Drenched Silicon Suppresses Disease and Insect Pests in Coffee Plant Grown in Controlled Environment by Improving Physiology and Upregulating Defense Genes
Abstract
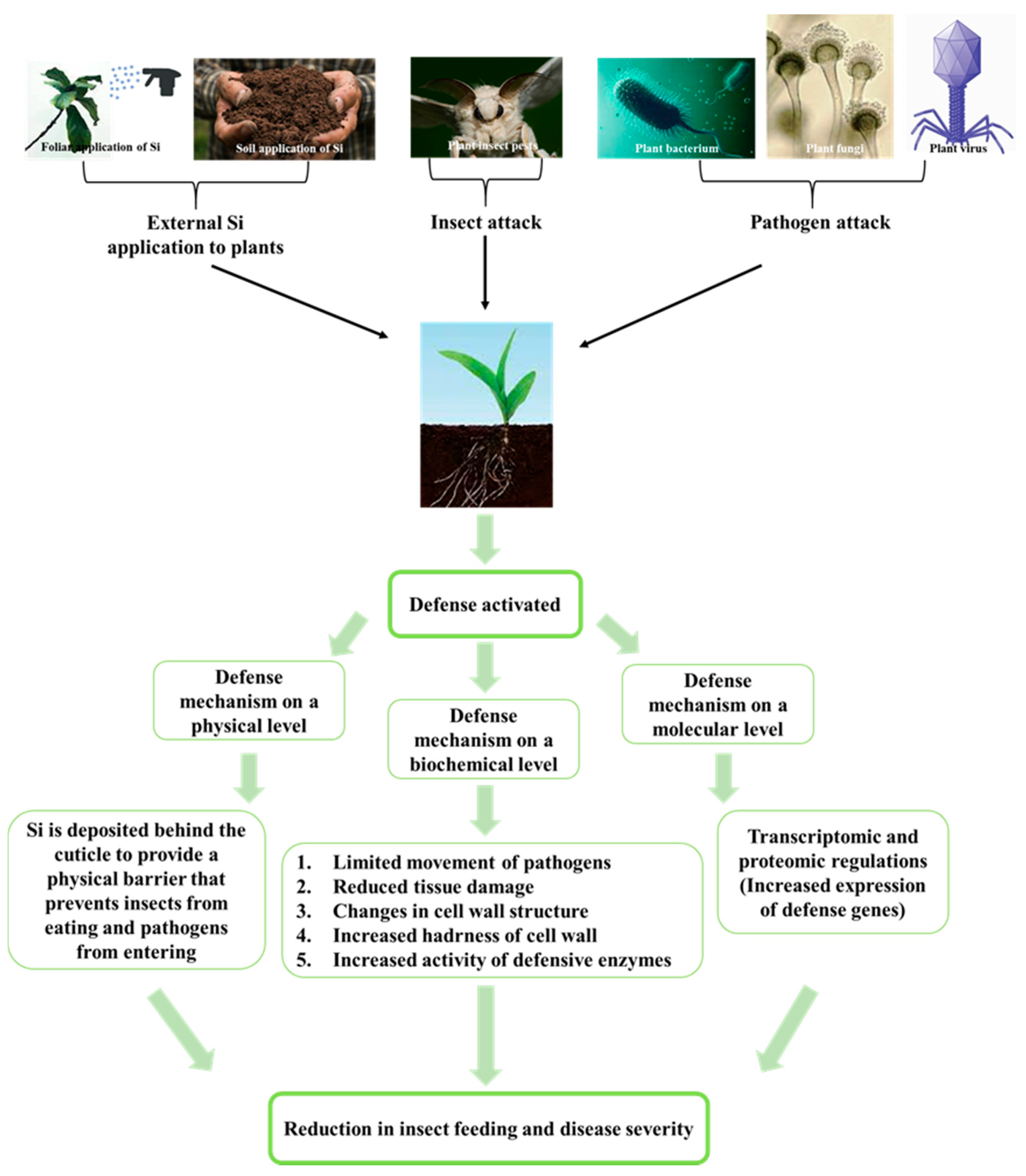
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphology and Plant Growth Parameters
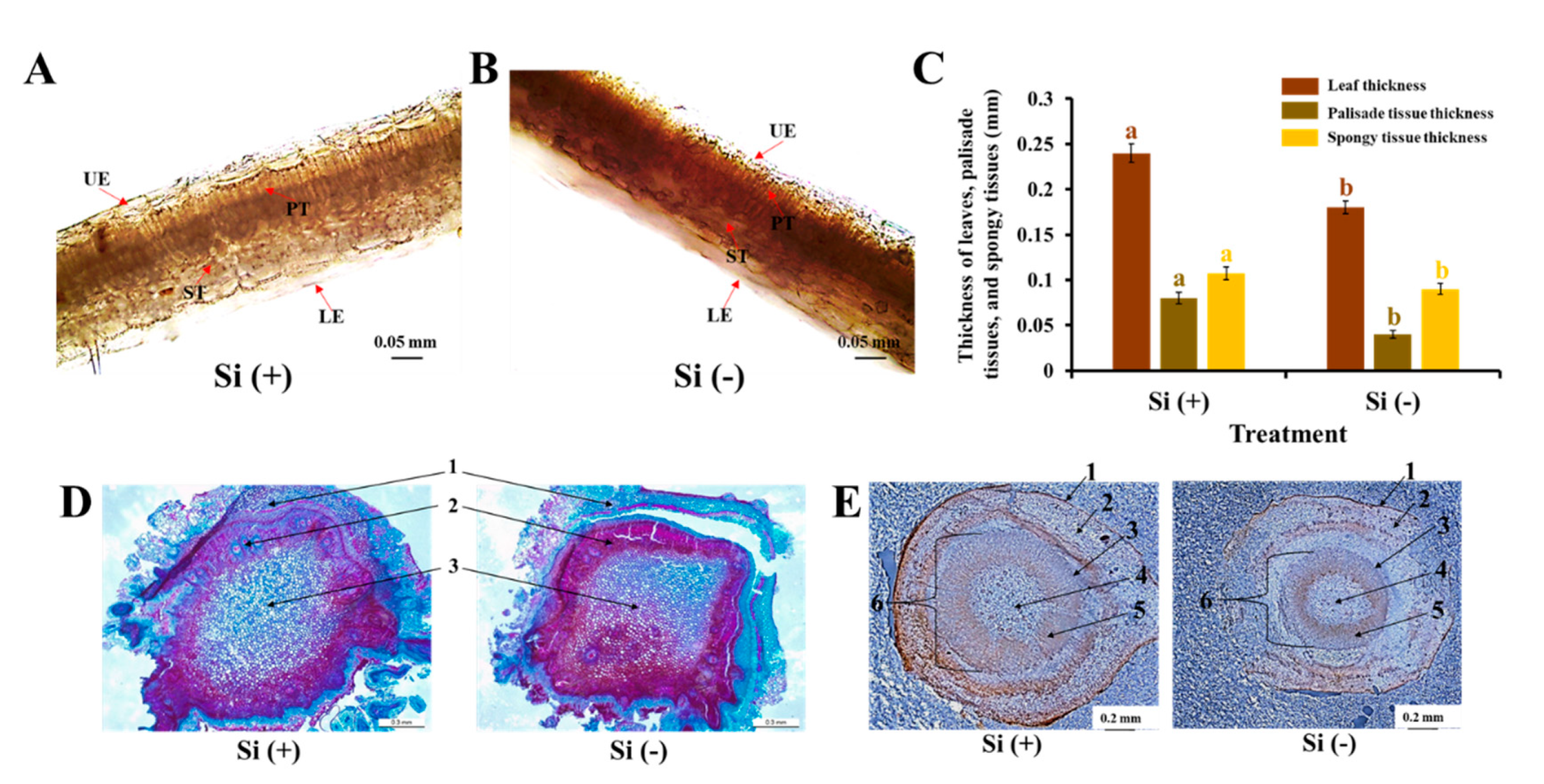
2.2. Anatomical Features of Leaves, Stems, and Roots
2.3. Morphological Characteristics of Stomata
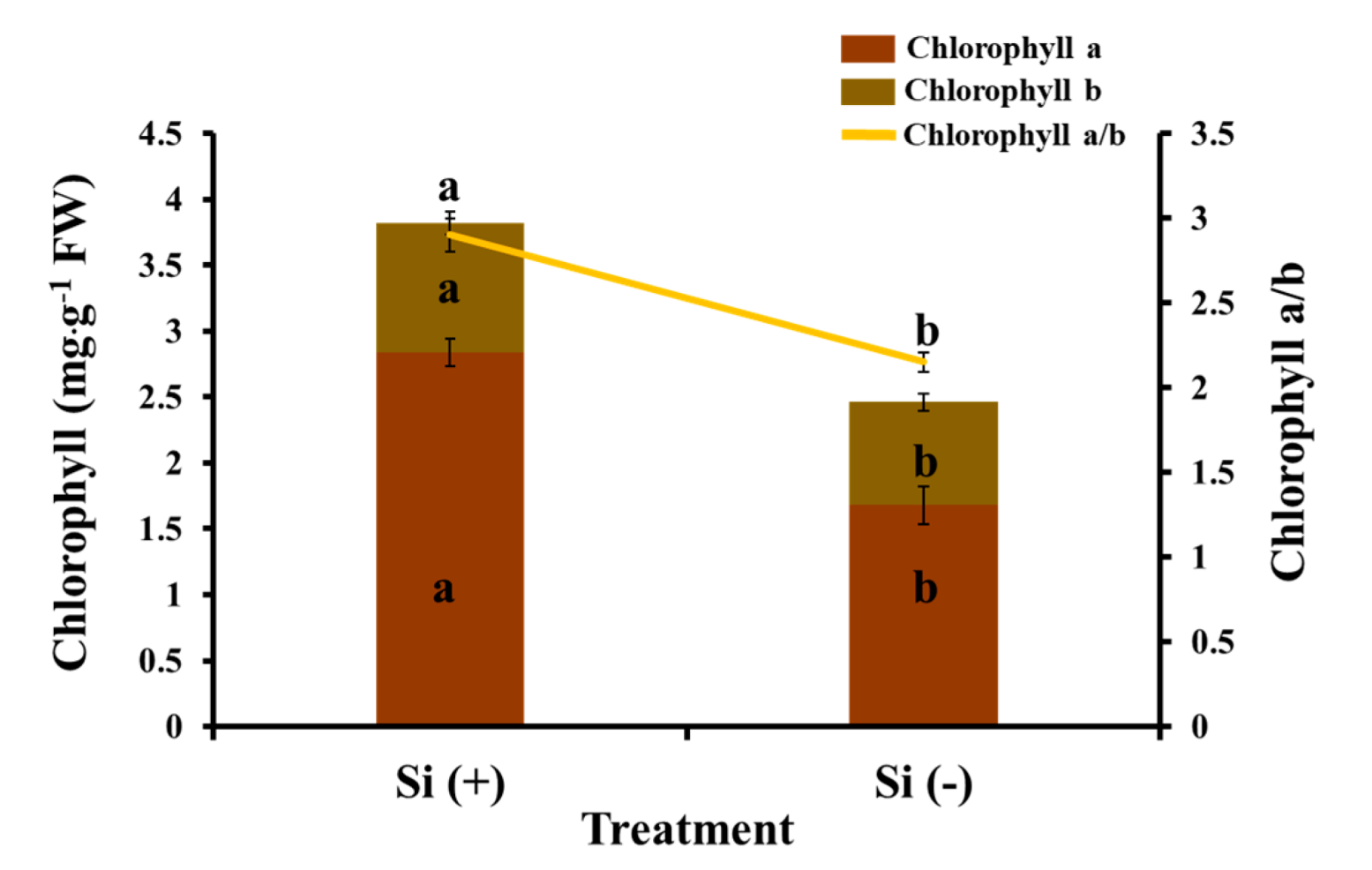
2.4. Chlorophyll Content, Photosynthesis, and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics
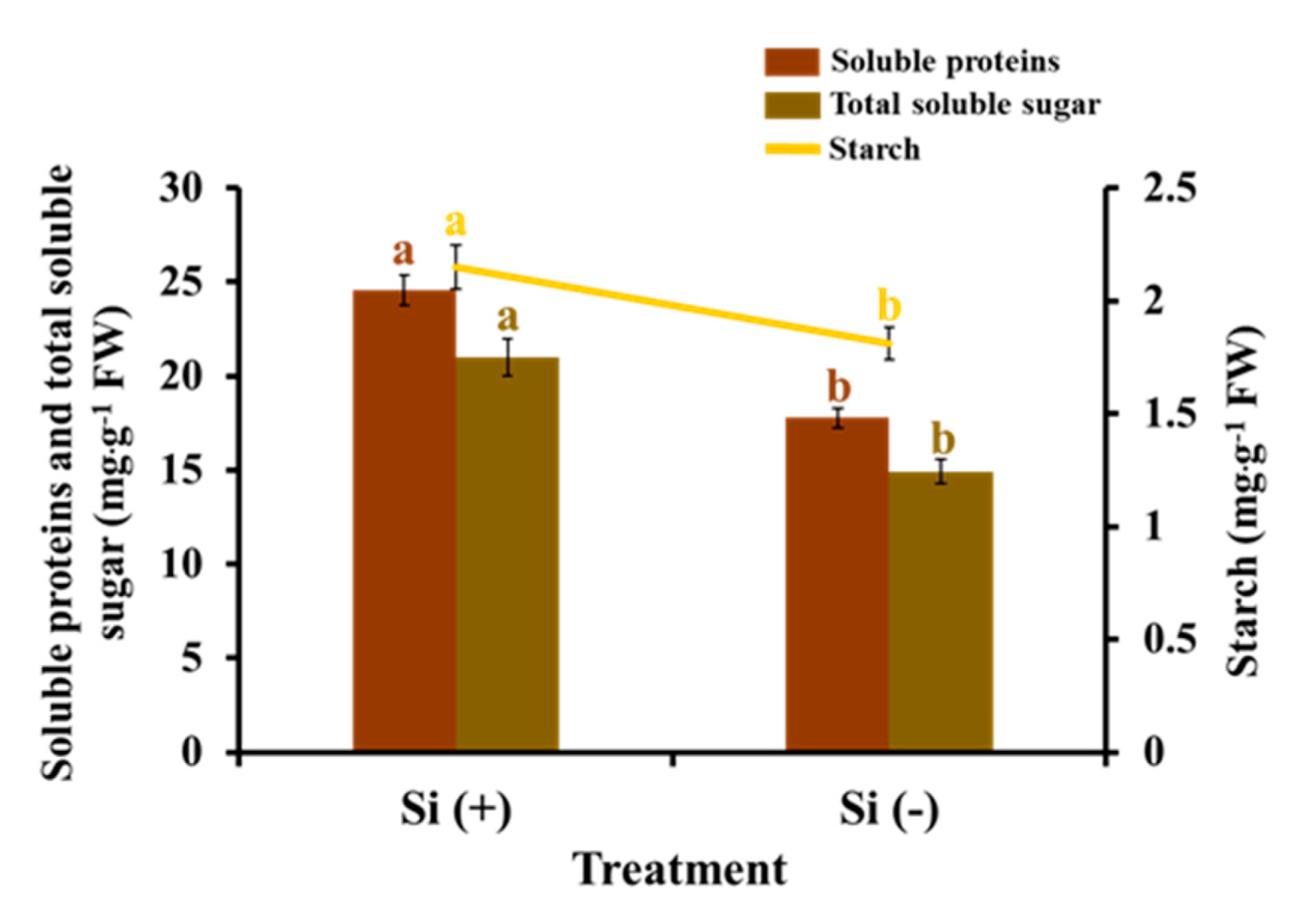
2.5. Carbohydrates and Soluble Proteins
2.6. Root Activity
2.7. Enzymatic Activity
2.8. Tissue Mineral Content
2.9. Gene Expression
3. Discussion
3.1. Si Mitigates Biotic Stress in Plants: Physical and Mechanical Level
3.2. Si Mitigates Biotic Stress in Plants: Physiological Level
3.3. Si Mitigates Biotic Stress in Plants: Molecular Level
3.4. An Environmentally Friendly Alternative: Si
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Supplementary Si Treatments
4.3. Measurements of the Morphological Parameters
4.4. Anatomical Features of Leaves, Stems, and Roots
4.5. Stomatal Density and Morphological Characteristics
4.6. Chlorophyll Content
4.7. Measurements of Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
4.8. Accumulation of Carbohydrates and Soluble Proteins
4.9. Root Activity
4.10. Enzyme Activities
4.11. Determination of Tissue Mineral Content
4.12. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Verification
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorito, M.; Woo, S.L. Trichoderma: A multi-purpose tool for integrated pest management. In Principles of Plant-Microbe Interactions; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, G.; Jindal, V.; Mohindru, B. Crop losses due to insect pests: Global and Indian scenario. Indian J. Entomol. 2015, 77, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiser, D.G. A nectria disease of coffee in western Guatemala. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1945, 32, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A. Agroecology: The Science of Sustainable Agriculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; 433p. [Google Scholar]
- Giese, A.C. Ultraviolet radiation and cell division. Nuclear sensitivity: Effect of irradiation of sea urchin sperm. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 1939, 14, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, N.; de Tombeur, F.; Walgraffe, Y.; Cornélis, J.T.; Verheggen, F.J. Silicon and plant natural defenses against insect pests: Impact on plant volatile organic compounds and cascade effects on multitrophic interactions. Plants 2019, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seal, P.; Das, P.; Biswas, A.K. Versatile potentiality of silicon in mitigation of biotic and abiotic stresses in plants: A review. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zargar, S.M.; Mahajan, R.; Bhat, J.A.; Nazir, M.; Deshmukh, R. Role of silicon in plant stress tolerance: Opportunities to achieve a sustainable cropping system. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datnoff, L.E.; Elmer, W.H.; Huber, D.M. Mineral Nutrition and Plant Disease; American Phytopathological Society (APS Press): Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qu, G.; Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Liang, D. Alleviation of adverse effects of drought stress on wheat seed germination using atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Farid, M.; Adrees, M.; Bharwana, S.A.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Abbas, F. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 15416–15431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.N.S.; Silva Júnior, G.B.D.; Prado, R.D.M.; David, C.H.O.D.; Souza Junior, J.P.D.; Teodoro, P.E. Silicon mitigates ammonium toxicity in plants. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarie, S.; Uchida, H.; Agata, W.; Kubota, F.; Kaufman, P.B. Effects of silicon on transpiration and leaf conductance in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Prod. Sci. 1998, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Hu, J.; Jeong, B.R. Method of silicon application affects quality of strawberry daughter plants during cutting propagation in hydroponic substrate system. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Yang, F.; Xu, H. Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 123, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Nikolic, M.; Bélanger, R.; Gong, H.; Song, A. Silicon-mediated tolerance to metal toxicity. In Silicon in Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 83–122. [Google Scholar]
- Resende, R.S.; Rodrigues, F.Á.; Costa, R.V.; Silva, D.D. Silicon and fungicide effects on anthracnose in moderately resistant and susceptible sorghum lines. J. Phytopathol. 2013, 161, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Xue, G.; Cui, P.; Fan, F.; Liu, H.; Yin, C.; Sun, W.; Liang, Y. The role of silicon in enhancing resistance to bacterial blight of hydroponic- and soil-cultured rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zellner, W.; Frantz, J.; Leisner, S. Silicon delays tobacco ringspot virus systemic symptoms in Nicotiana tabacum. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chérif, M.; Benhamou, N.; Menzies, J.G.; Bélanger, R. Silicon induced resistance in cucumber plants against Pythium ultimum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1992, 41, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, A.A.; Rodrigues, F.Á.; Baroni, J.C.P.; Soares, G.C.B.; Rodriguez, M.A.D.; Pereira, O.L. Silicon suppresses fusarium wilt development in banana plants. J. Phytopathol. 2012, 160, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, W.; Tayyab, M.; Khalil, F.; Hua, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.Y. Silicon-mediated plant defense against pathogens and insect pests. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.P.; Verma, K.K.; Tian, D.D.; Zhang, X.Q.; Liang, Y.J.; Huang, X.; Li, C.N.; Li, Y.R. Exploration of silicon functions to integrate with biotic stress tolerance and crop improvement. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.K.; Singh, P.; Song, X.P.; Malviya, M.K.; Singh, R.K.; Chen, G.L.; Solomon, S.; Li, Y.R. Mitigating climate change for sugarcane improvement: Role of silicon in alleviating abiotic stresses. Sugar Tech. 2020, 22, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauteux, F.; Rémus-Borel, W.; Menzies, J.G.; Bélanger, R.R. Silicon and plant disease resistance against pathogenic fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 249, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, O.L.; Keeping, M.G.; Meyer, J.H. Silicon-augmented resistance of plants to herbivorous insects: A review. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2009, 155, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, O.L.; Padula, M.P.; Zeng, R.; Gurr, G.M. Silicon: Potential to promote direct and indirect effects on plant defense against arthropod pests in agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooke, J.; Leishman, M.R. Consistent alleviation of abiotic stress with silicon addition: A meta-analysis. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1340–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Ahn, Y.K. Silicon regulates potential genes involved in major physiological processes in plants to combat stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, K.K.; Song, X.P.; Verma, C.L.; Malviya, M.K.; Guo, D.J.; Rajput, V.D.; Sharma, A.; Wei, K.J.; Chen, G.L.; Solomon, S. Predication of photosynthetic leaf gas exchange of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) leaves in response to leaf positions to foliar spray of potassium salt of active phosphorus under limited water irrigation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 2396–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, D.; Deshmukh, R.; Sonah, H.; Menzies, J.G.; Reynolds, O.; Ma, J.F.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Bélanger, R.R. The controversies of silicon’s role in plant biology. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, M.; Hausman, J.F.; Lutts, S.; Guerriero, G. Silicon and plants: Current knowledge and technological perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakr, N. The role of silicon (Si) in increasing plant resistance against fungal diseases. Hell. Plant Prot. J. 2016, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, M.A.; Dietz, K.J. Silicon as versatile player in plant and human biology: Overlooked and poorly understood. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frew, A.; Weston, L.A.; Reynolds, O.L.; Gurr, G.M. The role of silicon in plant biology: A paradigm shift in research approach. Ann. Bot. 2018, 121, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chérif, M.; Asselin, A.; Bélanger, R. Defense responses induced by soluble silicon in cucumber roots infected by Pythium spp. Phytopathology 1994, 84, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.A.; Dallagnol, L.J.; Duarte, H.S.S.; Datnoff, L.E. Silicon control of foliar diseases in monocots and dicots. In Silicon and Plant Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 67–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N. A cooperative system of silicon transport in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNaughton, S.; Tarrants, J. Grass leaf silicification: Natural selection for an inducible defense against herbivores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 790–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, O. Silica phytoliths in angiosperms: Phylogeny and early evolutionary history. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Kim, K.W.; Park, E.W.; Choi, D. Silicon-induced cell wall fortification of rice leaves: A possible cellular mechanism of enhanced host resistance to blast. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massey, F.P.; Ennos, A.R.; Hartley, S.E. Grasses and the resource availability hypothesis: The importance of silica-based defences. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeer, M.; Telugu, U.; Voleti, S.; Padmakumari, A. Soil application of silicon reduces yellow stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas (Walker) damage in rice. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, F.P.; Hartley, S.E. Experimental demonstration of the antiherbivore effects of silica in grasses: Impacts on foliage digestibility and vole growth rates. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 273, 2299–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frew, A.; Powell, J.R.; Sallam, N.; Allsopp, P.G.; Johnson, S.N. Trade-offs between silicon and phenolic defenses may explain enhanced performance of root herbivores on phenolic-rich plants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryalls, J.M.; Hartley, S.E.; Johnson, S.N. Impacts of silicon-based grass defences across trophic levels under both current and future atmospheric CO2 scenarios. Biol. Lett. 2017, 13, 20160912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bockhaven, J.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Höfte, M. Towards establishing broad-spectrum disease resistance in plants: Silicon leads the way. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domiciano, G.P.; Cacique, I.S.; Chagas Freitas, C.; Filippi, M.C.C.; DaMatta, F.M.; Do Vale, F.X.R.; Rodrigues, F.Á. Alterations in gas exchange and oxidative metabolism in rice leaves infected by Pyricularia oryzae are attenuated by silicon. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Han, Y.; Li, P.; Li, F.; Ali, S.; Hou, M. Silicon amendment is involved in the induction of plant defense responses to a phloem feeder. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debona, D.; Rodrigues, F.; Rios, J.; Nascimento, K.; Silva, L. The effect of silicon on antioxidant metabolism of wheat leaves infected by Pyricularia oryzae. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramputh, A.; Arnason, J.; Cass, L.; Simmonds, J. Reduced herbivory of the European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis) on corn transformed with germin, a wheat oxalate oxidase gene. Plant Sci. 2002, 162, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, L.F.; Tenhaken, R.; Lamb, C. Function of oxidative cross-linking of cell wall structural proteins in plant disease resistance. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etesami, H.; Jeong, B.R. Silicon (Si): Review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Sheikh, M.A.; Jamil, A.; Basra, S.M.A. Seed priming with sodium silicate enhances seed germination and seedling growth in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under water deficit stress induced by polyethylene glycol. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2013, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Yao, X.; Cai, K.; Chen, J. Silicon alleviates drought stress of rice plants by improving plant water status, photosynthesis and mineral nutrient absorption. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 142, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Chen, B.; Wen, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.D.; Li, J.W.; Xu, Z.C.; Huang, W.X. Effects of exogenous silicon on growth, leaf photosynthesis and physiological indexes of tobacco seedlings under drought stress. Biotechnol. Bull. 2019, 35, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Chang, H.; Yu, X.; Xu, H. Effects of silicon on rice leaf photosynthesis and ultrastructure. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2011, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.C.; Li, Q.F.; Shu, L.Z.; Zhang, J.Y. Preliminary explanation of the mechanism about effects of silicon on maize seed germination and seedling growth. Acta Agron. Sin. 2002, 28, 665–669. [Google Scholar]
- Kvedaras, O.L.; An, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Gurr, G. Silicon enhances natural enemy attraction and biological control through induced plant defences. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Han, L.; Reynolds, O.L.; Zeng, R.; Wu, J.; Shao, Y.; You, M.; Gurr, G.M. Silicon supplementation alters the composition of herbivore induced plant volatiles and enhances attraction of parasitoids to infested rice plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savant, N.; Snyder, G.; Datnoff, L. Silicon management and sustainable rice production. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 58, pp. 151–199. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Wallis, C.M.; Uddin, W. Silicon-induced systemic defense responses in perennial ryegrass against infection by Magnaporthe oryzae. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geromel, C.; Ferreira, L.P.; Guerreiro, S.M.C.; Cavalari, A.A.; Pot, D.; Pereira, L.F.P.; Leroy, T.; Vieira, L.G.E.; Mazzafera, P.; Marraccini, P. Biochemical and genomic analysis of sucrose metabolism during coffee (Coffea arabica) fruit development. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3243–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, A.; Ságio, S.; Chalfun-Junior, A.; Paiva, L. In silico characterization of putative members of the coffee (Coffea arabica) ethylene signaling pathway. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauss, H.; Seehaus, K.; Franke, R.; Gilbert, S.; Dietrich, R.A.; Kröger, N. Silica deposition by a strongly cationic proline-rich protein from systemically resistant cucumber plants. Plant J. 2003, 33, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauteux, F.; Chain, F.; Belzile, F.; Menzies, J.G.; Bélanger, R.R. The protective role of silicon in the Arabidopsis–powdery mildew pathosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17554–17559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pi, N.; Tam, N.; Wu, Y.; Wong, M.H. Root anatomy and spatial pattern of radial oxygen loss of eight true mangrove species. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 90, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzin, S.E. Plant Microtechnique and Microscopy; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 198. [Google Scholar]
- Sack, L.; Buckley, T.N. The developmental basis of stomatal density and flux. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N.; Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasseur, F.; Pantin, F.; Vile, D. Changes in light intensity reveal a major role for carbon balance in Arabidopsis responses to high temperature. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.X.; Xue, J.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Xue, Y.Q.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, H.D.; Zhang, X.X. Proteomic analysis of tree peony (Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’) seed germination affected by low temperature. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 224, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, B.R. Pre-and/or postharvest silicon application prolongs the vase life and enhances the quality of cut peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) flowers. Plants 2021, 10, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, S.; Soundararajan, P.; Jeong, B.R. Proteomic and antioxidant analysis elucidates the underlying mechanism of tolerance to hyperhydricity stress in vitro shoot cultures of Dianthus caryophyllus. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Zhang, W.H.; Hao, Z.B.; Li, X.R.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.M. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 118–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aeibi, H.; Bergmeyer, H. Methods in Enzymatic Analysis; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 3, p. 673. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, F.J.; Penel, C.; Greppin, H. Peroxidase release induced by ozone in sedum album leaves: Involvement of Ca2+. Plant Physiol. 1984, 74, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becana, M.; Tejo, P.A.; Irigoyen, J.J.; Sánchez-Díaz, M. Some enzymes of hydrogen peroxide metabolism in leaves and root nodules of Medicago sativa. Plant Physiol. 1986, 82, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar]
- Doehlert, D.C.; Kuo, T.M.; Felker, F.C. Enzymes of sucrose and hexose metabolism in developing kernels of two inbreds of maize. Plant Physiol. 1988, 86, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.S.; Cao, X.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Song, P. Studies on the relationship between the grain sink strength and its starch accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron. Sin. 1994, 20, 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Högberg, P.; Granström, A.; Johansson, T.; Lundmark-Thelin, A.; Näsholm, T. Plant nitrate reductase activity as an indicator of availability of nitrate in forest soils. Can. J. For. Res. 1986, 16, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Jeong, B.R. Putative silicon transporters and effect of temperature stresses and silicon supplementation on their expressions and tissue silicon content in poinsettia. Plants 2020, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, N.; Bausher, M.G.; Lee, S.B.; Jansen, R.K.; Daniell, H. The complete nucleotide sequence of the coffee (Coffea arabica L.) chloroplast genome: Organization and implications for biotechnology and phylogenetic relationships amongst angiosperms. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2007, 5, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
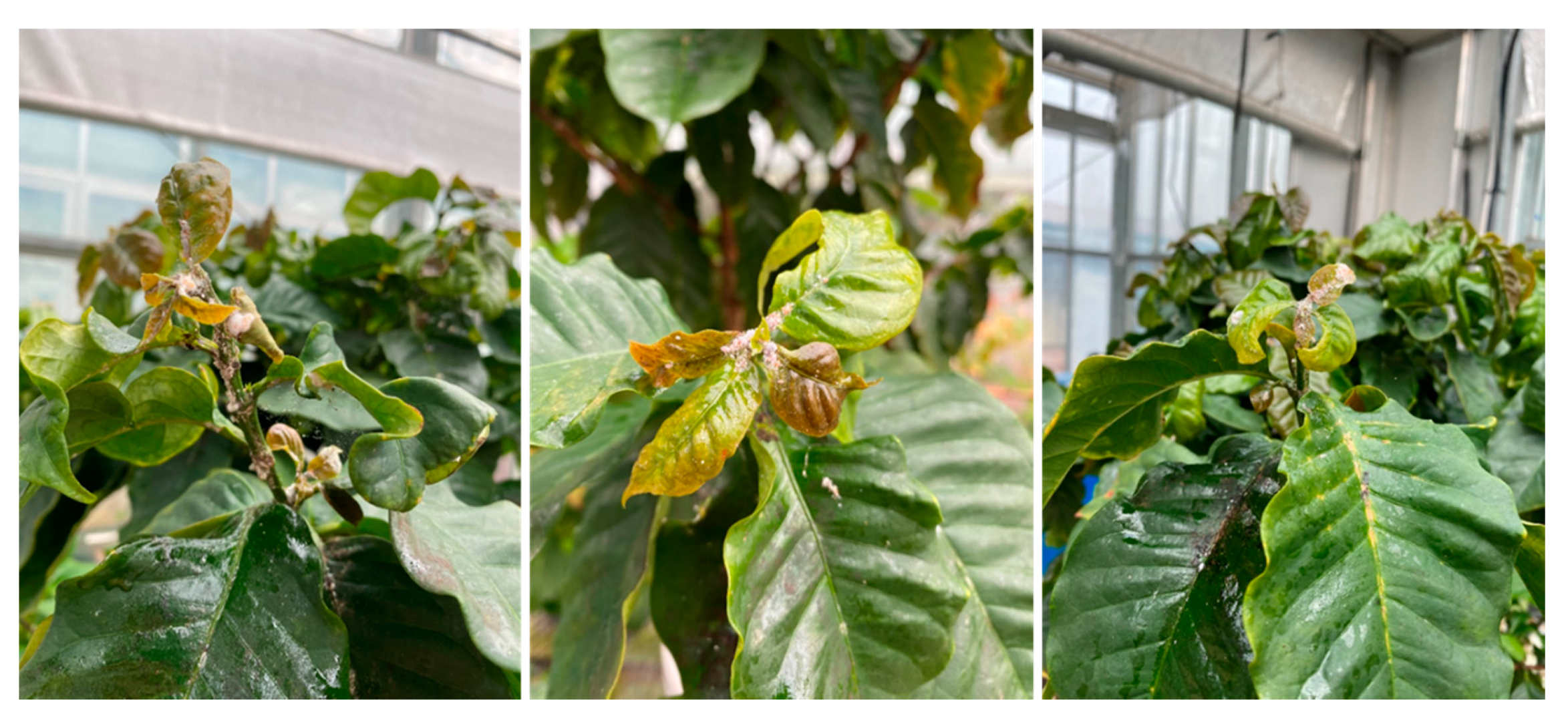



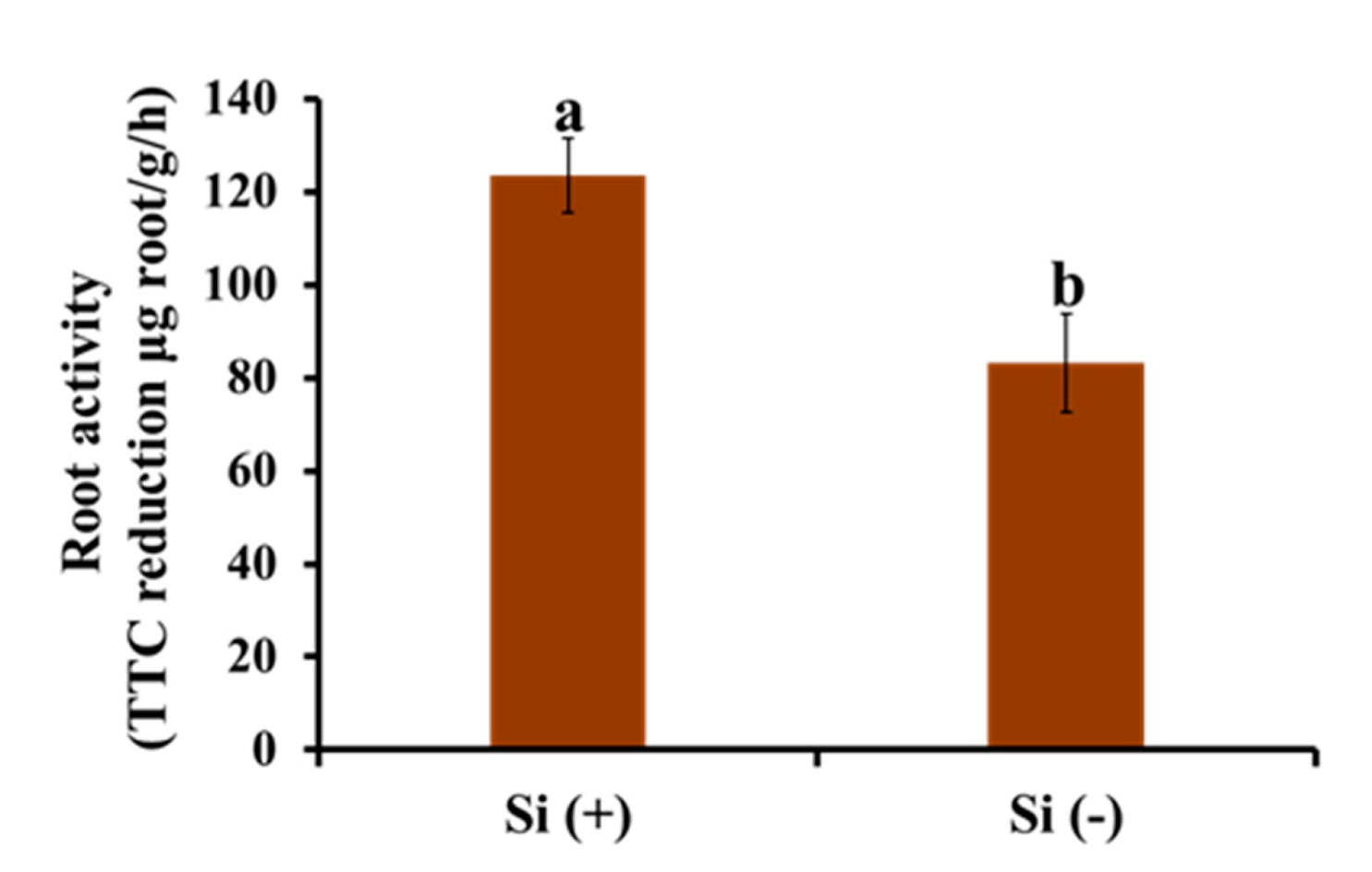
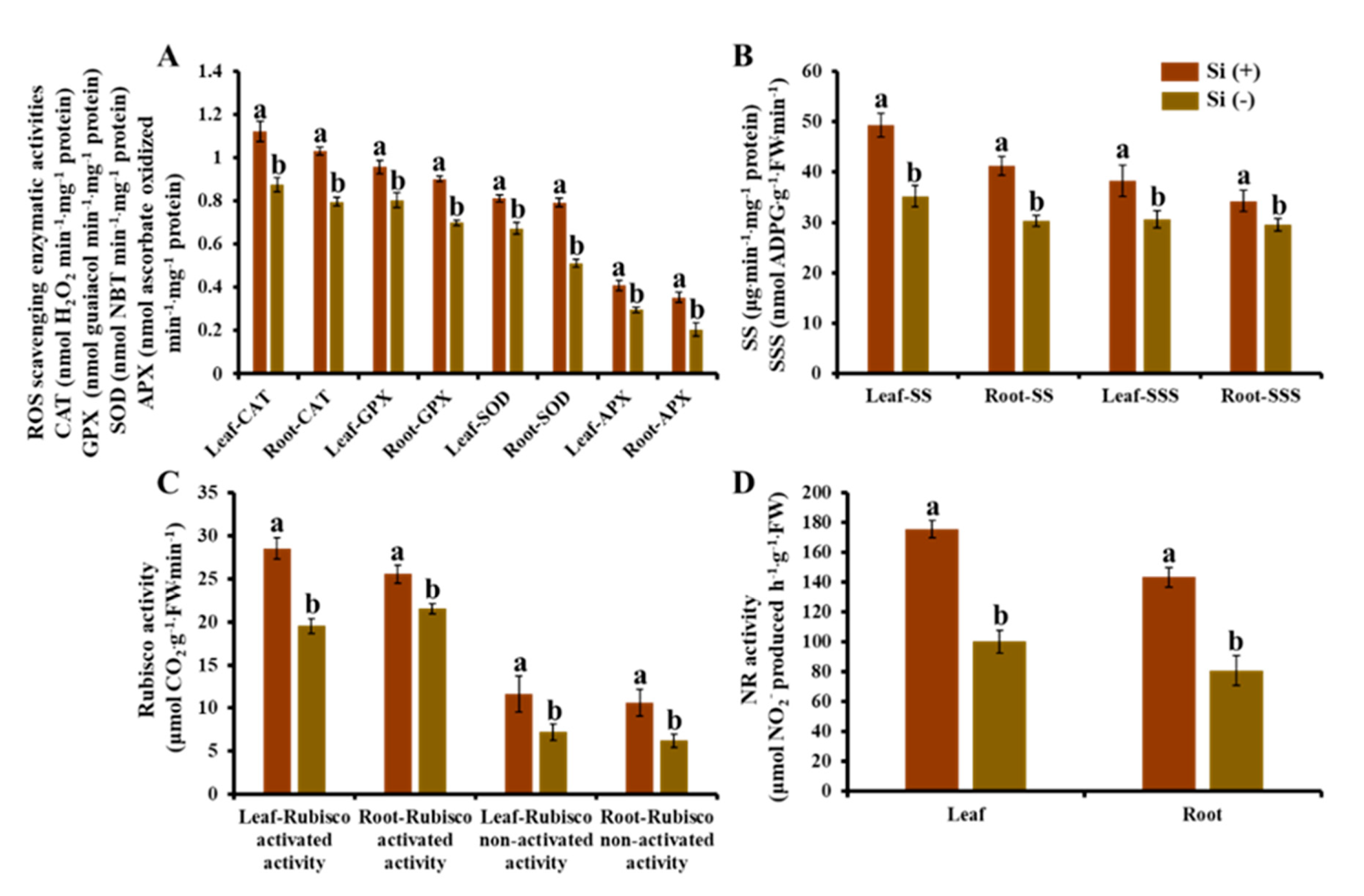
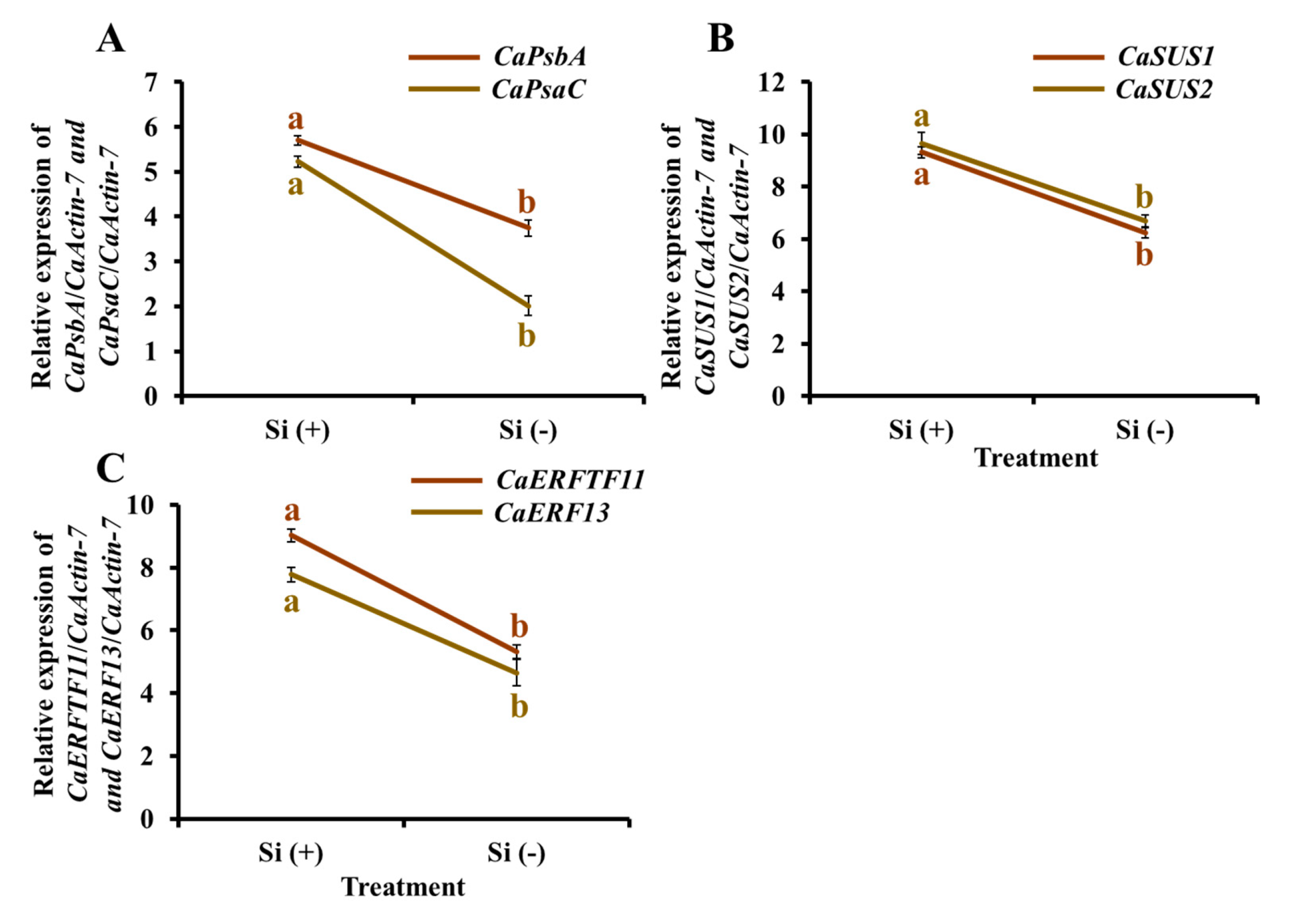

| Treatment 1 | Shoot | Leaf | Root | Symptoms of Disease or Insects | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Height (cm) | Canopy Diameter (cm) | Stem Diameter (mm) | FW (g) 2 | DW (g) 3 | Number | Length (cm) | Width (cm) | No. of Withered Leaves (Chlorosis) | The Adaxial Angle of the Top1st Leaves (°) | Length (cm) | FW (g) 2 | DW (g) 3 | ||
| MNS-Si (+) | 13.8 a 4 | 19.2 a | 3.1 a | 8.9 a | 2.7 a | 16.3 a | 10.1 a | 5.3 a | 0.1 b | 45.3 b | 20.0 a | 5.0 a | 0.9 a | No |
| MNS-Si (−) | 9.5 b | 11.3 b | 2.2 b | 5.3 b | 1.5 b | 11.4 b | 6.9 b | 3.8 b | 3.4 a | 88.7 a | 15.0 b | 1.2 b | 0.2 b | Yes |
| Treatment 1 | Pn 2 (μmol CO2.m−2·s−1) | Tr 3 (mmol H2O m−2·s−1) | Gs 4 (mol.H2O m−2·s−1) | Ci 5 (μmol CO2mol−1) | Fv/Fm 6 | Fv′/Fm′ 7 | NPQ 8 | qP9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNS-Si (+) | 21.54 a 10 | 1.91 b | 1.04 a | 536.47 a | 0.99 a | 0.88 a | 2.97 a | 0.74 a |
| MNS-Si (-) | 18.67 b | 2.68 a | 0.82 b | 467.26 b | 0.79 b | 0.71 b | 1.92 b | 0.54 b |
| Sample (A) 1 | Si (mg L−1) (B) | Si Content (mg g−1 Dry Weight) | Macronutrients (mg g−1 Dry Weight) | Micronutrients (μg g−1 Dry Weight) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | K | Ca | Mg | P | S | B | Cu | Fe | Mn | Zn | |||
| Shoot | 0 | 0.45 d 2 | 219.24 cd | 115.35 c | 60.41 b | 19.14 b | 12.00 b | 3.59 b | 0.19 c | 0.21 a | 0.67 a | 0.66 a | 0.08 b |
| 75 | 0.90 b | 304.19 b | 91.29 d | 72.50 a | 29.36 a | 15.17 a | 3.65 b | 0.10 cd | 0.18 ab | 0.41 b | 0.51 ab | 0.07 b | |
| Root | 0 | 0.58 c | 228.36 c | 209.57 a | 40.29 d | 9.12 cd | 7.56 d | 10.61 a | 0.63 a | 0.10 b | 0.69 a | 0.49 b | 0.13 a |
| 75 | 1.89 a | 327.24 a | 187.87 b | 52.54 c | 11.19 c | 10.14 c | 9.99 a | 0.50 b | 0.09 bc | 0.41 b | 0.38 c | 0.14 a | |
| F-test | A | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | NS | *** | *** |
| B | *** | ** | *** | *** | ** | *** | NS | ** | * | *** | ** | NS | |
| A × B | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ** | ** | *** | |
| Name | Gene ID | Gene bank Number | Description | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaActin-7 | 113701041 | - | Transcript variant X1 | TAGCAACTGGGATGACATGGA | AGTCAAGAGCCACATAGGCA |
| CaPsbA | 4421839 | - | Photosystem II protein D1 | CTGCAGCTATAGGTTTGCACTT | TGCAACAGCAATCCAAGGTC |
| CaPsaC | 4421852 | - | Photosystem I subunit VII | TAGAAATGATACCTTGGGACGGA | ACCCATACTGCGGGTTGTT |
| CaSUS1 | 113691468 | AM087674.1 | Sucrose synthase | GGGTTGCACTTGCTATTCGTC | AGCATCATTGTCTTGCCCTTG |
| CaSUS2 | 113718268 | AM087675 | Sucrose synthase 2-like | GCCGCTCTGAAGACCATTTAG | AGGTGTATCTTGTGGGAGCTTG |
| CaERFTF11 | 113726097 | KF743550.1 | Defense genes transcriptional activator PTI5-like. ERF transcription factor 11 | TTCGCGATTCGACGAGAAATG | TTCCTGTCGATCTAGGTTCAGC |
| CaERF13 | 113726097 | KF278730.1 | Defense genes transcriptional activator PTI5-like. Ethylene response factor 13 | GGCCATGGGGAAAATACGCA | CGTCCCAGACGAAACTTCAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Song, J.; Jeong, B.R. Drenched Silicon Suppresses Disease and Insect Pests in Coffee Plant Grown in Controlled Environment by Improving Physiology and Upregulating Defense Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073543
Yang J, Song J, Jeong BR. Drenched Silicon Suppresses Disease and Insect Pests in Coffee Plant Grown in Controlled Environment by Improving Physiology and Upregulating Defense Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073543
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jingli, Jinnan Song, and Byoung Ryong Jeong. 2022. "Drenched Silicon Suppresses Disease and Insect Pests in Coffee Plant Grown in Controlled Environment by Improving Physiology and Upregulating Defense Genes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073543
APA StyleYang, J., Song, J., & Jeong, B. R. (2022). Drenched Silicon Suppresses Disease and Insect Pests in Coffee Plant Grown in Controlled Environment by Improving Physiology and Upregulating Defense Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073543








