General Anesthesia and the Young Brain: The Importance of Novel Strategies with Alternate Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
1. General Anesthesia and Neurodevelopment
Impairment of Neuronal Networks Caused by an Early Exposure of the Developing Brain to General Anesthesia
2. Neuroactive Steroids as Promising Therapeutic Agents
3. Neuroactive Steroids: Endogenous and Synthetic Compounds with Hypnotic Properties but without Neurotoxic Effects
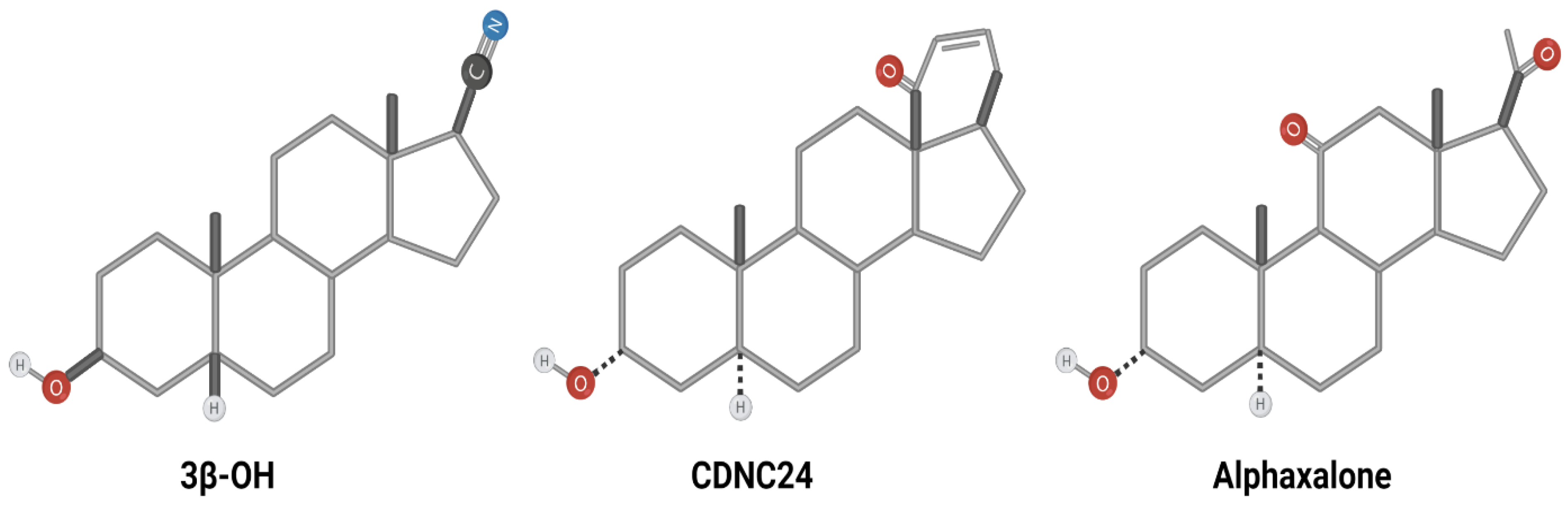
3.1. Chemical Structure and Related Functions of Neuroactive Steroids; Insights from Presently Available Structure-Activity Studies
- -
- 3β-OH ((3β,5β,17β)-3-hydroxyandrostane-17-carbonitrile);
- -
- CDNC24 ((3α,5α)-3-hydroxy-13,24-cyclo-18,21-dinorchol-22-en-24-ol); and
- -
- Alphaxalone (5α-pregnan-3α-ol-11,20-dione) (Figure 1).
3.2. Lack of Neurotoxicity after Prolonged Exposure Following Sufficient Depth of Hypnosis
3.3. Lack of Long-Term Consequences in Cognitive Development
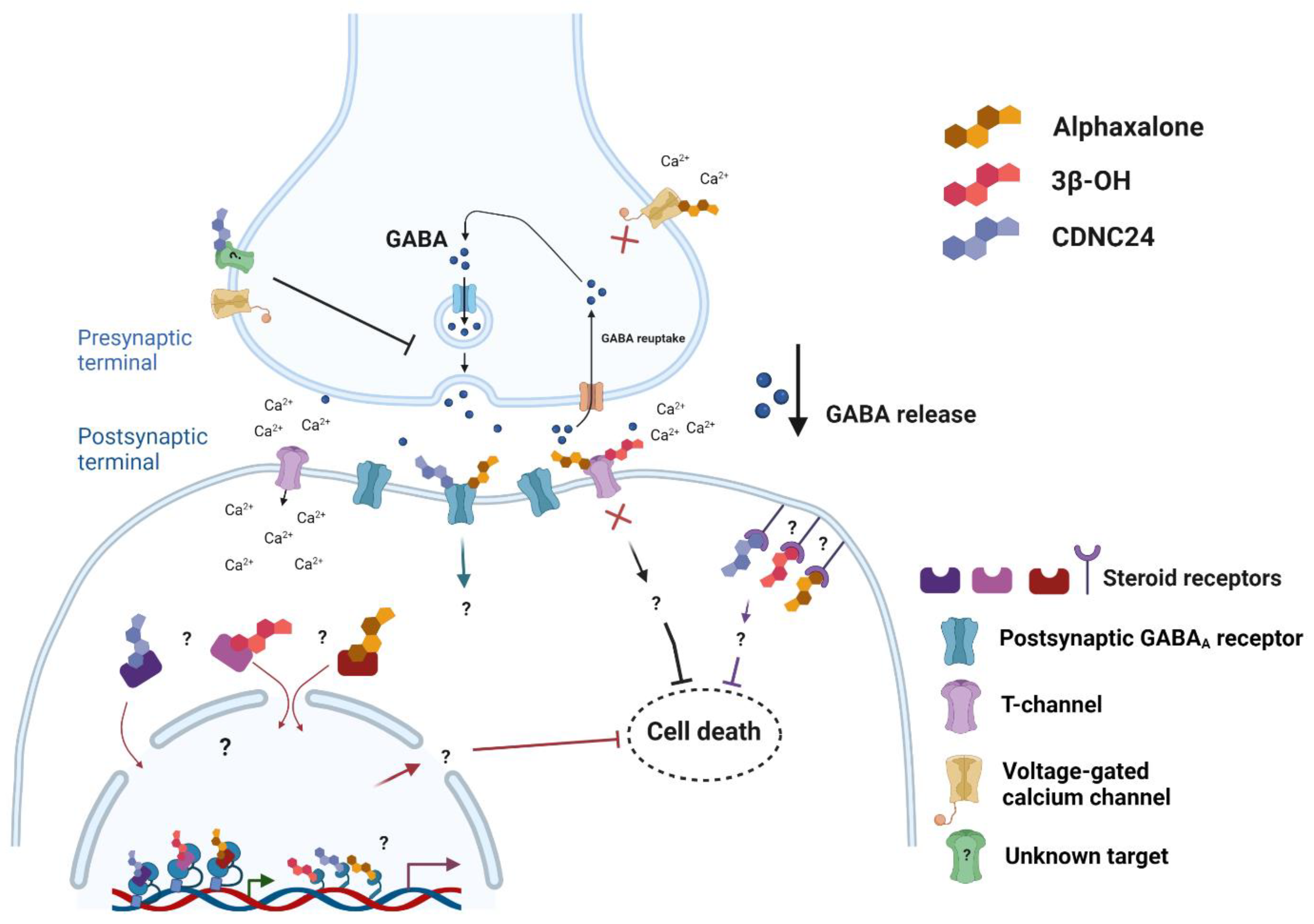
4. Novel Cellular Targets of Neuroactive Steroid Analogues Considered to Be Promising General Anesthetics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jevtović-Todorović, V.; Todorović, S.M.; Mennerick, S.; Powell, S.; Dikranian, K.; Benshoff, N.; Zorumski, C.F.; Olney, J.W. Nitrous oxide (laughing gas) is an NMDA antagonist, neuroprotectant and neurotoxin. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Hartman, R.E.; Izumi, Y.; Benshoff, N.D.; Dikranian, K.; Zorumski, C.F.; Olney, J.W.; Wozniak, D.F. Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yon, J.H.; Daniel-Johnson, J.; Carter, L.B.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Anesthesia induces neuronal cell death in the developing rat brain via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Qin, Y.Q.; Tenkova, T.; Wang, H.; Labruyere, J.; Olney, J.W. Potential of ketamine and midazolam, individually or in combination, to induce apoptotic neurodegeneration in the infant mouse brain. Br. J. Pharm. 2005, 146, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, S.; Carter, L.B.; Ori, C.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Clinical anesthesia causes permanent damage to the fetal guinea pig brain. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenning, K.J.; Noguchi, K.K.; Martin, L.D.; Manzella, F.M.; Cabrera, O.H.; Dissen, G.A.; Brambrink, A.M. Isoflurane exposure leads to apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes in 20- and 40-day old rhesus macaques. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creeley, C.; Dikranian, K.; Dissen, G.A.; Martin, L.; Olney, J.; Brambrink, A.M. Propofol-induced apoptosis of neurones and oligodendrocytes in fetal and neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110 (Suppl. S1), i29–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Pediatric anesthesia neurotoxicity: An overview of the 2011 SmartTots panel. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavis-Bloom, C.; Alvarado, M.C.; Bachevalier, J. Neonatal hippocampal damage impairs specific food/place associations in adult macaques. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 127, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, J.; Alvarado, M.C.; Murphy, K.L.; Baxter, M.G. Multiple Anesthetic Exposure in Infant Monkeys Alters Emotional Reactivity to an Acute Stressor. Anesthesiology 2015, 123, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, M.C.; Murphy, K.L.; Baxter, M.G. Visual recognition memory is impaired in rhesus monkeys repeatedly exposed to sevoflurane in infancy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Shen, R.; Wang, F. Early life exposure to sevoflurane impairs adulthood spatial memory in the rat. Neurotoxicology 2013, 39, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, P.; Joksimovic, S.M.; Faisant, A.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Early exposure to general anesthesia impairs social and emotional development in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Rossi, M.G.; Anghelescu, D.L.; Liu, W.; Breazeale, A.M.; Reddick, W.E.; Glass, J.O.; Phillips, N.S.; Jacola, L.M.; Sabin, N.D.; et al. Association Between Anesthesia Exposure and Neurocognitive and Neuroimaging Outcomes in Long-term Survivors of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, S.E.; Creeley, C.E.; Hartman, R.E.; Yuede, C.M.; Zorumski, C.F.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Dikranian, K.; Noguchi, K.K.; Farber, N.B.; Wozniak, D.F. Using animal models to evaluate the functional consequences of anesthesia during early neurodevelopment. Neurobiol. Learn Mem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenlocher, P.R.; Arun, S.D. Regional differences in synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 387, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.H.; Peng, B.; Zhang, F.C. The postoperative effect of sevoflurane inhalational anesthesia on cognitive function and inflammatory response of pediatric patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 22, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, R.T.; Flick, R.P.; Sprung, J.; Katusic, S.K.; Barbaresi, W.J.; Mickelson, C.; Gleich, S.J.; Schroeder, D.R.; Weaver, A.L.; Warner, D.O. Early exposure to anesthesia and learning disabilities in a population-based birth cohort. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, R.P.; Katusic, S.K.; Colligan, R.C.; Wilder, R.T.; Voigt, R.G.; Olson, M.D.; Sprung, J.; Weaver, A.L.; Schroeder, D.R.; Warner, D.O. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes after early exposure to anesthesia and surgery. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e1053-61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Review Results in New Warnings about Using General Anesthetics and Sedation Drugs in Young Children and Pregnant Women. 2016. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-review-results-new-warnings-about-using-general-anesthetics-and (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Sanchez, V.; Feinstein, S.D.; Lunardi, N.; Joksovic, P.M.; Boscolo, A.; Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. General Anesthesia Causes Long-term Impairment of Mitochondrial Morphogenesis and Synaptic Transmission in Developing Rat Brain. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2011, 115, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, A.; Milanovic, D.; Starr, J.A.; Sanchez, V.; Oklopcic, A.; Moy, L.; Ori, C.C.; Erisir, A.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Early exposure to general anesthesia disturbs mitochondrial fission and fusion in the developing rat brain. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, N.; Ori, C.; Erisir, A.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. General anesthesia causes long-lasting disturbances in the ultrastructural properties of developing synapses in young rats. Neurotox. Res. 2010, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, T.J.; Timic Stamenic, T.; Todorovic, S.M. Neonatal general anesthesia causes lasting alterations in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in the ventrobasal thalamus of adolescent female rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 127, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.L.; Perez, P.J.; Wang, M.; Gray, C.; Krall, C.; Sun, X.; Hunter, E.; Skinner, J.; Johns, R.A. Neonatal Isoflurane Anesthesia or Disruption of Postsynaptic Density-95 Protein Interactions Change Dendritic Spine Densities and Cognitive Function in Juvenile Mice. Anesthesiology 2020, 133, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Shen, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.M.; Cao, J.P.; Wu, Y.Q. Repeated exposure to propofol in the neonatal period impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and the recognition function of rats in adulthood. Brain Res. Bull 2021, 169, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J. Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane caused cognitive deficits by dysregulating SK2 channels and GluA2-lacking AMPA receptors in juvenile rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2018, 141, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Effect of repeated neonatal sevoflurane exposure on the learning, memory and synaptic plasticity at juvenile and adult age. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 4974–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Milanovic, D.; Pesic, V.; Loncarevic-Vasiljkovic, N.; Avramovic, V.; Tesic, V.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Kanazir, S.; Ruzdijic, S. Neonatal propofol anesthesia changes expression of synaptic plasticity proteins and increases stereotypic and anxyolitic behavior in adult rats. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 32, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Brambrick, A.M. General Anesthesia and Young Brain: What is New? J. Neurosurg. Anesth. 2018, 30, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antkowiak, B. How do general anaesthetics work? Naturwissenschaften 2001, 88, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, M.J.; Ikonomidou, C.; Tenkova, T.I.; Der, T.C.; Dikranian, K.; Sesma, M.A.; Olney, J.W. Distinguishing excitotoxic from apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 408, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastain-Potts, S.E.; Tesic, V.; Tat, Q.L.; Cabrera, O.H.; Quillinan, N.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Sevoflurane Exposure Results in Sex-Specific Transgenerational Upregulation of Target IEGs in the Subiculum. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atluri, N.; Joksimovic, S.M.; Oklopcic, A.; Milanovic, D.; Klawitter, J.; Eggan, P.; Krishnan, K.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. A neurosteroid analogue with T-type calcium channel blocking properties is an effective hypnotic, but is not harmful to neonatal rat brain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesic, V.; Joksimovic, S.M.; Quillinan, N.; Krishnan, K.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Neuroactive steroids alphaxalone and CDNC24 are effective hypnotics and potentiators of GABAA currents, but are not neurotoxic to the developing rat brain. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 124, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melcangi, R.C.; Panzica, G.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Neuroactive steroids: Focus on human brain. Neuroscience 2011, 191, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, R.; Holsboer, F. Neuroactive steroids: Mechanisms of action and neuropsychopharmacological perspectives. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belelli, D.; Hogenkamp, D.; Gee, K.W.; Lambert, J.J. Realising the therapeutic potential of neuroactive steroid modulators of the GABAA receptor. Neurobiol. Stress 2019, 12, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzella, F.M.; Covey, D.F.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Todorovic, S.M. Synthetic neuroactive steroids as new sedatives and anesthetics: Back to the future. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, e13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.S.; Yang, S.H.; Nilsson, K.R.; Kumar, A.S.; Covey, D.F.; Simpkins, J.W. The nonfeminizing enantiomer of 17β-estradiol exerts protective effects in neuronal cultures and a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghava, N.; Das, B.C.; Ray, S.K. Neuroprotective effects of estrogen in CNS injuries: Insights from animal models. Neurosci. Neuroecon. 2017, 6, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Short, K.L.; Hooper, S.B. The science of steroids. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2019, 24, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selye, H. Anesthetic effects of steroid hormones. Proc. Soc. Exper. Biol. Med. 1941, 46, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.J.; Belelli, D.; Hill-Venning, C.; Peters, J.A. Neurosteroids and GABAA receptor function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.J.; Belelli, D.; Harney, S.C.; Peters, J.A.; Frenguelli, B.G. Modulation of native and recombinant GABAA receptors by endogenous and synthetic neuroactive steroids. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 37, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S.; Carver, M.C.; Clossen, B.; Wu, X. Extrasynaptic GABA-A receptor-mediated sex differences in the antiseizure activity of neurosteroids in status epilepticus and complex partial seizures. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, S.M.; Lingle, C.J. Pharmacological properties of T-type Ca2+ current in adult rat sensory neurons: Effects of anticonvulsant and anesthetic agents. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, R.D.; Maayan, R.; Weizman, A. The relevance of neurosteroids to clinical psychiatry: From the laboratory to the bedside. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 16, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorumski, C.F.; Mennerick, S. Neurosteroids as therapeutic leads in psychiatry. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinder, O.; Dar, D.E. Neuroactive steroids: Their mechanism of action and their function in the stress response. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1999, 167, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange-Kiel, J.; Rune, G.M. Direct and indirect effects of estrogen on rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2006, 138, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Fester, L.; von Blittersdorff, B.; Hassu, B.; Nogens, H.; Prange-Kiel, J.; Jarry, H.; Wegscheider, K.; Rune, G.M. Aromatase inhibitors induce spine synapse loss in the hippocampus of ovariectomized mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fester, L.; Prange-Kiel, J.; Zhou, L.; Blittersdorf, B.v.; Böhm, J.; Jarry, H.; Schumacher, M.; Rune, G.M. Estrogen-regulated synaptogenesis in the hippocampus: Sexual dimorphism in vivo but not in vitro. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 131, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.T.; Manzella, F.M.; Huffman, J.; Cabrera, O.H.; Hoffman, J. Cognition in female rats after blocking conversion of androgens to estrogens. Horm. Behav. 2017, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penning, D.; Hong, X.; Cazacu, S.L.; Brodie, C. Neurotoxicity of Ketamine and the Neuroprotective Effects of Neurosteroids on Human Cultured Neurons. Anesthesiology 2019. Available online: http://www.asaabstracts.com/strands/asaabstracts/abstract.htm?year=2019&index=10&absnum=1299 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Howland, W.S.; Boyan, P.C.; Wang, K.-C. The use of a steroid (Viadril) as an anesthetic agent. Anesthesiology 1956, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbord, R.P.; Wild, W.N. Observations on steroid anaesthesia; a preliminary report. Proc. R Soc. Med. 1956, 49, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, J.M. Anaphylactic Reactions after use of CT 1341 (Althesin). Br. Med. J. 1975, 7, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fisher, M.M. Severe histamine mediated reactions to althesin. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1976, 4, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyermek, L.; Iriarte, J.; Crabbé, P. Steroids. CCCX. Structure-Activity Relationship of Some Steroidal Hypnotic Agents. J. Med. Chem. 1968, 11, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipps, G.H. Structure-activity relationships in steroidal anaesthetics. J. Steroid Biochem. 1975, 6, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zorumski, C.F.; Covey, D.F. Neurosteroid analogues. 4. The effect of methyl substitution at the C-5 and C-10 positions of neurosteroids on electrophysiological activity at GABAA receptors. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4218–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosie, A.M.; Wilkins, M.E.; Smart, T.G. Neurosteroid binding sites on GABAA receptors. Pharm. Ther. 2007, 116, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, M.C.; Reddy, D.S. Neurosteroid interactions with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABAA receptors: Regulation of subunit plasticity, phasic and tonic inhibition, and neuronal network excitability. J. Investig. Derm. 2015, 135, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, Y. Excitatory actions of gaba during development: The nature of the nurture. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, O.H.; Tesic, V.; Tat, Q.L.; Chastain, S.; Quillinan, N.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Sevoflurane-Induced Dysregulation of Cation-Chloride Cotransporters NKCC1 and KCC2 in Neonatal Mouse Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, S.M.; Prakriya, M.; Nakashima, Y.M.; Nilsson, K.R.; Han, M.; Zorumski, C.F.; Covey, D.F.; Lingle, C.J. Enantioselective blockade of T-type Ca2+ current in adult rat sensory neurons by a steroid that lacks gamma-aminobutyric acid-modulatory activity. Mol. Pharm. 1998, 54, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orestes, P.; Todorovic, S.M. Are neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels valid cellular targets for general anesthetics? Channels 2010, 4, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirathna, S.; Brimelow, B.C.; Jagodic, M.M.; Krishnan, K.; Jiang, X.; Zorumski, C.F.; Mennerick, S.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. New evidence that both T-type calcium channels and GABAA channels are responsible for the potent peripheral analgesic effects of 5α-reduced neuroactive steroids. Pain 2005, 114, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksovic, P.M.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M. Inhibition of T-type calcium current in the reticular thalamic nucleus by a novel neuroactive steroid. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1122, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leresche, N.; Lambert, R.C. T-type calcium channels in synaptic plasticity. Channels 2017, 11, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Reyes, E. Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channels. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 117–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimovic, S.L.; Covey, D.F.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Todorovic, S.M. Neurosteroids in Pain Management: A New Perspective on an Old Player. Front Pharm. 2018, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orestes, P.; Bojadzic, D.; Chow, R.M.; Todorovic, S.M. Mechanisms and functional significance of inhibition of neuronal T-Type calcium channels by isoflurane. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 75, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. T-type voltage-gated calcium channels as targets for the development of novel pain therapies. Br. J. Pharm. 2011, 163, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.M.; Todorovic, S.M.; Covey, D.F.; Lingle, C.J. The anesthetic steroid (+)-3α-hydroxy-5α-androstane-17β-carbonitrile blocks N-, Q-, and R-type, but Not L- and P-Type, high voltage-activated Ca2+ current in hippocampal and dorsal root ganglion neurons of the rat. Mol. Pharm. 1998, 54, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckle, V.S.; DiGruccio, M.R.; Uebele, V.N.; Renger, J.J.; Todorovic, S.M. Inhibition of T-type calcium current in rat thalamocortical neurons by isoflurane. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksovic, P.M.; Brimelow, B.C.; Murbartián, J.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Todorovic, S.M. Contrasting anesthetic sensitivities of T-type Ca2+ channels of reticular thalamic neurons and recombinant Ca v3.3 channels. Br. J. Pharm. 2005, 144, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timic Stamenic, T.; Feseha, S.; Manzella, F.M.; Wallace, D.; Wilkey, D.; Corrigan, T.; Fiedler, H.; Doerr, P.; Krishnan, K.; Raol, Y.H.; et al. The T-type calcium channel isoform Cav3.1 is a target for the hypnotic effect of the anaesthetic neurosteroid (3β,5β,17β)-3-hydroxyandrostane-17-carbonitrile. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimovic, S.M.; Izumi, Y.; Joksimovic, S.L.; Tesic, V.; Krishnan, K.; Asnake, B.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Covey, D.F.; Zorumski, C.F.; Todorovic, S.M. Novel neurosteroid hypnotic blocks T-type calcium channel-dependent rebound burst firing and suppresses long-term potentiation in the rat subiculum. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.V.; Chandra, D.; Homanics, G.E. GABAA-R α4 subunits are required for the low dose locomotor stimulatory effect of alphaxalone, but not for several other behavioral responses to alphaxalone, etomidate or propofol. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Serrao, J.M.; Goodchild, C.S. Alfaxalone activates Human Pregnane-X Receptors with greater efficacy than Allopregnanolone: An in-vitro study with implications for neuroprotection during anesthesia. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, V.; Yasuda, K.; Lamba, J.K.; Assem, M.; Davila, J.; Strom, S.; Schuetz, E.G. PXR (NR1I2): Splice variants in human tissues, including brain, and identification of neurosteroids and nicotine as PXR activators. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2004, 199, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnuk, A.; Kajta, M. Steroid and xenobiotic receptor signalling in apoptosis and autophagy of the nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, G.; Wang, Z.; Luo, J.; Hao, X. Sub-anesthetic doses of ketamine exert antidepressant-like effects and upregulate the expression of glutamate transporters in the hippocampus of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 639, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.H.; Kamatchi, G.L.; Washington, J.M.; Zuo, Z. Effects of volatile anesthetics on glutamate transporter, excitatory amino acid transporter type 3: The role of protein kinase C. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2002, 96, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maksimovic, S.; Useinovic, N.; Quillinan, N.; Covey, D.F.; Todorovic, S.M.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. General Anesthesia and the Young Brain: The Importance of Novel Strategies with Alternate Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031889
Maksimovic S, Useinovic N, Quillinan N, Covey DF, Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V. General Anesthesia and the Young Brain: The Importance of Novel Strategies with Alternate Mechanisms of Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031889
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaksimovic, Stefan, Nemanja Useinovic, Nidia Quillinan, Douglas F. Covey, Slobodan M. Todorovic, and Vesna Jevtovic-Todorovic. 2022. "General Anesthesia and the Young Brain: The Importance of Novel Strategies with Alternate Mechanisms of Action" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031889
APA StyleMaksimovic, S., Useinovic, N., Quillinan, N., Covey, D. F., Todorovic, S. M., & Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. (2022). General Anesthesia and the Young Brain: The Importance of Novel Strategies with Alternate Mechanisms of Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031889





