mishchenko, T.A.; Vedunova, M.V.; Fimognari, C.; Bachert, C.; Coppieters, F.; et al. Vaccination with early ferroptotic cancer cells induces efficient antitumor immunity. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuynck, R.; Efimova, I.; Naessens, F.; Krysko D, V. Immunogenic ferroptosis and where to find it? J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Immune parameters affecting the efficacy of chemotherapeutic regimens. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.; Tesniere, A.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Fimia, G.M.; Apetoh, L.; Perfettini, J.-L.; Castedo, M.; Mignot, G.; Panaretakis, T.; Casares, N.; et al. Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M. ERP57 membrane translocation dictates the immunogenicity of tumor cell death by controlling the membrane translocation of calreticulin. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2533–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casares, N.; Pequignot, M.O.; Tesniere, A.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Roux, S.; Chaput, N.; Schmitt, E.; Hamai, A.; Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Obeid, M.; et al. Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, M.; Martins, I.; Sukkurwala, A.Q.; Adjemian, S.; Ma, Y.; Pellegatti, P.; Shen, S.; Kepp, O.; Scoazec, M.; Mignot, G.; et al. Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science 2011, 334, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattarollo, S.R.; Loi, S.; Duret, H.; Ma, Y.; Zitvogel, L.; Smyth, M.J. Pivotal role of innate and adaptive immunity in anthracycline chemotherapy of established tumors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4809–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Warren, S.; Adjemian, S.; Agostinis, P.; Martinez, A.B.; Chan, T.A.; Coukos, G.; Demaria, S.; Deutsch, E.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the definition, detection and interpretation of immunogenic cell death. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Zloza, A. Oncolytic viruses: A new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 642–662, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senzer, N.N.; Kaufman, H.L.; Amatruda, T.; Nemunaitis, M.; Reid, T.; Daniels, G.; Gonzalez, R.; Glaspy, J.; Whitman, E.; Harrington, K.; et al. Phase II Clinical Trial of a Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor–Encoding, Second-Generation Oncolytic Herpesvirus in Patients With Unresectable Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5763–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, I.; Milhem, M.M.; Minor, D.; Hamid, O.; Li, A.; Chen, L.; Chastain, M.; Gorski, K.S.; Anderson, A.; Chou, J.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec in Combination With Ipilimumab in Previously Untreated, Unresectable Stage IIIB-IV Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conry, R.M.; Westbrook, B.; McKee, S.; Norwood, T.G. Talimogene laherparepvec: First in class oncolytic virotherapy. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhapp, F.J.; Kaufman, H.L. Molecular Pathways: Mechanism of Action for Talimogene Laherparepvec, a New Oncolytic Virus Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bommareddy, P.K.; Zloza, A.; Rabkin, S.D.; Kaufman, H.L. Oncolytic virus immunotherapy induces immunogenic cell death and overcomes STING deficiency in melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1591875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, A.; Masui, A.; Hamada, M.; Imai, T.; Iwai, S.; Yura, Y. Immunogenic cell death by oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Munck, J.; Binks, A.; McNeish, I.A.; Aerts, J.L. Oncolytic virus-induced cell death and immunity: A match made in heaven? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calmeiro, J.; Carrascal, M.A.; Tavares, A.R.; Ferreira, D.A.; Gomes, C.; Falcão, A.; Cruz, M.T.; Neves, B.M. Dendritic Cell Vaccines for Cancer Immunotherapy: The Role of Human Conventional Type 1 Dendritic Cells. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Blasio, S.; Wortel, I.M.N.; van Bladel, D.A.G.; de Vries, L.E.; Duiveman-de Boer, T.; Worah, K.; De Haas, N.; Buschow, S.; De Vries, I.J.M.; Figdor, C.G.; et al. Human CD1c(+) DCs are critical cellular mediators of immune responses induced by immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1192739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tesniere, A.; Schlemmer, F.; Boige, V.; Kepp, O.; Martins, I.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Aymeric, L.; Michaud, M.; Apetoh, L.; Barault, L.; et al. Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene 2010, 29, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Schlemmer, F.; Adjemian, S.; Tailler, M.; Shen, S.; Michaud, M.; Menger, L.; Gdoura, A.; Tajeddine, N.; et al. Restoration of the immunogenicity of cisplatin-induced cancer cell death by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncogene 2010, 30, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer, D.M.; Mobarrez, F.; Wallén, H.; Pisetsky, D.S. The Expression of HMGB1 on Microparticles from Jurkat and HL-60 Cells Undergoing Apoptosis in vitro. Scand. J. Immunol. 2014, 80, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Li, Y.; Shelton, J.M.; Richardson, J.A.; Spencer, E.; Chen, Z.J.; Wang, X.; Williams, R. Cytochrome c Deficiency Causes Embryonic Lethality and Attenuates Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Cell 2000, 101, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Yang, C.; Jian, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, R.; Li, K.; Qu, F.; Tao, K.; Fu, Y.; Luo, F.; et al. Sulfasalazine-induced ferroptosis in breast cancer cells is reduced by the inhibitory effect of estrogen receptor on the transferrin receptor. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijtgat, J.; De Munck, J.; Dufait, I.; Schwarze, J.K.; Van Riet, I.; Franceschini, L.; Breckpot, K.; Aerts, J.L.; Neyns, B.; Tuyaerts, S. Unraveling the Effects of a Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC)-Induced Tumor Oncolysate on Myeloid Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 733506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Omoto, S.; Harris, P.A.; Finger, J.N.; Bertin, J.; Gough, P.J.; Kaiser, W.J.; Mocarski, E.S. Herpes simplex virus suppresses necroptosis in human cells. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dufour, F.; Sasseville, A.J.; Chabaud, S.; Massie, B.; Siegel, R.M.; Langelier, Y. The ribonucleotide reductase R1 subunits of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 protect cells against TNFα- and FasL-induced apoptosis by interacting with caspase-8. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Wu, G.; Shu, Z.; Yu, D.; Nan, N.; Yuan, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. ICP6 Prevents RIP1 Activation to Hinder Necroptosis Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.L.; Robinson, M.; Han, Z.-Q.; Branston, R.H.; English, C.; Reay, P.; McGrath, Y.; Thomas, S.K.; Thornton, M.; Bullock, P.; et al. ICP34.5 deleted herpes simplex virus with enhanced oncolytic, immune stimulating and anti-tumour properties. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Head, T.; Dau, P.; Duffort, S.; Daftarian, P.; Joshi, P.M.; Vazquez-Padron, R.; Deo, S.K.; Daunert, S. An enhanced bioluminescence-based Annexin V probe for apoptosis detection in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Meng, X.W.; Flatten, K.S.; Loegering, D.A.; Kaufmann, S.H. Phosphatidylserine exposure during apoptosis reflects bidirectional trafficking between plasma membrane and cytoplasm. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.M.; Bui, V.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.G. FTY720 induces non-canonical phosphatidylserine externalization and cell death in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Deng, F.; Jia, W. Inhibition of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Immunogenic Chemotherapeutics in Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2019, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malogolovkin, A.; Gasanov, N.; Egorov, A.; Weener, M.; Ivanov, R.; Karabelsky, A. Combinatorial Approaches for Cancer Treatment Using Oncolytic Viruses: Projecting the Perspectives through Clinical Trials Outcomes. Viruses 2021, 13, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, K.; Lecocq, Q.; De Keersmaecker, B.; Raes, G.; Corthals, J.; Lion, E.; Thielemans, K.; Devoogdt, N.; Keyaerts, M.; Breckpot, K. Single Domain Antibody-Mediated Blockade of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 on Dendritic Cells Enhances CD8 T-cell Activation and Cytokine Production. Vaccines 2019, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribas, A.; Dummer, R.; Puzanov, I.; VanderWalde, A.; Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Michielin, O.; Olszanski, A.J.; Malvehy, J.; Cebon, J.; Fernandez, E.; et al. Oncolytic Virotherapy Promotes Intratumoral T Cell Infiltration and Improves Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 170, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribas, A.; Chesney, J.; Long, G.V.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Dummer, R.; Puzanov, I.; Hoeller, C.; Gajewski, T.F.; Gutzmer, R.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. 1037O MASTERKEY-265: A phase II.I.; randomized, placebo (Pbo)-controlled study of talimogene laherparepvec (T) plus pembrolizumab (P) for unresectable stage IIIB–IVM1c melanoma (MEL). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S868–S869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy, P.K.; Aspromonte, S.; Zloza, A.; Rabkin, S.D.; Kaufman, H.L. MEK inhibition enhances oncolytic virus immunotherapy through increased tumor cell killing and T cell activation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaau0417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Ramachandran, M.; Jin, C.; Quijano-Rubio, C.; Martikainen, M.; Yu, D.; Essand, M. Characterization of virus-mediated immunogenic cancer cell death and the consequences for oncolytic virus-based immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamano, T.; Kubo, S.; Fukumoto, M.; Yano, A.; Mawatari-Furukawa, Y.; Okamura, H.; Tomita, N. Whole cell vaccination using immunogenic cell death by an oncolytic adenovirus is effective against a colorectal cancer model. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 16031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarze, J.K.; Awada, G.; Cras, L.; Tijtgat, J.; Forsyth, R.; Dufait, I.; Tuyaerts, S.; Van Riet, I.; Neyns, B. Intratumoral Combinatorial Administration of CD1c (BDCA-1)+ Myeloid Dendritic Cells Plus Ipilimumab and Avelumab in Combination with Intravenous Low-Dose Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: A Phase IB Clinical Trial. Vaccines 2020, 8, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalus, P.; De Munck, J.; Vanbellingen, S.; Carreer, L.; Laeremans, T.; Broos, K.; Dufait, I.; Schwarze, J.K.; Van Riet, I.; Neyns, B.; et al. Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Induces Immunogenic Cell Death Resulting in Maturation of BDCA-1+ Myeloid Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094865
Kalus P, De Munck J, Vanbellingen S, Carreer L, Laeremans T, Broos K, Dufait I, Schwarze JK, Van Riet I, Neyns B, et al. Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Induces Immunogenic Cell Death Resulting in Maturation of BDCA-1+ Myeloid Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094865
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalus, Philipp, Jolien De Munck, Sarah Vanbellingen, Laura Carreer, Thessa Laeremans, Katrijn Broos, Inès Dufait, Julia K. Schwarze, Ivan Van Riet, Bart Neyns, and et al. 2022. "Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Induces Immunogenic Cell Death Resulting in Maturation of BDCA-1+ Myeloid Dendritic Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094865
APA StyleKalus, P., De Munck, J., Vanbellingen, S., Carreer, L., Laeremans, T., Broos, K., Dufait, I., Schwarze, J. K., Van Riet, I., Neyns, B., Breckpot, K., & Aerts, J. L. (2022). Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Induces Immunogenic Cell Death Resulting in Maturation of BDCA-1+ Myeloid Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094865





