Real-Time Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid Amplification of the N Gene of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Positions of the Real-Time RT-RAA Primers and Probe
2.2. Screening the Optimal Primers for Real-Time RT-RAA Amplification
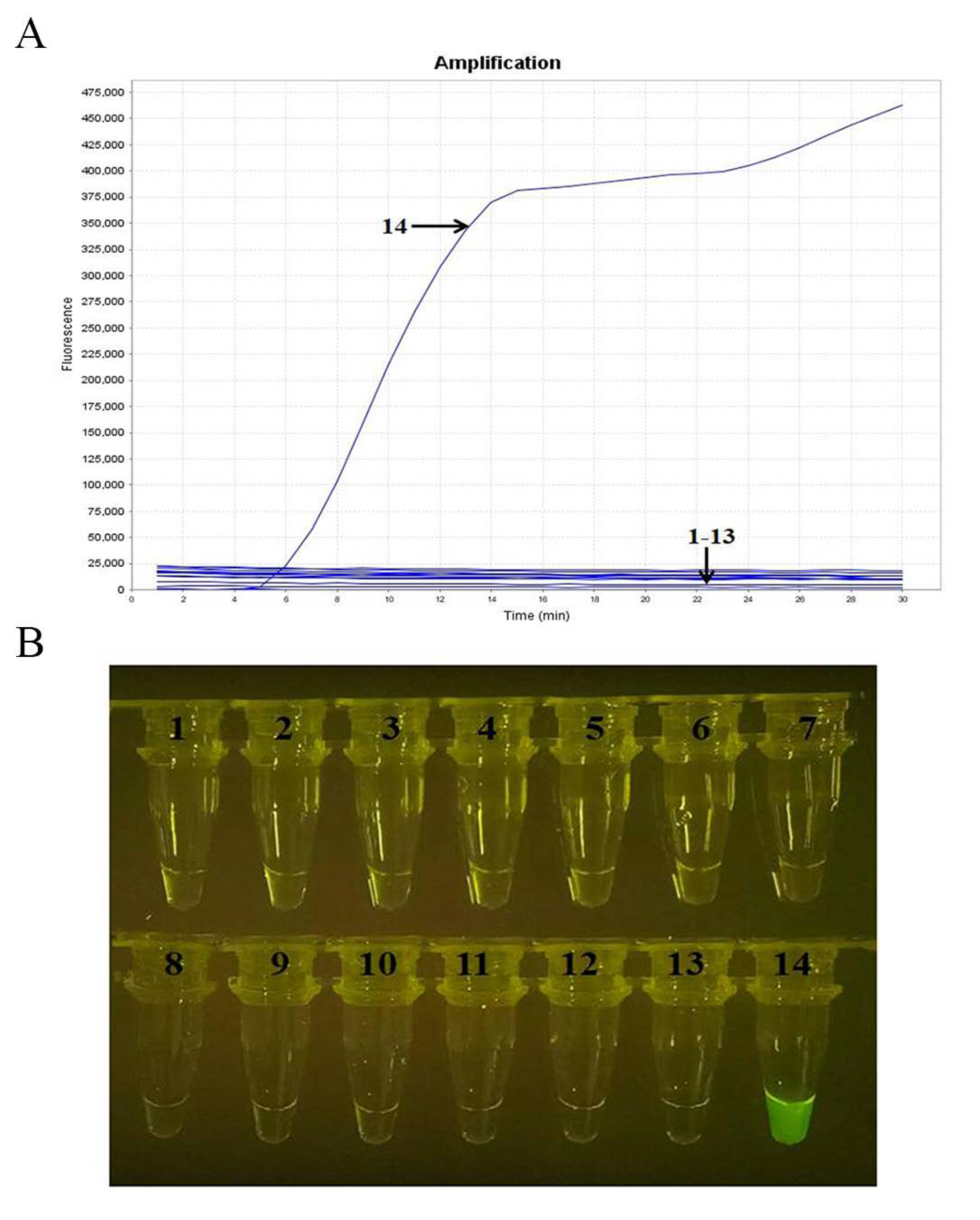
2.3. Specificity Analysis
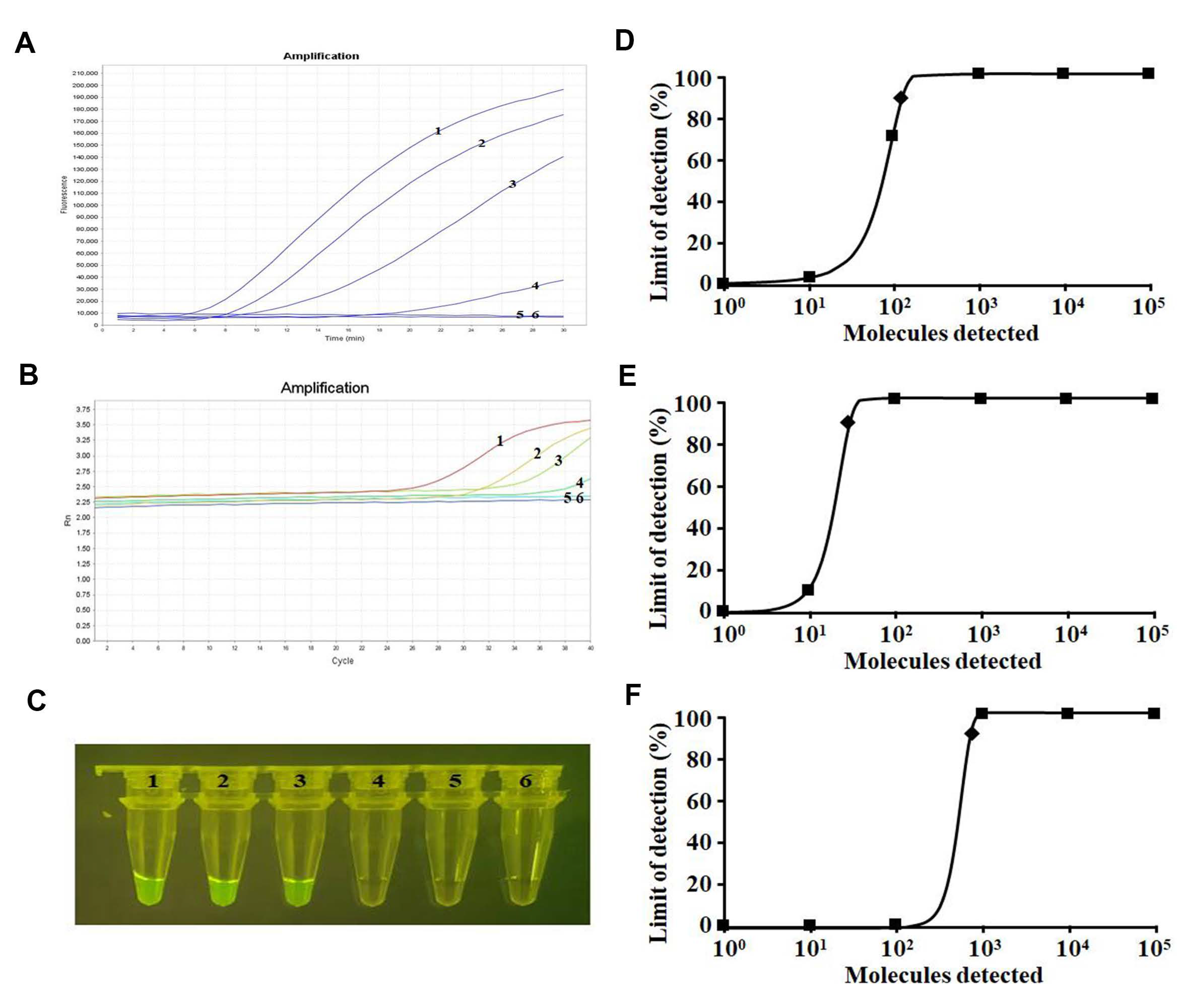
2.4. Sensitivity Analysis
2.5. Amplification of Clinical Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virus and Clinical Samples of SARS-CoV-2
4.2. Primers and Probe Design for Real-Time RT-RAA
4.3. Screening the Optimal Primers for Real-Time RT-RAA Amplification
4.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction
4.5. Real-Time RT-RAA Protocol
4.6. RT-qPCR Assay
4.7. Analytical Specificity
4.8. Analytical Sensitivity
4.9. Amplification of Clinical Samples
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, A.A.T.; Fatima, K.; Mohammad, T.; Fatima, U.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A.; Atif, S.M.; Hariprasad, G.; Hasan, G.M.; Hassan, M.I. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorouri, F.; Emamgholipour, Z.; Keykhaee, M.; Najafi, A.; Firoozpour, L.; Sabzevari, O.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Foroumadi, A.; Khoobi, M. The Situation of Small Molecules Targeting Key Proteins in combatting SARS-CoV-2: Synthesis, Metabolic Pathway, Mechanism of Action, and Potential Therapeutic Applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 273–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Fu, R.B.; Dong, Y.Z.; Chi, X.Y.; et al. Aerosol and Surface Distribution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Hospital Wards, Wuhan, China, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, H.; Li, E.; Guo, Z.; Wang, T.; Yan, F.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Meng, K.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 Variant Can Transmit in Rats But Not in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, N.; Cui, H.; Meng, K.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Impact of Prior Infection on Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Transmission in Syrian Hamsters. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 722178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Ni, H.; Wang, Y. Development of a recombinase-aided amplification assay for rapid and sensitive detection of porcine circovirus 3. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 282, 113904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Detection of pseudorabies virus with a real-time recombinase-aided amplification assay. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Li, F.; Shen, X.X.; Fu, S.H.; He, Y.; Lei, W.W.; Liang, G.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Ma, X.J. A Reverse-transcription Recombinase-aided Amplification Assay for the Rapid Detection of the Far-Eastern Subtype of Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2019, 32, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Development of a fluorescent probe-based real-time reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of classical swine fever virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, F.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, X. Development and Application of a Reverse-Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ao, C.; Wan, Z.; Dzakah, E.E.; Liang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, H.; Tang, S. A point-of-care rapid HIV-1 test using an isothermal recombinase-aided amplification and CRISPR Cas12a-mediated detection. Virus Res. 2021, 303, 198505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Ma, W.; Jiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ismail, R.G.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Reverse transcription-recombinase-aided amplification and CRISPR/Cas12a-based visual detection of maize chlorotic mottle virus. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Li, P.; Li, P.; Dong, H.; Chen, Q.; et al. A CRISPR-based nucleic acid detection method for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2022, 311, 198691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.X.; Qiu, F.Z.; Shen, L.P.; Yan, T.F.; Zhao, M.C.; Qi, J.J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, Z.S.; et al. A rapid and sensitive recombinase aided amplification assay to detect hepatitis B virus without DNA extraction. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Fan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K. Reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for H7 subtype avian influenza virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayittey, F.K.; Ayittey, M.K.; Chiwero, N.B.; Kamasah, J.S.; Dzuvor, C. Economic impacts of Wuhan 2019-nCoV on China and the world. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzrodt, C.L.; Maknojia, I.; McCarthy, R.D.P.; Oldfield, T.M.; Po, J.; Ta, K.T.L.; Stepp, H.E.; Clements, T.P. A Guide to COVID-19: A global pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3633–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberger, B.; Buder, F.; Lampl, B.; Ehrenstein, B.; Hitzenbichler, F.; Holzmann, T.; Schmidt, B.; Hanses, F. Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2. Infection 2021, 49, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Moradi, N.; Abdi, M. rRT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2: Analytical considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 516, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Primer design for quantitative real-time PCR for the emerging Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7150–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; Cai, G.; Lin, J.; Yue, X. A Salmonella Microfluidic Chip Combining Non-Contact Eddy Heater and 3D Fan-Shaped Mixer with Recombinase Aided Amplification. Biosensors 2022, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Lin, Z.; Huang, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, L.; Lou, Y. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Vibrio vulnificus Using CRISPR/Cas12a Combined With a Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 767315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Xu, J.; Nan, L.; Liu, F.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Based on CRISPR-Cas12a Combined With Recombinase-Aided Amplification. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 903298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Shen, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, J.; Fang, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, D.; et al. Development of Recombinase-Aided Amplification (RAA)-Exo-Probe and RAA-CRISPR/Cas12a Assays for Rapid Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in Food Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9557–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.S.; Noh, Y.J.; Shin, J.H.; Baek, S.Y.; Min, K.I.; Ryu, S.R.; Kim, B.G.; Park, M.K.; Choi, S.E.; Yang, E.H.; et al. Assessment of the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction using a cDNA standard for human group A rotavirus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 137, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yan, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C. SARS-CoV-2 Virus Culture, Genomic and Subgenomic RNA Load, and Rapid Antigen Test in Experimentally Infected Syrian Hamsters. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0103422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Assay | RT-qPCR | Sensitivity | Specificity | Kappa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||||
| Real-time RT-RAA (via real-time fluorescence read-out) | Positive | 36 | 0 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| Negative | 0 | 36 | ||||
| Total (72) | 36 | 36 | ||||
| Real-time RT-RAA (via visual detection) | Positive | 35 | 0 | 97.22% | 100% | 0.972 |
| Negative | 1 | 36 | ||||
| Total (72) | 36 | 36 | ||||
| Primers/Probes | Sequences (5′→3′) | Gene | Position 1 | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F253–282 | GGCTACTACCGAAGAGCTACCAGACGAATT | N | 253–282 | This study |
| R355–388 | TGCCGTCTTTGTTAGCACCATAGGGAAGTCCAGC | N | 355–388 | This study |
| p299–346 2 | AAATGAAAGATCTCAGTCCAAGATGGTATT(FAM-dT)(THF)(BHQ1-dT)ACTACCTAGGAACTG[C3-spacer] | N | 299–346 | This study |
| F | GGGGAACTTCTCCTGCTAGAAT | N | 608–629 | China CDC |
| R | CAGACATTTTGCTCTCAAGCTG | N | 685–706 | China CDC |
| Probe 3 | FAM-TTGCTGCTGCTTGACAGATT-TAMRA | N | 661–680 | China CDC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, H.; Tu, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, K.; Liu, J.; Dong, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z. Real-Time Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid Amplification of the N Gene of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315269
Cui H, Tu F, Zhang C, Zhang C, Zhao K, Liu J, Dong S, Chen L, Liu J, Guo Z. Real-Time Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid Amplification of the N Gene of SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):15269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315269
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Huan, Fei Tu, Cheng Zhang, Chunmao Zhang, Kui Zhao, Juxiang Liu, Shishan Dong, Ligong Chen, Jun Liu, and Zhendong Guo. 2022. "Real-Time Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid Amplification of the N Gene of SARS-CoV-2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 15269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315269
APA StyleCui, H., Tu, F., Zhang, C., Zhang, C., Zhao, K., Liu, J., Dong, S., Chen, L., Liu, J., & Guo, Z. (2022). Real-Time Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid Amplification of the N Gene of SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 15269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315269






