Recent Developments in Electrochemical-Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
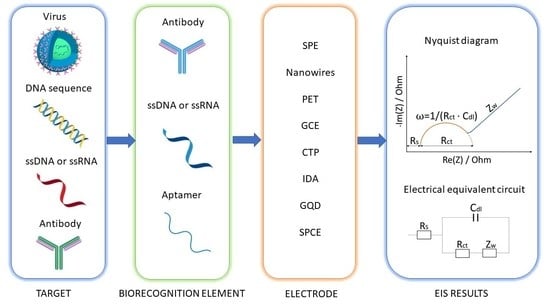
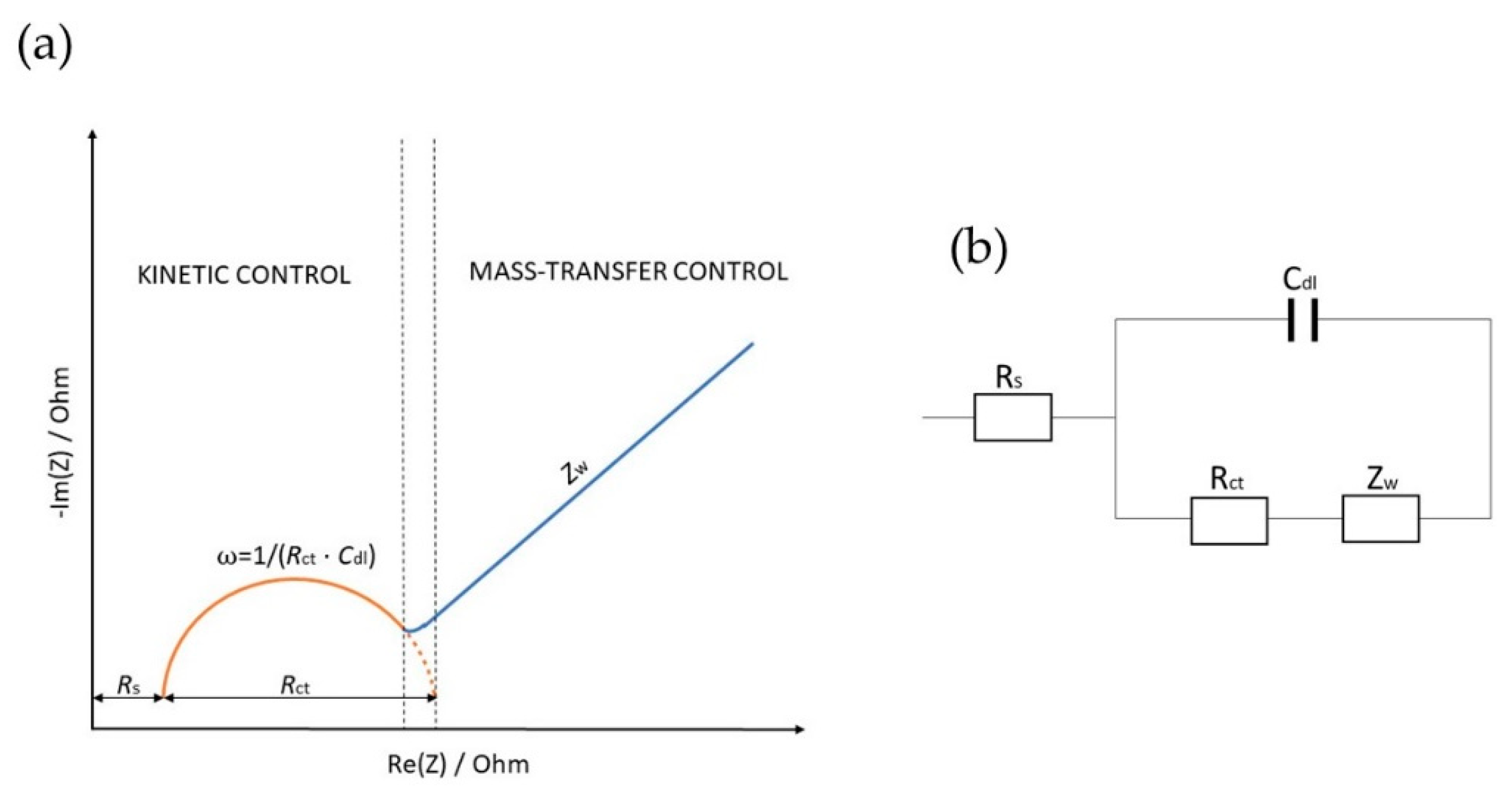
2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
3. Viruses
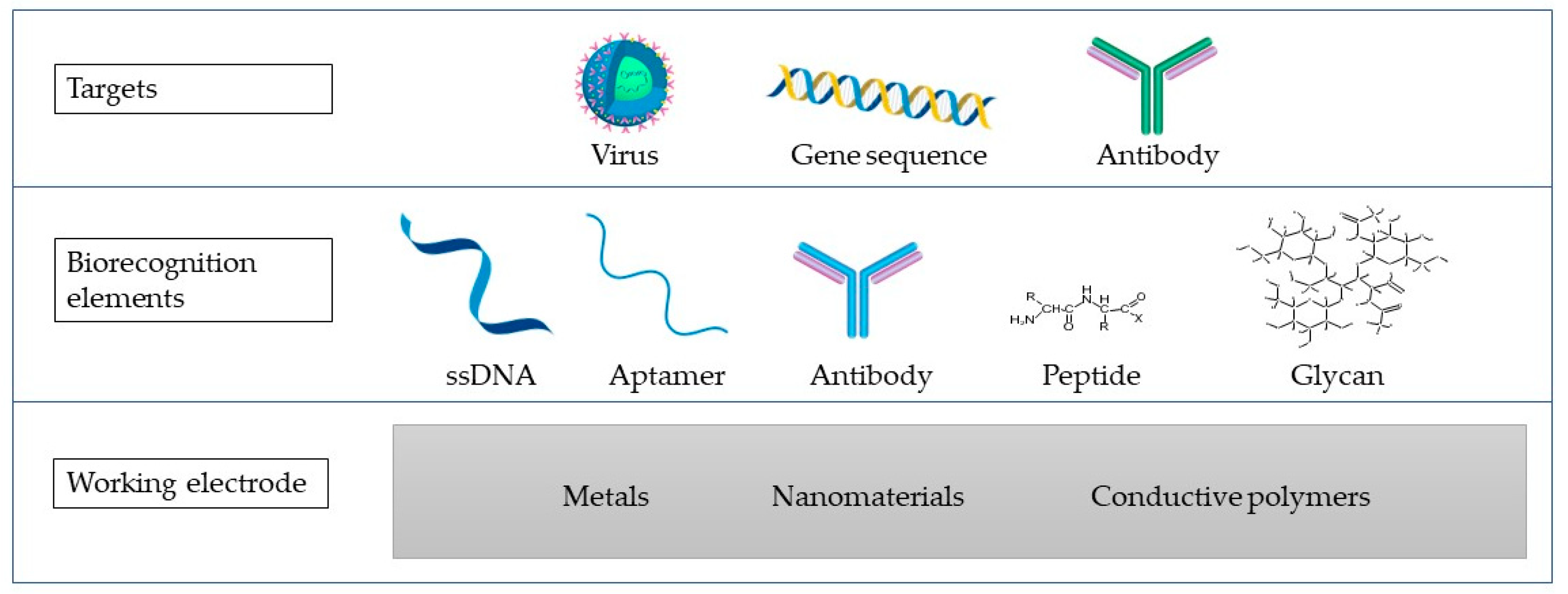
4. Electrochemical Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection
4.1. Genosensors for Virus Detection
4.2. Aptasensors for Virus Detection
4.3. Immunosensors for Virus Detection
5. SARS-CoV-2 Detection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Alternating current |
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| Au-IDE | Gold interdigitated microelectrode |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| Au-SPE | Gold surface- screen printed electrode |
| BDD | Boron doped diamond |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CD4 | Cluster of differentiation 4 |
| Cdl | Double-layer capacitance |
| CE | Counter electrode |
| CNPE | Carbon nanopowder paste electrode |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DC | Direct current |
| DENV | Dengue virus |
| DPP4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 |
| E | Envelope protein |
| EBOV | Ebola virus |
| EDIII | Domain III of the envelope protein |
| EEC | Equivalent electric circuit |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GCE | Glassy carbon electrode |
| GF | Glass fiber |
| GO-MoS2 | Graphene oxide encapsulated molybdenum disulfide |
| GQD | Graphene quantum dots |
| GTP | Tar pitch electrodes |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| HAV | Hepatitis A virus |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| ITO | Indium tin oxide |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| M | Membrane protein |
| MCH | 6-mercapto-1-hexanol |
| MERS-CoV | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| N | Nucleocapsid |
| NA | Neuraminidase |
| NCP | Nucleo capsid protein |
| NS1 | Non-structural protein |
| NV | Nanovesicle |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| Pd-NFT | Palladium nano-thin-film |
| PEDOT | Poly-(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene) |
| PPy | Polypyrrole |
| RBD | Receptor binding domain |
| Rct | Charge transfer resistance |
| RE | Reference electrode |
| rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| Rs | Ohmic resistance |
| S | Spike glycoprotein |
| SARS-CoV | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SELEX | Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment |
| SPCE | Screen-printed carbon electrode |
| SWV | Square wave voltammetry |
| TIM-1 | T-cell immunoglobulin mucin domain-1 |
| VACV | Vaccinia virus |
| WE | Working electrode |
| ZIKV | Zika virus |
| Zw | Warburg impedance |
References
- Kaya, H.O.; Cetin, A.E.; Azimzadeh, M.; Topkaya, S.N. Pathogen detection with electrochemical biosensors: Advantages, challenges and future perspectives. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goode, J.A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Millner, P.A. Biosensor Regeneration: A Review of Common Techniques and Outcomes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6267–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Henríquez, L.; Brenes-Acuña, M.; Castro-Rojas, A.; Cordero-Salmerón, R.; Lopretti-Correa, M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R. Biosensors for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Clinical Pathogens. Sensors 2020, 20, 6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazaca, L.C.; dos Santos, P.L.; de Oliveira, P.R.; Rocha, D.P.; Stefano, J.S.; Kalinke, C.; Abarza Muñoz, R.A.; Bonacin, J.A.; Janegitz, B.C.; Carrilho, E. Biosensing strategies for the electrochemical detection of viruses and viral diseases—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1159, 338384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Báscones, E.; Parra, F.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Aptamers against viruses: Selection strategies and bioanalytical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.L.; Francis, M.B. Impedance-Based Detection of Bacteria. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 700–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhiney, J.; Lawton, L.A. Detection of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukasov, R.; Dossym, D.; Filchakova, O. Detection of RNA viruses from influenza and HIV to Ebola and SARS-CoV-2: A review. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Giorgi, E.E.; Chakraborty, S.; Nguyen, K.; Bhattacharya, T.; Theiler, J.; Goloboff, P.A.; Yoon, H.; Abfalterer, W.; Foley, B.T.; et al. HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2: Patterns in the evolution of two pandemic pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Z.; Kong, Y.; Liu, S. Marine Toxins Detection by Biosensors Based on Aptamers. Toxins 2019, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štukovnik, Z.; Godec, R.F.; Bren, U. The Use of Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae as a Biorecognition element in the Development of a Model Impedimetric Biosensor for Caffeine Detection. Acta Chim. Slov. 2022, 69, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidic, J.; Manzano, M. Electrochemical biosensors for rapid pathogen detection. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 29, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors-Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhain, A.; Bonini, A.; Vivaldi, F.; Poma, N.; Di Francesco, F. Latest developments in non-faradic impedimetric biosensors: Towards clinical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 133, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Hasan, M.R.; Hossain, S.I.; Ahommed, M.S.; Daizy, M. Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic viruses with electrochemical biosensor: State of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y. New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors 2012, 12, 3449–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Lv, Y. Tag-Free Methodology for Ultrasensitive Biosensing of miRNA Based on Intrinsic Isotope Detection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8523–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S. Characteristics Analysis of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (Eis) for Different Electrode Patterns. Master’s Thesis, The University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Helali, S.; Zhang, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Minic, J.; Gorojankina, T.; Persuy, M.-A.; Pajot-Augy, E.; Salesse, R.; et al. Immobilization of rhodopsin on a self-assembled multilayer and its specific detection by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E.; Willner, I. Probing Biomolecular Interactions at Conductive and Semiconductive Surfaces by Impedance Spectroscopy: Routes to Impedimetric Immunosensors, DNA-Sensors, and Enzyme Biosensors. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 913–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Juřík, T.; Kovář, D.; Trnková, L.; Skládal, P. Nanoparticle-Based Immunochemical Biosensors and Assays: Recent Advances and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9973–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, D. Impedimetric biosensor based on cell-mediated bioimprinted films for bacterial detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekeres, K.J.; Vesztergom, S.; Ujvári, M.; Láng, G.G. Methods for the Determination of Valid Impedance Spectra in Non-stationary Electrochemical Systems: Concepts and Techniques of Practical Importance. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 1233–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azazy, M.; Min, M.; Annus, P. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEachern, F.; Harvey, E.; Merle, G. Emerging Technologies for the Electrochemical Detection of Bacteria. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 2000140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollarasouli, F.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ozkan, S.A. The Role of Electrochemical Immunosensors in Clinical Analysis. Biosensors 2019, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Impedimetric Biosensors. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 97, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Juska, V.; O’Riordan, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Based Label-Free Immunosensors. ChemRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congur, G.; Eksin, E.; Erdem, A. Impedimetric Detection of microRNA at Graphene Oxide Modified Sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 172, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsuphol, P.; Ng, H.H.; Pursey, J.P.; Arya, S.K.; Wong, C.C.; Stulz, E.; Park, M.K. EIS-based biosensor for ultra-sensitive detection of TNF-α from non-diluted human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, R.; Heneine, L.G.; Matencio, T.; Messaddeq, Y. Faradaic and non-faradaic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as transduction techniques for sensing applications. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 5, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.-Y.; Park, S.-M. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2010, 3, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, M.; Riccò, B. Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for biological analysis and food characterization: A review. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2017, 6, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.C.; Choudhury, S.; Rabbani, M.M.; Das, J. A Review on Potential Electrochemical Point-of-Care Tests Targeting Pandemic Infectious Disease Detection: COVID-19 as a Reference. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Kerman, K. Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Viruses. Micromachines 2021, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, M.; Porada, S.; Dykstra, J. The difference between Faradaic and non-Faradaic electrode processes. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-Free Impedance Biosensors: Opportunities and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertuğrul Uygun, H.; Uygun, Z.O. Impedimetric Biosensors for Label-Free and Enzymless Detection; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Zanasi, R.; Grossi, F.; Biagiotti, L. Qualitative graphical representation of Nyquist plots. Syst. Control. Lett. 2015, 83, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BahadÄąr, E.B.; SezgintĂźrk, M.K. Electrochemical biosensors for hormone analyses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asav, E.; Sağıroğlu, A.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Quantitative Analysis of a Promising Cancer Biomarker, Calretinin, by a Biosensing System Based on Simple and Effective Immobilization Process. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosel-Oliu, S.; Uria, N.; Abramova, N.; Bratov, A. Impedimetric Sensors for Bacteria Detection. In Biosensors-Micro and Nanoscale Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; pp. 257–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letardi, P. Electrochemical impedance measurements in the conservation of metals. In Radiation in Art and Archeometry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.Z.; Kopechek, J.A.; Priddy, M.C.; Hamorsky, K.T.; Palmer, K.E.; Mittal, N.; Valdez, J.; Flynn, J.; Williams, S.J. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using electrochemical impedance-based detector. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.-H.; Shaikh, M. Label-free impedance biosensors for Point-of-Care diagnostics. Point Care Diagn. New Prog. Perspect 2017, 3, 171–201. [Google Scholar]
- Pajkossy, T.; Jurczakowski, R. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in Interfacial Studies. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 1, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, B.; Demirbakan, B.; Yeşiller, G.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Introducing a new method for evaluation of the interaction between an antigen and an antibody: Single frequency impedance analysis for biosensing systems. Talanta 2014, 125, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.; Stoltenburg, R.; Strehlitz, B.; Frense, D.; Beckmann, D. Development of An Impedimetric Aptasensor for the Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, V.; Nawarathna, D. Design of Micro-interdigitated Electrodes and Detailed Impedance Data Analysis for Label-free Biomarker Quantification. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos-Nogués, M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. Antimicrobial Peptides: Powerful Biorecognition Elements to Detect Bacteria in Biosensing Technologies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Morens, D.M. The Pathology of Influenza Virus Infections. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2008, 3, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosillo, N.; Viceconte, G.; Ergonul, O.; Ippolito, G.; Petersen, E. COVID-19, SARS and MERS: Are they closely related? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Erdem, Ö.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. An Alternative Medical Diagnosis Method: Biosensors for Virus Detection. Biosensors 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, A.M. Virus receptors: Binding, adhesion strengthening, and changes in viral structure. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, W.C. Virus Infection. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.V.; Cordeiro, T.A.R.; Oliveira E Freitas, G.R.; Ferreira, L.F.; Franco, D.L. Biosensors for the detection of respiratory viruses: A review. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Tsai, B. How viruses use the endoplasmic reticulum for entry, replication, and assembly. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a013250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothes, W.; Sherer, N.M.; Jin, J.; Zhong, P. Virus Cell-to-Cell Transmission. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8360–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louten, J. Virus Replication. In Essential Human Virology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deusenbery, C.; Wang, Y.; Shukla, A. Recent Innovations in Bacterial Infection Detection and Treatment. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 695–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udommaneethanakit, T.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Frecer, V.; Seneci, P.; Miertus, S.; Bren, U. Drugs against Avian Influenza a Virus: Design of Novel Sulfonate Inhibitors of Neuraminidase N1. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 3478–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hushegyi, A.; Pihíková, D.; Bertok, T.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Tkac, J. Ultrasensitive detection of influenza viruses with a glycan-based impedimetric biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udommaneethanakit, T.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Bren, U.; Frecer, V.; Stanislav, M. Dynamic Behavior of Avian Influenza A Virus Neuraminidase Subtype H5N1 in Complex with Oseltamivir, Zanamivir, Peramivir, and Their Phosphonate Analogues. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, B.; D’Orsogna, M.R.; Webb, N.E.; Lee, B.; Chou, T. Quantifying the Sensitivity of HIV-1 Viral Entry to Receptor and Coreceptor Expression. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 6189–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilen, C.B.; Tilton, J.C.; Doms, R.W. HIV: Cell binding and entry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, B.; Rogers, K.; Phillips, E.K.; Brouillette, R.B.; Bouls, R.; Butler, N.S.; Maury, W. TIM-1 serves as a receptor for Ebola virus in vivo, enhancing viremia and pathogenesis. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0006983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labib, M.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Electrochemical Methods for the Analysis of Clinically Relevant Biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9001–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Amin, F.G.; Magdy, M.; Elgharib, A.M.; Azzam, E.B.; Nasser, F.; Yousry, K.; Shamkh, I.M.; Mahdy, S.M.; et al. A Review of Human Coronaviruses’ Receptors: The Host-Cell Targets for the Crown Bearing Viruses. Molecules 2021, 26, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; García-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Colet, P.; Baizhaxynova, A.; Mukhtarova, K.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Kanatova, K.; Asúnsolo, A.; Sarría-Santamera, A. Recapping the Features of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Main Variants: Status and Future Paths. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, I.; Ysrafil. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): An overview of viral structure and host response. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, F.; Zheng, X.; Zong, W.; Li, R.; Bao, Y. Identification of COVID-19-Associated DNA Methylation Variations by Integrating Methylation Array and scRNA-Seq Data at Cell-Type Resolution. Genes 2022, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ahmad, M.; Mustafa, F.; Panicker, N.; Rizvi, T.A. Development of an Optical Assay to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding Interactions with ACE2 and Disruption of these Interactions Using Electric Current. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, E.B.; Aydın, M.; Sezgintürk, M.K. New Impedimetric Sandwich Immunosensor for Ultrasensitive and Highly Specific Detection of Spike Receptor Binding Domain Protein of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 3874–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamani, B.S.; Uppal, T.; Verma, S.C.; Misra, M. Functionalized TiO2 Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sensors 2020, 20, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Huang, C.; Huang, Z.; Lin, F.; He, Q.; Tao, D.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Guo, Z. Advancements in electrochemical biosensing for respiratory virus detection: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 139, 116253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, A.M.; Wysocki, J.; Batlle, D. Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronavirus With ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 as Their Main Receptor. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, Ö.; Eş, I.; Saylan, Y.; Inci, F. Unifying the Efforts of Medicine, Chemistry, and Engineering in Biosensing Technologies to Tackle the Challenges of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenot, D.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.; Wilson, G. Electrochemical Biosensors: Recommended Definitions and Classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; Geiss, B.J.; Henry, C.S. Review—Chemical and Biological Sensors for Viral Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 167, 037523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, A.; Jalali, M.; Raeissi, K.; Karimzadeh, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Mahshid, S.S.; Mahshid, S. A review on recent advancements in electrochemical biosensing using carbonaceous nanomaterials. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhang, Z.L.; Li, T.H.; Rao, W. The Research Progress of Antibody Immobilization. China Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, T. A review on immobilization techniques of biosensors. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 3, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to Selecting a Biorecognition Element for Biosensors. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, J.I.A.; Yusof, N.A. The strategies of DNA immobilization and hybridization detection mechanism in the construction of electrochemical DNA sensor: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 16, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, W. Progress of new label-free techniques for biosensors: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.A.; Ahmed, M.U. CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Immunosensors. In Immunosensors; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, M.; Mallikarjunan, K. Challenges in Biosensor Development--Detection limit, detection time, and specificity. Resour. Mag. 2009, 16, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, H.; Kusaka, Y.; Wu, H.; Endo, H.; Tsuya, D.; Ohnuki, H. Toward a Practical Impedimetric Biosensor: A Micro-Gap Parallel Plate Electrode Structure That Suppresses Unexpected Device-to-Device Variations. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11017–11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Quadeer, A.A.; McKay, M.R. Preliminary Identification of Potential Vaccine Targets for the COVID-19 Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Based on SARS-CoV Immunological Studies. Viruses 2020, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-F.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z. Aptasensors for the detection of infectious pathogens: Design strategies and point-of-care testing. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashchenko, O.; Shelby, T.; Banerjee, T.; Santra, S. A Comparison of Optical, Electrochemical, Magnetic, and Colorimetric Point-of-Care Biosensors for Infectious Disease Diagnosis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1162–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walper, S.A.; Lasarte Aragonés, G.; Sapsford, K.E.; Brown, C.W., 3rd; Rowland, C.E.; Breger, J.C.; Medintz, I.L. Detecting Biothreat Agents: From Current Diagnostics to Developing Sensor Technologies. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1894–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adley, C.C. Past, Present and Future of Sensors in Food Production. Foods 2014, 3, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manring, N.; Ahmed, M.M.N.; Tenhoff, N.; Smeltz, J.L.; Pathirathna, P. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Tools for Virus Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 7149–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. A sensitive impedimetric DNA biosensor for the determination of the HIV gene based on graphene-Nafion composite film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, H.; Gill, P.S.; Kumar, A. Hemagglutinin gene based biosensor for early detection of swine flu (H1N1) infection in human. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, M.; Sadeghi, M. Ultrasensitive DNA biosensor for hepatitis B virus detection based on tin-doped WO3/In2O3 heterojunction nanowire photoelectrode under laser amplification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi-Nejad, F.; Teimouri, M.; Jafari Marandi, S.; Shariati, M. The highly sensitive impedimetric biosensor in label free approach for hepatitis B virus DNA detection based on tellurium doped ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkhani, H.; Farhad, S. A novel electrochemical DNA biosensor for Ebola virus detection. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 557, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, H.A.M.; Zucolotto, V. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for zika virus identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeter, E.Ç.; Şahin, S.; Caglayan, M.O.; Üstündağ, Z. An electrochemical label-free DNA impedimetric sensor with AuNP-modified glass fiber/carbonaceous electrode for the detection of HIV-1 DNA. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietrantonio, F.; Cannatà, D.; Benetti, M. Chapter 8-Biosensor technologies based on nanomaterials. In Functional Nanostructured Interfaces for Environmental and Biomedical Applications; Dinca, V., Suchea, M.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 181–242. [Google Scholar]
- Paniel, N.; Baudart, J.; Hayat, A.; Barthelmebs, L. Aptasensor and genosensor methods for detection of microbes in real world samples. Methods 2013, 64, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Kieboom, C.H.; van der Beek, S.L.; Mészáros, T.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Ferwerda, G.; de Jonge, M.I. Aptasensors for viral diagnostics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 74, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Abraham, P.R.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Aptamers: An Emerging Tool for Diagnosis and Therapeutics in Tuberculosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 656421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.M.; Kato, T.; Yoon, J.; Noh, S.; Park, E.Y.; Park, C.; Lee, T.; Choi, J.-W. Fabrication of MERS-nanovesicle biosensor composed of multi-functional DNA aptamer/graphene-MoS2 nanocomposite based on electrochemical and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karash, S.; Wang, R.; Kelso, L.; Lu, H.; Huang, T.J.; Li, Y. Rapid detection of avian influenza virus H5N1 in chicken tracheal samples using an impedance aptasensor with gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 236, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, K.; Roushani, M.; Azadbakht, A. Ultra-sensitive aptasensor based on a GQD nanocomposite for detection of hepatitis C virus core antigen. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 534, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, M.; Zamay, A.S.; Muharemagic, D.; Chechik, A.V.; Bell, J.C.; Berezovski, M.V. Aptamer-Based Viability Impedimetric Sensor for Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachour Junior, B.; Batistuti, M.R.; Pereira, A.S.; de Sousa Russo, E.M.; Mulato, M. Electrochemical aptasensor for NS1 detection: Towards a fast dengue biosensor. Talanta 2021, 233, 122527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A review on impedimetric biosensors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunajová, A.A.; Gál, M.; Tomčíková, K.; Sokolová, R.; Kolivoška, V.; Vaněčková, E.; Kielar, F.; Kostolanský, F.; Varečková, E.; Naumowicz, M. Ultrasensitive impedimetric imunosensor for influenza A detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 858, 113813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidzworski, D.; Siuzdak, K.; Niedziałkowski, P.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Sobaszek, M.; Ryl, J.; Weiher, P.; Sawczak, M.; Wnuk, E.; Goddard, W.A.; et al. A rapid-response ultrasensitive biosensor for influenza virus detection using antibody modified boron-doped diamond. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkapinyo, C.; Khownarumit, P.; Waraho-Zhmayev, D.; Poo-arporn, R.P. Development of a multiplex immunochromatographic strip test and ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for hepatitis B virus screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1095, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandli, J.; Attar, A.; Ennaji, M.M.; Amine, A. Indirect competitive electrochemical immunosensor for hepatitis A virus antigen detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 799, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; Takemura, K.; Li, T.-C.; Suzuki, T.; Park, E.Y. Electrical pulse-induced electrochemical biosensor for hepatitis E virus detection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Kumar, S.; Jayant, R.D.; Vashist, A.; Brown, A.N.; Li, C.-Z.; Nair, M. A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of Zika-virus protein. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Miranda, G.; Cardoso, A.R.; Ferreira, L.C.S.; Sales, M.G.F.; Bachmann, M.F. Biosensor-based selective detection of Zika virus specific antibodies in infected individuals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 113, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojsoska, B.; Larsen, S.; Olsen, D.A.; Madsen, J.S.; Brandslund, I.; Alatraktchi, F.A.a. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using Electrochemical Immunosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccariotto, G.C.; Silva, M.K.L.; Rocha, G.S.; Cesarino, I. A Novel Method for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Graphene-Impedimetric Immunosensor. Materials 2021, 14, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiew, L.-V.; Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wang, P.-W.; Heh, C.-H.; Liu, C.-T.; Cheng, C.-H.; Lu, Y.-X.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-X.; et al. Development of flexible electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based biosensing platform for rapid screening of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, A.L.; dos Santos, A.M.; dos Santos, L.P.; da Silva Pinto, L.; Conceição, F.R.; Wolfart, F. PEDOT-AuNPs-based impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, K.Y.P.S.; dos Santos, G.S.; Frías, I.A.M.; Silva-Junior, A.G.; Pereira, M.C.; Pitta, M.G.R.; de Araújo, B.C.; Errachid, A.; Oliveira, M.D.L.; Andrade, C.A.S. Nanostructured sensor platform based on organic polymer conjugated to metallic nanoparticle for the impedimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 at various stages of viral infection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Ismail, Z.H.; Md Arshad, M.K.; Poopalan, P. Aptasensing nucleocapsid protein on nanodiamond assembled gold interdigitated electrodes for impedimetric SARS-CoV-2 infectious disease assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, D.; Orozco, J. Peptide-based simple detection of SARS-CoV-2 with electrochemical readout. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1205, 339739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, H.A.; Kandeil, A.; Gomaa, M.; Mohamed El Nashar, R.; El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Hassan, R.Y.A. SARS-CoV-2-Impedimetric Biosensor: Virus-Imprinted Chips for Early and Rapid Diagnosis. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4098–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Sun, X.; Dai, Z.; Gao, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J.; Wen, W. Point-of-care testing detection methods for COVID-19. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 1634–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, B.; Khan, A.; Metezai, H.; Blyth, I.; Asad, H. The impact of false positive COVID-19 results in an area of low prevalence. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e54–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nehra, M.; Khurana, S.; Dilbaghi, N.; Kumar, V.; Kaushik, A.; Kim, K.H. Aspects of Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Personalized Health Wellness. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
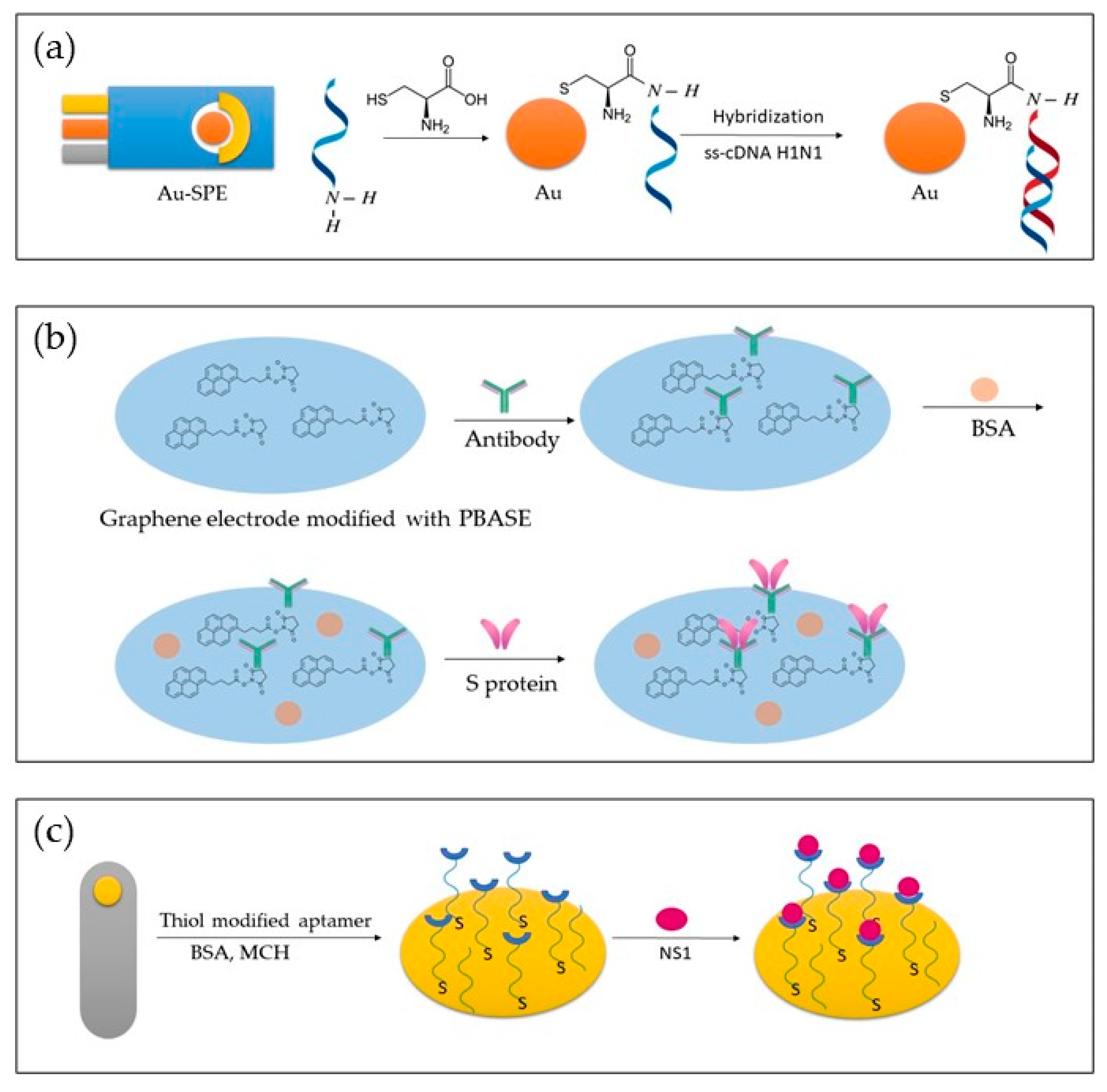
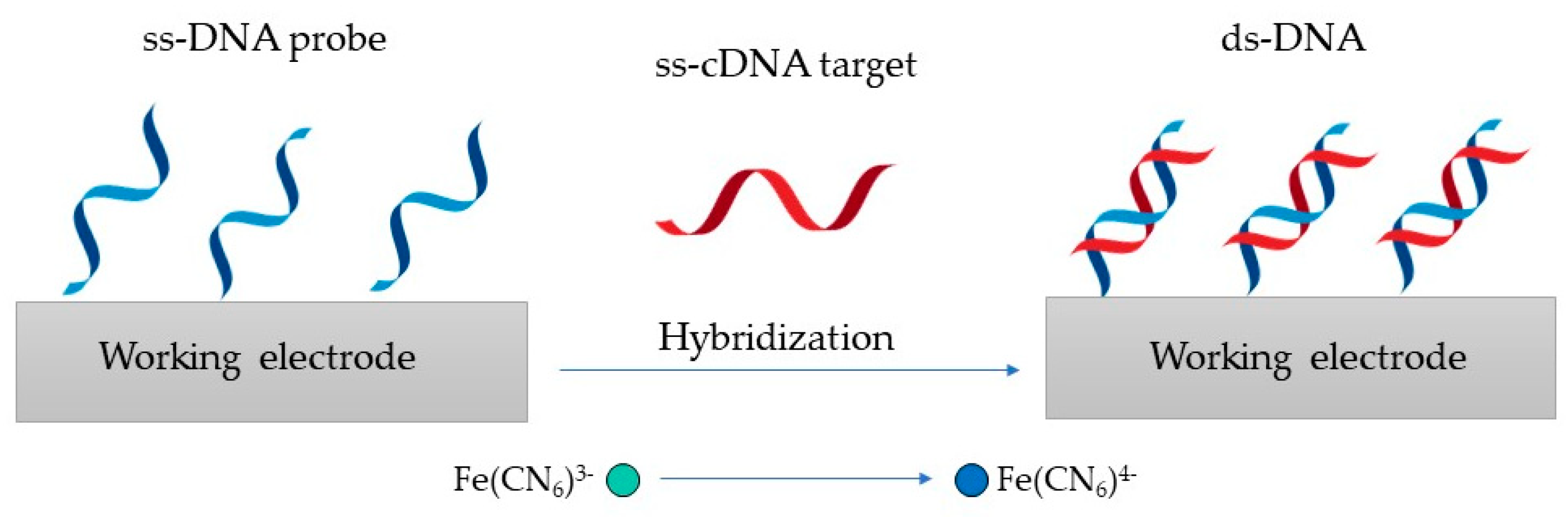
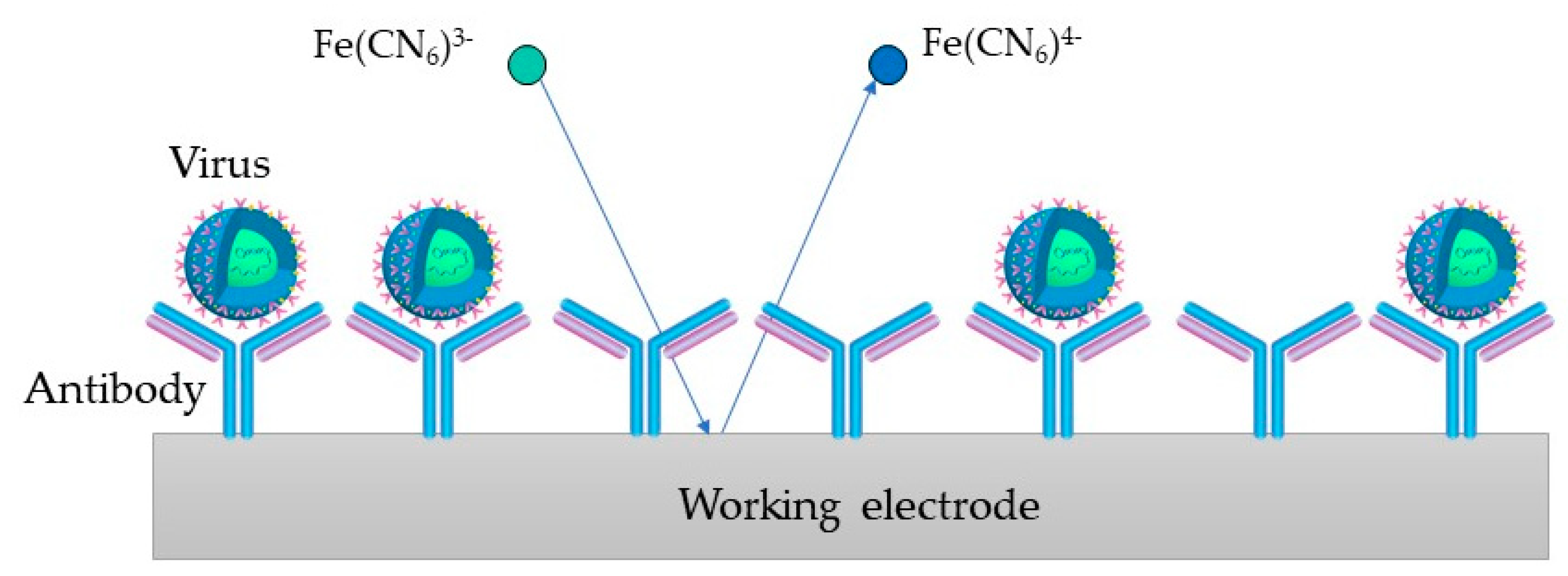
| Virus | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1N1 | ss-DNA H1N1 | ss-cDNA H1N1 (HA) | Cysteine modified Au-SPE | / | 0.667 ng/mL | [102] |
| HBV | ss-DNA HBV | ss-cDNA HBV | WO3/In2O3 nanowires | 0.1 pM–10 µM | 1 fM | [103] |
| HBV | ss-DNA HBV | ss-cDNA HBV | Te doped ZnO nanowires | 1 pM–1 µM | 0.1 pM | [104] |
| EBOV | ss-DNA EBOV | ss-cDNA EBOV | Au-SPE | / | 4.7 nM | [105] |
| ZIKV | ss-DNA ZIKV | RNA (NS5 protein) | Au-PET | 54–340 nM | 25 nM | [106] |
| HIV | ss-DNA HIV | ss-cDNA HIV | Graphene-Nafion modified GCE | 0.1 pM–100 nM | 23 fM | [101] |
| HIV | ss-DNA HIV | ss-cDNA HIV | AuNPs/GF/CTP | 0.1 pM–10 nM | 13 fM | [107] |
| Virus | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MERS-CoV-2 | MF DNA aptamer | MERS-NV | GO-MoS2 | 70–400 pg/mL | 0.4049 pg/mL | [112] |
| H5N1 | H5N1 aptamer | H5N1 | Au-IDA microelectrode | 16–0.125 HAU | 0.25 HAU | [113] |
| HCV | HCV aptamer | HCV core antigen | GCE/GQD | 10–70 pg/mL and 70–400 pg/mL | 3.3 pg/mL | [114] |
| VACV | VACV aptamer | VACV particles | Au microlectrode | 500–3000 PFU | 330 PFU | [115] |
| DENV | DENV aptamer | NS1 | MCH-Au electrodes | 10 pg/mL–1 μg/mL. | 22 pg/mL | [116] |
| Virus | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3N2 | Viral antibodies | Viral nucleoproteins | SPCE | 0.18 fM–0.18 nM | 0.79 fM | [119] |
| H1N1 | M1-antibody | M1 protein | BDD | 0–100 fg/mL | 1 fg/mL | [120] |
| HBV | Anti-HBs | HBsAg | BSA-SPCE | 5–3000 ng/mL | 2.1 ng/mL | [121] |
| HAV | Anti-HAs | HAsAg | CNPE | 2 × 10−4–5 × 10−3 IU/mL | 6 × 10−5 IU/mL | [122] |
| HEV | Anti-HEV antibody | HEV | PAc-GCE | / | 8 fg/mL | [123] |
| ZIKV | Zev-Abs | ZIKV-protein | IDE-Au | 10 pM–1 nM | 10 pM | [124] |
| ZIKV | Anti-NS1 | NS1 | SPCE | / | / | [125] |
| Type of Sensor | Recognition Element | Target | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunosensor | S-RBD antibody | S-RBD protein | ITO | 1.2 fg/mL–120 pg/mL | 0.58 fg/mL | [77] |
| Immunosensor | S-RBD antibody | S-RBD protein | Graphene | / | 20 μg/mL | [126] |
| Immunosensor | S-RBD antibody | S-RBD protein | rGO | 0.16–1.25 μg/mL | 150 ng/mL | [127] |
| Immunosensor | ACE2 | S-RBD protein | Pd-NTF | / | 0.1 μg/mL | [128] |
| Immunosensor | N protein (Naa160–406aa) | IgG | PEDOT-AuNPs | / | / | [129] |
| Genosensor | Oligonucleotide primer | N gene | ITO | 800–4000 copies/µL | 258.01 copies/µL | [130] |
| Aptasensor | N protein aptamer | N protein | AuIDE | 1 fM–100 pM | 0.389 fM | [131] |
| Peptide-based | Thiolated peptide | S-RBD protein | Au-SPE | 0.05–1.0 μg/mL | 18.2 ng/mL | [132] |
| Matrix | Polymeric matrix | virus particles | CNTs/WO3-SPE | 7–320 pg/mL | 57 pg/mL | [133] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štukovnik, Z.; Bren, U. Recent Developments in Electrochemical-Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415922
Štukovnik Z, Bren U. Recent Developments in Electrochemical-Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415922
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtukovnik, Zala, and Urban Bren. 2022. "Recent Developments in Electrochemical-Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415922
APA StyleŠtukovnik, Z., & Bren, U. (2022). Recent Developments in Electrochemical-Impedimetric Biosensors for Virus Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415922