Conformational Stabilization of Gp41-Mimetic Miniproteins Opens Up New Ways of Inhibiting HIV-1 Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
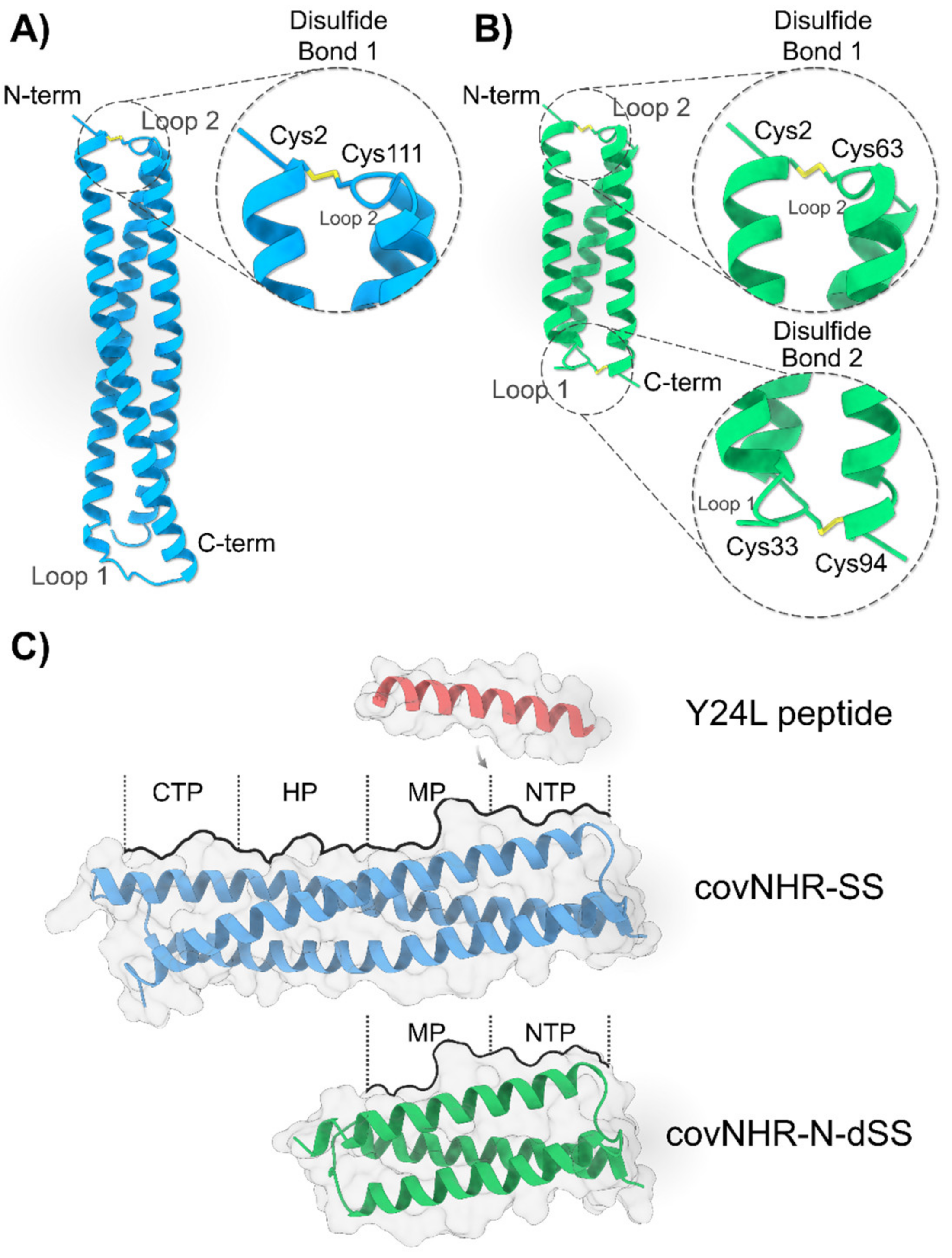
2.1. Design and Stabilization of CovNHR Miniproteins
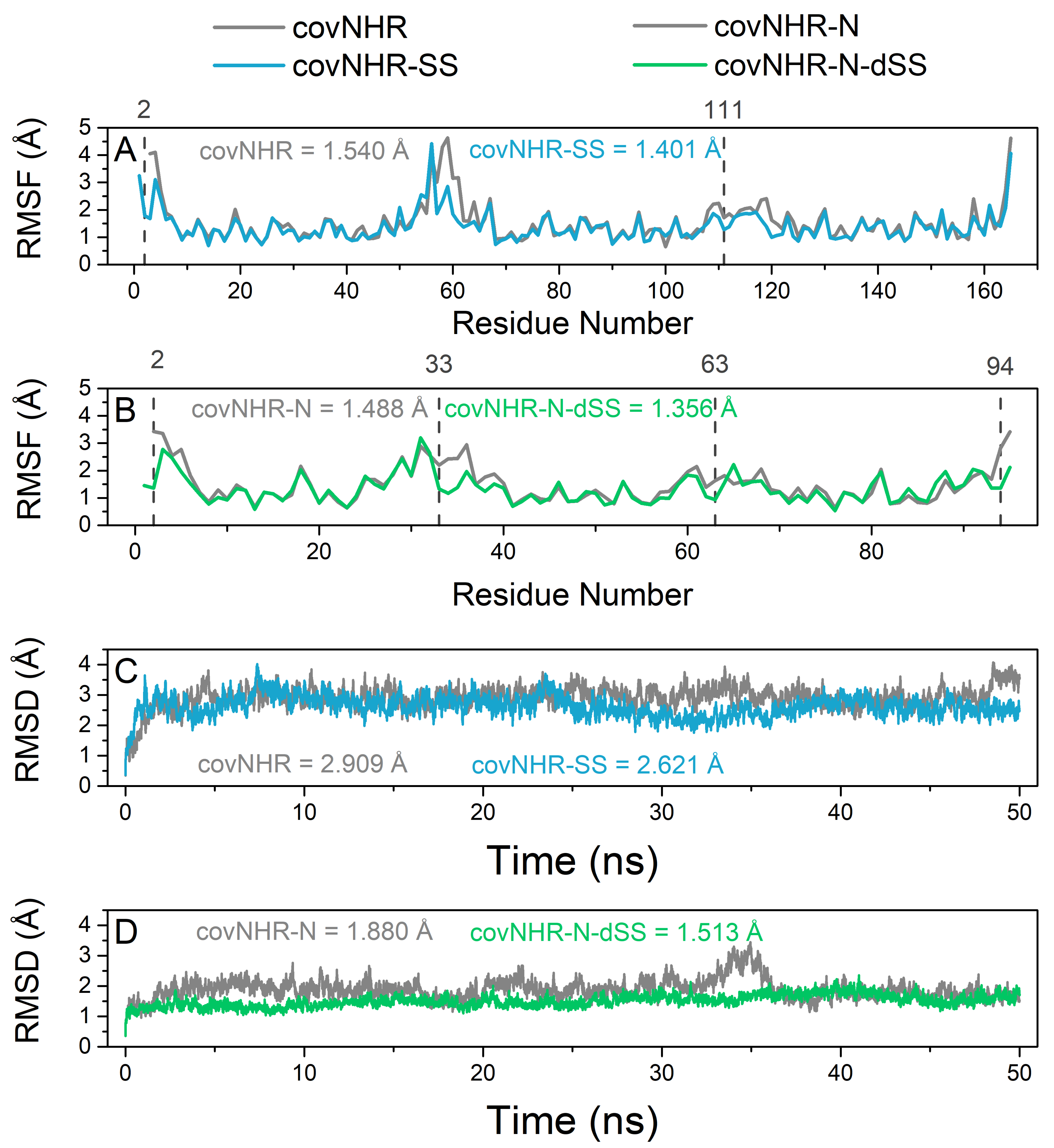
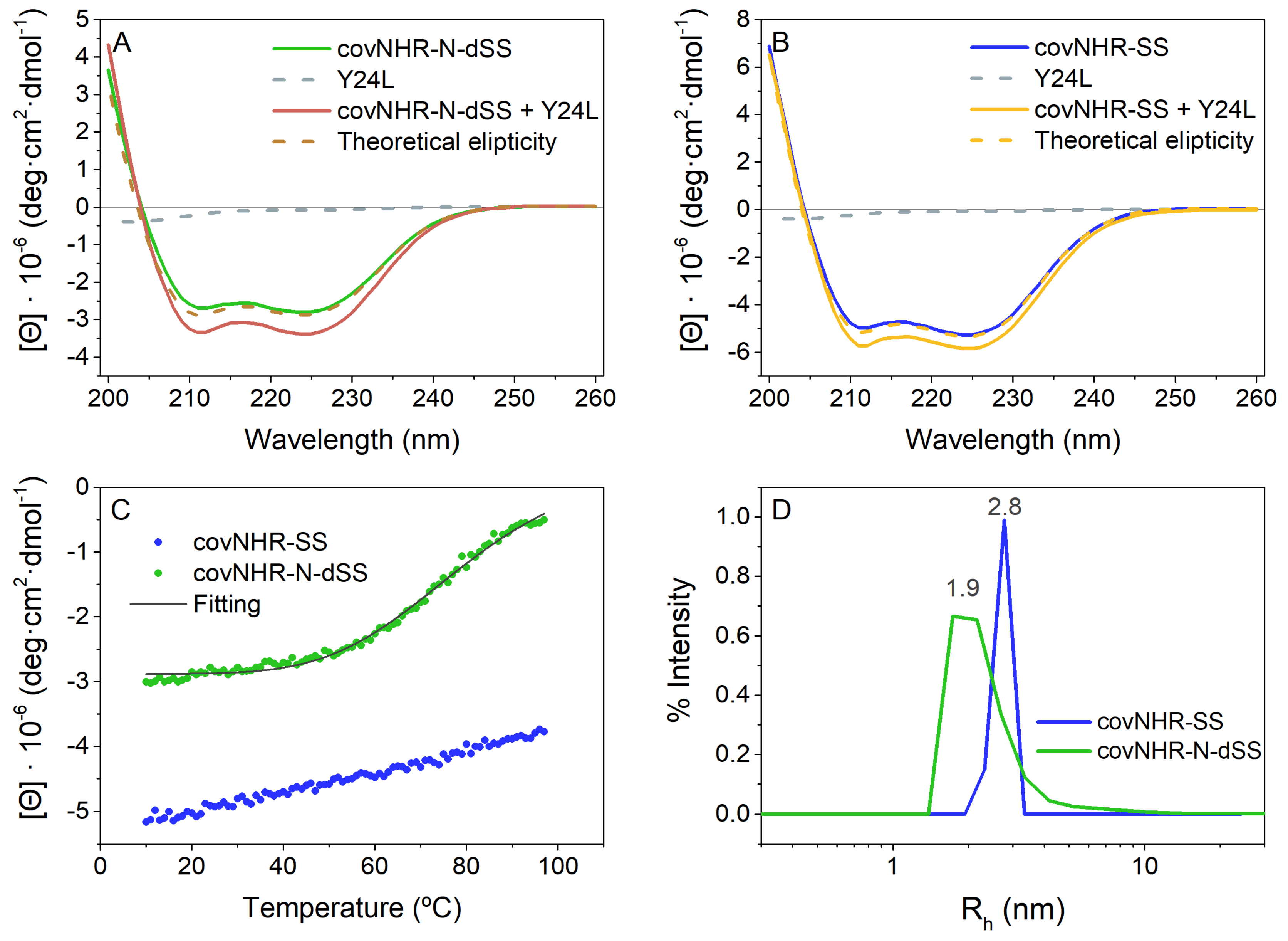
2.2. Biophysical Characterization of CovNHR Variants
2.3. Binding of the CHR Peptide to CovNHR Miniproteins
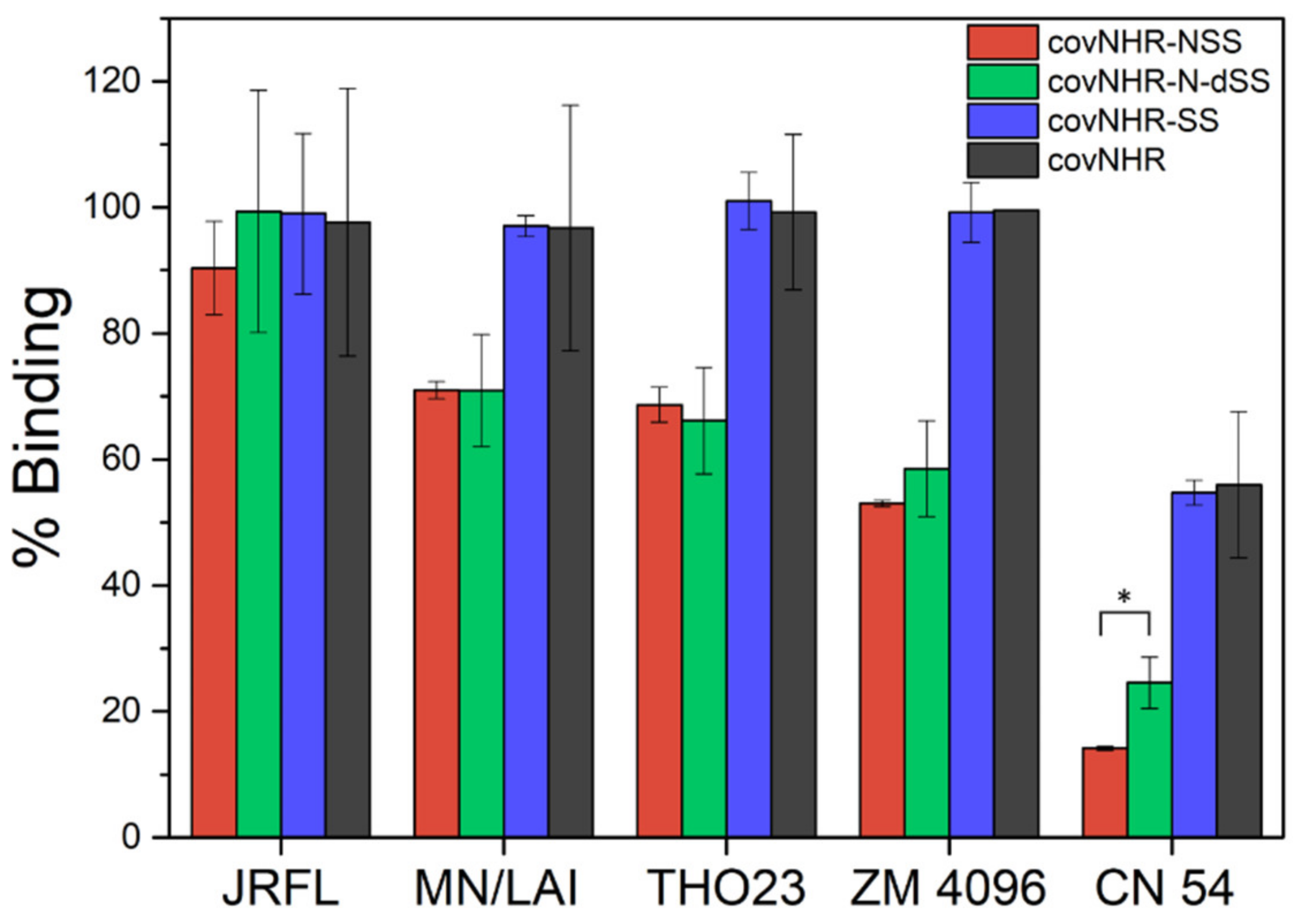
2.4. Binding to Envelope Proteins
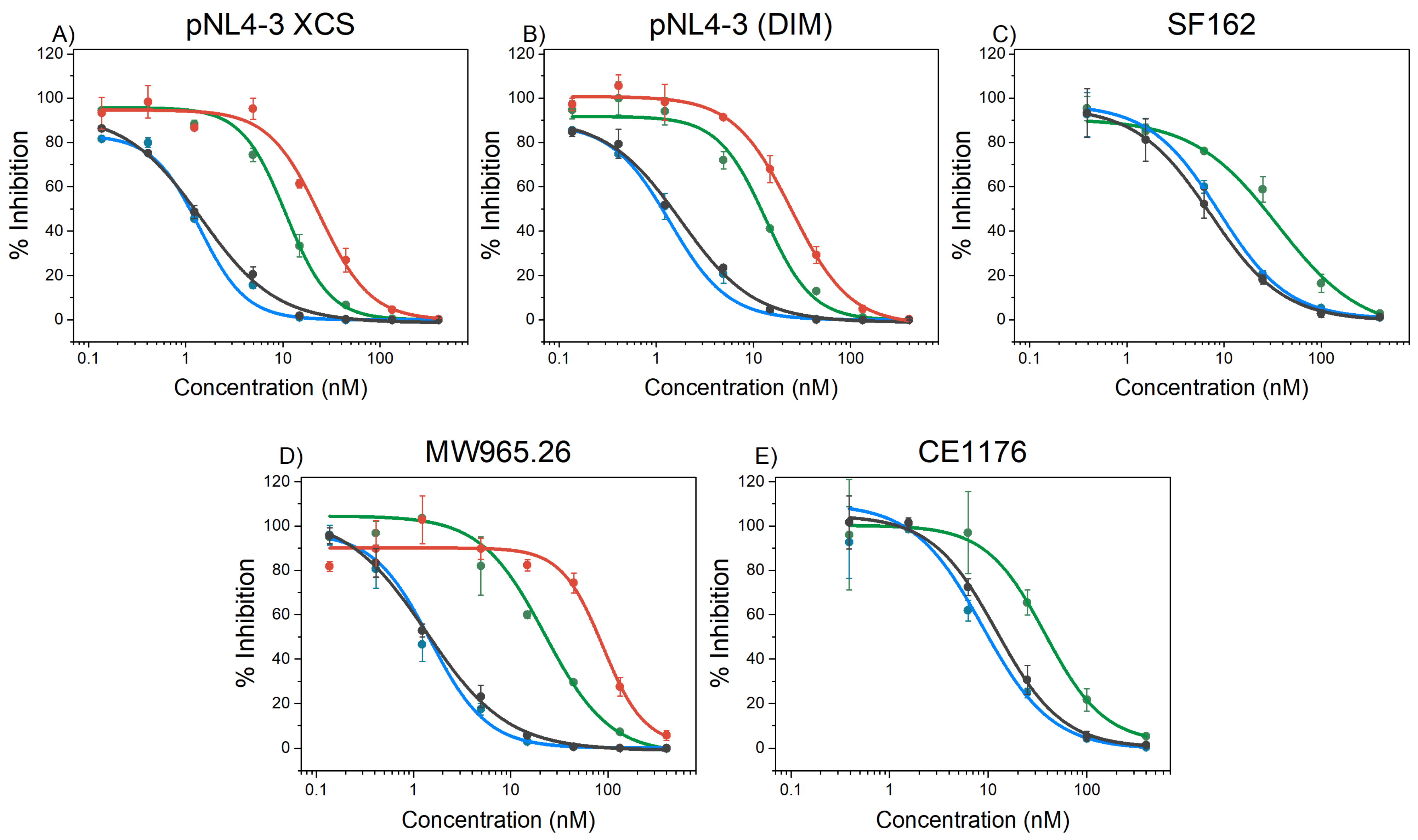
2.5. HIV-1 Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.2. Protein and Peptide Samples
4.3. Circular Dichroism
4.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
4.5. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.6. Binding to HIV-1 Envelope Spikes
4.7. HIV-1 Inhibitory Assays
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLaren, P.J.; Fellay, J. HIV-1 and human genetic variation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Muñoz, M.; Jurado, S.; Morel, B.; Conejero-Lara, F. Conformational flexibility of the conserved hydrophobic pocket of HIV-1 gp41. Implications for the discovery of small-molecule fusion inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L. HIV upsurge in China’s students. Science 2019, 364, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steichen, J.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Pecetta, S.; Ozorowski, G.; Willis, J.R.; Toy, L.; Sok, D.; Liguori, A.; Kratochvil, S.; et al. A generalized HIV vaccine design strategy for priming of broadly neutralizing antibody responses. Science 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng’uni, T.; Chasara, C.; Ndhlovu, Z.M. Major Scientific Hurdles in HIV Vaccine Development: Historical Perspective and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, S.G.; Overbaugh, J.; Phillips, A.; Buchbinder, S. HIV infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.B.; Wilson, I.A. The HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure: Nailing down a moving target. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.A.; Fochtman, B.C.; Rizzo, R.C.; Jacobs, A. Inhibition of HIV Entry by Targeting the Envelope Transmembrane Subunit gp41. Curr. HIV Res. 2016, 14, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, D.M.; Malashkevich, V.N.; Hong, L.H.; Carr, P.A.; Kim, P.S. Inhibiting HIV-1 entry: Discovery of D-peptide inhibitors that target the gp41 coiled-coil pocket. Cell 1999, 99, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, D.M.; Kim, P.S. Design of potent inhibitors of HIV-1 entry from the gp41 N-peptide region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11187–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Fass, D.; Berger, J.M.; Kim, P.S. Core Structure of gp41 from the HIV Envelope Glycoprotein. Cell 1997, 89, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenhorn, W.; Dessen, A.; Harrison, S.C.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C.; Weissenhorn, W.; Dessen, A.; Harrison, S.C.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Atomic structure of the ectodomain from HIV-1 gp41. Nature 1997, 387, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilby, J.M.; Hopkins, S.; Venetta, T.M.; DiMassimo, B.; Cloud, G.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Alldredge, L.; Hunter, E.; Lambert, D.; Bolognesi, D.; et al. Potent suppression of HIV-1 replication in humans by T-20, a peptide inhibitor of gp41-mediated virus entry. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Dai, Q. Potent HIV fusion inhibitors against Enfuvirtide-resistant HIV-1 strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16332–16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-O’donnell, M.; Rivas, F.; Reyes-Zurita, F.J.; Cano-Muñoz, M.; Martinez, A.; Lupiañez, J.A.; Parra, A. Oleanolic Acid Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of HIV-1 Protease. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2886–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, B.D.; VanDemark, A.P.; Heroux, A.; Hill, C.P.; Kay, M.S. Potent D-peptide inhibitors of HIV-1 entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16828–16833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, G.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Zhang, X.Q.; Schooley, R.T.; Chen, B.; Harrison, S.C. Small molecules that bind the inner core of gp41 and inhibit HIV envelope-mediated fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13938–13943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yu, F.; Cai, L.; Debnath, A.K.; Jiang, S. Development of Small-molecule HIV Entry Inhibitors Specifically Targeting gp120 or gp41. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 1074–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.D.; Geleziunas, R.; Bianchi, E.; Lennard, S.; Hrin, R.; Zhang, H.; Lu, M.; An, Z.; Ingallinella, P.; Finotto, M.; et al. A human monoclonal antibody neutralizes diverse HIV-1 isolates by binding a critical gp41 epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14759–14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Synthesized Peptide Inhibitors of HIV-1 gp41-dependent Membrane Fusion. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespillo, S.; Cámara-Artigas, A.; Casares, S.; Morel, B.; Cobos, E.S.; Mateo, P.L.; Mouz, N.; Martin, C.E.; Roger, M.G.; El Habib, R.; et al. Single-chain protein mimetics of the N-terminal heptad-repeat region of gp41 with potential as anti–HIV-1 drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18207–18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Cano-Muñoz, M.; Morel, B.; Standoli, S.; Santarossa, E.; Moog, C.; Schmidt, S.; Laumond, G.; Cámara-Artigas, A.; Conejero-Lara, F. Structural and Thermodynamic Analysis of HIV-1 Fusion Inhibition Using Small gp41 Mimetic Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3091–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Cano-Muñoz, M.; Polo-Megías, D.; Conejero-Lara, F.; Morel, B. Thermodynamic dissection of the interface between HIV-1 gp41 heptad repeats reveals cooperative interactions and allosteric effects. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 688, 108401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Moog, C.; Cano-Muñoz, M.; Schmidt, S.; Laumond, G.; Ruocco, V.; Standoli, S.; Polo-Megías, D.; Conejero-Lara, F.; Morel, B. Probing Vulnerability of the gp41 C-Terminal Heptad Repeat as Target for Miniprotein HIV Inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5577–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancera, M.; Zhou, T.; Druz, A.; Georgiev, I.S.; Soto, C.; Gorman, J.; Huang, J.; Acharya, P.; Chuang, G.; Ofek, G.; et al. Structure and immune recognition of trimeric pre-fusion HIV-1 Env. Nature 2014, 514, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ozorowski, G.; Ward, A.B. Cryo-EM structure of a native, fully glycosylated, cleaved HIV-1 envelope trimer. Science 2016, 351, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.B.; Dombkowski, A.A. Disulfide by Design 2.0: A web-based tool for disulfide engineering in proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCamp, A.; Hraber, P.; Bailer, R.T.; Seaman, M.S.; Ochsenbauer, C.; Kappes, J.; Gottardo, R.; Edlefsen, P.; Self, S.; Tang, H.; et al. Global Panel of HIV-1 Env Reference Strains for Standardized Assessments of Vaccine-Elicited Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2489–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Finotto, M.; Ingallinella, P.; Hrin, R.; Carella, A.V.; Hou, X.S.; Schleif, W.A.; Miller, M.D.; Geleziunas, R.; Pessi, A. Covalent stabilization of coiled coils of the HIV gp41 N region yields extremely potent and broad inhibitors of viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12903–12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, M.J.; Kay, M.S.; Kim, P.S. Protein Design of an HIV-1 Entry Inhibitor. Science 2001, 291, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-muñoz, M.; Cesaro, S.; Morel, B.; Lucas, J.; Moog, C.; Conejero-lara, F. Extremely thermostabilizing core mutations in coiled-coil mimetic proteins of HIV-1 gp41 produce diverse effects on target binding but do not affect their inhibitory activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.J.; Hasan, A.; Wilson, K.L.; White, J.M.; Matthews, T.J.; Delmedico, M.K. The hydrophobic pocket contributes to the structural stability of the N-terminal coiled coil of HIV gp41 but is not required for six-helix bundle formation. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 4945–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombkowski, A.A.; Sultana, K.Z.; Craig, D.B. Protein disulfide engineering. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, P.; Lu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, F.; Zou, P.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. An engineered HIV-1 gp41 trimeric coiled coil with increased stability and anti-HIV-1 activity: Implication for developing anti-HIV microbicides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Chutkowski, C.T.; Kim, P.S. Evidence that a prominent cavity in the coiled coil of HIV type 1 gp41 is an attractive drug target. Med. Sci. 1998, 95, 15613–15617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiyev, V.; Kaur, H.; Snyder, B.A.; Hogan, P.A.; Ptak, R.G.; Hwang, P.; Gochin, M. Enhanced potency of bivalent small molecule gp41 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochin, M.; Cai, L. The Role of Amphiphilicity and Negative Charge in Glycoprotein 41 Interactions in the Hydrophobic Pocket. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4338–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Steger, H.K.; Root, M.J. Kinetic dependence to HIV-1 entry inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25813–25821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, K.M.; Steger, H.K.; Root, M.J. Asymmetric deactivation of HIV-1 gp41 following fusion inhibitor binding. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Garcia, N.K.; Cupo, A.; Matsui, T.; Julien, J.P.; Sanders, R.W.; Wilson, I.A.; Moore, J.P.; Lee, K.K. CD4-induced activation in a soluble HIV-1 Env trimer. Structure 2014, 22, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, B.; Harrison, S.C. Cryo-EM Structure of Full-length HIV-1 Env Bound with the Fab of Antibody PG16. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. YASARA View—Molecular graphics for all devices—From smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Nielsen, J.E.; Spronk, C.A.E.M.; Vriend, G. Fast empirical pKa prediction by Ewald summation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Baldwin, R.L. Mechanism of helix induction by trifluoroethanol: A framework for extrapolating the helix-forming properties of peptides from trifluoroethanol/water mixtures back to water. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 8413–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Turk, E.; Lin, C.; Bilska, M.; Greene, K.M.; Gao, H.; Todd, C.A.; Ozaki, D.A.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Optimization and validation of the TZM-bl assay for standardized assessments of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 409, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
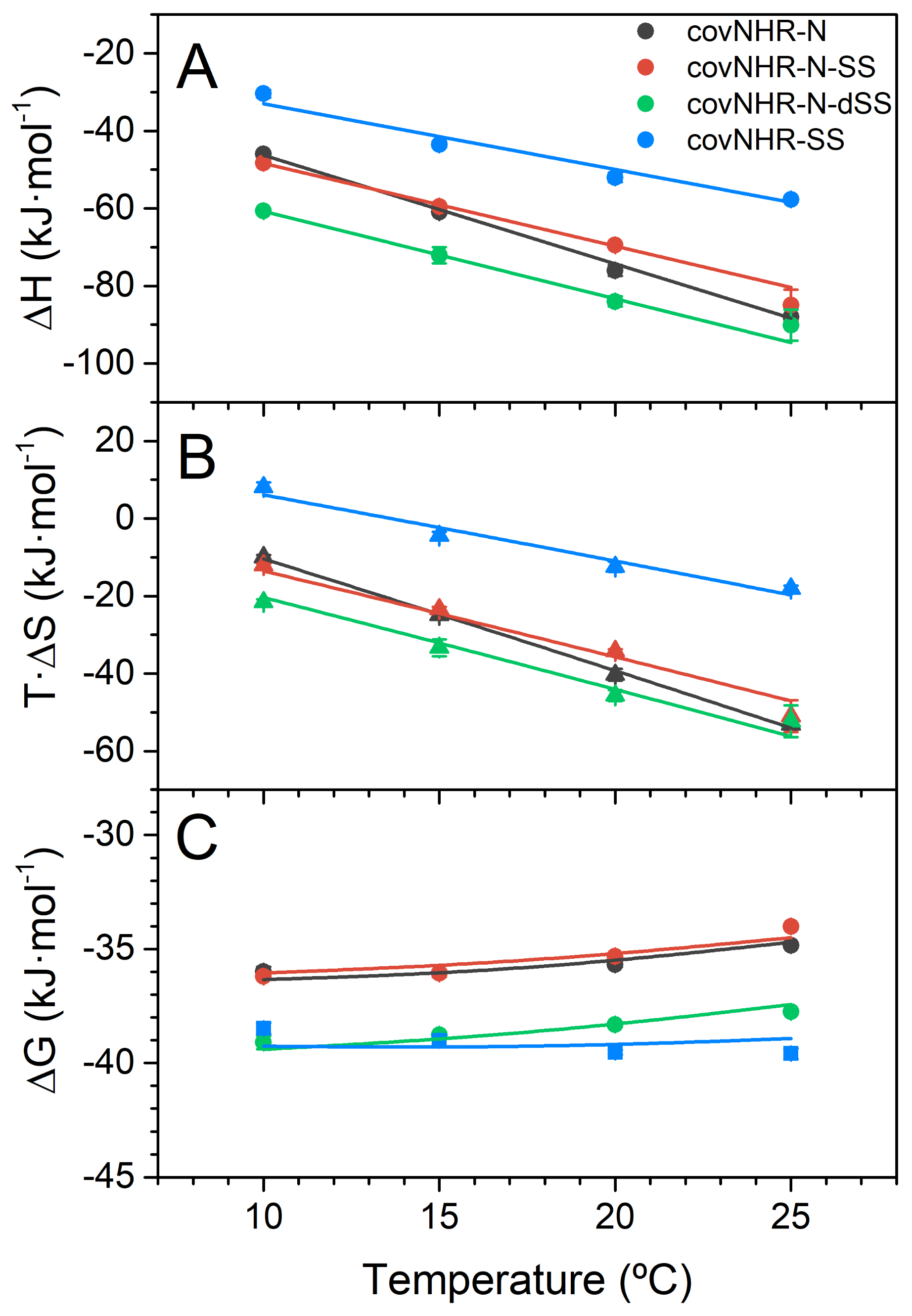
| Protein | Peptide | Temperature (°C) | Kd (nM) | ΔHb (kJ·mol−1) | n | ΔCpb (kJ·K−1·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| covNHR-SS | Y24L | 10 | 80 ± 8 | −30.4 ± 1.0 | 0.75 | −1.70 ± 0.21 |
| 15 | 85 ± 9 | −43.5 ± 0.8 | 0.77 | |||
| 20 | 91 ± 4 | −52.0 ± 1.2 | 0.8 | |||
| 25 | 116 ± 11 | −57.7 ± 0.6 | 0.83 | |||
| covNHR-N-dSS | Y24L | 10 | 61 ± 8 | −60.7 ± 0.4 | 0.76 | −2.26 ± 0.11 |
| 15 | 94.3 ± 2.4 | −72.1 ± 2.1 | 0.77 | |||
| 20 | 149 ± 6 | −84.0 ± 1.3 | 0.78 | |||
| 25 | 243 ± 10 | −90 ± 4 | 0.89 |
| Pseudovirus | covNHR-N-SS | covNHR-N-dSS | covNHR | covNHR-SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pNL4-3 XCS a | 25.6 ± 2.4 | 11 ± 4 ** | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| pNL4-3 (DIM) a | 24.8 ± 2.0 | 13 ± 1.3 ** | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| SF162 | n.d. | 36 ± 12 | 8.0 ± 1.3 | 8.9 ± 0.9 |
| MW965.26 | 96 ± 12 | 23 ± 3 *** | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.5 |
| CE1176 b | n.d | 37.9 ± 1.1 | 10.8 ± 1.3 | 8.8 ± 1.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano-Muñoz, M.; Lucas, J.; Lin, L.-Y.; Cesaro, S.; Moog, C.; Conejero-Lara, F. Conformational Stabilization of Gp41-Mimetic Miniproteins Opens Up New Ways of Inhibiting HIV-1 Fusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052794
Cano-Muñoz M, Lucas J, Lin L-Y, Cesaro S, Moog C, Conejero-Lara F. Conformational Stabilization of Gp41-Mimetic Miniproteins Opens Up New Ways of Inhibiting HIV-1 Fusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(5):2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052794
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano-Muñoz, Mario, Julie Lucas, Li-Yun Lin, Samuele Cesaro, Christiane Moog, and Francisco Conejero-Lara. 2022. "Conformational Stabilization of Gp41-Mimetic Miniproteins Opens Up New Ways of Inhibiting HIV-1 Fusion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 5: 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052794
APA StyleCano-Muñoz, M., Lucas, J., Lin, L.-Y., Cesaro, S., Moog, C., & Conejero-Lara, F. (2022). Conformational Stabilization of Gp41-Mimetic Miniproteins Opens Up New Ways of Inhibiting HIV-1 Fusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052794







