3-Dimensional Immunostaining and Automated Deep-Learning Based Analysis of Nerve Degeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
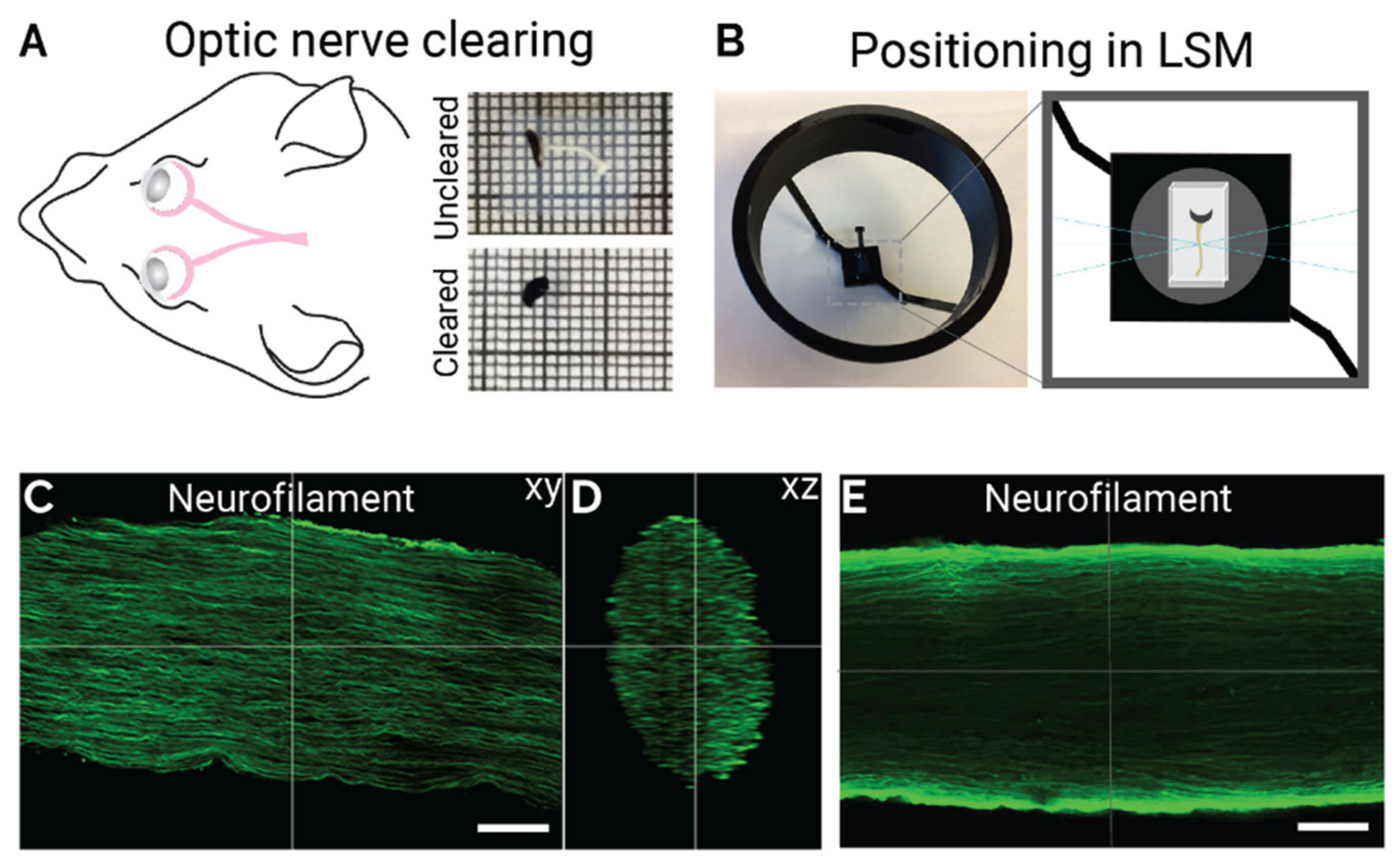
2.1. Optimized iDISCO Protocol for Labelling Mouse Optic Nerve
2.2. 3D Imaging of Immune Cell Infiltration and Inflammation in EAE
2.3. Axon Degeneration in EAE Optic Nerve
2.4. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Quantification of Axonal Blebs
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
4.3. Optic Nerve Crush
4.4. Whole Mount Optic Nerve iDISCO
4.5. Retina Immunohistochemistry and Imaging
4.6. Neural Network Architecture
4.7. Training
4.8. Post-Processing
4.9. Code Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- London, A.; Benhar, I.; Schwartz, M. The retina as a window to the brain-from eye research to CNS disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Sanchez-Dalmau, B.; Fraga-Pumar, E.; Ortiz-Perez, S.; Tercero-Uribe, A.I.; Torres-Torres, R.; Villoslada, P. The visual pathway as a model to understand brain damage in multiple sclerosis: Clinical and Laboratory Research. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández Blanco, L.; Marzin, M.; Leistra, A.; van der Valk, P.; Nutma, E.; Amor, S. Immunopathology of the optic nerve in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 209, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martin, E.; Ara, J.R.; Martin, J.; Almarcegui, C.; Dolz, I.; Vilades, E.; Gil-Arribas, L.; Fernandez, F.J.; Polo, V.; Larrosa, J.M.; et al. Retinal and Optic Nerve Degeneration in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Followed up for 5 Years. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreyer-Alster, S.; Gal, A.; Achiron, A. Optical Coherence Tomography Is Associated With Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2022, 42, e14–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, A.; Murphy, O.C.; Fitzgerald, K.C.; Button, J.; Gordon-Lipkin, E.; Ratchford, J.N.; Newsome, S.D.; Mowry, E.M.; Sotirchos, E.S.; Syc-Mazurek, S.B.; et al. Retinal measurements predict 10-year disability in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohowetz, L.J.; Vu, Q.; Ablabutyan, L.; Gratton, S.M.; Kunjukunju, N.; Wallace, B.S.; Koulen, P. Microperimetry as a diagnostic tool for the detection of early, subclinical retinal damage and visual impairment in multiple sclerosis. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngamsombat, C.; Tian, Q.; Fan, Q.; Russo, A.; Machado, N.; Polackal, M.; George, I.C.; Witzel, T.; Klawiter, E.C.; Huang, S.Y. Axonal damage in the optic radiation assessed by white matter tract integrity metrics is associated with retinal thinning in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 27, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davion, J.B.; Lopes, R.; Drumez, É.; Labreuche, J.; Hadhoum, N.; Lannoy, J.; Vermersch, P.; Pruvo, J.P.; Leclerc, X.; Zéphir, H.; et al. Asymptomatic optic nerve lesions: An underestimated cause of silent retinal atrophy in, M.S. Neurol. 2020, 94, e2468–e2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candeliere Merlicco, A.; Gabaldón Torres, L.; Villaverde González, R.; Fernández Romero, I.; Aparicio Castro, E.; Lastres Arias, M.C. Transorbital ultrasonography for measuring optic nerve atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2018, 138, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasner, P.; Sabisz, A.; Chylińska, M.; Komendziński, J.; Wyszomirski, A.; Karaszewski, B. Retinal nerve fiber and ganglion cell complex layer thicknesses mirror brain atrophy in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2022, 40, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Barnett, M.H.; Yiannikas, C.; Parratt, J.D.E.; Matthews, J.G.; Graham, S.L.; Klistorner, A. Interferon-β Is Less Effective Than Other Drugs in Controlling the Rate of Retinal Ganglion Cell Loss in, M.S. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.; Hernandez Martínez de Lapiscina, E.; Taylor, C.; Nguyen, A.L.; Alba-Arbalat, S.; Devonshire, V.; Sayao, A.L.; Carruthers, R.; Costello, F.; Traboulsee, A. Long-Term Stability of Neuroaxonal Structure in Alemtuzumab-Treated Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Patients. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2020, 40, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mey, G.M.; Evonuk, K.S.; Chappell, M.K.; Wolfe, L.M.; Singh, R.; Batoki, J.C.; Yu, M.; Peachey, N.S.; Anand-Apte, B.; Bermel, R.; et al. Visual imaging as a predictor of neurodegeneration in experimental autoimmune demyelination and multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcer, L.J.; Raynowska, J.; Nolan, R.; Galetta, S.L.; Kapoor, R.; Benedict, R.; Phillips, G.; LaRocca, N.; Hudson, L.; Rudick, R.; et al. Validity of low-contrast letter acuity as a visual performance outcome measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manogaran, P.; Walker-Egger, C.; Samardzija, M.; Waschkies, C.; Grimm, C.; Rudin, M.; Schippling, S. Exploring experimental autoimmune optic neuritis using multimodal imaging. Neuroimage 2018, 175, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manogaran, P.; Samardzija, M.; Schad, A.N.; Wicki, C.A.; Walker-Egger, C.; Rudin, M.; Grimm, C.; Schippling, S. Retinal pathology in experimental optic neuritis is characterized by retrograde degeneration and gliosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishioka, C.; Liang, H.F.; Barsamian, B.; Sun, S.W. Sequential phases of RGC axonal and somatic injury in EAE mice examined using DTI and, O.C.T. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 27, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Herranz, A.; Dietrich, M.; Hilla, A.M.; Yiu, H.H.; Levin, M.H.; Hecker, C.; Issberner, A.; Hallenberger, A.; Cordano, C.; Lehmann-Horn, K.; et al. Monitoring retinal changes with optical coherence tomography predicts neuronal loss in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflammat. 2019, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.H.; Chiang, C.W.; Perez-Torres, C.J.; Sun, P.; Wallendorf, M.; Schmidt, R.E.; Cross, A.H.; Song, S.K. Diffusion MRI quantifies early axonal loss in the presence of nerve swelling. J. Neuroinflammat. 2017, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Smith, M.D.; Kersbergen, C.J.; Kam, T.-I.; Viswanathan, M.; Martin, K.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L.; Zack, D.J.; Whartenby, K.; et al. Glial pathology and retinal neurotoxicity in the anterior visual pathway in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toader, L.E.; Rosu, G.C.; Catalin, B.; Tudorica, V.; Pirici, I.; Taisescu, O.; Muresanu, D.F. Clinical and Histopathological Assessment on an Animal Model with Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2018, 44, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morquette, B.; Juźwik, C.A.; Drake, S.S.; Charabati, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lécuyer, M.A.; Galloway, D.A.; Dumas, A.; de Faria Junior, O.; Paradis-Isler, N.; et al. MicroRNA-223 protects neurons from degeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain 2019, 142, 2979–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, T.; Ahn, M.; Kim, J.; Jung, K.; Moon, C.; Kim, M.D. Visual Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis and its Animal Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3484–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renier, N.; Wu, Z.; Simon, D.J.; Yang, J.; Ariel, P.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. iDISCO: A simple, rapid method to immunolabel large tissue samples for volume imaging. Cell 2014, 159, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.F.P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann, L.; Schmid, H.; Heinen, A.P.; Kurschus, F.C.; Dick, H.B.; Joachim, S.C. Inflammatory demyelination induces glia alterations and ganglion cell loss in the retina of an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. J. Neuroinflammat. 2013, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plemel, J.R.; Stratton, J.A.; Michaels, N.J.; Rawji, K.S.; Zhang, E.; Sinha, S.; Baaklini, C.S.; Dong, Y.; Ho, M.; Thorburn, K.; et al. Microglia response following acute demyelination is heterogeneous and limits infiltrating macrophage dispersion. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairless, R.; Williams, S.K.; Hoffmann, D.B.; Stojic, A.; Hochmeister, S.; Schmitz, F.; Storch, M.K.; Diem, R. Preclinical retinal neurodegeneration in a model of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 5585–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stojic, A.; Bojcevski, J.; Williams, S.K.; Bas-Orth, C.; Nessler, S.; Linington, C.; Diem, R.; Fairless, R. Preclinical stress originates in the rat optic nerve head during development of autoimmune optic neuritis. Glia 2019, 67, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guy, J.; McGorray, S.; Fitzsimmons, J.; Beck, B.; Rao, N.A. Disruption of the blood-brain barrier in experimental optic neuritis: Immunocytochemical co-localization of H2O2 and extravasated serum albumin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.S.; Baumann, B.; Dine, K.; Song, Y.; Dunaief, J.L.; Kim, S.F.; Shindler, K.S. Dexras1 Deletion and Iron Chelation Promote Neuroprotection in Experimental Optic Neuritis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.K.T.; Chitsaz, D.; Brown, R.A.; Cui, Q.L.; Dabarno, M.A.; Antel, J.P.; Kennedy, T.E. Deep learning for high-throughput quantification of oligodendrocyte ensheathment at single-cell resolution. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charabati, M.; Grasmuck, C.; Ghannam, S.; Bourbonnière, L.; Fournier, A.P.; Lécuyer, M.A.; Tastet, O.; Kebir, H.; Rébillard, R.M.; Hoornaert, C.; et al. DICAM promotes TH17 lymphocyte trafficking across the blood-brain barrier during autoimmune neuroinflammation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj0473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drake, S.S.; Charabati, M.; Simas, T.; Xu, Y.K.T.; Maes, E.J.P.; Shi, S.S.; Antel, J.; Prat, A.; Morquette, B.; Fournier, A.E. 3-Dimensional Immunostaining and Automated Deep-Learning Based Analysis of Nerve Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314811
Drake SS, Charabati M, Simas T, Xu YKT, Maes EJP, Shi SS, Antel J, Prat A, Morquette B, Fournier AE. 3-Dimensional Immunostaining and Automated Deep-Learning Based Analysis of Nerve Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314811
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrake, Sienna S., Marc Charabati, Tristan Simas, Yu Kang T. Xu, Etienne J. P. Maes, Shan Shan Shi, Jack Antel, Alexandre Prat, Barbara Morquette, and Alyson E. Fournier. 2022. "3-Dimensional Immunostaining and Automated Deep-Learning Based Analysis of Nerve Degeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314811
APA StyleDrake, S. S., Charabati, M., Simas, T., Xu, Y. K. T., Maes, E. J. P., Shi, S. S., Antel, J., Prat, A., Morquette, B., & Fournier, A. E. (2022). 3-Dimensional Immunostaining and Automated Deep-Learning Based Analysis of Nerve Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314811





